Submitted:
27 June 2023
Posted:
27 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
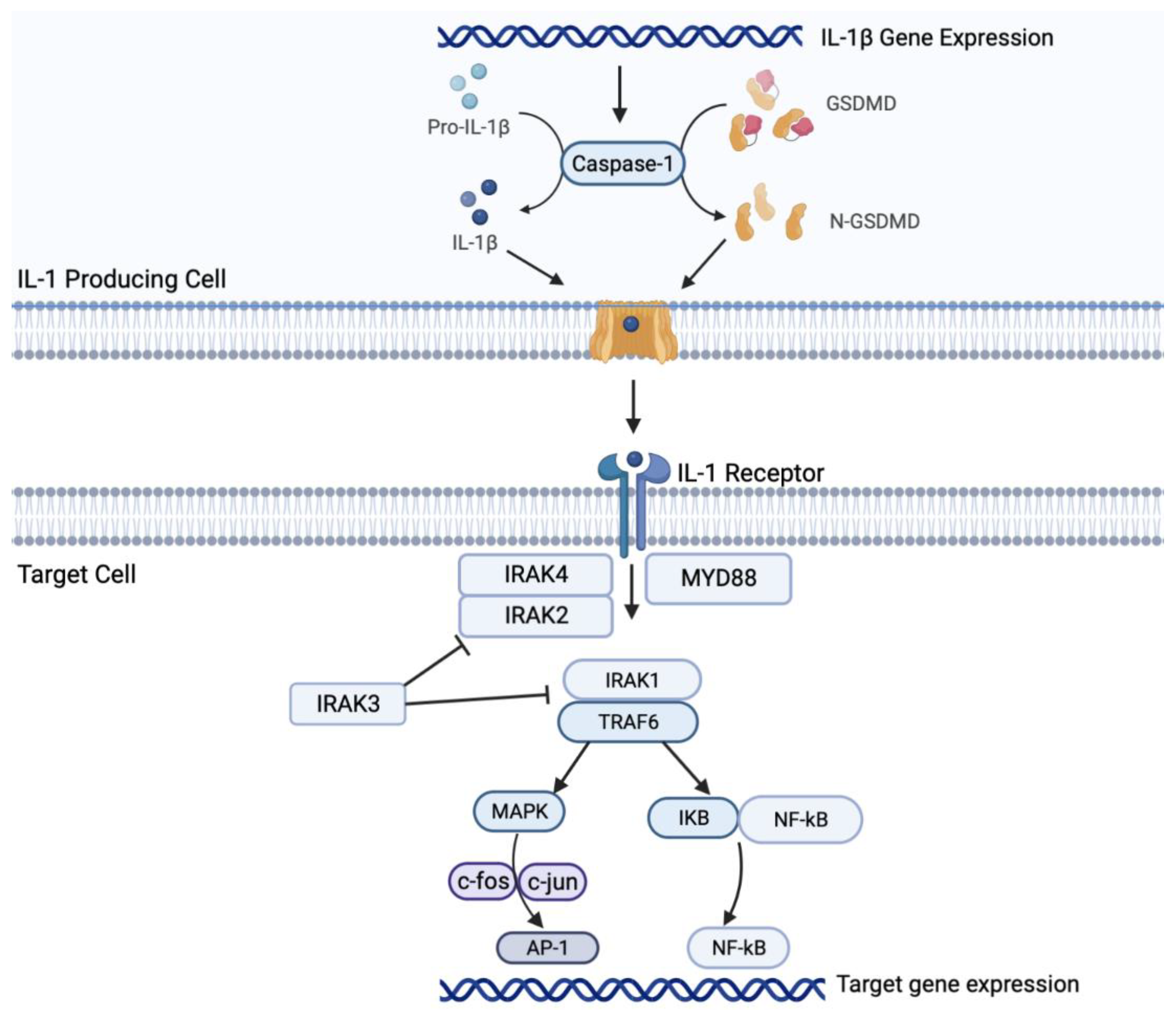
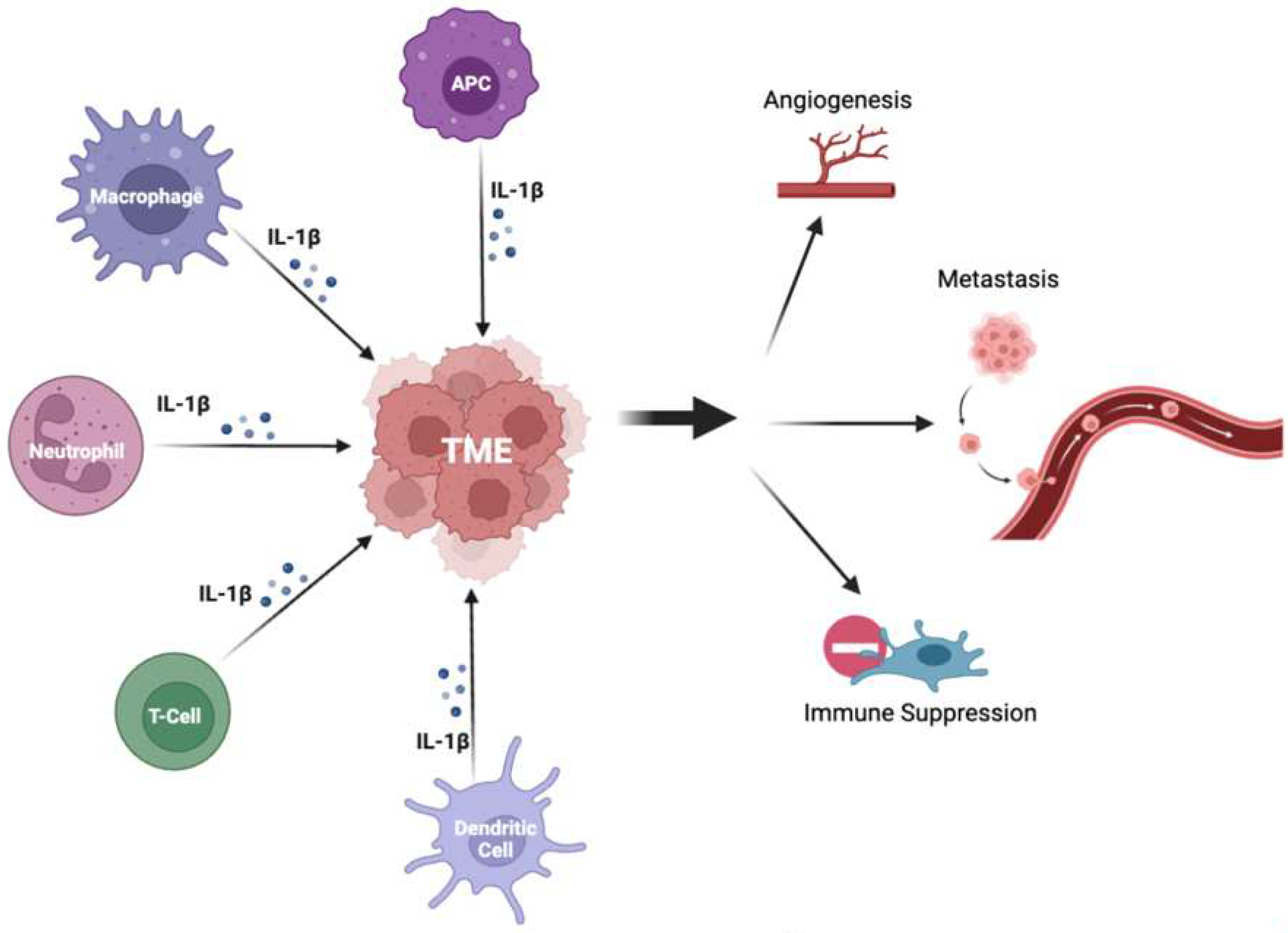
Il-1β signaling in NSCLC
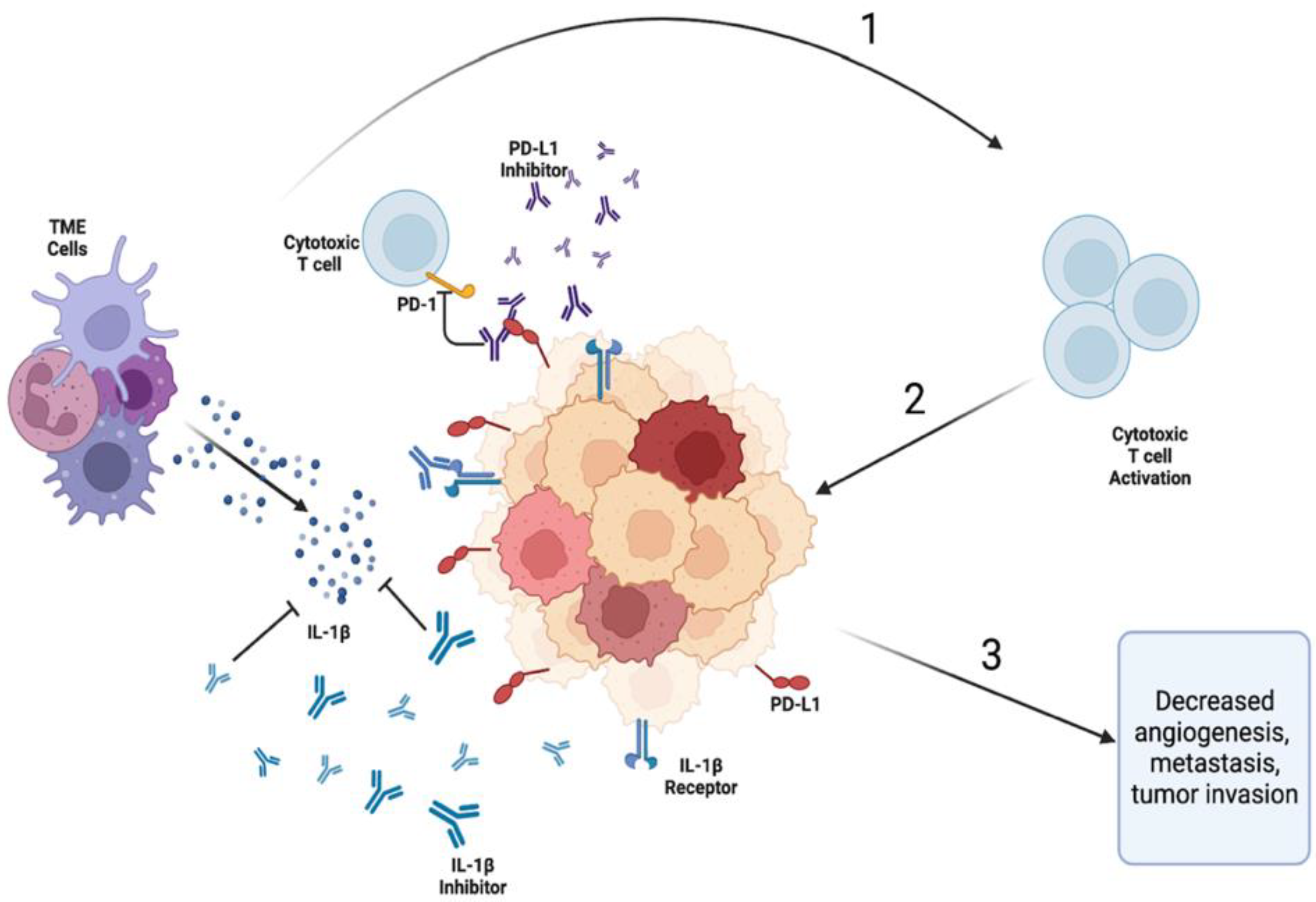
Complex networking in the IL-1β/PD-1/PD-L1 pathway
Biomarkers of response
Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding/Acknowledgment
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
List of Abbreviations
| non-small cell lung cancer | NSCLC |
| immune-checkpoint inhibitor | ICI |
| programmed death ligand 1 | PD-L1 or B7-H1 |
| tumor microenvironment | TME |
| interleukin-1 beta | IL-1β |
| the Canakinumab Anti-inflammatory Thrombosis Outcome Study | CANTOS trial |
| trial programmed cell death protein 1 | PD-1 |
| interferon | IFN |
| microsatellite instability | MSI |
| high tumor mutational burden | TMB |
| toll-like receptor | TLR |
| tumor necrosis factor | TNF |
| IL-1β-converting enzyme | ICE |
| dendritic cell | DC |
| antigen-presenting cell | APC |
| IL-1 receptors | IL-1R and IL-1R2 |
| overall survival | OS |
| progression-free survival | PFS |
| myeloid differentiation primary response-88 | MyD88 |
| IL-1R associated kinase | IRAK |
| tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6 | TRAF6 |
| mitogen activated protein kinase | MAPK |
| Gasdermin D | GSDMD |
| Inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa B | IkB |
| Nuclear factor kappa B | NF-kB |
| Activator protein 1 | AP-1 |
| myeloid-derived suppressor cell | MDSC |
| regulatory T cell | Treg |
| tumor-associated macrophage | TAM |
| monocyte chemoattractant protein | MCP-1 |
| vascular endothelial growth factor | VEGF |
| basic fibroblast growth factor | bFGF |
| transforming growth factor | TGF-αβ |
| platelet-derived endothelial growth factor | PDGF |
| interleukin-8 | IL-8 |
| fibroblast growth factor | FGF |
| matrix metalloproteinase | MMP |
| extracellular matrix | ECM |
| phosphatase and tensin homolog | PTEN |
| epithelial-mesenchymal transition | EMT |
| cyclooxygenase 2 | COX2 |
| inducible nitric oxide synthase | iNOS |
| renal cell carcinoma | RCC model |
| BRAF inhibitors | BRAFi |
| cancer-associated fibroblast | CAF |
| tumor infiltrating lymphocyte | TIL |
| M-MDSC | monocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cell |
| lung adenocarcinoma | LUAD |
| C-reactive protein | CRP |
| overall response rate | ORR |
| odds ratio | OR |
| circulating tumor DNA | ctDNA |
| immune-related adverse event | irAE |
References
- de Alencar, V.T.L.; Figueiredo, A.B.; Corassa, M.; Gollob, K.J.; de Lima, V.C.C. Lung cancer in never smokers: Tumor immunology and challenges for immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 984349. [CrossRef]
- Gridelli C, Rossi A, Carbone DP, et al. Non-small-cell lung cancer. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2015, 1, 1500.
- Zhang, J.; Veeramachaneni, N. Targeting interleukin-1β and inflammation in lung cancer. Biomark. Res. 2022, 10, 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.M.; Tsuboi, M.; Kim, E.S.; Mok, T.S.; Garrido, P. Overcoming immunosuppression and pro-tumor inflammation in lung cancer with combined IL-1β and PD-1 inhibition. Futur. Oncol. 2022, 18, 3085–3100. [CrossRef]
- Ridker PM, MacFadyen JG, Thuren T, et al. Effect of interleukin-1β inhibition with canakinumab on incident lung cancer in patients with atherosclerosis: exploratory results from a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2017, 390, 1833-1842. [CrossRef]
- Yi, M.; Niu, M.; Xu, L.; Luo, S.; Wu, K. Regulation of PD-L1 expression in the tumor microenvironment. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 1–13. [CrossRef]
- Budimir N, Thomas GD, Dolina JS, Salek-Ardakani S. Reversing T-cell Exhaustion in Cancer: Lessons Learned from PD-1/PD-L1 Immune Checkpoint Blockade. Cancer Immunol Res. 2022, 10, 146-153. [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yuan, P.; Mao, B.; Li, N.; Ying, J.; Tao, X.; Tang, W.; Zhang, L.; Geng, X.; Zhang, F.; et al. Genomic features and tumor immune microenvironment alteration in NSCLC treated with neoadjuvant PD-1 blockade. npj Precis. Oncol. 2022, 6, 1–8. [CrossRef]
- Huang J, Lan X, Wang T, et al. Targeting the IL-1β/EHD1/TUBB3 axis overcomes resistance to EGFR-TKI in NSCLC. Oncogene. 2020, 39, 1739-1754. [CrossRef]
- Herbst, R.S.; Morgensztern, D.; Boshoff, C. The biology and management of non-small cell lung cancer. Nature 2018, 553, 446–454. [CrossRef]
- Yan X, Han L, Zhao R, Fatima S, Zhao L, Gao F. Prognosis value of IL-6, IL-8, and IL-1β in serum of patients with lung cancer: A fresh look at interleukins as a biomarker. Heliyon. 2022, 8, e09953. [CrossRef]
- Rébé, C.; Ghiringhelli, F. Interleukin-1β and Cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 1791. [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Li, T.; Li, S.; Yang, H.; Wu, C.; Zheng, C.; You, F.; Liu, Y. The tumor biochemical and biophysical microenvironments synergistically contribute to cancer cell malignancy. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 17, 1186–1187. [CrossRef]
- Litmanovich, A.; Khazim, K.; Cohen, I. The Role of Interleukin-1 in the Pathogenesis of Cancer and its Potential as a Therapeutic Target in Clinical Practice. Oncol. Ther. 2018, 6, 109–127. [CrossRef]
- Elkabets, M.; Ribeiro, V.S.G.; Dinarello, C.A.; Ostrand-Rosenberg, S.; Di Santo, J.P.; Apte, R.N.; Vosshenrich, C.A.J. IL-1β regulates a novel myeloid-derived suppressor cell subset that impairs NK cell development and function. Eur. J. Immunol. 2010, 40, 3347–3357. [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, W.; Zhang, N.; Ma, T.; Zhao, C. IL-1β mediates MCP-1 induction by Wnt5a in gastric cancer cells. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 480–480. [CrossRef]
- Kolb, R.; Phan, L.; Borcherding, N.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, F.; Janowski, A.M.; Xie, Q.; Markan, K.R.; Li, W.; Potthoff, M.J.; et al. Obesity-associated NLRC4 inflammasome activation drives breast cancer progression. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13007. [CrossRef]
- Carmi Y, Dotan S, Rider P, et al. The role of IL-1β in the early tumor cell-induced angiogenic response. J Immunol. 2013, 190, 3500-3509. [CrossRef]
- Fahey, E.; Doyle, S.L. IL-1 Family Cytokine Regulation of Vascular Permeability and Angiogenesis. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1426. [CrossRef]
- Ping P.H., Bo T.F., Li L., Hui Y.N., Zhu H. IL-1β/NF-kb signaling promotes colorectal cancer cell growth through miR-181a/PTEN axis. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2016, 604, 20–26. [CrossRef]
- Wu C., Xu B., Zhou Y., Ji M., Zhang D., Jiang J., Wu C. Correlation between serum IL-1β and miR-144-3p as well as their prognostic values in LUAD and LUSC patients. Oncotarget. 2016, 7, 85876-85887. [CrossRef]
- Sanmamed, M.F.; Perez-Gracia, J.L.; Schalper, K.A.; Fusco, J.P.; Gonzalez, A.; Rodriguez-Ruiz, M.E.; Oñate, C.; Perez, G.; Alfaro, C.; Martín-Algarra, S.; et al. Changes in serum interleukin-8 (IL-8) levels reflect and predict response to anti-PD-1 treatment in melanoma and non-small-cell lung cancer patients. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 1988–1995. [CrossRef]
- Coffelt, S.B.; Kersten, K.; Doornebal, C.W.; Weiden, J.; Vrijland, K.; Hau, C.-S.; Verstegen, N.J.M.; Ciampricotti, M.; Hawinkels, L.J.A.C.; Jonkers, J.; et al. IL-17-producing γδ T cells and neutrophils conspire to promote breast cancer metastasis. Nature 2015, 522, 345–348. [CrossRef]
- Jin C, Lagoudas GK, Zhao C, et al. Commensal Microbiota Promote Lung Cancer Development via γδ T Cells. Cell. 2019, 176, 998-1013.e16.
- Syn, N.L.; Teng, M.W.L.; Mok, T.S.K.; Soo, R.A. De-novo and acquired resistance to immune checkpoint targeting. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, e731–e741. [CrossRef]
- Garon, E.B.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Dubinett, S.M. The Role of Interleukin 1β in the Pathogenesis of Lung Cancer. JTO Clin. Res. Rep. 2020, 1, 100001. [CrossRef]
- Gelfo, V.; Romaniello, D.; Mazzeschi, M.; Sgarzi, M.; Grilli, G.; Morselli, A.; Manzan, B.; Rihawi, K.; Lauriola, M. Roles of IL-1 in Cancer: From Tumor Progression to Resistance to Targeted Therapies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6009. [CrossRef]
- Yan, N.; Guo, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, S.; Li, X. BRAF-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Current Treatment Status and Future Perspective. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 863043. [CrossRef]
- Hajek, E.; Krebs, F.; Bent, R.; Haas, K.; Bast, A.; Steinmetz, I.; Tuettenberg, A.; Grabbe, S.; Bros, M. BRAF inhibitors stimulate inflammasome activation and interleukin 1 beta production in dendritic cells. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 28294–28308. [CrossRef]
- Davies, A.M.; Lara, P.N.; Mack, P.C.; Gumerlock, P.H.; Bold, R.J.; Gandara, D.R. Bortezomib-Based Combinations in the Treatment of Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Lung Cancer 2005, 7, S59–S63. [CrossRef]
- McLoed AG, Sherrill TP, Cheng DS, et al. Neutrophil-Derived IL-1β Impairs the Efficacy of NF-κB Inhibitors against Lung Cancer. Cell Rep. 2016, 16, 120-137. [CrossRef]
- Russano, M.; La Cava, G.; Cortellini, A.; Citarella, F.; Galletti, A.; Di Fazio, G.R.; Santo, V.; Brunetti, L.; Vendittelli, A.; Fioroni, I.; et al. Immunotherapy for Metastatic No n-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Therapeutic Advances and Biomarkers. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 2366–2387. [CrossRef]
- Addeo, A.; Passaro, A.; Malapelle, U.; Banna, G.L.; Subbiah, V.; Friedlaender, A. Immunotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer harbouring driver mutations. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2021, 96, 102179. [CrossRef]
- Negrao, M.V.; Skoulidis, F.; Montesion, M.; Schulze, K.; Bara, I.; Shen, V.; Xu, H.; Hu, S.; Sui, D.; Elamin, Y.Y.; et al. Oncogene-specific differences in tumor mutational burden, PD-L1 expression, and outcomes from immunotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e002891. [CrossRef]
- Simon S, Labarriere N. PD-1 expression on tumor-specific T cells: Friend or foe for immunotherapy? Oncoimmunology. 2017, 7, e1364828.
- Kumagai, S.; Togashi, Y.; Kamada, T.; Sugiyama, E.; Nishinakamura, H.; Takeuchi, Y.; Vitaly, K.; Itahashi, K.; Maeda, Y.; Matsui, S.; et al. The PD-1 expression balance between effector and regulatory T cells predicts the clinical efficacy of PD-1 blockade therapies. Nat. Immunol. 2020, 21, 1346–1358. [CrossRef]
- Sari MI, Ilyas S. The Expression Levels and Concentrations of PD-1 and PD-L1 Proteins in Septic Patients: A Systematic Review. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022, 12, 2004.
- Xu, X.; Hou, B.; Fulzele, A.; Masubuchi, T.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Z.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wang, H.; et al. PD-1 and BTLA regulate T cell signaling differentially and only partially through SHP1 and SHP2. J. Cell Biol. 2020, 219. [CrossRef]
- Lei Q, Wang D, Sun K, Wang L, Zhang Y. Resistance Mechanisms of Anti-PD1/PDL1 Therapy in Solid Tumors. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020, 8, 672. [CrossRef]
- Han Y, Liu D, Li L. PD-1/PD-L1 pathway: current researches in cancer. Am J Cancer Res. 2020, 10, 727-742.
- Reck, M.; Rodríguez-Abreu, D.; Robinson, A.G.; Hui, R.; Csőszi, T.; Fülöp, A.; Gottfried, M.; Peled, N.; Tafreshi, A.; Cuffe, S.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus Chemotherapy for PD-L1–Positive Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1823–1833. [CrossRef]
- Reck, M.; Rodríguez-Abreu, D.; Robinson, A.G.; Hui, R.; Csőszi, T.; Fülöp, A.; Gottfried, M.; Peled, N.; Tafreshi, A.; Cuffe, S.; et al. Five-Year Outcomes With Pembrolizumab Versus Chemotherapy for Metastatic Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer With PD-L1 Tumor Proportion Score ≥ 50%. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 2339–2349. [CrossRef]
- Herbst, R.S.; Garon, E.B.; Kim, D.-W.; Cho, B.C.; Gervais, R.; Perez-Gracia, J.L.; Han, J.-Y.; Majem, M.; Forster, M.D.; Monnet, I.; et al. Five Year Survival Update From KEYNOTE-010: Pembrolizumab Versus Docetaxel for Previously Treated, Programmed Death-Ligand 1–Positive Advanced NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 1718–1732. [CrossRef]
- Horn L, Spigel DR, Vokes EE, et al. Nivolumab Versus Docetaxel in Previously Treated Patients With Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Two-Year Outcomes From Two Randomized, Open-Label, Phase III Trials (CheckMate 017 and CheckMate 057). J Clin Oncol. 2017, 35, 3924-393. [CrossRef]
- Sezer, A.; Kilickap, S.; Gümüş, M.; Bondarenko, I.; Özgüroğlu, M.; Gogishvili, M.; Turk, H.M.; Cicin, I.; Bentsion, D.; Gladkov, O.; et al. Cemiplimab monotherapy for first-line treatment of advanced non-small-cell lung cancer with PD-L1 of at least 50%: a multicentre, open-label, global, phase 3, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet 2021, 397, 592–604. [CrossRef]
- Antonia, S.J.; Villegas, A.; Daniel, D.; Vicente, D.; Murakami, S.; Hui, R.; Yokoi, T.; Chiappori, A.; Lee, K.H.; De Wit, M.; et al. Durvalumab after Chemoradiotherapy in Stage III Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1919–1929. [CrossRef]
- Rizvi NA, Cho BC, Reinmuth N, et al. Durvalumab With or Without Tremelimumab vs Standard Chemotherapy in First-line Treatment of Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: The MYSTIC Phase 3 Randomized Clinical Trial [published correction appears in JAMA Oncol. 2020 Nov 1, 6, 1815]. JAMA Oncol. 2020, 6, 661-674. [CrossRef]
- Jotte, R.; Cappuzzo, F.; Vynnychenko, I.; Stroyakovskiy, D.; Rodríguez-Abreu, D.; Hussein, M.; Soo, R.; Conter, H.J.; Kozuki, T.; Huang, K.-C.; et al. Atezolizumab in Combination With Carboplatin and Nab-Paclitaxel in Advanced Squamous NSCLC (IMpower131): Results From a Randomized Phase III Trial. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, 1351–1360. [CrossRef]
- West, H.; McCleod, M.; Hussein, M.; Morabito, A.; Rittmeyer, A.; Conter, H.J.; Kopp, H.-G.; Daniel, D.; McCune, S.; Mekhail, T.; et al. Atezolizumab in combination with carboplatin plus nab-paclitaxel chemotherapy compared with chemotherapy alone as first-line treatment for metastatic non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer (IMpower130): a multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 924–937. [CrossRef]
- Socinski, M.A.; Nishio, M.; Jotte, R.M.; Cappuzzo, F.; Orlandi, F.; Stroyakovskiy, D.; Nogami, N.; Rodríguez-Abreu, D.; Moro-Sibilot, D.; Thomas, C.A.; et al. IMpower150 Final Overall Survival Analyses for Atezolizumab Plus Bevacizumab and Chemotherapy in First-Line Metastatic Nonsquamous NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 1909–1924. [CrossRef]
- Rittmeyer, A.; Barlesi, F.; Waterkamp, D.; Park, K.; Ciardiello, F.; von Pawel, J.; Gadgeel, S.M.; Hida, T.; Kowalski, D.M.; Dols, M.C.; et al. Atezolizumab versus docetaxel in patients with previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer (OAK): a phase 3, open-label, multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 255–265; Erratum in Lancet 2017, 389, e5. [CrossRef]
- Pathak R, Pharaon RR, Mohanty A, Villaflor VM, Salgia R, Massarelli E. Acquired Resistance to PD-1/PD-L1 Blockade in Lung Cancer: Mechanisms and Patterns of Failure. Cancers (Basel). 2020, 12, 3851. [CrossRef]
- Passaro, A.; Brahmer, J.; Antonia, S.; Mok, T.; Peters, S. Managing Resistance to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Lung Cancer: Treatment and Novel Strategies. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 598–610. [CrossRef]
- Vesely, M.D.; Zhang, T.; Chen, L. Resistance Mechanisms to Anti-PD Cancer Immunotherapy. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2022, 40, 45–74. [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.; Wolchok, J.D.; Chen, L. PD-L1 (B7-H1) and PD-1 pathway blockade for cancer therapy: Mechanisms, response biomarkers, and combinations. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 328rv4–328rv4. [CrossRef]
- Cheng C, Zhuge L, Xiao X, Luan S, Yuan Y. Overcoming resistance to PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors in esophageal cancer. Front Oncol. 2022, 12, 955163. [CrossRef]
- Walsh, R.J.; Soo, R.A. Resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer: biomarkers and therapeutic strategies. Ther. Adv. Med Oncol. 2020, 12. [CrossRef]
- Bagchi, S.; Yuan, R.; Engleman, E.G. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors for the Treatment of Cancer: Clinical Impact and Mechanisms of Response and Resistance. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2021, 16, 223–249. [CrossRef]
- Zhang Y, Chen L. Classification of Advanced Human Cancers Based on Tumor Immunity in the MicroEnvironment (TIME) for Cancer Immunotherapy [published correction appears in JAMA Oncol. 2016 Nov 1, 2, 1511]. JAMA Oncol. 2016, 2, 1403-1404.
- Zhuang Y, Liu C, Liu J, Li G. Resistance Mechanism of PD-1/PD-L1 Blockade in the Cancer-Immunity Cycle. Onco Targets Ther. 2020, 13, 83-94. [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Chen, J.Q.; Liu, C.; Malu, S.; Creasy, C.; Tetzlaff, M.T.; Xu, C.; McKenzie, J.A.; Zhang, C.; Liang, X.; et al. Loss of PTEN Promotes Resistance to T Cell–Mediated Immunotherapy. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 202–216. [CrossRef]
- Ngiow, S.F.; Young, A.; Jacquelot, N.; Yamazaki, T.; Enot, D.; Zitvogel, L.; Smyth, M.J. A threshold level of intratumor CD8 + T-cell PD1 expression dictates therapeutic response to anti-PD1. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 3800–3811. [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Yuan, X.; Wang, M.; He, Z.; Li, H.; Wang, J.; Li, Q. Gut microbiota influence immunotherapy responses: mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 1–20. [CrossRef]
- Sivan, A.; Corrales, L.; Hubert, N.; Williams, J.B.; Aquino-Michaels, K.; Earley, Z.M.; Benyamin, F.W.; Lei, Y.M.; Jabri, B.; Alegre, M.-L.; et al. Commensal Bifidobacterium promotes antitumor immunity and facilitates anti-PD-L1 efficacy. Science 2015, 350, 1084–1089. [CrossRef]
- Goodman, A.M.; Kato, S.; Bazhenova, L.; Patel, S.P.; Frampton, G.M.; Miller, V.; Stephens, P.J.; Daniels, G.A.; Kurzrock, R. Tumor Mutational Burden as an Independent Predictor of Response to Immunotherapy in Diverse Cancers. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2017, 16, 2598–2608. [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.-Y.; Zhang, J.-T.; Liu, S.-Y.; Su, J.; Zhang, C.; Xie, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Tu, H.-Y.; Xu, C.-R.; Yan, L.-X.; et al. EGFR mutation correlates with uninflamed phenotype and weak immunogenicity, causing impaired response to PD-1 blockade in non-small cell lung cancer. OncoImmunology 2017, 6, e1356145. [CrossRef]
- Gainor, J.F.; Shaw, A.T.; Sequist, L.V.; Fu, X.; Azzoli, C.G.; Piotrowska, Z.; Huynh, T.G.; Zhao, L.; Fulton, L.; Schultz, K.R.; et al. EGFR Mutations and ALK Rearrangements Are Associated with Low Response Rates to PD-1 Pathway Blockade in Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Retrospective Analysis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 4585–4593. [CrossRef]
- Sakai, T.; Udagawa, H.; Matsumoto, S.; Yoh, K.; Nosaki, K.; Ikeda, T.; Zenke, Y.; Kirita, K.; Niho, S.; Akimoto, T.; et al. Morphological, immune and genetic features in biopsy sample associated with the efficacy of pembrolizumab in patients with non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 147, 1227–1237. [CrossRef]
- Giustini, N.; Bazhenova, L. Recognizing Prognostic and Predictive Biomarkers in the Treatment of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors (ICIs). Lung Cancer: Targets Ther. 2021, ume 12, 21–34. [CrossRef]
- Mortezaee, K.; Majidpoor, J. Checkpoint inhibitor/interleukin-based combination therapy of cancer. Cancer Med. 2022, 11, 2934–2943. [CrossRef]
- Zong, Z.; Zou, J.; Mao, R.; Ma, C.; Li, N.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, L.; Shi, Y. M1 Macrophages Induce PD-L1 Expression in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells Through IL-1β Signaling. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1643. [CrossRef]
- Perrichet A, Ghiringhelli F, Rébé C. Understanding Inflammasomes and PD-1/PD-L1 Crosstalk to Improve Cancer Treatment Efficiency. Cancers (Basel). 2020, 12, 3550. [CrossRef]
- Numata, Y.; Akutsu, N.; Ishigami, K.; Koide, H.; Wagatsuma, K.; Motoya, M.; Sasaki, S.; Nakase, H. Synergistic effect of IFN-γ and IL-1β on PD-L1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2022, 30, 101270. [CrossRef]
- Lu X, Li Y, Yang W, Tao M, Dai Y, Xu J, Xu Q. Inhibition of NF-κB is required for oleanolic acid to downregulate PD-L1 by promoting DNA demethylation in gastric cancer cells. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2021, 35, e22621. [CrossRef]
- Khalili, J.S.; Liu, S.; Rodríguez-Cruz, T.G.; Whittington, M.; Wardell, S.; Liu, C.; Zhang, M.; Cooper, Z.A.; Frederick, D.T.; Li, Y.; et al. Oncogenic BRAF(V600E) Promotes Stromal Cell-Mediated Immunosuppression Via Induction of Interleukin-1 in Melanoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 5329–5340. [CrossRef]
- Bar, N.; Costa, F.; Das, R.; Duffy, A.; Samur, M.; McCachren, S.; Gettinger, S.N.; Neparidze, N.; Parker, T.L.; Bailur, J.K.; et al. Differential effects of PD-L1 versus PD-1 blockade on myeloid inflammation in human cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 5. [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, R.; Macchini, M.; Sunagawa, M.; Jiang, Z.; Tanaka, T.; Valenti, G.; Renz, B.W.; A White, R.; Hayakawa, Y.; Westphalen, C.B.; et al. Interleukin-1β-induced pancreatitis promotes pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma via B lymphocyte–mediated immune suppression. Gut 2020, 70, 330–341. [CrossRef]
- Aggen, D.H.; Ager, C.R.; Obradovic, A.Z.; Chowdhury, N.; Ghasemzadeh, A.; Mao, W.; Chaimowitz, M.G.; Lopez-Bujanda, Z.A.; Spina, C.S.; Hawley, J.E.; et al. Blocking IL1 Beta Promotes Tumor Regression and Remodeling of the Myeloid Compartment in a Renal Cell Carcinoma Model: Multidimensional Analyses. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 608–621. [CrossRef]
- Chen J, Del Valle L, Lin HY, et al. Expression of PD-1 and PD-Ls in Kaposi's sarcoma and regulation by oncogenic herpesvirus lytic reactivation. Virology. 2019, 536, 16-19. [CrossRef]
- Li R, Ong SL, Tran LM, et al. Chronic IL-1β-induced inflammation regulates epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition memory phenotypes via epigenetic modifications in non-small cell lung cancer [published correction appears in Sci Rep. 2020, 10, 4386. Sci Rep. 2020, 10, 377. [CrossRef]
- Kaplanov, I.; Carmi, Y.; Kornetsky, R.; Shemesh, A.; Shurin, G.V.; Shurin, M.R.; Dinarello, C.A.; Voronov, E.; Apte, R.N. Blocking IL-1β reverses the immunosuppression in mouse breast cancer and synergizes with anti–PD-1 for tumor abrogation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 1361–1369. [CrossRef]
- Jayaraman, P.; Millholland, J.; O’brien, N.; Wong, C.; Diwanji, R.; Wang, M.; Choi, E.; Linnartz, R.; Rose, K.; Rodrik-Outmezguine, V.; et al. Abstract C103: Targeting IL-1β pathway for cancer immunotherapy. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2019, 18, C103–C103. [CrossRef]
- Loeuillard, E.; Yang, J.; Buckarma, E.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Conboy, C.B.; Pavelko, K.D.; Li, Y.; O’brien, D.; Wang, C.; et al. Targeting tumor-associated macrophages and granulocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells augments PD-1 blockade in cholangiocarcinoma. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 5380–5396. [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Chu, T.H.; Nienhüser, H.; Jiang, Z.; Del Portillo, A.; Remotti, H.E.; White, R.A.; Hayakawa, Y.; Tomita, H.; Fox, J.G.; et al. PD-1 Signaling Promotes Tumor-Infiltrating Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells and Gastric Tumorigenesis in Mice. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 781–796. [CrossRef]
- Long H, Jia Q, Wang L, Fang W, Wang Z, Jiang T, Zhou F, Jin Z, Huang J, Zhou L, Hu C, Wang X, Zhang J, Ba Y, Gong Y, Zeng X, Zeng D, Su X, Alexander PB, Wang L, Wang L, Wan YY, Wang XF, Zhang L, Li QJ, Zhu B. Tumor-induced erythroid precursor-differentiated myeloid cells mediate immunosuppression and curtail anti-PD-1/PD-L1 treatment efficacy. Cancer Cell. 2022, 40, 674-693.e7. [CrossRef]
- Tengesdal IW, Dinarello A, Powers NE, Burchill MA, Joosten LAB, Marchetti C, Dinarello CA. Tumor NLRP3-Derived IL-1β Drives the IL-6/STAT3 Axis Resulting in Sustained MDSC-Mediated Immunosuppression. Front Immunol. 2021, 12, 661323. [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Zhang, J.; Shi, M.; Liu, D.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, R.; Su, B.; Ai, K. High expression level of interleukin-1β is correlated with poor prognosis and PD-1 expression in patients with lung adenocarcinoma. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2020, 23, 35–42. [CrossRef]
- Pretre, V.; Papadopoulos, D.; Regard, J.; Pelletier, M.; Woo, J. Interleukin-1 (IL-1) and the inflammasome in cancer. Cytokine 2022, 153, 155850. [CrossRef]
- Paz-Ares L, Goto Y, Lim WDT, Halmos B, Cho BC, Dols MC, et al. 1194MO Canakinumab (CAN) + docetaxel (DTX) for the second- or third-line (2/3L) treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): CANOPY-2 phase III results. Ann Oncol. 2021, 32, S953–4. [CrossRef]
- AG NP. Novartis provides update on Phase III CANOPY-A study evaluating canakinumab as adjuvant treatment in non-small cell lung cancer. GlobeNewswire News Room. 2022. Available online: https://www.globenewswire.com/en/news-release/2022/08/15/2497914/0/en/Novartis-provides-update-on-Phase-III-CANOPY-A-study-evaluating-canakinumab-as-adjuvant-treatment-in-non-small-cell-lung-cancer.html (accessed on 28 April 2023).
- Wang, G.-C.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, H.-M.; Chiang, S.-T.; Chen, Q.; Han, T.-Z.; Li, R.-X. Screening and identifying a novel M-MDSCs-related gene signature for predicting prognostic risk and immunotherapeutic responses in patients with lung adenocarcinoma. Front. Genet. 2023, 13, 989141. [CrossRef]
- Mizuno T, Katsuya Y, Sato J, Koyama T, Shimizu T, Yamamoto N. Emerging PD-1/PD-L1 targeting immunotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer: Current status and future perspective in Japan, US, EU, and China. Front Oncol. 2022, 12, 925938. [CrossRef]
- Keegan, A.; Ricciuti, B.; Garden, P.; Cohen, L.; Nishihara, R.; Adeni, A.; Paweletz, C.; Supplee, J.; A Jänne, P.; Severgnini, M.; et al. Plasma IL-6 changes correlate to PD-1 inhibitor responses in NSCLC. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e000678. [CrossRef]
- Calu, V.; Ionescu, A.; Stanca, L.; Geicu, O.I.; Iordache, F.; Pisoschi, A.M.; Serban, A.I.; Bilteanu, L. Key biomarkers within the colorectal cancer related inflammatory microenvironment. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–14. [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Clowers, M.J.; Velasco, W.V.; Peng, S.; Peng, Q.; Shi, Y.; Ramos-Castaneda, M.; Zarghooni, M.; Yang, S.; Babcock, R.L.; et al. Targeting IL-1β as an immunopreventive and therapeutic modality for K-ras–mutant lung cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 7. [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Shapiro, B.; Vucic, E.A.; Vogt, S.; Bar-Sagi, D. Tumor Cell–Derived IL1β Promotes Desmoplasia and Immune Suppression in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Res 2020, 80, 1088–1101. [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, A.K.; Caporaso, N.E.; Katki, H.A.; Wong, H.-L.; Chatterjee, N.; Pine, S.R.; Chanock, S.J.; Goedert, J.J.; Engels, E.A. C-Reactive Protein and Risk of Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 2719–2726. [CrossRef]
- Kanoh, Y.; Abe, T.; Masuda, N.; Akahoshi, T. Progression of non-small cell lung cancer: Diagnostic and prognostic utility of matrix metalloproteinase-2, C-reactive protein and serum amyloid A. Oncol. Rep. 2012, 29, 469–473. [CrossRef]
- Riedl, J.M.; Barth, D.A.; Brueckl, W.M.; Zeitler, G.; Foris, V.; Mollnar, S.; Stotz, M.; Rossmann, C.H.; Terbuch, A.; Balic, M.; et al. C-Reactive Protein (CRP) Levels in Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Response and Progression in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Bi-Center Study. Cancers 2020, 12, 2319. [CrossRef]
- Assaf, Z.J.F.; Zou, W.; Fine, A.D.; Socinski, M.A.; Young, A.; Lipson, D.; Freidin, J.F.; Kennedy, M.; Polisecki, E.; Nishio, M.; et al. A longitudinal circulating tumor DNA-based model associated with survival in metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 859–868. [CrossRef]
- Wong CC, Baum J, Silvestro A, Beste MT, Bharani-Dharan B, Xu S, et al. Inhibition of IL1β by Canakinumab May Be Effective against Diverse Molecular Subtypes of Lung Cancer: An Exploratory Analysis of the CANTOS Trial. Cancer Research. 2020, 80, 5597-605. [CrossRef]
- Kumar V, Chaudhary N, Garg M, Floudas CS, Soni P, Chandra AB. Current Diagnosis and Management of Immune-Related Adverse Events (irAEs) Induced by Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy [published correction appears in Front Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 311]. Front Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 49. [CrossRef]
- Gogishvili, M.; Melkadze, T.; Makharadze, T.; Giorgadze, D.; Dvorkin, M.; Penkov, K.; Laktionov, K.; Nemsadze, G.; Nechaeva, M.; Rozhkova, I.; et al. Cemiplimab plus chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone in non-small cell lung cancer: a randomized, controlled, double-blind phase 3 trial. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 2374–2380. [CrossRef]
- Kelly K, Infante JR, Taylor MH, et al. Safety profile of avelumab in patients with advanced solid tumors: A pooled analysis of data from the phase 1 JAVELIN solid tumor and phase 2 JAVELIN Merkel 200 clinical trials. Cancer. 2018, 124, 2010-2017. [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Zhang, D.; Cui, X.; Zhang, L. Meta-analysis of immune-related adverse events of immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy in cancer patients. Thorac. Cancer 2020, 11, 2406–2430. [CrossRef]
- Gross, N.D.; Miller, D.M.; Khushalani, N.I.; Divi, V.; Ruiz, E.S.; Lipson, E.J.; Meier, F.; Su, Y.B.; Swiecicki, P.L.; Atlas, J.; et al. Neoadjuvant Cemiplimab for Stage II to IV Cutaneous Squamous-Cell Carcinoma. New Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 1557–1568. [CrossRef]
- Vaddepally R, Doddamani R, Sodavarapu S, et al. Review of Immune-Related Adverse Events (irAEs) in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)-Their Incidence, Management, Multiorgan irAEs, and Rechallenge. Biomedicines. 2022, 10, 790. [CrossRef]
| IL-1β inhibitors | Type | Target | Trials | Phase, progress | Experimental arms | Primary outcome | Results of the primary outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Canakinumab | human IgGκ mAb | IL-1β | NCT03968419 (CANOPY-N) | Phase II, completed | canakinumab +/- pembrolizumab; pembrolizumab monotherapy | MPR | MPR: 2.9% (CAN)/ 17.1% (CAN+PEM)/11.1% (PEM), does not meet the primary endpoint |
| NCT03626545 (CANOPY-2) | Phase III, completed | docetaxel +/- canakinumab | OS and incidence of DLTs | Median OS: 10.5m (CAN) /11.3m (Placebo) (HR 1.06 95% CI, 0.76-1.48); does not meet the primary endpoint | |||
| NCT03631199 (CANOPY-1) | Phase III, active, not recruiting | pembrolizumab + platinum-based doublet chemotherapy +/- canakinumab | OS, PFS, and incidence DLTs | Median OS: 20.8m (CAN) /20.2 m (Placebo) (HR 0.87, 95% CI, 0.70-1.10; one-sided P=0.123); median PFS: 6.8m for both treatment arms (hazard ratio [HR], 0.85; 95% CI, 0.67-1.09; P =.1); does not meet the primary endpoint | |||
| NCT03447769 (CANOPY-A) | Phase III, terminated | Canakinumab (Canakinumab versus Placebo | DFS | Median DFS: 35m (CAN)/ 29.7m (Placebo) (HR 0.94; 95% CI 0.78–1.14; one-sided p=0.258); does not meet the primary endpoint | |||
| NCT04905316 (CHORUS) | Phase II, recruiting | Canakinumab + Chemoradiation + Durvalumab (Single-arm, prospective, phase I/II study) |
PFS | Recruiting, no result yet |
| IL-1 inhibitors | Type | Target | Trials | Phase, progress | Experimental arms | Primary outcome | Results of the primary outcome |
| Anakinra | IL-1 receptor mAb | IL-1 receptor | NCT01624766A888A | Phase I, completed | Everolimus (mTOR Inhibitor) + Anakinra/Denosumab | Incidence of AEs, MTD of everolimus | No result published yet |
| IL-1R inhibitors | Type | Target | Trials | Phase, progress | Experimental arms | Primary outcome | Results of the primary outcome |
| Nadunolimab (CAN04) | first-in-class fully humanized and ADCC enhanced mAb | IL1RAP | NCT03267316A888A(CANFOUR) | Phase I/II, Recruiting | CAN04 +/- standard of care treatment | Incidence of Treatment-Emergent AE (Safety and Tolerability) | infusion-related reactions (41%), fatigue (32%), constipation (27%), diarrhea (27%), decreased appetite (23%), nausea (23%), and vomiting (23%); ORR 53% |
| NCT05116891A888A(CESTAFOUR) | Phase I/II, active, not recruiting | CAN04 + chemotherapy (mFOLFOX or DTX or G/C) | ORR, frequency, duration, and severity of AEs | No result yet | |||
| NCT04452214 (CIRIFOUR) | Phase I, active, not recruiting | CAN04 +pembrolizumab +/- carboplatin and pemetrexed | TEAEs, DLEs, SAEs | No result yet |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





