1. Introduction
In 2019, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) was identified as the causative agent of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) [
1,
2]. In a short time, the disease spread to other countries, and in March 2020, the World Health Organization (WHO) officially declared it a pandemic [
3]. COVID-19 has a major impact on the respiratory system, with symptoms of flu-like illness that can progress to progressive respiratory infection, acute respiratory distress syndrome, and death. However, the disease can compromise other organs and systems such as the kidneys, leading to different clinical behaviours, laboratory findings, and sequelae [
4,
5].
Kidney involvement in the acute phase is present in 0.5%–15% of this population, and 20%–50% of patients are admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU), with approximately 6% requiring renal substitutive therapy, such as haemodialysis [
6,
7,
8,
9]. The most common renal alterations were increased urea and creatinine levels, which tended to reflect a reduction in the glomerular filtration rate (GFR); alterations in the urinary sediment, such as proteinuria and haematuria; and in more severe cases, a reduction in the urinary volume, or even anuria. Acute kidney injury (AKI) is associated with poor clinical outcome and mortality [
7,
10].
However, part of the population affected by COVID-19 manifested persistent clinical symptoms several systems weeks after the diagnosis of the disease. According to the definition by the National Institute for Health and Care of Excellence, the persistence or appearance of symptoms 4 weeks after the diagnosis of the disease, which cannot be explained by other causes, is called post-COVID syndrome or long COVID [
11,
12,
13,
14,
15]. Long COVID is considered a multisystemic condition, with >200 symptoms described, compromising the health and quality of life of patients [
11,
12].
Kidney injury occurs through multiple mechanisms that are influenced by individual factors such as age and comorbidities, and by factors such as direct viral injury, inflammatory state, hypercoagulability, states of shock and hypovolaemia, endothelial micro- and macrovascular injury, nephrotoxic drugs, and rhabdomyolysis. [
16]. The importance of compromising the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system has also been highlighted considering that angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE-2) is the main receptor for SARS-CoV-2 in human cells. Hence, a trend towards reduced availability of functioning ACE-2, with a consequent reduction in the production of angiotensin 1–7 and a decrease in its anti-inflammatory, vasodilatory, and anti-thrombotic effects has been observed [
17,
18].
Renal alterations resulting from these processes can cause sequelae of varying degrees in long COVID, causing lesions that can last for long periods and are potentially irreversible [
19,
20]. In the face of long COVID-19 conditions, surviving patients, after 30 days of infection, exhibited an increased risk of acute renal failure, a decline in the estimated GFR, and other kidney-related adverse events. The risk and kidney damage increase with the severity of acute infections [
21]. The possibility of developing metabolic syndromes with the onset of diabetes mellitus (DM) and systemic arterial hypertension (SAH) has also been described, which may further contribute to the development of kidney disease considering the strong association of chronic kidney disease (CKD) with these conditions [
22].
By the end of 2022, >861,000 cases were recorded in Pará. According to estimates by the WHO, approximately 10%–20% of the infected population develops some type of sequela. Therefore, the number of affected people who may need care for long COVID is worrying and further overloads the weakened public health system in the Amazon region [
23]. The lack of data and dissemination of the possibility of renal sequelae are worrying factors locally and worldwide [
24]. According to studies by the National Kidney Foundation-Harris Poll, only 17% of Americans are aware of the risks of kidney damage; therefore, little information is available on renal sequelae in patients with long COVID, thus delaying proper diagnosis and treatment [
20].
Therefore, this study aimed to evaluate renal function, alterations, and sequelae evidenced by clinical and laboratory findings. It also aimed to establish the incidence, clinical and laboratory factors, and types of kidney injuries in the affected population, allowing the identification of risk and predictive factors of chronic kidney injury and guiding public policy measures to avoid greater social and economic impacts on the health scenario in the Amazon region and Brazil.
2. Materials and Methods
This prospective, observational, cross-sectional, descriptive, and analytical study was conducted in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. This study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the State University of Pará (UEPA) (Opinion No. 4.252.664) and was conducted between 2020 and 2022, involving clinical and laboratory evaluation and investigation of renal function, as well as analysis of inflammatory markers, in patients with long COVID. All the participants signed an informed consent form (ICF).
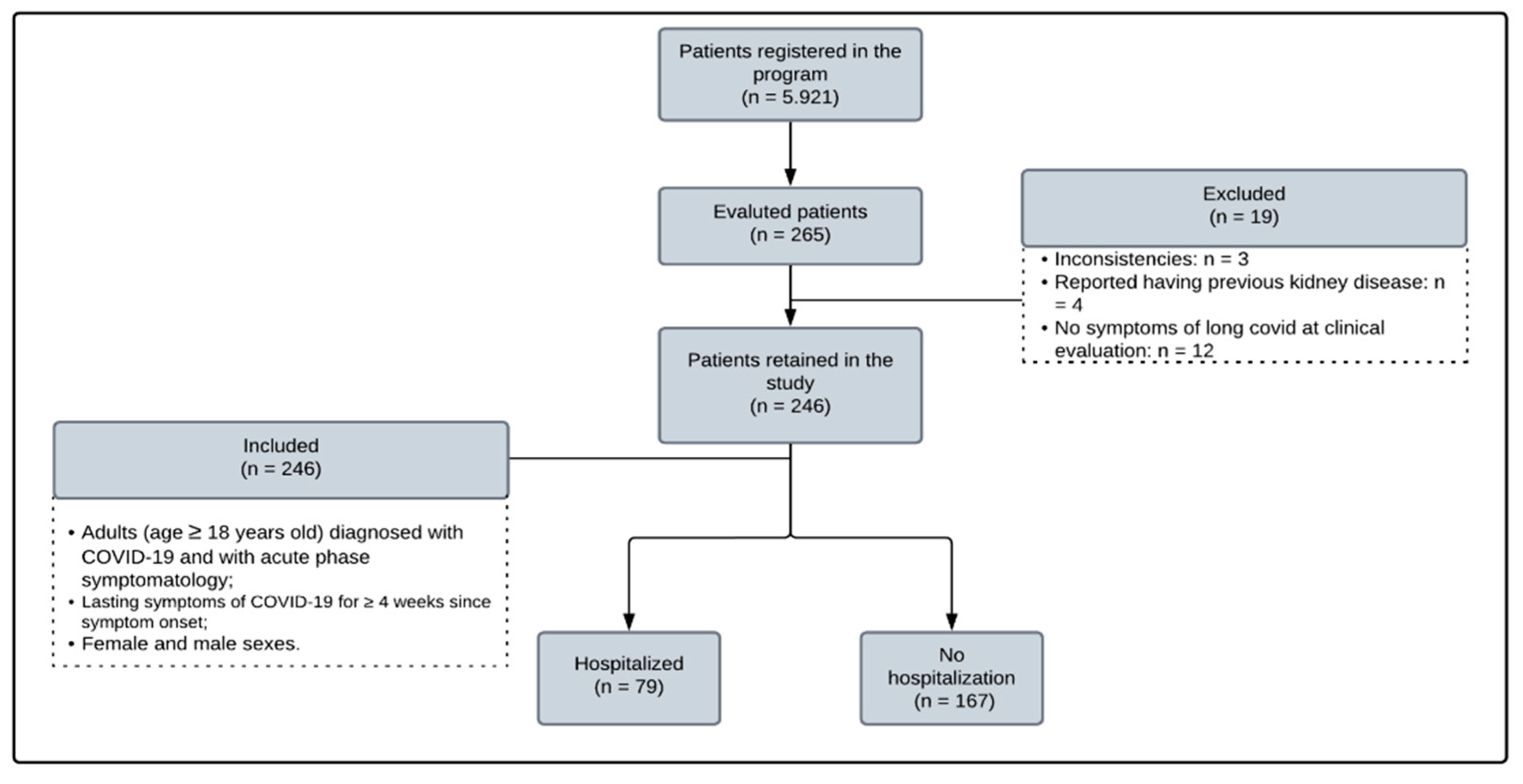
The study was conducted on adult individuals (>18 years old) with a confirmed diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 through a reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test of a throat swab and a history of a clinical picture compatible with COVID-19 not attributable to any other cause. Participants were selected according to the inclusion criteria proposed in the research (
Figure 1) and the order of voluntary registration in a UEPA program aimed at caring for patients with long COVID (Post-COVID Program). The participants only started the follow-up protocol after prior telephone contact 30 days after the first symptoms of infection. Patients with previous reports of CKD and pregnant women were excluded.
Information was extracted from interviews with each individual by completing a specific protocol form (
Appendix A) from which general information, clinical data, anthropometric data, and information including past illnesses, smoking, age, need for hospitalisation, and use of medications such as angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACE) or angiotensin receptor blockers (ARB) were collected. The collected laboratory data broadly evaluated the patient's health with haematimetric, coagulation, metabolic, hepatic, immunological profiles, inflammatory markers, and above all, urea and creatinine levels for better evaluation of renal function, as well as urine tests with active urinary sediment. The Clinical Analysis Laboratory of the State University of Pará was selected for performing the necessary clinical analyses.
Blood samples were collected from patients who had fasted for at least 8 h. This collection consisted of puncturing the peripheral vessel with a needle and collecting samples in 3-ml Vacuette tubes (Greiner Bio-One, Kremsmunster, Austria). Three blood tubes were collected from each patient as follows: (a) tubes containing the anticoagulant ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid for analysis of whole blood, (b) tubes containing separator gel and clot activator for serum analysis, and (c) tubes with citrate for performing coagulation tests. The respective reagent manufacturers adopted standard reference ranges for the tests mentioned above (
Appendix B,
Table A2). Urinalysis was performed using an isolated sample of morning urine and was analysed using reagent strips and microscopy.
GFR was measured to evaluate renal function. For its realisation, indirect markers can be used, such as the determination of creatinine and cystatin C in the blood or the performance of the glomerular filtration rate with indicators such as inulin or other substances [
25]. In this study, serum creatinine dosage was the option for assessing GFR because it was performed in the UEPA reference laboratory and because of its low cost, although it has a low sensitivity for detecting less advanced degrees of renal function loss. To minimise possible difficulties, the Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI) equation, which uses sex, age, and serum creatinine level as the main variables, was used.
The formula proposed by Levey et al. [
26] is as follows:
where k is 0.7 for women and 0.9 for men, α is −0.329 for women and −0.411 for men, min is minimum serum creatinine/k or 1, and max is maximum serum creatinine/k or 1.
After data collection, an electronic spreadsheet was created to store the data using Microsoft Excel 360. For the descriptive representation of the data, tables and graphs were created using the Microsoft Word 360® Software, representing the means, standard deviation, median, interquartile ranges, and minimum and maximum of numerical variables. Categorical variables are presented as absolute and relative percentage frequencies. Data analysis was performed using the Jamovi 2.3.24 program. For all analyses, a significance level of 5% was used (p-value<0.05). To compare quantitative variables such as age (in years), erythrocyte sedimentation rate, ferritin, albumin, creatine phosphokinase, lactic dehydrogenase, pyocytes, haemoglobin, red blood cells, glucose, glycated haemoglobin, and bodymass index (BMI), the mean and median values were evaluated between groups of patients with and without renal alterations. For this analysis, the t-student test was used when the data exhibited a normal distribution, while the Mann-Whitney test was employed when the assumptions of normality were violated according to the Shapiro-Wilk test. The Yates-corrected chi-square test was used to compare the proportion of female sex, age (>60 years), DM, SAH, use of ACEI/ARB variables, hospitalisation, ICU or ward admission, long COVID symptoms, kidneys, protein C reagent positivity, time of long COVID evaluation, and proteinuria due to the presence or absence of renal alteration.
3. Results
Of the 246 selected patients, 155 (64.01%) were female, and 72 (29.63%) were aged >60 years. DM and SAH were the most common comorbidities, reported by 32 (13.01%) and 88 (35.77%) patients, respectively. Only 75 patients previously reported using ACE inhibitors or ARBs, and the mean BMI was 29.24 kg/m2, indicating the prevalence of overweight. Only 79 patients required hospitalisation for the treatment of COVID-19, with only nine in the ICU.
Table 1.
Clinical and laboratory profile of the studied patients.
Table 1.
Clinical and laboratory profile of the studied patients.
| Variable |
n = 246 |
% |
| Female |
155 |
64.01% |
| Male |
91 |
35.99% |
| >60 years old |
72 |
29.63% |
| >18 and <60 years old |
174 |
70.37% |
| Diabetes mellitus |
32 |
13.01% |
| SAH |
88 |
35.77% |
| CVD |
19 |
7.72% |
| Previous lung disease |
16 |
6.50% |
| Non-smoker |
182 |
73.98% |
| Current smoker |
9 |
3.66% |
| Former smoker |
55 |
22.36% |
| ACE inhibitors/ARB use |
75 |
30.49% |
| Hospitalisation |
79 |
32.11% |
| ICU |
9 |
3.66% |
| Otorhinolaryngological |
34 |
13.82% |
| Neurological |
84 |
34.15% |
| Dermatological |
12 |
4.88% |
| Psychiatric |
11 |
4.47% |
| Cardiovascular |
55 |
22.36% |
| Renal |
25 |
10.16% |
| Post SAH |
90 |
36.59% |
| Muscular |
61 |
24.80% |
| Respiratory |
110 |
44.72% |
| Osteoarticular |
20 |
8.13% |
| Gastrointestinal |
16 |
6.50% |
Neurological (n = 84), muscular (n = 61), and respiratory (n = 110) symptoms were the most frequently reported. Renal symptoms were observed in 25 patients. Findings related to SAH stand out, in which 38 new cases emerged and 52 patients with previous hypertension demonstrated worsening blood pressure levels, requiring an increase in the dose of antihypertensive drugs.
Study participants were evaluated at various time points after COVID-19 at 0–3 months, 3–6 months, 6–12 months, and >12 months (
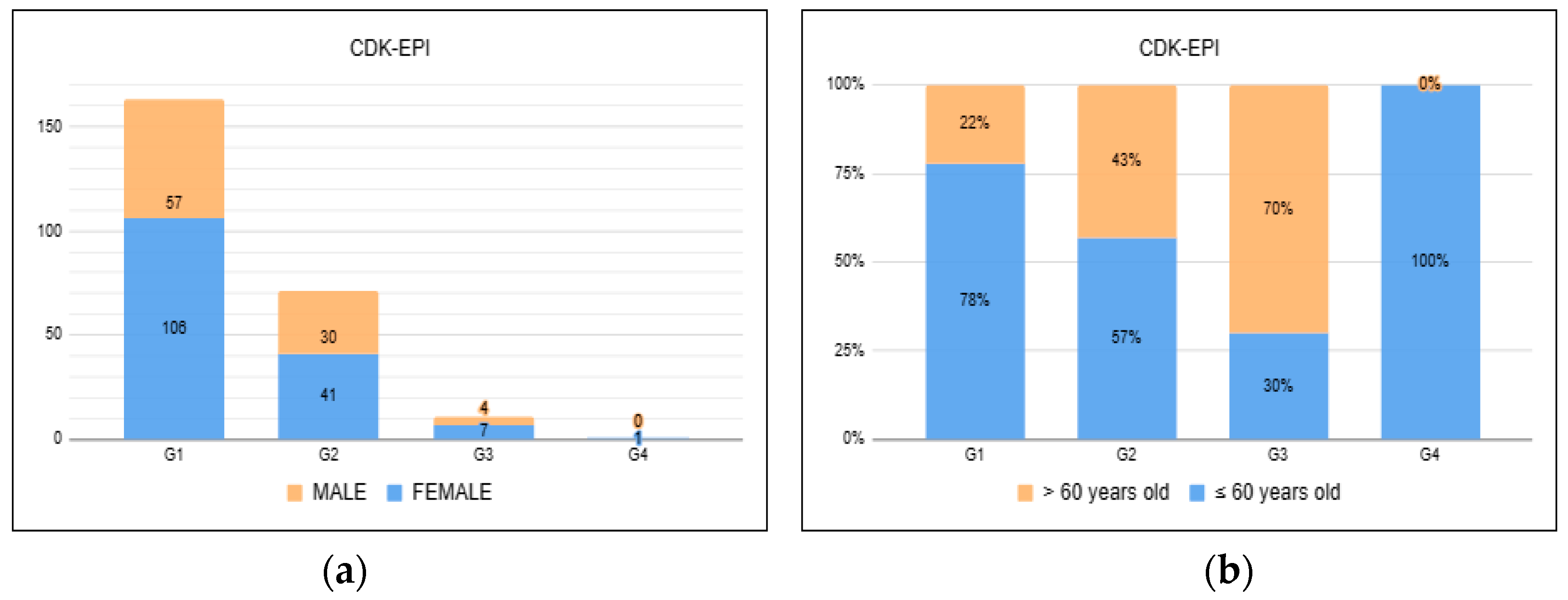
Figure 2). Moreover, 83 (33.74%) patients presented changes in renal function measured through GFR using the CKD-EPI equation, suggesting a slightly lower incidence at 0–3 months.
Regarding metabolic issues, 103 (41.87%) patients had high fasting glycaemia, and of the 188 participants in whom glycated haemoglobin markers were analysed, 122 (64.89%) had alterations, of which 65 (34, 57%) were within the criteria for pre-diabetes and 57 (30.32%) were suggestive of DM according to the WHO criteria [
27].
Table 2.
Qualitative variables in patients evaluated with long COVID.
Table 2.
Qualitative variables in patients evaluated with long COVID.
| Variable |
n = 246 |
% |
| HB>12 |
210 |
85.71% |
| GLYC>100 |
103 |
41.87% |
| Positive CRP |
35 |
14.23% |
| COLT>200 |
120 |
48.78% |
| HDL>50 |
89 |
36.18% |
| TG>150 |
104 |
42.28% |
| PTNS URINE |
|
|
| 0 |
233 |
94.72% |
| 1 |
5 |
2.03% |
| 2 |
6 |
2.44% |
| 3 |
2 |
0.81% |
| HB URINE |
|
|
| 0 |
229 |
93.09% |
| 1 |
10 |
4.07% |
| 2 |
4 |
1.63% |
| 3 |
3 |
1.22% |
| GLYC URINE |
|
|
| 0 |
228 |
92.68% |
| 1 |
2 |
0.81% |
| 2 |
1 |
0.41% |
| 3 |
12 |
4.88% |
| 4 |
3 |
1.22% |
| GFR <90 ml/min |
83 |
33.74% |
| Long COVID time (months) |
|
|
| 0 to 3m |
59 |
23.98% |
| >3 and <6m |
59 |
23.98% |
| >6 and <12m |
60 |
24.39% |
| >12m |
68 |
27.64% |
| Glycated Hb |
|
|
| Normal |
66 |
35.11% |
| Prediabetes |
65 |
34.57% |
| Diabetes |
57 |
30.32% |
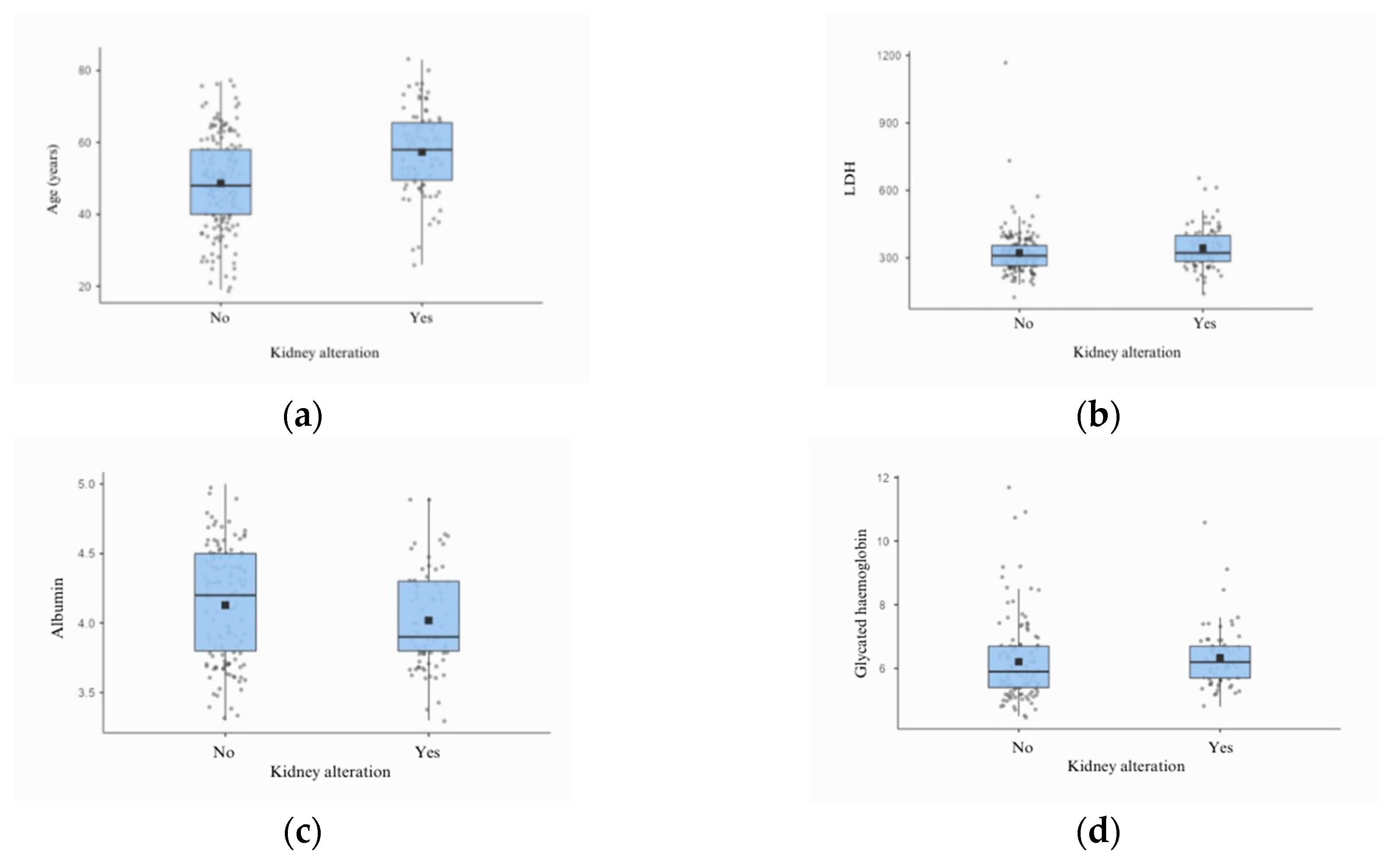
In the analysis of clinical and laboratory data related to renal function, 35 (14.23%) patients had a positive PCR test, and insignificant alterations in the urinary sediment occurred in <7% of the cases. A trend towards low albumin levels was also observed in the group that presented with alterations in GFR, as well as higher levels of LDH and glycated haemoglobin.
Table 3.
Clinical data correlated with renal function.
Table 3.
Clinical data correlated with renal function.
| Variable |
No kidney Alteration, n (%) |
With Kidney Alteration, n (%) |
p-Value |
| Female sex |
106 (65%) |
49 (59%) |
0.43* |
| Age (>60 years) |
35 (21.60%) |
37 (45.68%) |
0.00019* |
| DM |
21 (12.8%) |
11 (13.2%) |
0.99* |
| SAH |
56 (34.4%) |
34 (40.9%) |
0.38* |
| CVD |
12 (7.3%) |
7 (8.4%) |
0.96* |
| ACE inhibitors/ARB use |
44 (26.9%) |
31 (37.3%) |
0.12* |
| Hospitalisation |
48 (29.4%) |
31 (37.3%) |
0.26* |
| ICU |
5 (3.1%) |
4 (4.8%) |
0.49** |
| Nursery |
42 (25.7%) |
27 (32.5%) |
0.33* |
| Long COVID symptoms |
163 (100%) |
83 (100%) |
– |
| Renal |
14 (8.6%) |
11 (13.2%) |
0.35* |
| Positive long COVID |
21 (12.8%) |
14 (16.8%) |
0.42* |
| Time long COVID |
|
|
0.20** |
| 0–3m |
45 (27.6%) |
14 (16.8%) |
|
| >3 m and <6 m |
37 (22.7%) |
23 (27.7%) |
|
| >6 m and <12 m |
46 (28.2%) |
22 (26.5%) |
|
| >12 m |
35 (21.5%) |
24 28.9%) |
|
| PTNS |
|
|
0.55** |
| 0 |
154 (94.5%) |
79 (95.2%) |
|
| 1 |
4 (2.4%) |
1 (1.2%) |
|
| 2 |
3 (1.8%) |
3 (3.6%) |
|
| 3 |
2 (1.2%) |
0 (0%) |
|
Table 4.
Laboratory data correlated with renal function.
Table 4.
Laboratory data correlated with renal function.
| Variable |
No Kidney Alteration |
With Kidney Alteration |
p-Value |
| Median |
AIQ |
Median |
AIQ |
| Age (years)a
|
48.6 |
12,9 |
57.3 |
11.7 |
0.0000** |
| ESR |
31 |
(32.500) |
34 |
(32.000) |
0.749* |
| ferritin |
134 |
(192.250) |
130 |
(124.000) |
0.594* |
| albumin |
4.2 |
(0,7) |
3.9 |
(0,5) |
0.053* |
| CPK |
81.5 |
(63.500) |
88.5 |
(84.000) |
0.247* |
| DHL |
309 |
(90.000) |
321.5 |
(115.250) |
0.036* |
| pYoc |
3 |
92.000) |
3 |
(2.500) |
0.589* |
| Hba
|
13.2 |
(1.23) |
13.3 |
(1,49) |
0.552** |
| hcs |
0 |
(2.000) |
0 |
(2.500) |
0.762* |
| glyc |
0 |
(0) |
0 |
(0) |
0.995* |
| HbGlyc |
5.9 |
(1.300) |
6.2 |
(1.000) |
0.049* |
| BMI |
28 |
(7.500) |
28 |
(6.000) |
0.149* |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
4. Discussion
SARS-CoV-2 infection is now recognised not only as a respiratory tract condition but also as a multiorgan syndrome that commonly leads to AKI [
28]. The persistence of symptoms after the acute phase of the disease can lead to potential sequelae in different organs and systems, which refers to the so-called long COVID [
29,
12]. Data on renal dysfunction in patients with long COVID remain scarce and require further study [
24].
Our study included 246 patients (155 women, 174 aged 18–59 years). Of the patients, 79 required hospitalization during the acute phase of COVID-19; however, they demonstrated no kidney injury outcomes. The most frequently reported symptoms in long COVID include neurological, muscular, and respiratory symptoms. Furthermore, regarding the presence of comorbidities, we identified 32 patients with a previous diagnosis of DM and 88 patients with SAH; 100 patients had a BMI of >30 kg/m2. Alterations in renal function through GFR were identified in 83 patients, with a statistically significant relationship observed in patients aged >60 years. However, the findings related to changes in urinary sediment proved to be of little relevance in the sample, where proteinuria, haematuria, and glycosuria were present in <7% of the patients and indicated no relationship with GFR changes.
Evidence in the literature demonstrates that kidney injury occurs in patients with >12 months of long COVID [
11,
30]. This perspective corroborates the findings of this study, in which kidney injury was present at all evaluated periods. These data demonstrate the potential of renal sequelae developed by patients with long COVID, known to have a multifactorial cause related to the maintenance of inflammatory factors, intrinsic tubular damage, and incomplete resolution of the condition, causing an impact on morbidity and the health system, considering the increase in number of patients with chronic non-communicable diseases such as CKD [
31,
32,
33].
A statistically relevant relationship between changes in renal function and patients aged >60 years was demonstrated using GFR, which is in line with studies on long COVID [
34]. Of the 83 patients who had impaired renal function, 71 had a GFR between <90 ml/min and ≥60 ml/min. What the literature brings so far regarding long COVID is the perpetuation of changes compatible with a decline in GFR, with the most frequent range being G2 [
30] consistent with our findings.
In the literature, DM and SAH were also the most reported comorbidities in individuals who developed long COVID, and the development of these conditions was also identified in some previously healthy patients with post-COVID syndrome [
13,
32,
35,
36]. This perspective is worrisome because hyperglycaemia is known to cause kidney damage and complications, with genetic, haemodynamic, and metabolic factors related to its pathophysiology [
37,
38]. Regarding BMI, the association between obesity and severe cases of COVID-19 in the acute phase is well known; therefore, obesity has a greater potential for sequelae and the development of long COVID-19 [
39].
Laboratory data revealed a significant correlation between LDH levels and kidney damage (p = 0.036) and glycated haemoglobin levels (p = 0.049). A trend towards an association between albumin levels (p = 0.053) was also observed. These aspects suggest possible associations already identified in other studies, indicating that LDH levels are closely related to inflammation and hypercoagulability states [
32,
40]. Evidence points to a tendency towards lower levels of serum albumin in long COVID owing to cellular hypercatabolism, which leads to a reduction in circulating albumin levels [
40]. The higher levels of glycated haemoglobin in this study are consistent with data in the literature, as several studies have demonstrated an increased incidence of DM in the long COVID phase [
41,
42,
43]. This is concerning because of the high incidence of this disease worldwide and its impact on healthcare systems [
44,
45].
Figure 3.
Boxplot presenting the list of variables that correlated with changes in glomerular filtration rate.
Figure 3.
Boxplot presenting the list of variables that correlated with changes in glomerular filtration rate.
As for the use of medications, 75 patients used medications such as ACE inhibitors and ARBs. The possibility of worse clinical and renal outcomes in patients using these medications has been described in the literature because of the suspicion of positive regulation of ACE2 and the consequent increase in viral load [
31,
46]. This would also influence the production of angiotensin 1-7, which has antagonistic actions on angiotensin II, such as vasodilation and antiproliferative actions [
47]. However, in our study, this association was not observed, which is in line with recent findings in the literature [
48,
49,
50].
This study has some limitations. The availability of information such as the previous renal function of these patients and details regarding hospitalisation, considering the need for ventilatory support, drugs used, and even the development of AKI, makes it difficult to understand the process of renal illness. The follow-up of these patients for a longer period could provide greater support for assessing the evolution of renal function in patients with long COVID. However, our data are greatly valuable to the medical and scientific community, as they allowed us to identify which patients with long COVID are at risk of developing kidney damage for a period of >12 months after the acute phase of the disease. The elderly population and those with glycaemic alterations have been identified as being at a greater risk of developing such alterations, and monitoring of renal function should be more comprehensive in such individuals. Therefore, further studies are warranted.
5. Conclusions
Kidney injury in patients with long COVID in this study was observed in one-third of the population studied, with no significant differences between groups with comorbidities, use of medications such as ACE inhibitors and ARBs, need for hospitalisation, and even evaluation time after the acute phase, indicating that kidney damage can persist for >12 months after contact with SARS-CoV-2. Moreover, the elderly population and those who developed glycaemic alterations were at a greater risk of renal dysfunction with long COVID. Therefore, we must be attentive to laboratory findings related to the outcomes of renal injury, such as LDH, glycated haemoglobin, and serum albumin levels.
The lack of similar investigations in the Amazon region emphasises the importance of this study. These findings reinforce the need to establish programs that include renal evaluation in the follow-up of patients with long COVID, in a more comprehensive way, since even young people without comorbidities present alterations suggestive of renal disease. Thus, the implementation of therapeutic measures and health strategies aimed at reducing the medium- and long-term impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic on the health of the population in the Amazon region and worldwide may be related to better prognoses.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.M.C.C.A., I.G.V., R.N.R.R. and P.D.L.L.; methodology, G.M.C.C.A., I.G.V., R.N.R.R. and P.D.L.L.; formal analysis and investigation, G.M.C.C.A. and L.F.M.F.; resources, J.R.S. and L.F.M.F.; data curation, G.M.C.C.A., S.S.X., L.F.M.F. and P.D.L.L.; writing—original draft preparation, G.M.C.C.A; validation, J.R.S., J.A.S.Q., L.F.M.F. and P.D.L.L.; writing—review and editing, G.M.C.C.A., D.C.M, J.R.S., J.A.S.Q., L.F.M.F. and P.D.L.L.; visualization, supervision and project administration, J.A.S.Q., L.F.M.F. and P.D.L.L.; funding acquisition, L.F.M.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Amazon Foundation for Research Support (FAPESPA), grant number #006/2020, the Secretary of Science, Technology, and Higher, Professional, and Technological Education (SECTET), grant number #09/2021, the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior—Brazil (CAPES), grant number ‘Notice n◦ 13/2020’ and the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico—Brazil, grant number ‘INCT:406360/2022-7’.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee of the State University of Pará (protocol code no. 4.252.664 / 1 September 2020) for human studies.
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent has been obtained from the patients to publish this paper.
Data Availability Statement
The data supporting the study findings are available upon request from the corresponding author, L.F.M.F. The data are not publicly available because they contain information that could compromise the privacy of the participants.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Federal University of Pará for this publication through PROPESP/UFPA (Programa de Apoio a Publicação Qualificada).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the study design; collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; writing of the manuscript; or decision to publish the results.
Appendix A
POST-COVID NEPHROLOGICAL PROTOCOL
1. AGE: RACE:
2. GENDER ( ) FEM ( ) MAL
3. CONFIRMATORY EXAMINATION: DATE:
4. COMORBIDITIES:
( )DIABETES MELLITUS
( )SYSTEMIC ARTERIAL HYPERTENSION
( )CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE
( )OVERWHEIGHT/OBESITY BMI: _________
( ) COPD /ASTHMA/PNEUMOPATHY
( )VASCULOPATHY
( ) SMOKING
( ) OTHERS : ___________
5. USED ACEI OR ARB DURING ILLNESS: ( ) YES ( ) NO
6. NEED FOR HOSPITALIZATION ( ) YES ( ) NO
7. NEED FOR HEMODIALYSIS DURING HOSPITALIZATION ( ) YES ( ) NO
7. INFORMATIONS ABOUT MEDICAL TREATMENT DURING COVID-19
_________________________________________________
8. CURRENT SYMPTOMS
( ) SAH / ARTERIAL PRESSURE: ________
( ) HEMATURIA
( ) EDEMA
( ) PROTEINURIA
( ) OTHERS ___________
9. CURRENT TREATMENTS: ____________________
10. NEED FOR FOLLOW-UP WITH NEPHROLOGIST ( ) YES ( ) NO
11. LABORATORY
Table A1.
Laboratory parameters
Table A1.
Laboratory parameters
| |
DATE |
| HEMOGRAM |
|
| TGP/TG0 |
|
| ALKALINE PHOSPHATASE |
|
| GAMMA GT |
|
| UREA |
|
| CREATININE |
|
| ESR |
|
| RCP |
|
| ColT/HDL/LDL |
|
| TRIGLYCERIDES |
|
| GLUCOSE |
|
| FERRITIN |
|
| CPK |
|
| SODIUM |
|
| POTASSIUM |
|
| LDH |
|
| aPTT/PT |
|
| ALBUMIN |
|
| URINE TEST |
|
| Protein URINE |
|
| RedBloodCels URINE |
|
| Gluc URINE |
|
| GLYCATEDHEMOG |
|
OBSERVATIONS:
REFERRAL:
Appendix B
Table A2.
Reference range (adult men and women) of laboratory parameters.
Table A2.
Reference range (adult men and women) of laboratory parameters.
| Exam |
Min |
Max |
Measure |
| Haemoglobin |
13,5 |
18,0 |
g/dl |
| Haematocrit |
40,0 |
54,0 |
% |
| Leukocytes |
5,000 |
10,000 |
mm |
| Erythrocyte Sedimentation rate (ESR) |
0 |
20 |
mm |
| Prothrombin Time (PT) |
70 |
180 |
% |
| Activated Partial Thromboplastin (APTT) |
24 |
39 |
seconds |
| Glycated Haemoglobin |
4,8 |
5,9 |
% |
| C-Reactive Protein * |
Negative |
Positive |
|
| Glucose |
65 |
99 |
mg/dl |
| Total Cholesterol |
- |
200 |
mg/dl |
| HDL |
60 |
- |
mg/dl |
| LDL |
- |
100 |
mg/dl |
| Triglycerides |
- |
150 |
mg/dl |
| TGO |
- |
38 |
U/L |
| TGP |
- |
41 |
U/L |
| Alkaline Phosphatase |
65 |
300 |
U/L |
| Gamma GT |
11 |
50 |
U/L |
| Urea |
15 |
45 |
mg/dl |
| Creatinine |
0,4 |
1,3 |
mg/dl |
| Calcium |
8,5 |
10,5 |
mg/dl |
| Iron |
65 |
175 |
ug/dL |
| Ferritin |
50 |
300 |
mg |
| Potassium |
3,5 |
5,5 |
mEq/L |
| Sodium |
134 |
149 |
mEq/L |
| Creatine phosphokinase (CPK) |
- |
195 |
U/L |
| Creatine phosphokinase MB |
- |
25 |
U/L |
| Lactic dehydrogenase(LDH) |
230 |
460 |
U/L |
| Albumin |
3,5 |
4,8 |
g/dL |
| Leukocytes urine |
- |
4 |
field |
| Red blood cells urine |
- |
2 |
field |
| Proteins urine |
- |
- |
field |
References
- McMichael, T.M.; Currie, D.W.; Clark, S.; Pogosjans, S.; Kay, M.; Schwartz, N.G.; Lewis, J.; Baer, A.; Kawakami, V.; Lukoff, M.D.; et al. Epidemiology of Covid-19 in a Long-Term Care Facility in King County, Washington. N Engl J Med 2020, 382, 2005–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lippi, G.; Favaloro, E.J. D-Dimer Is Associated with Severity of Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Pooled Analysis. ThrombHaemost 2020, 120, 876–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.-R.; Cao, Q.-D.; Hong, Z.-S.; Tan, Y.-Y.; Chen, S.-D.; Jin, H.-J.; Tan, K.-S.; Wang, D.-Y.; Yan, Y. The Origin, Transmission and Clinical Therapies on Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Outbreak – an Update on the Status. Mil Med Res 2020, 7, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabarre, P.; Dumas, G.; Dupont, T.; Darmon, M.; Azoulay, E.; Zafrani, L. Acute Kidney Injury in Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19. Intensive Care Med 2020, 46, 1339–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagliardi, I.; Patella, G.; Michael, A.; Serra, R.; Provenzano, M.; Andreucci, M. COVID-19 and the Kidney: From Epidemiology to Clinical Practice. J Clin Med 2020, 9, 2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acute Kidney Injury in Patients Hospitalized with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A Single-Center Retrospective Observational Study. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da XueXueBao 2021, 41, 157–163. [CrossRef]
- Carriazo, S.; Kanbay, M.; Ortiz, A. Kidney Disease and Electrolytes in COVID-19: More than Meets the Eye. Clinical Kidney Journal 2020, 13, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Luo, R.; Wang, K.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Z.; Dong, L.; Li, J.; Yao, Y.; Ge, S.; Xu, G. Kidney Disease Is Associated with In-Hospital Death of Patients with COVID-19. Kidney Int 2020, 97, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moledina, D.G.; Simonov, M.; Yamamoto, Y.; Alausa, J.; Arora, T.; Biswas, A.; Cantley, L.G.; Ghazi, L.; Greenberg, J.H.; Hinchcliff, M.; et al. The Association of COVID-19 With Acute Kidney Injury Independent of Severity of Illness: A Multicenter Cohort Study. Am J Kidney Dis 2021, 77, 490–499e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kormann, R.; Jacquot, A.; Alla, A.; Corbel, A.; Koszutski, M.; Voirin, P.; Garcia Parrilla, M.; Bevilacqua, S.; Schvoerer, E.; Gueant, J.-L.; et al. Coronavirus Disease 2019: Acute Fanconi Syndrome Precedes Acute Kidney Injury. Clin Kidney J 2020, 13, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, C.; Shibata, S.; Kishi, T.; Morimoto, S.; Mogi, M.; Yamamoto, K.; Kobayashi, K.; Tanaka, M.; Asayama, K.; Yamamoto, E.; et al. Long COVID and Hypertension-Related Disorders: A Report from the Japanese Society of Hypertension Project Team on COVID-19. Hypertens Res 2023, 46, 601–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, H.E.; McCorkell, L.; Vogel, J.M.; Topol, E.J. Long COVID: Major Findings, Mechanisms and Recommendations. Nat Rev Microbiol 2023, 21, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19). Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019 (accessed on 4 June 2023).
- Brito-Zerón, P.; Acar-Denizli, N.; Romão, VC; Armagan, B.; Seror, R.; Carubbi, F.; Melchor, S.; Priori, R.; Valim, V.; Retamozo, S. Post-COVID-19 syndrome in patients with primary Sjögren’s syndrome after acute SARS-CoV-2 infection. Clin. Exp. Reumatol 2021, 39 Supl 133, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimeno-Almazán, A.; Pallarés, J.G.; Buendía-Romero, Á.; Martínez-Cava, A.; Franco-López, F.; Sánchez-AlcarazMartínez, B.J.; Bernal-Morel, E.; Courel-Ibáñez, J. Post-COVID-19 Syndrome and the Potential Benefits of Exercise. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2021, 18, 5329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti, C.; Waldman, M.; Zaza, G.; Riella, L.V.; Cravedi, P. COVID-19 and the Kidneys: An Update. Front Med (Lausanne) 2020, 7, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadian, E.; HosseiniyanKhatibi, S.M.; RaziSoofiyani, S.; Abediazar, S.; Shoja, M.M.; Ardalan, M.; ZununiVahed, S. Covid-19 and Kidney Injury: Pathophysiology and Molecular Mechanisms. Rev Med Virol 2021, 31, e2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumbers, E.R.; Head, R.; Smith, G.R.; Delforce, S.J.; Jarrott, B.; H. Martin, J.; Pringle, K.G. The Interacting Physiology of COVID-19 and the Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone System: Key Agents for Treatment. Pharmacol Res Perspect 2022, 10, e00917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecly, I.M.D.; Azevedo, R.B.; Muxfeldt, E.S.; Botelho, B.G.; Albuquerque, G.G.; Diniz, P.H.P.; Silva, R.; Rodrigues, C.I.S. A Review of Covid-19 and Acute Kidney Injury: From Pathophysiology to Clinical Results. J Bras Nefrol 2021, 43, 551–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LONG, J.D.; STROHBEHN, I.; SAWTELL, R.; BHATTACHARYYA, R.; SISE, M.E. COVID-19 Survival and Its Impact on Chronic Kidney Disease. Transl Res 2022, 241, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowe, B.; Xie, Y.; Xu, E.; Al-Aly, Z. Kidney Outcomes in Long COVID. J Am SocNephrol 2021, 32, 2851–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covid longa podedeixarsequelas que durammuitosmeses. Available online: https://revistapesquisa.fapesp.br/covid-longa-pode-deixar-sequelas-que-duram-muitos-meses/ (accessed on 4 June 2023).
- Covid-19 Casos e Óbitos. Available online: https://infoms.saude.gov.br/extensions/covid-19_html/covid-19_html.html (accessed on 4 June 2023).
- Tan, B.W.L.; Tan, B.W.Q.; Tan, A.L.M.; Schriver, E.R.; Gutiérrez-Sacristán, A.; Das, P.; Yuan, W.; Hutch, M.R.; García Barrio, N.; Pedrera Jimenez, M.; et al. Long-Term Kidney Function Recovery and Mortality after COVID-19-Associated Acute Kidney Injury: An International Multi-Centre Observational Cohort Study. eClinicalMedicine 2023, 55, 101724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inker, L.A.; Eneanya, N.D.; Coresh, J.; Tighiouart, H.; Wang, D.; Sang, Y.; Crews, D.C.; Doria, A.; Estrella, M.M.; Froissart, M.; et al. New Creatinine- and Cystatin C–Based Equations to Estimate GFR without Race. N Engl J Med 2021, 385, 1737–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levey, A.S.; Stevens, L.A. Estimating GFR Using the CKD Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI) Creatinine Equation: More Accurate GFR Estimates, Lower CKD Prevalence Estimates, and Better Risk Predictions. Am J Kidney Dis 2010, 55, 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organization, WH. Global Reporton Diabetes; Organização Mundial da Saúde: Genebra, Suíça, 2016; p. 83. [Google Scholar]
- Ramakrishnan, R.K.; Kashour, T.; Hamid, Q.; Halwani, R.; Tleyjeh, I.M. Unraveling the Mystery Surrounding Post-Acute Sequelae of COVID-19. Front Immunol 2021, 12, 686029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechner-Scott, J.; Levy, M.; Hawkes, C.; Yeh, A.; Giovannoni, G. Long COVID or Post COVID-19 Syndrome. MultSclerRelatDisord 2021, 55, 103268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Huang, L.; Cui, D.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Shang, L.; Fan, G.; Cao, B. Association of Acute Kidney Injury with 1-Year Outcome of Kidney Function in Hospital Survivors with COVID-19: A Cohort Study. EBioMedicine 2022, 76, 103817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahalingasivam, V.; Su, G.; Iwagami, M.; Davids, M.R.; Wetmore, J.B.; Nitsch, D. COVID-19 and Kidney Disease: Insights from Epidemiology to Inform Clinical Practice. Nat Rev Nephrol 2022, 18, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copur, S.; Berkkan, M.; Basile, C.; Tuttle, K.; Kanbay, M. Post-Acute COVID-19 Syndrome and Kidney Diseases: What Do We Know? J Nephrol 2022, 35, 795–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yende, S.; Parikh, C.R. Long COVID and Kidney Disease. Nat Rev Nephrol 2021, 17, 792–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long-haulers COVID podemestaremrisco de doença renal grave | CIDRAP. Available online: https://www.cidrap.umn.edu/covid-long-haulers-may-be-risk-severe-kidney-disease (accessed on 4 June 2023).
- Bai, F.; Tomasoni, D.; Falcinella, C.; Barbanotti, D.; Castoldi, R.; Mulè, G.; Augello, M.; Mondatore, D.; Allegrini, M.; Cona, A.; et al. Female Gender Is Associated with Long COVID Syndrome: A Prospective Cohort Study. ClinMicrobiol Infect 2022, 28, 611.e9–611e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, P.F. da; Carvalho, L.V.B. de; Henriques, C.; Correa, M.J.M. Rede de informações e comunicaçãosobre a exposiçãoao SARS-CoV-2 emtrabalhadores no Brasil: informe 10. 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Morais, BA.; Rodrigues, GM.; Santos, WL. Complicaçõesrenaisrelacionadas a lesõesglomerularesocasionadasporhiperglicemiaempacientes com Diabetes Mellitus descompensada. Rev Bras InterdiscipSaúde 2022, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Azevedo, G.; Felizardo, J.R.; Moser, M.P.; Savi, D.C. Fisiopatologia e diagnóstico da nefropatiadiabética: umarevisãointegrativa / Physiopathologyanddiagnosisofdiabeticnephropathy: anintegrative review. Brazilian Journal of Health Review 2022, 5, 3615–3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, J.R. Implicações da obesidadenaocorrência de sequelas Pós-Covid-19. Trabalho de Conclusão de Curso, UniversidadeEstadualPaulista, São Paulo, 31 de janeiro de 2023.
- Pasini, E.; Corsetti, G.; Romano, C.; Scarabelli, T.M.; Chen-Scarabelli, C.; Saravolatz, L.; Dioguardi, F.S. Serum Metabolic Profile in Patients With Long-Covid (PASC) Syndrome: Clinical Implications. Front Med (Lausanne) 2021, 8, 714426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathmann, W.; Kuss, O.; Kostev, K. Incidence of Newly Diagnosed Diabetes after Covid-19. Diabetologia 2022, 65, 949–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montefusco, L.; Ben Nasr, M.; D’Addio, F.; Loretelli, C.; Rossi, A.; Pastore, I.; Daniele, G.; Abdelsalam, A.; Maestroni, A.; Dell’Acqua, M.; et al. Acute and Long-Term Disruption of Glycometabolic Control after SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Nat Metab 2021, 3, 774–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezel-Potts, E.; Douiri, A.; Sun, X.; Chowienczyk, P.J.; Shah, A.M.; Gulliford, M.C. Cardiometabolic Outcomes up to 12 Months after COVID-19 Infection. A Matched Cohort Study in the UK. PLoS Med 2022, 19, e1004052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, K.M.V.; Staimez, L.R. Rising Diabetes Diagnosis in Long COVID. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2022, 10, 298–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Al-Aly, Z. Risks and Burdens of Incident Diabetes in Long COVID: A Cohort Study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2022, 10, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsampasian, V.; Corballis, N.; Vassiliou, V.S. Renin–Angiotensin–Aldosterone Inhibitors and COVID-19 Infection. CurrHypertens Rep 2022, 24, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Wysocki, J.; William, J.; Soler, M.J.; Cokic, I.; Batlle, D. Glomerular Localization and Expression of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 and Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme: Implications for Albuminuria in Diabetes: Implications for Albuminuria in Diabetes. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol 2006, 17, 3067–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, K.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, Q.; Li, W.; Yang, S.; Zhao, X.; et al. Association of Hypertension and Antihypertensive Treatment with COVID-19 Mortality: A Retrospective Observational Study. Eur Heart J 2020, 41, 2058–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancia, G.; Rea, F.; Ludergnani, M.; Apolone, G.; Corrao, G. Renin–Angiotensin–Aldosterone System Blockers and the Risk of Covid-19. N Engl J Med 2020, NEJMoa2006923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, H.R.; Adhikari, S.; Pulgarin, C.; Troxel, A.B.; Iturrate, E.; Johnson, S.B.; Hausvater, A.; Newman, J.D.; Berger, J.S.; Bangalore, S.; et al. Renin–Angiotensin–Aldosterone System Inhibitors and Risk of Covid-19. N Engl J Med 2020, 382, 2441–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).