Submitted:
27 June 2023
Posted:
28 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and methods
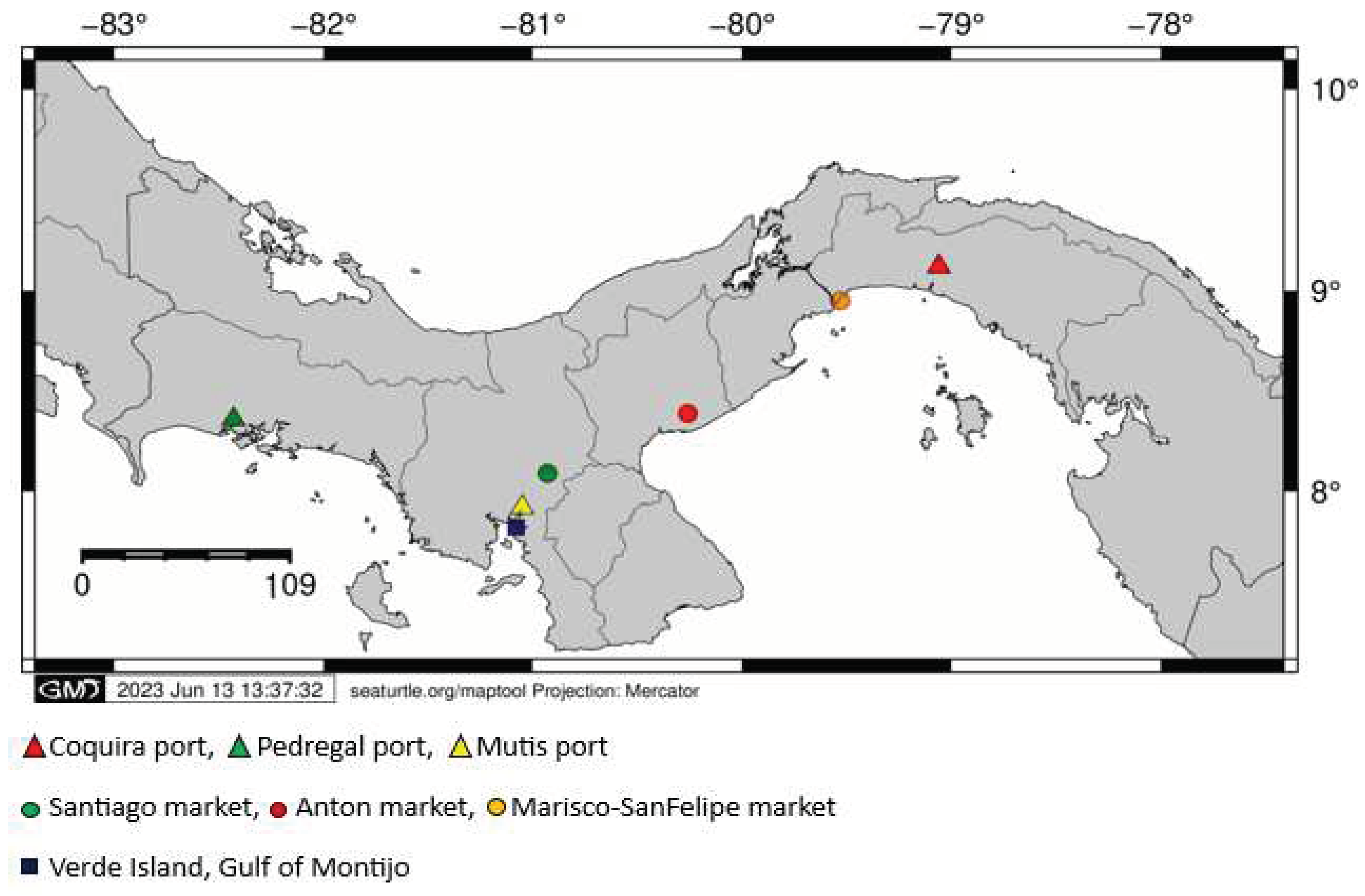
2.1. Sample collection on local markets and fish gathering centers.
2.2. DNA extraction and pcr amplification
2.3. Sequence analysis
2.4. Species and genetic diversity in Panama pacific fisheries
2.4.1. Species and family diversity
2.4.2. Genetic diversity
2.4.3. Genetic connectivity and demographic history
2.4.4. Developing tools for molecular taxonomy and traceability
3. Results
3.1. Sequence analysis
3.2. Species, family and genetic diversity in Panama pacific fisheries
3.3. Genetic diversity
3.3.1. Genetic connectivity and demographic history.
3.3.2. Developing tools for molecular taxonomy and traceability:
4. Discussion
4.1. Species diversity
4.2. Genetic connectivity and demographic history
4.3. Developing tools for molecular taxonomy and traceability:
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Helyar, S.J.; Lloyd, H.A.D.; De Bruyn, M.; Leake, J.; Bennett, N.; Carvalho, G.R. Fish Product Mislabelling: Failings of Traceability in the Production Chain and Implications for Illegal, Unreported and Unregulated (IUU) Fishing. PLoS One 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa Leal, M.; Pimentel, T.; Ricardo, F.; Rosa, R.; Calado, R. Seafood Traceability: Current Needs, Available Tools, and Biotechnological Challenges for Origin Certification. Trends Biotechnol 2015, 33, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, E.A.; Hebert, P.D.N. Assessing Dna Barcodes for Species Identification in North American Reptiles and Amphibians in Natural History Collections. PLoS One 2016, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radulovici, A.E.; Archambault, P.; Dufresne, F. DNA Barcodes for Marine Biodiversity: Moving Fast Forward? Diversity (Basel) 2010, 2, 450–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, P.D.N.; Cywinska, A.; Ball, S.L.; DeWaard, J.R. Biological Identifications through DNA Barcodes. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 2003, 270, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, R.D.; Hanner, R.; Hebert, P.D.N. The Campaign to DNA Barcode All Fishes, FISH-BOL. J Fish Biol 2009, 74, 329–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen G & Robertson R Fishes of the Tropical Eastern Pacific; Univ. Hawaii Press.; Honolulu, Hawaii., 1994.
- Paul Humann; Ned DeLoach Reef Fish Identification : Baja to Panama; 1st ed.; Jacksonville, Fla. : New World, 2004.
- Froese, R. and D.P. FishBase. http://www.fishbase.org/search.php 2000, 344.
- Comerciales, M.; Pacífico De Panamá, D.; Garcés, H. LISTA SISTEMÁTICA PRELIMINAR DE LOS PECESMARINOS COMERCIALES DEL PACÍFICO DE PANAMÁ. Tecnociencia (Panama) 2021, 23, 198–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnew, D.J.; Pearce, J.; Pramod, G.; Peatman, T.; Watson, R.; Beddington, J.R.; Pitcher, T.J. Estimating the Worldwide Extent of Illegal Fishing. PLoS One 2009, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Arriati Plan de Acción Nacional Para La Conservación y Ordenación de Las Pesquerías de Tiburones; Ciudad de Panamá, Panamá, 2010.
- Díaz-Ferguson E; Justo S; Posada J; Ramos C; Del Cid V Fishery and Conservation Implications of Molecular Characterization and Traceability of Ceviche Samples from Pacific Panama; Panamá, 2023. 2023.
- Olsen, P.; Borit, M. How to Define Traceability. Trends Food Sci Technol 2013, 29, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanda Naaum; Robert Hanner Seafood Authenticity and Traceability for Fisheries Compliance 2016, 1–188.
- Poghosyan, A.; Gonzalez-Diaz; F., B.; Y., M.; F., G.; H., H.; V., S.S.; Marino, M.; Mena, S.A.; Ahmedov, Z.; et al. Traceability and Assurance Protocols in the Global Food System. International Food and Agribusiness Management Review 2004, 7, 118–126. [CrossRef]
- Alfaro, J.A.; Rábade, L.A. Traceability as a Strategic Tool to Improve Inventory Management: A Case Study in the Food Industry. Int J Prod Econ 2009, 118, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogden, R. Fisheries Forensics: The Use of DNA Tools for Improving Compliance, Traceability and Enforcement in the Fishing Industry. Fish and Fisheries 2008, 9, 462–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galimberti, A.; De Mattia, F.; Losa, A.; Bruni, I.; Federici, S.; Casiraghi, M.; Martellos, S.; Labra, M. DNA Barcoding as a New Tool for Food Traceability. Food Research International 2013, 50, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marín, A.; Serna, J.; Robles, C.; Ramírez, B.; Reyes-Flores, L.E.; Zelada-Mázmela, E.; Sotil, G.; Alfaro, R. A Glimpse into the Genetic Diversity of the Peruvian Seafood Sector: Unveiling Species Substitution, Mislabeling and Trade of Threatened Species. PLoS One 2018, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlebois, S.; Sterling, B.; Haratifar, S.; Naing, S.K. Comparison of Global Food Traceability Regulations and Requirements. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf 2014, 13, 1104–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maralit, B.A.; Aguila, R.D.; Ventolero, M.F.H.; Perez, S.K.L.; Willette, D.A.; Santos, M.D. Detection of Mislabeled Commercial Fishery By-Products in the Philippines Using DNA Barcodes and Its Implications to Food Traceability and Safety. Food Control 2013, 33, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Ferguson E; Duran I Evaluación de La Trazabilidad de Los Productos de La Pesca Del Corredor Marino Del Pacífico Este Tropical – Panamá; Panamá, 2012 .
- Díaz-Ferguson, E. Introducción a La Ecología Molecular Marina : Aplicaciones y Perspectivas; Primera Edición.; Panamá, 2012; ISBN 9789962686743 .
- Díaz Uribe; J. Gabriel; Ernesto A.; Garay, E.; F. Juan Assessment of the Pacific Red Snapper (Lutjanus Peru) Fishery in the Southwestern Gulf of California. Cienc Mar 2004, 30, 561–574. [CrossRef]
- Amezcua, F.; Soto-Avila, C.; Green-Ruiz, Y. Age, Growth, and Mortality of the Spotted Rose Snapper Lutjanus Guttatus from the Southeastern Gulf of California. Fish Res 2006, 77, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mair, J.M.; Cipriani, R.; Guzman, H.M.; Usan, D. Fishery of the Green Jack Caranx Caballus (Osteichytes: Carangidae) in Las Perlas Archipelago, Pacific Panama. Rev. Biol. Trop. (Int. J. Trop. Biol. ISSN 2012, 60, 1271–1288 . [CrossRef]
- Nava-Ortega R; Espino-Barr E; Gallardo-Cabello M; Garcia-Boa A; Puente-Gomez M; Cabral-Solis E Growth Analysis of the Pacific Sierra Scomberomorus Sierra in Colima, México. Revista de Biologia Marina y Oceanografia 2012, 47, 273–281 . [CrossRef]
- Guzman, H.M.; Díaz-Ferguson, E.; Vega, A.J.; Robles, Y.A. Assessment of the Dolphinfish Coryphaena Hippurus (Perciformes: Coryphaenidae) Fishery in Pacific Panama. Rev. Biol. Trop. (Int. J. Trop. Biol. ISSN 2015, 63, 705–716. [Google Scholar]
- Caballero S; Puentes V Genetic Characterization of the Main Tuna Species (Yellow Fin Tuna, Big Eye Tuna and Skipjack Tuna) and Tuna by Catch Species (Sharks, Mahi-Mahi, Wahoo, Sea Turtles, Marine Mammals and Billfishes) Regulated by the Interamerican Tropical Tuna Commission in the Eastern Pacific Ocean. 2011, 0–25.
- Landínez-García, R.M.; Ospina-Guerrero, S.P.; Rodríguez-Castro, D.J.; Arango, R.; Márquez, E. Análisis Genético de Lutjanus Synagris En Poblaciones Del Caribe Colombiano. Cienc Mar 2009, 35, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayona-Vásquez, N.J.; Hernández-Álvarez, C.A.; Glenn, T.; Domínguez-Domínguez, O.; Uribe-Alcocer, M.; Díaz-Jaimes, P. Complete Mitogenome Sequences of the Pacific Red Snapper (Lutjanus Peru) and the Spotted Rose Snapper (Lutjanus Gutattus). Mitochondrial DNA A DNA Mapp Seq Anal 2017, 28, 223–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez López, M.; Alcocer, M.U.; Jaimes, P.D. Phylogeography and Historical Demography of the Pacific Sierra Mackerel (Scomberomorus Sierra) in the Eastern Pacific. BMC Genet 2010, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theisen, T.C.; Bowen, B.W.; Lanier, W.; Baldwin, J.D. High Connectivity on a Global Scale in the Pelagic Wahoo, Acanthocybium Solandri (Tuna Family Scombridae). Mol Ecol 2008, 17, 4233–4247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marko PB; Lee SC; Rice AM, G.J.; Fitzhenry TM; Mcallister JS; Harper GR; Moran AL Mislabeling of Depleted Reef Fish. Nature 2004, 430, 309–310. [CrossRef]
- Veneza, I.; Silva, R.; Freitas, L.; Silva, S.; Martins, K.; Sampaio, I.; Schneider, H.; Gomes, G. Molecular Authentication of Pargo Fillets Lutjanus Purpureus (Perciformes: Lutjanidae) by DNA Barcoding Reveals Commercial Fraud. Neotropical Ichthyology 2018, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega A; Robles Y; Boniche S; Rodrígues M ASPECTOS BIOLÓGICO – PESQUEROS DEL GÉNERO (PISCES: SCIAENIDAE) EN EL GOLFO DE MONTIJO, PACÍFICO PANAMEÑO. Tecnociencia (Panama) 2008, 10.
- Vega, Á.J.; Quezada, F.; Robles, Y.A. Aspectos Biológicos y Pesqueros de Scomberomorus Sierra (Perciformes:Scombridae) En El Golfo de Montijo Pacífico de Panamá. Tecnociencia (Panama) 2013, 15, 23–70. [Google Scholar]
- Vega, A.J.; Nelva Villarreal, Y. PECES ASOCIADOS A ARRECIFES Y MANGLARES EN EL PARQUE NACIONAL COIBA. Tecnociencia (Panama) 2003, 5, 65–74. [Google Scholar]
- Dominici-Arosemena, A.; Wolff, M. Reef Fish Community Structure in the Tropical Eastern Pacific (Panamá): Living on a Relatively Stable Rocky Reef Environment. Helgol Mar Res 2006, 60, 287–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benfield, S.; Baxter, L.; Guzman, H.M.; Mair, J.M. A Comparison of Coral Reef and Coral Community Fish Assemblages in Pacific Panama and Environmental Factors Governing Their Structure. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom 2008, 88, 1331–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beleño F; Adames P Estudio de La Abundacia y Determinacion Taxonomica de Las Especies de Peces Comerciales Del Pacifico Veraguense., Universidad de Panamá, 1992.
- Joint FAO/WHO Codex Alimentarius Commission.; World Health Organization.; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Code of Practice for Fish and Fishery Products.; World Health Organization, 2012; ISBN 9789251070185.
- Ward, R.D.; Zemlak, T.S.; Innes, B.H.; Last, P.R.; Hebert, P.D.N. DNA Barcoding Australia’s Fish Species. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 2005, 360, 1847–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, A.; Stones-Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; Buxton, S.; Cooper, A.; Markowitz, S.; Duran, C.; et al. Geneious Basic: An Integrated and Extendable Desktop Software Platform for the Organization and Analysis of Sequence Data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnasingham, S.; Hebert, P.D.N. BOLD: The Barcode of Life Data System: Barcoding. Mol Ecol Notes 2007, 7, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Librado, P.; Rozas, J. DnaSP v5: A Software for Comprehensive Analysis of DNA Polymorphism Data. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1451–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonilla-Gómez, J.L.; Robles, Y.A.; Vega, A.J. Length-Weight Relationship and Biological Information of the Yellow Snapper Lutjanus Argentiventris from a Tropical Estuary: Río Caté, Gulf of Montijo, Panama. Journal of Applied Ichthyology 2014, 30, 227–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega Angel; Mate, J. Robles Yolani First Report of Reproductive Aggregations for Pacific Red Snappers Lutjanus Peru (Nicholson y Murphy, 1992) and Spotted Rose Snapper L. Guttatus (Steindachner, 1869) in the Coiba National Park, Pacific of Panama. GCF 2015, 68, 112–117.
- Gomes, G.; Schneider, H.; Vallinoto, M.; Santos, S.; Orti, G.; Sampaio, I. Can Lutjanus Purpureus (South Red Snapper) Be “Legally” Considered a Red Snapper (Lutjanus Campechanus)? Genet Mol Biol 2008, 31, 372–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, L.; Adcock, G.J.; Smith, P.J.; Bernal Ramírez, J.H.; Carvalho, G.R. Loss of Microsatellite Diversity and Low Effective Population Size in an Overexploited Population of New Zealand Snapper (Pagrus Auratus). Prog Nucl Energy 6 Biol Sci 2002, 99, 11742–11747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waples, R.S.; Luikart, G.; Faulkner, J.R.; Tallmon, D.A. Simple Life-History Traits Explain Key Effective Population Size Ratios across Diverse Taxa. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 2013, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, A.S.; Willoughby, J.R.; Christie, M.R. Genetic Diversity in Fishes Is Influenced by Habitat Type and Life-History Variation. Ecol Evol 2018, 8, 12022–12031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward R; Woodwark M; Skibinski O A Comparison of Genetic Diversity Levels in Marine, Freshwater and Anadromous Fishes. Fish Biology 1994, 44, 213–232. [CrossRef]
- DeWoody, J.A.; Avise, J.C. Microsatellite Variation in Marine, Freshwater and Anadromous Fishes Compared with Other Animals. J Fish Biol 2000, 56, 461–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiwen, L.; Chen, X.; Xu, Q.; Zhu, J.; Dai, X.; Xu, L. Genetic Population Structure of Thunnus Albacares in the Central Pacific Ocean Based on MtDNA COI Gene Sequences. Biochem Genet 2015, 53, 8–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergara-Chen, C.; González-Wangüemert, M.; Bermingham, E.; D’Croz, L. Identification of Weakfish Cynoscion (Gill) in the Bay of Panama with RFLP Markers. J Fish Biol 2009, 75, 1101–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgardo Díaz-Ferguson Diversidad y Conectividad Genética de Tres Especies de Teleósteos de Importancia Pesquera En El Pacífico de Costa Rica. Informe Final de Proyecto. ; 2022.
- Justo, S. Estructura y Variabilidad Genética de Tiburones Del Género Mustelus Spp. En El Golfo de Chiriquí y Montijo Como Áreas de Influencia Del Parque Nacional Coiba. Thesis, International Maritime University of Panama: Panamá, 2022.
- Robertson, D.R.; Angulo, A.; Baldwin, C.C.; Pitassy, D.; Driskell, A.; Weigt, L.; Navarro, I.J.F. Deep-Water Bony Fishes Collected by the B/O Miguel Oliver on the Shelf Edge of Pacific Central America: An Annotated, Illustrated and DNA-Barcoded Checklist. Zootaxa 2017, 4348, 1–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Ferguson, E. Desarrollo de Marcadores Moleculares y Determinación de La Estructura Genético Poblacional de Poblaciones Naturales de Solea Senegalensis (Perciformes: Soleidae), En El Golfo de Cádiz. Tesis Doctoral, Universidad de Cádiz: Cádiz, España, 2004.
- Gold, J.R.; Willis, S.C.; Renshaw, M.A.; Buentello, A.; Walker, H.J.; Puritz, J.B.; Hollenbeck, C.M.; Voelker, G. Phylogenetic Relationships of Tropical Eastern Pacific Snappers (Lutjanidae) Inferred from Mitochondrial DNA Sequences. Syst Biodivers 2015, 13, 916–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha-Olivares A; Sandoval Castillo J Diversidad Mitocondrial y Estructura Genética En Poblaciones Alopátricas Delhuachinango Del Pacífico Lutjanus Peru. Cienc Mar 2003, 29, 197–209.
- Lago, F.C.; Herrero, B.; Vieites, J.M.; Espiñeira, M. Genetic Identification of Horse Mackerel and Related Species in Seafood Products by Means of Forensically Informative Nucleotide Sequencing Methodology. J Agric Food Chem 2011, 59, 2223–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Ferguson, E.; Allard, A.; Mendizabal, M.; Ramos, C. Genetic Structure of the Invasive Nile Tilapia Oreochromis Niloticus (Perciformes, Cichlidae) and Molecular Identification of Tilapia Species in Panama Using Barcode. Panam J Aquat Sci 2022, 17, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi, S.; Andayani, N.; Muttaqin, E.; Simeon, B.M.; Ichsan, M.; Subhan, B.; Madduppa, H. Genetic Connectivity of the Scalloped Hammerhead Shark Sphyrna Lewini across Indonesia and the Western Indian Ocean. PLoS One 2020, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán, H.M.; Beaver, C.E.; Díaz-Ferguson, E. Novel Insights Into the Genetic Population Connectivity of Transient Whale Sharks (Rhincodon Typus) in Pacific Panama Provide Crucial Data for Conservation Efforts. Front Mar Sci 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Ferguson, E.; Herod, J.; Galvez, J.; Moyer, G. Development of Molecular Markers for EDNA Detection of the Invasive African Jewelfish (Hemichromis Letourneuxi): A New Tool for Monitoring Aquatic Invasive Species in National Wildlife Refuges. Management of Biological Invasions 2014, 5, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Ferguson, E.E.; Moyer, G.R. History, Applications, Methodological Issues and Perspectives for the Use of Environmental DNA (EDNA) in Marine and Freshwater Environments. Rev. Biol. Trop. (Int. J. Trop. Biol. ISSN 2014, 62, 1273–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgardo Díaz-Ferguson; Margaret Hunter; Héctor M. Guzmán Genetic Composition and Connectivity of the Antillean Manatee (Trichechus Manatus Manatus) in Panama. Panama Aquatic Mammals 2017, 43, 378–386. [CrossRef]
- Cardeñosa, D. Genetic Identification of Threatened Shark Species in Pet Food and Beauty Care Products. Conservation Genetics 2019, 20, 1383–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, M. V.; Ariede, R.B.; Hata, M.E.; Mastrochirico-Filho, V.A.; Pazo, F. Del; Villanova, G. V.; Mendonça, F.F.; Porto-Foresti, F.; Hashimoto, D.T. Haplotypes Traceability and Genetic Variability of the Breeding Population of Pacu (Piaractus Mesopotamicus) Revealed by Mitochondrial Dna. Genet Mol Biol 2021, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, S.G.; Boyle, M. The Expanding Role of Traceability in Seafood: Tools and Key Initiatives. J Food Sci 2017, 82, A13–A21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Site | Family | Species | Common name | GenBank Accession number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GP _1_SFelipe | Scombridae | Scomberomorus sierra | Pacific Sierra | OQ790166 -OQ790174 |
| Euthynnus affinis | Tuna | OQ844071 | ||
| Carangidae | Caranx vinctus | Cocinero | OQ790077 | |
| Caranx caninus | Pacific Crevalle Jack | OQ801572 | ||
| Centropomus unionensis | Bigeye trevally | OQ850133 | ||
| Caranx caballus | Green Jack | OQ789895 | ||
| Selene peruviana | Peruvian moonfish | OQ843845 | ||
| Haemulidae | Pomadasys panamensis | Panama grunt | OQ789718 | |
| Lobotidae | Lobotes surinamensis* | Atlantic Triple Tail | OQ844072 | |
| Lobotes pacificus | Pacific Triple Tail | OQ844073 | ||
| Serranidae | Mycteroperca xenarcha* | Caribbean grouper | OQ844067 | |
| Hyporthodus acanthistius | Pacific grouper | OQ844070 | ||
| Sphyraenidae | Sphryraena ensis | Pacific barracuda | OQ850073 | |
| Scianidae | Nebris occidentalis | Guabina | OQ843562 | |
| Cynoscion phoxocephalus | Cachema weakfish | OQ843904 | ||
| Lutjanidae | Lutjanus guttatus | Rose spotted snapper | OQ850300 | |
| Lutjanus argentiventris | Yellow snapper | OQ790134- OQ790136 | ||
| Melacanthidae | Caulolatilus affinis | Bighead tilefish | OQ844074 | |
| GP_2_Anton | Scombridae | Scomberomorus sierra | Sierra fish | OQ790166 -OQ790174 |
| Carangidae | Caranx caballus | Green Jack | OQ789895 | |
| Caranx caninus | Pacific Crevalle Jack | OQ801572 | ||
| Selene peruviana | Peruvian Moonfish | OQ843845 | ||
| Centropomidae | Centropomus robalito | Yellowfin Snook | OQ844075 | |
| Lutjanidae | Lutjanus guttatus | Spotted rose snapper | OQ850300 | |
| Scianidae | Cynoscion othonopterus | Gulf weakfish | OQ850144 | |
| Ophioscion scierus | Tuza croaker | OQ848437 | ||
| Paralonchurus dumerilii | Banded croacker | OQ848738 | ||
| Stromateidae | Peprilus medius | Pacific Harvest Fish | OQ848659 | |
| GP_3Coquira | ||||
| Carangidae | Caranx caninus | Pacific crevalle Jack | OQ801572 | |
| Caranx caballus | Green Jack | OQ789895 | ||
| Centropomidae | Centropomus viridis* | Common Snook | ||
| Centropomus medius | Blackfin snook | OQ848755 | ||
| Lutjanidae | Lutjannus gutattus | Rose spotted snapper | OQ850300 | |
| Haemulidae | Haemulopsis leuciscus | Raucous grunt | OQ849145 | |
| Orthopristis chalceus | Brassy grunt | OQ849164 | ||
| Scianidae | Nebris occidentalis | Pacific smalleye croaker | OQ843562 | |
| Cynoscion phoxocephalus | Cachema weakfish | OQ843904 | ||
| Cynoscion leiarchus* | Smooth weak fish | |||
| Larimus pacificus | Pacific drum | OQ849155 | ||
| Guerridae | Gerres simillimus | Yellow fin mojarra | OQ872776 | |
| Lobotidae | Lobotus pacificus | Pacific Triple Tail | OQ844073 | |
| Ariidae | Bagre marinus* | Gafftopsail catfish | ||
| Mugilidade | Mugil curema* | White mullet | ||
| GCH_1-Pedregal | ||||
| Carangidae | Caranx caballus | Green Jack | OQ789895 | |
| Lutjanidae | Lutjanus argentiventris | Yellow snapper | OQ790134- OQ790136 | |
| Lutjanus guttatus | Rose spotted snapper | OQ850300 | ||
| Lutjanus peru | Red Snapper | OQ791284 | ||
| Scombridae | Scomberomorus sierra | Pacific sierra | OQ790166 - OQ790174 | |
| GMon_1-Mutis | ||||
| Scombridae | Scomberomorus sierra | Pacific sierra | OQ790166 - OQ790174 | |
| Scianidae | Cynoscion phoxocephalus | Cachema weakfish | OQ843904 | |
| Stromatidae | Peprilus medius | Pacific Harvest fish | OQ848659 | |
| Lutjanidae | Lutjanus argentiventris | Yellow snapper | OQ790134- OQ790136 | |
| Lutjanus guttatus | Rose spotted snapper | OQ850300 | ||
| GMon_2-Santiago | ||||
| Carangidae | Caranx vinctus | Jack | OQ790077 | |
| Caranx caninus | Pacific Crevalle Jack | OQ801572 | ||
| Caranx caballus | Green Jack | OQ789895 | ||
| Lutjanidae | Lutjanus Colorado | Colorado snapper | OQ801537-OQ801540 | |
| GCH_PixCOIBA | Lutjanidae | Lutjanus guttatus | Rose spotted snapper | OQ850300 |
| Lutjanus peru | Red Snapper | OQ791284 |
| Common name | Species | Familia | Total de secuencias | Haplotype diversity (Hd) | Nucleotide diversity (π) | Tajima’s D |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spotted rose snapper | Lutjanus guttatus | Lutjanidae | 36 | 0.775 | 0.020 | -0.155 |
| Yellow snapper | Lutjanus argentiventris | Lutjanidae | 12 | 0.63 | 0.031 | -2.25** |
| Red snapper |
Lutjanus peru |
Lutjanidae | 17 | 0.86 | 0.010 | -2.17** |
| Pacific Sierra | Scomberomorus sierra | Scombridae | 16 | 0.90 | 0.0045 | -1.09 |
| Green jack | Caranx caballus | Caranjidae | 13 | 0.91 | 0.0039 | -1.26 |
| Pacific crevalle jack | Caranx caninus | Caranjidae | 10 | 0.93 | 0.0038 | -0.86 |
| Lutjanus guttatus | Gulf of Panama | Gulf of Montijo | Gulf of Chiriqui | Overall by species Hudson 2000 Snn P<0.0001 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gulf of Panama | 0.00 | |||
| Gulf of Montijo | 0.087 | 0.00 | ||
| Gulf of Chiriqui | 0.41 | 0.45 | 0.00 | L.guttatus** |
| Coiba-Pixvae | 0.052 | 0.00 | 0.44 | |
| Caranx caballus | ||||
| Gulf of Panama | 0.00 | |||
| Gulf of Montijo | 0.424 | 0.00 | C.caballus (P>0.05 ns) | |
| Gulf of Chiriqui | 0.500 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| Scomberomorus sierra | ||||
| Gulf of Panama | 0.00 | |||
| Gulf of Montijo | 0.0694 | 0.00 | S.sierra (P>0.05 ns) | |
| Gulf of Chiriqui | 0.0614 | -0.058 | 0.00 |
| Species | Primers sequences | Probe name and sequence | Amplicon size |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lutjanus guttatus | L-GATCGGAGGATTCGGGAACT R-GGGTAGACTGTTCACCCAGT |
5’FAM-TCCAGCACCGGCTTCTACTCCA-3´TAMRA | 168bp |
| Lutjanus argentiventris | L-TACTACTCGCCTCCTCTGGA R-TGGTTAGGTCAACAGACGCT |
5´FAM-TCCTGTTCCGGCACCGGCTT- 3´TAMRA | 108bp |
| Caranx caballus | L-TGGGACTGGCTGAACTGTTT R-CCCTGCTAGGTGAAGGGAAA |
5´FAM-TGCCCACGCGGGAGCATCAGT-TAMRA | 97bp |
| Caranx caninus | L-GCTTCTGACTTCTCCCTCCT R-GGCATGGGCAAGATTACCAG |
5´FAM-AGCCTGTTCCAGCTCCGGCT-TAMRA | 116bp |
| Scomberomorus sierra | L-AGCCCTTCTTGGAGATGACC R-TCAGTTTCCAAACCCTCCGA |
5´FAM-ACAATGTAATCGTTACGGCCCATGCC-TAMRA | 109bp |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





