Submitted:
29 June 2023
Posted:
30 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Biofilm formation on biomaterials
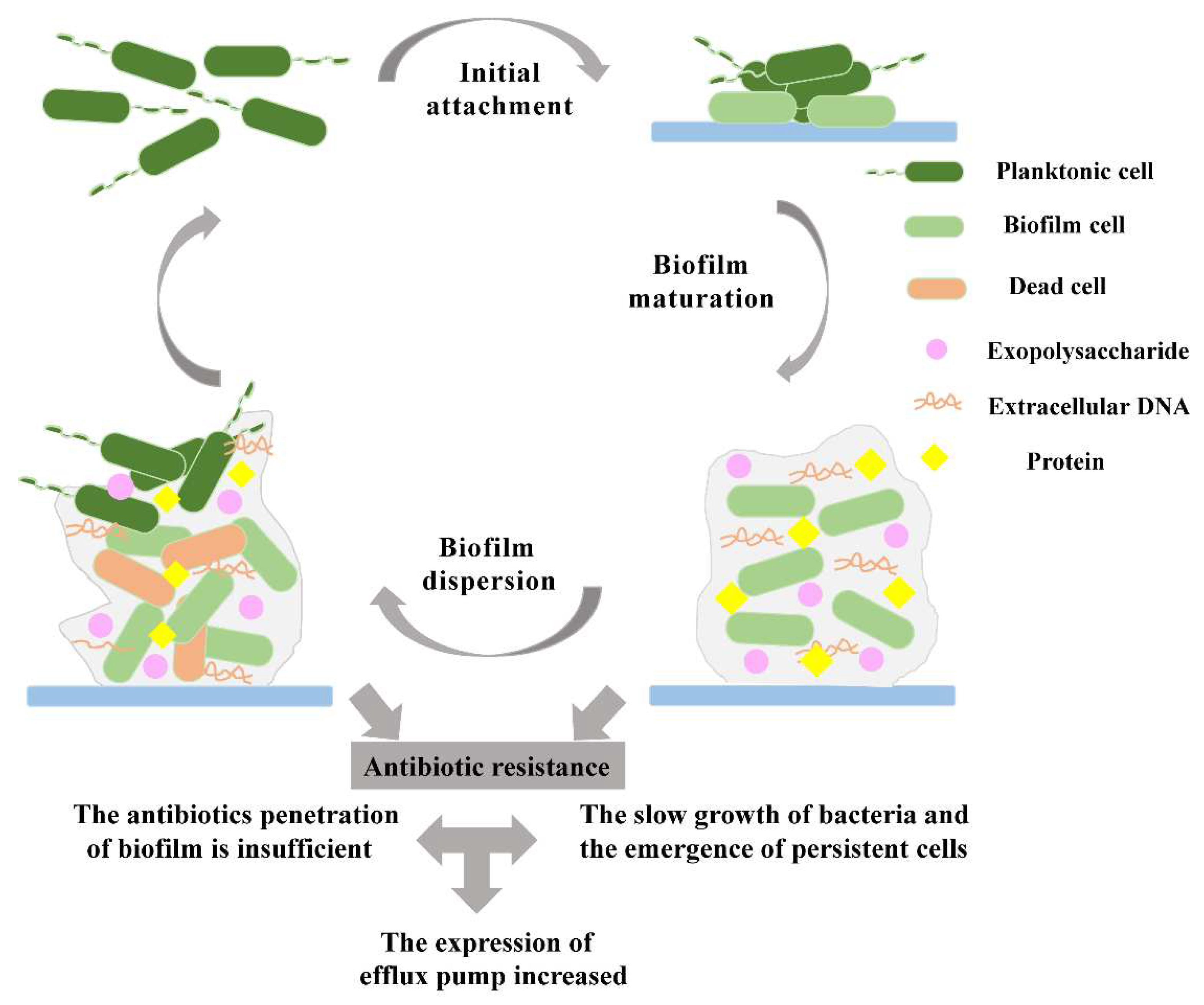
2.1. Biofilm initial attachment
2.2. Biofilm maturation
2.3. Biofilm dispersion
3. Mechanisms of antibiotic-resistant biofilms
3.1. Prevention of antibiotic penetration by biofilms
3.2. Presence of slow-growing or persistent cells in biofilms
3.3. Increased expression of efflux pumps in biofilms
4. Clinical characteristics of biomaterial-associated biofilms
5. Treatment of biofilms on the surface of biomaterials
5.1. Antibacterial coatings
5.2. Active coatings
5.3. Passive coatings
5.4. Modification of the surface of medical implants
5.5. Physical modifications
5.6. Chemical modification
| Types | Mechanisms of action | Materials | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antibacterial coatings | Active coatings | Fight infection by releasing antimicrobial agents | Antibiotic or silver compound coatings, enzymes, antimicrobial peptides | [40,116,119,120,123] |
| Passive coatings | Prevent bacteria from attaching using hydrophilic materials | Hyaluronic acid, hydrogel coatings | [127,128,129] | |
| Modification of the surface of medical implants | Physical modification | Affect cell adhesion by changing the surface roughness and generating hydrophobic surfaces | Femtosecond laser-induced surfaces, superhydrophobic non-planar 3D surfaces, nano and shark micropattern surfaces | [140,141,148,149,150,151,152] |
| Chemical modification | Regulate the formation of biofilms by changing the chemical properties of the material surface | Chitosan hydrogel films, surface-immobilized brominated furanones | [162,169] | |
6. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Costerton, J.W.; Stewart, P.S.; Greenberg, E.P. Bacterial biofilms: a common cause of persistent infections. Science. 1999, 284, 1318–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Z.; Huang, M.; Melander, C.; Kjellerup, B.V. Dispersal and inhibition of biofilms associated with infections. J Appl Microbiol. 2020, 128, 1279–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assefa, M.; Amare, A. Biofilm-associated multi-drug resistance in hospital-acquired infections: A review. Infect Drug Resist. 2022, 15, 5061–5068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, H.M.; Tran, H.; Booth, M.A.; Fox, K.E.; Nguyen, T.H.; Tran, N.; Tran, P.A. Nanomaterials for treating bacterial biofilms on implantable medical devices. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020, 10, 2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, D.; Yan, W. Mechanisms and control strategies of antibiotic resistance in pathological biofilms. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology. 2021, 31, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Gupta, A.; Upadhye, V.; Singh, S.C.; Sinha, R.P.; Häder, D.P. Therapeutic strategies against biofilm infections. Life (Basel). 2023, 13, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yao, H.; Zhao, X.; Ge, C. Biofilm formation and control of foodborne pathogenic bacteria. Molecules. 2023, 28, 2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatoon, Z.; McTiernan, C.D.; Suuronen, E.J.; Mah, T.F.; Alarcon, E.I. Bacterial biofilm formation on implantable devices and approaches to its treatment and prevention. Heliyon. 2018, 4, e01067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Fletcher, G.C.; On, S.L.W.; Palmer, J.S.; Gagic, D.; Flint, S.H. Biofilm formation, sodium hypochlorite susceptibility and genetic diversity of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Int J Food Microbiol. 2023, 385, 110011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, K.; Stoodley, P.; Goeres, D.M.; Hall-Stoodley, L.; Burmølle, M.; Stewart, P.S.; Bjarnsholt, T. The biofilm life cycle: expanding the conceptual model of biofilm formation. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2022, 20, 608–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, F.Y.; Darcan, C.; Kariptaş, E. The determination, monitoring, molecular mechanisms and formation of biofilm in E. coli. Braz J Microbiol. 2023, 54, 259–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabin, N.; Zheng, Y.; Opoku-Temeng, C.; Du, Y.; Bonsu, E.; Sintim, H.O. Biofilm formation mechanisms and targets for developing antibiofilm agents. Future Med Chem. 2015, 7, 493–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, R.; Cheng, J.; Wang, J.; Li, P.; Lin, J. Treatment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infectious biofilms: Challenges and strategies. Front Microbiol. 2022, 13, 955286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Silva, L.; Heo, G.J. Biofilm formation of pathogenic bacteria isolated from aquatic animals. Arch Microbiol. 2022, 205, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abebe, G.M. The role of bacterial biofilm in antibiotic resistance and food contamination. Int J Microbiol. 2020, 2020, 1705814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Sarkar, S.; Das, B.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Tribedi, P. Biofilm, pathogenesis and prevention--a journey to break the wall: a review. Arch Microbiol. 2016, 198, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoica, P.; Chifiriuc, M.C.; Rapa, M.; Lazăr, V. Overview of biofilm-related problems in medical devices. Biofilms and Implantable Medical Devices 2017, 3–23. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Zong, W.; Zhang, Z.; Lv, W.; Ji, X.; Zhu, D.; Du, X.; Wang, S. Effects and molecular mechanism of flagellar gene flgK on the motility, adhesion/invasion, and desiccation resistance of Cronobacter sakazakii. Food Res Int. 2023, 164, 112418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedeljković, M.; Sastre, D.E.; Sundberg, E.J. Bacterial flagellar filament: A supramolecular multifunctional nanostructure. Int J Mol Sci. 2021, 22, 7521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolenda, R.; Ugorski, M.; Grzymajlo, K. Everything you always wanted to know about salmonella type 1 fimbriae, but were afraid to ask. Front Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puri, D.; Fang, X.; Allison, K.R. Evidence of a possible multicellular life cycle in Escherichia coli. iScience. 2023, 26, 105795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azara, E.; Longheu, C.M.; Attene, S.; Sanna, S.; Sale, M.; Addis, M.F.; Tola, S. Comparative profiling of agr locus, virulence, and biofilm-production genes of human and ovine non-aureus staphylococci. BMC Vet Res. 2022, 18, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mack, D.; Fischer, W.; Krokotsch, A.; Leopold, K.; Hartmann, R.; Egge, H.; Laufs, R. The intercellular adhesin involved in biofilm accumulation of Staphylococcus epidermidis is a linear beta-1,6-linked glucosaminoglycan: purification and structural analysis. J Bacteriol. 1996, 178, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Federle, M.J.; Bassler, B.L. Interspecies communication in bacteria. J Clin Invest. 2003, 112, 1291–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Zou, H.; Li, J.; Song, T.; Lv, W.; Wang, W.; Wang, Z.; Tao, S. Impact of quorum sensing signaling molecules in gram-negative bacteria on host cells: current understanding and future perspectives. Gut Microbes. 2022, 14, 2039048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Cheng, J.; Wang, Y.; Shen, X. The Pseudomonas Quinolone Signal (PQS): Not just for quorum sensing anymore. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018, 8, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Bian, Z.; Wang, Y. Biofilm formation and inhibition mediated by bacterial quorum sensing. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022, 106, 6365–6381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, A.C.; Florez, C.; Dunshee, E.B.; Lieber, A.D.; Terry, M.L.; Light, C.J.; Schertzer, J.W. Pseudomonas Quinolone Signal-induced outer membrane vesicles enhance biofilm dipersion in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. mSphere 2020, 5, e01109-01120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allesen-Holm, M.; Barken, K.B.; Yang, L.; Klausen, M.; Webb, J.S.; Kjelleberg, S.; Molin, S.; Givskov, M.; Tolker-Nielsen, T. A characterization of DNA release in Pseudomonas aeruginosa cultures and biofilms. Mol Microbiol. 2006, 59, 1114–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, Q.; Ding, L.; Ren, H. The role of immobilized quorum sensing strain in promoting biofilm formation of Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor during long-term stable operation. Environ Res. 2022, 215, 114159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamal, M.; Ahmad, W.; Andleeb, S.; Jalil, F.; Imran, M.; Nawaz, M.A.; Hussain, T.; Ali, M.; Rafiq, M.; Kamil, M.A. Bacterial biofilm and associated infections. J Chin Med Assoc. 2018, 81, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karygianni, L.; Ren, Z.; Koo, H.; Thurnheer, T. Biofilm Matrixome: Extracellular Components in Structured Microbial Communities. Trends Microbiol. 2020, 28, 668–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsek, M.R.; Singh, P.K. Bacterial biofilms: an emerging link to disease pathogenesis. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2003, 57, 677–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauer, K.; Cullen, M.C.; Rickard, A.H.; Zeef, L.A.; Davies, D.G.; Gilbert, P. Characterization of nutrient-induced dispersion in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 biofilm. J Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 7312–7326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostakioti, M.; Hadjifrangiskou, M.; Hultgren, S.J. Bacterial biofilms: development, dispersal, and therapeutic strategies in the dawn of the postantibiotic era. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2013, 3, a010306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, D.; Langenheder, S.; Jürgens, K. Dispersal modifies the diversity and composition of active bacterial communities in response to a salinity disturbance. Front Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wille, J.; Coenye, T. Biofilm dispersion: The key to biofilm eradication or opening Pandora's box? Biofilm. 2020, 2, 100027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, D.; Rumbaugh, K.P. Approaches to dispersing medical biofilms. Microorganisms. 2017, 5, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppenheimer-Shaanan, Y.; Steinberg, N.; Kolodkin-Gal, I. Small molecules are natural triggers for the disassembly of biofilms. Trends Microbiol. 2013, 21, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerachamy, S.; Yarlagadda, T.; Manivasagam, G.; Yarlagadda, P.K. Bacterial adherence and biofilm formation on medical implants: a review. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2014, 228, 1083–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.Z.; Wang, D.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wozniak, D.J. Regulation of biofilm exopolysaccharide biosynthesis and degradation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2022, 76, 413–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutherland, I.W. Polysaccharases for microbial exopolysaccharides. Carbohydrate Polymers. 1999, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, M.; Resch, M.D.; Cherny, K.E.; Sauer, K. The alginate and motility regulator AmrZ is essential for the regulation of the dispersion response by Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. mSphere. 2022, 7, e0050522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colvin, K.M.; Irie, Y.; Tart, C.S.; Urbano, R.; Whitney, J.C.; Ryder, C.; Howell, P.L.; Wozniak, D.J.; Parsek, M.R. The Pel and Psl polysaccharides provide Pseudomonas aeruginosa structural redundancy within the biofilm matrix. Environ Microbiol. 2012, 14, 1913–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.T.; Niu, Y.T.; Zhang, H.; Li, P.X.; Zhang, N.M.; Cheng, J.L.; LIN, J.S. An engineered bacterium for the targeted delivery of proteins to destroy Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Acta Microbiologica Sinica 2021, 61, 2726–2748. [Google Scholar]
- Tsagkari, E.; Connelly, S.; Liu, Z.; McBride, A.; Sloan, W.T. The role of shear dynamics in biofilm formation. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2022, 8, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.C.; Morgenroth, E. Monitoring biofilm detachment under dynamic changes in shear stress using laser-based particle size analysis and mass fractionation. Water Sci Technol. 2003, 47, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, G.; Klein, M.I.; Koo, H. Analysis of the mechanical stability and surface detachment of mature Streptococcus mutans biofilms by applying a range of external shear forces. Biofouling. 2014, 30, 1079–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oulahal-Lagsir, N.; Martial-Gros, A.; Bonneau, M.; Blum, L.J. "Escherichia coli-milk" biofilm removal from stainless steel surfaces: synergism between ultrasonic waves and enzymes. Biofouling. 2003, 19, 159–168. [Google Scholar]
- Oulahal, N.; Martial-Gros, A.; Bonneau, M.; Blum, L.J.J.B. Combined effect of chelating agents and ultrasound on biofilm removal from stainless steel surfaces. Application to Escherichia coli milk and Staphylococcus aureus milk biofilms. 2004, 1, 65–73. [Google Scholar]
- Nigri, G.R.; Tsai, S.; Kossodo, S.; Waterman, P.; Fungaloi, P.; Hooper, D.C.; Doukas, A.G.; LaMuraglia, G.M. Laser-induced shock waves enhance sterilization of infected vascular prosthetic grafts. Lasers Surg Med. 2001, 29, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otto, M. Staphylococcal infections: mechanisms of biofilm maturation and detachment as critical determinants of pathogenicity. Annu Rev Med. 2013, 64, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, D.; Yan, W. Mechanisms and control strategies of antibiotic resistance in pathological biofilms. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021, 31, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceri, H.; Olson, M.E.; Stremick, C.; Read, R.R.; Morck, D.; Buret, A. The calgary biofilm device: New technology for rapid determination of antibiotic susceptibilities of bacterial biofilms. J Clin Microbiol. 1999, 37, 1771–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michael, *!!! REPLACE !!!*; Waturangi, D.E. Antibiofilm activity from endophyte bacteria, Vibrio cholerae strains, and actinomycetes isolates in liquid and solid culture. BMC Microbiol. 2023, 23, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pokharel, K.; Dawadi, B.R.; Shrestha, L.B. Role of biofilm in bacterial infection and antimicrobial resistance. JNMA J Nepal Med Assoc. 2022, 60, 836–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cascioferro, S.; Carbone, D.; Parrino, B.; Pecoraro, C.; Giovannetti, E.; Cirrincione, G.; Diana, P. Therapeutic strategies to counteract antibiotic resistance in MRSA biofilm-associated infections. ChemMedChem. 2021, 16, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, K.; Høiby, N.; Jensen, P.; Ciofu, O.; Moser, C. Immune response to biofilm growing pulmonary Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection. Biomedicines. 2022, 10, 2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güneş, B.; Akçelik, N. The role of eDNA in biofilm structure of Enterococcus faecalis and investigation of the efficiency of enzyme and antibiotic application in biofilm eradication. Mikrobiyol Bul. 2022, 56, 606–619. [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wu, W.; Lu, Y. Engineered organic nanoparticles to combat biofilms. Drug Discov Today. 2023, 28, 103455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.; Yuan, M.; Tao, Q.; Xu, T.; Liu, J.; Huang, Z.; Wu, Q.; Pan, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Z. Discovery of novel resistance mechanisms of Vibrio parahaemolyticus biofilm against aminoglycoside antibiotics. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023, 12, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulcahy, H.; Charron-Mazenod, L.; Lewenza, S. Extracellular DNA chelates cations and induces antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciofu, O.; Rojo-Molinero, E.; Macià, M.D.; Oliver, A. Antibiotic treatment of biofilm infections. Apmis. 2017, 125, 304–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoiby, N.; Bjarnsholt, T.; Givskov, M.; Molin, S.; Ciofu, O. Antibiotic resistance of bacterial biofilms. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2010, 35, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, H.M.A.; Alnasser, S.M.; Abd-Elhafeez, H.H.; Alotaibi, M.; Batiha, G.E.; Younis, W. detection of β-Lactamase resistance and biofilm genes in Pseudomonas species isolated from chickens. Microorganisms. 2022, 10, 1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Moreau, A.; Khodaparast, S.; Perazzo, A.; Feng, J.; Fei, C.; Mao, S.; Mukherjee, S.; Košmrlj, A.; Wingreen, N.S.; Bassler, B.L.; Stone, H.A. Bacterial biofilm material properties enable removal and transfer by capillary peeling. Adv Mater. 2018, 30, e1804153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spoering, A.L.; Lewis, K. Biofilms and planktonic cells of Pseudomonas aeruginosa have similar resistance to killing by antimicrobials. J Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 6746–6751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mah, T.F. Biofilm-specific antibiotic resistance. Future Microbiol. 2012, 7, 1061–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, P.S. Mechanisms of antibiotic resistance in bacterial biofilms. Int J Med Microbiol. 2002, 292, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costerton, J.W.; Lewandowski, Z.; Caldwell, D.E.; Korber, D.R.; Lappin-Scott, H.M. Microbial biofilms. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1995, 49, 711–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamp, S.J.; Gjermansen, M.; Johansen, H.K.; Tolker-Nielsen, T. Tolerance to the antimicrobial peptide colistin in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms is linked to metabolically active cells, and depends on the pmr and mexAB-oprM genes. Mol Microbiol. 2008, 68, 223–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaurav, A.; Bakht, P.; Saini, M.; Pandey, S.; Pathania, R. Role of bacterial efflux pumps in antibiotic resistance, virulence, and strategies to discover novel efflux pump inhibitors. Microbiology (Reading). 2023, 169, 001333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seukep, A.J.; Mbuntcha, H.G.; Kuete, V.; Chu, Y.; Fan, E.; Guo, M.Q. What approaches to thwart bacterial efflux pumps-mediated resistance? Antibiotics (Basel). 2022, 11, 1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Başaran, S.N.; Öksüz, L. The role of efflux pumps ın antıbıotıc resıstance of gram negatıve rods. Arch Microbiol. 2023, 205, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mudde, S.E.; Schildkraut, J.A.; Ammerman, N.C.; de Vogel, C.P.; de Steenwinkel, J.E.M.; van Ingen, J.; Bax, H.I. Unraveling antibiotic resistance mechanisms in Mycobacterium abscessus: the potential role of efflux pumps. J Glob Antimicrob Resist. 2022, 31, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnabas, V.; Kashyap, A.; Raja, R.; Newar, K.; Rai, D.; Dixit, N.M.; Mehra, S. The extent of antimicrobial resistance due to efflux pump regulation. ACS Infect Dis. 2022, 8, 2374–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reygaert, W.C. An overview of the antimicrobial resistance mechanisms of bacteria. AIMS Microbiol. 2018, 4, 482–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, T.M.; Chakraborty, A.J.; Khusro, A.; Zidan, B.R.M.; Mitra, S.; Emran, T.B.; Dhama, K.; Ripon, M.K.H.; Gajdács, M.; Sahibzada, M.U.K.; Hossain, M.J.; Koirala, N. Antibiotic resistance in microbes: History, mechanisms, therapeutic strategies and future prospects. J Infect Public Health. 2021, 14, 1750–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, T.H. Tetracycline antibiotics and resistance. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2016, 6, a025387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, N.; Perumal, G.; Doble, M. Bacterial resistance in biofilm-associated bacteria. Future Microbiol. 2015, 10, 1743–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Cao, M.; Li, C.; Huang, J.; Zheng, S.; Wang, G. Efflux proteins MacAB confer resistance to arsenite and penicillin/macrolide-type antibiotics in Agrobacterium tumefaciens 5A. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019, 35, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadian, L.; Haghshenas, M.R.; Mirzaei, B.; Khalili, Y.; Goli, H.R. Role of MexAB-OprM efflux pump in the emergence of multidrug-resistant clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Mazandaran province of Iran. Mol Biol Rep. 2023, 50, 2603–2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrer-Espada, R.; Shahrour, H.; Pitts, B.; Stewart, P.S.; Sánchez-Gómez, S.; Martínez-de-Tejada, G. A permeability-increasing drug synergizes with bacterial efflux pump inhibitors and restores susceptibility to antibiotics in multi-drug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains. Sci Rep. 2019, 9, 3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.J.; Bayer, A.S.; Mishra, N.N.; Meehl, M.; Ledala, N.; Yeaman, M.R.; Xiong, Y.Q.; Cheung, A.L. The Staphylococcus aureus two-component regulatory system, GraRS, senses and confers resistance to selected cationic antimicrobial peptides. Infect Immun. 2012, 80, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.; Costa, S.K.; Wierzbicki, R.M.; Rigby, W.F.C.; Cheung, A.L. The extracellular loop of the membrane permease VraG interacts with GraS to sense cationic antimicrobial peptides in Staphylococcus aureus. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiron, A.; Falord, M.; Valle, J.; Débarbouillé, M.; Msadek, T. Bacitracin and nisin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus: a novel pathway involving the BraS/BraR two-component system (SA2417/SA2418) and both the BraD/BraE and VraD/VraE ABC transporters. Mol Microbiol. 2011, 81, 602–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arii, K.; Kawada-Matsuo, M.; Oogai, Y.; Noguchi, K.; Komatsuzawa, H. Single mutations in BraRS confer high resistance against nisin A in Staphylococcus aureus. Microbiologyopen. 2019, 8, e791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babushkina, I.V.; Bondarenko, A.S.; Ulyanov, V.Y.; Mamonova, I.A. Biofilm formation by gram-negative bacteria during implant-associated infection. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2020, 169, 365–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, J.; Monteiro, F.J.; Ferraz, M.P. Bioengineering approaches to fight against orthopedic biomaterials related-infections. Int J Mol Sci. 2022, 23, 11658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouirfa, H.; Bouloussa, H.; Migonney, V.; Falentin-Daudré, C. Review of titanium surface modification techniques and coatings for antibacterial applications. Acta Biomater. 2019, 83, 37–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Høiby, N.; Bjarnsholt, T.; Moser, C.; Bassi, G.L.; Coenye, T.; Donelli, G.; Hall-Stoodley, L.; Holá, V.; Imbert, C.; Kirketerp-Møller, K.; Lebeaux, D.; Oliver, A.; Ullmann, A.J.; Williams, C. ESCMID guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of biofilm infections 2014. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2015, 21 Suppl 1, S1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wi, Y.M.; Patel, R. Understanding biofilms and novel approaches to the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of medical devicea-Associated infections. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2018, 32, 915–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebeaux, D.; Fernández-Hidalgo, N.; Chauhan, A.; Lee, S.; Ghigo, J.M.; Almirante, B.; Beloin, C. Management of infections related to totally implantable venous-access ports: Challenges and perspectives. Lancet Infect Dis. 2014, 14, 146–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gominet, M.; Compain, F.; Beloin, C.; Lebeaux, D. Central venous catheters and biofilms: where do we stand in 2017? Apmis. 2017, 125, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangner, N.; Woitek, F.; Haussig, S.; Schlotter, F.; Stachel, G.; Höllriegel, R.; Wilde, J.; Lindner, A.; Holzhey, D.; Leontyev, S.; Mohr, F.W.; Schuler, G.; Linke, A. Incidence, predictors, and outcome of patients developing infective endocarditis following transfemoral transcatheter aortic valve replacement. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016, 67, 2907–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elgharably, H.; Hussain, S.T.; Shrestha, N.K.; Blackstone, E.H.; Pettersson, G.B. Current hypotheses in cardiac surgery: biofilm in infective endocarditis. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2016, 28, 56–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nappi, F.; Iervolino, A.; Singh, S.S.A. The new challenge for heart endocarditis: from conventional prosthesis to new devices and platforms for the treatment of structural heart disease. Biomed Res Int. 2021, 2021, 7302165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izakovicova, P.; Borens, O.; Trampuz, A. Periprosthetic joint infection: current concepts and outlook. EFORT Open Rev. 2019, 4, 482–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamihata, S.; Ando, W.; Nakahara, I.; Enami, H.; Takashima, K.; Uemura, K.; Hamada, H.; Sugano, N. Optimizing vancomycin release from novel carbon fiber-reinforced polymer implants with small holes: periprosthetic joint infection treatment. J Artif Organs. (Online ahead of print). 2023, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgiovine, C.; Pellegrino, L.; Bulgarelli, A.; Lauta, F.C.; Di Claudio, A.; Ciceri, R.; Cancellara, A.; Calcaterra, F.; Mavilio, D.; Grappiolo, G.; Chiappetta, K.; Loppini, M.; Rusconi, R. Interaction of bacteria, immune cells, and surface topography in periprosthetic joint infections. Int J Mol Sci. 2023, 24, 9028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gbejuade, H.O.; Lovering, A.M.; Webb, J.C. The role of microbial biofilms in prosthetic joint infections. Acta Orthop. 2015, 86, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osmon, D.R.; Berbari, E.F.; Berendt, A.R.; Lew, D.; Zimmerli, W.; Steckelberg, J.M.; Rao, N.; Hanssen, A.; Wilson, W.R. Diagnosis and management of prosthetic joint infection: clinical practice guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2013, 56, e1–e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacqueline, C.; Caillon, J. Impact of bacterial biofilm on the treatment of prosthetic joint infections. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2014, 69 Suppl 1, i37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Misba, L.; Khan, A.U. Antibiotics versus biofilm: an emerging battleground in microbial communities. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2019, 8, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, F.; Pham, D.T.N.; Tabassum, N.; Oloketuyi, S.F.; Kim, Y.M. Treatment strategies targeting persister cell formation in bacterial pathogens. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2020, 46, 665–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, V.; Mardas, N.; Spratt, D.; Hassan, I.A.; Walters, N.J.; Beltrán, V.; Donos, N. The effect of microcosm biofilm decontamination on surface topography, chemistry, and biocompatibility dynamics of implant titanium surfaces. Int J Mol Sci. 2022, 23, 10033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folliero, V.; Franci, G.; Dell'Annunziata, F.; Giugliano, R.; Foglia, F.; Sperlongano, R.; De Filippis, A.; Finamore, E.; Galdiero, M. Evaluation of antibiotic resistance and biofilm production among clinical strain isolated from medical devices. Int J Microbiol. 2021, 2021, 9033278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivares, E.; Badel-Berchoux, S.; Provot, C.; Prévost, G.; Bernardi, T.; Jehl, F. Clinical impact of antibiotics for the treatment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm infections. Front Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, R.; Santhakumari, S.; Poonguzhali, P.; Geetha, M.; Dyavaiah, M.; Xiangmin, L. Bacterial biofilm inhibition: A focused rview on recent therapeutic strategies for combating the biofilm mediated infections. Front Microbiol. 2021, 12, 676458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloutier, M.; Mantovani, D.; Rosei, F. Antibacterial coatings: Challenges, perspectives, and opportunities. Trends Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 637–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmo, J.A.-D.; Ruiz-Rubio, L.; Pérez-Alvarez, L.; Sáez-Martínez, V.; Vilas-Vilela, J.L. Antibacterial Coatings for Improving the Performance of Biomaterials. Coatings. 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruna, T.; Maldonado-Bravo, F.; Jara, P.; Caro, N. Silver nanoparticles and their antibacterial applications. Int J Mol Sci. 2021, 22, 7202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romanò, C.L.; Scarponi, S.; Gallazzi, E.; Romanò, D.; Drago, L. Antibacterial coating of implants in orthopaedics and trauma: a classification proposal in an evolving panorama. J Orthop Surg Res. 2015, 10, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuehl, R.; Brunetto, P.S.; Woischnig, A.K.; Varisco, M.; Rajacic, Z.; Vosbeck, J.; Terracciano, L.; Fromm, K.M.; Khanna, N. Preventing implant-associated infections by silver coating. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 2467–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haktaniyan, M.; Bradley, M. Polymers showing intrinsic antimicrobial activity. Chem Soc Rev. 2022, 51, 8584–8611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, P.A.; Hocking, D.M.; O'Connor, A.J. In situ formation of antimicrobial silver nanoparticles and the impregnation of hydrophobic polycaprolactone matrix for antimicrobial medical device applications. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2015, 47, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, C.; Hung, H.C.; Sun, S.; Wang, D.; Li, Y.; Jiang, S.; Chen, Z. Probing the surface hydration of nonfouling zwitterionic and PEG materials in contact with proteins. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015, 7, 16881–16888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Faria, A.F.; Ma, J.; Elimelech, M. Mitigation of biofilm development on thin-film composite membranes functionalized with zwitterionic polymers and silver nanoparticles. Environ Sci Technol. 2017, 51, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haidari, H.; Kopecki, Z.; Bright, R.; Cowin, A.J.; Garg, S.; Goswami, N.; Vasilev, K. Ultrasmall AgNP-impregnated biocompatible hydrogel with highly effective biofilm elimination properties. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020, 12, 41011–41025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, K.; Fernandes, M.M.; Mendoza, E.; Tzanov, T. Enzyme multilayer coatings inhibit Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation on urinary catheters. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 4373–4385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, B.; Martínez-de-Tejada, G.; Gomes, P.A.C.; MC, L.M.; Costa, F. Antimicrobial peptides in the battle against orthopedic implant-related infections: A review. Pharmaceutics. 2021, 13, 1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, M.; Costa, F.; Monteiro, C.; Duarte, F.; Martins, M.C.L.; Gomes, P. Antimicrobial coatings prepared from Dhvar-5-click-grafted chitosan powders. Acta Biomater. 2019, 84, 242–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez Lopez, A.L.; Lee, M.R.; Ortiz, B.J.; Gastfriend, B.D.; Whitehead, R.; Lynn, D.M.; Palecek, S.P. Preventing S. aureus biofilm formation on titanium surfaces by the release of antimicrobial beta-peptides from polyelectrolyte multilayers. Acta Biomater. 2019, 93, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Zhu, X.; Loh, X.J. Controlling cell adhesion using layer-by-layer approaches for biomedical applications. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017, 70, 1163–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, D.; van den Boogaert, I.; Miller, J.; Presswell, R.; Jouhara, H. Hydrophilic and hydrophobic materials and their applications. Energy Sources, Part A: Recovery, Utilization, and Environmental Effects 2018, 40, 2686–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drago, L.; Cappelletti, L.; De Vecchi, E.; Pignataro, L.; Torretta, S.; Mattina, R. Antiadhesive and antibiofilm activity of hyaluronic acid against bacteria responsible for respiratory tract infections. APMIS. 2014, 122, 1013–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhang, H.; Wu, Y.; Lin, Y.; Cheng, J.; Lu, K.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.; Yu, Q. Three lines of defense: A multifunctional coating with anti-adhesion, bacteria-killing and anti-quorum sensing properties for preventing biofilm formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Acta Biomater. 2022, 151, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, S.; Vimalraj, S.; Thanikaivelan, P.; Banudevi, S.; Manivasagam, G. A review on injectable chitosan/beta glycerophosphate hydrogels for bone tissue regeneration. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019, 121, 38–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, B.; Chenthamara, D.; Subramaniam, S. Fabrication and biomedical applications of Arabinoxylan, Pectin, Chitosan, soy protein, and silk fibroin hydrogels via laccase - Ferulic acid redox chemistry. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules. 2022, 201, 539–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemani, S.K.; Annavarapu, R.K.; Mohammadian, B.; Raiyan, A.; Sojoudi, H.J.A.M.I. Surface modification: Surface modification of polymers: methods and applications. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 5, 1870121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Gunaid, T.A.; Krupa, I.; Ouederni, M.; Krishnamoorthy, S.K.; Popelka, A. Enhancement of adhesion characteristics of low-density polyethylene using atmospheric plasma iitiated-grafting of polyethylene glycol. Polymers (Basel). 2021, 13, 1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterzenbach, T.; Helbig, R.; Hannig, C.; Hannig, M. Bioadhesion in the oral cavity and approaches for biofilm management by surface modifications. Clin Oral Investig. 2020, 24, 4237–4260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemani, S.K.; Annavarapu, R.K.; Mohammadian, B.; Raiyan, A.; Heil, J.; Haque, M.A.; Abdelaal, A.; Sojoudi, H. Surface Modification of Polymers: Methods and Applications. Advanced Materials Interfaces. 2018, 5, 1870121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klodzinska, S.N.; Wan, F.; Jumaa, H.; Sternberg, C.; Rades, T.; Nielsen, H.M. Utilizing nanoparticles for improving anti-biofilm effects of azithromycin: A head-to-head comparison of modified hyaluronic acid nanogels and coated poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanoparticles. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 555, 595–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, J.; Kumari, R.M.; Verma, V.; Nimesh, S. Recent development in therapeutic strategies targeting Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms – A review. Materials Today: Proceedings 2021, 46, 2359–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Encinas, N.; Pantoja, M.; Abenojar, J.; Martínez, M.A. Control of Wettability of Polymers by Surface Roughness Modification. Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology. 2010, 24, 1869–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epperlein, N.; Menzel, F.; Schwibbert, K.; Koter, R.; Bonse, J.; Sameith, J.; Krüger, J.; Toepel, J. Influence of femtosecond laser produced nanostructures on biofilm growth on steel. Applied Surface Science. 2017, 418, 420–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillett, A.; Waugh, D.; Lawrence, J.; Swainson, M.; Dixon, R. Laser surface modification for the prevention of biofouling by infection causing Escherichia Coli. Journal of Laser Applications. 2016, 28, 022503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Long, M.; Han, R.; Cao, K.; Zhang, S.; Feng, D.; Jia, T.; Sun, Z.; Qiu, J.; Xu, H. Femtosecond laser-induced periodic structures: mechanisms, techniques, and applications. Opto-Electronic Science 2022, 1, 220005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalil, S.A.; Akram, M.; Bhat, J.A.; Hayes, J.J.; Singh, S.C.; ElKabbash, M.; Guo, C. Creating superhydrophobic and antibacterial surfaces on gold by femtosecond laser pulses. Appl Surf Sci. 2020, 506, 144952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, A.; Kumar, A.; Sreedharan, S.; Muralidharan, G.; Pramanik, A.; Nandi, D.; Sen, P. Fabrication of low-cost flexible superhydrophobic antibacterial surface with dual-scale roughness. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2018, 4, 2213–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wu, Y.; Cao, Y.; Li, G.; Liao, Y. Influence of surface roughness on contact angle hysteresis and spreading work. Colloid and Polymer Science. 2020, 298, 1107–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Altenried, S.; Zogg, A.; Zuber, F.; Maniura-Weber, K.; Ren, Q. Role of the surface nanoscale roughness of stainless steel on bacterial adhesion and microcolony formation. ACS Omega. 2018, 3, 6456–6464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozmos, M.; Virant, P.; Rojko, F.; Abram, A.; Rudolf, R.; Raspor, P.; Zore, A.; Bohinc, K. Bacterial adhesion of Streptococcus mutans to dental material surfaces. Molecules. 2021, 26, 1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, A.; Gao, Y.; Jin, T.; Luo, X.; Zeng, Q.; Shang, Z. Effects of surface roughness and texture on the bacterial adhesion on the bearing surface of bio-ceramic joint implants: An in vitro study. Ceramics International. 2020, 46, 6550–6559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, G.R.M. Surface roughness of dental implant and osseointegration. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2021, 20, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarov, D.V.; Smirnov, V.M.; Zemtsova, E.G.; Yudintceva, N.M.; Shevtsov, M.A.; Valiev, R.Z. Enhanced osseointegrative properties of ultra-fine-grained titanium implants modified by chemical etching and atomic layer deposition. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2018, 4, 3268–3281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, J.; Jain, S.; Padmarajan, R.; Purighalla, S.; Sambandamurthy, V.K.; Chatterjee, K. Multi-scale surface topography to minimize adherence and viability of nosocomial drug-resistant bacteria. Mater Des. 2018, 140, 332–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, R.M.; Hoffman, M.G.; Sogo, M.J.; Parker, A.E.; O'Toole, G.A.; Brennan, A.B.; Reddy, S.T. Micro-patterned surfaces reduce bacterial colonization and biofilm formation in vitro: Potential for enhancing endotracheal tube designs. Clin Transl Med. 2014, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Wei, Q.; Mettetal, M.R.; Han, J.; Rau, L.; Tie, J.; May, R.M.; Pathe, E.T.; Reddy, S.T.; Sullivan, L.; Parker, A.E.; Maul, D.H.; Brennan, A.B.; Mann, E.E. Surface micropattern reduces colonization and medical device-associated infections. J Med Microbiol. 2017, 66, 1692–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, R.M.; Magin, C.M.; Mann, E.E.; Drinker, M.C.; Fraser, J.C.; Siedlecki, C.A.; Brennan, A.B.; Reddy, S.T. An engineered micropattern to reduce bacterial colonization, platelet adhesion and fibrin sheath formation for improved biocompatibility of central venous catheters. Clin Transl Med. 2015, 4, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rostami, S.; Puza, F.; Ucak, M.; Ozgur, E.; Gul, O.; Ercan, U.K.; Garipcan, B. Bifunctional sharkskin mimicked chitosan/graphene oxide membranes: Reduced biofilm formation and improved cytocompatibility. Applied Surface Science. 2021, 544, 148828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardhono, E.Y.; Pinem, M.P.; Susilo, S.; Siom, B.J.; Sudrajad, A.; Pramono, A.; Meliana, Y.; Guénin, E. Modification of physio-mechanical properties of chitosan-based films via physical treatment approach. Polymers (Basel). 2022, 14, 5216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Seenivasan, M.K.; Inbarajan, A. A literature review on biofilm formation on silicone and poymethyl methacrylate used for maxillofacial prostheses. Cureus. 2021, 13, e20029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desrousseaux, C.; Sautou, V.; Descamps, S.; Traoré, O. Modification of the surfaces of medical devices to prevent microbial adhesion and biofilm formation. J Hosp Infect. 2013, 85, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renner, L.D.; Weibel, D.B. Physicochemical regulation of biofilm formation. MRS Bull. 2011, 36, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, F.Z.; Zhao, X.X.; Liao, Y.H. Effect of material surface characteristics on biofilm formation and its application. Microbiol China 2018, 45, 155–165. [Google Scholar]
- Freitas, S.C.; Correa-Uribe, A.; Martins, M.C.L.; Pelaez-Vargas, A. Self-assembled monolayers for dental implants. Int J Dent. 2018, 2018, 4395460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somasundaram, S. Silane coatings of metallic biomaterials for biomedical implants: A preliminary review. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2018, 106, 2901–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicosia, C.; Huskens, J. Reactive self-assembled monolayers: from surface functionalization to gradient formation. Mater Horiz. 2014, 1, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekaran, M.; Kim, K.D.; Chun, S.C. Antibacterial Activity of Chitosan Nanoparticles: A Review. Processes. 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He M, W.Q.; Zhao, W. A self-defensive bilayer hydrogel coating with bacteria triggered switching from cell adhesion to antibacterial adhesion. Polymer Chemistry. 2017, 8, 5344–5353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.-S.; Law, J.W.-F.; Law, L.N.-S.; Letchumanan, V.; Chan, K.-G. Insights into quorum sensing (QS): QS-regulated biofilm and inhibitors. Progress In Microbes & Molecular Biology 2020, 3, a0000141. [Google Scholar]
- Sionov, R.V.; Steinberg, D. Targeting the holy triangle of quorum sensing, biofilm formation, and antibiotic resistance in pathogenic bacteria. Microorganisms. 2022, 10, 1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashistha, A.; Sharma, N.; Nanaji, Y.; Kumar, D.; Singh, G.; Barnwal, R.P.; Yadav, A.K. Quorum sensing inhibitors as Therapeutics: Bacterial biofilm inhibition. Bioorganic Chemistry. 2023, 136, 106551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ge, Y.; Zhu, X.; Pan, J. Regulatory mechanisms and promising applications of quorum sensing-inhibiting agents in control of bacterial biofilm Formation. Front Microbiol. 2020, 11, 589640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, S.; Hachicha, M.; Boukraa, M.; Soulère, L.; Efrit, M.L.; Queneau, Y. Heterocyclic chemistry applied to the design of N-Acyl homoserine lactone analogues as bacterial quorum sensing signals mimics. Molecules. 2021, 26, 5135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolenbrander, P.E.; Palmer, R.J., Jr.; Periasamy, S.; Jakubovics, N.S. Oral multispecies biofilm development and the key role of cell-cell distance. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2010, 8, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.S.; Ryu, E.J.; Li, L.; Choi, B.K.; Kim, B.M. New bicyclic brominated furanones as potent autoinducer-2 quorum-sensing inhibitors against bacterial biofilm formation. Eur J Med Chem. 2017, 137, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





