Submitted:
28 June 2023
Posted:
29 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Nucleic acids from field samples and isolates
2.2. RNA standards for testing and validation
2.3. Selection of primers and probes
2.4. RT-qPCR protocol
2.5. Optimization of primer and probe concentrations
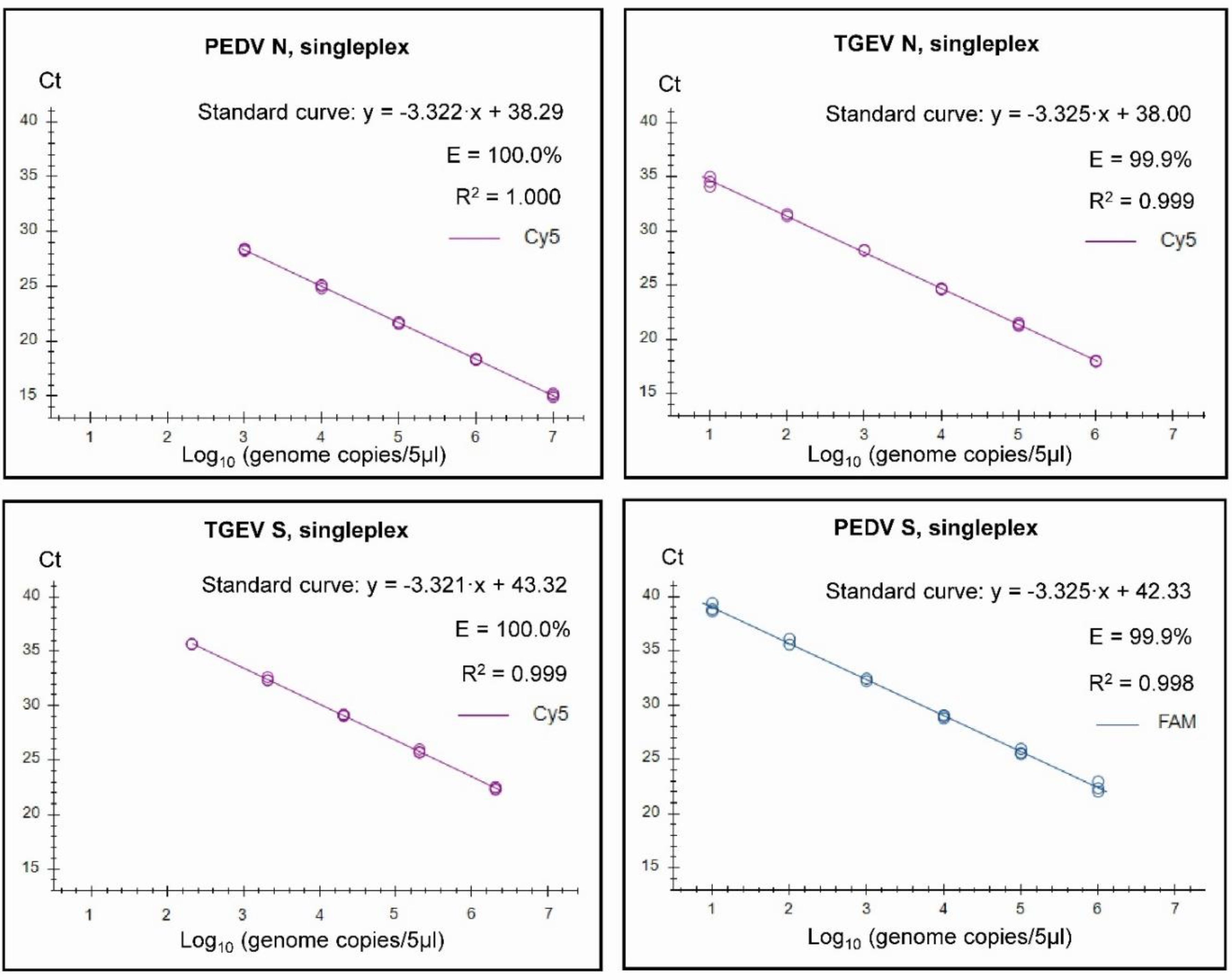
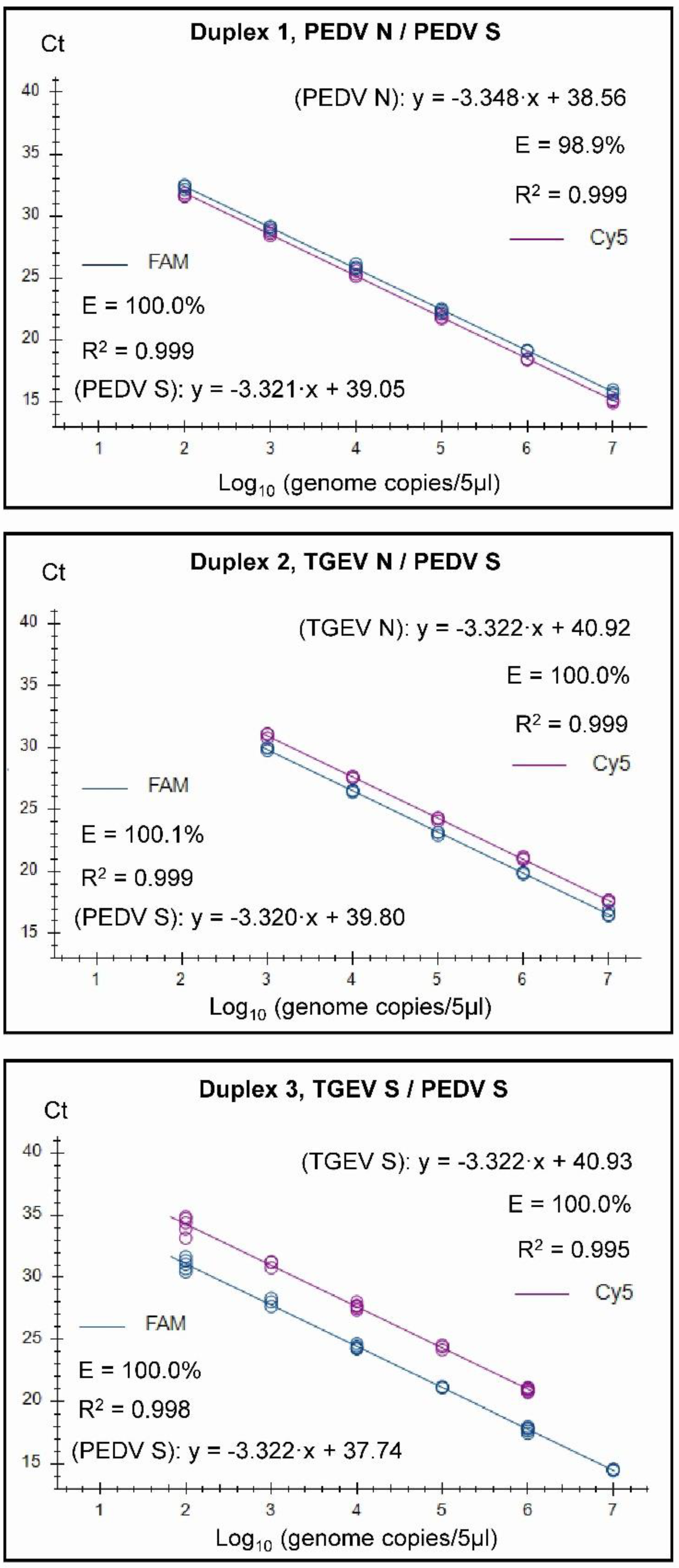
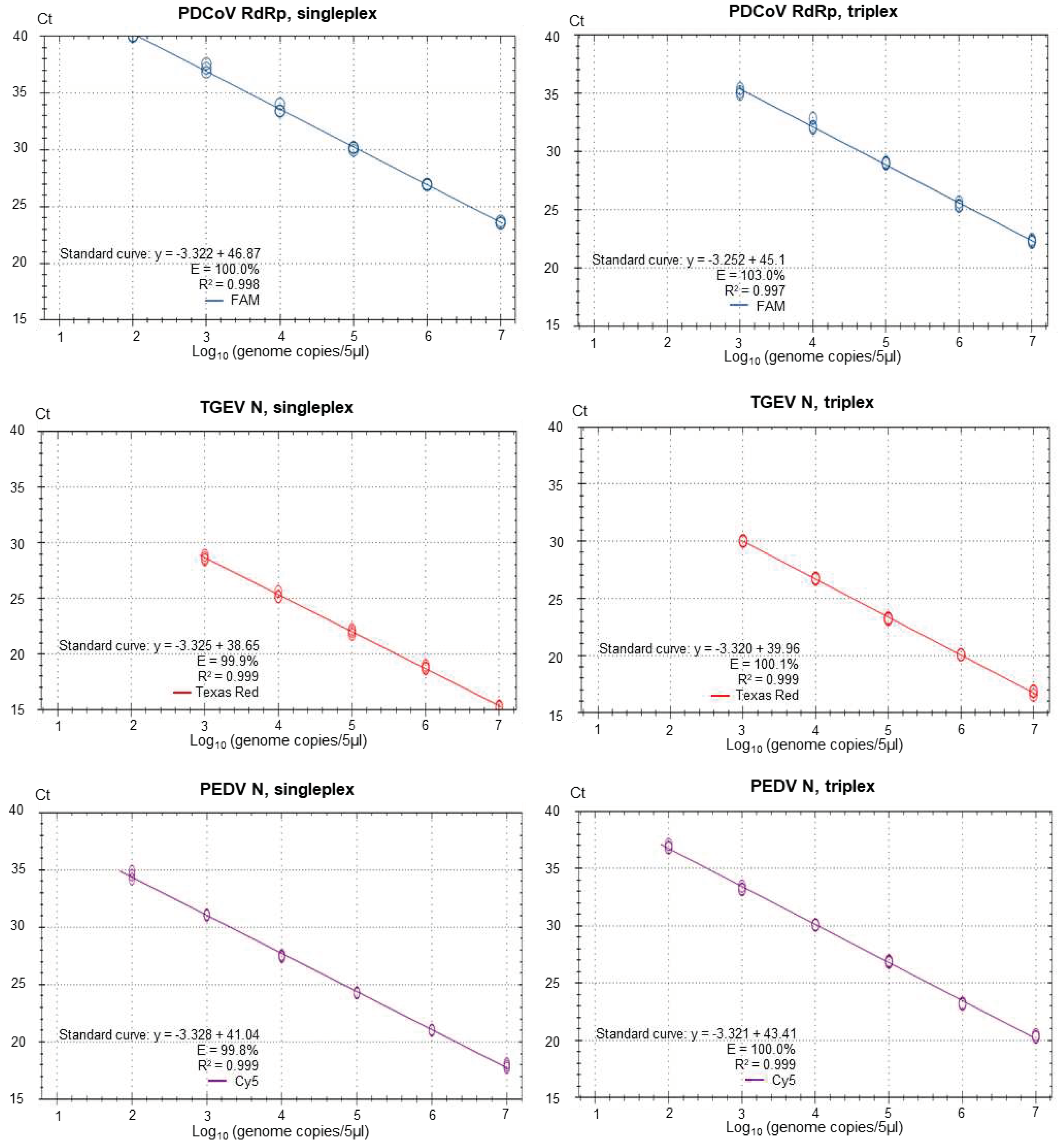
2.6. Standard curves
2.7. Validation steps
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jung, K.; Saif, L.J.; Wang, Q. Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV): An update on etiology, transmission, pathogenesis, and prevention and control. Virus Research 2020, 286, 198045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C. Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus: An emerging and re-emerging epizootic swine virus. Virology Journal 2015, 12, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Knutson, T.P.; Rossow, S.; Saif, L.J.; Marthaler, D.G. Decline of transmissible gastroenteritis virus and its complex evolutionary relationship with porcine respiratory coronavirus in the United States. Scientific Reports 2019, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Fan, H.; Lan, T.; Yang, X.; Lou, Shi, W.F.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.W.; Xie, Q.M.; Mani, S.; Zheng, X.S.; Li, B.; Li, J.M.; Guo, H.; Pei, G.Q.; An, X.P.; Chen, J.W.; Zhou, L.; Mai, K.J.; … Ma, J.Y. Fatal swine acute diarrhoea syndrome caused by an HKU2-related coronavirus of bat origin. Nature 2018, 556, 255–259. [CrossRef]
- Woo, P.C. Y. ; Lau, S.K. P. ; Lam, C.S. F. ; Lau, C.C. Y. ; Tsang, A.K. L. ; Lau, J.H. N. ; Bai, R. ; Teng, J.L. L. ; Tsang, C.C. C. ; Wang, M. ; Zheng, B.-J. ; Chan, K.-H. ; Yuen, K.-Y. Discovery of Seven Novel Mammalian and Avian Coronaviruses in the Genus Deltacoronavirus Supports Bat Coronaviruses as the Gene Source of Alphacoronavirus and Betacoronavirus and Avian Coronaviruses as the Gene Source of Gammacoronavirus and Deltacoronavi. Journal of Virology 2012, 86, 3995–4008. [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Byrum, B.; Zhang, Y. Detection and genetic characterization of deltacoronavirus in pigs, Ohio, USA, 2014. Emerging Infectious Diseases 2014, 20, 1227–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akimkin, V.; Beer, M.; Blome, S.; Hanke, D.; Höper, D.; Jenckel, M.; Pohlmann, A. New chimeric porcine coronavirus in Swine Feces, Germany, 2012. Emerging Infectious Diseases 2016, 22, 1314–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belsham, G.J.; Rasmussen, T.B.; Normann, P.; Vaclavek, P.; Strandbygaard, B.; Bøtner, A. Characterization of a Novel Chimeric Swine Enteric Coronavirus from Diseased Pigs in Central Eastern Europe in 2016. Transboundary and Emerging Diseases 2016, 63, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boniotti, M.B.; Papetti, A.; Lavazza, A.; Alborali, G.; Sozzi, E.; Chiapponi, C.; Faccini, S.; Bonilauri, P.; Cordioli, P.; Marthaler, D. Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus and discovery of a recombinant swine enteric coronavirus, Italy. Emerging Infectious Diseases 2016, 22, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Nova, P.J.G.; Cortey, M.; Díaz, I.; Puente, H.; Rubio, P.; Martín, M.; Carvajal, A. A retrospective study of porcine epidemic diarrhoea virus (PEDV) reveals the presence of swine enteric coronavirus (SeCoV) since 1993 and the recent introduction of a recombinant PEDV-SeCoV in Spain. Transboundary and Emerging Diseases 2020, 67, 2911–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papetti, A.; Bonilauri, P.; Chiapponi, C.; Baioni, L.; Boniotti, M.B. Complete Genome Sequence of an Italian Swine Enteric Coronavirus Strain 77590/2019. Microbiology Resource Announcements 2022, 15, e00386–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boniotti, M.B.; Papetti, A.; Bertasio, C.; Giacomini, E.; Lazzaro, M.; Cerioli, M.; Faccini, S.; Bonilauri, P.; Vezzoli, F.; Lavazza, A.; Alborali, G.L. Porcine Epidemic Diarrhoea Virus in Italy: Disease spread and the role of transportation. Transboundary and Emerging Diseases 2018, 65, 1935–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valkó, A.; Biksi, I.; Cságola, A.; Tuboly, T.; Kiss, K.; Ursu, K.; Dán, Á. Porcine epidemic diarrhoea virus with a recombinant S gene detected in Hungary, 2016. Acta Veterinaria Hungarica 2017, 65, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valkó, A.; Albert, E.; Cságola, A.; Varga, T.; Kiss, K.; Farkas, R.; Rónai, Z.; Biksi, I.; Dán, Á. Isolation and characterisation of porcine epidemic diarrhoea virus in Hungary. Acta Veterinaria Hungarica 2019, 67, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, I.M.; Arden, K.E.; Nitsche, A. Real-time PCR in virology. Nucleic Acids Research 2002, 30, 1292–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertasio, C.; Giacomini, E.; Lazzaro, M.; Perulli, S.; Papetti, A.; Lavazza, A.; Lelli, D.; Alborali, G.; Boniotti, M.B. Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus shedding and antibody response in swine farms: A longitudinal study. Frontiers in Microbiology 2016, 7, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Kim, I.J.; Pyo, H.M.; Tark, D.S.; Song, J.Y.; Hyun, B.H. Multiplex real-time RT-PCR for the simultaneous detection and quantification of transmissible gastroenteritis virus and porcine epidemic diarrhea virus. Journal of Virological Methods 207, 146, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigault, L.; Brown, P.; Bernard, C.; Blanchard, Y.; Grasland, B. Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus: Viral RNA detection and quantification using a validated one-step real time RT-PCR. Journal of Virological Methods 2020, 283, 113906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, C.; Goede, D.P.; Morrison, R.B.; Davies, P.R.; Rovira, A.; Marthaler, D.G.; Torremorell, M. Evidence of infectivity of airborne porcine epidemic diarrhea virus and detection of airborne viral RNA at long distances from infected herds. Veterinary Research 2014, 45, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Li, G.; Stasko, J.; Thomas, J.T.; Stensland, W.R.; Pillatzki, A.E.; Gauger, P.C.; Schwartz, K.J.; Madson, D.; Yoon, K.J.; Stevenson, G.W.; Burrough, E.R.; Harmon, K.M.; Main, R.G.; Zhang, J. Isolation and characterization of porcine epidemic diarrhea viruses associated with the 2013 disease outbreak among swine in the united states. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 2014, 52, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vemulapalli, R.; Gulani, J.; Santrich, C. A real-time TaqMan® RT-PCR assay with an internal amplification control for rapid detection of transmissible gastroenteritis virus in swine fecal samples. Journal of Virological Methods 2009, 162, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xing, G.; Hao, H.; Wei, Q.; Liang, Y.; Xie, W.; Li, D.; Huang, H.; Deng, R.; Zhang, G. A novel duplex TaqMan probe-based real-time RT-qPCR for detecting and differentiating classical and variant porcine epidemic diarrhea viruses. Molecular and Cellular Probes 2018, 37, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bustin, S.A.; Benes, V.; Garson, J.A.; Hellemans, J.; Huggett, J.; Kubista, M.; Mueller, R.; Nolan, T.; Pfaffl, M.W.; Shipley, G.L.; Vandesompele, J.; Wittwer, C.T. The MIQE guidelines: Minimum information for publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clinical Chemistry 2009, 55, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broeders, S.; Huber, I.; Grohmann, L.; Berben, G.; Taverniers, I.; Mazzara, M.; Roosens, N.; Morisset, D. Guidelines for validation of qualitative real-time PCR methods. Trends in Food Science and Technology 2014, 37, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, V.; Lewis, P.; Alsop, J.; Templeton, C.; Saif, L.J. Respiratory and fecal shedding of Porcine respiratory coronavirus (PRCV) in sentinel weaned pigs and sequence of the partial S-gene of the PRCV isolates. Archives of Virology 2004, 149, 957–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, G.; Fu, Y.; Li, B.; Chen, J.; Wang, J.; Yin, B.; Sha, W.; Liu, G. Development of a multiplex RT-PCR for the detection of major diarrhoeal viruses in pig herds in China. Transboundary and Emerging Diseases 2020, 67, 678–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuda, T.; Tsuchiaka, S.; Ashiba, T.; Yamasato, H.; Fukunari, K.; Omatsu, T.; Furuya, T.; Shirai, J.; Mizutani, T.; Nagai, M. Development of one-step real-time reverse transcriptase-PCR-based assays for the rapid and simultaneous detection of four viruses causing porcine diarrhea. Japanese Journal of Veterinary Research 2016, 64, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, G.; Niu, J.; Zhou, X.; Xie, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, G.; Chen, R.; He, D. Use of dual priming oligonucleotide system-based multiplex RT-PCR assay to detect five diarrhea viruses in pig herds in South China. AMB Express 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goecke, N.B.; Hjulsager, C.K.; Krog, J.S.; Skovgaard, K.; Larsen, L.E. Development of a high-throughput real-time PCR system for detection of enzootic pathogens in pigs. Journal of Veterinary Diagnostic Investigation 2020, 32, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puente, H.; Argüello, H.; Mencía-Ares, Ó.; Gómez-García, M.; Rubio, P.; Carvajal, A. Detection and Genetic Diversity of Porcine Coronavirus Involved in Diarrhea Outbreaks in Spain. Frontiers in Veterinary Science 2021, 8, 651999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza Luna, L.K.; Heiser, V.; Regamey, N.; Panning, M.; Drexler, J.F.; Mulangu, S.; Poon, L.; Baumgarte, S.; Haijema, B.J.; Kaiser, L.; Drosten, C. Generic Detection of Coronaviruses and Differentiation at the Prototype Strain Level by Reverse Transcription-PCR and Nonfluorescent Low-Density Microarray. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 2007, 45, 1049–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escutenaire, S.; Mohamed, N.; Isaksson, M.; Thorén, P.; Klingeborn, B.; Belák, S.; Berg, M.; Blomberg, J. SYBR Green Real-Time Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction Assay for the Generic Detection of Coronaviruses. Archives of Virology 2007, 152, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Jung, K.; Wang, Q.; Saif, L.J.; Vlasova, A.N. Development of a one-step RT-PCR assay for detection of pancoronaviruses (α-, β-, γ-, and δ-coronaviruses) using newly designed degenerate primers for porcine and avian fecal samples. Journal of Virological Methods 2018, 256, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijgen, L.; Moës, E.; Keyaerts, E.; Li, S.; Van Ranst, M. A Pancoronavirus RT-PCR Assay for Detection of All Known Coronaviruses. Methods in Molecular Biology 2008, 454, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazov, C.M.; Chriél, M.; Baagøe, H.J.; Fjederholt, E.; Deng, Y.; Kooi, E.A.; Belsham, G.J.; Bøtner, A.; Rasmussen, T.B. Detection and Characterization of Distinct Alphacoronaviruses in Five Different Bat Species in Denmark. Viruses 2018, 10, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.; Song, D.S.; Park, B.K. Differential detection of transmissible gastroenteritis virus and porcine epidemic diarrhea virus by duplex RT-PCR. Journal of Veterinary Diagnostic Investigation 2001, 13, 516–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Oligo | Sequence 5´ - 3´ | Location** | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Duplex assays | PEDV-N-R | TTGCCTCTGTTGTTACTTGGAGAT | 26,853-26,876 | [17] |
| PEDV-N-F | CGCAAAGACTGAACCCACTAATTT | 26,679-26,702 | ||
| PEDV-N-US-F | CGCAAAGACTGAACCCACTAACCT | 26,679-26,702 | [17,20] | |
| PEDV-N-P | TGTTGCCATTRCCACGACTCCTGC | 26,819-26,842 | ||
| TGEV-N-F | GCAGGTARAGGTGATGTGACAA | 27,637-27,658 | [17] | |
| TGEV-N-R | ACATTCAGCCARTTGTGGGTAA | 27,735-27,756 | ||
| TGEV-N-P | TGGCACTGCTCCCATTGGCAACGA | 27,707-27,730 | ||
| PEDV-S-F | ACGTCCCTTTACTTTCAATTCACA | 22,474-22,497 | [19] | |
| PEDV-S-R | TATACTTGGTACACACATCCAGAGTCA | 22,559-22,585 | ||
| PEDV-S-P | TGAGTTGATTACTGGCACGCCTAAACCAC | 22,503-22,531 | ||
| TGEV-S-F | TCTGCTGAAGGTGCTATTATATGC | 20,734-20,757 | [21] | |
| TGEV-S-R | CCACAATTTGCCTCTGAATTAGAA* | 20,856-20,879 | ||
| TGEV-S-P | *AAGGGCTCACCACCTACTACCACCA | 20,764-20,788 | ||
| Triplex assay | PDCoV-RdRp-F | AACTGACATGAATGTTGGCCCT | 13,777-13,798 | This study |
| PDCoV-RdRp-R | CATGCACCCAGAATGCGAGA | 13,874-13,893 | ||
| PDCoV-RdRp-P | AGCATACTGTGTTAGCAGAGCATGATGGT | 13,815-13,843 | ||
| TGEV-N-F | GCAGGTARAGGTGATGTGACAA | 27,637-27,658 | [17] | |
| Triplex-TGEV-N-R | TGCTRGACACAGATGGAACACA | 27,754-27,775 | ||
| Triplex-TGEV-N-P | GGAGCAGTGCCAAGCATTACCCACAA | 27,719-27,744 | ||
| Triplex-PEDV-N-F | CGCAAAGACTGAACCCACTAAC | 26,679-26,699 | [22] | |
| Triplex-PEDV-N-R | TGGTTRTTGCCTCTGTTGTTACT | 26,860-26,882 | ||
| Triplex-PEDV-N-P | TGTTGCCATTGCCACGACTCCTGC | 26,819-26,842 |
| Expected assay characteristics | Duplex 1 | Duplex 2 | Duplex 3 | Triplex |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target genes | PEDV N + PEDV S |
TGEV N + PEDV S |
TGEV S + PEDV S |
PDCoV + TGEV N + PEDV N |
| Detects PEDV | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Detects SeCoV | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Detects TGEV | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Detects PRCV | No | Yes | No | Yes |
| Detects PDCoV | No | No | No | Yes |
| Distinguishes PEDV from SeCoV | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| Distinguishes SeCoV from TGEV/PRCV | N/A | Yes | Yes | No |
| Distinguishes TGEV from PRCV | N/A | No | N/A | No |
| Assay | Gene target (Virus detected) | Forward primer | Conc. | Reverse primer | Conc. | Probe | Conc. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Duplex 1 |
PEDV N (PEDV) |
PEDV-N-F | 400 nM | PEDV-N-R | 800 nM | PEDV-N-probe (Cy5) |
240 nM |
| PEDV-N-US-F | 400 nM | ||||||
|
PEDV S (PEDV + SeCoV) |
PEDV-S-F | 900 nM | PEDV-S-R | 900 nM | PEDV-S-probe (FAM) |
200 nM | |
| Duplex 2 |
TGEV N (TGEV/PRCV + SeCoV) |
TGEV-N-F | 700 nM | TGEV-N-R | 700 nM | TGEV-N-probe (Cy5) |
200 nM |
|
PEDV S (PEDV + SeCoV) |
PEDV-S-F | 900 nM |
PEDV-S-R | 900 nM | PEDV-S-probe (FAM) |
200 nM | |
| Duplex 3 |
TGEV S (TGEV) |
TGEV-S-F | 900 nM | TGEV-S-R | 900 nM | TGEV-S-probe (Cy5) |
200 nM |
|
PEDV S (PEDV + SeCoV) |
PEDV-S-F | 900 nM | PEDV-S-R | 900 nM | PEDV-S-probe (FAM) |
200 nM | |
| Triplex | PDCoV RdRp(PDCoV) | PDCoV-RdRp-F | 900 nM | PDCoV-RdRp-R | 900 nM | PDCoV-RdRp-P (FAM) | 200 nM |
|
TGEV N (TGEV/PRCV + SeCoV) |
TGEV-N-F | 900 nM | TGEV-N-R | 900 nM | TGEV-N-P (Texas Red) |
200 nM | |
|
PEDV N (PEDV) |
PEDV-N-F | 700 nM | PEDV-N-R | 700 nM | PEDV-N-P (Cy5) |
200 nM |
| LOD of duplex assays | LOD of triplex assay | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Assay | Singleplex | Duplex 1 | Duplex 2 | Duplex 3 | Singleplex | Triplex |
| PEDV N | 1000* | 50 | - | - | ||
| PEDV S | 10 | 25 | 25 | 25 | ||
| TGEV N | 25 | - | 100 | - | ||
| TGEV S** | 50 | - | - | 100 | ||
| PDCoV RdRp | 100 | 1000 | ||||
| TGEV N | 25 | 25 | ||||
| PEDV N | 10 | 25 | ||||
| Tested sample for repeatability | Tested sample for reproducibility | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Assay | High conc. | Intermediate conc. | Low Conc | High conc. |
Intermediate conc. | Low conc. | |
| Duplex 1 | PEDV N | 4% | 6% | 17% | 27% | 27% | 16% |
| PEDV S | 7% | 8% | 31% | 29% | 34% | 22% | |
| Duplex 2 | TGEV N | 4% | 6% | 43% | 27% | 27% | 24% |
| PEDV S | 6% | 7% | 19% | 29% | 33% | 43% | |
| Duplex 3 | TGEV S | 7% | 11% | 110% | 19% | 21% | *37% |
| PEDV S | 4% | 3% | 11% | 32% | 34% | 35% | |
| Triplex | PDCoV RdRp | 10% | 16% | 9% | 14% | 16% | 4% |
| TGEV N | 5% | 7% | 13% | 10% | 6% | 32% | |
| PEDV N | 5% | 8% | 22% | 5% | 7% | 16% | |
| Duplex 1 | Duplex 2 | Duplex 3 | Triplex | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pathogen samples | No. tested | PEDV N positive (%) | PEDV S positive (%) | TGEV N positive (%) | PEDV S positive (%) | TGEV S positive (%) | PEDV S positive (%) | PDCoV RdRp positive (%) | TGEV N positive (%) | PEDV N positive (%) |
| PEDV | 24 | 23 (96) | 24 (100) | 0 (0) | 24 (100) | 0 (0) | 24 (100) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 23 (96) |
| Rec. SeCoV/PEDV | 22 | 22 (100) | 22 (100) | 0 (0) | 22 (100) | 0 (0) | 22 (100) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 20 (91) |
| SeCoV | 9 | 0 (0) | 9 (100) | 9 (100) | 9 (100) | 0 (0) | 9 (100) | 0 (0) | 9 (100) | 0 (0) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





