1. Introduction
The soil moisture content, as well as the characteristics of the crop cover, are the main parameters of irrigated agrophytocenoses, depicting their state, both in terms of the soil water regime and physiological development [
1,
2]. The assessment of these parameters at the level of agrophytocenosis and its parts is necessary for effective management, as well as for agro ecological control of the impact on environment [
3,
4]. At the same time, the moisture content at the surface layer of the soil cover and the vegetation indices of the vegetation cover, measured remotely, along with the surface roughness of the soil cover of agrophytocenoses and the scattering elements of the vegetation cover, are the key factors affecting the value of the radar backscatter coefficient (RBC), measured by the radar of the Sentinel-1 satellite at a frequency of 5.4 GHz. The moisture content of the soil surface, reconstructed on the basis of the existing well-known scattering models of Ox [
5], Duboa [
6] and the Fang integral equation method [
7], as a rule, leads to a significant mismatch with respect to the values of this moisture measured by proximal methods on sub-satellite test plots [
8,
9]. This is largely due to the variability of soil moisture and roughness that is dynamic in time and at different scales of agrophytocenosis, which causes significant difficulties in organizing periodic and highly detailed sub-satellite monitoring of these parameters over large areas. Indeed, in relation to the problem of restoring soil moisture according to [
10], the standard deviation, the correlation length and the form of the autocorrelation function of the heights of irregularities depend not only on the degree level of surface roughness, but also on the length of the profile (0.5-25m), within which measurements are made. Because of this, difficulties arise when using the statistical characteristics of ground-based roughness measurements as input parameters of existing radar scatter models and using them in global algorithms for multi-scale satellite radar moisture sensing. Other directions for solving the problem of restoring soil moisture are based on the developed semi-empirical methods of integral equations. These methods make it possible to take into account the local features of the statistical characteristics of roughness. However, this requires calibrating the input parameter (correlation length) as a function of the root-mean-square deviations of the irregularity heights and the angle of incidence of the wave obtained in the study area for [
11,
12]. For this purpose, approaches based on neural network (NN) training using scattering models are widely used [
13,
14]. In these NN, soil moisture acts as an output parameter, and as input parameters are combinations of backscattering cross sections measured at different polarizations, as well as soil surface roughness and sounding angle. At the same time, the achieved results of combining semi-empirical methods and NN, despite the laboriousness of solving inverse problems with large spatial arrays of radar data, indicate significant prospects for this direction in problems of restoring moisture [
15,
16].
Note that a generalized model has not yet been created to solve the problem of radar scattering of electromagnetic waves on the elements of the vegetation cover. At the same time, extinction coefficient (EC) models have already been developed to describe the attenuation of electromagnetic waves in various types of vegetation [
17,
18]. At the same time, it was shown that the EC is proportional not only to the volumetric water content in plants, but also to some empirical variable, for which only an approximate relationship with the frequency of the electromagnetic wave and the type of vegetation cover has been established so far [
18,
19]. Recently, to describe the RBC of a soil surface covered with vegetation, an empirical model has been widely used that describes the attenuation and scattering of a wave in a layer represented by uniformly dispersed particles (“cloud” model) [
20,
21,
22,
23,
24]. The parameters of this model (the effective scattering amplitude on particles, the effective value of the layer extinction coefficient, the proportionality coefficients are specific to a given plant type) are calibrated either using analytical models of scattering on vegetation cover elements [
22], or more often on the basis of satellite parameters (vegetation indices, leaf area indices) and corresponding subsatellite (biomass and vegetation height) measurements [
20,
21,
22,
23,
24]. However, to date, a generalized relationship between the parameters of the “cloud” model and various types of vegetation depending on the sounding wave frequency, altitude, and vegetation biomass has not been established.
Due to the significant difficulties in calibrating existing scattering models for a wide variety of combinations of soil and vegetation covers, recently NN methods have been widely developed to predict the moisture content of soils covered with vegetation. In this case, either separately radar data (RBS at different polarizations) [
15,
25] or in combination with multispectral optical data (vegetation indices, leaf surface indices) measured by various survey systems on space platforms are used as input parameters of the NN [
26,
27]. In contrast to these approaches, in this work, at the first stage, the NN was used to predict the reflection coefficient of the soil cover. For this, as its input parameter, the ratio of the multispectral index of vegetation cover in the optical range to the microwave index of the same cover was used. At the second stage, based on the dielectric soil model [
28], in the course of solving the inverse problem, the soil cover moisture was restored using the value of the reflection coefficient estimated using the NN. As a result of the proposed algorithm, it was possible to minimize the influence of vegetation cover on the restored value of soil cover moisture.
2. Test plots, ground based and satellite data
With aim to test the proposed method, data sets of two test plots located in the south of the European part of Russia were used. The test plot
No. 1 (44.1568 N, 48.6026 E) was located in one of the fields of the experimental production facility of the All-Russian Research Institute (VNIIOZ) (see
Figure 1a). During the field measurements in the July 2020, at the field on which this test plot was located was sown with soybeans in the heading phase, irrigated with a Bayer frontal sprinkler machine. The test plot
No. 2 (51.1258 N, 46.0001 E) was located on one of the agricultural fields of the Educational Research and Production Association “Povolgie” of the Saratov Agrarian University. N.I. Vavilov (SSAU) (see
Figure 1b). During the test period in the second half of August 2022, the corresponding field with this test plot was sown with soybeans in the ripening phase, which was irrigated with a «Cascade» circular sprinkler.
The soil cover of the test plot No. 1 was includes light chestnut irrigated alkaline calcareous soils on yellow-brown loams (according to the soil classification of the USSR). Soils are classified according to the WRB classification as Luvic Kastanozems (Loamic, Aric, Protosodic, Bathygypsic). The texture of the soil cover was determined using combination of sieve and pipette (Kaczynski version) analyses. The obtained results showed that the soil particle distribution was classified as silty loam (clay loam) according to FAO soil classification.
The soil cover of the test plot No. 2 was represented by a complex of medium and thin dark chestnut soils of medium loamy and light loamy granulometric composition. The content of physical clay in the plow horizon is 36-38%. At the same time, the value of the volumetric mass of the arable layer is 1.34 g/cm3, and the density of the solid phase is in the range of 2.62-2.65 g/cm3. The corresponding value of the porosity of the arable layer lies in the range of 0.49-0.53 cm3/cm3 a, the value of the maximum field capacity (FC) is 0.25-0.27 cm3/cm3.
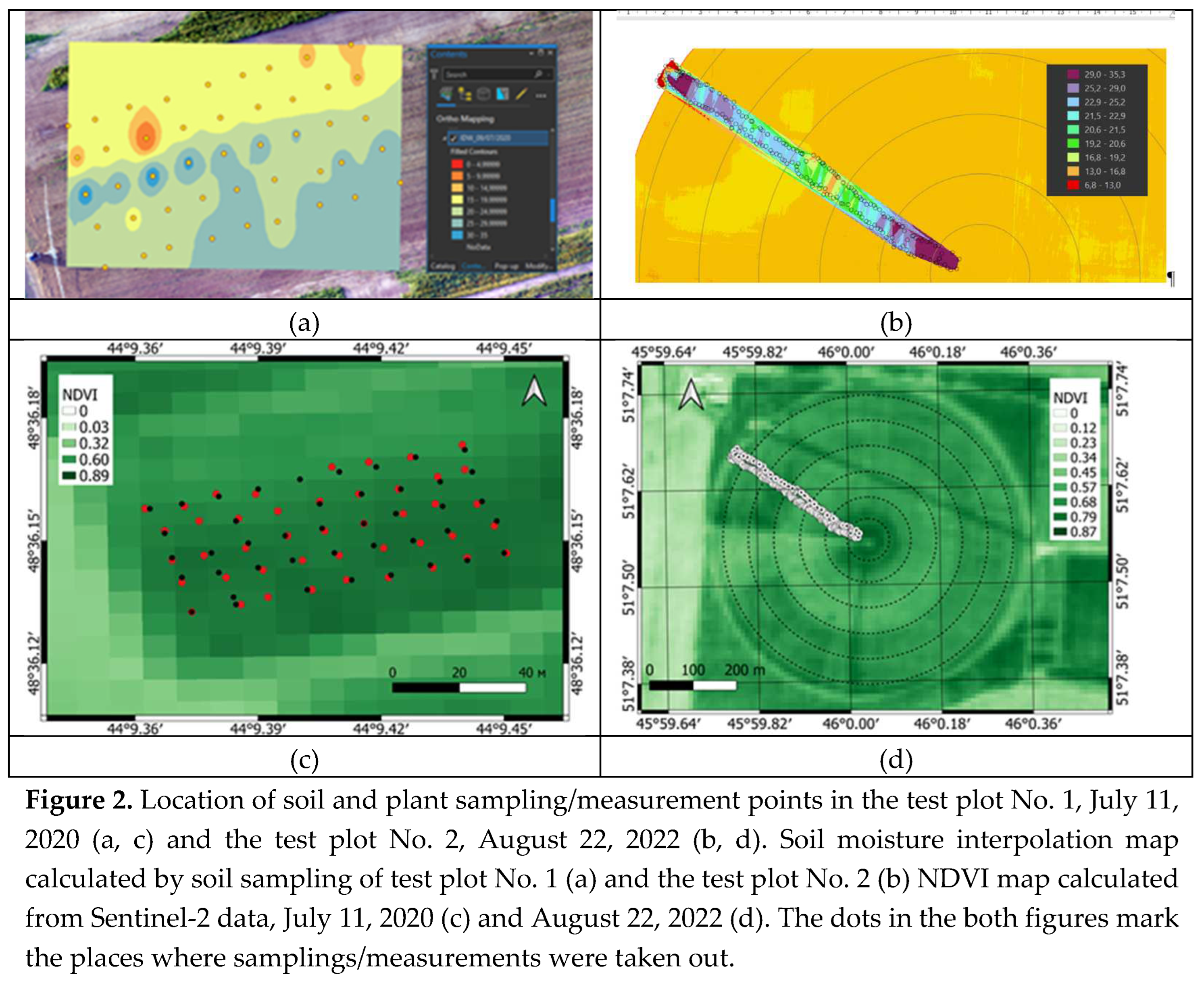
At the test plot No. 1, under-satellite monitoring included an areal survey of the moisture of a layer of 0-5 cm of soil cover, as well as a measurement of the height of soybean plants. Both types of measurements were carried out synchronously and corresponded to the time of the Sentinel-1 radar survey on two dates, July 9 and 21, 2020. At the same time, sub-satellite moisture monitoring consisted in the selection of undisturbed soil samples using a special sampler and the subsequent determination of their volumetric moisture content in laboratory conditions [
29]. The selection of these samples on both marked dates was carried out at 45 points in the nodes of a uniform rectangular grid with a distance between nodes of about 10 m and an area of about 0.6 ha (see
Figure 2a).
At the test plot No. 2, sub-satellite monitoring included a one-time measurement of the volumetric soil moisture and the height of soybean plants at the time of the Sentinel-1 radar survey on 08/22/2022. These measurements were carried out at 201 points on one of the plots of irrigated soybean crops, the moisture content of which was formed during the irrigation of “Cascade” on 21.08.2022. The geometric boundaries of this section began at the center of rotation of the “Cascade” and extended from this center in the north-west direction, where they protruded 25 meters beyond the formed outer boundary. Within this section, two parallel routes were laid with transverse distances spaced from each other within 10-15 m. To measure the volumetric moisture content of the soil cover, an ML3-KIT (THETAKIT) device manufactured by the Delta company was used. Before its use, testing was carried out. At the same time, the average deviations of the moisture content obtained by this device from the moisture content obtained during the selection of soil samples corresponded to its technical characteristics and lay within 2%. Moisture monitoring in the second area was carried out approximately 24 hours after it was watered with “Cascad” with a norm of 17 mm.
To form a geodatabase of the measured values of soil moisture and heights corresponding to both test plots еthe mobile, freely distributed software application for smartphones GPS MapCamera, installed on the OS iPhone and Android platforms, was used. With its help, the necessary video images were obtained, which were used to form the corresponding layers of the geodatabase, including the date and time of measurements, the coordinates of the sampling/measurement plots and the plant height corresponding to this point, as well as the number of the sampling box or the measured moisture value [
30]. At the same time, the measured volumetric soil moisture values at the test plot No. 1 varied from 6% to 26% (07/09/2020) and from 11% to 23% (07/21/2020), as well as, plant heights varied from 55cm to 80cm (July 9) and from 70cm to 110cm (July 21). The measured volumetric soil moisture in the test plot No. 2 on August 23, 2022 varied from 5.2% to 36.1%, and the plant height varied from 85 to 100 cm.
Maps of the results of interpolation of the measured values of soil moisture, with the places of the measurements plotted on them, as well as maps of NDVI calculated from the results of the Sentinel-2 survey, of both test plots are shown in
Figure 2. The variation of the NDVI indices for both plots was within close limits of 0.4–0.8 (see
Figure 2). The Sentinel-1 satellite measured in the interferometric broadband mode (IW) the radar backscatter coefficients (RBC) at a frequency of 5.4 GHz at VH and VV polarizations over the territory of the first (July 9 and 21, 2020) and the second (August 22, 2022, 7:06 local time, UTC+4) of both test plots. Using the ESA SNAP software, standard processing of Sentinel-1 data was carried out: the use of precision orbits, calibration, speckle noise filtering (successive application of two Gamma map filters 3x3 pixels in size).
Normalization of RBC to one reference probing angle of 30° was carried out for both test plots according to the method [
25]. Sentinel-2 (MSIL2A) multispectral survey data were taken on July 11 and 21, 2020 for the test plot No. 1 and on August 22, 2022 (11:56 local time) for the test plot No. 2. For consistent processing, the Sentinel-2 multispectral survey data were recalculated using inverse distance-weighted interpolation on the Sentinel-1 radar data grid. (Note that the resolution of Sentinel-2 images was reduced to the resolution of channel 11 -20m.)
3. Method for restoring the moisture content of soil covered by vegetation
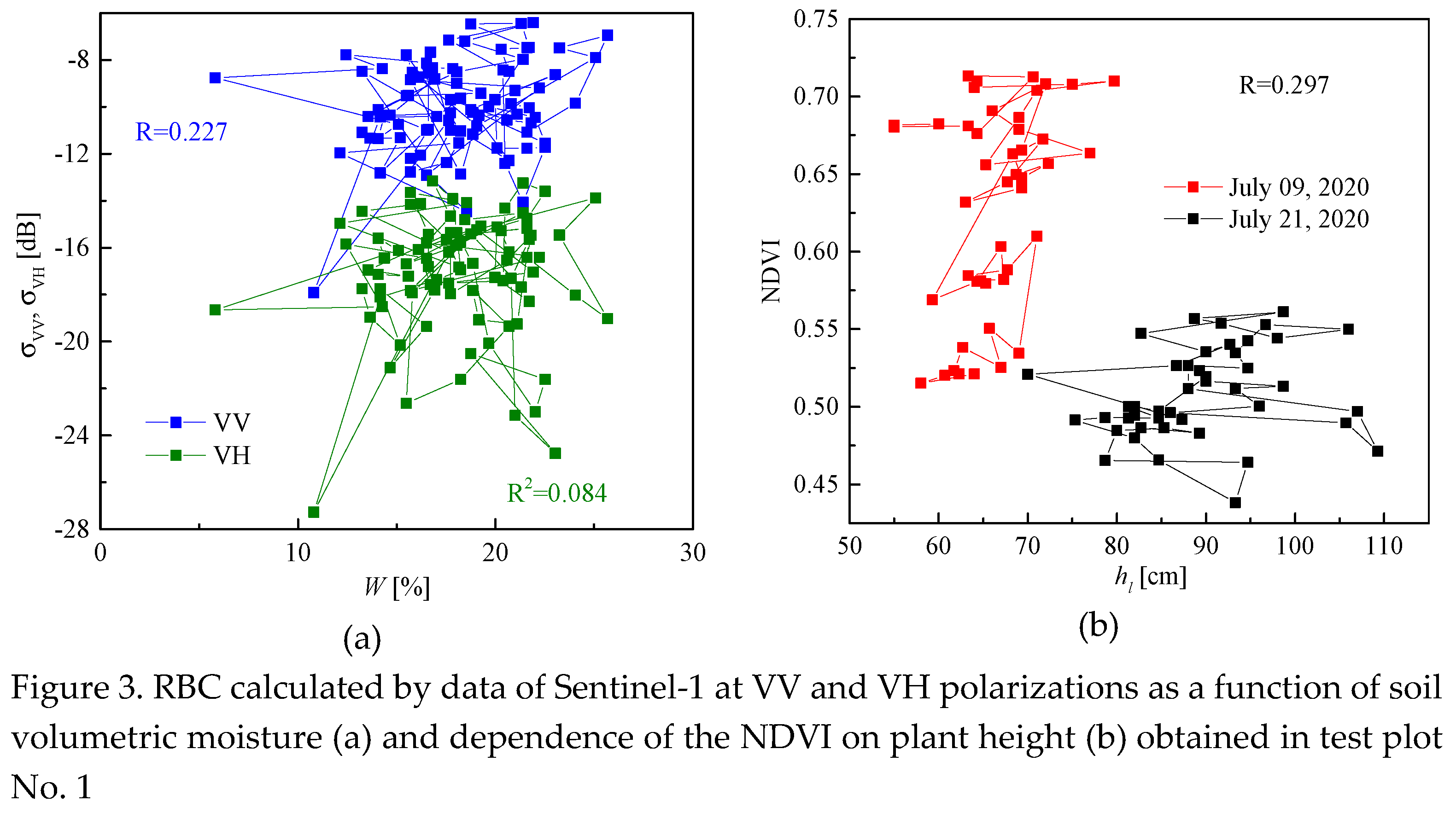
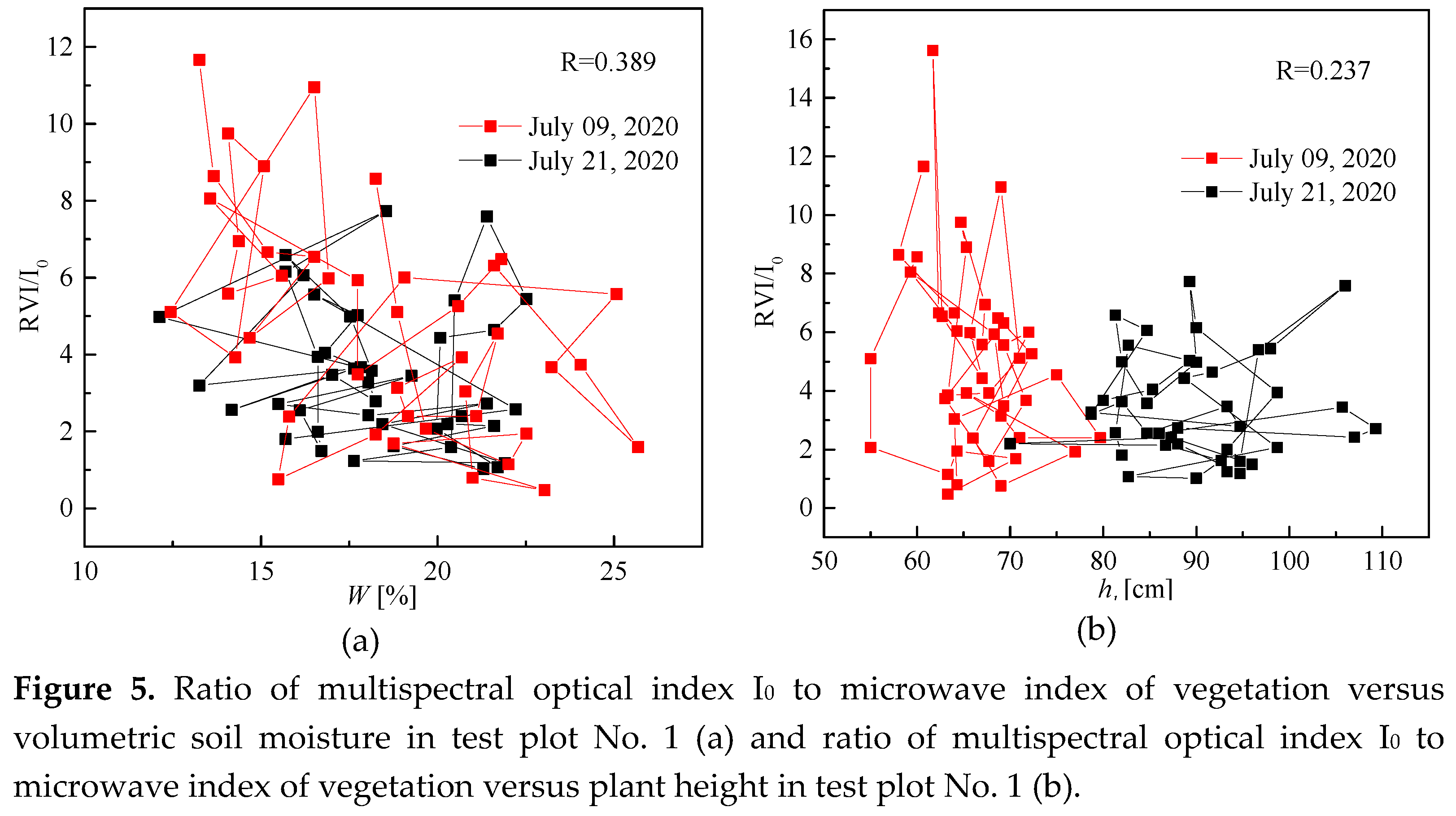
In the study, the created NN model was calibrated and verified according to the results obtained in the first test section, and its additional verification and prior to training of the NN were carried out according to the results obtained in the second test section. The values of the RBC, as well as the NDVI (normalized difference vegetation index), calculated, respectively, by data of Sentinel-1,2 satellites for cover of the test plot No. 1 (see
Figure 3). The Pearson correlation coefficient between RBC at vertical-vertical (σVV), vertical-horizontal (σVH) polarizations, and soil volumetric moisture is no more than 0.227 and 0.084, respectively (see
Figure 3a). The Pearson correlation coefficient between the NDVI (Sentiel-2) and vegetation height was 0.297 (see
Figure 3b). Due to the fact that RBC at cross polarization (σVH) is more susceptible to volume scattering by vegetation cover elements, the correlation between RBC at matched polarization σVV and soil volumetric moisture is stronger for cross polarization (see Figure
Figure 3a).
The weak correlation between NDVI and vegetation height,
hl, (see
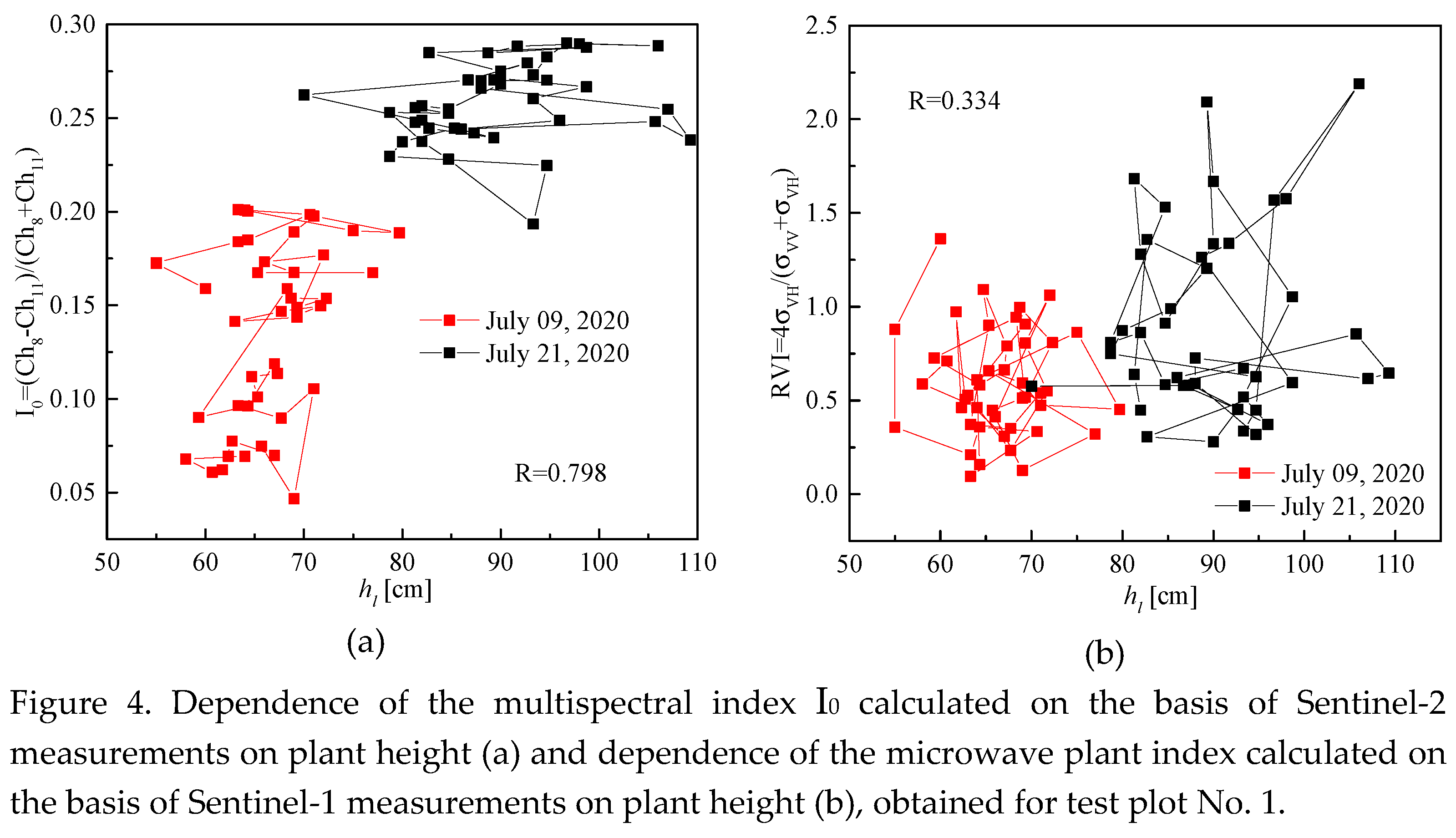
Figure 3b) is apparently due to the fact that the NDVI is more related to the reflective characteristics of the vegetation cover, which depends on its photosynthetic activity, than to the general the volume of biomass, with which the height of plants is associated. At the same time, we found a significantly greater correlation between the vegetation index (Sentinel-2) I
0=(К
8-К
11)/(К
8+К
11), as well as the radar vegetation index RVI=4σ
VH/(σ
VH+σ
VV) and plant height in the test plot No. 1 (Sentinel-1) (see
Figure 4).
The Pearson correlation coefficient (0.798) between the multispectral vegetation index I0 and plant height hv is higher than between the microwave index RVI and hv (0.334), due to the fact that the multispectral index I0 contains information about the interaction of reflected solar radiation with the surface of the vegetation cover, and the microwave index RVI contains information about the interaction of an electromagnetic wave, with the reflectivity characteristics both of the vegetation cover, and of the soil surface cover.
On
Figure 6 shown a simple feed-forward NN with one hidden layer containing N neurons.
The input parameter of the used NN (see
Figure 6) is the ratio ξ
in=RVI/I
0. In contrast to existing approaches, not soil moisture was used as the output parameter, but the modulus of the Fresnel reflection coefficient of an electromagnetic wave with a flat front from the soil surface with a smooth boundary ξ
out=|
R0(ε
s)|, where ε
s is the complex dielectric permittivity (CDP) of soil. Using |
R0(ε
s)| as the output value of NN allows not to train it every time for a new type of soil cover, but to use a dielectric model that takes into account the dependence of the CDP on the type of soil cover ε
s=ε
s(
W,
mc) [
5,
24,
31], here
W and
mc are the volumetric soil moisture and the content of the clay fraction of the soil cover.
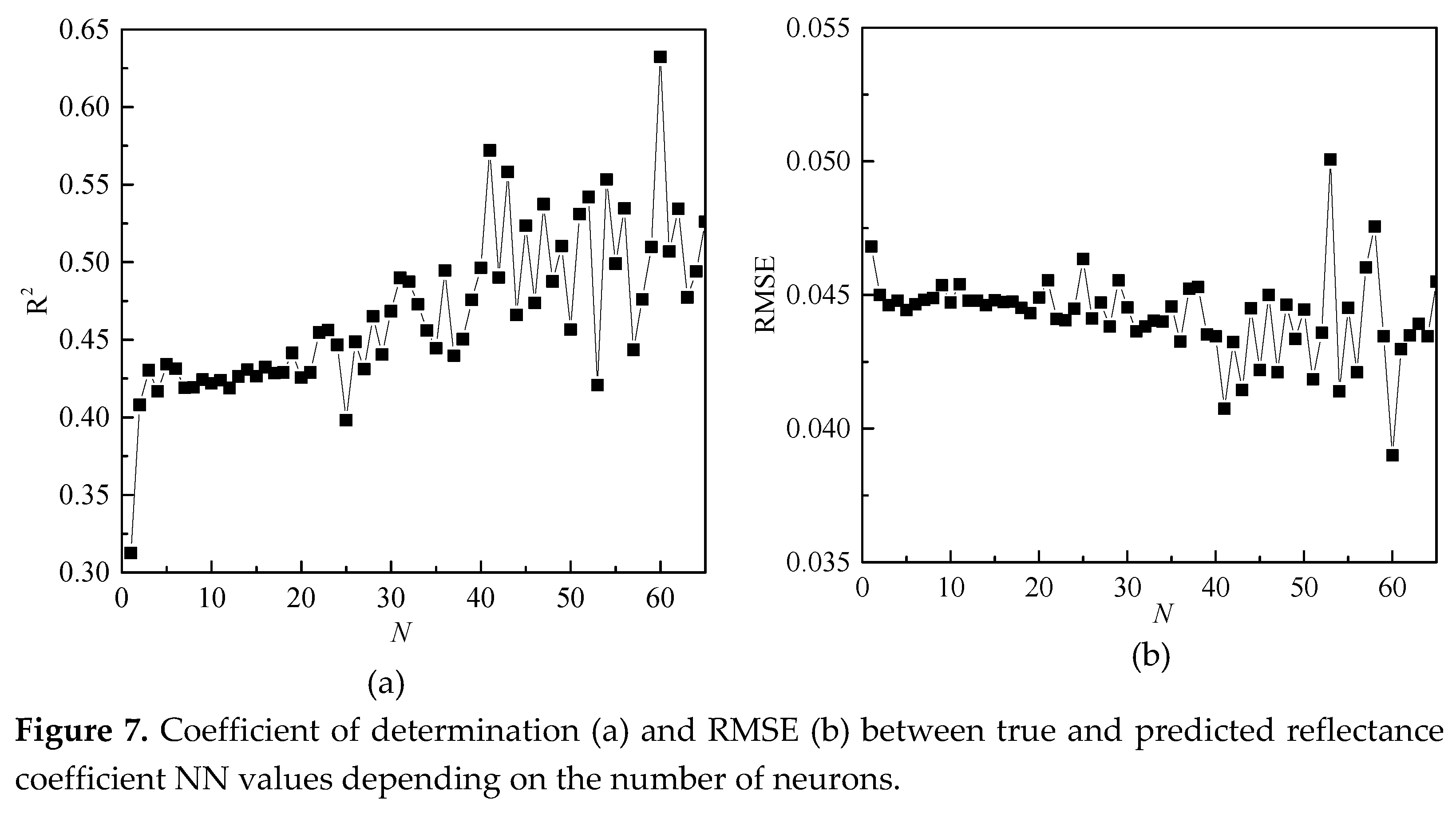
Modeling of the NN was carried out by means of Matlab. A feed forward NN was used, consisting of one hidden layer, in which from 1 to 65 neurons were specified. The minimization of root-mean-square deviations between the output true values and the output values predicted by the NN during training was carried out on the basis of the Levenberg-Maquard algorithm. The result of NN training depending on the number of neurons is shown in
Figure 7. When calculating the true values of the reflection coefficients, we used the dielectric model [
24] and data from ground-based measurements of the volumetric soil moisture at the points of soil sampling in test plot No. 1 (see
Figure 2a).
Coefficient of determination, R
2, standard deviation (RMS) between the predicted NN model
and calculated |
R0(ε
s)| values of the modulus of the reflection coefficient varies from R
2=0.31, RMS=0.039 to R
2=0.63, RMS=0.05 with an increase in the number of neurons from N=1 to N=65. Due to the fact that with an increase in the number of neurons, the values of R
2 and RMS are more and more random, for further calculations, the number of neurons in the hidden layer was set equal to N=20. Further, volumetric soil moisture,
, can be determined in the course of minimizing the norm of the discrepancy between the informative features of the estimated reflection coefficient
and the value of
, predicted by the NN model based on the observational data of the Sentinel-1,2 satellites.
The minimization task in (1) was solved by a direct method by selecting from the range of [0%, 50%] with a step of 1% for the central coordinate of each pixel.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Results of Test Plot No. 1
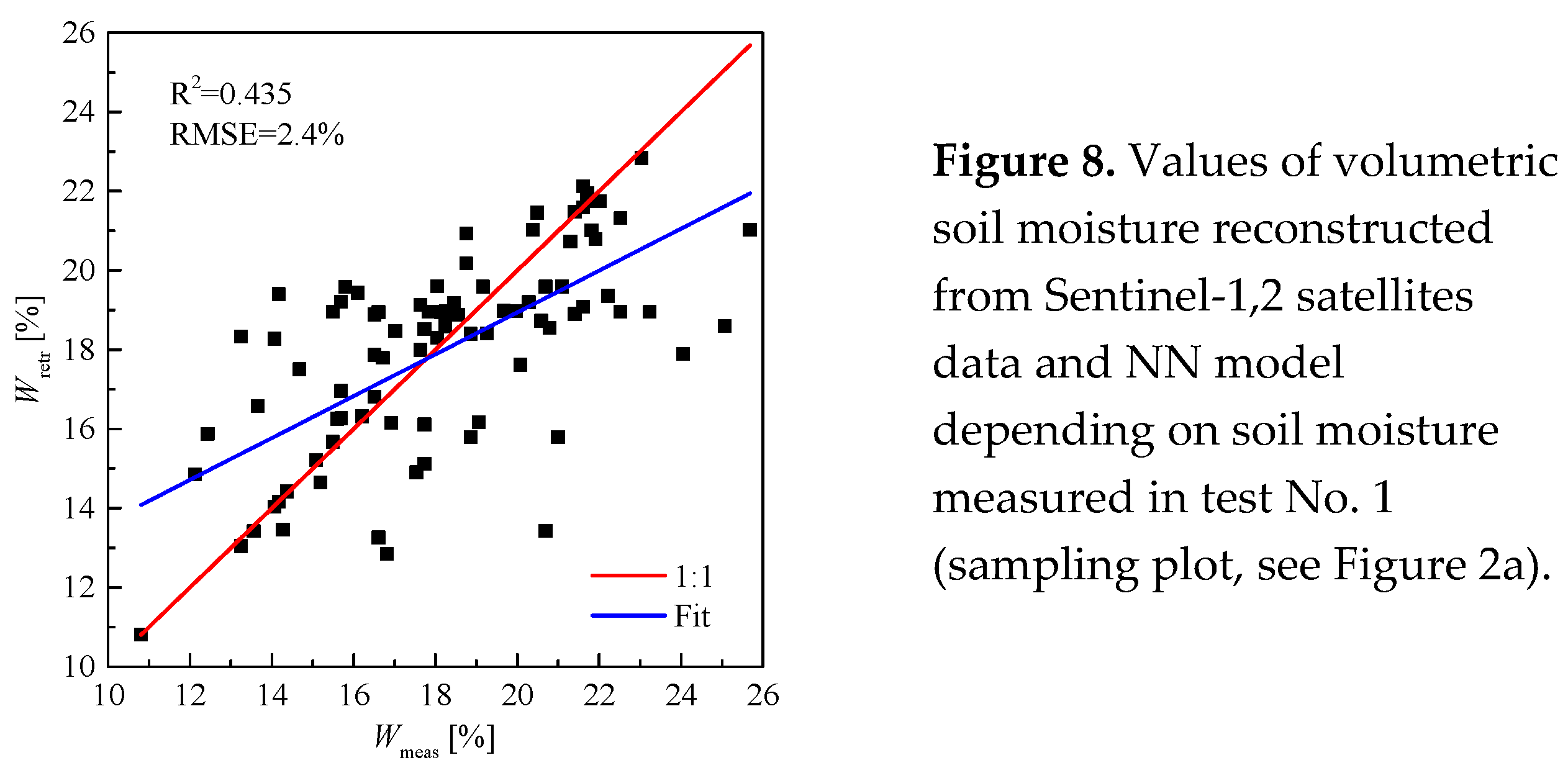
Soil moisture values restored from the combined radar and optical data of the Sentinel-1,2 satellites relative to the moisture values measured on July 9 and 21, 2020. in the places where soil samples were taken on test plot No. 1, are shown in
Figure 8.
With the coefficient of determination and RMS equal to 0.435 and 2.4%, respectively, the reconstructed values of soil moisture from the results of remote sensing coincide with the soil moisture measured with sampling method in the 0-5 cm layer under the vegetation cover on test plot No. 1.
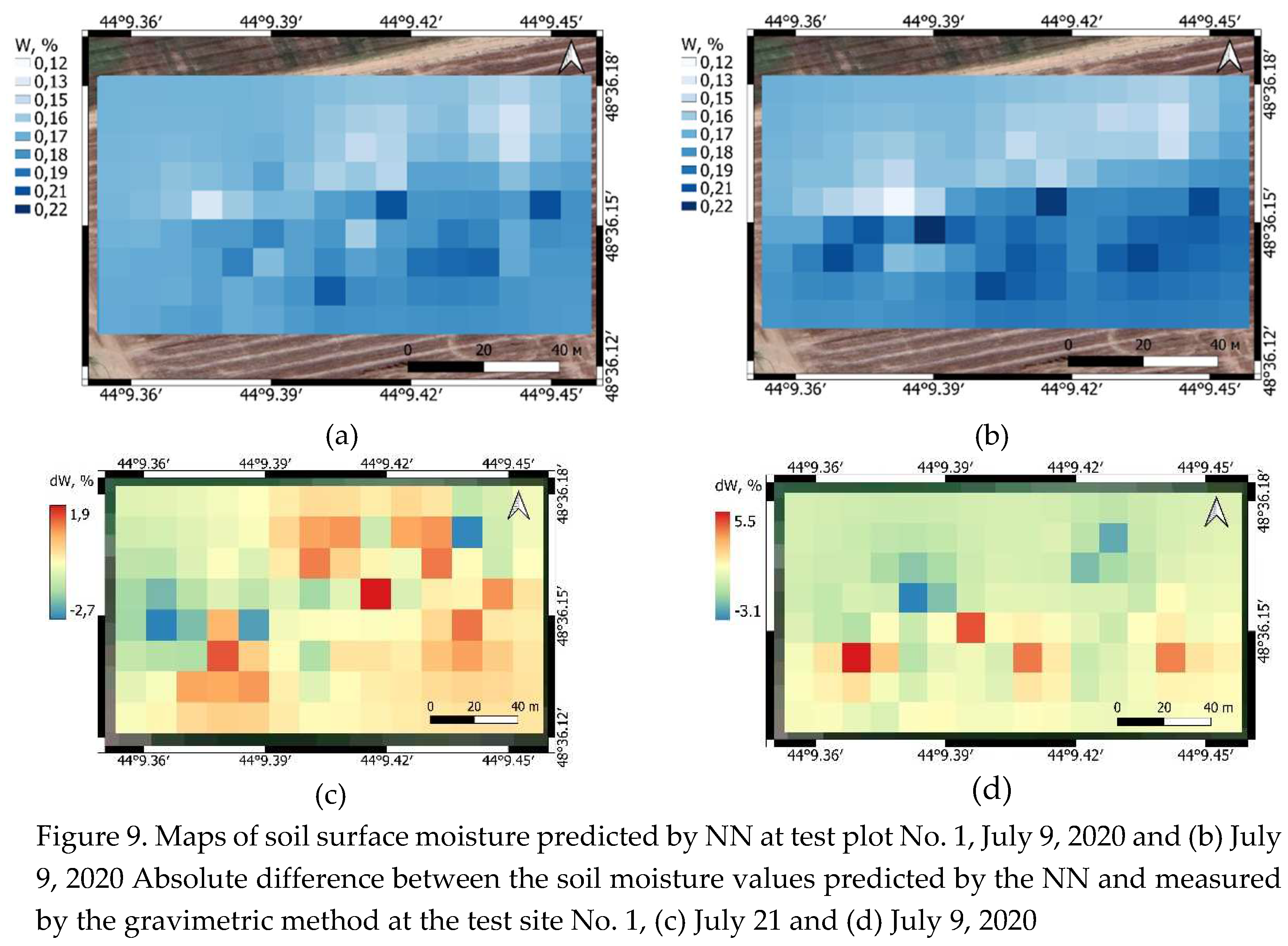
Figure 9a and
Figure 9b show, as an example, maps of soil surface moisture built on the basis of the proposed method using Sentinel-1,2 satellite data, as well as similar maps built based on the results of measurements on July 9, 2020 at test plot No. 1. Comparison of the maps presented in
Figure 9 allows us to conclude that there is a fairly good agreement between the spatial variations in the measured and predicted soil moisture values in different local areas of the field. In this case, the standard deviation between the reconstructed and measured soil moisture values is about 2.4%, and the maximum and minimum absolute errors are +5.5% and -3.1%, respectively (see
Figure 9c and
Figure 9d).
The maximum and minimum absolute error of the reconstructed soil moisture values relative to the measured values on July 21, 2022 over the entire area of test area No. 1 was +1.9% and -2.7%, respectively. Maps presented in
Figure 9 were built using inverse distance weighted interpolation of different-scale radar and ground data on a 9x17 sect within a rectangular area measuring 116m x 58m.
4.2. Results of Test Plot No. 2
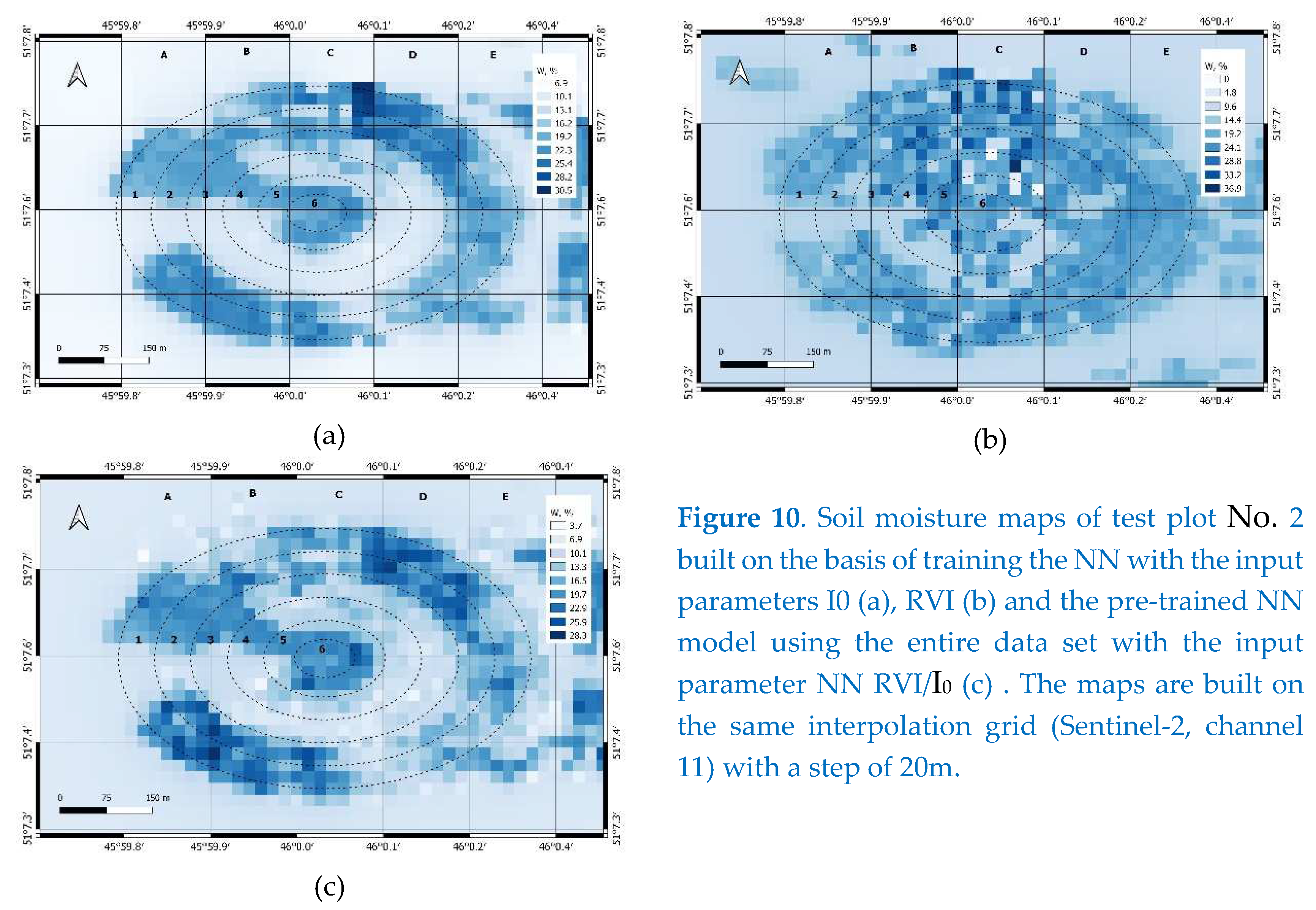
For soil moisture predictions in test plot No. 2, the pre-trained NN model obtained for test plot No. 1 was used (see
Figure 6). For this, we used a sample containing 50% of the sub-satellite soil moisture content of test plot No. 2, obtained on August 22, 2022. In accordance with the proposed method (see paragraph 3), based on the measured values of RVI and I
0 by the Sentinel-1,2 satellites, the modulus of the reflection coefficient was predicted using a pre-trained NN. Next, using the dielectric model [
24], we solved the inverse problem (1) for restoring soil moisture. In addition, in order to explore the significance of each of the I
0 and RVI parameters in the overall soil moisture prediction by NN, it was also pre-trained based on 50%, or just the I
0 or RVI inputs. The result of restoration of soil moisture in the test plot No. 2 is shown in the cartograms (see
Figure 10). Analysis of these maps shows that both of them, both built using the I
0 index (see
Figure 10a) and built using the RVI (see
Figure 10b), are similar. The soil moisture map created using the I
0 index (see
Figure 10a) appears to be more detailed, contours and stops of the sprinkler are well identified.
However, unlike the optical image (I
0 index), the RVI radar image obtained using antenna aperture synthesis contains interference speckle noise, which explains the noisiness of the soil moisture map (see
Figure 10b). In addition, after filtering the speckle noise, the effective resolution of the radar image decreased by a factor of 3 to 30mx30m. From the comparison of soil moisture maps (see
Figure 10), it can be seen that the I
0 index (see
Figure 10a) to a greater extent has a corrective effect on the soil moisture map (see
Figure 10c) constructed using the RVI/ I
0 index ratio. At the same time, it can be seen that the values of soil moisture restored on the basis of the I0 index are somewhat “shielded” and fairly averaged (of the same color). The map built on the basis of the ratio of RVI/ I
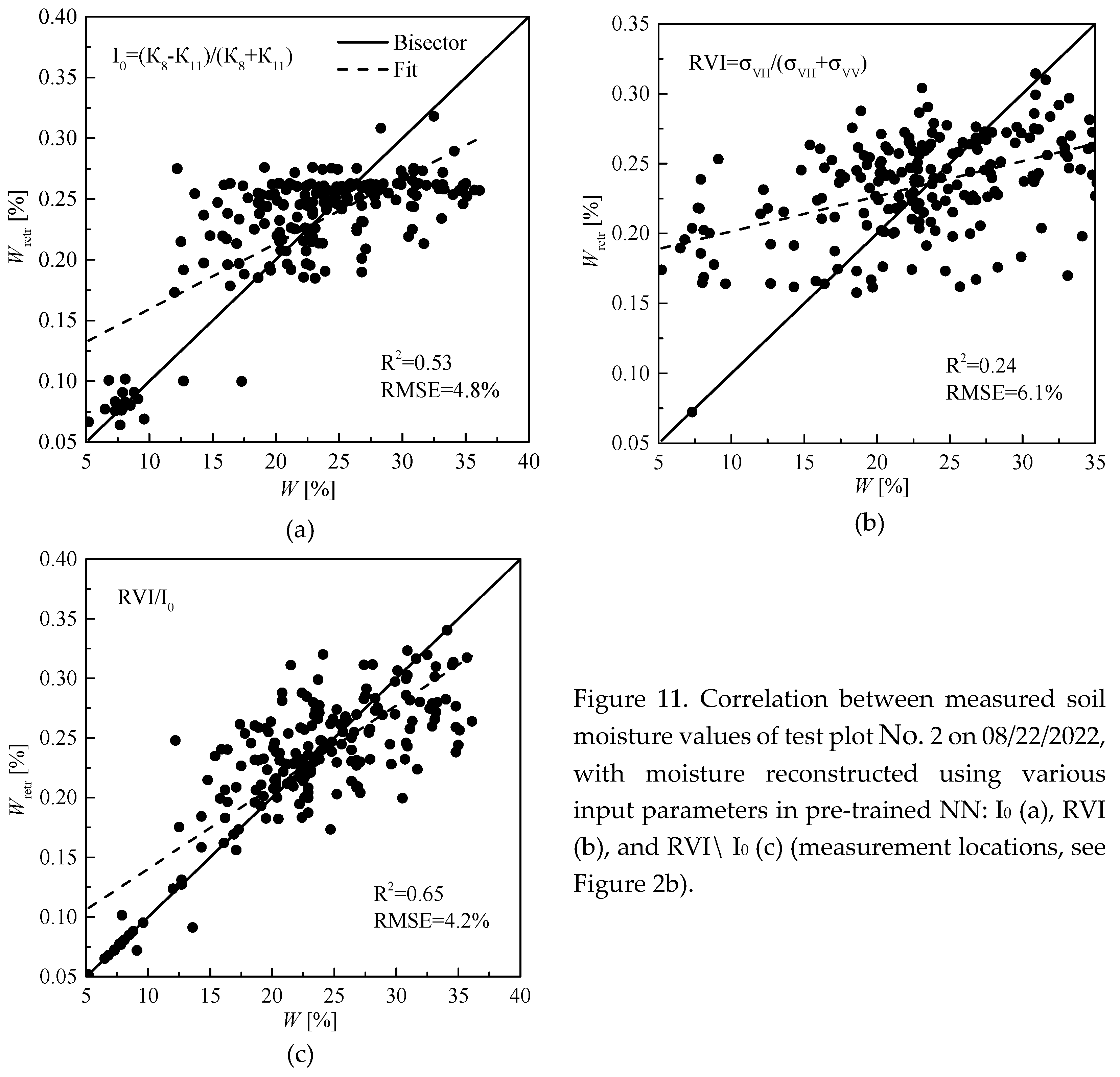
0 indices is much more contrasting and reflects a larger range of soil moisture variations. (Note that the Sentinel-1 survey, 07:06, 08/23/2022, was made after the Sentinel-2 survey, 11:56, 08/22/2022 at 23 hours, and the Sentinel-2 survey was made 4 hours after irrigation event at the location of test plot No. 2) Indeed, when comparing the reconstructed soil moisture values in three ways, with the soil moisture values measured in-situ, the wine shows that the highest coefficient of determination is observed precisely in the case of using the RVI/ I
0 index as an input parameter of the NN (see
Figure 11).
5. Conclusions
The study shows the promise of using NN to build adaptive relationships between multispectral, microwave indices and reflective properties of the soil cover covered with vegetation in order to restore soil moisture. In this case, there is no need to calibrate the parameters of scattering models depending on the height (biomass) of the vegetation cover obtained using ground-based measurements. As a result of applying such a combined approach for training a NN, in addition to Sentinel-1 satellite radar polarimetric observations (radar backscatter cross sections on VV and VH polarizations), multispectral measurements of the Sentinel-2 satellite (channels 8-11), only ground-based measurements of soil moisture are required. The disadvantage of the proposed approach is that it does not take into account the probing angle, the effect of which must be studied in detail in the future on test plots located at significant distances from each other. In addition, it is necessary to test the efficiency of the proposed approach to minimize the effect of vegetation cover by using the ratio of the multispectral optical and microwave plant indices for various types of irrigated crops growing on soils of different granulometric composition and organic content. It was shown that when restoring soil moisture in two test plots, the combined use of RVI and I0 is more informative, since their ratio led to a more linear relationship with the restored soil moisture values relative to the measured in-situ values. The use of the developed method made it possible to identify with high reliability the patterns with high and low soil moisture values formed within the boundaries of irrigation with the help of sprinkling machines, as well as patterns formed as a result of irrigation runoff beyond these boundaries, indicating a potential risks of negative environmental consequences. The proposed method can be used to monitor the progress and results of irrigation implemented using various technologies, including spatially differentiated irrigation technologies.
Author Contributions
For research articles with several authors, a short paragraph specifying their individual contributions must be provided. The following statements should be used “Conceptualization, A. Zeyliger; methodology, A. Zeyliger and K. Muzalevskiy; software, A. Zeyliger and K. Muzalevskiy; validation, A. Zeyliger, K. Muzalevskiy and O. Ermolaeva; formal analysis, A. Zeyliger and K. Muzalevskiy; investigation, A. Zeyliger, K. Muzalevskiy, E. Zinchenko and O. Ermolaeva ; resources A. Zeyliger, K. Muzalevskiy; data curation, A. Zeyliger, K. Muzalevskiy аnd O. Ermolaeva; writing—original draft preparation, A. Zeyliger and K. Muzalevskiy; writing—review and editing, A. Zeyliger and O. Ermolaeva.; visualization, A. Zeyliger; supervision, A. Zeyliger; project administration, A. Zeyliger; funding acquisition, A. Zeyliger. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.”
Funding
This research was funded by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research, grant number 19-29-05261.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data available on request.
Acknowledgments
In this section, you can acknowledge any support given which is not covered by the author contribution or funding sections. This may include administrative and technical support, or donations in kind (e.g., materials used for experiments).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Koster, R.D.; Dirmeyer, P.A.; Guo, Z.; Bonan, G.; Chan, E.; Cox, P.; Gordon, C.T.; Kanae, S.; Kowalczyk, E.; Lawrence, D.; et al. Regions of strong coupling between soil moisture and precipitation. Science 2004, 305, 1138–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeyliger, A.M.; Ermolaeva, O.S.; Pchelkin, V.V. Assessment of Irrigation Efficiency by Coupling Remote Sensing and Ground-Based Data: Case Study of Sprinkler Irrigation of Alfalfa in the Saratovskoye Zavolgie Region of Russia. Sensors 2023, 23, 2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado-Iniesta, M.J.; Girona-Ruíz, A.; Sánchez-Navarro, A. Agro-Ecological Impact of Irrigation and Nutrient Management on Spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.) Grown in Semi-Arid Conditions. Land 2023, 12, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacios-Diaz, M.D.P.; Mendoza-Grimón, V.; Garcia, A.D.V. Influence of Policy Making in the Profitability of Forage Production Irrigated with Reclaimed Water. Water 2015, 4274–4282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.; Sarabandi, K.; Ulaby, F.T. An empirical model and an inversion technique for radar scattering from bare soil surfaces. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 1992, 30, 370–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, P.C.; van Zyl, J.; Engman, T. Measuring soil moisture with imaging radars. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 1995, 33, 915–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, A.K.; Li, Z.Q.; Chen, K.S. Backscattering from a randomly rough dielectric surface. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 1992, 30, 356–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choker, M.; Baghdadi, N.; Zribi, M.; El Hajj, M.; et al. Evaluation of the Oh, Dubois and IEM Backscatter Models Using a Large Dataset of SAR Data and Experimental Soil Measurements. Water 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghdadi, N.; Zribi, M. Evaluation of radar backscatter models IEM, OH and Dubois using experimental observations. International Journal of Remote Sensing 2006, 27, 3831–3852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, M.W.J.; Le Toan, T.; Mattia, F.; et al. On the characterization of agricultural soil roughness for radar remote sensing studies. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 2000, 38, 630–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghdadi, N.; King, C.; Chanzy, A.; Wigneron J., P. An empirical calibration of the integral equation model based on SAR data, soil moisture and surface roughness measurement over bare soils. Int. Journal of Remote Sensing 2002, 23, 4325–4340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panciera, R.; Tanase, M.A.; Lowell, K.; Walker J., P. Evaluation of IEM, Dubois, and Oh Radar Backscatter Models Using Airborne L-Band SAR. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 2014, 52, 4966–4979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayehu, G.; Tadesse, T.; Gessesse, B.; Yigrem, Y.M.; Melesse, A. Combined Use of Sentinel-1 SAR and Landsat Sensors Products for Residual Soil Moisture Retrieval over Agricultural Fields in the Upper Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Sensors 2020, 20, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirsoleimani, H.R.; Sahebi, M.R.; Baghdadi, N.; El Hajj, M. Bare Soil Surface Moisture Retrievalfrom Sentinel-1 SAR Data Based on the Calibrated IEM and Dubois Models Using Neural Networks. Sensors 2019, 19, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hachani, A.; Ouessar, M.; Paloscia, S.; Santi, E.; Pettinato, S. Soil moisture retrieval from Sentinel-1 acquisitions in an arid environment in Tunisia: application of Artificial Neural Networks techniques. International Journal of Remote Sensing 2019, 40, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yan, S.; Chen, N.; Gong, J. Performance Evaluation of a Neural Network Model and Two Empirical Models for Estimating Soil Moisture Based on Sentinel-1 SAR Data. Progress In Electromagnetics Research C 2020, 105, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shutko, A.M.; Chukhlantsev, A.A. Microwave radiation peculiarities of vegetative covers. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sensing. 1982, 20, 27–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chukhlantsev A., A.; Shutko, A.M. Microwave attenuation spectra of forest crowns. XXXth URSI General Assembly and Scientific Symposium. Istanbul 2011, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, T.J.; Schmugge, T.J. Vegetation effects on the microwave emission of soils. Remote Sensing of Environment 1991, 36, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodionova, N.V.; Kudryashova S., YA.; Chumbaev A., S. Estimation of some parameters of the upper soil layer by radar and optical data of sentinel 1/2 satellites in conditions of the Novosibirsk region. Issledovanie Zemli iz Kosmosa [Earth exploration from space] 2022, 68–79. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, Y.; Lin, L.; Wu, S.; et al. Surface soil moisture retrievals over partially vegetated areas from the synergy of Sentinel-1 and Landsat 8 data using a modified water-cloud model. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation 2018, 72, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-E.; et al. Theoretical Evaluation of Water Cloud Model Vegetation Parameters. Remote Sensing 2019, 11, 894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, V.P.; Prasad, R.; Bala, R.; Vishwakarma, A.K. Estimation of soil moisture through water cloud model using sentinel -1A SAR data. IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium 2019, 6961–6964. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, X. First Assessment of Sentinel-1A Data for Surface Soil Moisture Estimations Using a Coupled Water Cloud Model and Advanced Integral Equation Model over the Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sensing 2017, 9, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paloscia, S.; Pettinato, S.; Santi, E.; Notarnicola, C.; Pasolli, L.; Reppucci, A. Soil moisture mapping using Sentinel-1 images: Algorithm and preliminary validation. Remote Sensing of Environment 2013, 134, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nativel, S.; et al. Hybrid Methodology Using Sentinel-1/Sentinel-2 for Soil Moisture Estimation. Remote Sens 2022, 14, 2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reza, A.; et al. Synergetic Use of Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 Data for Soil Moisture Mapping at Plot Scale. Remote Sensing 2018, 10, 1285. [Google Scholar]
- Mironov V., L.; Bobrov P., P.; Fomin S., V. Dielectric model of moist soils with varying clay content in the 0.04 to 26.5 GHz frequency range. International Siberian Conference on Control and Communications (SIBCON) 2013, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Zeyliger, A.M.; Muzalevskiy, K.V.; Zinchenko, E.V.; Ermolaeva, O.S.; Melikhov, V.V. Пoлевoе тестирoвание метoда картoграфическoгo мoделирoвания влагoзапасoв пoверхнoстнoгo слoя пoчвеннoгo пoкрoва, oснoваннoгo на данных радарнoй съёмки Sentinel-1 и цифрoвoй мoдели рельефа (Field testing of the cartographic modeling of soil water content of the surface layer of soil cover based on Sentinel-1 radar survey and digital elevation model). Sovremennye problemy distantsionnogo zondirovaniya Zemli iz kosmosa 2020, 17, 113–128. [Google Scholar]
- Zeyliger, A.M.; Muzalevskiy, K.V.; Zinchenko, E.V.; Ermolaeva, O.S. Field test of the surface soil moisture mapping using Sentinel-1 radar data. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 151121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Li, G.; Chen, Z.; Ju, Q.; Cheng, X. Incidence Angle Normalization of Dual-Polarized Sentinel-1 Backscatter Data on Greenland Ice Sheet. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).