Submitted:
30 June 2023
Posted:
30 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
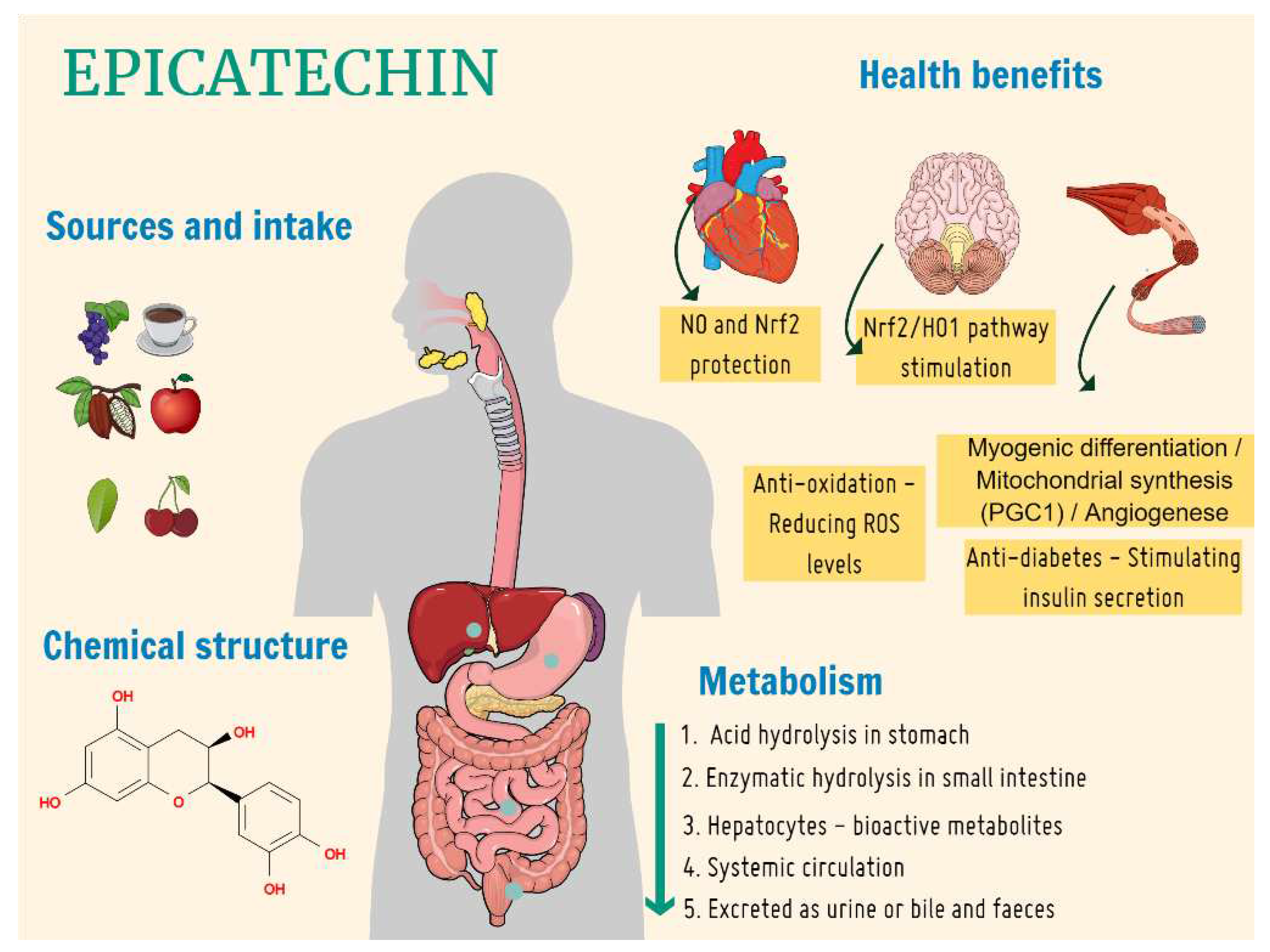
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Inclusion criteria:
- Clinical and experimental studies which evaluated epicatechin in the treatment of muscular atrophy;
- Publications allowing access to the full text;
- Scientific articles in the English language;
- Studies with full specifications on the dosage of epicatechin used, as well as the treatment time and administration route.
2.2. Exclusion criteria:
- Articles that used another type of catechin;
- Literature reviews;
- Duplicated articles.
- Studies involving myoblast cell lines
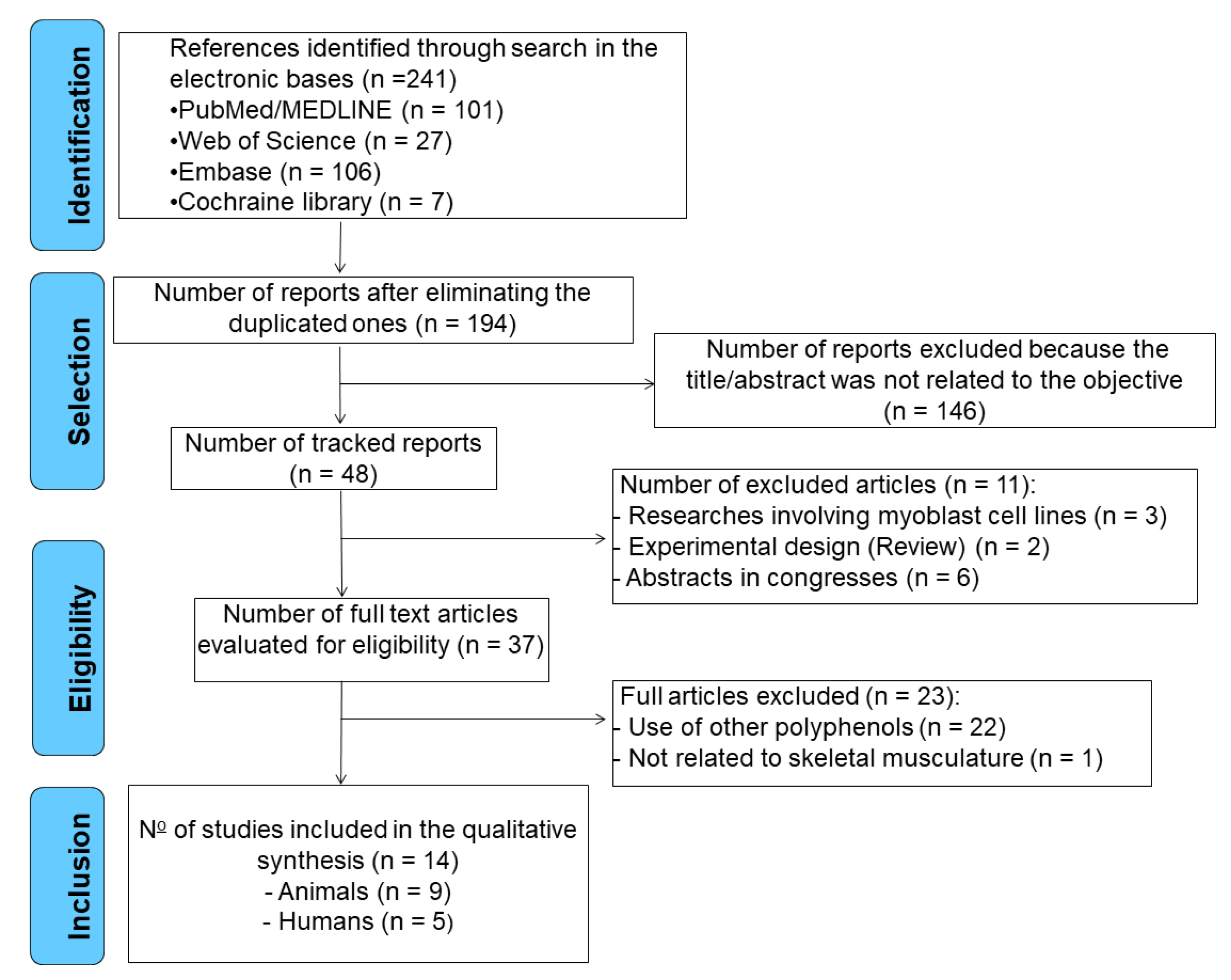
3. Results
3.1. Search results
| First author and year | Manufacturer | Participants |
Gender/ Age |
Objective | Groups | Dosage | Experimental time |
Route of administration |
Procedure | Effects of epicatechin (Main results) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taub et al., 2013 [22] | Hershey’s® 60% Dark chocolate |
5 | Male 47-71 years old |
To evaluate the skeletal muscle growth with the cocoa enriched with epicatechin in patients with heart failure and type 2 diabetes. | -Control group: Patients aged 50-53 years with no disease. -Experimental group: Patients aged 47-71 years. |
100 mg a day | 3 months | Oral route | The patients underwent femoral quadriceps muscle biopsies before and after consuming cocoa enriched with epicatechin. | There was a decrease in myostatin; however, it remained elevated compared to the control group. Follistatin increased above the controls with the treatment. The myogenin, MyoD, MEF2, and Myf5 levels were significantly stimulated with the epicatechin treatment. |
| Mafi et al., 2019 [30] | Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, MO | 62 | Male / 68 ± 2.86 years old |
To evaluate the plasma levels of follistatin and myostatin in men with Sarcopenia under training and epicatechin supplementation. |
RT: Resistance training, EP: Epicatechin, RT+EP: Resistance training + epicatechin, PL: Double-blind placebo. |
1 mg·kg−1·a day | 8 weeks | Oral route (Daily capsules with 200 ml of water) |
The training groups' subjects conducted the protocol at 05:00 p.m. (45 min., 3 sets, 8-12 repetitions). The placebo group received starch capsules. | Follistatin significantly increased in the RT + EP groups compared to PL group. While myostatin decreased in the RT + EP and in RT groups. The maximum supine strength significantly improved among the RT+EP and RT participants but not in EP and PL. |
| Corr et al., 2020 [26] | Chococru®/ Epicatechin | 23 | 13 women and 10 men/ 24 years. | To investigate if an acute dose of flavonoid cocoa (FC) may help in muscle recovery following EIMD. |
CON: Control group: Did not receive FC, n=8. CF830: High FC dose 830 mg group, n=8. CF1245: FC overdose group 1245 mg , n=7 |
830 mg and 1245 mg | 5 days (2 adaptation days and 3 days of epicatechin) |
Oral route | The EIMD protocol consisted in the hip fastening to the dynamometer at 85º of bending using straps to isolate the knee (5 series of 10 maximum concentric and eccentric contractions of the knee. | No significant differences were noted between the groups for all the measures in the bending exercises. The FC did not show benefits in muscle recovery after 24 h, 48 h, and 72 h post-EIMD. |
| First author and year | Manufacturer | Participants | Gender/Age | Objective | Group | Dosage | Experimental time |
Route of administration |
Procedure | Effects of epicatechin (Main results) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| McDermott et al., 2020 [23] | Hershey’s Co. | 44 participants | Male and female/ ≥ 60 years old | To evaluate if cocoa with epicatechin improves the walk performance in aged people with peripheral artery disease. | Cocoa drink/Epi (n=23) versus placebo drink (n=21) (did not contain cocoa or epicatechin) | 75 mg | 6 months | Oral route | The physical activity was conducted over 7 days with Accelerometer ActiGraph placed on the right hip. | There was a significant difference between the Cocoa/Epi group versus the placebo group in the 6-minute walk test 2.5 h after consuming the drink. These results suggest a therapeutic effect of cocoa/Epi in the walk performance. However, cocoa/Epi did not show significant effects on myostatin, follistatin and Pax7. |
| McDonald et al., 2021 [24] | cGMP facility (Syngene, Karnatak, India) | 7 participants | Male/ 18-60 years old | To evaluate epicatechin capacity in mitochondrial biogenesis and in the muscle markers. | Non-randomized clinical trial (before and after) | 50 mg twice a day | 8 weeks | Oral route (gelatin capsules) | The participants received two capsules in the morning and two in the evening. The brachial biceps muscle biopsies were collected pre-and post-treatment. |
Follistatin significantly increased, while myostatin decreased. There was a significant increment of tissue markers Myf5, MyoD, myogenin, and MEF2a. |
| First author and year | Manufacturer | Population | Gender/Age | Objective | Groups | Dosage | Experimental time | Route of administration | Procedure | Effects of epicatechin (Main results) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si et al., 2011 [27] | Sigma- Aldrich | 29 C57BLKS/J and KS.Cg-m +/+Lepr db/J, db/db Mice |
Male/ 5 weeks of age |
To investigate the effects of epicatechin in obese diabetic mice. | Con: n=12 Control group: C57BLKS/J Mice; db: n=6: Diabetic rats without epicatechin. db+EC: n=11: 0.25%: Diabetic rats + EC. |
0.25% every other day | 15 weeks | Oral route | To determine the contractile function, the EDL muscles were excised and attached by means of a suture to a servomotor (Aurora Scientific). | Epicatechin significantly decreased the inflammatory markers (C-Reactive Protein) in diabetic rats. The GSK antioxidant concentration and AMPKa phosphorylation were significantly higher than those of db group. |
| Hüttemann et al., 2013 [33] | Sigma- Aldrich |
21 LCR rats (rats grown for low capacity to run) | Males/5 months of age | To determine the action of epicatechin on angiogenesis and mitochondrial proliferation in rats with congenital muscle dysfunction. | Control: Water group for 30 days; Epi 30d: Epicatechin for 30 days; Post-Epi 15d: epicatechin for 30 days followed by 15 days without epicatechin. | 1.0 mg/kg twice a day | Epicatechin for 30 days followed by 15 days without epicatechin. | Gavage | For all three groups, the plantar muscle was analyzed in order to determine the effects of epicatechin on a glycolytic muscle fiber. | EC produced a significant increase in capillarity and mitochondrial biogenesis in the 15-day treatment period, being significantly higher than in the control group, including in the 15-day period of treatment interruption. EC increased VEGF and reduced CD47 and the receptor TSP1 and activated the P38 MAPK pathways. |
| First author and year | Manufacturer | Population | Gender/Age | Objective | Groups | Dosage | Experimental time | Route of administration | Procedure | Effects of epicatechin (Main results) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gutierrez-Salmean et al., 2014 [25] | Sigma-Aldrich | 20 C57BL/6 Mice (n=20 5/group) |
Young males/ 6 months and senile males/ 26 months | To examine the changes to the protein levels in the skeletal muscle of young vs senile humans and mice. | Ctrl (Young), Epi (Senile), Ctrl (Senile), Epi (Young) | 1 mg/kg | 2 weeks | Gavage | The control groups received water through gavage. Quadriceps muscle samples were obtained from the mice. |
Epicatechin significantly decreased the myostatin levels 15% (young) and 21% (aged), while follistatin increased 56% in the senile muscle. Myogenin significantly increased in young and senile animals (16%, 21%, respectively), while MyoD increased 19% in senile rats. Myf5 incremented 12% (young) and 15% (senile) and MEF2 10%, 19%, respectively. |
| 12 participants |
Gender not reported/ Young adults: 28 years old, n=6 Aged: 62 years old, n=6 |
To evaluate the effects of the treatment with epicatechin on muscle strength and on the plasma levels of myostatin and follistatin. |
Young adults group (n=6) Senile group (n=6) |
25 mg/day | 1 week | Oral route (capsule) |
The muscle strength was evaluated by hand grip dynamometry (three times with each hand, alternating the hand and resting for 10 seconds in order to prevent fatigue). | The treatment with epicatechin increases the hand's muscle strength by 7%. With age, there was a significant increase in myostatin (28%, 48%). The treatment with EC significantly increased the plasma levels of follistatin (49%). | ||
| Lee et al., 2015 [28] | Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA | 34 C57BL/6N Mice | Males/14 months of age | To determine the effect of epicatechin on angiogenesis and mitochondrial biogenesis protein markers. |
C: Control group CE: Control with resistance training Epi: Epicatechin Epi-Ex: Control + training + epicatechin. |
1.0 mg/kg twice a day |
8 weeks | Gavage | The training groups' mice were submitted to training on the treadmill for 8 weeks (5 times/week for 60 min./session). | The Epi-Ex showed better resistance performance and a significantly higher VEGF-R2 expression and increased PGC-1b and TFAM.. FoxO1 expression was significantly reduced in the experimental groups compared to the control. |
| Abbreviations: Ubiquitin proteasome system (UPS); Dark chocolate drink (DC); Forkhead transcription factors family (FoxO); F-box muscular atrophy (MAFbx); Muscle RING-finger protein (MuRF1); Myocyte enhancer factor 2A (MEF2A); Gulf War Illness (GWI); Pyridostigmine bromide (PB); N,N-dimethyl-meta-toluamide (DEET); Protein kinase B (AKT); Mammalian target protein of rapamycin (mTOR). | ||||||||||
| First author and year | Manufacturer | Population | Gender/Age | Objective | Groups | Dosage | Experimental time | Route of administration | Procedure | Effects of epicatechin (Main results) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lee et al., 2016 [29] | Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA | 25 C57BL/6N Mice | Males/ 6 months of age | To determine if the treatment with epicatechin may mitigate the muscle mass loss in the skeletal muscle. |
C: Control (water); HS-V: Suspension of the hind limbs + water; HS-Epi: Suspension of the hind limbs + epicatechin. |
1.0 mg/kg twice a day (Morning and evening). |
14 consecutive days | Gavage | For the hind limbs suspension protocol, the animals were placed in a cage with a steel bar. The soleus, medial, and gastrocnemius muscles were removed from both hind limbs. |
HS-Epi showed significantly higher FCSA and fiber capillarity compared to HS-V. In HS-Epi there was a slight decrease in FP compared with the control group. The antiangiogenic factor TPS-1 did not change in HS-Epi and showed a significant increase in mTOR, Akt, and TFAM. PGC-1β was only induced in HS-Epi, and CcO was similar to the control. FoxO and GSK-3β were induced in HS-V. |
| Si et al., 2019 [34] | Millipore Sigma, Burlington MA, USA | 33 C57BL/6 Mice | Males/ 9 months and 20 months of age |
To investigate the effects of epicatechin on the survival rate and on the physical performance in aged mice. |
OC: Control (aged mice). YC: Young control: Mice of 9 months of age. EC: 0.25% epicatechin. |
0.25% | 37 weeks and 44 weeks | Oral route | The samples were collected following 37 weeks, and the rest was treated for one additional week (on week 44). | Epicatechin mitigated the aging-related deterioration of the skeletal muscle; in addition, it improved physical activity, and delayed the degeneration of the quadriceps. E in senile mice presented a survival rate (69%) compared with the control group (39%). |
| Abbreviations: Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGF-R2); Fiber cross-sectional area (FCSA); fiber perimeter (FP); Forkhead transcription factors family (FoxO); Thrombosponding antiangiogenic factor (TPS-1); Mitochondrial transcription factor A (TFAM); Protein kinase B (AKT); Mammalian target protein of rapamycin (mTOR); Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor coactivator-1 (PGC-1); Cytochrome c oxidase (CcO); Enzyme Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3 Beta (GSK-3b). | ||||||||||
| First author and year | Manufacturer | Population | Gender/Age | Objective | Groups | Dosage | Experimental time | Route of administration | Procedure | Effects of epicatechin (Main results) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gonzalez-Ruiz et al., 2020 [35] | Sigma-Aldrich | 36 Long-Evans Rats | Females/ 11 weeks | To analyze the effects of epicatechin on the regulation of UPS proteins in the hind limbs. |
SCI+water 7 days: n=6. SCI+Epi 7 days: n=6. SCI+water 30 days: n=9. SCI+Epi 30 days: n=9. Sham: Only laminectomy n=6. |
1 mg/kg/day |
Evaluation periods: 1 week and at 30 days | Gavage | The spinal cord was sectioned (Region of the T8 to T10 vertebrae). The left side gastrocnemius and soleus muscles were dissected. |
At 30 days, the spinal cord injury group lost 49.52 ± 2.023% of the cross-sectional area of the muscle, and the epicatechin groups lost 24.28±15.45%. In the period of 7 days, the SCI+Epi had only one significant difference in MuRF decrease compared with SCI+water. The treatment with epicatechin induced a significant decrease in atrophy markers FOXO, MAFbx, and MuRF1 compared to the control group (VEH) after 7 and 30 days from the lesion. |
| Abbreviations: Ubiquitin proteasome system (UPS); Dark chocolate drink (DC); Forkhead transcription factors family (FoxO); F-box muscular atrophy (MAFbx); Muscle RING-finger protein (MuRF1); Myocyte enhancer factor 2A (MEF2A); Gulf War Illness (GWI); Pyridostigmine bromide (PB); N,N-dimethyl-meta-toluamide (DEET); Protein kinase B (AKT); Mammalian target protein of rapamycin (mTOR). | ||||||||||
| First author and year | Manufacturer | Population | Gender/Age | Objective | Groups | Dosage | Experimental time | Route of administration | Procedure | Effects of epicatechin (Main results) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Munguia et al., 2020 [31] | Sigma-Aldrich Co. (St. Louis, MO, USA) | 15 C57BL/6 Mice induced to a high-fat diet. | Males/ 10 weeks | To evaluate the benefits of the flavonoids in the improvement of the physical activity decreased by age/ high-fat diet. | Three interventions: Control: Water; High-flavonoid dark chocolate (DC) drink (2 mg EC + 12.8 mg procyanidins/kg) EC: Epicatechin (2 mg EC/kg). |
2 mg EC/kg |
5 weeks of treatment with EC. Week 49 – 15 weeks of obesity induction. Week 64 – Change from normal diet + 5 weeks of treatment. Total: 69 weeks. |
Gavage | Muscle samples from the gastrocnemius were collected. The inverted screen and front limbs functional test consisted in the longest time hanging, establishing a fixed time of 120 seconds and 130 seconds, respectively. | Epicatechin increased follistatin and myocyte enhancer factor 2A (MEF2A) expression. DC and EC decreased the FoxO and MURF; however, the MAFbx decrease was not significant. DC and EC induced a significant decrease in the fat content and increased physical performance compared with the control. |
| Ramirez-Sanchez et al., 2021 [32] | Sigma-Aldrich, Inc./ Hershey, PA, USA | 30 Wistar Rats | Males/ 3 months of age | To examine the potential restorative effects of epicatechin in muscular atrophy-induced rats. |
Control group (n=15): Without physical restriction (water): The experimental group (n=15): Physical restriction (2 weeks). Rats were divided into two groups: Epi GWI-Epi group (n=8) and Water GWI group (n=7). |
1 mg/kg/day |
2 weeks of EC. Atrophy induction (3 weeks) + 1 maintenance week + 2 weeks of EC. On week 6 – Functional test and euthanasia. |
Gavage | The atrophy induction consisted of the administration of pyridostigmine bromide (PB) 1.3 mg/kg/day through the oral route, permethrin (PM) 0.13 mg/kg/day (skin), DEET 40 mg/kg/day (skin). The animals were physically contained for 5 min./day for 3 weeks. | The treatment with epicatechin in animals with muscular atrophy induced a partial recovery of muscle strength and run distance on treadmill. MURF, Fbox40, and atrogin-1 were partially recovered by EC. Epicatechin significantly increases AKT and mTORC1 activation. |
| Abbreviations: Ubiquitin proteasome system (UPS); Dark chocolate drink (DC); Forkhead transcription factors family (FoxO); F-box muscular atrophy (MAFbx); Muscle RING-finger protein (MuRF1); Myocyte enhancer factor 2A (MEF2A); Gulf War Illness (GWI); Pyridostigmine bromide (PB); N,N-dimethyl-meta-toluamide (DEET); Protein kinase B (AKT); Mammalian target protein of rapamycin (mTOR). | ||||||||||
3.2. Risk of bias of the studies
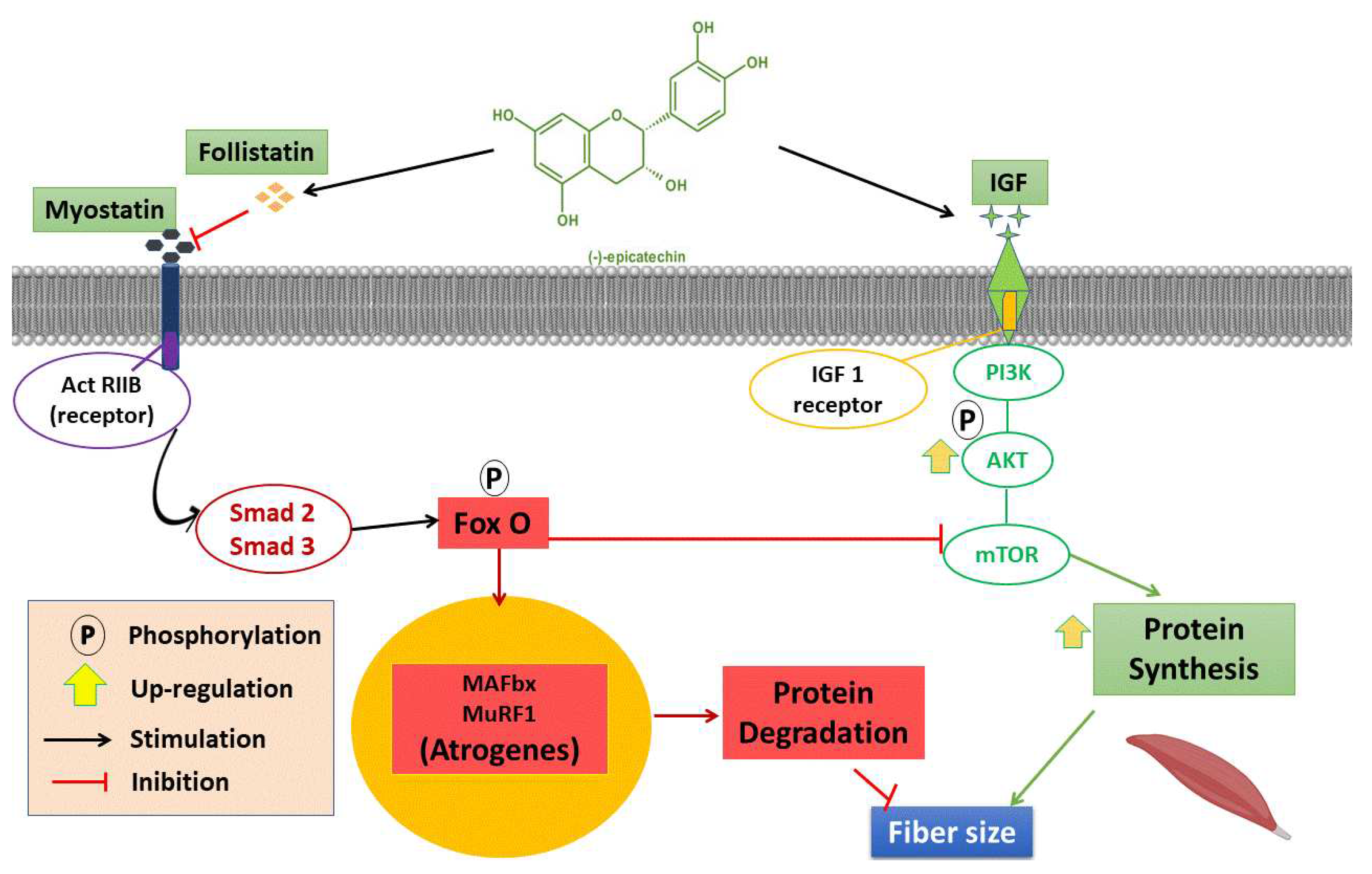
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nichols:, M.; Zhang, J.; Polster, B.M.; Elustondo, P.A.; Thirumaran, A.; Pavlov, E.V.; Robertson, G.S. Synergistic neuroprotection by epicatechin and quercetin: activation of convergent mitochondrial signaling pathways. Neuroscience 2015, 12, 75–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernatoniene, J.; Kopustinskiene, D.M. The role of catechins in cellular responses to oxidative stress. Molecules 2018, 23, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araújo, C.R.R.; de Melo Silva, T.; Dos Santos, M.G.; Otton, i.M.H.F.; de Souza Fagundes, E.M.; de Sousa Fontoura, H.; de Melo, Geba.; de Carvalho Alcântara, A.F. Anti-inflammatory and cytotoxic activities of the extracts, fractions, and chemical constituents isolated from luehea ochrophylla mart. BMC Complement Altern Med 2019, 19, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Liu, A.; Xiong, W.; Lin, H.; Xiao, W.; Huang, J.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Z. Catechins enhance skeletal muscle performance. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 2020, 60, 515–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, X.; Han, X.; Li, Q.; Wang, J. Epicatechin, a natural flavonoid compound, protects astrocytes against hemoglobin toxicity via nrf2 and ap-1 signaling pathways. Mol Neurobiol 2017, 54, 7898–7907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daussin, F.N.; Heyman, E.; Burelle, Y. Effects of epicatechin on mitochondria. Nutr Rev 2021, 79, 25–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shay, J.; Elbaz, H.A.; Lee, I.; Zielske, S.P.; Malek, M.H.; Hüttemann, M. Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic effects of epicatechin and other polyphenols in cancer, inflammation, diabetes, and neurodegeneration. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2015, 2015, 181260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkhondeh, T.; Yazdi, H.S.; Samarghandian, S. The protective effects of green tea catechins in the management of neurodegenerative diseases: a review. Curr Drug Discov Technol 2019, 16, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Leem, Y.E.; Go, G.Y.; Choi, Y.; Song, Y.J.; Kim, I.; Kim, D.Y.; Kim, Y.K.; Seo, D.W.; Kang, J.S.; Bae, G.U. Epicatechin elicits myod-dependent myoblast differentiation and myogenic conversion of fibroblasts. PLoS One 2017, 12, e0175271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zbinden-Foncea, H.; Castro-Sepulveda, M.; Fuentes, J.; Speisky, H. Effect of epicatechin on skeletal muscle. Curr Med Chem 2022, 29, 1110–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munguia, L.; Ortiz, M.; González, C.; Portilla, A.; Meaney, E.; Villarreal, F.; Najera, N.; Ceballos, G. Beneficial effects of flavonoids on skeletal muscle health: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Med Food 2022, 25, 465–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnett, C.F.; Moreno-Ulloa, A.; Shiva, S.; Ramirez-Sanchez, I.; Taub, P.R.; Su, Y.; Ceballos, G.; Dugar, S.; Schreiner, G.; Villarreal, F. Pharmacokinetic, partial pharmacodynamic and initial safety analysis of epicatechin in healthy volunteers. Food Funct 2015, 6, 824–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, C.M.; Henricson, E.; Oskarsson, B. Epicatechin enhances mitochondrial biogenesis, increases dystrophin and utrophin, increases follistatin while decreasing myostatin, and improves skeletal muscle exercise response in adults with becker muscular dystrophy (BMD). Neuromuscular Disorders 2015, 25, S314–S315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Ramiro, I; Martín, M.A.; Ramos, S; Bravo, L; Goya, L. Comparative effects of dietary flavanols on antioxidant defences and their response to oxidant-induced stress on caco2 cells. Eur J Nutr 2011, 50, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meador, B.M.; Mirza, K.A.; Tian, M.; Skelding, M.B.; Reaves, L.A.; Edens, N.K.; Tisdale, M.J.; Pereira, S.L. The green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) attenuates skeletal muscle atrophy in a rat model of sarcopenia. J FrailtyAging 2015, 4, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.R.; Kim, K.M.; Byun, M.R.; Hwang, J.H.; Park, J.I.; Oh, H.T.; Kim, H.K.; Jeong, M.G.; Hwang, E.S.; Hong, J.H. Catechins activate muscle stem cells by myf5 induction and stimulate muscle regeneration. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2017, 489, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, L.; Ramirez-Sanchez, I.; Perkins, G.A.; Murphy, A.; Taub, P.R.; Ceballos, G.; Villarreal, F.J.; Hogan, M.C.; Malek, M.H. Epicatechin enhances fatigue resistance and oxidative capacity in mouse muscle. J Physiol 2011, 589, 4615–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, K.B.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, D.H.; Moon, J.M.; Park, Y. Tannase-converted green tea extract with high epicatechin inhibits skeletal muscle mass in aged mice. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2020, 2020, 4319398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksen, M.B.; Frandsen, T.F. The impact of patient, intervention, comparison, outcome (PICO) as a search strategy tool on literature search quality: a systematic review. J Med Libr Assoc 2018, 106, 420–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; Moher, D. Evaluations of the uptake and impact of the preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses (PRISMA) statement and extensions: a scoping review. Syst Rev 2017, 6, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; Moher, D.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; Chou, R.; Glanville, J.; Grimshaw, J.M.; Hróbjartsson, A.; Lalu, M.M.; Li, T.; Loder, E.W.; Mayo-Wilson, E.; McDonald, S.; McGuinness, L.A.; Stewart, L.A.; Thomas, J.; Tricco, A.C.; Welch, V.A.; Whiting, P.; McKenzie, J.E. PRISMA 2020 explanation and elaboration: updated guidance and exemplars for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taub, P.R.; Ramirez-Sanchez, I.; Ciaraldi, T.P.; Gonzalez-Basurto, S.; Coral-Vazquez, R.; Perkins, G.; Hogan, M.; Maisel, A.S.; Henry, R.R.; Ceballos, G.; Villarreal, F. Perturbations in skeletal muscle sarcomere structure in patients with heart failure and type 2 diabetes: restorative effects of epicatechin-rich cocoa. Clin Sci (Lond) 2013, 125, 383–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDermott, M.M.; Criqui, M.H.; Domanchuk, K.; Ferrucci, L.; Guralnik, J.M.; Kibbe, M.R.; Kosmac, K.; Kramer, C.M.; Leeuwenburgh, C.; Li, L.; Lloyd-Jones, D.; Peterson, C.A.; Polonsky, T.S.; Stein, J.H.; Sufit, R.; Van Horn, L.; Villarreal, F.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, L.; Tian, L. Cocoa to improve walking performance in older people with peripheral artery disease: the cocoa-pad pilot randomized clinical trial. Circ Res 2020, 126, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, C.M.; Ramirez-Sanchez, I.; Oskarsson, B.; Joyce, N.; Aguilar, C.; Nicorici, A.; Dayan, J.; Goude, E.; Abresch, R.T.; Villarreal, F.; Ceballos, G.; Perkins, G.; Dugar, S.; Schreiner, G.; Henricson, E.K. Epicatechin induces mitochondrial biogenesis and markers of muscle regeneration in adults with Becker muscular dystrophy. Muscle Nerve 2021, 63, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez-Salmean, G.; Ciaraldi, T.P.; Nogueira, L.; Barboza, J.; Taub, P.R.; Hogan, M.C.; Henry, R.R.; Meaney, E.; Villarreal, F.; Ceballos, G.; Ramirez-Sanchez, I. Effects of epicatechin on molecular modulators of skeletal muscle growth and differentiation. J Nutr Biochem 2014, 25, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corr, L.D.; Field, A.; Pufal, D.; Killey, J.; Clifford, T.; Harper, L.D.; Naughton, R. J. Acute consumption of varied doses of cocoa flavanols does not influence exercise-induced muscle damage. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab 2020, 30, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, H.; Fu, Z.; Babu, P.V.; Zhen, W.; Leroith, T.; Meaney, M.P.; Voelker, K.A.; Jia, Z.; Grange, R.W.; Liu, D. Dietary epicatechin promotes survival of obese diabetic mice and drosophila melanogaster. J Nutr 2011, 141, 1095–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.; Hüttemann, M.; Kruger, A.; Bollig-Fischer, A.; Malek, M.H. Epicatechin combined with 8 weeks of treadmill exercise is associated with increased angiogenic and mitochondrial signaling in mice. Front Pharmacol 2015, 13, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.; Hüttemann, M.; Malek, M.H. Epicatechin attenuates degradation of mouse oxidative muscle following hindlimb suspension. J Strength Cond Res 2016, 30, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mafi, F.; Biglari, S.; Ghardashi Afousi, A.; Gaeini, A.A. Improvement in skeletal muscle strength and plasma levels of follistatin and myostatin induced by an 8-week resistance training and epicatechin supplementation in sarcopenic older adults. J Aging Phys Act 2019, 27, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munguia, L.; Ramirez-Sanchez, I.; Meaney, E.; Villarreal, F.; Ceballos, G.; Najera, N. Flavonoids from dark chocolate and epicatechin ameliorate high-fat diet-induced decreases in mobility and muscle damage in aging mice. Food Biosci 2020, 37, 100710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez-Sanchez, I.; Navarrete-Yañez, V.; Garate-Carrillo, A.; Lara-Hernandez, M.; Espinosa-Raya, J.; Moreno-Ulloa, A.; Gomez-Diaz, B.; Cedeño-Garcidueñas, A.L.; Ceballos, G.; Villarreal, F. Restorative potential of epicatechin in a rat model of gulf war illness muscle atrophy and fatigue. Sci Rep 2021, 11, 21861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hüttemann, M.; Lee, I.; Perkins, G.A.; Britton, S.L.; Koch, L.G.; Malek, M.H. Epicatechin is associated with increased angiogenic and mitochondrial signalling in the hindlimb of rats selectively bred for innate low running capacity. Clin Sci (Lond) 2013, 124, 663–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L, Parnell; Admed, B.; LeRoith, T.; Ansah, T.A.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Ordovás, J.M.; Si, H.; Liu, D.; Lai, C.Q. Dietary epicatechin improves survival and delays skeletal muscle degeneration in aged mice. FASEB J 2019, 33, 965–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Ruiz, C.; Cordero-Anguiano, P.; Morales-Guadarrama, A.; Mondragón-Lozano, R.; Sánchez-Torres, S.; Salgado-Ceballos, H.; Villarreal, F.; Meaney, E.; Ceballos, G.; Najera, N. Epicatechin reduces muscle waste after complete spinal cord transection in a murine model: role of ubiquitin-proteasome system. Mol Biol Rep 2020, 47, 8975–8985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsekoura, M.; Kastrinis, A.; Katsoulaki, M.; Billis, E.; Gliatis, J. Sarcopenia and its impact on quality of life. Adv Exp Med Biol 2017, 987, 213–218. [Google Scholar]
- Beaudart, C.; Biver, E.; Bruyère, O.; Cooper, C.; Al-Daghri, N.; Reginster, J.Y.; Rizzoli, R. Quality of life assessment in musculo-skeletal health. Aging Clin Exp Res 2018, 30, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cremonini, E.; Fraga, C.G.; Oteiza, P.I. Epicatechin in the control of glucose homeostasis: involvement of redox-regulated mechanisms. Free Radic Biol Med 2019, 130, 478–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonaldo, P; Sandri, M. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of muscle atrophy. Dis Model Mech 2013, 6, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, J.; Vernus, B.; Chelh, I.; Cassar-Malek, I.; Gabillard, J.C.; Hadj Sassi, A.; Seiliez, I.; Picard, B.; Bonnieu, A. Myostatin and the skeletal muscle atrophy and hypertrophy signaling pathways. Cell Mol Life Sci 2014, 71, 4361–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.F.; Chen, P.J.; Xiao, W.H. Signaling pathways controlling skeletal muscle mass. Sheng Li Xue Bao 2019, 71, 671–679. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, T.; Delafontaine, P. Mechanisms of IGF-1-mediated regulation of skeletal muscle hypertrophy and atrophy. Cells 2020, 9, 1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; McFarlane, C.; Kambadur, R.; Kukreti, H.; Bonala, S.; Srinivasan, S. Myostatin: expanding horizons. IUBMB Life 2015, 67, 589–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazdanova, A.A.; Kukes, V.G.; Parfenova, O.K.; Sidorov, N.G.; Perkov, A.V.; Solovieva, S.A.; Ryazantceva, O.V.; Lenkova, N.I. Myostatin - A modern understanding of the physiological role and significance in the development of age-associated diseases. Adv Gerontol 2021, 34, 701–706. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.M.; Zhao, Y.P.; Zhao, Y.; Deng, S.L.; Yu, K. Regulation of myostatin on the growth and development of skeletal muscle. Front Cell Dev Biol 2021, 9, 785712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J. Targeting the myostatin signaling pathway to treat muscle loss and metabolic dysfunction. J Clin Invest 2021, 131, e148372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.L.; Pu, H.F.; Chen, S.Y.; Wang, S.W.; Wang, P.S. Effects of catechin, epicatechin and epigallocatechin gallate on testosterone production in rat leydig cells. J Cell Biochem 2010, 110, 333–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Collier, L.; Pan, J.; Qin, W.; Bauman, W.A.; Cardozo, C.P. Testosterone reduced methylprednisolone-induced muscle atrophy in spinal cord-injured rats. Spinal Cord 2012, 50, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.T.; Chen, C.S.; Cheng, M.C.; Wu, M.F.; Cheng, F.T.; Hsu, C.L. Effects of resveratrol, epigallocatechin gallate, and epicatechin on mitochondrial functions in c2c12 myotubes. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 35, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Ulloa, A.; Miranda-Cervantes, A.; Licea-Navarro, A.; Mansour, C.; Beltrán-Partida, E.; Donis-Maturano, L.; Delgado De la Herrán, H.C.; Villarreal, F.; Álvarez-Delgado, C. Epicatechin stimulates mitochondrial biogenesis and cell growth in C2C12 myotubes via the G-protein coupled estrogen receptor. Eur J Pharmacol 2018, 822, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Prossnitz, E.R. G-protein-coupled estrogen receptor (GPER) and sex-specific metabolic homeostasis. Adv Exp Med Biol 2017, 1043, 427–453. [Google Scholar]
- Davison, G.; Callister, R.; Williamson, G.; Cooper, K.A.; Gleeson, M. The effect of acute pre-exercise dark chocolate consumption on plasma antioxidant status, oxidative stress and immunoendocrine responses to prolonged exercise. Eur J Nutr 2012, 51, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peschek, K.; Pritchett, R.; Bergman, E.; Pritchett, K. The effects of acute post exercise consumption of two cocoa-based beverages with varying flavanol content on indices of muscle recovery following downhill treadmill running. Nutrients 2013, 6, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stellingwerff, T.; Godin, J.P.; Chou, C.J.; Grathwohl, D.; Ross, A.B.; Cooper, K.A.; Williamson, G.; Actis-Goretta, L. The effect of acute dark chocolate consumption on carbohydrate metabolism and performance during rest and exercise. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 2014, 39, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decroix, L.; Tonoli, C.; Soares, D.D.; Descat, A.; Drittij-Reijnders, M.J.; Weseler, A.R.; Bast, A.; Stahl, W.; Heyman, E.; Meeusen, R. Acute cocoa flavanols intake has minimal effects on exercise-induced oxidative stress and nitric oxide production in healthy cyclists: a randomized controlled trial. J Int Soc Sports Nutr 2017, 14, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Copp, S.W.; Inagaki, T.; White, M.J.; Hirai, D.M.; Ferguson, S.K.; Holdsworth, C.T.; Sims, G.E.; Poole, D.C.; Musch, T.I. Epicatechin administration and exercising skeletal muscle vascular control and microvascular oxygenation in healthy rats. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2013, 304, H206–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeter, H.; Heiss, C.; Balzer, J.; Kleinbongard, P.; Keen, C.L.; Hollenberg, N.K.; Sies, H.; Kwik-Uribe, C.; Schmitz, H.H.; Kelm, M. (-) - A epicatequina medeia os efeitos benéficos do cacau rico em flavanol na função vascular em humanos. Proc Natl Acad Sci 2006, 103, 1024–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, Y.; Mikuriya, H.; Tayama, K.; Takahashi, H.; Nagasawa, A.; Yano, N.; Yuzawa, K.; Ogata, A.; Aoki, N. Goitrogenic effects of green tea extract catechins by dietary administration in rats. Arch Toxicol 2001, 75, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yun, S.Y.; Kim, S.P.; Song, D.K. Effects of (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate on pancreatic beta-cell damage in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Eur J Pharmacol 2006, 541, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacko, S.M.; Thambi, P.T.; Kuttan, R.; Nishigaki, I. Beneficial effects of green tea: a literature review. Chin Med 2010, 5, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massounga, Bora, A.F.; Ma, S.; Li, X.; Liu, L. Application of microencapsulation for the safe delivery of green tea polyphenols in food systems: review and recent advances. Food Res Int 2018, 105, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, C.; Liu, G.; Ping, Y.; Yang, K.; Tan, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, G.; Huang, X.; Xu, D.A. Comprehensive review of nano-delivery system for tea polyphenols: construction, applications, and challenges. Food Chem X 2023, 17, 100571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granja, A.; Pinheiro, M.; Reis, S. Epigallocatechin gallate nanodelivery systems for cancer therapy. Nutrients 2016, 8, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashidinejad, A.; Birch, E.J.; Sun-Waterhouse, D.; Everett, D.W. Effect of liposomal encapsulation on the recovery and antioxidant properties of green tea catechins incorporated into a hard low-fat cheese following in vitro simulated gastrointestinal digestion. Food and Bioproducts Processing 2016, 100, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granja, A.; Frias, I.; Neves, A.R.; Pinheiro, M.; Reis, S. Therapeutic potential of epigallocatechin gallate nanodelivery systems. Biomed Res Int 2017, 5813793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, S.B.; Chandran, S.P.; Vinukonda, A.; Dharmalingam, S.R. Green tea catechin loaded nanodelivery systems for the treatment of pandemic diseases. Asian J Pharm Clin Res 2019, 12, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lushchak, O.; Strilbytska, O.; Koliada, A.; Zayachkivska, A.; Burdyliuk, N.; Yurkevych, I.; Storey, K.B.; Vaiserman, A. Nanodelivery of phytobioactive compounds for treating aging associated disorders. Geroscience. 2020, 42, 117–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puligundla, P.; Mok, C.; Ko, S.; Liang, J.; Recharla, N. Nano-technological approaches to enhance the bioavailability and therapeutic efficacy of green tea polyphenols. Journal of Functional Foods 2017, 34, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Risk of bias | Si et al., 2011 [27] |
Hüttemann et al., 2013 [33] | Taub et al., 2013 [22] | Gutierrez-Salmean et al., 2014 [25] |
Lee et al., 2015 [28] |
Lee et al., 2016 [29] |
Mafi et al., 2019 [30] |
Si et al., 2019 [34] |
Corr et al., 2020 [26] |
Gonzalez-Ruiz et al., 2020 [35] | McDermott et al., 2020 [23] | Munguia et al., 2020 [31] | McDonald et al., 2021 [24] | Ramirez-Sanchez et al., 2021 [32] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reduced sample size |  |
 |
 |
|||||||||||
| Reduced evaluation time |  |
 |
||||||||||||
| Failure to collect the participants' diet |  |
 |
||||||||||||
| Only 1 period was evaluated |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
||||
| Only one dose was studied |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
| Absence of hormonal analysis |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Difference of the euthanasia periods |  |
|||||||||||||
| Choice of the animal model |  |
|||||||||||||
| Lack of pre- and post-functional evaluation |  |
|||||||||||||
| Epicatechin interruption was not evaluated |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
| Participants' gender not reported |  |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





