Submitted:
27 June 2023
Posted:
28 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
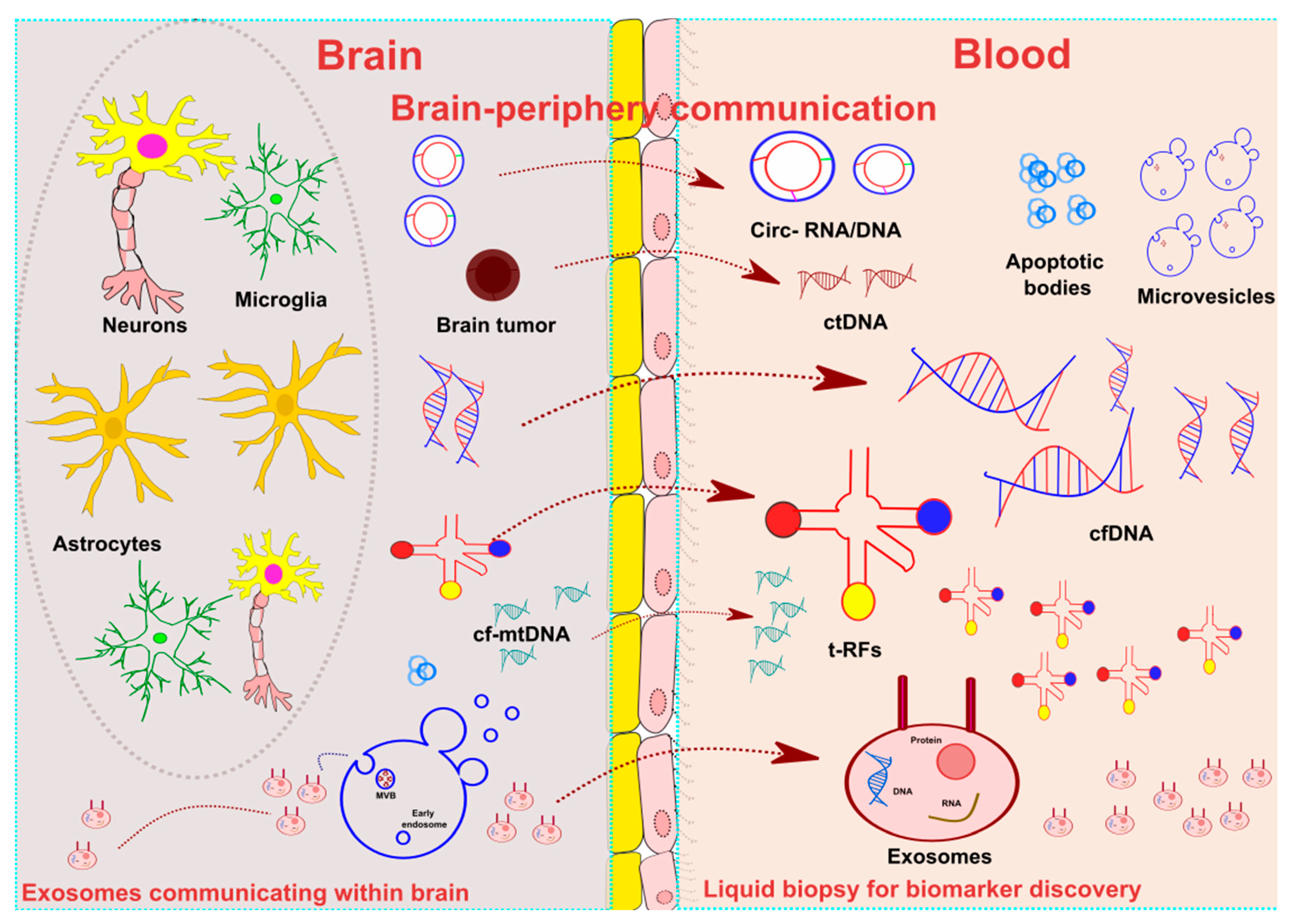
1. Introduction
2. Liquid biopsy: definition and applications
3. Liquid biopsy in neurological diseases
3.1. Alzheimer’s disease
3.2. Parkinson’s disease
3.3. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
3.4. Multiple Sclerosis
3.5. Epilepsy
3.6. Stroke
3.7. Traumatic Brain Injury
3.8. CNS tumors
3.9. Neuroinfectious diseases
4. Conclusions and future directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Loyfer, N.; Magenheim, J.; Peretz, A.; Cann, G.; Bredno, J.; Klochendler, A.; Fox-Fisher, I.; Shabi-Porat, S.; Hecht, M.; Pelet, T.; Moss, J.; et al. A DNA methylation atlas of normal human cell types. Nature 2023, 613, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, L.; Ai, X.; Venkataramani, V.; Kilic, E.; Hermann, D.M.; Majid, A.; Bähr, M.; Doeppner, T.R. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells reduce autophagy in stroke mice by extracellular vesicle transfer of miR-25. J Extracell vesicles 2020, 10, e12024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanninen, K.M.; Bister, N.; Koistinaho, J.; Malm, T. Exosomes as new diagnostic tools in CNS diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta 2016, 1862, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.P.; Breakefield, X.O. Role of exosomes/microvesicles in the nervous system and use in emerging therapies. Front Physiol. 2012, 3, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.E.; Tan, H.S.; Datta, A.; Lai, R.C.; Zhang, H.; Meng, W.; Lim, S.K.; Sze, S.K. Hypoxic tumor cell modulates its microenvironment to enhance angiogenic and metastatic potential by secretion of proteins and exosomes. Mol Cell Proteomics 2010, 9, 1085–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verderio, C.; Cagnoli, C.; Bergami, M.; Francolini, M.; Schenk, U.; Colombo, A.; Riganti, L.; Frassoni, C.; Zuccaro, E.; Danglot, L.; et al. TI-VAMP/VAMP7 is the SNARE of secretory lysosomes contributing to ATP secretion from astrocytes. Biol Cell 2012, 104, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Stoica, B.A.; Loane, D.J.; Yang, M.; Abulwerdi, G.; Khan, N.; Kumar, A.; Thom, S.R.; Faden, A.I. Microglial-derived microparticles mediate neuroinflammation after traumatic brain injury. J Neuroinflammation 2017, 14, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Kan, P.; Zhang, B. The Diagnostic Value of Serum miRNA-221-3p, miRNA-382-5p, and miRNA-4271 in Ischemic Stroke. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2017, 26, 1055–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vajpeyee, A.; Wijatmiko, T.; Vajpeyee, M.; Taywade, O. Cell free DNA: A Novel Predictor of Neurological Outcome after Intravenous Thrombolysis and/or Mechanical Thrombectomy in Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients. Neurointervention 2018, 13, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayhanian, S.; Young, A.M.H.; Ewen, R.L.; Piper, R.J.; Guilfoyle, M.R.; Donnelly, J.; Fernandes, H.M.; Garnett, M.; Smielewski, P.; Czosnyka, M.; et al. Thresholds for identifying pathological intracranial pressure in paediatric traumatic brain injury. Sci Rep. 2019, 9, 3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessoa, L.S.; Heringer, M.; Ferrer, V.P. ctDNA as a cancer biomarker: A broad overview. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2020, 155, 103109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Shen, L.; Luo, M.; Zhang, K.; Li, J.; Yang, Q.; Zhu, F.; Zhou, D.; Zheng, S.; Chen, Y.; et al. Circulating tumor cells: biology and clinical significance. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021, 6, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winek, K.; Lobentanzer, S.; Nadorp, B.; Dubnov, S.; Dames, C.; Jagdmann, S.; Moshitzky, G.; Hotter, B.; Meisel, C.; Greenberg, D.S.; et al. Transfer RNA fragments replace microRNA regulators of the cholinergic poststroke immune blockade. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2020, 117, 32606–32616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Liu, K.; Xiong, Y.; Zhao, C.; Liu, L. Increased expression of fragmented tRNA promoted neuronal necrosis. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.L.; Wang, W.; Jin, Z.B. Circular RNAs in the Central Nervous System. Front Mol Biosci. 2021, 8, 629593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Alexandrov, P.N.; Jaber, V.; Lukiw, W.J. Deficiency in the Ubiquitin Conjugating Enzyme UBE2A in Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) is Linked to Deficits in a Natural Circular miRNA-7 Sponge (circRNA; ciRS-7). Genes (Basel) 2016, 7, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosal, S.; Das, S.; Sen, R.; Basak, P.; Chakrabarti, J. Circ2Traits: a comprehensive database for circular RNA potentially associated with disease and traits. Front Genet. 2013, 4, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, K.; Jin, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, B.; Wu, C.; Xu, H.; Fang, L. MicroRNA-7 inhibits proliferation, migration and invasion of thyroid papillary cancer cells via targeting CKS2. Int J Oncol. 2016, 49, 1531–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Tang, X.; Liu, K.; Hamblin, M.H.; Yin, K.J. Long Noncoding RNA Malat1 Regulates Cerebrovascular Pathologies in Ischemic Stroke. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci. 2017, 37, 1797–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Wang, Q.; Li, J.Q. , Guo, T.; Yu, D. Long non-coding RNA MEG3 promotes cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury through increasing pyroptosis by targeting miR-485/AIM2 axis. Exp Neurol. 2020, 325, 113139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhuang, C.; Chen, L. Exosomal Long Non-Coding RNA Expression from Serum of Patients with Acute Minor Stroke. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2020, 16, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eren, E.; Leoutsakos, J.M.; Troncoso, J.; Lyketsos, C.G.; Oh, E.S.; Kapogiannis, D. Neuronal-Derived EV Biomarkers Track Cognitive Decline in Alzheimer’s Disease. Cells 2022, 11, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, Q.; Chen, Z.B.; Koo, E.H.; Zhong, S. Presymptomatic Increase of an Extracellular RNA in Blood Plasma Associates with the Development of Alzheimer’s Disease. Curr Biol. 2020, 30, 1771–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaswamy, P.; Yadav, R.; Pal, P.K.; Christopher, R. Clinical Application of Circulating MicroRNAs in Parkinson’s Disease: The Challenges and Opportunities as Diagnostic Biomarker. Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2020, 23, 84–97. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, S.; Niu, W.; Xu, F.; Wang, Y.; Hu, S.; Niu, C. Differential expression and significance of miRNAs in plasma extracellular vesicles of patients with Parkinson’s disease. Int J Neurosci. 2022, 132, 673–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otake, K.; Kamiguchi, H.; Hirozane, Y. Identification of biomarkers for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis by comprehensive analysis of exosomal mRNAs in human cerebrospinal fluid. BMC Med Genomics 2019, 12, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joilin, G.; Gray, E.; Thompson, A.G.; Bobeva, Y.; Talbot, K.; Weishaupt, J.; Ludolph, A.; Malaspina, A.; Leigh, P.N.; Newbury, S.F.; et al. Identification of a potential non-coding RNA biomarker signature for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Brain Commun. 2020, 2, fcaa053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, I.; Yabe, I.; Hama, Y.; Uwatoko, H.; Shirai, S.; Matsushima, M.; Utsumi, J.; Sasaki, H.; et al. Evaluation of microRNAs in patients with sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis by liquid biopsy as a disease biomarker (P1.9-027). Neurology 2019, 92, P1.9-027. [Google Scholar]
- Gaitsch, H.; Franklin, R.J.M.; Reich, D.S. Cell-free DNA-based liquid biopsies in neurology. Brain 2023, 146, 1758–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selmaj, I.; Cichalewska, M.; Namiecinska, M.; Galazka, G.; Horzelski, W.; Selmaj, K.W.; Mycko, M.P. Global exosome transcriptome profiling reveals biomarkers for multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol. 2017, 81, 703–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Deshpande, M.; Suhail, H.; Rattan, R.; Giri, S. Targeted Stage-Specific Inflammatory microRNA Profiling in Urine During Disease Progression in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis: Markers of Disease Progression and Drug Response. J neuroimmune Pharmacol Off J Soc NeuroImmune Pharmacol. 2016, 11, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Zhang, H.; Xie, W.; Meng. ; F Zhang, K.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J. Altered microRNA profiles in plasma exosomes from mesial temporal lobe epilepsy with hippocampal sclerosis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 4136–4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitlock, J.H.; Soelter, T.M.; Williams, A.S.; Hardigan, A.A.; Lasseigne, B.N. Liquid biopsies in epilepsy: biomarkers for etiology, diagnosis, prognosis, and therapeutics. Hum Cell 2022, 35, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcatti, M.; Saada, J.; Okereke, I.; Wade, C.E.; Bossmann, S.H.; Motamedi, M.; Szczesny, B. Quantification of Circulating Cell Free Mitochondrial DNA in Extracellular Vesicles with PicoGreen™ in Liquid Biopsies: Fast Assessment of Disease/Trauma Severity. Cells 2021, 10, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sareen, H.; Garrett, C.; Lynch, D.; Powter, B.; Brungs, D.; Cooper, A.; Po, J.; Koh, E.S.; Vessey, J.Y.; McKechnie, S.; et al. The Role of Liquid Biopsies in Detecting Molecular Tumor Biomarkers in Brain Cancer Patients. Cancers (Basel) 2020, 12, 1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauman, M.M.J.; Bouchal, S.M.; Monie, D.D.; Aibaidula, A.; Singh, R.; Parney, I.F. Strategies, considerations, and recent advancements in the development of liquid biopsy for glioblastoma: a step towards individualized medicine in glioblastoma. Neurosurg Focus. 2022, 53, E14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhang, C.; Li, M.; Shen, Y.; Feng, S.; Liu, J.; Li, F.; Hou, L.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, J.; et al. Applications of cerebrospinal fluid circulating tumor DNA in the diagnosis of gliomas. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2020, 50, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, A.A.; Roy, M.; Tellier, B.R.; Ahmad, S. Capnocytophaga canimorsus meningitis diagnosed using next- generation sequencing of microbial cell-free DNA. IDCases 2021, 24, e01126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toribio, L.; Romano, M.; Scott, A.L.; Gonzales, I.; Saavedra, H.; Garcia, H.H.; Shiff, C. For The Cysticercosis Working Group In Peru. Detection of Taenia solium DNA in the Urine of Neurocysticercosis Patients. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2019, 100, 327–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera, I.M.; Kessler, A.; Ting, L.M.; Harawa, V.; Keller, T.; Allen, D.; Njie, M.; Moss, M.; Soko, M.; Ahmadu, A.; et al. Plasma cell-free DNA predicts pediatric cerebral malaria severity. JCI Insight. 2020, 5, e136279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheltens, P.; Blennow, K.; Breteler, M.M.B.; de Strooper, B.; Frisoni, G.B.; Salloway, S.; Van der Flier, W.M. Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet (London, England) 2016, 388, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria Lopez, J.A.; González, H.M.; Léger, G.C. Alzheimer’s disease. Handb Clin Neurol. 2019, 167, 231–255. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Shen, Q.; Xu, S.; Yu, H.; Pei, S.; Zhang, Y.; He, X.; Wang, Q.; Li, D. 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Signatures in Circulating Cell-Free DNA as Diagnostic Biomarkers for Late-Onset Alzheimer’s Disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 2022, 85, 573–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dube, U.; Del-Aguila, J.L.; Li, Z.; Budde, J.P.; Jiang, S.; Hsu, S.; Ibanez, L.; Fernandez, M.V.; Farias, F.; Norton, J.; et al. An atlas of cortical circular RNA expression in Alzheimer disease brains demonstrates clinical and pathological associations. Nat Neurosci. 2019, 22, 1903–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigarré, I.M.; Trombetta, B.A.; Guo, Y.J.; Arnold, S.E.; Carlyle, B.C. IGF2R circular RNA hsa_circ_0131235 expressions in the middle temporal cortex is associated with AD pathology. Brain Behav. 2021, 11, e02048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuscu, C.; Kumar, P.; Kiran, M.; Su, Z.; Malik, A.; Dutta, A. tRNA fragments (tRFs) guide Ago to regulate gene expression post-transcriptionally in a Dicer-independent manner. RNA 2018, 24, 1093–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Lee, I.; Spratt, H.; Fang, X.; Bao, X. tRNA-Derived Fragments in Alzheimer’s Disease: Implications for New Disease Biomarkers and Neuropathological Mechanisms. J Alzheimers Dis. 2021, 79, 793–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poewe, W.; Seppi, K.; Tanner, C.M.; Halliday, G.M.; Brundin, P.; Volkmann, J.; Schrag, A.E.; Lang, A.E. Parkinson disease. Nat Rev Dis Prim. 2017, 3, 17013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolosa, E.; Garrido, A.; Scholz, S.W.; Poewe, W. Challenges in the diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; Pei, F.; Zeng, C.; Yao, Y.; Liao, W.; Zhao, Z. Extracellular Vesicles in Liquid Biopsies: Potential for Disease Diagnosis. Biomed Res Int. 2021, 2021, 6611244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgos, K.; Malenica, I.; Metpally, R.; Courtright, A. , Rakela, B.; Beach, T.; Shill, H.; Adler, C.; Sabbagh, M.; Villa, S.; et al. Profiles of extracellular miRNA in cerebrospinal fluid and serum from patients with Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases correlate with disease status and features of pathology. PLoS One 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlik, P.; Błochowiak, K. The Role of Salivary Biomarkers in the Early Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease and Parkinson’s Disease. Diagnostics (Basel, Switzerland) 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Zheng, Y.; Yu, Y. Urinary kynurenine as a biomarker for Parkinson’s disease. Neurol Sci. 2021, 42, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyle, A.; Brennan, R.; Kurzawa-Akanbi, M.; Yarnall, A.; Thouin, A.; Mollenhauer, B.; Burn, D.; Chinnery, P.F.; Hudson, G. Reduced cerebrospinal fluid mitochondrial DNA is a biomarker for early-stage Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol. 2015, 78, 1000–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardiman, O.; Al-Chalabi, A.; Chio, A.; Corr, E.M.; Logroscino, G.; Robberecht, W.; Shaw, P.J; Simmons, Z.; van den Berg, L.H.; et al. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nat Rev Dis Prim. 2017, 3, 17071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ince, P.G.; Highley, J.R.; Kirby, J.; Wharton, S.B.; Takahashi, H.; Strong, M.J.; Shaw, P.J.; et al. Molecular pathology and genetic advances in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: an emerging molecular pathway and the significance of glial pathology. Acta Neuropathol. 2011, 122, 657–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philips, T.; Robberecht, W. Neuroinflammation in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: role of glial activation in motor neuron disease. Lancet Neurol. 2011, 10, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjoqvist, S.; Otake, K. A pilot study using proximity extension assay of cerebrospinal fluid and its extracellular vesicles identifies novel amyotrophic lateral sclerosis biomarker candidates. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022, 613, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendioroz, M.; Martínez-Merino, L.; Blanco-Luquin, I.; Urdánoz, A.; Roldán, M.; Jericó, I. Liquid biopsy: a new source of candidate biomarkers in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2018, 5, 763–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joilin, G.; Gray, E.; Thompson, A.G.; Bobeva, Y.; Talbot, K.; Weishaupt, J.; Ludolph, A.; Malaspina, A.; Leigh, P.N.; Newbury, S.F.; et al. Identification of a potential non-coding RNA biomarker signature for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Brain Commun. 2020, 2, fcaa053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tur, C.; Carbonell-Mirabent, P.; Cobo-Calvo, Á.; Otero-Romero, S.; Arrambide, G.; Midaglia, L.; Castilló, J.; Vidal-Jordana, Á.; Rodríguez-Acevedo, B.; Zabalza, A.; et al. Association of Early Progression Independent of Relapse Activity With Long-term Disability After a First Demyelinating Event in Multiple Sclerosis. JAMA Neurol. 2023, 80, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iparraguirre, L.; Olaverri, D.; Blasco, T.; Sepúlveda, L.; Castillo-Triviño, T.; Espiño, M.; Costa-Frossard, L.; Prada, Á.; Villar, L.M.; Otaegui, D.; et al. Whole-Transcriptome Analysis in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells from Patients with Lipid-Specific Oligoclonal IgM Band Characterization Reveals Two Circular RNAs and Two Linear RNAs as Biomarkers of Highly Active Disease. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrad, M.F.; Saba, E.S.; Nakib, L.; Khoury, S.J. Exosomes from Subjects with Multiple Sclerosis Express EBV-Derived Proteins and Activate Monocyte-Derived Macrophages. Neurol Neuroimmunol neuroinflammation 2021, 8, e1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Apolito, M.; Rispoli, M.G.; Ajdinaj, P.; Digiovanni, A.; Tomassini, V.; Gentile, L.; De Luca, G. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy or severe multiple sclerosis relapse following COVID-19 vaccine: a diagnostic challenge. Neurol Sci. 2023, 44, 1141–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatchwell, E.; Smith, E.B.; Jalilzadeh, S.; Bruno, C.D.; Taoufik, Y.; Hendel-Chavez, H.; Liblau, R.; Brassat. D.; Martin-Blondel, G.; Wiendl, H.; et al. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy genetic risk variants for pharmacovigilance of immunosuppressant therapies. Front Neurol. 2022, 13, 1016377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngouth, N.; Monaco, M.C.; Walker, L.; Corey, S.; Ikpeama, I.; Fahle, G.; Cortese, I.; Das, S.; Jacobson, S. Comparison of qPCR with ddPCR for the Quantification of JC Polyomavirus in CSF from Patients with Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy. Viruses 2022, 14, 1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beghi, E. The Epidemiology of Epilepsy. Neuroepidemiology 2020, 54, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thijs, R.D. , Surges, R.; O’Brien, T.J.; Sander, J.W. Epilepsy in adults. Lancet (London, England) 2019, 393, 689–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshé, S.L.; Perucca, E.; Ryvlin, P.; Tomson, T. Epilepsy: new advances. Lancet (London, England) 2015, 385, 884–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemian, F.; Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Arsang-Jang, S.; Mirzajani, S.; Fallah, H.; Mehvari Habibabadi, J.; Sayad, A.; Taheri, M. Epilepsy Is Associated with Dysregulation of Long Non-coding RNAs in the Peripheral Blood. Front Mol Biosci. 2019, 6, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins-Ferreira, R.; Leal, B.G.; Costa, P.P. The Potential of Circulating Cell-Free DNA Methylation as an Epilepsy Biomarker. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022, 16, 852151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alapirtti, T.; Jylhävä, J.; Raitanen, J.; Mäkinen, R.; Peltola, J.; Hurme, M.A.; Liimatainen, S. The concentration of cell-free DNA in video-EEG patients is dependent on the epilepsy syndrome and duration of epilepsy. Neurol Res. 2016, 38, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhya, D.; Shetty, A.K. Promise of extracellular vesicles for diagnosis and treatment of epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 2021, 121, 106499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Long, L.; Zeng, C.; Ni, G.; Meng, Y.; Guo, Q.; Chen, Z.; Li, Z.; et al. LncRNA ILF3-AS1 mediated the occurrence of epilepsy through suppressing hippocampal miR-212 expression. Aging (Albany NY) 2020, 12, 8413–8422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cukovic, D.; Bagla, S.; Ukasik, D.; Stemmer, P.M.; Jena, B.P.; Naik, A.R.; Sood, S.; Asano, E.; Luat, A.; Chugani, D.C.; et al. Exosomes in Epilepsy of Tuberous Sclerosis Complex: Carriers of Pro-Inflammatory MicroRNAs. Non-coding RNA 2021, 7, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayo, S.; Gómez-Manjón, I.; Fernández-Martínez, F.J.; Camacho, A.; Martínez, F.; Benito-León, J. CfDNA Measurement as a Diagnostic Tool for the Detection of Brain Somatic Mutations in Refractory Epilepsy. Int J Mol Sci. 2022, 23, 4879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katan, M.; Luft, A. Global Burden of Stroke. Semin Neurol. 2018, 38, 208–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.S.; Tan, Z.X.; Wang, M.M.; Xing, Y.; Dong, F.; Zhang, F. Inhibition of NLRP3 Inflammasome: A Prospective Target for the Treatment of Ischemic Stroke. Front Cell Neurosci. 2020, 14, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Han, B.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, S.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Du, L.; Xu, L.; Wu, F.; et al. Extracellular Vesicle-Mediated Delivery of Circular RNA SCMH1 Promotes Functional Recovery in Rodent and Nonhuman Primate Ischemic Stroke Models. Circulation 2020, 142, 556–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Han, B.; Wu, S.; Yang, L.; Leng, S.; Li, M.; Liao, J.; Wang, G.; Ye, Q.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Circular RNA TLK1 Aggravates Neuronal Injury and Neurological Deficits after Ischemic Stroke via miR-335-3p/TIPARP. J Neurosci. 2019, 39, 7369–7393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, L.; Zhang, L.; Zu, J.; Wang, Z.; Han, B.; Chen, B.; Cheng, M.; Ju, M.; Li, M.; Shu, G.; et al. Circulating Circular RNAs as Biomarkers for the Diagnosis and Prediction of Outcomes in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2020, 51, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Hu, W.; Deng, F.; Chen, S.; Zhu, P.; Wang, M.; Chen, X; Wang, Y. ; Hu, X.; Zhao, B.; et al. Identification of Circular RNA hsa_circ_0001599 as a Novel Biomarker for Large-Artery Atherosclerotic Stroke. DNA Cell Biol. 2021, 40, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, C.A.; Bell, J.M.; Breiding, M.J.; Xu, L. Traumatic Brain Injury-Related Emergency Department Visits, Hospitalizations, and Deaths—United States, 2007 and 2013. Morb Mortal Wkly report Surveill Summ (Washington, DC 2002) 2017, 66, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, S.Y.; Lee, A.Y.W. Traumatic Brain Injuries: Pathophysiology and Potential Therapeutic Targets. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019, 13, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theakstone, A.G.; Brennan, P.M.; Ashton, K.; Czeiter, E.; Jenkinson, M.D.; Syed, K.; Reed, M.J.; Baker, M.J.; CENTER-TBI Participants and Investigators. Vibrational Spectroscopy for the Triage of Traumatic Brain Injury Computed Tomography Priority and Hospital Admissions. J Neurotrauma. 2022, 39, 773–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunda, S.; Zuccato, J.A.; Voisin, M.R.; Wang, J.Z.; Nassiri, F.; Patil, V.; Mansouri, S.; Zadeh, G. Liquid Biomarkers for Improved Diagnosis and Classification of CNS Tumors. Int J Mol Sci. 2021, 22, 4548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapointe, S.; Perry, A.; Butowski, N.A. Primary brain tumours in adults. Lancet 2018, 392, 432–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xu, M.; Shi, G.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, H. Trends and Developments in the Detection of Pathogens in Central Nervous System Infections: A Bibliometric Study. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022, 12, 856845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boruah, A.; Kroopnick, A.; Kim, C.; Thakkar, R.; Dugue, R.; Harrigan, E.; Lipkin, I.; Mishra, N.; Thakur, K. Application of Metagenomic Next-Generation Sequencing in the Diagnosis of Neuroinfectious Diseases (P2-9.004). Neurology 2022, 98, 2866. [Google Scholar]
| Biomarker | Source | Main Findings |
| Alzheimer’s Disease | ||
| ↑ Aβ42 | NDEVs |
|
| PHGDH’s exRNA | Plasma |
|
| Parkinson’s Disease | ||
|
↓miR-19b, miR-29c and miR-133b ↑miR-132 and miR-331-5p |
Blood, CSF and exosomes |
|
|
↑ hsa-miR-30c-2-3p ↓hsa-miR-15b-5p, hsa-miR-138-5p, hsa-miR-106b-3p |
Plasma EVs |
|
| Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis | ||
| CUEDC2 exosomal mRNA | CSF EVs |
|
| hsa-miR-16-5p, hsa-piR-33151 and TRV-AAC4-1.1 | Serum |
|
|
↓ hsa-miR-4299 ↑ hsa-miR-4649-5p |
Plasma |
|
| ↓ hsa-miR-663b and has-miR-4258 | CSF |
|
| Biomarker | Source | Main findings |
| Multiple sclerosis | ||
| EBV-derived cfDNA | CSF/ plasma |
|
| ↓ hsa-miR-196b-5p, hsa-miR-532-5p, hsa-miR-122-5p and hsa-miR-301a-3p | Serum |
|
| ↑ miR-155-5p | CSF/plasma/ urine exosomes |
|
| Epilepsy | ||
| miR-8071 | Plasma exosomes |
|
| miR-654-3p | Blood |
|
| Stroke | ||
| circRNA_0001599 | Plasma |
|
| Traumatic brain injury (TBI) | ||
| ↑ ccf-DNA: mtDNA (mtCOXIII, mtNADI) and nuDNA (nuACTB, nuSIRT1) | Serum |
|
| Biomarker | Source | Main findings |
| CNS tumours | ||
| IDH1-R132H | Blood/ CSF EVs |
|
| miR-2 and miR-15b | CSF |
|
| Tumour suppressor genes-derived ctDNA (TP53 and PTEN). | Blood |
|
| Mutation in RB1 and EGFR ctDNA |
|
|
|
Neuroinfectious diseases Bacterial meningitis |
||
| Mycobacterium tuberculosis cfDNA (IS6110 sequence) | CSF |
|
| Capnocytophaga canimorsus meningitis cfDNA | Blood |
|
| Neurocysticercosis (infection by Taenia solium) | ||
| cf-DNA: pTsol19-gene amplification | Urine/CSF |
|
| Cerebral malaria (infection by Plasmodium falciparum) | ||
| Total cf-DNA: host cfDNA (in response to infection) and parasite cf-DNA | Plasma |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





