1. Introduction
At the
75th UN General Assembly, China proposed an initiative to strive to reach its carbon peak by 2030 and achieve carbon neutrality by 2060 [
1]. With current global warming, the
IPCC special report on a global warming value of
1.5°C clearly states that the global temperature has increased by
1.0°C since preindustrial levels [
2], where the main influence on climate change is the emission of carbon dioxide [
3]. In the context of global warming, extreme heat events have been frequently observed [
4]. Some studies demonstrate that extreme heat events pose a serious threat to human health, and that they are even life-threatening and fatal in severe cases [
5,
6]. The total global CO
2 emissions from the construction sector were
5.7 billion tons in 2009, accounting for
23% of the total CO
2 emissions from global economic activities [
7], and among the various strategies developed to meet energy demand and reduce CO
2 emissions, improving the energy efficiency of buildings has proven to be the best option [
8,
9]. According to the data from the China Building Energy Consumption Research Report (2020), the total energy consumption of the whole life cycle of buildings in China was
2.147 billion ton of standard coal equivalent in 2018, accounting for
46.5% of the total national energy consumption. The total carbon emissions of the whole building process in China were
4. 93 billion tce in 2018, accounting for
51.2% of the national carbon emissions, and the energy consumption of building materials accounted for more than
20%. The energy consumption and carbon emissions of the construction industry were much higher than those of other industries. A study showed that with the development of urbanization and the investment in rural revitalization, the total carbon emissions in rural areas of China increased from
408.53 Mt in 1997 to
619.57 Mt in 2015 [
10], rural residential buildings and household appliances such as air conditioners and hot water supply in daily life and their time of use have increased significantly, and rural areas are becoming the second largest source of greenhouse gas emissions [
11], of which residential living systems have become the main source of Greenhouse Gas emissions [
12]. Therefore, the country started to promote the low-carbon transition of rural residential buildings more thoroughly to reduce CO
2 emissions [
13], Therefore, this is essential to deal with reduce energy consumption, and safeguard residents' health [
14,
15]. There is a certain internal logical relationship between green building and achieving the carbon peak carbon neutrality goal, and green building development(
GBD) has an important role in improving the carbon emission reduction efficiency(
CEEOCI) of the construction industry and accelerating the achievement of the carbon neutrality goal in the construction industry [
16].
At the onset of the 21st century, to keep up with the pace of the world, China sought to reduce the pollution of building environments and improve the efficiency of energy consumption by the Chinese construction industry as well as develop and improve the Chinese green building evaluation system, which can better promote the development of green buildings. The early studies focused mainly on comparing the international mainstream green building evaluation system in terms of factors such as evaluation scope, evaluation indexes, and control items to analyze the advantages, disadvantages and development status [
17,
18] and to identify the problems encountered in its implementation in each phase of the whole building life cycle [
19] to propose improvement measures to continuously improve the Chinese green building evaluation standards. Using the definition of green buildings, some scholars have developed a multi-objective evaluation model for green buildings under the three dimensions of objective, professional and time (
OPT) [
20]; these theories have been validated with actual projects to propose new ideas for the construction of green building evaluation indexes. The limitations of the existing national and provincial green building evaluation standards, combined with the unique topography, ecological environment, architectural culture and building type of each region, to propose important regional green building factors, upon which an evaluation model was established to build a green building evaluation system that met the local regional characteristics [
21,
22]. At this stage, under the guidance of Chinese policies and relevant standards, China's green building evaluation standards have developed to the relatively mature third generation of green building evaluation standards after two revisions. With the introduction of China's
GB/T50378-2019 Green Building Evaluation Standard, research on the differences in the framework structure, scoring criteria, evaluation objects, evaluation process and methods of the latest domestic and foreign standards in the horizontal aspect has been carried out [
23]. The aim is to reveal the differences of different green building evaluation standards at home and abroad through the comparison of the same index and weight, combining the current conditions such as the complex climate environment and the lack of professional talent in China, to refine the transparent evaluation process; the new standard is more concerned with the life specific green technology to the people to improve the living environment. Green buildings pay more attention to the deep-seated demand for the human living environment and healthy buildings and pay more attention to the health of personnel [
24].
In the past, the most used questionnaire for constructing evaluation system indicators was the Delphi expert questionnaire method, through which experts' opinions on indicators were repeatedly solicited, summarized and modified and finally used formed the basic unanimous opinion of experts. The fuzzy Delphi method is a good way to predict the results. In contrast, the fuzzy Delphi method can overcome the ambiguity and uncertainty problems of the Delphi method in the investigation when constructing green building evaluation indexes [
25], and the constructed building evaluation indexes are more objective and scientific. In terms of practical application, the hierarchical analysis method has been used by many experts and scholars over many years of research. The use of hierarchical analysis can be used to simplify and draw conclusions that are scientific and accurate. Second, the solution process of using hierarchical analysis is clear and makes it easy to organize ideas, which can ensure the accuracy of the results [
26]and build a green building evaluation system that is optimized for the country, province and city as well as the region [
27].
However, a green building is an extremely complex system that requires different evaluation systems to support it from the national to the traditional residential building levels within a specific geographical area [
28]. Currently, green buildings, as sustainable buildings, are an effective way to achieve the dual carbon goal. However, the latest version of
GB/T50378-2019 "Green Building Evaluation Standard" lacks a calculation model and quantification method for the evaluation index of carbon emissions in each stage of the building life cycle. Compared with international research, research on the calculation of building carbon emissions in China is still immature, and the establishment of a database on building carbon emissions needs to be improved. Although China promulgated the national standard "Building Carbon Emission Calculation Standard" in 2019 to make up for the deficiency in this regard, the new version of the "Green Building Evaluation Criteria" does not have the relevant hard requirements of the "Building Carbon Emission Calculation Standard" and lacks targeted calculation data, and thus, it cannot meet the existing requirements for constructing green building evaluation indexes. With the low-carbon and dual-carbon policies, domestic scholars began to establish carbon calculation models for typical green civil buildings based on life cycle theory for different regions [
29]; therefore, it is of great practical significance to incorporate building life cycle carbon emission indexes and calculation models into green building evaluation.
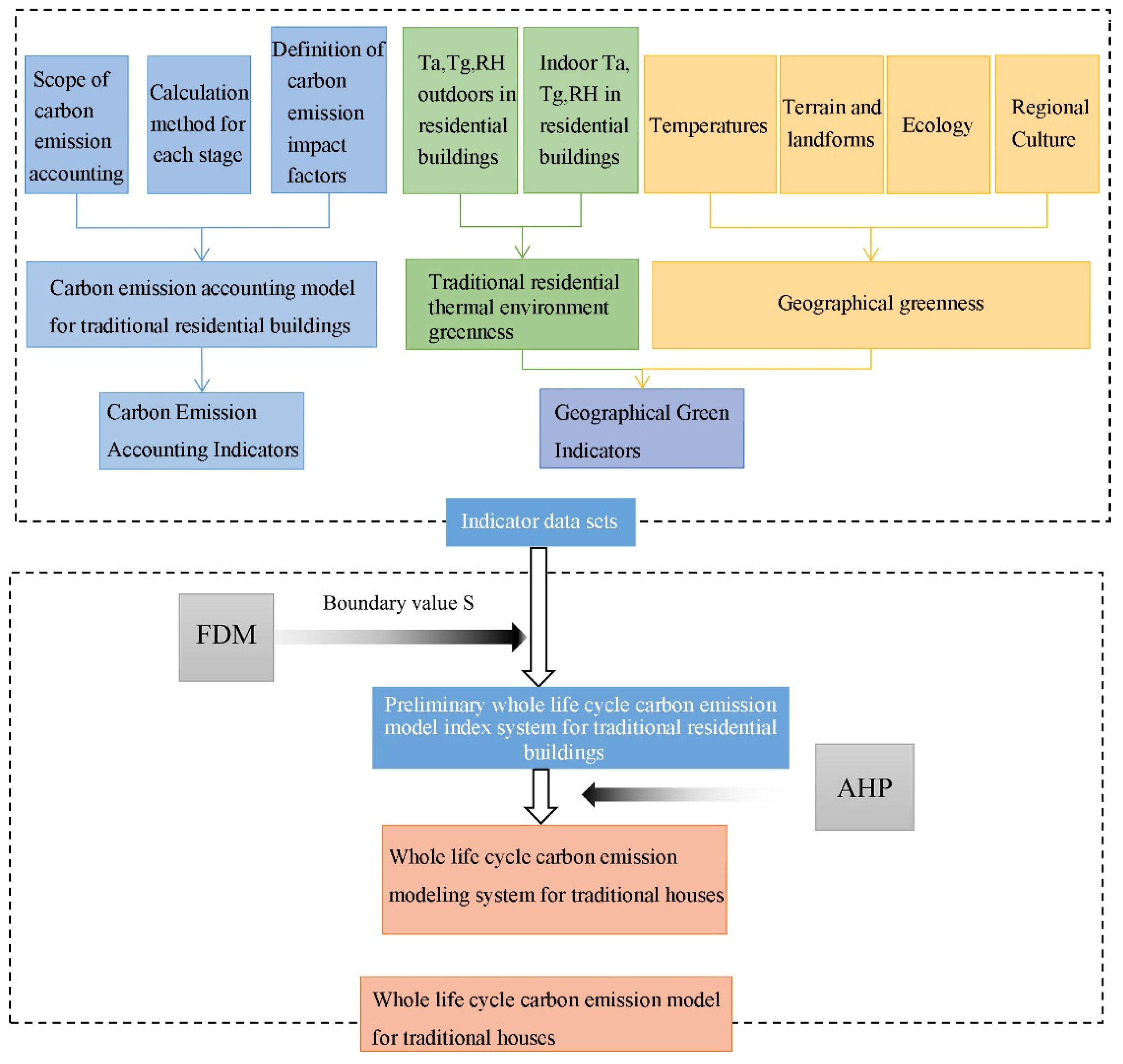
The objectives of this study under carbon emissions intervention were as follows:(1) establish a life-cycle carbon emission accounting model for traditional residential houses; (2) compare and analyze DBJ52/T065-2017 "Green Building Evaluation Standards of Guizhou Province" and the indoor and outdoor heat and humidity environments of the actual measured residential houses and refine the important factors about regional green buildings; The purpose of this study was to explore the construction of a building life cycle carbon emission model for traditional residential buildings in the context of carbon emissions. The research results can improve the building life cycle carbon emission system in China and provide a scientific evaluation method for quantitative research on zero-carbon and low-carbon buildings.
2. Research areas and information
2.1. Research areas
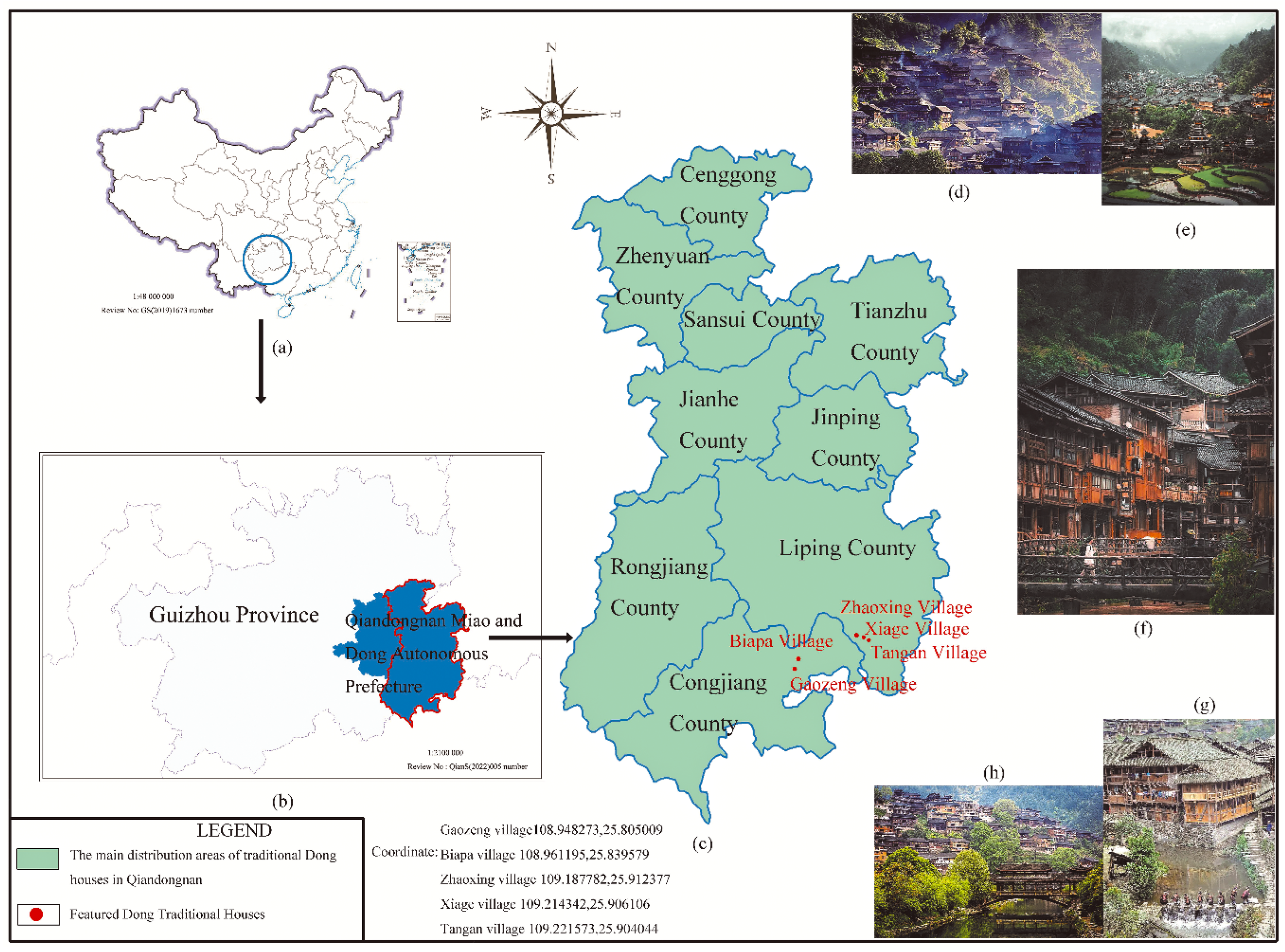
The energy saving of rural residential buildings is a key field and an important link for China to achieve the goal of "2030 carbon emission reduction". China's "Carbon Peak in Urban and Rural Construction Implementation Plan" proposes to promote the construction of green and low-carbon rural housing, promote the large-scale development of low-carbon buildings, and encourage the construction of zero-carbon buildings in rural areas. There are many minority characteristic villages in Guizhou Province, and from the distribution of national and provincial minority characteristic villages, Qiandongnan Prefecture occupies the first position of minority villages in the province; the Dong ethnic group is an important part of the minority in Qiandongnan, and the number of characteristic villages ranks among the top three in the state. Most are distributed in nine counties, such as Congjiang, Rongjiang, and Liping, as marked in the green block of
Figure 1. To ensure that the residential physical environment was measured with sufficient sample size, the sample was selected from five representative Dong traditional villages: Biapa Village, Xiage Village, Tangan Village, Gaozeng Village, Zhaoxing Village (
from the official website of Chinese Traditional Villages, http://www.chuantongcunluo.com/ ).
2.2. Physical environment measurements of civil houses
Over time, there have been many studies on the physical environment of buildings, and the thermal environment of buildings is the most important part of the physical category of buildings; thus, the thermal environment received the earliest human research and attention. Domestic and foreign scholars of the physical environment have also focused more on the thermal environment of buildings. The main factors affecting the thermal environment of buildings are determined by the indoor and outdoor thermal environments of buildings, namely, the indoor air temperature, humidity, heat emitted from production and life, outdoor air temperature, humidity and wind, and rain and snow. Using relevant instruments to take actual measurements, the indoor and outdoor air temperatures (Ta), the relevant humidity (RH), and the black bulb temperature (Tg) were selected for actual measurement in this study.
Actual measurement time: When conducting the actual measurement, the local winter and summer representative extreme weather times were selected as follows: winter: January 15, 2022, continuous temperature testing time of 24:00 h; summer: July 24, 2022, continuous temperature testing time of 24:00 h; method: indoor and outdoor halls, bedroom layer measurement point location temperature and humidity for 24 hours of continuous testing, outdoor air temperature and humidity measurement points 1 arranged 1 m from the wall; indoor air temperature and humidity measurement points 2 hall, bedroom, the instrument is arranged in the center of the room, 1 m from the ground; every hour the instrument automatically collects a set of data, the measured meteorological parameters include the air temperature (
Ta), relative humidity (
RH) and black ball temperature (
Tg).
Table 1 shows the basic information such as the accuracy and range of the measurement instruments. Therefore, the instruments were in compliance with the
ASHRAE Standard 55-2017 [
30], as shown in
Table 1.
ASHRAE stands for the American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers.
2.3. Scope of carbon emissions accounting for traditional residential buildings
From a large number of studies in the literature, it was found that the scope of carbon emissions accounting for buildings still differed to some extent. The current research on carbon emissions accounting in the field of construction is mainly divided into two levels: one is the micro level, i.e., the longitudinal life-cycle carbon emissions accounting of single building units, and the other is the macro level, i.e., the accounting of global, national, provincial and municipal regional building carbon emissions. The measurement of microscopic single building carbon emissions is mainly used for the determination of single building carbon emission levels when carrying out green building evaluation and building carbon emissions trading. This paper focused on the carbon emissions of the life cycle of traditional residential buildings, combining China GB/T50378-2019 "Building Carbon Emission Calculation Standard" and CECS 374:2014 "Building Carbon Emission Measurement Standard", from a microscopic single building life cycle carbon emission perspective. It is proposed that the life cycle carbon emissions of traditional residential buildings should include the sum of the carbon emissions from four aspects: the production and transportation stage of building materials, the construction stage, the operation stage and the demolition and disposal stage.
2.4. Carbon emission calculation methods for each stage of the life cycle of traditional residential buildings
At present, the commonly used methods in carbon emissions accounting research are the actual measurement method, carbon emissions factor method and mass balance method. After comparing and analyzing the three methods in terms of their characteristics, advantages, limitations, applicable scales and application statuses, the carbon emissions factor method was found to be most suitable for carbon emissions accounting in the construction field. The carbon emissions factor method is the most dominant method used for calculating carbon emissions and is also the method used in the Standard for Carbon Emission Calculation in Buildings (from GB/T50378-2019 Standard for Carbon Emission Calculation in Buildings). Therefore, the carbon emissions factor method was used in the study for carbon emissions accounting of traditional residential buildings. The functional unit for carbon emissions accounting of the life cycle of traditional residential buildings is the carbon emissions per square meter of a building per year, and the unit of measurement is kgCO2eq/(a•m2), which is calculated using the carbon emissions factor method in the 2006 IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories. It is calculated by multiplying the materials, energy and machinery used in each stage of the building life cycle with their corresponding carbon emissions factors to find the sum.
That is, total carbon emissions = total building life cycle (× emission factor ()
where the total building life cycle () is the amount of building materials consumed and the total amount of energy consumed in each activity, and the emission factor () is the amount of carbon dioxide equivalent produced per unit of building activity data, also known as the carbon emissions factor.
According to the definition of the scope of carbon emissions accounting for the life cycle of traditional residential buildings, the whole life cycle of residential buildings has four stages: production and transportation of building materials, construction, operation and demolition and disposal. Combined with the evaluation requirements of the national standard
GB/T50378-2019 "Green Building Evaluation Standard" and factors such as the geographic location and natural environment of Qiandongnan, the total carbon emissions of the building life cycle are the sum of the carbon emissions of each stage, and the calculation formula is as follows.
Type:
- indicates the total carbon emissions over the lifetime of the traditional dwelling (
kgCO2eq).
- indicates the carbon emissions during the production and transportation phase of the building materials (kgCO2eq).
- indicates the carbon emissions during the construction phase of the building (kgCO2eq).
- indicates the carbon emissions during the operational phase (kgCO2eq).
-indicates the carbon emissions from the dismantling and disposal phase (kgCO2eq).
2.5. Selection of carbon emissions impact factors for traditional residential buildings
The Dong traditional dwellings in Qiandongnan still retain wood as the main building support and maintenance structure from ancient times to the present. In this study, the building types involved refer only to traditional residential dwellings, while the energy used in the operation of residential dwellings mainly refers to the energy consumed by rural households for cooking and heating. The main types of energy used in operation are electricity and biomass (straw and fuel wood). Among them, biomass energy consumption is an important part of rural residential energy use. Building construction activities involve many energy-use aspects, and this study considered mainly the energy consumption involved in the production of building materials and the transportation and construction of building materials. The production of building materials refers to the process from the entry of raw materials into the factory to the delivery of finished building materials. The transportation of building materials refers to the process from the delivery of building materials to the arrival of building materials at the construction site. The energy consumption of the construction stage mainly includes the energy consumption of construction personnel and on-site construction equipment, and the demolition and disposal stage is the energy consumption of on-site construction personnel carbon emissions caused by the energy consumption of the demolition of buildings and that of various machinery, the carbon emissions from the transportation and disposal of construction waste, and the carbon emissions from the recycling of construction materials. In this study, the carbon emissions factors were selected from four aspects: energy and fuel, building materials, transportation and human and mechanical equipment.
4. Results
4.1. Building material production and transportation stage
Qiandongnan prefecture of Guizhou, has special topography and geography, and the forest area of the whole region occupies more than
67% of the national forest area (
from Qiandongnan Forestry Bureau, http://ly.qdn.gov.cn/), but the state has strict requirements for the cutting of forest trees to protect the Dong architecture with ethnic characteristics. Thus, the Qiandongnan state according to the Forest Law of the People's Republic of China and the State Council Management Measures for the Renewal of Forest Harvesting Sites" and related regulations the "Measures for the Renewal of Harvesting Sites in Qiandongnan Prefecture" were formulated, and after residents cut down the needed timber according to their requirements, the harvesting sites should be completed for reforestation in the current year or the following spring. The production and transportation of materials was divided into two parts: production of building materials and transportation of building materials:
Type: - carbon emissions from the production and transportation phase of building materials (kgCO2eq).
- indicates the carbon emissions from the production of construction materials (kgCO2eq).
- indicates the carbon emissions from the transportation of construction materials (kgCO2eq).
Carbon emissions are calculated for each phase as follows:
Carbon emissions from the production of construction materials
, the carbon emissions from the production of construction materials refer to the carbon emissions from the development of raw construction materials, the transportation to processing plants and the energy consumed in the production of materials, which can be obtained from the product of the consumption of construction materials and the carbon emissions factor per unit of construction materials, calculated as follows:
Type: - the type of building materials.
- the amount of building materials used in category
.
- the carbon emissions factor for the building materials of category
.
Carbon emissions from transportation of construction materials
, the carbon emissions from material transportation are mainly related to factors such as the mode of transportation, transportation distance and transportation volume of materials. The road traffic situation is complicated by high mountains, narrow roads, sharp curves, and the poor resistance of road foundations in the territories of Qiandongnan Miao and Dong Autonomous Prefecture. According to relevant studies, generally for roads with large slopes and poor road surfaces, transporting the same weight of goods by the same transport mode consumes more energy than when transportation occurs roads with small slopes and good levelness; therefore, when calculating the amount of energy consumed by the road conditions for transportation into villages in the state, statistics can be made according to the actual situation and fuel consumption, and the calculation formula is as follows:
Type: - the number of types of building materials.
- the consumption of building materials from category .
- the average transport distance of the transport of building materials from category .
- the carbon emissions factor per unit weight of transportation distance for the type of building material.
- the number of transport mode categories.
- the actual amount of energy consumed by each mode of transport.
- the carbon emissions factor per unit mass per unit transport distance for transport mode .
4.2. Construction phase
The construction of rural houses is self-built, and a construction team basically builds each house. The team mainly relies on manpower, and the workers start the construction with their years of accumulated experience. This construction method can start quickly to improve the project’s progress and shorten the construction period; therefore, there are few opportunities to use machinery and equipment during the construction process, and the carbon emissions at this stage come from the CO
2 emitted by the construction personnel on site due to concentration and the carbon emissions generated during the use of machinery and equipment. The carbon emissions released from the process of construction machinery are mainly generated by the energy consumption of diesel, gasoline and electricity consumed by the operation of machinery. The calculation formula is as follows:
Type: - the number of mechanical types.
- the number of machinery units used for machinery of category during the construction phase of the building.
- the carbon emissions factors released by construction machinery of category .
- the number of types of construction methods in the construction process.
- the amount of construction for each construction method.
- the carbon emissions factor for each construction method.
- the number of construction workers.
- the number of working days.
- the artificial carbon emissions factor, taken as 7.30 kgCO2/(man-working day).
4.3. Operation phase
The carbon emissions in the building operation phase mainly involve the comprehensive calculation of carbon emissions from energy consumed by air conditioning, heating, domestic hot water, lighting, and ventilation, as well as carbon reductions from renewable energy systems and building carbon sinks. However, the operational energy consumption of rural buildings is influenced not only by local climatic conditions and economic factors but also by many uncertain factors, such as the ethnic background, cultural quality, and behavior of indoor occupants. Furthermore, a hot summer and cold winter building climate is typical in Qiandongnan, Guizhou. However, the rural areas in the state seldom use air conditioning for cooling in summer and still retain the habit of burning charcoal for heating in winter; therefore, burning charcoal for heating in winter is the main energy consumed by residential dwellings. With the development of society, although household appliances have become popular, only televisions are used every day with the exception of lamps and lanterns for lighting, which are necessary for daily life. In addition, high-grade household appliances such as refrigerators, air conditioners and computers have not yet become popular.
With the deepening of China's awareness of the ecological environment, rural dwellings are added to green building technology or renewable energy systems when new and existing dwellings are reconstructed to improve the living environment of residents and the protection of the natural environment. In Qiandongnan, as a forest resource with more than
67% of the national forest area, the local dwelling buildings are still mainly made of wood, which is a renewable green material and has the function of long-term carbon storage. In summary, the carbon emissions of the building operation stage are calculated as follows:
Type: - the number of energy types.
- the annual consumption of energy in .
- the carbon emissions factor of the -th energy source.
- the annual consumption of charcoal.
- the carbon emissions factor for charcoal.
- the annual savings of the -th energy source.
- the annual carbon reduction of the green system.
- the life of the building.
4.3.1. Calculation of energy consumption and carbon emissions
Energy consumption data in the operation phase of buildings can be obtained through actual surveys and statistics, and when specific values are not available, they can be calculated using relevant energy consumption simulation software. Statistical data for domestic surveys were mainly obtained from the China Energy Statistical Yearbook, the China Rural Statistical Yearbook and statistics from government authorities at all levels from 2001-2019. Among the more mature energy consumption simulation software both at home and abroad, DeST has a strong geographic presence, and this energy consumption software can be used to simulate the building operation phase and calculate the carbon emissions in this phase.
4.3.2. Carbon reductions from renewable energy, plants, and building wood carbon sinks
At present, renewable energy systems include solar domestic hot water systems, photovoltaic systems, ground source heat pump systems and wind power generation systems, combined with the current national standard "Green Building Evaluation Standard" GB/T 50378 for renewable energy in three forms: renewable energy to provide domestic hot water, air conditioning with cold and heat, and electricity. These three forms correspond to the solar photo thermal system, ground source heat pump system (including the buried pipe type and water source type), solar photovoltaic power generation system, etc. (from GB/T51366-2019 "Carbon Emission Calculation Standard for Buildings"). The pristine green mountains and water and farming crops in Qiandongnan have provided abundant biomass for many years. The development of rural renewable energy in Qiandongnan over time has been based mainly on the utilization of biomass energy supplemented by micro-hydropower and solar energy. The utilization of biomass energy is also based mainly on the burning and utilization of fuel wood (called fuel wood in rural areas) and on crop straw, which comes from forestry biomass and agricultural biomass. Fuel wood does not contain harmful elements such as sulfur and does not pollute the atmosphere when burned, making it a clean fuel; in contrast, the direct burning of straw will produce many harmful gases such as carbon dioxide, which cause atmospheric pollution. Thus, there must be a method of turning straw into clean energy, e.g., a special boiler inside the combustion, so that the waste can be converted to clean fuel or straw processing called clean energy fuel. However, in the territory of Qiandongnan, due to various factors such as transportation and economics, the region does not currently have the ability to turn straw into clean energy. Therefore, this study in the residential area focused on the following: apply the energy system of renewable energy directly deducted from the consumption of fuel wood; give the solar thermal system energy and photovoltaic power generation system an energy calculation formula and install the method in rural areas using these systems, and calculate the annual energy provided according to the local climate, the amount of sunshine and the relevant design information and product parameters using the calculation formula reference GB/T51366-2019 "Building carbon emissions calculation standards".
The annual carbon reduction (
LH) of the greening system is the amount of CO
2 in the atmosphere that is reduced by the vegetation at the building site through photosynthesis, which absorbs CO
2 from the atmosphere and fixes it in the vegetation and soil. There are abundant plant species in Qian southeast China; thus, the intensity of photosynthesis varies among different plant types, and the amount of carbon reduction varies. The amount of carbon reduction of vegetation is affected by the climate, growth environment, species and other factors. Currently, the agriculture and forestry industries have developed relevant calculation methods, such as the Methodology of Carbon Sink Measurement and Monitoring for Bamboo Forestry Projects issued by the State Forestry Administration. However, no official methodology has been issued for the carbon sink methodology of green vegetation in residential buildings. In this paper, we refer to the relevant algorithm in the Technical Assessment Manual for Green Low-carbon Settlements in China for calculation, and the calculation formula is as follows:
Type: - the different planting methods in the greening system.
- the carbon sequestration per unit area of 40 years for the -th planting method.
- the green area of the -th planting method.
- the green space ratio, %.
- the total land area of the building.
4.4. Dismantling and disposal stage
The stage of building demolition is equivalent to the reverse process of building construction. After the demolition of residential houses in Qiandongnan, the building materials were divided into two methods of treatment, namely, recycling and disposal. Metal materials such as steel and aluminum alloy used in residential buildings are recycled, and building materials such as wood and glass, which have been exposed for a long time and are no longer suitable for the recycling of building materials, are processed with certain technologies and used for household items or other objects. For abandoned building materials such as bricks that have lost their load-bearing capacity, a general simple treatment is use as roadbed filling. The calculation formulas are as follows:
Type: =the number of types of machinery
- the carbon emissions from building demolition.
- the amount of machinery shifts used for machinery of category in the construction demolition phase.
- the carbon emissions factors released by the construction machinery of category .
- the number of types of demolition methods in the demolition process.
- the amount of construction for each demolition method.
- the carbon emissions factors for each demolition method.
Type: - the carbon emissions from construction waste transportation.
- the number of types of building materials.
- the consumption of building materials of category .
- the average transport distance of the transport of building materials category .
- the carbon emissions factor per unit weight of transport distance for the -th type of building material.
- the number of transport mode categories.
- the actual amount of energy consumed by each mode of transport.
- the carbon emissions factor per unit mass per unit transport distance for transport mode .
- the average transport distance of no recyclable waste from the demolition site to the waste treatment plant.
- the average transport distance of recyclable waste from the demolition site to the recycling station.
Type: - the carbon emissions from construction waste disposal (including landfill and incineration).
- the total mass of waste of category .
, , - the proportion of category waste that is landfilled, incinerated, and recycled, respectively.
, - the carbon emissions factors for landfill and incineration of category waste, respectively.
4.5. Selection of carbon emissions factors
4.5.1. Selection of the energy fuel factor
Energy carbon emissions factors can be subdivided into fossil energy carbon emissions factors corresponding to direct carbon emissions and electricity and heat carbon emissions factors corresponding to indirect carbon emissions. According to the energy balance sheet data of Guizhou Province in previous years, heat accounts for a relatively small proportion of domestic consumption, mostly concentrated in industrial consumption, and heat data were missing from 2009-2014. Therefore, in the calculation of carbon emissions from secondary energy consumption in residential life, only carbon emissions from electricity were calculated.
CO2 emissions from fossil fuel combustion are the most important source of greenhouse gases, and accurate accounting of CO2 emissions from fossil fuel combustion is the basis for emission reduction policy formulation and implementation. The accuracy of building carbon emissions accounting comes from the selection of carbon emissions factors. Though the analysis of the current domestic and foreign selection of building carbon emissions factors vary, there are some differences. This paper mainly selected China in 2019 to develop the "building carbon emission calculation standards" in carbon emission factors.
Electricity carbon emissions factor, different regions of China have different grid structures. At present, there is no unified standard for calculating electricity carbon emissions in China, and there are two main electricity carbon emissions factors in the process of accounting for electricity carbon emissions: one is the baseline emissions factor of the regional grid, and the other is the average carbon emissions factor of the regional grid. China has vigorously developed clean energy generation in recent years, and the energy structure in the building operation phase has changed significantly, which has reduced the electricity carbon emissions factor. Therefore, the latest published weighted average of OM and BM in 2019, was chosen in this study to calculate the electricity carbon emissions of southern residential buildings,The baseline emission factors of regional power grid include power marginal emission factor (OM) and capacity marginal emission factor (BM). The electricity marginal emission factor is used to calculate the carbon reduction of Clean Development Mechanism (CDM) projects in China's key emission reduction areas when the grid is saturated. The capacity margin emission factor is used to calculate the carbon emission reduction under the condition of grid saturation.
4.5.2. Carbon emissions factor of building materials
The acquisition of carbon emissions factors for building materials requires the analysis of the whole process of building material production, which is difficult to calculate because of the wide variety of building materials and the different production and processing processes of different building materials. Currently, there are mature building material databases for building material carbon emissions factors at home and abroad, but the authoritative database in China is preferred in consideration of the study site. At present, the main Chinese building foundation databases are the China Material Environment Database (Sino center), the China Life Cycle Foundation Database (CLCD) and the CTC-Green Building Materials Evaluation System. The carbon emissions factors of building materials in China's Standard for Calculating Building Carbon Emissions (GB/T 51366-2019) were all from the China Life Cycle Foundation Database, and considering the accessibility of data, the relevant data from the China Life Cycle Foundation Database were also selected for the carbon emissions factors of building materials in this study.
4.5.3. Transportation carbon emissions factor
Since there are many types of transportation vehicles and the types and amounts of energy consumed when transporting construction materials vary from one vehicle to another, the carbon emissions generated are also different, and the data are difficult to obtain. Thus, this study used the carbon emissions factors for the transportation of building materials given in the Standard for Calculating Carbon Emissions from Buildings (GB/T 51366-2019).
4.5.4. Carbon emissions factors for machinery and equipment
The machinery and equipment involved in this study were mainly construction machinery and equipment used in the building construction and demolition stages, such as cranes, bulldozers, and excavators. Considering the availability and accuracy of data, the carbon emissions factors of machinery and equipment given in the Standard for Calculation of Carbon Emission of Construction (GB/T 51366-2019) were used.
4.6. Implementation analysis of Dong traditional houses in Guizhou southeast based on current standards
4.6.1. Limitations of the current standard in terms of temperature
Because of the complex and varied environment and landscape and climate in Guizhou, many indicators and clauses in the Guizhou Green Building Evaluation Standard DBJ52/T066-2017 are not relevant when evaluating the Dong traditional dwellings in Qiandongnan .
Tier 1 indicators: Energy saving and energy use.
Not enough: For the traditional residents of the Dong ethnic group in Qiandongnan, the winter is damp and cold with a temperature close to 0 degrees due to various factors such as temperature and humidity, and the summer is hot and humid, when the envelope structure of residential buildings will cause a large waste of resources if it cannot play a good role in heat insulation and thermal insulation, which will cause the local residents to cool down in winter and summer by using air conditioners and heat preservation by electric ovens. Therefore, the shape design, orientation arrangement, Window-to-Wall ratio and thermal performance of the building itself are more important in the Qiandongnan region and should not be given a lower rating score. The Qiandongnan Dong villages are mostly combined with mountain contour areas or river valleys in a narrow strip of site selection and construction; due to the low surrounding air pressure, there are often valley winds formed by the local thermal environment, the reasonable use of valley wind resources; therefore, the use of natural ventilation to improve the indoor environment is one of the effective methods and should improve the value of this score.
4.6.2. Limitations of the current standard in terms of terrain
The current Guizhou Green Building Evaluation Standard DBJ52/T065-2017 is mainly reflected in the land saving and outdoor environment.
Tier 1 indicators: Land saving and outdoor environment.
Not enough: The weight of this indicator is too low for the mostly mountainous region of Qiandongnan.
4.6.3. Limitations of the current standard in the ecological environment
Some indicators in the existing Guizhou green building evaluation system in the first-level indicators of land saving and outdoor environment, material saving and material resource utilization were closely related to the ecological environment.
Tier 1 indicators: Material saving and material resource utilization.
Not enough: The topography of the Qiandongnan region is complex and varied, and the region is rich in forest ring resources to produce wood and stone for local construction. To adapt to this situation, the green building standards should give a higher score to "the use of locally produced wood, stone and other building materials" to better achieve material conservation. The current Guizhou Province "Standard" gives too low a score to this aspect and is not applicable to the unique forest environment of Qiandongnan.
4.6.4. Limitations of the current standard in terms of the regional cultural characteristics
Each nationality has its own unique culture and tradition, and if it does not do a good job in greening the national culture, it will not be recognized by local residents. The regional technical characteristics of the Dong traditional dwellings in Qiandongnan form dry appendage buildings in the mountainous terrain; under the condition of abundant tree resources, the Dong people make use of the materials and make the best use of them in building construction. Second, the natural economy of self-sufficiency has led the Dong people to form a value system based on nature, which is reflected in the spatial form of the villages and single buildings, which can be constructed only as small villages with mainly residential functions and a clear spatial form of functional division within the dwellings. Finally, the Dong people of Qiandongnan China have made use of their unique natural conditions to build a low-carbon and energy-saving water circulation system, and they have a harmonious coexistence of rice, fish and duck production, as well as other national ideals of pursuing a sustainable life cycles.
4.7. Empirical analysis of the physical environment of the Dong traditional dwellings in Qiandongnan
4.7.1. Regional ambient (alleyway) air temperature and wet and black bulb temperature analysis
As shown in
Table 3, the average air temperature (
Ta 35.5°C in summer and
Ta 6.9°C in winter) and the average black-bulb temperature (
Tg 38.6°C in summer and
Tg 7.0°C in winter) of Gaozeng Village were the highest compared to the other four villages in winter and summer because Biapa, Xiage and Tangan Village are mountainous villages built on sunny slopes near water sources. The forest vegetation around the villages can regulate the physical environment of the villages and the external environment of the dwellings, and the microclimate of the areas with a large amount of vegetation can be effectively improved. Although Gaozeng Village and Zhaoxing Village are both flat dam-type villages formed by the impact of rivers causing flat dams, Zhaoxing Village is 180
m higher in elevation than Gaozeng Village, making the maximum
Ta and
Tg in summer lower than those in Gaozeng Village.
Table 3 shows that the average
Ta, the highest
Ta and the lowest
Ta of Lane 1 are higher than those of Lane 2 in winter, and the average
Ta, the highest
Ta and the lowest
Ta of Lane 1
Ta are lower than those of Lane 2
Ta in summer because although Lane 1 and Lane 2 are parallel east‒west, Lane 1 is wider than Lane 2, and Lane 1 (
D/H > 1) and Lane 2 (
D/H < 1). In winter, as Lane 2 is narrow, the cold wind passes through and makes
Ta fluctuate greatly compared with Lane 1. Therefore, under the condition that the wind direction is certain and the road is built downwind, a suitable lane size can change the
Ta value of the environment at the building site to a certain extent.
4.7.2. Analysis of the internal environment of traditional houses
As shown in
Table 4 shows that the summer village dwelling
Ta is as follows: Gaozeng Village (
35.5°C) > Biapa Village (
34.6°C) > Xiage Village (
34.5°C) > Zhaoxing Village (
34.3°C) > Tangan Village (
32.9°C), the bedroom
Ta of Xiage Village (
34.5°C) > Gaozeng Village (
34.1°C) > Biapa Village (
34.0°C) > Zhaoxing Village (
33.2°C) > Tangan Village(
32.3°C) ,this is because many factors determine the indoor
Ta, mainly because these two dwellings have a common feature: the opening ratio of doors and windows in the building is small and some walls do not have windows. The maximum, minimum and average
RH values of the dormitory and bedroom of Gaozeng Village were the lowest among the five residential measurement points of
RH in winter and summer because the vegetation cover of the Gaozeng Village residential site is small compared with the other four measurement points, and plants have the function of moisture retention. The shielding effect of plants reduces the transpiration of water, making the indoor
RH of the other four residential houses higher than that of Gaozeng Village at the five points.
In winter, excluding the influence of the altitude factor, the average indoor Ta of the selected village residential buildings, except for Xiage Village, was as follows: bedroom Ta > hall Ta > outdoor Ta, mainly because the outdoor open space is directly affected by the external climate, while the building envelope of residential buildings can delay the rapid change of indoor temperature with the change of outdoor temperature. Thus, the indoor temperature is higher than the outdoor temperature, and the bedroom is a relatively small space; as a result, the bedroom loses the least amount of heat during the day. The average indoor/outdoor Ta of Xiage Village in winter follows the order of living room > bedroom > outdoor because the Dong people have implemented the habit of "fire ward" in winter since ancient times, and fire pits are usually placed in the hall, making the average temperature of the hall higher than that of the bedroom during the day.
4.8. Constructing locality model evaluation indicators provides important indicator choices
Based on the limitations of green building evaluation indexes in Guizhou Province in terms of temperature, topography, ecological environment and regional culture for the application evaluation of Dong traditional dwellings in Qiandongnan, combined with the field research of Dong traditional dwellings in Qiandongnan and the quantitative analysis of the thermal environment inside and outside the dwellings and villages using relevant instruments, we provide important index choices for the construction of a regional traditional dwelling whole life cycle carbon emission model evaluation index system.
4.8.1. Energy use
Village street building D/H (width to height ratio): When the village street building D/H (width to height ratio) ≥ 1, the outdoor environment of residential houses uses the street ratio to form artificial wind ducts in summer to remove the excess heat brought by solar radiation in the street; in winter, it reduces the air circulation of cold outdoor air in the street.
Indoor air circulation: Use the dominant summer wind direction to remove excess heat from the room and increase the comfort of the indoor thermal environment. The further reduces the input of related energy and saves energy.
4.8.2. Site ecology and landscape
Application of plants in the landscape: Using the characteristics of plants themselves, the natural landscape of the village building is shaped by plants, and the visual, physical and psychological comforts of the site around the building are enhanced by the planting techniques with horizontal and vertical layers.
Use of plants in the physical environment: The rational use of plants' own ability to sequester carbon, maintain the humidity of the surrounding air and block solar radiation from affecting the physical environment of residential buildings optimizes the overall quality of the building's indoor and outdoor environments.
4.8.3. Land saving
Building site selection and safety: The all-round use of the local geographical environment for building site selection and safety considerations can reduce economic losses due to natural disasters, save resources and reduce the investment of human and material resources.
Building orientation: A reasonable building orientation can reduce the comfort because of cold air entering the room in winter and can form a wind tunnel with doors and windows in summer to remove excess heat from the room and improve the overall thermal stability and comfort of the room.
Building window and door hole ratio: The proportion of the window and door openings in the envelope directly affects the thermal stability of the building’s interior, and a reasonable window and door hole ratio largely affects the natural ventilation of the building’s interior in summer and the intake of indoor light in winter.
4.8.4. Material saving
Envelope materials: Choosing the right building envelope can improve the indoor thermal environment and enhance the comfort of residents indoors.
4.9. Life-cycle carbon emission model of traditional Dong houses in Qiandongnan
4.9.1. Composition of the indicator system
Combining qualitative analysis and quantitative physical environment measurements, we initially constructed 4 primary indicators, 7 secondary indicators and 17 tertiary indicators, as shown in
Table 5, following the four principles of scientific selection of indicators, combining qualitative and quantitative factors, highlighting regional characteristics and providing foresight.
4.9.2. Determination of model indicators for the whole life cycle carbon emissions of traditional houses
Using the fuzzy Delphi expert questionnaire method, a detailed survey was completed with relevant personnel in three fields: construction experts, architectural designers, and building constructors. The preliminary whole life cycle carbon emission model index system for traditional residential buildings was established by determining the weight scores of each index through the AHP method.
A hierarchical analysis method was used to construct a recursive hierarchical structure model of multilevel indicators, and the importance of each indicator was quantified using the hierarchical structure model. Its importance was divided into nine scales, and the importance of the indicators was judged based on the size of the numbers derived from each indicator. After that, a judgment matrix was constructed to compare the weights of two indicators, and then a consistency test was conducted by calculating the maximum eigenvalue and related parameters. Under the condition of passing the consistency test, the weight coefficient of each indicator was calculated, upon which a complete evaluation system was finally constructed. The multilevel structure model was established, the hierarchical structure model used in this paper referred to the typical
AHP method, and the model was divided into four levels in total, as shown in
Table 6.
Since there were 4 primary indicators, 7 secondary indicators and 15 tertiary indicators in this study, using the professional calculation software of
AHP, yaahp, reduced both the workload and the errors of software calculation. A complete model was created using
yaahp software, and the software was used to calculate all the indicators of the study by itself, i.e., as shown in
Table 7.
6. Conclusions
To implement the concept of green development, promote the green development of construction and better achieve the goals of energy saving and carbon reductions in the construction industry, building carbon emission evaluation index and green building evaluation system can not only ensure the authenticity of green building energy saving and carbon reduction but also help promote energy saving and carbon reductions in the construction industry. Combined with the regional characteristics of the Dong traditional dwellings in Qiandongnan, the "Whole Life Cycle Carbon Emission Model of Traditional Houses in Qiandongnan”, was constructed. (1) The life cycle carbon emission calculation model of residential buildings was divided into four stages: production and transportation of building materials, construction, operation and demolition and disposal. (2) Analyzing the limitations of the existing local standards in China and the actual measurement of the physical environment of the Dong traditional dwellings in Qiandongnan, the 2019 national version of the Green Building Evaluation Criteria was combined with the reorganization and construction of an index system suitable for the Dong traditional dwellings in Qiandongnan, with the following primary indicators: resource conservation, environmental livability, culture of ethnic characteristics and ecological quality, and the following special features: increasing the primary indicators. Under the people-oriented main theme, the new indicators could better reflect the construction of the local environment and the regional characteristics. (3) The carbon emissions generated by construction workers during the construction phase were an important part of the total carbon emissions in this phase, so carbon emissions generated by construction workers cannot be ignored. In this paper, carbon emissions from construction personnel activities were considered in the calculation of the life-cycle carbon emissions of residential buildings, and a corresponding calculation method was proposed. In addition, due to the difference in building types and regions, the carbon sink capacity of wood in the operation stage of the building was not emphasized in previous studies, which will result in errors in the carbon emissions calculation of traditional residential buildings with wood as the main building material; thus, this paper included the carbon sink capacity of wood in the operation stage of the building. In this paper, the carbon emissions reduction from the production stage of building materials was underestimated. To address this issue, this paper considered the carbon emissions of building material recycling in the demolition and disposal stage, which was more in line with the actual situation.