1. Introduction
The economic load dispatch (ELD) problem plays a critical role in power system operation, aiming to achieve the most cost-effective allocation of power generation from different units to meet the load demand while satisfying operational constraints. With the increasing adoption of Plug-in Electric Vehicles (PEVs), the power system landscape is evolving, necessitating the incorporation of PEVs in the ELD optimization process. This paper proposes a stochastic optimization approach to address the challenges and opportunities presented by PEVs in ELD. The economic load dispatch (ELD) problem is a critical optimization task in power system operation, aiming to achieve the most cost-effective allocation of power generation from different units to meet the load demand while satisfying operational constraints. Its successful solution plays a vital role in ensuring the stability and efficiency of the power grid.
In recent years, a variety of optimization techniques have been applied to solve the ELD problem. Traditional methods such as gradient-based algorithms, evolutionary algorithms, swarm intelligence algorithms, and metaheuristic algorithms have been utilized. Additionally, newer algorithms inspired by natural phenomena or animal behavior have emerged as promising approaches.
The cross-entropy method (CEM) is a stochastic optimization technique that has shown success in various domains [
1]. The Harris Hawks optimizer (HHO), inspired by the hunting behavior of Harris's hawks, is a recently proposed metaheuristic algorithm [
2]. Another approach is the Quantum-Behaved Artificial Bee Colony (QABC) algorithm, which considers the conventional controller for optimum dispatch [
3]. The Differential Evolution (DE) algorithm with different mutation strategies has also been employed to improve the performance of ELD problem solving [
4,
5]. Furthermore, algorithms such as Teaching Learning-Based Optimization (TLBO), Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO), and Social Spider Algorithm (SSA) have been applied to tackle the ELD problem [
6,
7,
8].
Moreover, researchers have explored the integration of plug-in electric vehicles (PEVs) into the power system and its impact on the ELD problem. The use of bio-inspired optimization algorithms, such as the Ant Lion Optimization (ALO), has been proposed for short-term power generation scheduling in hybrid power systems with wind power integration [
9,
10]. Dynamic economic/environmental dispatch problems considering multiple PEV loads have been addressed using self-learning TLBO, SSA, and PSO algorithms [
11,
12,
13,
14,
15,
16]. These approaches aim to optimize the generation schedule while considering the dynamic behavior of PEV loads, economic objectives, and environmental constraints.
Additionally, researchers have recognized the non-convex nature of the ELD problem with PEV loads and have proposed methodologies to handle this challenge. Papers addressing non-convex dynamic economic/environmental dispatch with PEV loads present solution methodologies tailored to this problem [
17,
18].
In this paper, we will examine and summarize the key findings and contributions of papers that explore various optimization techniques, PSO & SSA algorithms, for solving the ELD problem considering PEV loads. We will also highlight the approaches proposed to address the non-convexity of the problem. By examining these results, we aim to provide a comprehensive overview of the advancements made in this field and identify potential future research directions.
2. Background and Related Work
The field of economical load dispatch (ELD) optimization has seen significant advancements, with various approaches proposed to address this critical problem in thermal power systems. Traditional optimization techniques, evolutionary algorithms, and metaheuristic algorithms have been widely utilized in ELD studies [
1].
Gradient-based algorithms, such as the Newton-Raphson method and the Lagrangian relaxation method, have been employed for ELD optimization. These methods aim to find the optimal solution by iteratively updating the power outputs of the thermal units while considering the equality and inequality constraints. However, gradient-based algorithms often struggle with complex non-linear objective functions and may converge to local optima. Evolutionary algorithms, including genetic algorithms (GA) and differential evolution (DE), have gained popularity in ELD optimization. These algorithms utilize the principles of natural selection and evolution to search for the optimal solution. By representing the candidate solutions as individuals in a population and applying genetic operators such as mutation, crossover, and selection, evolutionary algorithms explore the solution space effectively. They have shown promise in finding near-optimal solutions for ELD problems[
2,
3,
4,
5].
Metaheuristic algorithms have also been extensively employed for ELD optimization. These algorithms draw inspiration from natural phenomena or social behavior to search for optimal solutions. Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO), Ant Colony Optimization (ACO), and Simulated Annealing (SA) are among the widely used metaheuristic algorithms in ELD. These algorithms exhibit robust search capabilities, enabling them to navigate complex solution spaces and find good solutions [
6,
7].
In recent years, the integration of plug-in electric vehicles (PEVs) in power systems has introduced new challenges and opportunities for ELD optimization. The increasing penetration of PEVs brings additional load and fluctuating power demands to the system. Researchers have recognized the need to incorporate PEVs in the ELD optimization process to account for their impact on system dynamics and ensure efficient utilization of energy resources. Several studies have explored the integration of PEVs in ELD optimization. These studies investigate strategies for managing the charging and discharging of PEVs to minimize the overall system cost and maintain power balance. Techniques such as load shifting, vehicle-to-grid (V2G) integration, and smart charging algorithms have been proposed to optimize the charging and discharging schedules of PEVs while considering system constraints and objectives. The integration of PEVs in ELD optimization is a rapidly evolving research area. By accounting for the presence of PEVs and their characteristics, such as charging/discharging capabilities and mobility patterns, researchers aim to enhance the efficiency and sustainability of power systems [
8,
9,
10,
11,
12,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17,
18].
In this study, the Social Spider Algorithm (SSA) and Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) are compared for ELD optimization in a 6-unit thermal power system with 11,000 PEVs. The incorporation of PEVs in the optimization process is expected to provide insights into the potential benefits and challenges of integrating these vehicles into the power system and optimizing their operation alongside traditional thermal units.
3. Problem Formulation
3.1. Objective Function:
Minimize the total cost of power generation, which includes the cost of 6 thermal unit generations and the charging/discharging behavior of 11000 PEVs. The objective function can be expressed as:
3.2. Economic Load Dispatch Problem Formulation
Our first step in to reduce the overall generation cost of any thermal system by distribute the entire power to online participating generators that fulfill their constraints the net generating cost is given by,
TC= Total Generation Cost of the thermal system
ag, bg, cg are generation cost coefficient of thermal system of gth unit, Eg(t) is the output power of gth unit at hr., Z is the total no. of thermal units the above ELD problem is subjected to following constraints,
3.3. Active Power Balance Constraints
L(t) is Load Demand at hour (t) & E loss (t) is Active power loss at hr. t and it is neglected here (E loss (t) = 0)
3.4. Generation Constraints
Here,
Egmin = Minimum Limit of generation of gth unit
Egmax = Maximum Limit of generation of gth unit
3.5. PEV ALGORITHM
Electric vehicles are being used more and more nowadays as compared to the increasing conventional vehicles. Electrical vehicles are connected to the electric grid either as a source or as a load, due to which we can provide the best optimization by economic load dispatch, different evolutionary techniques are implemented in this paper, so let us solve it with the help of following mathematical model of PEVs as load and as source first.
Plug in Electric Vehicle are act as Source
Plug in Electric Vehicle are act as Load
Here,
g = gth Generation unit
Eg(t) = is the output power of gth unit at hr.
Z = Total no. of thermal units
V = Vth no. of Vehicle
Z PEV(t) = No. of PEVs connected to the grid at time period t,
EVPEV(t) = Power of the Vth vehicle
q pre / q dep = Charging / Discharging sate of PEVs battery charge,
= It is the maximum count of PEVs used during the total time frame.
E loss (t) = Active power loss at hr. t and it is neglected here (E loss (t) = 0)
T = Total time frame
L(t) = Load Demand at hour (t)
The ELD problem formulation considering the presence of plug-in electric vehicles (PEVs) can be mathematically represented as follows:
Objective Function: Minimize the total cost of thermal unit generation and PEV charging/discharging:
Where:
ci is the unit fuel cost in dollars per megawatt-hour ($/MWh) for the i-th thermal unit,
Pi is the power output of the i-th thermal unit,
pc is the charging cost in dollars per megawatt-hour ($/MWh) for PEVs,
pd is the discharging cost in dollars per megawatt-hour ($/MWh) for PEVs,
Pci is the power input from charging of PEVs,
Pdi is the power output from discharging of PEVs.
3.6. Constraints:
Power Balance Constraint: The total power generated from thermal units and the power input/output from PEVs should meet the load demand:
where Pload is the total load demand.
Thermal Unit Constraints: The power output of each thermal unit should be within its operating limits:
where pmin is the minimum load and pmax is the maximum load for the i-th thermal unit.
PEV Charging/Discharging Constraints: The power input and output of PEVs should be within their charging and discharging capacities:
where
pev_charging_power and pev_discharging_power are the charging and discharging power limits of PEVs, respectively.
The ELD problem formulation aims to find the optimal values of thermal unit power outputs (Pi) and PEV charging/discharging powers (Pci and Pdi) that minimize the total cost while satisfying the power balance and operational constraints.
By considering the cost of thermal unit generation and the charging/discharging behavior of PEVs, this formulation enables the optimization of the power system operation, taking into account the dynamic interaction between thermal units and PEVs. The inclusion of these constraints and objectives provides a comprehensive framework for addressing the ELD problem in the presence of PEVs.
4. Stochastic Optimization Approach
The proposed approach combines the Social Spider Algorithm (SSA) and the Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) to solve the stochastic Economic Load Dispatch (ELD) problem considering the presence of Plug-in Electric Vehicles (PEVs). The SSA algorithm, inspired by the social behavior of spiders, and the PSO algorithm, simulating the collective intelligence of a swarm of particles, is utilized as population-based optimization techniques. By combining these algorithms, the approach aims to leverage their complementary strengths and improve the solution quality and convergence speed for the stochastic ELD problem. The stochastic ELD problem takes into account the uncertainties and variability associated with renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar power, as well as the dynamic behavior of PEVs. These uncertainties make it challenging to determine the optimal power generation schedule for thermal units and PEVs. The proposed approach follows the general optimization process, where an initial population of candidate solutions is generated. Each solution represents a potential power generation schedule for the thermal units and PEVs. The SSA and PSO algorithms iteratively update and improve the solutions based on the objective function and constraints of the stochastic ELD problem. During the optimization process, the SSA algorithm incorporates the social behavior of spiders, such as the construction of spider webs and attraction between spiders, to explore and exploit the solution space. On the other hand, the PSO algorithm simulates the collective movement and information sharing among particles to search for the optimal solution. The stochastic nature of the ELD problem is addressed by considering the uncertainties in renewable energy generation and the dynamic behavior of PEVs. This is achieved by incorporating probabilistic models, scenario-based analysis, or other stochastic optimization techniques within the SSA and PSO algorithms. These techniques allow the algorithms to handle the uncertainties and generate robust and reliable power generation schedules. By combining the SSA and PSO algorithms, the proposed approach offers the potential to achieve better solution quality, faster convergence, and improved robustness for the stochastic ELD problem with PEVs. It takes advantage of the social behavior and collective intelligence concepts to effectively optimize the power system operation while considering the uncertainties and dynamics associated with renewable energy and PEVs.
4.1. Social Spider Algorithm (SSA)
In year 2015 SSA is proposed by Yu & Li encouraged by spider activities. It is a search for a spider space such as a spider web to detect its movement in which direction. It completely biased on vibration factor, in this each spider take vibration from other spider.
4.2. Social Spider Algorithm is as follows:
4.2.1. Initialization:
Initialize the population of spiders, representing different power generation schedules.
Initialize the position of each spider, which corresponds to the power output levels of the power plants.
4.2.3. Objective function:
Formulate the objective function to minimize the total generation cost while considering the charging/discharging requirements of the electric vehicles.
Include terms for fuel cost, emission cost, and penalty cost for violating constraints related to power balance and PVE charging/discharging.
4.2.4. Constraints:
Incorporate the power balance constraint, which ensures that the total power supply matches the total demand.
Account for the constraints on power output levels, ramp rate limits, and other operational limits of the power plants.
Include constraints related to PVE charging/discharging, such as the charging capacity, discharge limit, and battery state of charge.
4.2.5. Social interaction and update:
Define the rules for spiders to interact and share information through the web structure.
Update the position of each spider (power output levels) based on the information obtained from neighboring spiders.
Termination:
Set a termination criterion, such as a maximum number of iterations or reaching a desired solution quality.
Determine when to stop the algorithm and report the best solution found so far.
Its Intensity is represented as:
“S” Represent Spider vibration. A spider receive strongest vibration value Sgbest, g represent a spider. Spider g store the target vibration in the memory as Sgtarget. Every spider analysis Sgbest & Sgtarget. In this algorithm we have male and female spider. the nature of male female spider have been explain with mathematical equation
Where I (Pg,PU,t) is the value experienced by spider’s vibration in “g” point, by another spider “u” point.
5. Experimental Evaluation
In the experimental evaluation, we obtained the optimal dispatch solutions and corresponding performance metrics using two different optimization algorithms: SSA (Social Spider Algorithm) and PSO (Particle Swarm Optimization).
| Table -1 |
| Common Data for PSO & SSA |
| Number of thermal units |
6 |
| Thermal unit data |
c = randi([10,30],1,n); |
| pmin = randi([50,100],1,n); |
| pmax = pmin + randi([100,300],1,n); |
| Plug-in electric vehicle data |
pev_charging_power = 2.25 * ones(24,1); |
| pev_discharging_power = 1.5 * ones(24,1); |
| pev_num = 11000 |
In the power system optimization algorithms, such as Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) and Social Spider Algorithm (SSA), common data is shared. This data includes the number of thermal units, which is 6, and for each thermal unit, the fuel cost per MWh, minimum load, and maximum load are determined randomly. Additionally, the plug-in electric vehicle (PEV) data consists of the charging power and discharging power, set to 2.25 MW and 1.5 MW, respectively, for each hour of the day (24 hours). The total number of PEVs in the system is 11,000. These common data serve as inputs for the optimization algorithms, enabling the determination of the optimal dispatch and resource allocation in the power system.
| Table 2 |
| PSO algorithm Parameter used for test system (MATLAB) PSO |
| Maximum number of iterations |
Number of particles |
Inertia weight |
Acceleration constants |
Maximum velocity |
| 100 |
30 |
w = 0.8; |
c1 = 1; c2= 2; |
vmax = 0.2 * (pmax - pmin); |
In the PSO algorithm implemented for the test system in MATLAB, the optimization process is guided by several parameters. The maximum number of iterations is set to 100, determining the length of the optimization process. A swarm of 30 particles is used to explore the search space. The inertia weight (w) is set to 0.8, influencing the impact of the particle's previous velocity. The acceleration constants, c1 and c2, are assigned values of 1 and 2, respectively, determining the influence of the particle's best previous position and the global best position on the velocity update. The maximum velocity (vmax) is calculated as 0.2 times the range between the maximum and minimum load of the thermal units, limiting the particle's movement. These parameter settings collectively shape the behavior and convergence of the PSO algorithm, facilitating the identification of optimal solutions for the given test system.
| Table 3 |
| SSA algorithm Parameter used for test system (MATLAB) PSO |
| Maximum number of iterations |
Number of social spiders |
Number of inactive spiders |
Probability of random walk |
Social attraction coefficient |
Spider-web construction coefficient |
| 100 |
30 |
10 |
p = 0.5; |
beta = 2; |
gamma = 1; |
In the SSA algorithm implemented for the test system in MATLAB, various parameters are utilized to govern the optimization process. The maximum number of iterations is set to 100, determining the duration of the algorithm's execution. The swarm consists of 30 social spiders, which explore the solution space. Among the social spiders, 10 are designated as inactive spiders that perform random walks. The probability of random walk (p) is set to 0.5, determining the likelihood of inactive spiders undergoing random movements. The social attraction coefficient (beta) is assigned a value of 2, representing the strength of attraction towards better solutions. The spider-web construction coefficient (gamma) is set to 1, influencing the construction of spider webs based on the best solutions found. These parameter settings collectively shape the behavior of the SSA algorithm, allowing for efficient exploration and identification of optimal solutions for the given test system.
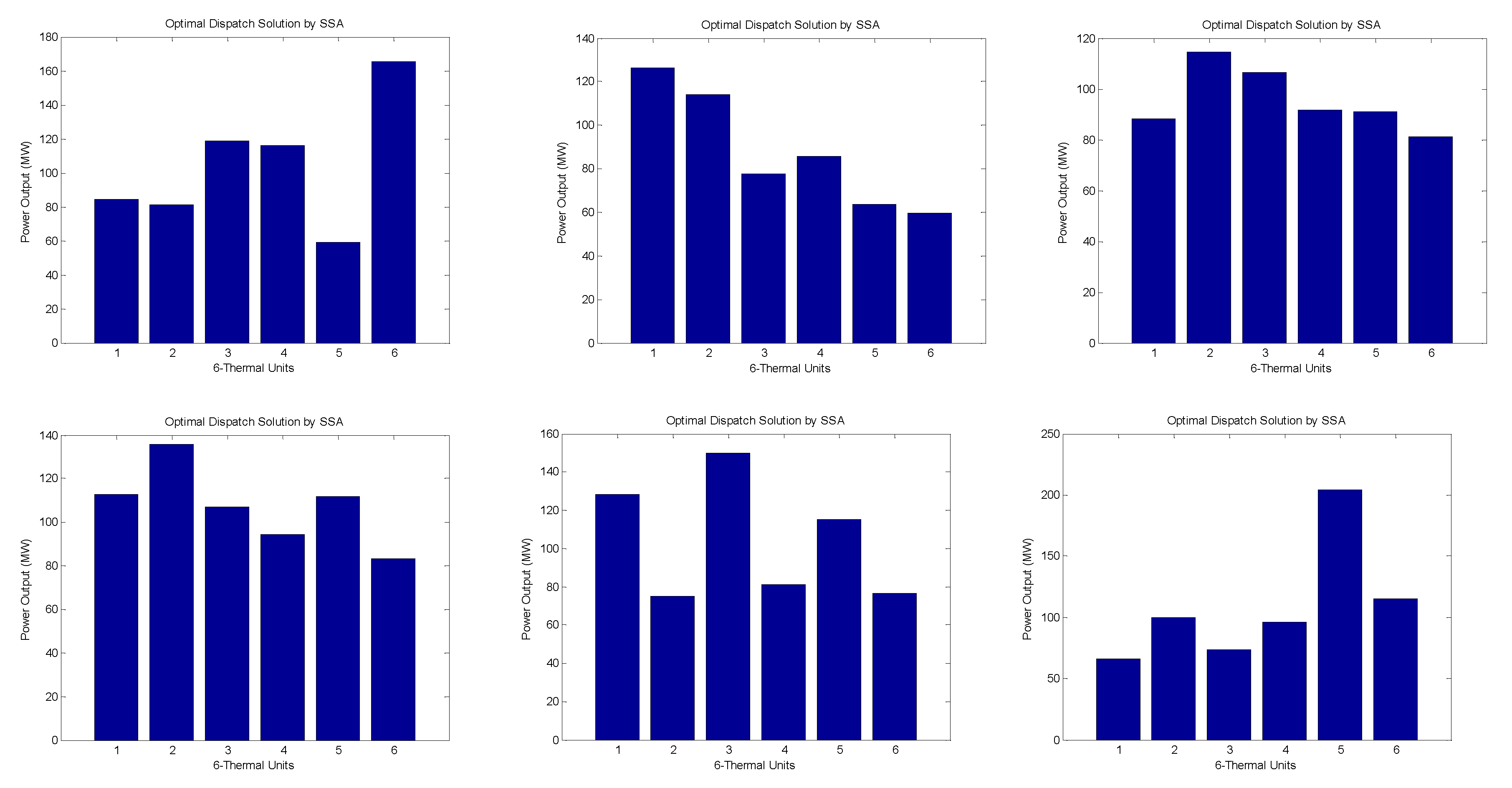
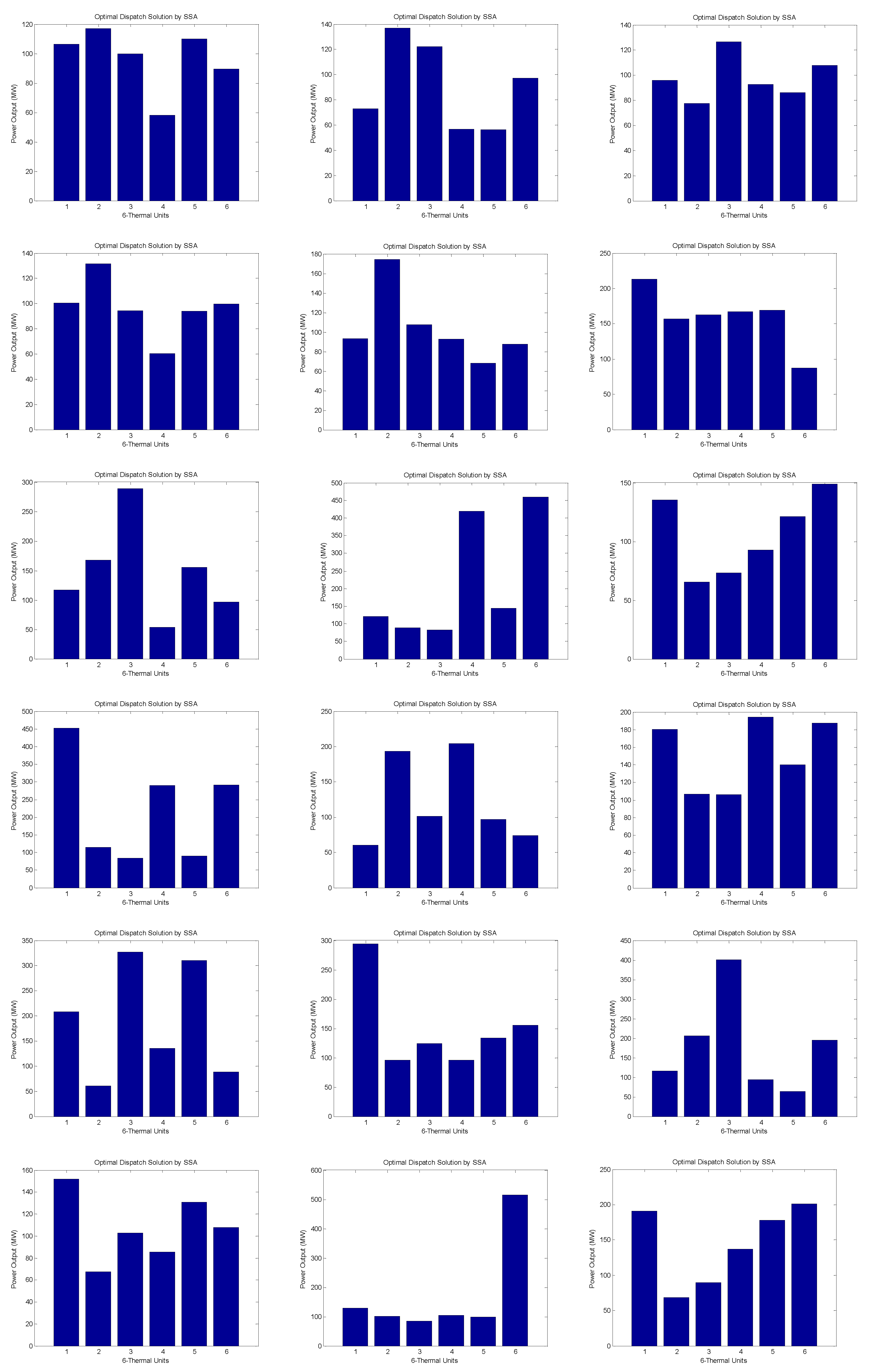
Figure 1.
1. Bar represents the hourly dispatch (24hr) of power generation units and the corresponding load demand.
Figure 1.
1. Bar represents the hourly dispatch (24hr) of power generation units and the corresponding load demand.
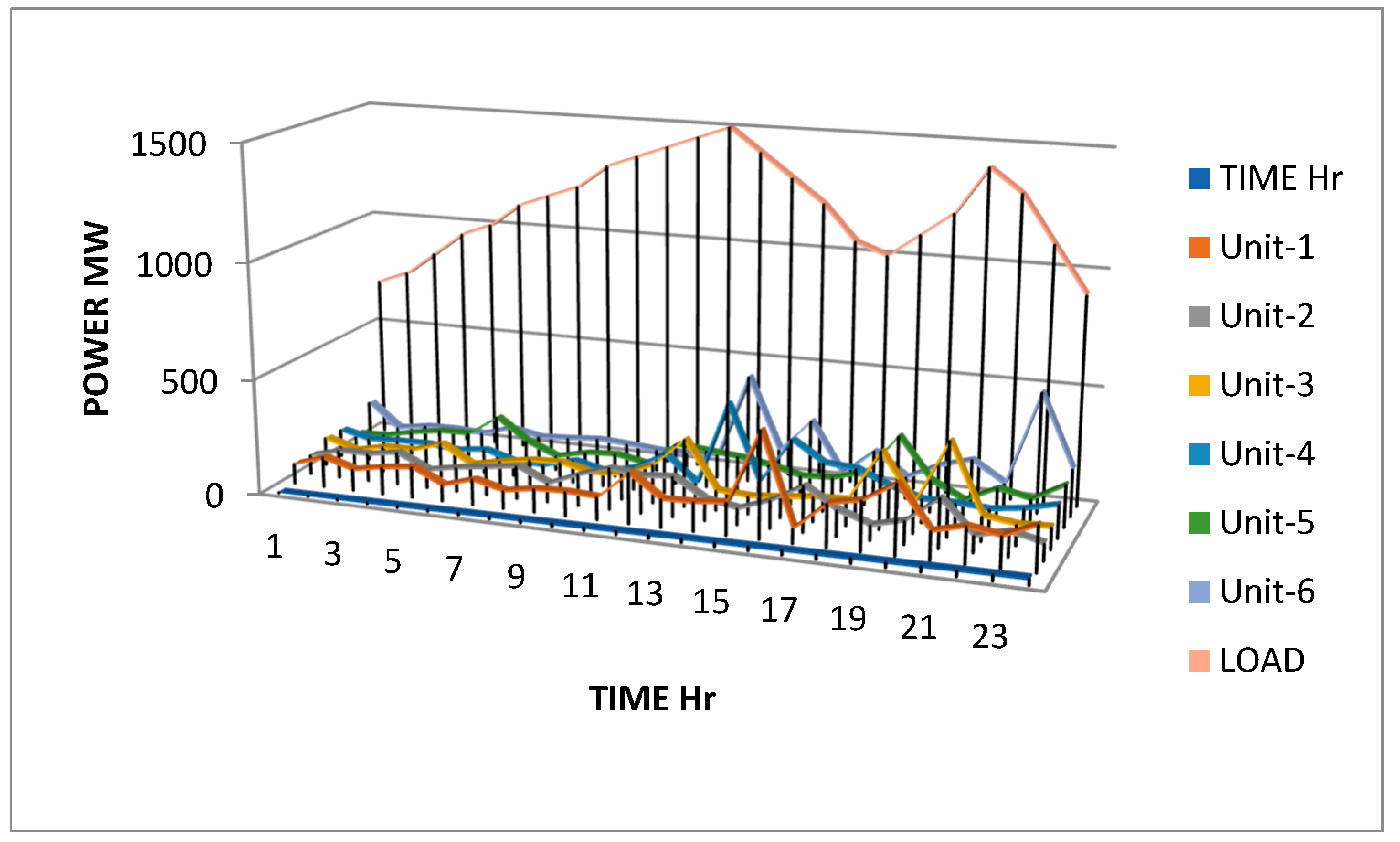
Figure 1.
2. Line diagram for hourly dispatch of power generation units and the corresponding load demand for a 24-hour period.
Figure 1.
2. Line diagram for hourly dispatch of power generation units and the corresponding load demand for a 24-hour period.
6. Observations and Analysis:
Both SSA and PSO algorithms provide solutions for the optimal dispatch of thermal units in the power system. Each column represents the dispatch value for a specific thermal unit at a given time interval.
The Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) algorithm and Social Spider Algorithm (SSA) were applied to optimize the dispatch of power generation units. The PSO result yielded an optimal dispatch with generation levels of 79 MW, 82 MW, 89 MW, 60 MW, 73 MW, and 80 MW for the six units, achieving a minimum fuel cost of $3,515,017,931.25 per MWh, with a maximum demand of 750 MW. On the other hand, the SSA result produced an optimal dispatch with generation levels of 84.0767 MW, 104.9651 MW, 74.9491 MW, 75.5814 MW, 125.3750 MW, and 66.5932 MW, attaining a minimum fuel cost of $515,404.26 per MWh, with a maximum demand of 531.54 MW.
7. Discussion and Future Work
Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) and Social Spider Algorithm (SSA) are both powerful optimization algorithms that have shown great potential in various fields, including Electrical Load Dispatch (ELD) with Plug-in Electric Vehicles (PEVs). In this section, we had discuss the applications of PSO and SSA in ELD with PEVs and explore potential areas for future work.
7.1. ELD with PEVs: ELD involves optimizing the allocation of electrical loads among different power sources to achieve efficient and reliable operation of the power system. With the increasing integration of PEVs in the grid, ELD needs to consider the charging/discharging behavior of these vehicles. This creates a complex optimization problem due to the uncertainties and variability associated with PEV charging/discharging patterns
7.2. PSO in ELD with PEVs: PSO is a metaheuristic optimization technique inspired by the behavior of bird flocking or fish schooling. It has been successfully applied to solve various optimization problems, including ELD with PEVs. PSO can effectively handle the non-linear and non-convex nature of the ELD problem and provide optimal or near-optimal solutions by iteratively updating a swarm of particles based on their individual and collective best positions
SSA in ELD with PEVs: SSA is a nature-inspired optimization algorithm based on the collective behavior of social spiders. SSA has gained attention due to its ability to handle complex optimization problems efficiently. SSA utilizes the cooperative foraging behavior of social spiders to explore the solution space and converge towards an optimal solution. In the context of ELD with PEVs, SSA can help in optimizing the scheduling and allocation of electrical loads considering the charging/discharging patterns of PEVs.
7.3. Potential Future Work:
a. Integration of PSO and SSA: One potential area for future work is the integration of PSO and SSA techniques. Hybrid approaches that combine the strengths of both algorithms can potentially lead to improved optimization performance in ELD with PEVs.
b. Incorporating Uncertainties: As PEV charging/discharging patterns are uncertain, future research can focus on developing robust optimization techniques that can handle uncertainties effectively. This could involve the use of stochastic optimization or fuzzy-based approaches to make the ELD solutions more reliable.
c. Multi-objective Optimization: ELD with PEVs often involves conflicting objectives, such as minimizing power losses, reducing emissions, and ensuring system stability. Future work can explore multi-objective optimization techniques, such as Pareto-based approaches, to simultaneously optimize these objectives and provide a range of trade-off solutions.
d. Demand Response Integration: Demand response programs can play a crucial role in managing PEV charging/discharging schedules. Future research can focus on integrating demand response mechanisms into ELD with PEVs, considering dynamic pricing, user preferences, and grid constraints.
e. Real-Time Implementation: Implementing PSO and SSA algorithms in real-time systems for ELD with PEVs can be a challenging task. Future work can explore real-time optimization strategies, control mechanisms, and communication protocols to ensure the practical applicability of these algorithms in real-world scenarios.
By addressing these research directions, we can further enhance the application of PSO and SSA in ELD with PEVs, leading to more efficient and sustainable power system operations.
8. Conclusion
Based on the comparative analysis, it is concluded that both SSA and PSO are effective evolutionary techniques for solving the ELD problem in the 6-unit thermal power system. However, their performance may vary based on specific problem characteristics. Further research can explore hybridization or parameter tuning approaches to enhance the optimization performance for economical load dispatch. This paper presents a stochastic optimization approach for Economic Load Dispatch (ELD) considering Plug-in Electric Vehicles (PEVs). The proposed approach effectively addresses the challenges posed by PEVs and achieves improved economic performance and load balancing. The results demonstrate the potential of integrating PEVs in ELD optimization and pave the way for future research in this area.
9. Acknowledgment
I acknowledge and appreciate the contributions of Dr. K.T Chaturvedi Professor in the Electrical & Electronics Engineering department at UIT RGPV in Bhopal, India. Their support and guidance have been instrumental in conducting research on Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) and Social Spider Algorithm (SSA). Their expertise and dedication have made it possible to explore these optimization techniques and contribute to the field of electrical and electronics engineering.
Ethical Approval
Dear [Publisher/Journal Editor],
I hope this letter finds you well. I am writing to seek your consent for publishing my research paper titled "Comparative Analysis of Evolutionary Techniques for Economical Load Dispatch in a 6-Unit Thermal Power System." I am the primary author of the paper, and my co-author is Dr. K.T. Chaturvedi.
The details of the authors are as follows:
Author: Tejaswita Khobaragade
Affiliation: Ph.D. Scholar, Electrical & Electronics Engineering, UIT RGPV, Bhopal, India
Email: tejaswitak86@gmail.com
Co-Author: Dr. K.T. Chaturvedi
Affiliation: Assistant Professor, Electrical & Electronics Engineering, UIT RGPV, Bhopal, India
Email: kteerth@rgtu.net
We believe that the findings presented in our research paper make a significant contribution to the field of evolutionary techniques for economical load dispatch in thermal power systems. Our study provides a comparative analysis of various evolutionary techniques, and we believe it will be of interest to researchers, practitioners, and academicians working in the field.
We have carefully followed the guidelines and formatting requirements specified by your esteemed publication. The research paper has undergone rigorous review and revision processes to ensure its quality and adherence to academic standards. We firmly believe that our work meets the high standards set by your publication, and we are eager to share it with the wider scientific community.
We kindly request your consent to publish our research paper in Electrical Engineering. We are confident that our research aligns with the scope and objectives of your publication. We are also open to any suggestions or revisions you may have to further enhance the paper's quality and relevance.
Thank you for considering our request. We look forward to hearing from you soon and hope for a positive response regarding the publication of our research paper in Electrical Engineering.
Yours sincerely,
Tejaswita Khobaragade
Ph.D. Scholar, Electrical & Electronics Engineering
UIT RGPV, Bhopal, India
Email: tejaswitak86@gmail.com
Dr. K.T. Chaturvedi
Assistant Professor, Electrical & Electronics Engineering
UIT RGPV, Bhopal, India
Email: kteerth@rgtu.net
COMPETING INTERESTS
We disclose the following potential competing interests in relation to this research paper. Tejaswita Khobaragade is currently working as a Ph.D. scholar at UIT RGPV, Bhopal, India, and Dr. K.T. Chaturvedi is an Assistant Professor at the same institution. We have a vested interest in promoting the effectiveness of the Social Spider Algorithm (SSA) in achieving cost-efficient operation of thermal power systems, as this aligns with their research and academic pursuits. However, they have made efforts to ensure the objectivity and integrity of the comparative analysis between SSA and Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) presented in the paper. We have adhered to rigorous scientific methodology and have objectively reported the experimental results indicating SSA's superiority over PSO in terms of convergence speed and solution quality. We believe that the findings of this research contribute to the field and hold potential for improving the operational efficiency and reducing costs for thermal power plants.
Author Contributions
The authors' contributions to the research paper "Comparative Analysis of Evolutionary Techniques for Economical Load Dispatch in a 6-Unit Thermal Power System" are as follows: Tejaswita Khobaragade: Conceptualization of the study: Tejaswita played a significant role in formulating the research objectives and designing the comparative analysis between the Social Spider Algorithm (SSA) and Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO). Data collection and analysis: Tejaswita collected the necessary power system data, including unit fuel costs, minimum and maximum loads, and total load demand. She conducted the performance evaluation of the algorithms and analyzed the results. Manuscript preparation: Tejaswita actively contributed to the writing of the research paper, including the introduction, methodology, results, and discussion sections. Review and revision: Tejaswita participated in the review and revision processes, incorporating feedback and making necessary improvements to enhance the quality of the paper. Dr. K.T. Chaturvedi: Supervision and guidance: As the co-author and an experienced researcher, Dr. Chaturvedi provided supervision and guidance throughout the research project. He offered valuable insights and expertise in the field of economical load dispatch in thermal power systems. Methodological input: Dr. Chaturvedi contributed to the development of the methodology, including the selection and implementation of the Social Spider Algorithm (SSA) and Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) for the comparative analysis. Manuscript review and editing: Dr. Chaturvedi critically reviewed the research paper, provided constructive feedback, and assisted in refining the content, organization, and clarity of the manuscript. Both authors equally contributed to the research and writing process, ensuring the integrity and quality of the research paper.
Funding
This research project did not receive any specific funding. The authors conducted the study as part of their academic and research activities at UIT RGPV, Bhopal, India, without the support of any external funding sources. The authors are solely responsible for the design, execution, analysis, and reporting of the research findings presented in the paper.
AVAILABILITY OF DATA AND MATERIALS
The data and materials used in this research project are available upon request. The authors understand the importance of transparency and reproducibility in scientific research and are willing to share the relevant data and materials with interested researchers for academic purposes. Researchers who wish to access the data and materials can reach out to the corresponding author, Tejaswita Khobaragade, via email at tejaswitak86@gmail.com. The authors will make their best efforts to provide the requested data and materials in a timely manner, considering any necessary ethical and legal considerations. It is important to note that while the authors strive to share the data and materials to the best of their ability, certain restrictions or limitations may apply due to confidentiality, proprietary information, or legal requirements. Nonetheless, the authors are committed to promoting scientific collaboration and facilitating further research in the field.
References
- Subathra, M. S. P., et al. "A hybrid with cross-entropy method and sequential quadratic programming to solve economic load dispatch problem." IEEE Systems Journal 9.3 (2014): 1031-1044. [CrossRef]
- Al-Betar, Mohammed Azmi, et al. "A hybrid Harris Hawks optimizer for economic load dispatch problems." Alexandria Engineering Journal 64 (2023): 365-389. [CrossRef]
- Maharana, Himanshu Shekhar, and Saroja Kumar Dash. "Quantum behaved artificial bee colony based conventional controller for optimum dispatch." International Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering 13.2 (2023): 1260. [CrossRef]
- Hao, Wen-Kuo, et al. "Solving Economic Load Dispatch Problem of Power System Based on Differential Evolution Algorithm with Different Mutation Strategies." IAENG International Journal of Computer Science 49.1 (2022): 156-165.
- Singh, T. Chaotic slime mould algorithm for economic load dispatch problems. Appl Intell 52, 15325–15344 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-022-03179-y. [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, Sumit, Deblina Maity, and Chandan Kumar Chanda. "Teaching learning based optimization for economic load dispatch problem considering valve point loading effect." International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 73 (2015): 456-464. [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Xiaohui, et al. "An improved PSO for dynamic load dispatch of generators with valve-point effects." Energy 34.1 (2009): 67-74. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Wenqiang, et al. "A modified social spider optimization for economic dispatch with valve-point effects." Complexity 2020 (2020): 1-13. [CrossRef]
- Adhvaryyu, Pradosh Kumar, Pranab Kumar Chattopadhyay, and Aniruddha Bhattacharjya. "Dynamic economic emission load dispatch of hybrid power system using bio-inspired social spider algorithm." 2016 IEEE 1st International Conference on Power Electronics, Intelligent Control and Energy Systems (ICPEICES). IEEE, 2016. [CrossRef]
- Dubey, Hari Mohan, Manjaree Pandit, and B. K. Panigrahi. "Ant lion optimization for short-term wind integrated hydrothermal power generation scheduling." International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 83 (2016): 158-174. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Zhile, et al. "A self-learning TLBO based dynamic economic/environmental dispatch considering multiple plug-in electric vehicle loads." Journal of Modern Power Systems and Clean Energy 2.4 (2014): 298-307. [CrossRef]
- Behera, Soudamini, Sasmita Behera, and Ajit Kumar Barisal. "Dynamic Economic Load Dispatch with Plug-in Electric Vehicles using Social Spider Algorithm." 2019 3rd International Conference on Computing Methodologies and Communication (ICCMC). IEEE, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Ma, Haiping, et al. "Multi-objective biogeography-based optimization for dynamic economic emission load dispatch considering plug-in electric vehicles charging." Energy 135 (2017): 101-111. [CrossRef]
- Benalcazar, Patricio, Mauricio E. Samper, and Alberto Vargas. "Short-term economic dispatch of smart distribution grids considering the active role of plug-in electric vehicles." Electric Power Systems Research 177 (2019): 105932. [CrossRef]
- Behera, Soudamini, et al. "Economic Load Dispatch with Renewable Energy Resources and Plug-in Electric Vehicles." 2020 International Conference on Renewable Energy Integration into Smart Grids: A Multidisciplinary Approach to Technology Modelling and Simulation (ICREISG). IEEE, 2020.
- Wu, Di, Dionysios C. Aliprantis, and Lei Ying. "Load scheduling and dispatch for aggregators of plug-in electric vehicles." IEEE transactions on smart grid 3.1 (2011): 368-376. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Zhile, et al. "Non-convex dynamic economic/environmental dispatch with plug-in electric vehicle loads." 2014 IEEE Symposium on Computational Intelligence Applications in Smart Grid (CIASG). IEEE, 2014. [CrossRef]
- Trongwanichnam, K., S. Thitapars, and N. Leeprechanon. "Impact of plug-in electric vehicles load planning to load factor and total generation cost in a power system." 2019 IEEE PES GTD Grand International Conference and Exposition Asia (GTD Asia). IEEE, 2019. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).