Submitted:
28 June 2023
Posted:
29 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
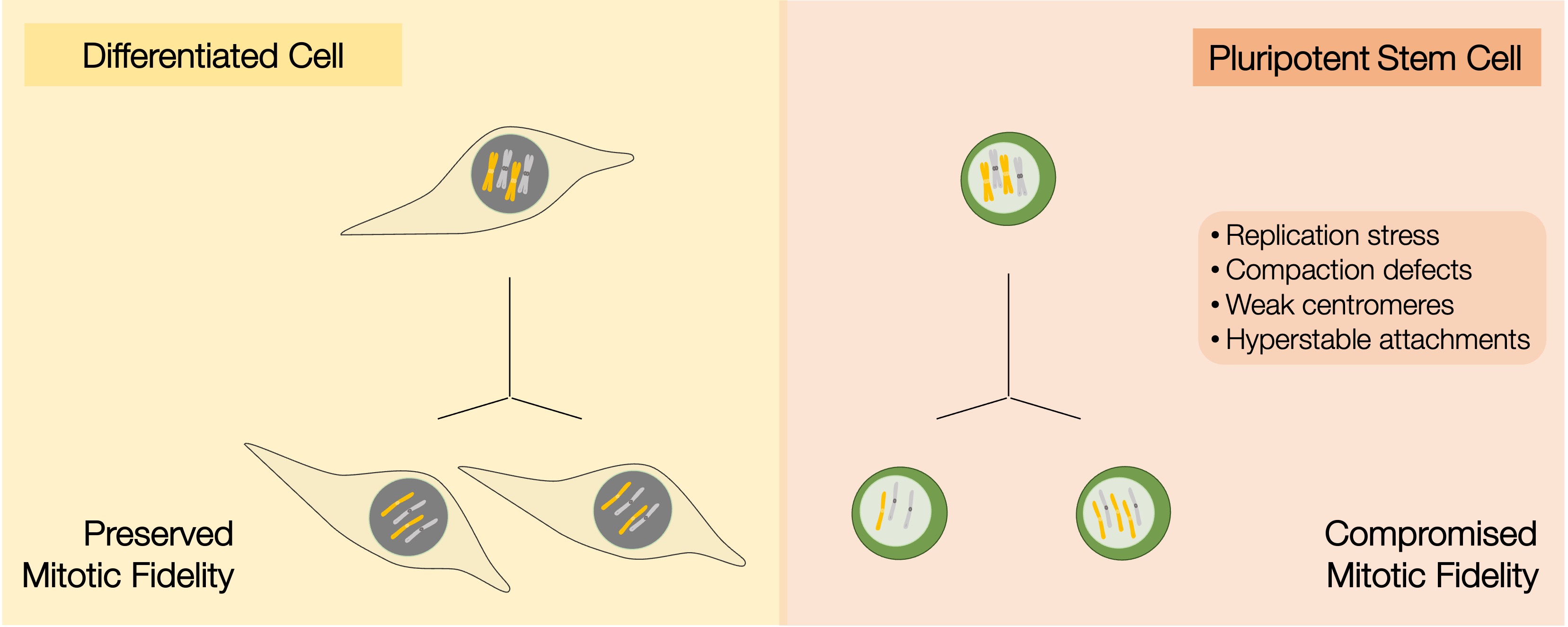
1. Human pluripotent stem cells present frequent karyotypic abnormalities
2. Molecular mechanisms underlying the compromised mitotic fidelity in pluripotent stem cells
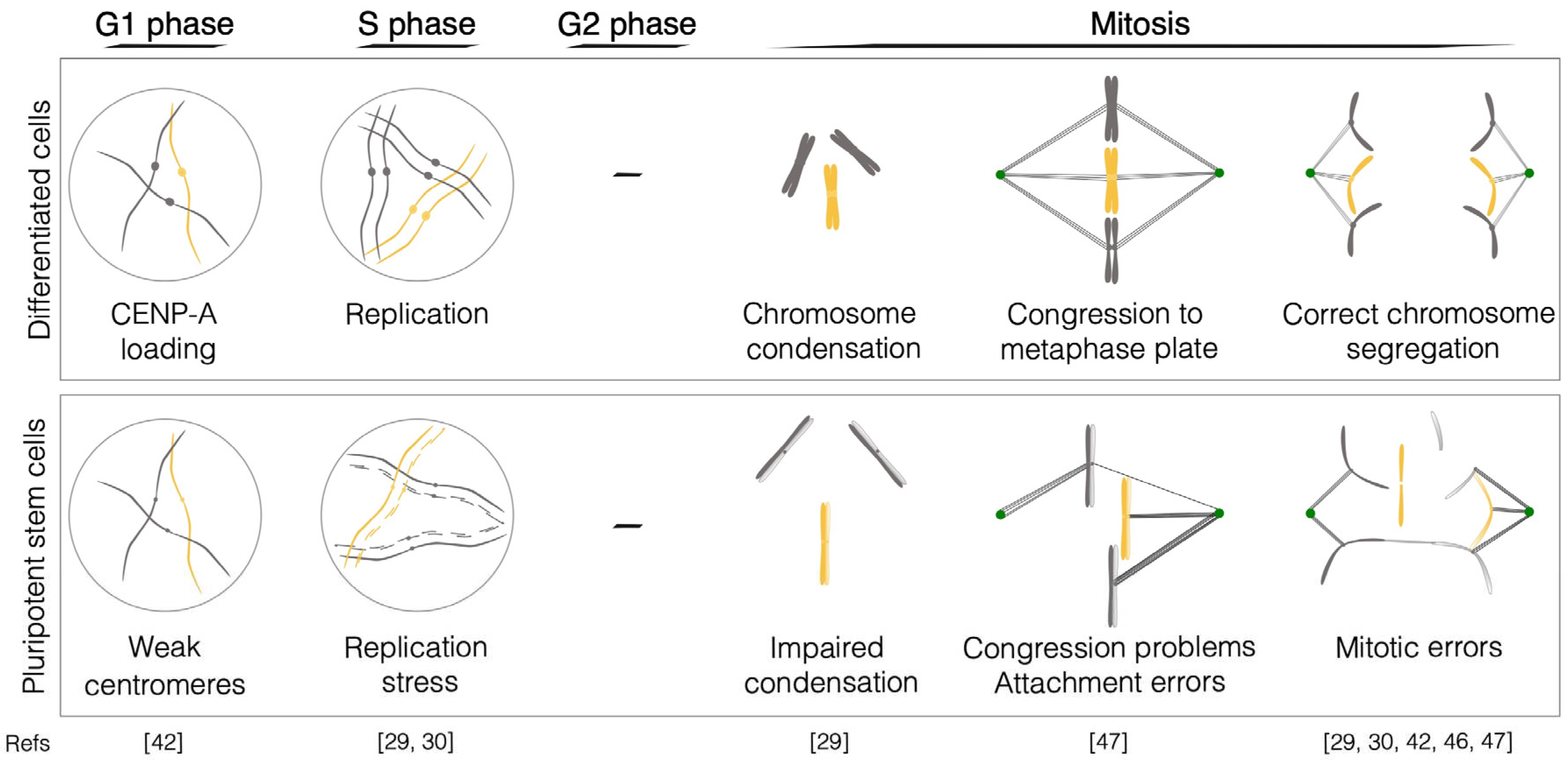
2.1. DNA replication
2.2. Chromosome condensation
2.3. The centromere
2.4. Kinetochore-microtubule dynamics
2.5. Spindle Assembly Checkpoint
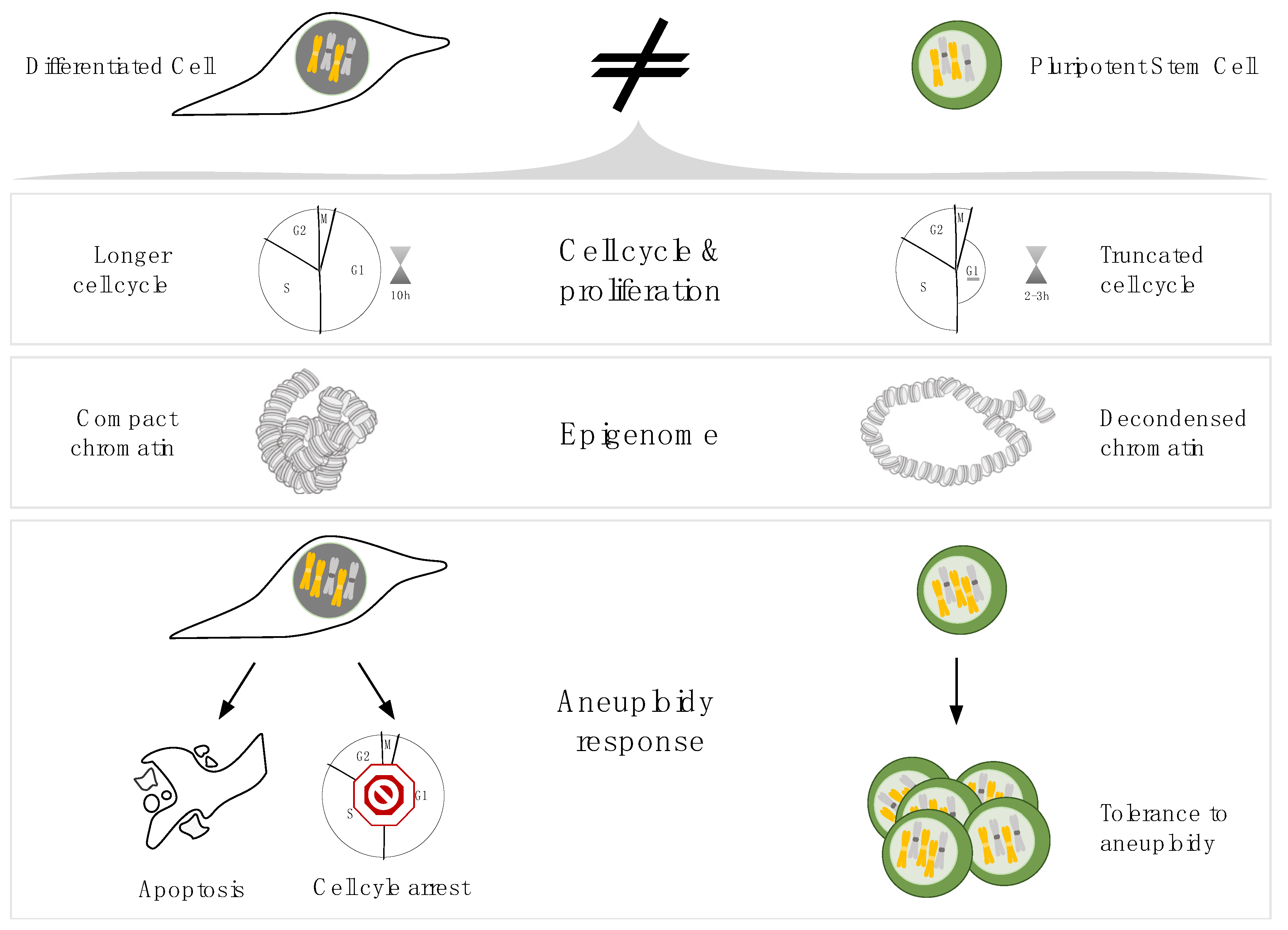
3. Physiological properties of PSCs which can affect mitotic fidelity
3.1. Cell cycle
3.2. Histone post-translational modifications
3.3. Mitotic machinery of PSCs
4. Consequences of decreased mitotic fidelity in pluripotent stem cells
5. Can we increase mitotic fidelity of PSCs?
6. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Takahashi, K.; Yamanaka, S. Induction of Pluripotent Stem Cells from Mouse Embryonic and Adult Fibroblast Cultures by Defined Factors. Cell 2006, 126, 663–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellin, M.; Marchetto, M.C.; Gage, F.H.; Mummery, C.L. Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells: The New Patient? Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2012, 13, 713–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, J.A.; Itskovitz-Eldor, J.; Shapiro, S.S.; Waknitz, M.A.; Swiergiel, J.J.; Marshall, V.S.; Jones, J.M. Embryonic Stem Cell Lines Derived from Human Blastocysts. Science 1998, 282, 1145–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, K.; Tanabe, K.; Ohnuki, M.; Narita, M.; Ichisaka, T.; Tomoda, K.; Yamanaka, S. Induction of Pluripotent Stem Cells from Adult Human Fibroblasts by Defined Factors. Cell 2007, 131, 861–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wernig, M.; Meissner, A.; Foreman, R.; Brambrink, T.; Ku, M.; Hochedlinger, K.; Bernstein, B.E.; Jaenisch, R. In Vitro Reprogramming of Fibroblasts into a Pluripotent ES-Cell-like State. Nature 2007, 448, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Vodyanik, M.A.; Smuga-Otto, K.; Antosiewicz-Bourget, J.; Frane, J.L.; Tian, S.; Nie, J.; Jonsdottir, G.A.; Ruotti, V.; Stewart, R.; et al. Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Lines Derived from Human Somatic Cells. Science 2007, 318, 1917–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, S. Pluripotent Stem Cell-Based Cell Therapy—Promise and Challenges. Cell Stem Cell 2020, 27, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, P.W.; Ben-David, U.; Benvenisty, N.; Coffey, P.; Eggan, K.; Knowles, B.B.; Nagy, A.; Pera, M.; Reubinoff, B.; Rugg-Gunn, P.J.; et al. Assessing the Safety of Human Pluripotent Stem Cells and Their Derivatives for Clinical Applications. Stem Cell Reports 2017, 9, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santaguida, S.; Amon, A. Short- and Long-Term Effects of Chromosome Mis-Segregation and Aneuploidy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2015, 16, 473–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The International Stem Cell Initiative Screening Ethnically Diverse Human Embryonic Stem Cells Identifies a Chromosome 20 Minimal Amplicon Conferring Growth Advantage. Nat Biotechnol 2011, 29, 1132–1144. [CrossRef]
- Taapken, S.M.; Nisler, B.S.; Newton, M.A.; Sampsell-Barron, T.L.; Leonhard, K.A.; McIntire, E.M.; Montgomery, K.D. Karyotypic Abnormalities in Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells and Embryonic Stem Cells. Nat Biotechnol 2011, 29, 313–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayshar, Y.; Ben-David, U.; Lavon, N.; Biancotti, J.-C.; Yakir, B.; Clark, A.T.; Plath, K.; Lowry, W.E.; Benvenisty, N. Identification and Classification of Chromosomal Aberrations in Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. Cell Stem Cell 2010, 7, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Draper, J.S.; Smith, K.; Gokhale, P.; Moore, H.D.; Maltby, E.; Johnson, J.; Meisner, L.; Zwaka, T.P.; Thomson, J.A.; Andrews, P.W. Recurrent Gain of Chromosomes 17q and 12 in Cultured Human Embryonic Stem Cells. Nat Biotechnol 2004, 22, 53–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins-Taylor, K.; Nisler, B.S.; Taapken, S.M.; Compton, T.; Crandall, L.; Montgomery, K.D.; Lalande, M.; Xu, R.-H. Recurrent Copy Number Variations in Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. Nat Biotechnol 2011, 29, 488–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, D.E.C.; Harrison, N.J.; Maltby, E.; Smith, K.; Moore, H.D.; Shaw, P.J.; Heath, P.R.; Holden, H.; Andrews, P.W. Adaptation to Culture of Human Embryonic Stem Cells and Oncogenesis in Vivo. Nat Biotechnol 2007, 25, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, L.C.; Ulitsky, I.; Slavin, I.; Tran, H.; Schork, A.; Morey, R.; Lynch, C.; Harness, J.V.; Lee, S.; Barrero, M.J.; et al. Dynamic Changes in the Copy Number of Pluripotency and Cell Proliferation Genes in Human ESCs and IPSCs during Reprogramming and Time in Culture. Cell Stem Cell 2011, 8, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.; Cavazza, T.; Schuh, M. Aneuploidy in Human Eggs: Contributions of the Meiotic Spindle. Biochem Soc Trans 2021, 49, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chunduri, N.K.; Storchová, Z. The Diverse Consequences of Aneuploidy. Nat Cell Biol 2019, 21, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, B.A.; Cleveland, D.W. Does Aneuploidy Cause Cancer? Current Opinion in Cell Biology 2006, 18, 658–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, K.; Zambelli, F.; Mertzanidou, A.; Smolders, I.; Geens, M.; Nguyen, H.T.; Barbé, L.; Sermon, K.; Spits, C. Higher-Density Culture in Human Embryonic Stem Cells Results in DNA Damage and Genome Instability. Stem Cell Reports 2016, 6, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, D.J.; Resio, B.; Pellman, D. Causes and Consequences of Aneuploidy in Cancer. Nat Rev Genet 2012, 13, 189–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compton, D.A. Mechanisms of Aneuploidy. Current Opinion in Cell Biology 2011, 23, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musacchio, A.; Salmon, E.D. The Spindle-Assembly Checkpoint in Space and Time. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2007, 8, 379–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirkovic, M.; Oliveira, R.A. Centromeric Cohesin: Molecular Glue and Much More. Prog Mol Subcell Biol 2017, 56, 485–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piskadlo, E.; Oliveira, R.A. A Topology-Centric View on Mitotic Chromosome Architecture. IJMS 2017, 18, 2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto, M.; Raaijmakers, J.A.; Medema, R.H. Consequences of Genomic Diversification Induced by Segregation Errors. Trends in Genetics 2019, 35, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, K.A.; Ghule, P.N.; Therrien, J.A.; Lian, J.B.; Stein, J.L.; van Wijnen, A.J.; Stein, G.S. Self-Renewal of Human Embryonic Stem Cells Is Supported by a Shortened G1 Cell Cycle Phase. Journal of Cellular Physiology 2006, 209, 883–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, H.; Kikyo, N. Epigenetic Regulation of Open Chromatin in Pluripotent Stem Cells. Translational Research 2015, 165, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamm, N.; Ben-David, U.; Golan-Lev, T.; Storchová, Z.; Benvenisty, N.; Kerem, B. Genomic Instability in Human Pluripotent Stem Cells Arises from Replicative Stress and Chromosome Condensation Defects. Cell Stem Cell 2016, 18, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliwell, J.A.; Frith, T.J.R.; Laing, O.; Price, C.J.; Bower, O.J.; Stavish, D.; Gokhale, P.J.; Hewitt, Z.; El-Khamisy, S.F.; Barbaric, I.; et al. Nucleosides Rescue Replication-Mediated Genome Instability of Human Pluripotent Stem Cells. Stem Cell Reports 2020, 14, 1009–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simara, P.; Tesarova, L.; Rehakova, D.; Matula, P.; Stejskal, S.; Hampl, A.; Koutna, I. DNA Double-Strand Breaks in Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Reprogramming and Long-Term in Vitro Culturing. Stem Cell Research & Therapy 2017, 8, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallabhaneni, H.; Lynch, P.J.; Chen, G.; Park, K.; Liu, Y.; Goehe, R.; Mallon, B.S.; Boehm, M.; Hursh, D.A. High Basal Levels of ΓH2AX in Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells Are Linked to Replication-Associated DNA Damage and Repair. Stem Cells 2018, 36, 1501–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kislova, A.V.; Zheglo, D.; Pozhitnova, V.O.; Sviridov, P.S.; Gadzhieva, E.P.; Voronina, E.S. Replication Stress Causes Delayed Mitotic Entry and Chromosome 12 Fragility at the ANKS1B Large Neuronal Gene in Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells; In Review, 2023.
- Mankouri, H.W.; Huttner, D.; Hickson, I.D. How Unfinished Business from S-Phase Affects Mitosis and Beyond. EMBO J 2013, 32, 2661–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, S.; Lopez-Contreras, A.J.; Gabut, M.; Marion, R.M.; Gutierrez-Martinez, P.; Bua, S.; Ramirez, O.; Olalde, I.; Rodrigo-Perez, S.; Li, H.; et al. Limiting Replication Stress during Somatic Cell Reprogramming Reduces Genomic Instability in Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. Nat Commun 2015, 6, 8036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desmarais, J.A.; Hoffmann, M.J.; Bingham, G.; Gagou, M.E.; Meuth, M.; Andrews, P.W. Human Embryonic Stem Cells Fail to Activate CHK1 and Commit to Apoptosis in Response to DNA Replication Stress. Stem Cells 2012, 30, 1385–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vessoni, A.T.; Zhang, T.; Quinet, A.; Jeong, H.-C.; Munroe, M.; Wood, M.; Tedone, E.; Vindigni, A.; Shay, J.W.; Greenberg, R.A.; et al. Telomere Erosion in Human Pluripotent Stem Cells Leads to ATR-Mediated Mitotic Catastrophe. Journal of Cell Biology 2021, 220, e202011014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Shu, X.; Zhu, P.; Pei, D. Chromatin Accessibility Dynamics during Cell Fate Reprogramming. EMBO Rep 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkins, B.J.; Rall, N.A.; Ostwal, Y.; Kruitwagen, T.; Hiragami-Hamada, K.; Winkler, M.; Barral, Y.; Fischle, W.; Neumann, H. A Cascade of Histone Modifications Induces Chromatin Condensation in Mitosis. Science 2014, 343, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weir, J.R.; Faesen, A.C.; Klare, K.; Petrovic, A.; Basilico, F.; Fischböck, J.; Pentakota, S.; Keller, J.; Pesenti, M.E.; Pan, D.; et al. Insights from Biochemical Reconstitution into the Architecture of Human Kinetochores. Nature 2016, 537, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, B.E.; Jansen, L.E.T.; Foltz, D.R.; Cleveland, D.W. Centromere Identity, Function, and Epigenetic Propagation across Cell Divisions. Cold Spring Harbor Symposia on Quantitative Biology 2010, 75, 403–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milagre, I.; Pereira, C.; Oliveira, R.A.; Jansen, L.E.T. Reprogramming of Human Cells to Pluripotency Induces CENP-A Chromatin Depletion. Open Biology 2020, 10, 200227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodor, D.L.; Valente, L.P.; Mata, J.F.; Black, B.E.; Jansen, L.E.T. Assembly in G1 Phase and Long-Term Stability Are Unique Intrinsic Features of CENP-A Nucleosomes. MBoC 2013, 24, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, L.E.T.; Black, B.E.; Foltz, D.R.; Cleveland, D.W. Propagation of Centromeric Chromatin Requires Exit from Mitosis. Journal of Cell Biology 2007, 176, 795–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fachinetti, D.; Han, J.S.; McMahon, M.A.; Ly, P.; Abdullah, A.; Wong, A.J.; Cleveland, D.W. DNA Sequence-Specific Binding of CENP-B Enhances the Fidelity of Human Centromere Function. Developmental Cell 2015, 33, 314–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Hirst, A.J.; Duan, F.; Qiu, H.; Huang, R.; Ji, Y.; Bai, L.; Zhang, F.; Robinson, D.; Jones, M.; et al. Anti-Apoptotic Mutations Desensitize Human Pluripotent Stem Cells to Mitotic Stress and Enable Aneuploid Cell Survival. Stem Cell Reports 2019, 12, 557–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Ya, A.; Compton, D.A.; Godek, K.M. A Pluripotent Developmental State Confers a Low Fidelity of Chromosome Segregation. Stem Cell Reports 2023, 18, 475–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregan, J.; Polakova, S.; Zhang, L.; Tolić-Nørrelykke, I.M.; Cimini, D. Merotelic Kinetochore Attachment: Causes and Effects. Trends Cell Biol 2011, 21, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitagawa, M.; Lee, S.H. The Chromosomal Passenger Complex (CPC) as a Key Orchestrator of Orderly Mitotic Exit and Cytokinesis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2015, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vukušić, K.; Tolić, I.M. Polar Chromosomes—Challenges of a Risky Path. Cells 2022, 11, 1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, R.; Wu, X.; Ma, N.; Wang, D.; Sun, S.; Luo, Y.; Zhou, J.; Lu, X.; Liu, M.; Li, D. The Specialized Mitotic Behavior of Human Embryonic Stem Cells. Cell Tissue Res 2022, 387, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francois, L.; Boskovic, P.; Knerr, J.; He, W.; Sigismondo, G.; Schwan, C.; More, T.H.; Schlotter, M.; Krijgsveld, J.; Hiller, K.; et al. BCAT1 Redox Function Maintains Mitotic Fidelity. Cell Reports 2022, 41, 111524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Z.; Prifti, D.; Gui, P.; Liu, X.; Elowe, S.; Yao, X. Recent Progress on the Localization of the Spindle Assembly Checkpoint Machinery to Kinetochores. Cells 2019, 8, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantel, C.; Guo, Y.; Lee, M.R.; Kim, M.-K.; Han, M.-K.; Shibayama, H.; Fukuda, S.; Yoder, M.C.; Pelus, L.M.; Kim, K.-S.; et al. Checkpoint-Apoptosis Uncoupling in Human and Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells: A Source of Karyotpic Instability. Blood 2007, 109, 4518–4527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padgett, J.; Santos, S.D.M. From Clocks to Dominoes: Lessons on Cell Cycle Remodelling from Embryonic Stem Cells. FEBS Letters 2020, 594, 2031–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnum, K.J.; O’Connell, M.J. Cell Cycle Regulation by Checkpoints. In Cell Cycle Control; Noguchi, E., Gadaleta, M.C., Eds.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer New York: New York, NY, 2014; ISBN 978-1-4939-0887-5. [Google Scholar]
- Damelin, M.; Sun, Y.E.; Sodja, V.B.; Bestor, T.H. Decatenation Checkpoint Deficiency in Stem and Progenitor Cells. Cancer Cell 2005, 8, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieder, C.L.; Maiato, H. Stuck in Division or Passing Through. Developmental Cell 2004, 7, 637–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, K.A.; Stein, J.L.; Lian, J.B.; van Wijnen, A.J.; Stein, G.S. Human Embryonic Stem Cells Are Pre-Mitotically Committed to Self-Renewal and Acquire a Lengthened G1 Phase upon Lineage Programming. J Cell Physiol 2010, 222, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipczyk, A.A.; Laslett, A.L.; Mummery, C.; Pera, M.F. Differentiation Is Coupled to Changes in the Cell Cycle Regulatory Apparatus of Human Embryonic Stem Cells. Stem Cell Res 2007, 1, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauklin, S.; Vallier, L. The Cell-Cycle State of Stem Cells Determines Cell Fate Propensity. Cell 2013, 155, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzales, K.A.U.; Liang, H.; Lim, Y.-S.; Chan, Y.-S.; Yeo, J.-C.; Tan, C.-P.; Gao, B.; Le, B.; Tan, Z.-Y.; Low, K.-Y.; et al. Deterministic Restriction on Pluripotent State Dissolution by Cell-Cycle Pathways. Cell 2015, 162, 564–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagana, A.; Dorn, J.F.; De Rop, V.; Ladouceur, A.-M.; Maddox, A.S.; Maddox, P.S. A Small GTPase Molecular Switch Regulates Epigenetic Centromere Maintenance by Stabilizing Newly Incorporated CENP-A. Nat Cell Biol 2010, 12, 1186–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nashun, B.; Hill, P.W.; Hajkova, P. Reprogramming of Cell Fate: Epigenetic Memory and the Erasure of Memories Past. EMBO J 2015, 34, 1296–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milagre, I.; Stubbs, T.M.; King, M.R.; Spindel, J.; Santos, F.; Krueger, F.; Bachman, M.; Segonds-Pichon, A.; Balasubramanian, S.; Andrews, S.R.; et al. Gender Differences in Global but Not Targeted Demethylation in IPSC Reprogramming. Cell Reports 2017, 18, 1079–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.-S.; Shin, J.-Y.; Tonge, P.D.; Puri, M.C.; Lee, S.; Park, H.; Lee, W.-C.; Hussein, S.M.I.; Bleazard, T.; Yun, J.-Y.; et al. An Epigenomic Roadmap to Induced Pluripotency Reveals DNA Methylation as a Reprogramming Modulator. Nat Commun 2014, 5, 5619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, J.H.; Saha, K.; Jaenisch, R. Pluripotency and Cellular Reprogramming: Facts, Hypotheses, Unresolved Issues. Cell 2010, 143, 508–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacchiarelli, D.; Trapnell, C.; Ziller, M.J.; Soumillon, M.; Cesana, M.; Karnik, R.; Donaghey, J.; Smith, Z.D.; Ratanasirintrawoot, S.; Zhang, X.; et al. Integrative Analyses of Human Reprogramming Reveal Dynamic Nature of Induced Pluripotency. Cell 2015, 162, 412–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koche, R.P.; Smith, Z.D.; Adli, M.; Gu, H.; Ku, M.; Gnirke, A.; Bernstein, B.E.; Meissner, A. Reprogramming Factor Expression Initiates Widespread Targeted Chromatin Remodeling. Cell Stem Cell 2011, 8, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Nuland, R.; Gozani, O. Histone H4 Lysine 20 (H4K20) Methylation, Expanding the Signaling Potential of the Proteome One Methyl Moiety at a Time. Molecular & Cellular Proteomics 2016, 15, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, J.H.; Rodríguez, M.G.; Martins, N.M.C.; Kimura, H.; Kelly, D.A.; Masumoto, H.; Larionov, V.; Jansen, L.E.T.; Earnshaw, W.C. Epigenetic Engineering Shows H3K4me2 Is Required for HJURP Targeting and CENP-A Assembly on a Synthetic Human Kinetochore: H3K4me2 and Kinetochore Maintenance. The EMBO Journal 2011, 30, 328–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, O.; Vargiu, G.; Abad, M.A.; Zhiteneva, A.; Jeyaprakash, A.A.; Masumoto, H.; Kouprina, N.; Larionov, V.; Earnshaw, W.C. Epigenetic Engineering Reveals a Balance between Histone Modifications and Transcription in Kinetochore Maintenance. Nat Commun 2016, 7, 13334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Tanasa, B.; Tyurina, O.V.; Zhou, T.Y.; Gassmann, R.; Liu, W.T.; Ohgi, K.A.; Benner, C.; Garcia-Bassets, I.; Aggarwal, A.K.; et al. PHF8 Mediates Histone H4 Lysine 20 Demethylation Events Involved in Cell Cycle Progression. Nature 2010, 466, 508–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schalch, T.; Steiner, F.A. Structure of Centromere Chromatin: From Nucleosome to Chromosomal Architecture. Chromosoma 2017, 126, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, Y.; Sako, K.; Takagaki, K.; Hirayama, Y.; Uchida, K.S.K.; Herman, J.A.; DeLuca, J.G.; Hirota, T. HP1-Assisted Aurora B Kinase Activity Prevents Chromosome Segregation Errors. Developmental Cell 2016, 36, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Higgins, J.M.G. Histone Modifications and Mitosis: Countermarks, Landmarks, and Bookmarks. Trends in Cell Biology 2013, 23, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soufi, A.; Dalton, S. Cycling through Developmental Decisions: How Cell Cycle Dynamics Control Pluripotency, Differentiation and Reprogramming. Development 2016, 143, 4301–4311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kagey, M.H.; Newman, J.J.; Bilodeau, S.; Zhan, Y.; Orlando, D.A.; van Berkum, N.L.; Ebmeier, C.C.; Goossens, J.; Rahl, P.B.; Levine, S.S.; et al. Mediator and Cohesin Connect Gene Expression and Chromatin Architecture. Nature 2010, 467, 430–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, B.; Bar-Nur, O.; Golan-Lev, T.; Benvenisty, N. The Anti-Apoptotic Gene Survivin Contributes to Teratoma Formation by Human Embryonic Stem Cells. Nat Biotechnol 2009, 27, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payer, B.; Lee, J.T. X Chromosome Dosage Compensation: How Mammals Keep the Balance. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2008, 42, 733–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Tsai, H.-J.; Gordon, M.R.; Li, R. Cellular Stress Associated with Aneuploidy. Developmental Cell 2018, 44, 420–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schukken, K.M.; Sheltzer, J.M. Extensive Protein Dosage Compensation in Aneuploid Human Cancers. Genome Res. 2022, 32, 1254–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senger, G.; Santaguida, S.; Schaefer, M.H. Regulation of Protein Complex Partners as a Compensatory Mechanism in Aneuploid Tumors. eLife 2022, 11, e75526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, P.; Zhao, X.; Katsnelson, L.; Camacho-Hernandez, E.M.; Mermerian, A.; Mays, J.C.; Lippman, S.M.; Rosales-Alvarez, R.E.; Moya, R.; Shwetar, J.; et al. Proteogenomic Analysis of Cancer Aneuploidy and Normal Tissues Reveals Divergent Modes of Gene Regulation across Cellular Pathways. eLife 2022, 11, e75227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, B.R.; Prabhu, V.R.; Hunter, K.E.; Glazier, C.M.; Whittaker, C.A.; Housman, D.E.; Amon, A. Aneuploidy Affects Proliferation and Spontaneous Immortalization in Mammalian Cells. Science 2008, 322, 703–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, J.M.; Macedo, J.C.; Mattingly, A.J.; Wangsa, D.; Camps, J.; Lima, V.; Gomes, A.M.; Dória, S.; Ried, T.; Logarinho, E.; et al. Chromosome Mis-Segregation and Cytokinesis Failure in Trisomic Human Cells. eLife 2015, 4, e05068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbazi, M.N.; Wang, T.; Tao, X.; Weatherbee, B.A.T.; Sun, L.; Zhan, Y.; Keller, L.; Smith, G.D.; Pellicer, A.; Scott, R.T.; et al. Developmental Potential of Aneuploid Human Embryos Cultured beyond Implantation. Nat Commun 2020, 11, 3987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Lin, G.; Tan, Y.-Q.; Zhou, D.; Deng, L.-Y.; Cheng, D.-H.; Luo, S.-W.; Liu, T.-C.; Zhou, X.-Y.; Sun, Z.; et al. Tumor Progression of Culture-Adapted Human Embryonic Stem Cells during Long-Term Culture. Genes, Chromosomes and Cancer 2008, 47, 665–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-David, U.; Arad, G.; Weissbein, U.; Mandefro, B.; Maimon, A.; Golan-Lev, T.; Narwani, K.; Clark, A.T.; Andrews, P.W.; Benvenisty, N.; et al. Aneuploidy Induces Profound Changes in Gene Expression, Proliferation and Tumorigenicity of Human Pluripotent Stem Cells. Nat Commun 2014, 5, 4825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Cheng, L.; Jia, Y.; Liu, G.; Li, C.; Song, S.; Bradley, A.; Huang, Y. Aneuploid Embryonic Stem Cells Exhibit Impaired Differentiation and Increased Neoplastic Potential. EMBO J 2016, 35, 2285–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haim-Abadi, G.; Golan-Lev, T.; Koren, A.; Benvenisty, N. Generation, Genomic Characterization, and Differentiation of Triploid Human Embryonic Stem Cells. Stem Cell Reports 2023, 18, 1049–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirkovic, M.; Guilgur, L.G.; Tavares, A.; Passagem-Santos, D.; Oliveira, R.A. Induced Aneuploidy in Neural Stem Cells Triggers a Delayed Stress Response and Impairs Adult Life Span in Flies. PLoS Biol 2019, 17, e3000016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkle, F.T.; Ghosh, S.; Kamitaki, N.; Mitchell, J.; Avior, Y.; Mello, C.; Kashin, S.; Mekhoubad, S.; Ilic, D.; Charlton, M.; et al. Human Pluripotent Stem Cells Recurrently Acquire and Expand Dominant Negative P53 Mutations. Nature 2017, 545, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen-Sharir, Y.; McFarland, J.M.; Abdusamad, M.; Marquis, C.; Bernhard, S.V.; Kazachkova, M.; Tang, H.; Ippolito, M.R.; Laue, K.; Zerbib, J.; et al. Aneuploidy Renders Cancer Cells Vulnerable to Mitotic Checkpoint Inhibition. Nature 2021, 590, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barroso-Vilares, M.; Macedo, J.C.; Reis, M.; Warren, J.D.; Compton, D.; Logarinho, E. Small-molecule Inhibition of Aging-associated Chromosomal Instability Delays Cellular Senescence. EMBO Reports 2020, 21, e49248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orr, B.; Talje, L.; Liu, Z.; Kwok, B.H.; Compton, D.A. Adaptive Resistance to an Inhibitor of Chromosomal Instability in Human Cancer Cells. Cell Reports 2016, 17, 1755–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




