Submitted:
29 June 2023
Posted:
30 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Patient Characteristics
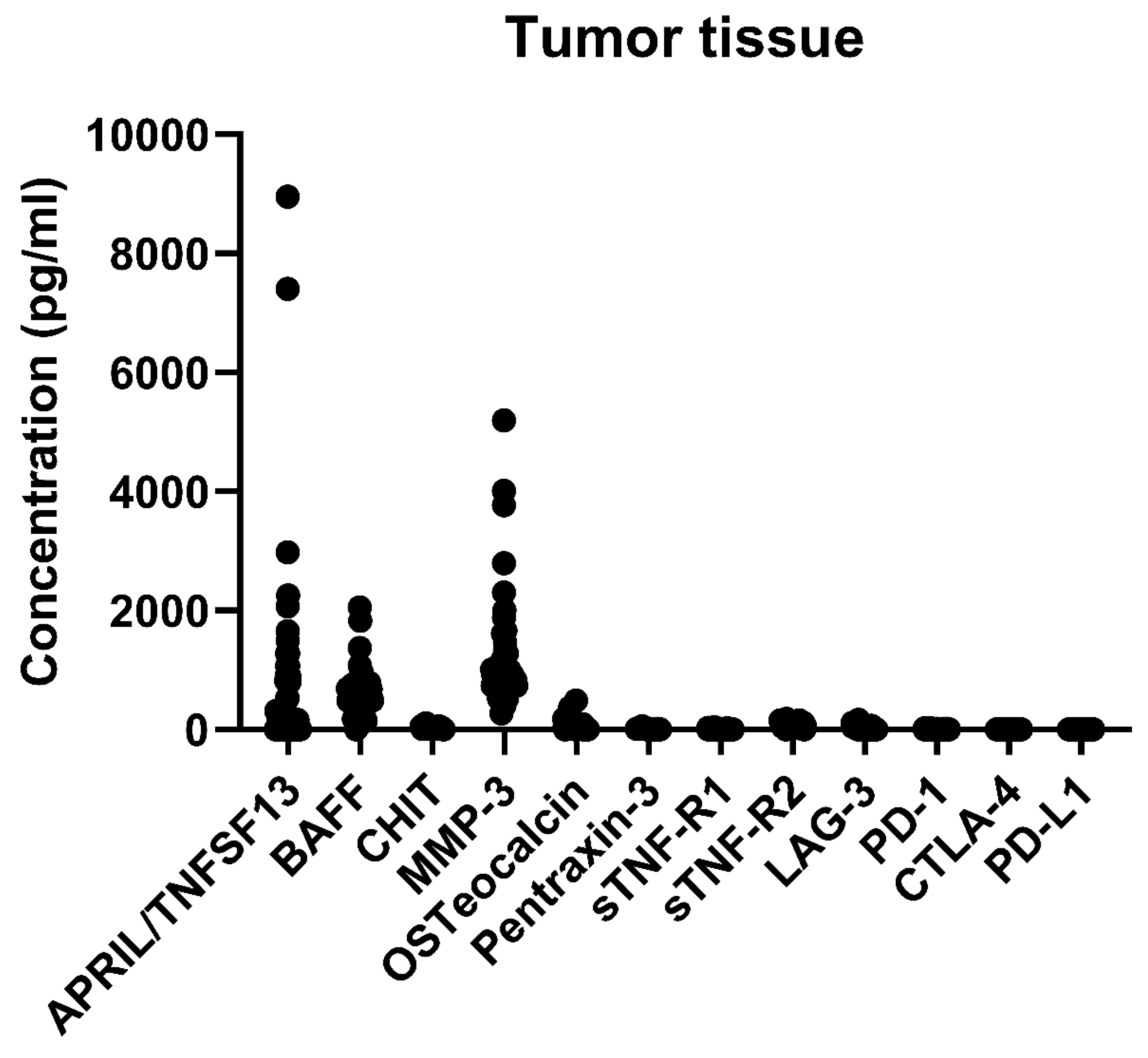
2.2. Immune-Related and Inflammatory Markers in Tumor Tissues
2.3. Relationships between Immune-Related and Inflammatory Markers and Clinicopathologic Features
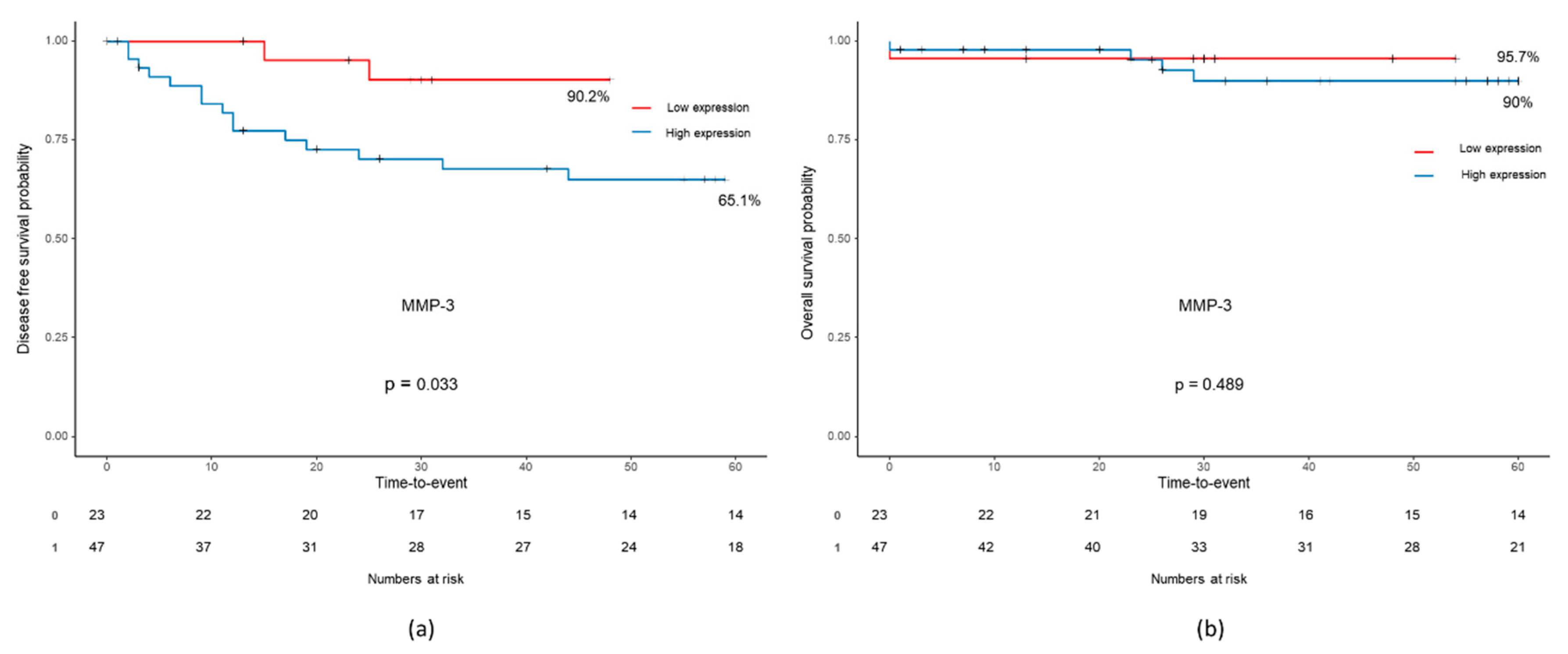
2.4. Relationships between Immune-Related and Inflammatory Markers and Long-Term Oncologic Outcomes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Ppulation
4.2. Tissue Sample Preparation
4.3. Bio-plex Multiplex Immunoassay System
4.4. Surgery and Pathological Examination
4.5. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sahin, I.H.; Akce, M.; Alese, O.; Shaib, W.; Lesinski, G.B.; El-Rayes, B.; Wu, C. Immune checkpoint inhibitors for the treatment of msi-h/mmr-d colorectal cancer and a perspective on resistance mechanisms. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 121, 809–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boukouris, A.E.; Theochari, M.; Stefanou, D.; Papalambros, A.; Felekouras, E.; Gogas, H.; Ziogas, D.C. Latest evidence on immune checkpoint inhibitors in metastatic colorectal cancer: A 2022 update. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2022, 173, 103663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlino, M.S.; Larkin, J.; Long, G.V. Immune checkpoint inhibitors in melanoma. Lancet 2021, 398, 1002–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatachalam, S.; McFarland, T.R.; Agarwal, N.; Swami, U. Immune checkpoint inhibitors in prostate cancer. Cancers (Basel) 2021, 13, 2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz-Ares, L.; Ciuleanu, T.E.; Cobo, M.; Schenker, M.; Zurawski, B.; Menezes, J.; Richardet, E.; Bennouna, J.; Felip, E.; Juan-Vidal, O. , et al. First-line nivolumab plus ipilimumab combined with two cycles of chemotherapy in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer (checkmate 9la): An international, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 198–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellmann, M.D.; Rizvi, N.A.; Goldman, J.W.; Gettinger, S.N.; Borghaei, H.; Brahmer, J.R.; Ready, N.E.; Gerber, D.E.; Chow, L.Q.; Juergens, R.A. , et al. Nivolumab plus ipilimumab as first-line treatment for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (checkmate 012): Results of an open-label, phase 1, multicohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, D.T.; Uram, J.N.; Wang, H.; Bartlett, B.R.; Kemberling, H.; Eyring, A.D.; Skora, A.D.; Luber, B.S.; Azad, N.S.; Laheru, D. , et al. Pd-1 blockade in tumors with mismatch-repair deficiency. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2509–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overman, M.J.; McDermott, R.; Leach, J.L.; Lonardi, S.; Lenz, H.J.; Morse, M.A.; Desai, J.; Hill, A.; Axelson, M.; Moss, R.A. , et al. Nivolumab in patients with metastatic DNA mismatch repair-deficient or microsatellite instability-high colorectal cancer (checkmate 142): An open-label, multicentre, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1182–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San-Roman-Gil, M.; Torres-Jimenez, J.; Pozas, J.; Esteban-Villarrubia, J.; Albarran-Fernandez, V.; Alvarez-Ballesteros, P.; Chamorro-Perez, J.; Rosero-Rodriguez, D.; Orejana-Martin, I.; Martinez-Delfrade, I.; et al. Current landscape and potential challenges of immune checkpoint inhibitors in microsatellite stable metastatic colorectal carcinoma. Cancers (Basel) 2023, 15, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatalica, Z.; Vranic, S.; Xiu, J.; Swensen, J.; Reddy, S. High microsatellite instability (msi-h) colorectal carcinoma: A brief review of predictive biomarkers in the era of personalized medicine. Fam. Cancer 2016, 15, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islekel, H.; Oktay, G.; Terzi, C.; Canda, A.E.; Fuzun, M.; Kupelioglu, A. Matrix metalloproteinase-9,-3 and tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase-1 in colorectal cancer: Relationship to clinicopathological variables. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2007, 25, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roeb, E.; Arndt, M.; Jansen, B.; Schumpelick, V.; Matern, S. Simultaneous determination of matrix metalloproteinase (mmp)-7, mmp-1, -3, and -13 gene expression by multiplex pcr in colorectal carcinomas. Int. J. Colorectal Dis. 2004, 19, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calu, V.; Ionescu, A.; Stanca, L.; Geicu, O.I.; Iordache, F.; Pisoschi, A.M.; Serban, A.I.; Bilteanu, L. Key biomarkers within the colorectal cancer related inflammatory microenvironment. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, W.; Wolchok, J.D.; Chen, L. Pd-l1 (b7-h1) and pd-1 pathway blockade for cancer therapy: Mechanisms, response biomarkers, and combinations. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 328rv324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gialeli, C.; Theocharis, A.D.; Karamanos, N.K. Roles of matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression and their pharmacological targeting. FEBS J. 2011, 278, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; He, Z.; He, X.; Luo, Z.; Lian, L.; Wu, B.; Lan, P.; Chen, H. Comprehensive analysis of the expression and prognosis for mmps in human colorectal cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 771099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, E.A.; Bergin, F.G.; Leaper, D.J. Matrix metalloproteinases, their tissue inhibitors and colorectal cancer staging. Br. J. Surg. 2000, 87, 1215–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobin, E.; Bagwell, K.; Wagner, J.; Mysona, D.; Sandirasegarane, S.; Smith, N.; Bai, S.; Sharma, A.; Schleifer, R.; She, J.X. A pan-cancer perspective of matrix metalloproteases (mmp) gene expression profile and their diagnostic/prognostic potential. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowacka, K.H.; Jabłońska, E. Role of the april molecule in solid tumors. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2021, 61, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Castro, A.; Zonca, M.; Florindo-Pinheiro, D.; Carvalho-Pinto, C.E.; Cordero, A.; Gutierrez del Fernando, B.; Garcia-Grande, A.; Manes, S.; Hahne, M.; Gonzalez-Suarez, E. , et al. April promotes breast tumor growth and metastasis and is associated with aggressive basal breast cancer. Carcinogenesis 2015, 36, 574–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, X.; Tao, J.; Xiang, G.; Cao, H.; Liu, Z.; Yang, K.; Lv, C.; Ni, S. April induces cisplatin resistance in gastric cancer cells via activation of the nf-kappab pathway. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 35, 571–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mhawech-Fauceglia, P.; Allal, A.; Odunsi, K.; Andrews, C.; Herrmann, F.R.; Huard, B. Role of the tumour necrosis family ligand april in solid tumour development: Retrospective studies in bladder, ovarian and head and neck carcinomas. Eur. J. Cancer 2008, 44, 2097–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bat-Erdene, U.; Quan, E.; Chan, K.; Lee, B.M.; Matook, W.; Lee, K.Y.; Rosales, J.L. Neutrophil tlr4 and pkr are targets of breast cancer cell glycosaminoglycans and effectors of glycosaminoglycan-induced april secretion. Oncogenesis 2018, 7, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lascano, V.; Hahne, M.; Papon, L.; Cameron, K.; Roeder, C.; Schafmayer, C.; Driessen, L.; van Eenennaam, H.; Kalthoff, H.; Medema, J.P. Circulating april levels are correlated with advanced disease and prognosis in rectal cancer patients. Oncogenesis 2015, 4, e136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Ding, W.; Wang, J.; Jing, R.; Wang, X.; Cong, H.; Wang, Y.; Ju, S.; Wang, H. Identification of microrna-target interaction in april-knockdown colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Gene Ther. 2011, 18, 500–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Wang, J.; Wang, F.; Wang, G.; Wu, Q.; Ju, S.; Cong, H.; Wang, H. Serum sapril: A potential tumor-associated biomarker to colorectal cancer. Clin. Biochem. 2013, 46, 1590–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreaux, J.; Veyrune, J.L.; De Vos, J.; Klein, B. April is overexpressed in cancer: Link with tumor progression. BMC Cancer 2009, 9, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelekanou, V.; Notas, G.; Athanasouli, P.; Alexakis, K.; Kiagiadaki, F.; Peroulis, N.; Kalyvianaki, K.; Kampouri, E.; Polioudaki, H.; Theodoropoulos, P. , et al. Bcma (tnfrsf17) induces april and baff mediated breast cancer cell stemness. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koizumi, M.; Hiasa, Y.; Kumagi, T.; Yamanishi, H.; Azemoto, N.; Kobata, T.; Matsuura, B.; Abe, M.; Onji, M. Increased b cell-activating factor promotes tumor invasion and metastasis in human pancreatic cancer. PLoS One 2013, 8, e71367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warakomska, M.; Tynecka, M.; Lemancewicz, D.; Grubczak, K.; Dzieciol, J.; Moniuszko, M.; Eljaszewicz, A.; Bolkun, L. The effects of baff and april signaling on non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation and invasiveness. Oncol. Lett. 2021, 22, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Tian, L.; Shen, S.; Ma, J.; Ai, F. Histone deacetylase (hdac) 11 inhibits matrix metalloproteinase (mmp) 3 expression to suppress colorectal cancer metastasis. J. Cancer 2022, 13, 1923–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Wang, F.; Ding, W.; Wang, J.; Jing, R.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Ju, S.; Wang, H. April induces tumorigenesis and metastasis of colorectal cancer cells via activation of the pi3k/akt pathway. PLoS One 2013, 8, e55298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Luo, S.; Burgess, R.; Yi, Y.H.; Huang, G.F.; Huang, R.P. New insights into the tumor microenvironment utilizing protein array technology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Zhu, J.; Van Eyk, J.E. Comparison of multiplex immunoassay platforms. Clin. Chem. 2010, 56, 314–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Merbs, S.L.; Sokoll, L.J.; Chan, D.W.; Zhang, Z. A multiplex immunoassay of serum biomarkers for the detection of uveal melanoma. Clin. Proteomics 2019, 16, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doseeva, V.; Colpitts, T.; Gao, G.; Woodcock, J.; Knezevic, V. Performance of a multiplexed dual analyte immunoassay for the early detection of non-small cell lung cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurkovetsky, Z.; Skates, S.; Lomakin, A.; Nolen, B.; Pulsipher, T.; Modugno, F.; Marks, J.; Godwin, A.; Gorelik, E.; Jacobs, I. , et al. Development of a multimarker assay for early detection of ovarian cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 2159–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Sokoll, L.J.; Pasay, J.J.; Rubin, A.L.; Li, H.; Bach, D.M.; Chan, D.W.; Zhang, Z. Identification of serum biomarker panels for the early detection of pancreatic cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2019, 28, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Tong, W.; Su, Z.; Han, T.; Han, J.; Puri, R.K.; Fang, H.; Frueh, F.W.; Goodsaid, F.M.; Guo, L. , et al. Microarray scanner calibration curves: Characteristics and implications. BMC Bioinformatics 2005, 6(Suppl 2), S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Number of patients (%) (n=70) |
|
|---|---|
| Age, mean ± SD | 69.6 ± 10.8 |
| Gender | |
| Male | 38 (54.3) |
| Female | 32 (45.7) |
| Body mass index, mean ± SD | 23.4 ± 3.5 |
| ASA score | |
| II | 35 (50.0) |
| III | 35 (50.0) |
| Medical history | |
| None | 19 (27.1) |
| One | 18 (25.7) |
| Two or more | 33 (47.1) |
| Tumor location | |
| Right | 19 (27.1) |
| Left | 27 (38.6) |
| Rectum | 24 (34.3) |
| CEA | |
| <5 | 45 (64.3) |
| ≥5 | 25 (35.7) |
| Operation method | |
| Open | 15 (21.4) |
| MIS | 55 (78.6) |
| T stage | |
| Tis | 1 (1.4) |
| 3 | 53 (75.7) |
| 4 | 16 (22.9) |
| N stage | |
| 0 | 28 (40.0) |
| 1 | 28 (40.0) |
| 2 | 14 (20.0) |
| M stage | |
| 0 | 57 (81.4) |
| 1 | 13 (18.6) |
| TNM stage | |
| 0 | 1 (1.4) |
| 2 | 25 (35.7) |
| 3 | 31 (44.3) |
| 4 | 13 (18.6) |
| Metastatic lymph node, mean ± SD | 2.2 ± 3.6 |
| Harvested lymph node, mean ± SD | 24.8 ± 11.1 |
| Tumor differentiation | |
| Well differentiation | 13 (18.8) |
| Moderate differentiation | 53 (76.8) |
| Poorly differentiation | 1 (1.4) |
| Mucinous adenocarcinoma | 2 (2.9) |
| Tumor size (cm), mean ± SD | 5.0 ± 2.0 |
| Lymphatic invasion | |
| Negative | 38 (54.3) |
| Positive | 32 (45.7) |
| Venous invasion | |
| Negative | 63 (90.0) |
| Positive | 7 (10.0) |
| Perineural invasion | |
| Negative | 50 (71.4) |
| Positive | 20 (28.6) |
| EGFR | |
| Negative | 5 (7.6) |
| Positive | 61 (92.4) |
| MSI | |
| MSS | 63 (94.0) |
| MSI-H | 4 (6.0) |
| KRAS | |
| Wild | 39 (58.2) |
| Mutant | 28 (41.8) |
| NRAS | |
| Wild | 47 (92.2) |
| Mutant | 2 (3.9) |
| BRAF | |
| Wild | 62 (95.4) |
| Mutant | 3 (4.6) |
| Laboratory markers, mean ± SD | |
| WBC (103/μL) | 7.6 ± 3.1 |
| Hb (g/dL) | 11.9 ± 2.4 |
| PLT (103/μL) | 288.0 ± 100.3 |
| Neutrophil count (103/μL) | 5.4 ± 3.0 |
| Lymphocyte count (103/μL) | 1.5 ± 0.6 |
| NLR | 4.5 ± 4.9 |
| C-reactive protein (mg/dL) | 1.7 ± 2.7 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 3.8 ± 0.6 |
| Chemotherapy | |
| No | 24 (34.3) |
| Yes | 46 (65.7) |
| Radiotherapy | |
| No | 69 (98.6) |
| Yes | 1 (1.4) |
| Recurrence | |
| No | 42 (60.0) |
| Yes | 17 (24.3) |
| Death | |
| No | 45 (64.3) |
| Yes | 5 (7.1) |
| Median [IQR] | Range | |
|---|---|---|
| APRIL/TNFSF13 | 166.02 [0, 806.4] | 0~8954.58 |
| BAFF | 485.6 [355.3, 664.0] | 0~2053.2 |
| CHIT | 21.3 [10.24, 31.24] | 0~101.19 |
| MMP-3 | 905.1 [736.2, 1106.9] | 270.5~5198.8 |
| Osteocalcin | 16.33 [2.37, 41.34] | 0~487.48 |
| Pentraxin-3 | 8.98 [7.41, 12.19] | 3.23~57.43 |
| sTNF-R1 | 6.67 [5.43, 7.87] | 2.28~36.20 |
| sTNF-R2 | 60.99 [35.78, 106.93] | 0~177.87 |
| LAG-3 | 0 [0, 11.46] | 0~164.96 |
| PD-1 | 5.3 [5.30, 10.84] | 0~21.77 |
| PD-L1 | 0 [0, 0.43] | 0~4.49 |
| CTLA-4 | 0 [0, 0] | 0~3.1 |
| APRIL/TNFSF13 (806.4) | BAFF (664.0) | MMP-3 (736.2) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low (N=51) | High (N=19) | p | Low (N=52) | High (N=18) | p | Low (N=23) | High (N=47) | p | |
| Age, mean ± SD | 69.8 ± 10.7 | 69.2 ± 11.0 | 0.82 | 69.4 ± 11.1 | 70.3 ± 10.1 | 0.74 | 70.7 ± 11.4 | 69.1 ± 10.5 | 0.59 |
| Gender | |||||||||
| Male | 27 (52.9) | 11 (57.9) | 0.92 | 25 (48.1) | 13 (72.2) | 0.13 | 15 (65.2) | 23 (48.9) | 0.30 |
| Female | 24 (47.1) | 8 (42.1) | 27 (51.9) | 5 (27.8) | 8 (34.8) | 24 (51.1) | |||
| BMI | 23.5 ± 3.7 | 23.1 ± 3.1 | 0.70 | 23.4 ± 3.7 | 23.4 ± 3.0 | 0.96 | 23.3 ± 3.6 | 23.4 ± 3.5 | 0.90 |
| ASA score | |||||||||
| II | 28 (54.9) | 7 (36.8) | 0.28 | 29 (55.8) | 6 (33.3) | 0.17 | 13 (56.5) | 22 (46.8) | 0.61 |
| III | 23 (45.1) | 12 (63.2) | 23 (44.2) | 12 (66.7) | 10 (43.5) | 25 (53.2) | |||
| Medical history | |||||||||
| None | 14 (27.5) | 5 (26.3) | 0.95* | 12 (23.1) | 7 (38.9) | 0.22* | 6 (26.1) | 13 (27.7) | 0.81 |
| One | 14 (27.5) | 4 (21.1) | 16 (30.8) | 2 (11.1) | 5 (21.7) | 13 (27.7) | |||
| T or more | 23 (45.1) | 10 (52.6) | 24 (46.2) | 9 (50.0) | 12 (52.2) | 21 (44.7) | |||
| Tumor location | |||||||||
| Right | 15 (29.4) | 4 (21.1) | 0.65 | 17 (32.7) | 2 (11.1) | 0.13* | 8 (34.8) | 11 (23.4) | 0.51 |
| Left | 20 (39.2) | 7 (36.8) | 20 (38.5) | 7 (38.9) | 7 (30.4) | 20 (42.6) | |||
| Rectum | 16 (31.4) | 8 (42.1) | 15 (28.8) | 9 (50.0) | 8 (34.8) | 16 (34.0) | |||
| CEA | |||||||||
| <5 | 34 (66.7) | 11 (57.9) | 0.68 | 34 (65.4) | 11 (61.1) | 0.96 | 19 (82.6) | 26 (55.3) | 0.04 |
| ≥5 | 17 (33.3) | 8 (42.1) | 18 (34.6) | 7 (38.9) | 4 (17.4) | 21 (44.7) | |||
| Operation method | |||||||||
| Open | 10 (19.6) | 5 (26.3) | 0.53* | 11 (21.2) | 4 (22.2) | 1* | 6 (26.1) | 9 (19.1) | 0.54* |
| MIS | 41 (80.4) | 14 (73.7) | 41 (78.8) | 14 (77.8) | 17 (73.9) | 38 (80.9) | |||
| T stage | |||||||||
| Tis | 0 (0.0) | 1 (5.3) | 0.29* | 0 (0.0) | 1 (5.6) | 0.09* | 0 (0.0) | 1 (2.1) | 0.01* |
| 3 | 40 (78.4) | 13 (68.4) | 42 (80.8) | 11 (61.1) | 22 (95.7) | 31 (66.0) | |||
| 4 | 11 (21.6) | 5 (26.3) | 10 (19.2) | 6 (33.3) | 1 (4.3) | 15 (31.9) | |||
| N stage | |||||||||
| 0 | 22 (43.1) | 6 (31.6) | 0.60* | 20 (38.5) | 8 (44.4) | 0.81* | 13 (56.5) | 15 (31.9) | 0.15* |
| 1 | 20 (39.2) | 8 (42.1) | 22 (42.3) | 6 (33.3) | 6 (26.1) | 22 (46.8) | |||
| 2 | 9 (17.6) | 5 (26.3) | 10 (19.2) | 4 (22.2) | 4 (17.4) | 10 (21.3) | |||
| M stage | |||||||||
| 0 | 45 (88.2) | 12 (63.2) | 0.03* | 45 (86.5) | 12 (66.7) | 0.08* | 21 (91.3) | 36 (76.6) | 0.19* |
| 1 | 6 (11.8) | 7 (36.8) | 7 (13.5) | 6 (33.3) | 2 (8.7) | 11 (23.4) | |||
| TNM stage | |||||||||
| 0 | 0 (0.0) | 1 (5.3) | 0.02* | 0 (0.0) | 1 (5.6) | 0.06* | 0 (0.0) | 1 (2.1) | 0.04* |
| 2 | 21 (41.2) | 4 (21.1) | 19 (36.5) | 6 (33.3) | 13 (56.5) | 12 (25.5) | |||
| 3 | 24 (47.1) | 7 (36.8) | 26 (50.0) | 5 (27.8) | 8 (34.8) | 23 (48.9) | |||
| 4 | 6 (11.8) | 7 (36.8) | 7 (13.5) | 6 (33.3) | 2 (8.7) | 11 (23.4) | |||
| Metastatic lymph node | 1.8 ± 3.3 | 3.2 ± 4.3 | 0.23 | 2.0 ± 3.3 | 2.8 ± 4.4 | 0.45 | 1.1 ± 1.7 | 2.7 ± 4.2 | 0.02 |
| Harvested lymph node | 24.4 ± 9.4 | 25.9 ± 14.9 | 0.68 | 25.3 ± 9.8 | 23.4 ± 14.4 | 0.62 | 27.1 ± 13.1 | 23.7 ± 9.9 | 0.27 |
| Tumor differentiation | |||||||||
| WD | 10 (19.6) | 3 (16.7) | 0.79* | 9 (17.3) | 4 (23.5) | 0.63* | 4 (17.4) | 9 (19.6) | 0.91* |
| MD | 39 (76.5) | 14 (77.8) | 41 (78.8) | 12 (70.6) | 19 (82.6) | 34 (73.9) | |||
| PD | 1 (2.0) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (1.9) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (2.2) | |||
| Mucinous | 1 (2.0) | 1 (5.6) | 1 (1.9) | 1 (5.9) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (4.3) | |||
| Tumor size (cm), mean ± SD | 4.9 ± 2.2 | 5.2 ± 1.3 | 0.50 | 4.9 ± 2.2 | 5.1 ± 1.5 | 0.64 | 4.8 ± 2.0 | 5.0 ± 2.1 | 0.74 |
| Lymphatic invasion | |||||||||
| Negative | 28 (54.9) | 10 (52.6) | 1 | 28 (53.8) | 10 (55.6) | 1 | 11 (47.8) | 27 (57.4) | 0.61 |
| Positive | 23 (45.1) | 9 (47.4) | 24 (46.2) | 8 (44.4) | 12 (52.2) | 20 (42.6) | |||
| Venous invasion | |||||||||
| Negative | 47 (92.2) | 16 (84.2) | 0.37* | 47 (90.4) | 16 (88.9) | 1* | 21 (91.3) | 42 (89.4) | 1* |
| Positive | 4 (7.8) | 3 (15.8) | 5 (9.6) | 2 (11.1) | 2 (8.7) | 5 (10.6) | |||
| Perineural invasion | |||||||||
| Negative | 40 (78.4) | 10 (52.6) | 0.06 | 40 (76.9) | 10 (55.6) | 0.15 | 19 (82.6) | 31 (66.0) | 0.24 |
| Positive | 11 (21.6) | 9 (47.4) | 12 (23.1) | 8 (44.4) | 4 (17.4) | 16 (34.0) | |||
| EGFR | |||||||||
| Negative | 1 (2.1) | 4 (22.2) | 0.01* | 1 (2.0) | 4 (25.0) | 0.01* | 0 (0.0) | 5 (11.6) | 0.15* |
| Positive | 47 (97.9) | 14 (77.8) | 49 (98.0) | 12 (75.0) | 23 (100.0) | 38 (88.4) | |||
| MSI | |||||||||
| MSS | 46 (92.0) | 17 (100.0) | 0.56* | 47 (92.2) | 16 (100.0) | 0.56* | 21 (91.3) | 42 (95.5) | 0.60* |
| MSI-H | 4 (8.0) | 0 (0.0) | 4 (7.8) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (8.7) | 2 (4.5) | |||
| KRAS | |||||||||
| Wild | 27 (56.2) | 12 (63.2) | 0.80 | 29 (59.2) | 10 (55.6) | 1 | 12 (57.1) | 27 (58.7) | 1 |
| Mutant | 21 (43.8) | 7 (36.8) | 20 (40.8) | 8 (44.4) | 9 (42.9) | 19 (41.3) | |||
| NRAS | |||||||||
| Wild | 33 (97.1) | 14 (93.3) | 0.52* | 35 (97.2) | 12 (92.3) | 0.46* | 16 (100.0) | 31 (93.9) | 1* |
| Mutant | 1 (2.9) | 1 (6.7) | 1 (2.8) | 1 (7.7) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (6.1) | |||
| BRAF | |||||||||
| Wild | 45 (95.7) | 17 (94.4) | 1* | 45 (93.8) | 17 (100.0) | 0.56* | 19 (95.0) | 43 (95.6) | 1* |
| Mutant | 2 (4.3) | 1 (5.6) | 3 (6.2) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (5.0) | 2 (4.4) | |||
| Laboratory markers, median [IQR] | |||||||||
| WBC (103/μL) | 6.6 [5.4, 9.2] | 7.1 [6.5, 8.8] | 0.53 | 7.2 [5.5, 9.2] | 6.7 [5.9, 8.9] | 0.83 | 6.5 [4.9, 7.6] | 7.2 [5.9, 9.4] | 0.10 |
| Hb (g/dL) | 12.6 [10.4, 13.6] | 11.1 [9.7, 12.5] | 0.13 | 12.4 [10.2, 13.4] | 12.4 [9.8, 13.8] | 0.87 | 12.4 [10.1, 13.8] | 12.3 [10.2, 13.6] | 0.58 |
| PLT (103/μL) | 272.0 [209.5, 323.0] | 253.0 [231.0, 331.0] | 0.92 | 275.5 [212.2, 333.5] | 242.0 [224.5, 294.2] | 0.37 | 260.0 [193.0, 307.0] | 259.0 [222.5, 332.5] | 0.42 |
| Neutrophil (103/μL) | 4.7 [3.0, 6.4] | 5.1 [4.4, 7.1] | 0.17 | 4.7 [3.1, 6.9] | 4.9 [4.3, 6.8] | 0.38 | 3.6 [3.0, 5.8] | 4.9 [3.7, 7.1] | 0.08 |
| Lymphocyte (103/μL) | 1.6 [1.3, 1.9] | 1.3 [1.0, 1.8] | 0.20 | 1.5 [1.2, 1.9] | 1.3 [1.0, 1.8] | 0.49 | 1.4 [1.2, 1.7] | 1.6 [1.1, 1.9] | 0.48 |
| NLR | 2.7 [2.1, 4.2] | 4.1 [2.7, 6.0] | 0.04 | 2.7 [2.2, 4.4] | 3.9 [2.7, 5.4] | 0.15 | 2.5 [2.1, 4.1] | 3.6 [2.5, 5.2] | 0.16 |
| CRP (mg/dL) | 0.4 [0.3, 1.6] | 1.0 [0.3, 2.3] | 0.25 | 0.5 [0.3, 1.8] | 0.7 [0.3, 1.3] | 0.97 | 0.6 [0.3, 1.3] | 0.7 [0.3, 1.8] | 0.99 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 3.9 [3.6, 4.3] | 3.7 [3.2, 4.0] | 0.07 | 3.9 [3.6, 4.2] | 3.8 [3.3, 4.2] | 0.58 | 3.8 [3.2, 4.2] | 3.9 [3.5, 4.3] | 0.31 |
| Chemotherapy | |||||||||
| No | 17 (33.3) | 7 (36.8) | 1 | 16 (30.8) | 8 (44.4) | 0.44 | 9 (39.1) | 15 (31.9) | 0.74 |
| Yes | 34 (66.7) | 12 (63.2) | 36 (69.2) | 10 (55.6) | 14 (60.9) | 32 (68.1) | |||
| Radiotherapy | |||||||||
| No | 50 (98.0) | 19 (100.0) | 1* | 51 (98.1) | 18 (100.0) | 1* | 22 (95.7) | 47 (100.0) | 0.32* |
| Yes | 1 (2.0) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (1.9) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (4.3) | 0 (0.0) | |||
| Recurrence | |||||||||
| No | 34 (66.7) | 8 (42.1) | 0.06* | 35 (67.3) | 7 (38.9) | 0.03* | 16 (69.6) | 26 (55.3) | 0.08* |
| Yes | 12 (23.5) | 5 (26.3) | 12 (23.1) | 5 (27.8) | 2 (8.7) | 15 (31.9) | |||
| Death | |||||||||
| No | 36 (70.6) | 9 (47.4) | 0.11* | 37 (71.2) | 8 (44.4) | 0.08* | 16 (69.6) | 29 (61.7) | 0.78* |
| Yes | 4 (7.8) | 1 (5.3) | 3 (5.8) | 2 (11.1) | 1 (4.3) | 4 (8.5) | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





