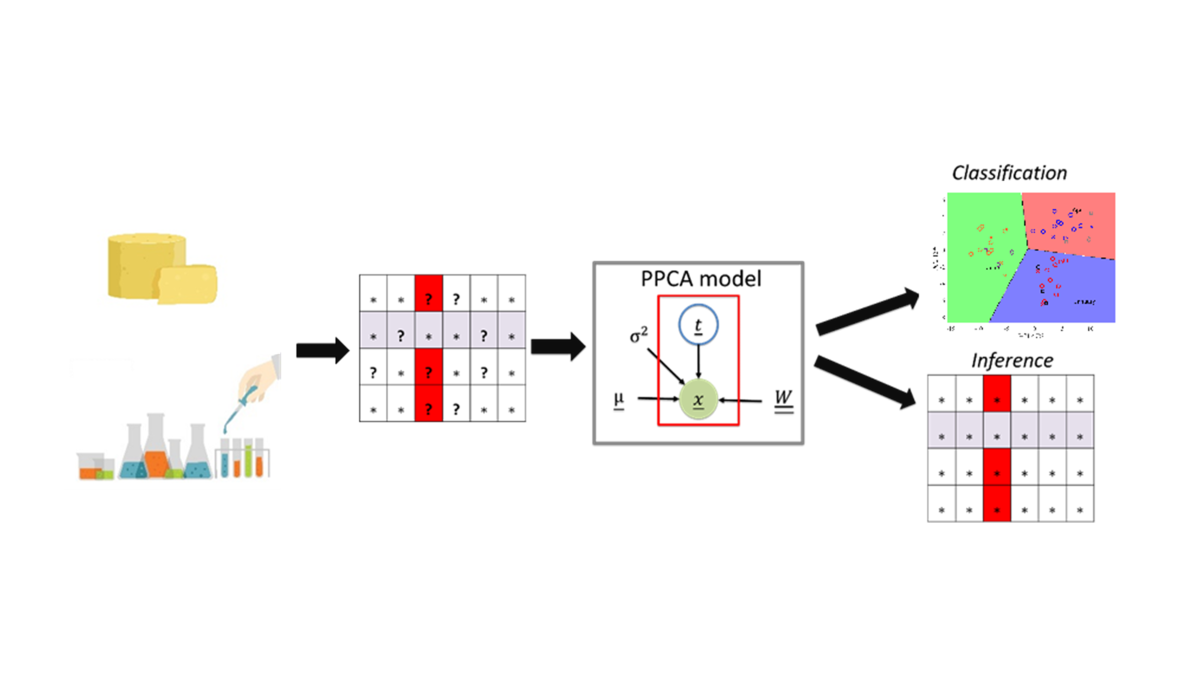
1. Introduction
In the context of increasingly complex industrial processes characterized by several highly correlated variables, common univariate analysis approaches often fail to describe a system's characteristics comprehensively. The introduction of multivariate statistical analysis has received significant attention in several fields of the process industry, such as quality control, fault detection, process monitoring, process control, and predictive modelling [
1,
2]
Within the framework of the food industry, the increasing consumer awareness of food quality and safety has led to a growing demand for the development of healthier products [
3,
4], thus driving the food sector to the implementation of improved technological and manufacturing techniques [
5]. Specifically, dairy manufacturers are focused on monitoring and controlling the levels of lipids, proteins, minerals and vitamins in their products, as these compounds strongly impact human health [
6].
Different studies reported that sheep's milk cheese could have a beneficial effect on human health due to the presence of bioactive compounds such as conjugated linoleic acids (CLA, e.g.,
C18:2 cis 9,
trans 11), vaccenic acid (
C18:1 trans 11) and omega-3 family compounds, which play an important role as nutraceutical substances [
7,
8]. The concentration of these nutritional compounds in cheese products is known to vary significantly throughout different cheese production seasons owing to many factors, such as changes in animal feed fatty acid composition and lactation stages [
7]. Therefore, developing an effective classification tool for cheese samples to study the effect of a specific stimulus or treatment, such as seasonality, on the food's properties is imperative for ensuring product characteristics control. To date, metabolomics is a powerful discipline for analyzing food products, especially dairy ones, as it enables the employment of a variety of analytical techniques together with statistical tools, which facilitate the assessment of product quality and safety for several food matrices [
9,
10,
11]. Principal Component Analysis (PCA) is a commonly used multivariate technique for reducing data dimensionality [
12], owing to its simplicity and effectiveness in identifying the variables that primarily contribute to explaining data variability in a high-dimensional data matrix. Nevertheless, due to its absence of a probabilistic formulation, PCA cannot handle datasets with missing data [
13]. The challenge of managing missing data in the food industry remains an issue of concern across various food matrices, such as pasta [
14] and tea [
15].
Missing data are ubiquitous in food processes since only a subset of product properties of interest can be generally observed because of cost, time or technical limitations [
14,
16]. Such missing information may significantly impair modelling performance. In these cases, when employing a traditional modelling approach, the sole method for handling missing data is discarding observations with incomplete information, which results in a loss of valuable data and penalizes the prediction of characteristics that are intended to be inferred [
17].
Probabilistic Principal Component Analysis (PPCA) is a multivariate model that addresses some limitations of its deterministic formulation [
18], as it provides the ability to reconstruct the data matrix wherever missing data are present while retaining a model parameter solution equivalent to that obtained from the conventional formulation [
19]. In addition, PPCA offers a more robust classification model thanks to its probabilistic notion, which enables a better assessment of the uncertainty in the resulting model response. To the best of the authors' knowledge, the study of the impact of seasonality on cheese nutritional properties through modelling methods able to deal with missing data appears to be lacking.
This study aims to expand the current advancements in food-omics by addressing the presence of missing values, specifically investigating the influence of seasonality on the fatty acid and mineral profiles of Pecorino Romano cheese samples. PPCA coupled with Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA) was first employed to classify cheese samples produced during winter (January), mid-spring (April), and early summer (June) and to identify the variables responsible for such classification. Then, the model was involved in reconstructing the missing information. The analysis reported in this study is presented from a comparative perspective, as PPCA model performances were compared with more consolidated approaches, namely Partial Least Square Discriminant Analysis (PLS-DA) in the case of classification problem and Partial Least Square Regression (PLSR) in the case of unknown data values inference [
20]. The robustness of the models was evaluated using a hybrid cross-external validation approach for classification and Montecarlo cross-validation for missing data inference.
2. Materials and Methods
The dataset examined in this study was obtained from Pecorino Romano PDO cheese samples produced in 12 dairies situated in Sardinia (Italy) during three distinct months, namely January, April, and June. Once the % FAME and mineral concentration are experimentally determined, a 45 × 81 matrix is obtained. Specifically, 73 variables are related to % FAME, and the remaining 8 are minerals (Ca, Mg, Na, K, P, S, Zn, and Fe). A total of 45 samples were analyzed, of which 33 have complete % FAME and mineral concentration information, while the remaining 12 lack this information. In more detail, regarding January and April, there are 24 samples (12 per production month) for which both the % FAME and mineral concentration are known. Hereafter, these samples will be referred to as "complete samples". In addition to these complete samples, four samples per month are lacking the % FAME, which represents the missing data series of the experimental data matrix. Hereafter, these samples will be referred to as “partial samples”, as only their mineral content is known. Similarly, there are nine complete samples for June, combined with six additional partial samples. The dataset is thus balanced for all three seasons.
2.1. Analytical methods
2.1.1. Cheese composition and nitrogen fractions
Cheese samples were analyzed for pH (pH meter 420 A, Orion, Boston, USA), dry matter (DM) [
21], fat (Soxhlet method [
22]), total nitrogen (TN) [
23], protein (TN*6.38), soluble nitrogen at pH 4.6 (pH 4.6 SN), soluble nitrogen in 12% trichloroacetic acid (SN-TCA), and soluble nitrogen in 10% phosphotungstic acid (SN-PTA) [
24], NaCl [
25] (ISO 5943-IDF 88, 2006) and ash. To determine the ash content cheese sample (5 g) was previously dried at 102°C for 24 h and then calcined at 550°C in a muffle furnace (Gelman Instrument, Opera, Italy). The operating conditions were set to reach 550°C in 8 h and hold 550°C for another 8 h. The effect of the cheese production season on the macro-components is first studied in this work.
2.1.2. Fatty Acid Methyl Esters Analysis
The Fatty Acid profile of cheese samples was determined according to the analytical procedure reported by [
7].
2.1.3. Element Analysis
Elements (Ca, Mg, Na, K, P, S, Zn, and Fe) were determined as reported by [
26].
2.2. Chemometric techniques
The effect of the cheese production season on the macro-components is first studied in this work. The Tukey test evaluates statistical significance between the mean values of two production months for each macro-component. The threshold p-value for the test is chosen as p < 0.05. Fatty acid profile and mineral content are analyzed through a qualitative and quantitative perspective. Concerning the classification task, an unsupervised method is here compared with a supervised approach. PPCA is a statistical method that enables dimensionality reduction in high-dimensional datasets while accounting for noise and missing data [
13]. More details on the technique are available in Supplementary Materials S1.a. After performing the PPCA, LDA is applied to the first two principal components to classify the data into three groups, one for each production season. LDA finds a linear combination of the principal components (PCs), thus constructing the boundaries where the Mahalanobis distance measure to centroids of each class is equal [
27]. Therefore, the linear boundaries maximize the separation between the groups. Once the sample scores are computed and LDA is performed, the presented model is employed to classify cheese samples. Partial Least Squares Discriminant Analysis (PLS-DA) is then proposed in order to carry out a comparison between the two classifiers' performances. After performing the classification, the estimation of % FAME from the mineral profile is performed using PPCA to assess its capability to manage missing data. PLS regression is also implemented for comparative analysis in this investigation. It is important to specify that the PLS algorithm is unsuitable for handling missing data, meaning that the only variables completely characterized for each sample (i.e., Mineral composition) were used as predictor variables for PLS-DA and PLS regression. A unity variance preprocessing step is conducted before executing the abovementioned algorithms.
2.3. Models’ validation
In order to properly validate the PPCA and PLS-DA models in classification, a Monte Carlo cross-validation [
28] combined with external validation was employed and can be described through the following 4-step procedure:
Step 1. Creation of the calibration set. The set is created by randomly selecting approximately 85% of the available complete samples. Further partial samples are added into the calibration set to constitute approximately 15 to 35% of the total calibration set.
Step 2. Validation set construction. The remaining complete samples from step 1 are included for model cross-validation. Additional partial samples are included in the validation set, comprising approximately 30% to 65% of the total validation set. These samples are exclusively used for external validation, meaning that they are not replaced in the calibration set.
Step 3. Calibrate the models. The entire calibration dataset is utilized to tune the PPCA and PLS-DA models.
Step 4. Calculate the percentage of correctly classified samples (%CC). The PPCA and PLS-DA models are tested through the validation samples, and their performance is assessed through classification accuracy.
The presented methodology is applied to select the optimal number of Principal Components (PCs) and Latent Variables (LVs) for PPCA and PLS-DA, respectively. For each PC's number (or LVs number), the abovementioned procedure is executed 20 times, and the models' performances are assessed by computing the average %CC obtained for validation samples across all iterations. The optimal number of PCs and LVs is determined as the one at which %CC was maximum. It is important to emphasize that in this procedure, the additional validation partial samples are not replaced across iterations and are never used for model calibration, thereby resembling an external validation. Indeed, the models inferred the class of these external partial samples in each iteration, while the calibration set comprises distinct sample groups each time it is randomly constructed. As a result, a different score estimation for external validation samples is obtained from each iteration as well, allowing the quantification of parameter estimation sensitivity when a fraction of samples in the calibration set is replaced.
Table 1 explains how the samples are distributed among the calibration and validation sets.
Concerning the assessment of PPCA and PLS in the quantitative estimation of % FAME, a Monte Carlo cross-validation method is employed to evaluate such models' performances. More in detail, 20% of the complete samples are randomly selected for each production month and used for the internal validation step, while the remaining ones are retained for calibration [
28]. Once calibrated, PPCA and PLS models are tested on the validation samples by predicting the %FAME using the mineral composition. In both models, the reliability of the % FAME prediction is assessed using the coefficient of determination (
R2) and the Root Mean Square of Errors in Cross-Validation (RMSECV). The procedure is carried out for a total of 20 iterations, and the overall
R2 and RMSECV are calculated by averaging the values obtained by each iteration.
Macro components data are first analyzed with the statistical software Minitab 21.1 (Minitab Inc., State College, PA, 2022). Then, the %FAME and mineral concentration (%w/w) analysis is carried out in the Matlab® environment. PPCA is carried out using the built-in functions provided by the Statistics toolbox, whereas validation is performed through an author-built routine. Conversely, LDA and PLS-DA are performed with the Classification Toolbox [
29].
3. Results and discussions
3.1. Pecorino Romano PDO cheese Macro composition analysis
Table 2 shows the physicochemical composition and proteolysis indices (SN/TN, SN-TCA/ TN, and SN-PTA/TN) for Pecorino Romano PDO cheese produced in January, April, and June. Based on the Tukey test, it is determined that the month of production statistically affected the fat and protein content of the cheese. In this study, it is observed that the fat content in cheese tends to decrease from winter to spring, and then it exhibits a significant increase in cheeses corresponding to the early summer. The protein content tends to have, in cheese, a complementary behaviour to the fat content, increasing in the cheese produced from January to April, and then it decreases in cheeses produced in early summer.
As reported by other authors, this behavior is mainly caused by the natural variation of the fat/protein ratio in milk induced by the advancing production season [
30]. The increase in the fat/protein ratio in sheep's milk and cheese as the season progresses is a typical phenomenon occurring in sheep's milk produced in Sardinia, and it is mainly linked to the stage of lactation, diet and rearing method practised on the island. In particular, in the final stage of lactation, there is a progressive decrease in the volume of milk produced with a concentration of certain macro-components (fat, in particular). Sheep's milk, produced in the summer period, is characterized by a high fat content, generally not compensated by an equal increase in protein content [
7].
3.2. Multivariate statistics analysis on %FAME and mineral profile
Many studies investigated the effect of production season and reported the strong influence on milk fatty acid profile and on the chemical composition of the sheep milk product [
31,
32,
33]. Indeed, it is well known that the production season strongly affects the fatty acid composition of milk and, then of cheese, consequently to variations in animal feed, pasture availability, and fatty acid composition of grass lipids [
7,
34]. Similarly, seasonal changes in animal diet have been found to affect the mineral composition profile of cheese [
35]. Therefore, the variations in % FAME and mineral concentration along the production season are expected to provide valuable information to develop a classifier that can discriminate Pecorino Romano PDO cheese based on its manufacturing period. PPCA coupled with LDA is employed for such a task since PPCA is reliable at reducing the complexity of a multivariate observed space and efficient in reconstructing missing information. In contrast, LDA enables the discrimination of cheese samples based on the coordinates of the first two PPCA scores in a two-dimensional latent space. By way of example,
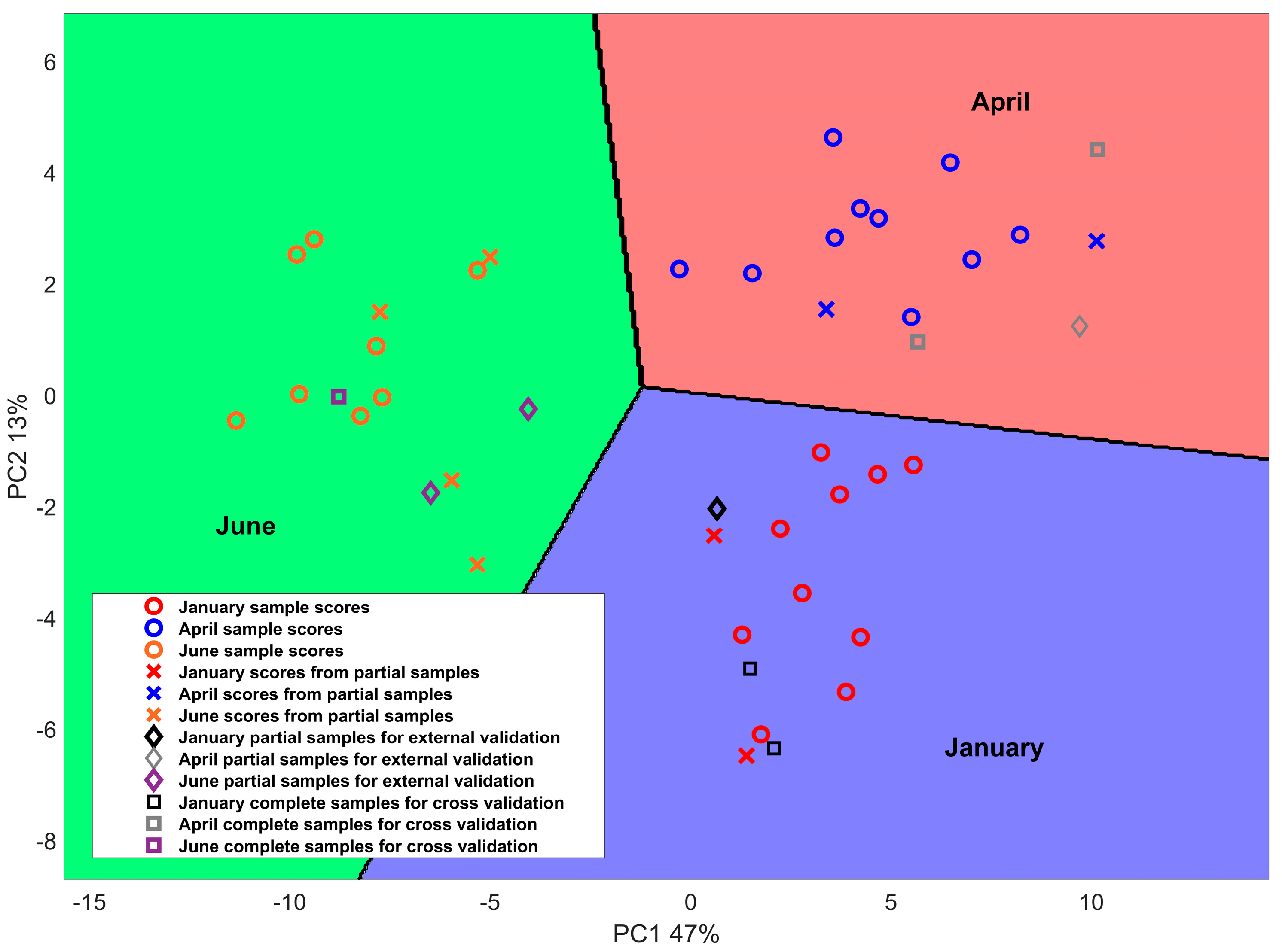
Figure 1 reports the score plot of the first two principal components and the results of LDA classification for calibration, cross-validation and external validation samples obtained in an iteration. The first two PCs, which explained 47% and 13% of the total variance in the calibration set, were used to identify the main differences among samples.
One observes that the PPCA+LDA method applied to % FAME and mineral information produces good classification results over different production times. Notably, cheeses produced during the winter and spring seasons show positive scores for PC1, while negative scores are reported for early summer. Concerning the PC2, cheeses produced in April exhibited positive score values, while negative scores were observed for January. Regarding June, both positive and negative PC2 score values are reported in the plot. Similar results are obtained by Nudda et al. reporting a multivariate statistical analysis of the FA content in cheese samples produced in different seasons [
8]. The same authors merged the early spring with the winter season and the late spring with the summer season, thus obtaining a binary analysis from the cheese seasonality point of view. The optimal number of PCs and LVs may vary depending on the overall dataset and the samples selected to calibrate the model. For this reason, cross-validation combined with external validation is proposed to ensure the generalizability and reliability of the results. Results are reported in
Figure 2.
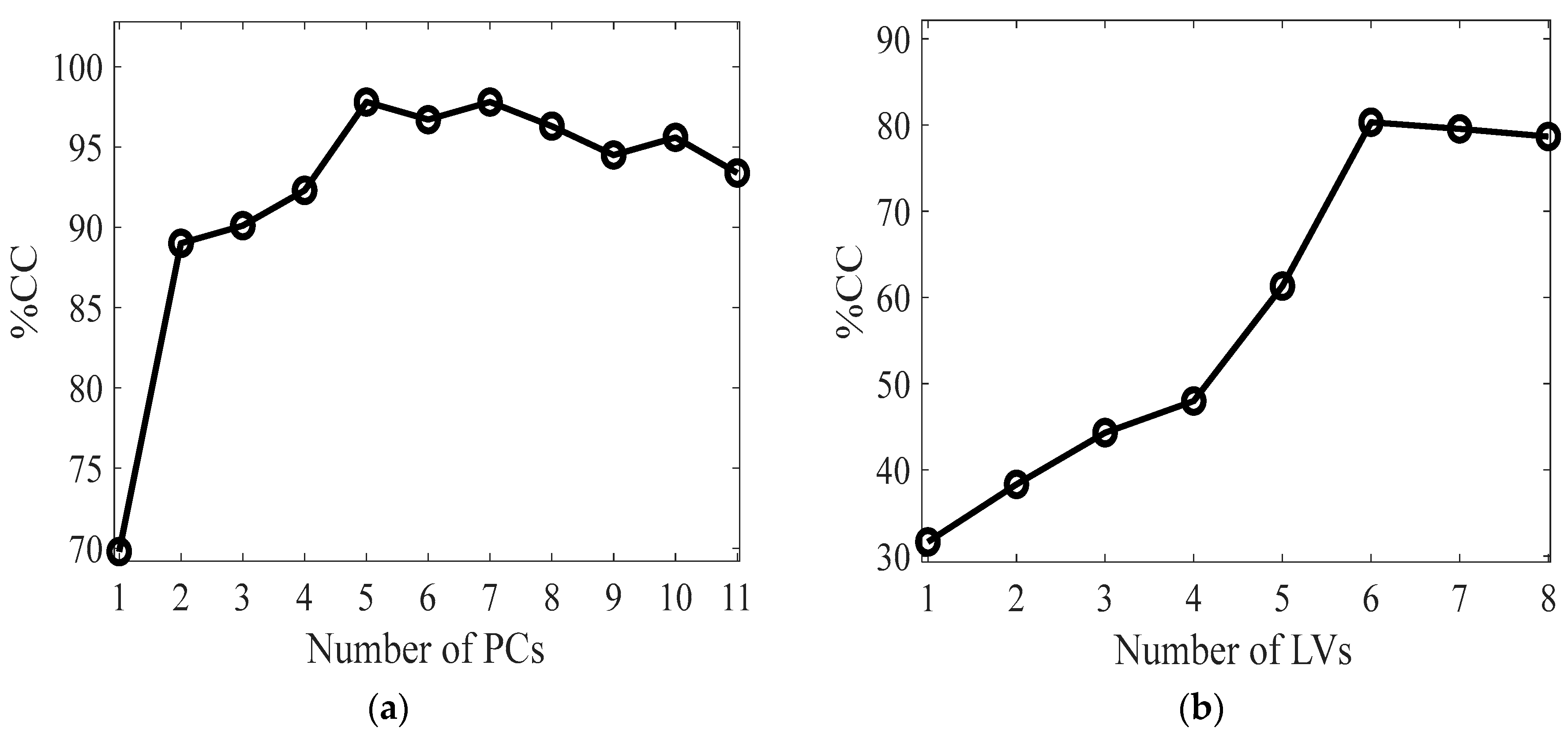
Figure 2a shows the relationship between the number of principal components and the percentage of correct classification (%CC) obtained in validation. It is observed that the maximum %CC, equal to 98%, is obtained from PPCA+LDA in correspondence of 5 principal components, which explains 77% of the total variance. The model demonstrates satisfactory accuracy and robustness using a moderate number of PCs. Regarding the PLS-DA, the highest accuracy is achieved when using 6 LVs, resulting in a %CC of 80%. It appears from this that introducing partial knowledge of %FAME into a PPCA model significantly improves the performance of the DA classifier. Conversely, using only mineral information coupled with a PLS-DA model leads to lower, yet still acceptable, goodness of performance in the classification (
Figure 2.b).
3.3. PPCA loading analysis
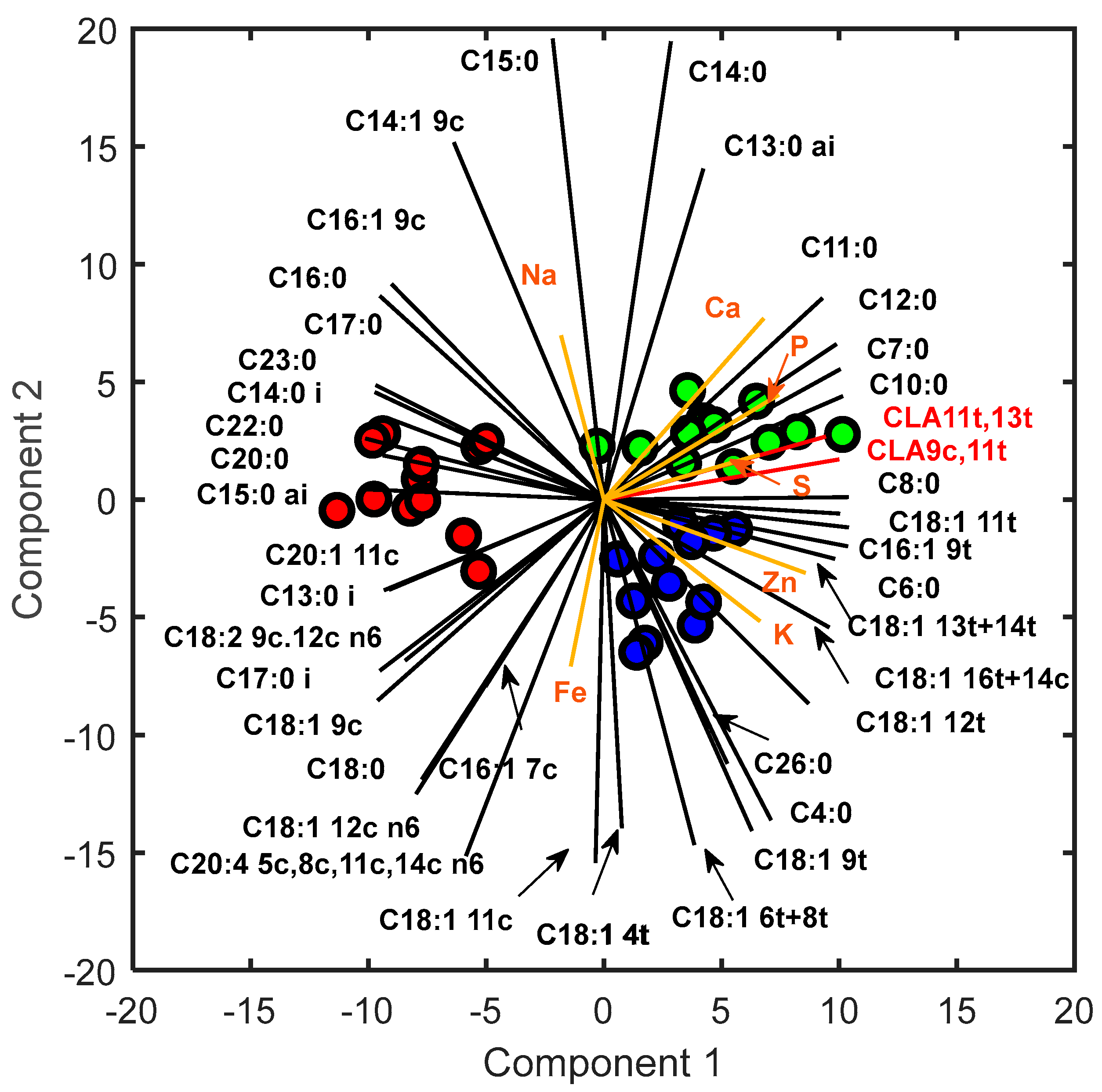
In order to assess the impact of cheese production seasons on the content of individual fatty acids (FAs) and minerals, an analysis of loadings derived from PPCA and the identification of the most important variables in constructing the first two PCs are reported. The results of this analysis can provide valuable insights into which variables have the greatest impact on the observed variability in data. Particular attention has been paid to specific fatty acids, namely rumenic acid, vaccenic acid, and omega-3 compounds, owing to their beneficial effects on human health.
Figure 3 shows the biplot obtained with the PPCA for the calibration dataset.
A detailed description of the first and second component loading values is reported in Supplementary Material S1.b. Regarding the % FAME analysis, both PC1 and PC2 displayed positive loadings for rumenic acid, vaccenic acid, and omega3 compounds, such as alpha-linolenic acid (
C18:3 9c,12c,15c n3) and eicosapentaenoic acid (
C20:5 5c,8c,11c,14c,17c n3), indicating a positive correlation with April. Furthermore, high negative PC1 loadings were observed for oleic acid, resulting in its positive correlation with June. Notably, these results are in line with previous studies [
7], even when examining different food matrices like cow milk [
36]. These findings can be explained by the combined effect of pasture quality and lactation stage [
9]. In particular, the abundance of CLA and omega-3 compounds in cheese produced in the spring season are strongly associated with the wide availability, in the grazed pasture, of their precursor (
C18:3 9c,12c,15c n3) during the grazing season [
7]. In contrast, the increase in oleic acid during the late lactation stages may be due to the energy requirement caused by the worsening of pasture quality [
8]. Particular attention is given to saturated fatty acids, which play a crucial role in defining the nutritional characteristics of food. Short-chain saturated FA are strongly correlated with January; medium-chain saturated FA are positively correlated with April. On the other hand, June is characterized by an abundance of long-chain saturated FA. These loadings trend highlights a clear dependence between the length of the saturated FA chain and the production season, probably due to the abovementioned reasons. Regarding the mineral loadings analysis, S, P, and Ca showed positive loadings for both PC1 and PC2, indicating a positive correlation between these minerals and April as the month of cheese production, likely owing to the abundance of minerals during spring when the pasture quality is high. The higher presence of protein (caseins) in cheese produced in April (
Table 2), respect to the other periods, could explain the high incidence in the spring cheese of Ca and P, as they are key elements in the formation of the cheese protein matrix. K and Zn display positive PC1 and negative PC2 loadings, suggesting a positive correlation with January. For Fe, a weak dependence on the winter season is observed, while Mg does not strongly contribute to constructing the first two principal components as its loading values are low. Interestingly, Na loadings are negative in the first PC and positive in the second one, indicating that Na content is prevalent in June. A simple explanation for this result is that cheeses produced in June show a tendentially, though not significantly, higher salt content than the other cheeses (
Table 2), as previously reported by other authors [
7]. Regarding the mineral profile behaviour, similar results were obtained in other studies [
31,
37,
38].
3.4. Missing data reconstruction
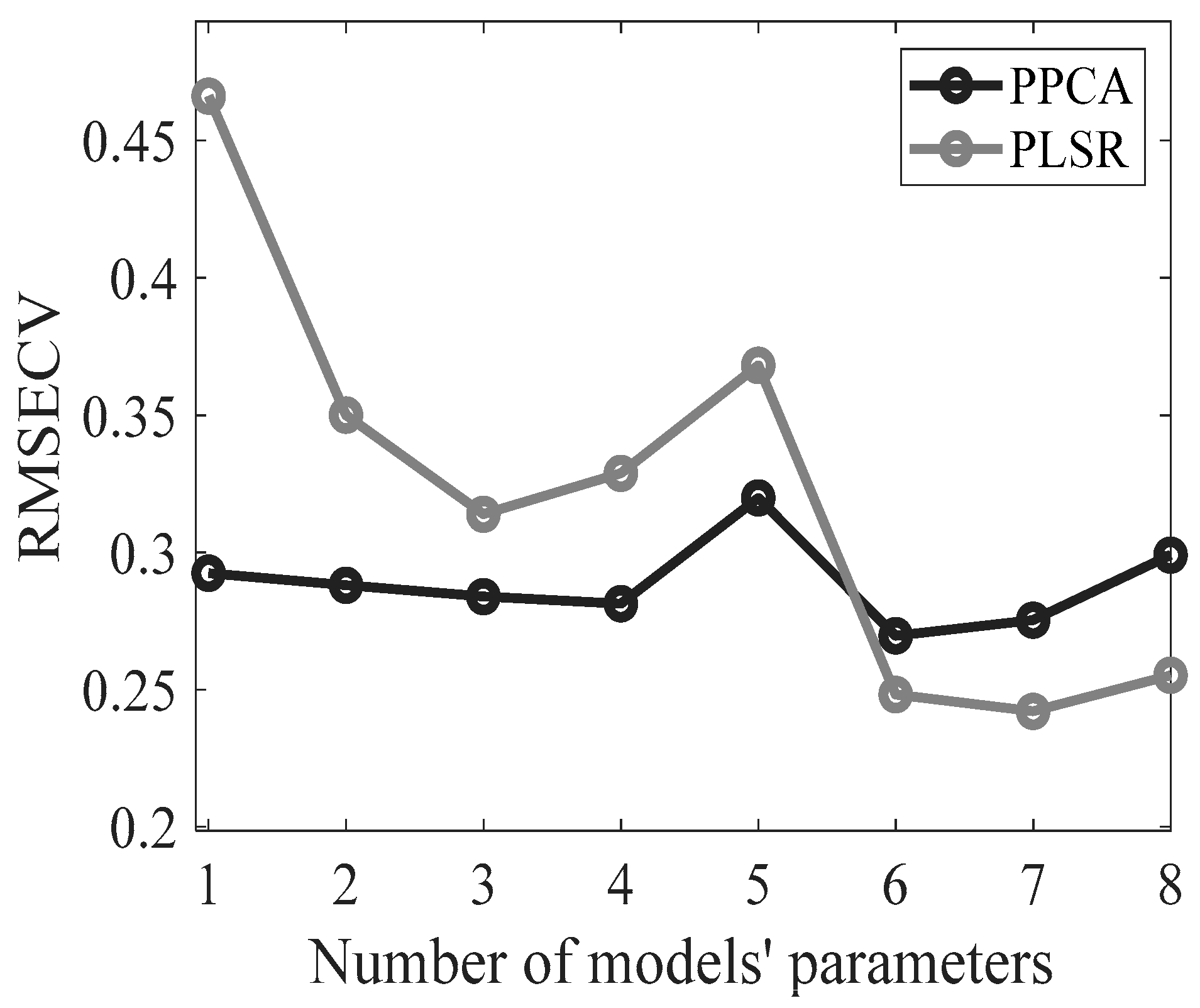
The PPCA model's effectiveness in reconstructing missing % FAME data is evaluated by comparing estimated values with their corresponding experimental values from cross-validation samples. During each iteration, %FAME information is removed from validation samples, estimated by the model, and residuals are computed.
Figure 4 compares the RMSECV for two models: PLS and PPCA. The x-axis shows the number of PCs/LVs involved in each model, while the y-axis shows the RMSECV values. According to the graph, the two models generally perform similarly, with PPCA performing better than PLS when a smaller number of components is taken into account. On the other hand, as the number of models' parameters increases, the performance of PLS appears to improve, while PPCA continues to perform well. At 6 components, the performance of PLS regression is slightly superior to that of PPCA, resulting in a lower RMSE. This slight difference is maintained at higher dimensions.
Cross-validation analysis shows that the best data fitting for the PPCA model is obtained with 6 PCs, resulting in an
R2 value of 99.43%. On the other hand, the optimal PLS model is set with 7 LVs, for which an
R2 value of 99.53% was obtained. The performance of the models is thus comparable. It is worth noting that the presented PPCA model, like any model suitable for handling missing data, can be used as a classification and inferential tool [
39]. Indeed, the same model can simultaneously provide informative score values that enable the classification of cheese samples and reconstruct the whole data matrix, facilitating the prediction of missing values. Specifically, when the optimal number of PCs obtained in classification (i.e., 5 PCs) is employed to reconstruct data with PPCA, it results in an
R2 value of 99.20% and an RMSE of 0.32 (
Figure 3), meaning that good performances are maintained for missing data inference. In contrast, the PLS approach requires two different models, namely PLS-DA and PLSR, to accomplish classification and inference tasks, respectively. In general, PPCA preserves high prediction performance even when implemented with a parsimonious number of parameters, whereas PLSR achieves superior results only when model complexity is relatively high due to the involvement of several latent variables. Furthermore, when implementing a PPCA model, the computational cost may drastically increase as the number of PCs increases, even when the dataset is relatively small. Hence, the ability of the PPCA model to retain good performance with a limited number of PCs may facilitate the application of a probabilistic model, such as the one proposed in this work.
4. Conclusions
The application of a probabilistic model such as PPCA opens up the possibility of monitoring food quality when missing values are present in the experimental observations. A comparative study is proposed here in order to assess the benefit offered by partial knowledge of the investigated variables when using a probabilistic model compared to a well-established multivariate model such as PLS. The case study reported in this work concerns the examination of the effect of seasonality on the Fatty Acid and mineral profiles for Pecorino Romano cheese, aiming to identify the key variables capable of discriminating cheese samples based on production month. For classification purposes, such models were coupled with Discriminant Analysis algorithms, and a Montecarlo cross-validation combined with external validation was implemented to assess the classifiers' reliability. The results showed that both models could effectively perform classification tasks, although PPCA showed remarkable performances. Then, the capability of PPCA in handling missing data was exploited to reconstruct missing % FAME information and compared with PLS regression for which % FAME are fitted by using only mineral compositions as predictor variables. Results showed that both models are highly predictive in the estimation of % FAME. Overall, it can be concluded that PPCA may be a valuable modelling strategy, as it simultaneously provides a classification tool and is capable of computing unknown information related to the presence of missing values, which is particularly wide-ranging in the food industry, thus giving a yet robust methodology for analyzing food-omics data.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at:
www.mdpi.com/xxx/s1, S1.a: Probabilistic Principal Component Analysis: Data projection onto latent space; S1.b: Loading Analysis for Probabilistic Principal Component Analysis
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.S., M.G. and P.C.; methodology, L.S., S.T., M.A., M.V. and M.G.; software, L.S.; validation, C.M., S.T. and M.E.; formal analysis, L.S., C.M., M.A., M.V. and P.C.; investigation, L.S., M.E., M.A., C.M. and P.C.; data curation, L.S., C.M. and P.C.; writing—original draft preparation, L.S. and M.G.; writing—review and editing, L.S., M.G., S.T., M.A., M.E. and P.C.; visualization, L.S., S.T. and M.G.; supervision, M.G., M.E., M.A. and P.C; project administration, M.G. and P.C.; funding acquisition, M.G. and M.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Regione Autonoma della Sardegna (Italy) POR FESR 2014–2020 Sviluppo nuovi prodotti nel settore agroalimentare “Azioni Cluster Nuovi Prodotti Food”. Project: “La diversificazione di prodotto nell’ambito del Pecorino Romano DOP”.
Data Availability Statement
On request, the software used for the PPCA validation can be made available by the authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- MacGregor, J.F.; Kourti, T. Statistical process control of multivariate processes. Control Eng. Pract. 1995, 3, 403–414. [CrossRef]
- Miletic, I.; Quinn, S.; Dudzic, M.; Vaculik, V.; Champagne, M. An industrial perspective on implementing on-line applications of multivariate statistics. J. Process Control 2004, 14, 821–836. [CrossRef]
- Renes, E.; Gómez-Cortés, P.; de la Fuente, M.A.; Linares, D.M.; Tornadijo, M.E.; Fresno, J.M. CLA-producing adjunct cultures improve the nutritional value of sheep cheese fat. Food Res. Int. 2019, 116, 819–826. [CrossRef]
- Mishra, B.; Mishra, A.K.; Kumar, S.; Mandal, S.K.; Lakshmayya, N.S.V.; Kumar, V.; Baek, K.H.; Mohanta, Y.K. Antifungal metabolites as food bio-preservative: Innovation, outlook, and challenges. Metabolites 2022, 12. [CrossRef]
- Khattab, A.R.; Guirguis, H.A.; Tawfik, S.M.; Farag, M.A. Cheese ripening: A review on modern technologies towards flavor enhancement, process acceleration and improved quality assessment. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 88, 343–360. [CrossRef]
- Matera, J.; Luna, A.S.; Batista, D.B.; Pimentel, T.C.; Moraes, J.; Kamimura, B.A.; Ferreira, M.V.S.; Silva, H.L.A.; Mathias, S.P.; Esmerino, E.A.; et al. Brazilian cheeses: A survey covering physicochemical characteristics, mineral content, fatty acid profile and volatile compounds. Food Res. Int. 2018, 108, 18–26. [CrossRef]
- Addis, M.; Fiori, M.; Riu, G.; Pes, M.; Salvatore, E.; Pirisi, A. Physico-chemical characteristics and acidic profile of PDO Pecorino Romano cheese: Seasonal variation. Small Rumin. Res. 2015, 126, 73–79. [CrossRef]
- Nudda, A.; Correddu, F.; Cesarani, A.; Pulina, G.; Battacone, G. Functional Odd- and Branched-Chain Fatty Acid in Sheep and Goat Milk and Cheeses. Dairy 2021, 2, 79–89. [CrossRef]
- Caboni, P.; Murgia, A.; Porcu, A.; Manis, C.; Ibba, I.; Contu, M.; Scano, P. A metabolomics comparison between sheep’s and goat’s milk. Food Res. Int. 2019, 119, 869–875. [CrossRef]
- Suh, J.H. Critical review: Metabolomics in dairy science – Evaluation of milk and milk product quality. Food Res. Int. 2022, 154. [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, T.; Winkvist, A.; Rådjursöga, M.; Ellegård, L.; Pedersen, A.; Lindqvist, H.M. Identification of Single and Combined Serum Metabolites Associated with Food Intake. Metabolites 2022, 12. [CrossRef]
- Cubero-Leon, E.; Peñalver, R.; Maquet, A. Review on metabolomics for food authentication. Food Res. Int. 2014, 60, 95–107. [CrossRef]
- Tipping, M.E.; Bishop, C.M. Probabilistic principal component analysis. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 1999, 61, 611–622.
- Mercier, S.; Mondor, M.; Marcos, B.; Moresoli, C.; Villeneuve, S. Estimation of missing values in a food property database by matrix completion using PCA-based approaches. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2017, 166, 37–48. [CrossRef]
- Delaporte, G.; Cladière, M.; Camel, V. Missing value imputation and data cleaning in untargeted food chemical safety assessment by LC-HRMS. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2019, 188, 54–62. [CrossRef]
- Gromski, P.; Xu, Y.; Kotze, H.; Correa, E.; Ellis, D.; Armitage, E.; Turner, M.; Goodacre, R. Influence of Missing Values Substitutes on Multivariate Analysis of Metabolomics Data. Metabolites 2014, 4, 433–452. [CrossRef]
- van Ginkel, J.R.; Linting, M.; Rippe, R.C.A.; van der Voort, A. Rebutting Existing Misconceptions About Multiple Imputation as a Method for Handling Missing Data. J. Pers. Assess. 2020, 102, 297–308.
- Gajjar, S.; Kulahci, M.; Palazoglu, A. Real-time fault detection and diagnosis using sparse principal component analysis. J. Process Control 2018, 67, 112–128. [CrossRef]
- Nyamundanda, G.; Brennan, L.; Gormley, I.C. Probabilistic principal component analysis for metabolomic data. BMC Bioinformatics 2010, 11. [CrossRef]
- Kalivodová, A.; Hron, K.; Filzmoser, P.; Najdekr, L.; Janečková, H.; Adam, T. PLS-DA for compositional data with application to metabolomics. J. Chemom. 2015, 29, 21–28. [CrossRef]
- ISO5534:2004 Cheese and processed cheese — Determination of the total solids content. ISO, Geneva, Switz. 2004.
- F. Soxhlet Die gewichtsanalytische Bestimmung des Milchfettes. Dinglers Polytech. J. 1879, 232, 461–465.
- IDF Milk and milk products— determination of nitrogen content - part 1: Kjeldahl principle and crude protein calculation. Iso 8968-12014 Idf 20-12014 2014.
- GRIPON, J.C.; DESMAZEAUD, M.J.; LE BARS, D.; BERGERE, J.L. Etude du rôle des micro-organismes et des enzymes au cours de la maturation des fromages. II. - Influence de la présure commerciale. Lait 1975, 55, 502–516.
- ISO/IDF Cheese and processed cheese products — Determination of chloride content — Potentiometric titration method. 2006.
- Lai, G.; Caboni, P.; Piras, C.; Pes, M.; Sitzia, M.; Addis, M.; Pirisi, A.; Scano, P. Development and Chemico-Physical Characterization of Ovine Milk-Based Ingredients for Infant Formulae. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13. [CrossRef]
- Brereton, R.G. Chemometrics for Pattern Recognition; 2009; ISBN 9780470987254.
- Xu, Q.S.; Liang, Y.Z. Monte Carlo cross validation. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2001, 56, 1–11. [CrossRef]
- Ballabio, D.; Consonni, V. Classification tools in chemistry. Part 1: Linear models. PLS-DA. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 3790–3798. [CrossRef]
- Guinee, T.P.; Mulholland, E.O.; Kelly, J.; Callaghan, D.J.O. Effect of protein-to-fat ratio of milk on the composition, manufacturing efficiency, and yield of cheddar cheese. J. Dairy Sci. 2007, 90, 110–123. [CrossRef]
- Altomonte, I.; Conte, G.; Serra, A.; Mele, M.; Cannizzo, L.; Salari, F.; Martini, M. Nutritional characteristics and volatile components of sheep milk products during two grazing seasons. Small Rumin. Res. 2019, 180, 41–49. [CrossRef]
- Serrapica, F.; Masucci, F.; Di Francia, A.; Napolitano, F.; Braghieri, A.; Esposito, G.; Romano, R. Seasonal variation of chemical composition, fatty acid profile, and sensory properties of a mountain pecorino cheese. Foods 2020, 9. [CrossRef]
- Todaro, M.; Bonanno, A.; Scatassa, M.L. The quality of Valle del Belice sheep’s milk and cheese produced in the hot summer season in Sicily. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2014, 94, 225–239. [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Meitei, N.S.; Gajbhiye, P.U.; Raftery, M.J.; Ambatipudi, K. Comparative analysis of milk triglycerides profile between jaffarabadi buffalo and holstein friesian cow. Metabolites 2020, 10, 1–27. [CrossRef]
- Bontempo, L.; Barbero, A.; Bertoldi, D.; Camin, F.; Larcher, R.; Perini, M.; Sepulcri, A.; Zicarelli, L.; Piasentier, E. Isotopic and elemental profiles of Mediterranean buffalo milk and cheese and authentication of Mozzarella di Bufala Campana PDO: An initial exploratory study. Food Chem. 2019, 285, 316–323. [CrossRef]
- Lopez, C.; Briard-Bion, V.; Ménard, O. Polar lipids, sphingomyelin and long-chain unsaturated fatty acids from the milk fat globule membrane are increased in milks produced by cows fed fresh pasture based diet during spring. Food Res. Int. 2014, 58, 59–68. [CrossRef]
- A., A.D.; R., K.J.; U., D.; A., A.K.; H., M.K.; M., C.S. Effects of physiological status and seasonal variation on plasma mineral profile of sheep in Kashmir valley. Sci. Res. Essays 2014, 9, 69–76. [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Delger, M.; Dave, A.; Singh, H.; Ye, A. Seasonal Variations in the Composition and Physicochemical Characteristics of Sheep and Goat Milks. Foods 2022, 11. [CrossRef]
- García-Laencina, P.J.; Sancho-Gómez, J.L.; Figueiras-Vidal, A.R. Pattern classification with missing data: A review. Neural Comput. Appl. 2010, 19, 263–282. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).