1. Introduction
Vitamin K is a liposoluble vitamin essential for maintaining proper human health, and its deficiency has been linked to age-related diseases, such as cardiovascular disease, osteoarthritis, dementia, cognitive impairment, mobility disability, and frailty [
1,
2]. Vitamin K has been historically described as a co-factor for the gamma-glutamylcarboxylation of vitamin K dependent proteins (VKDPs) with a multitude of functions in multiple body tissues and molecular processes. Vitamin K is considered an essential nutrient for blood coagulation and cardiovascular and bone health. In addition, vitamin K has been shown to exert novel roles independent of VKDPs carboxylation, such as anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antiferroptosis, transcriptional regulator of osteoblastic genes, inhibition of tumor progression and cognition promoter [
1,
2,
3].
Naturally occurring vitamin K includes phylloquinone (vitamin K1) and several forms of menaquinones (MKn or vitamin K2). Vitamin K1 (VK1) is mostly found in photosynthetic organisms including green leafy vegetables, herbs, algae, vegetable oils. Vitamin K2 (VK2) is primarily produced by bacteria, and obtained through the consumption of meat, fermented foods and dairy products [
1,
4]. Although collectively VK1 and VK2 comprise the generally described vitamin K, these isoforms differ not only in the source, but also in absorption rates, tissue distribution, bioavailability, and target activity [
1]. Despite that vitamin K can be recycled, microbiota can produce VK2 and MK-4 is a product of conversion from vitamin K at tissue level, vitamin K1 and K2 sources are mainly dietary [
5,
6]. According to estimated dietary consumption, vitamin K1 accounts for 90% of the total vitamin K in the diet [
7], but evidence from basic research and clinical studies has highlighted the importance of VK2. In fact, it was suggested that VK2 might account for 70% of total extrahepatic activity while VK1 contribute with only 5% [
8]. Vitamin K has a Recommended Daily Intake (RDI) based on the median intake of VK1 in American adults, and an adequate intake recommendation (Adequate Intake - AI) set at 120 μg/day for men and 90 μg/day for women [
9]. In Europe, 75 μg vitamin K have been recommended as daily allowance (Commission Directive 2008/100/EC). Additionally, VK2 has been suggested suitable for consideration for a specific dietary recommendation intake [
8].
While most diets are considered to contain an adequate amount of vitamin K, further research is needed, especially because the intake estimates of vitamin K are not consistent and mostly focused on VK1. Also, habitual intake is influenced by factors including food diversity, eating patterns, and different content of vitamin K, which may vary with soil, climate and agricultural conditions [
10].
Food-frequency questionnaires (FFQ) are commonly used to assess dietary intake in epidemiological studies because they are relatively easy to administer, cost-effective, and able to capture long-term habitual intake [
11]. However, the validity of FFQ is dependent on the accuracy of the food composition database and the ability of participants to recall their intake over a specific period [
12].
Validated FFQ to assess vitamin K intake exist, constructed using American populations, but these tools cannot be directly applied to a Mediterranean population, which traditionally follows an eating pattern where vitamin K rich foods, such are leafy green vegetables and different types of cheeses, are frequently consumed.
The aim of this study was to develop and validate a new FFQ for assessing vitamin K intake, including VK1 and VK2, in a Mediterranean-based sample. To our knowledge, this is the first study to evaluate the validity of a FFQ specifically designed to assess vitamin K intake in this setting.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
We conducted a prospective study in a non-random sample of healthy adult volunteers, recruited by direct contact and through social media. Inclusion criteria were: i) age ≥18 years; ii) cognitive ability to fulfil the data collection tools. Exclusion criteria were: i) currently under treatment for serious chronic illness, such as cancer or autoimmune diseases; ii) diagnosis of a disease that impairs nutrition or food choice, such as Crohn’s disease, other malabsorption syndromes or food allergies; iii) on anticoagulant therapy.
Sample size calculation, according to methods propose by Huley et al. [
11], considering 90% power, 5% statistical significance, and a minimum predicted correlation coefficient of 0.55 between vitamin K intake estimated by FFQ and estimated by dietary recalls, yielded a minimum sample size of 30 individuals. Accounting for a 10% dropout rate, we set the minimum sample size at 35 individuals. On recruitment, 38 participants were eligible, and all proceeded to be a part of the study and concluded data collection.
All participants signed informed consent and this study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the University of Algarve, Portugal.
2.2. Data collection
To apply the inclusion criteria, participants were recruited in a face-to-face interview and all details of the study were explained. Intake of vitamin K was assessed by one 24h-recall, conducted by a trained dietitian at the day of recruitment, and two self-fulfilment dietary records, comprising three, consecutive, complete days each. The first dietary record was completed in the days following recruitment, and the final record was completed one month later. One of the records was relative to weekend days (Friday, Saturday, and Sunday), and researchers contacted participants by e-mail to encourage them to fulfil the dietary records on the set dates.
Participants were asked to report the brand and type of each food item whenever possible. In the recruitment interview, participants were provided with forms to record their dietary intake, and any questions regarding this stage were addressed. Forms for the study were based on the EPIC-Norfolk dietary records forms [
12] and in the Portuguese National Health and Physical Activity Survey [
13] forms, which include detailed instructions and images showing portion sizes and common measurement cups and spoons. Researchers were available by phone at any time to address any additional questions during data collection.
After fulfilling the second dietary record, participants were also asked to complete the FFQ created for this study as detailed below. Participants were also asked to report their heigh, weight, education level, age, and gender.
2.3. Food-frequency questionnaire (FFQ)
To construct the FFQ for this study, we based our food list on a validated Portuguese FFQ used in nationally representative studies [
13]. Based on previous research [
14,
15,
16] and on published food composition tables for vitamin K [
7,
17], we identified and selected foods with ≥ 5μg of vitamin K/100g of food and included them in the FFQ. Additionally, we identified foods that, despite having < 5μg of vitamin K/100g of food, are commonly included in a Mediterranean diet, such as some types of soft cheese, boiled chickpeas, pumpkin, bell pepper, mackerel, sardines, almonds, walnuts, and coffee [
18,
19]. The initial FFQ included a total of 103 food items. Statistical analysis for this validation study, detailed in the results, allowed us to propose a final FFQ with 54 food items.
Participants were asked to report the frequency of intake, in the last month, of all listed food items, by choosing one of eight frequency options: never or less than once per month, 1-3 per month, 1 per week, 2-4 per week, 5-6 per week, 1 per day, 2-3 per day, 4+ per day.
All food items were presented with a photograph with recommended portion weight, also used in the Portuguese National Health and Physical Activity Survey [
13], and participants reported if their average portion was the same, smaller (defined as 0.5 times smaller) or larger (1.5 times larger) than recommended size.
Vitamin K intake for each food item was computed based on the following formula: nutrient content in portion × average portion size x frequency conversion factor. The conversion factors were those proposed in previous research on this subject [
20,
21,
22] and are presented in
Table 1.
Vitamin K intake was calculated using a food composition database constructed for this study in Microsoft Excel, which included data on vitamin K content of foods from previous research [
7] and data from both McCance and Widdowson’s and United States Department of Agriculture food composition databases [
17,
23].
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Data were analysed using IBM SPSS for Windows (version 29.0, 2022, IBM Corporation). Mean, median, standard deviation (SD) and interquartile range (IQR) were computed whenever appropriate, and we used the Shapiro-Wilk test to assess adherence to the Normal distribution of variables regarding vitamin K intake. As the distribution of these variables was non-Gaussian for both food records and FFQ, data were log-transformed for some statistical inference tests.
Agreement was analysed using Student’s t-tests and plotted according to the Bland-Altman method [
24]. We also computed Pearson’s correlation coefficient on the log transformed data.
Statistical significance for all procedures was set at 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Participants
All participants (n=38) followed the data collection procedures for the study and completed the food records and the FFQ.
Participants were predominantly females (n=23; 60,5%). All of the men (n=15; 100%) and 48% of the women (n=11) had a college level degree. Mean body mass index (BMI) was 24.6±0.6 kg/m
2 and ages ranged between 18 and 65 years old. Female participants were significantly older (p=0.004) and with a lower educational level than males (p=0.002).
Table 2 summarizes the characteristics of participants.
3.2. Food-frequency questionnaire items
To analyse the adequacy of the food item list in the FFQ, we conducted multiple regression analyses, with a stepwise method, using vitamin K intake as the dependent variable and all other food items as independent variables. The food items that contributed cumulatively up to 90% of vitamin K intake in a statistically significant model (F=7.5, p=0,004), were retained for the final version of the FFQ. From the initial list of 103 food items, we eliminated 43, and thus included 54 food items in our FFQ. The included food items are shown in
Table 3.
3.3. Comparison between food records and food frequency questionnaire
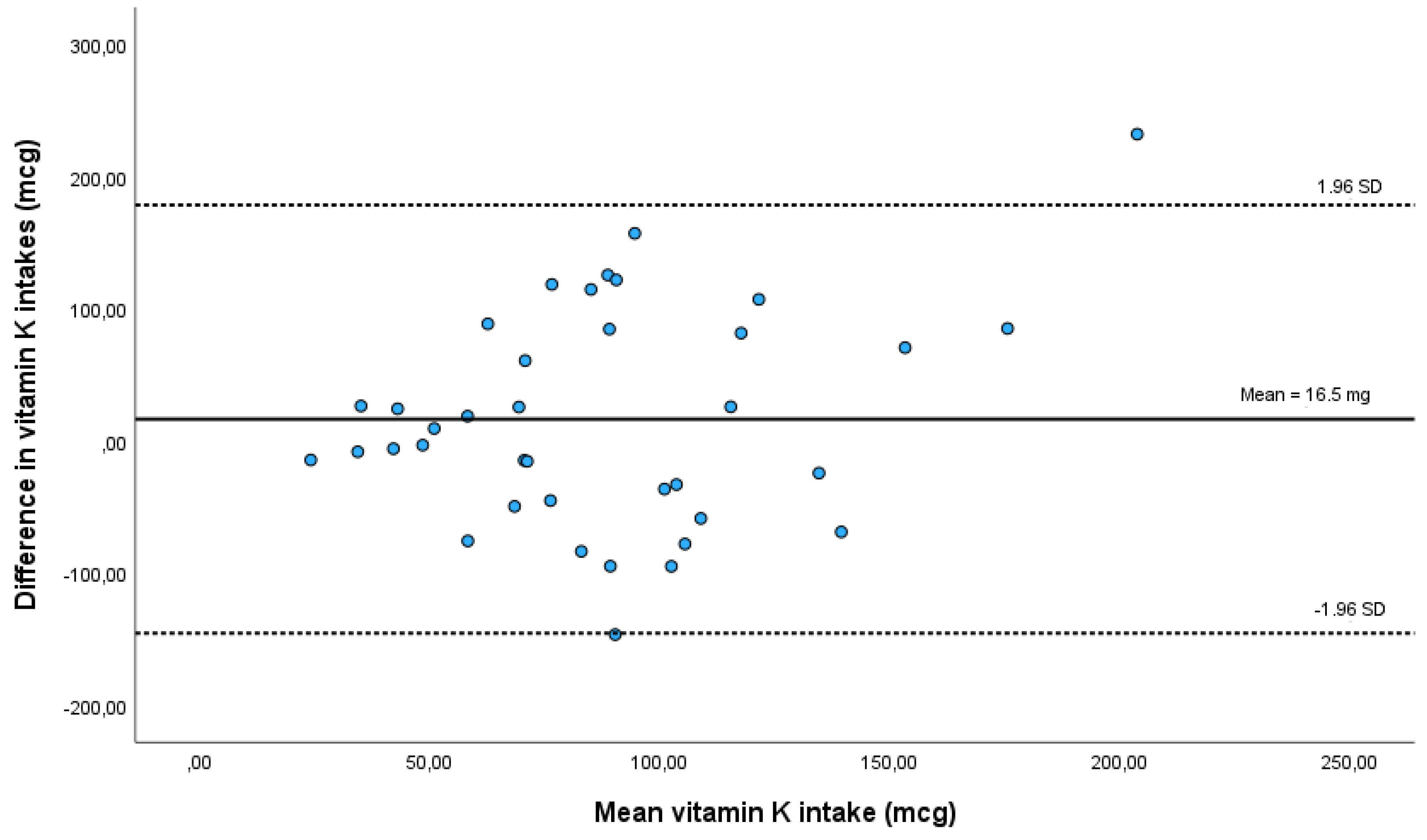
Mean vitamin K intake was 80 mcg (±47.7) according to food records and 96.5 mcg (±64.3) according to the FFQ. Vitamin K estimates from the FFQ were, on average, 16.5 mcg (±82.57) higher than estimates from food records. This difference is statistically non-significant (p=0.226), supporting the existence of proper absolute agreement between both methods. The same results are observed in a paired Student’s t-test on log transformed vitamin K intake data (p=0.293). We also found a strong, statistically significant, correlation (r= 0.697; p=0.003) between the FFQ and diet records, which suggests a good relative agreement and that the FFQ is a valid instrument to assess vitamin K intake in this population.
Table 4 summarises the results from the comparison between FFQ and food records.
A Bland-Altman plot to assess agreement also shows that most participants fall in the acceptable limits of agreement in individual differences between both dietary estimate methods (
Figure 1).
4. Discussion
Literature suggests that FFQ are valid, reliable, and easy-to-use tools in populational studies, but their accuracy in estimating some nutrients, particularly micronutrients, is still subject of ongoing research [
22,
25,
26,
27]. Thus, the development of a valid FFQ for vitamin K that can be used in surveys, cohort studies, and other populational assessments, can constitute worthwhile research, especially if the FFQ is aimed at populations that are associated with a specific dietary pattern, which includes vitamin K-rich foods.
Our study allowed the development of a valid FFQ for assessment of vitamin K intake in a sample of Portuguese adults, with a very low cost of administration and processing, and with low respondent burden. Moreover, this FFQ is directed to estimate VK1 and VK2 intake as a more representative measurement of vitamin K status. Most FFQs developed to estimate dietary consumption of vitamin K have specifically focused on VK1 mainly because, in the Western diet, it accounts for nearly 90% of total vitamin K intake [
7]. However, accumulating evidence from basic research and clinical studies has highlighted the health beneficial effects of VK2, particularly due to its long half-life and extrahepatic distribution. While VK1 is preferentially accumulated in the liver and poorly retained in the organism with a half-life time of 1–2 h, VK2 with a half-life time of 68 h is available to extrahepatic tissues through circulation, resulting in increased bioavailability to whole body [
1,
2]. Also, in terms of functionality VK2, particularly MK-7 and MK-4, has been shown to have higher bioactivity than VK1 in different molecular processes, such as gamma-glutamylcarboxylation cofactor, inhibitory effect on bone resorption, antioxidant, activator of sphingolipid metabolism and anticancer [
28,
29,
30,
31,
32,
33]. In fact, it was suggested that VK2 is the major vitamin K active form accounting for 70% of total extrahepatic activity while VK1 contribute with only 5%, and that the beneficial effects of VK2 are not covered by current RDI guidelines [
8]. However, it should be noticed that MK-4 is a result of vitamin K conversion and dependent from VK1 intake, and that MK-4 is present in most extrahepatic tissues [
5,
6,
34,
35]. In this context more attention should be given to dietary intake of both VK1 and VK2.
Although we recorded some overestimation (16.5±82.57 mcg) of vitamin K intake when compared with food records, this overestimation was statistically non-significant and on par with the variability which, according to previous research, is to be expected [
36,
37,
38,
39]. Our FFQ showed an adequate relative agreement with food records, with a correlation coefficient of 0.697, which is above the minimum threshold of 0.4 proposed for FFQ validation studies [
22,
40]. Previous FFQ studies regarding vitamin K intake report correlations from 0.5 to 0.8 [
15,
16,
38,
41,
42,
43]. The Bland-Altman method of analysis also indicates good relative agreement, with one outlier participant above the 95% agreement limit, and one participant in the borderline of the lower agreement limit. Although this study is not intended to evaluate vitamin K intake in our population, mean vitamin K of 96.5±64.3 ug/day in our sample is within the RDI established for the American population and above the 75 μg/day recommended by the European Commission.
We identified several limitations of this study and propose future research directions in this topic. Although VK1 intake has been suggested not the vary significantly with season [
44], we cannot rule out the interference of the seasonal nature of dietary patterns, particularly considering a Mediterranean-based diet. We included items in the FFQ food list that cover the wide variety of products that are common in all harvesting seasons, but data were collected in springtime. This can imply that the final food list that derived from the regression analysis may not include items that provide an important intake of vitamin K, because these are mainly consumed during winter. We believe that wintertime products are represented in the final list, but additional studies to confirm this, conducted during colder months, are needed. Some research suggests that there is a high within-person variance in the intake of vitamin K [
39] and green vegetables [
40,
41]. Therefore, additional studies assessing reproducibility of our FFQ should also be undertaken, as we did not assess this parameter. Although the sample size of our study is adequate to compare methods of assessing dietary intake, our participants constituted a non-probabilistic, convenience sample, mainly composed by adults with high educational level. Ages ranged from 18 to 65 years of age and, therefore, our data does not allow us to assess the validity of our FFQ in older adults, or in individuals with different sociodemographic characteristics, compromising generalization of our results.
It is also important to note that we focused on collecting vitamin K intake during a period of one month. The initial 24h recall and the food records that were used to establish usual intake were collected during a 30-day interval and the FFQ was specifically constructed such that participants recall their intake for an equivalent period.
Overall, we constructed a valid, practical, cost-effective tool to estimate vitamin K intake for a 30-day period. Our FFQ showed good absolute and relative agreement with food records and includes a list of food products that account for most of the VK1 and VK2 intake in a Mediterranean dietary pattern in the Portuguese population. Additional research is needed to assess the reproducibility of this tool, to confirm that seasonality does not affect its validity, and to test its applicability to different populations.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.P., C.V., D.S.; methodology, E.P., P.V.M; software, P.V.M; formal analysis, E.P., T.N.; investigation, E.P., C.V., D.S.; resources, L.S.; ; writing—original draft preparation, E.P., C.V., D.S. ; writing—review and editing, E.P., C.V., L.S., D.S.; project administration, E.P., D.S.; funding acquisition, E.P., C.V., P.V.M., D.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Portuguese National Funds from FCT—Foundation for Science and Technology, through transitional provision DL57/2016/CP1361/CT0006, projects EXPL/BTM-TEC/0990/2021, UIDB/04326/2020, UIDP/04326/2020 and LA/P/0101/2020 and AAC nº 41/ALG/2020 - Project nº 072583 – NUTRISAFE.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the ethics committee of the University of Algarve, Faro, Portugal (code CEUAlg Pn°01/2022, approved 21 January 2022).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Data available on request due to privacy restrictions.
Conflicts of Interest
Dina Simes and Carla Viegas are cofounders of Genogla Diagnostics. The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
References
- Simes, D.C.; Viegas, C.S.B.; Araújo, N.; Marreiros, C. Vitamin K as a Diet Supplement with Impact in Human Health: Current Evidence in Age-Related Diseases. Nutrients 2020, 12, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simes, D.C.; Viegas, C.S.B.; Araújo, N.; Marreiros, C. Vitamin K as a Powerful Micronutrient in Aging and Age-Related Diseases: Pros and Cons from Clinical Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishima, E.; Ito, J.; Wu, Z.; et al. A non-canonical vitamin K cycle is a potent ferroptosis suppressor. Nature 2022, 608, 778–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Booth, S.L. Vitamin K: Food composition and dietary intakes. Food Nutr. Res. 2012, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shearer, M.J.; Newman, P. Recent trends in the metabolism and cell biology of vitamin K with special reference to vitamin K cycling and MK-4 biosynthesis. J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 345–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thijssen, H.H.; Drittij-Reijnders, M.J. Vitamin K distribution in rat tissues: Dietary phylloquinone is a source of tissue menaquinone-4. Br. J. Nutr. 1994, 72, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schurgers, L.J.; Vermeer, C. Determination of phylloquinone and menaquinones in food. Effect of food matrix on circulating vitamin K concentrations. Haemostasis 2000, 30, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbulut, A.C.; Pavlic, A.; Petsophonsakul, P.; Halder, M.; Maresz, K.; Kramann, R.; Schurgers, L. Vitamin K2 Needs an RDI Separate from Vitamin K1. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Institute of Medicine (US) Panel on Micronutrients. Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin A, Vitamin K, Arsenic, Boron, Chromium, Copper, Iodine, Iron, Manganese, Molybdenum, Nickel, Silicon, Vanadium, and Zinc. National Academies Press (US) 2001.
- Passarelli, S.; Free, C.M.; Allen, L.H.; Batis, C.; Beal, T.; Biltoft-Jensen, A.P.; Bromage, S.; Cao, L.; Castellanos-Gutiérrez, A.; Christensen, T.; Crispim, S.P.; Dekkers, A.; De Ridder, K.; Kronsteiner-Gicevic, S.; Lee, C.; Li, Y.; Moursi, M.; Moyersoen, I.; Schmidhuber, J.; Shepon, A.; Viana, D.F.; Golden, C.D. Estimating national and subnational nutrient intake distributions of global diets. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 116, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browner, W.; Newman, T.; Hulley, S. Estimating Sample Size and Power: Applications and Examples. In Designing Clinical Research: An Epidemiologic Approach, 4th ed.; Hulley, S., Cummings, S., Browner, W., Grady, D., Newman, T., Eds.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, USA, 2013; pp. 55–83. [Google Scholar]
- Wareham, N.; Luben, R.; Oakes, S.; et al. Nutritional methods in the European Prospective Investigation of Cancer in Norfolk. Public Health Nutr. 2008, 4, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- University of Porto, National Health Institute Doutor Ricardo Jorge, University of Lisbon, SilicoLife Lda, Lopes C, Torres D, Oliveira A, Severo M, Guiomar S, Alarcão V, Vilela S, Ramos E, Rodrigues S, Oliveira L, Nicola P, Mota J, Teixeira P, Soares S. National Food, Nutrition and Physical Activity Survey of the Portuguese general population. EFSA supporting publication 2017:14(12):EN-1341. 37 pp. [CrossRef]
- Bingham, S.A.; Gill, C.; Welch, A.; Cassidy, A.; Runswick, S.A.; Oakes, S.; Lubin, R.; Thurnham, D.I.; Key, T.J.; Roe, L.; Khaw, K.T.; Day, N.E. Validation of dietary assessment methods in the UK arm of EPIC using weighed records, and 24-hour urinary nitrogen and potassium and serum vitamin C and carotenoids as biomarkers. Int. J. Epidemiol. 1997, 26, S137–S151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Presse, N.; Shatenstein, B.; Kergoat, M.J.; Ferland, G. Validation of a Semi-Quantitative Food Frequency Questionnaire Measuring Dietary Vitamin K Intake in Elderly People. J. Am. Diet Assoc. 2009, 109, 1251–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias Mendonça, D.; Zuchinali, P.; Souza, G.C. Development of a food frequency questionnaire to determine vitamin k intake in anticoagulated patients: A pilot study. Rev. Chil. Nut. 2018, 45, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roe, M.; Pinchen, H.; Church, S.; Finglas, P. McCance and Widdowson’s The Composition of Foods Seventh Summary Edition and updated Composition of Foods Integrated Dataset. Nutr. Bull. 2015, 40, 36–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, K.; Takeda, A.; Martin, N.; Ellis, L.; Wijesekara, D.; Vepa, A.; Das, A.; Hartley, L.; Stranges, S. Mediterranean-style diet for the primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 3, CD009825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willett, W. Mediterranean Dietary Pyramid. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willett, W. Nutritional Epidemiology, 3rd ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, USA, 2013; pp. 70–95. [Google Scholar]
- Cade, J.; Thompson, R.; Burley, V.; Warm, D. Development, validation and utilisation of food-frequency questionnaires – a review. Public Health Nutr. 2003, 5, 567–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, M. The validation of dietary assessment. In Design Concepts in Nutritional Epidemiology, 2nd ed.; Barrie, M., Margetts, B.M., Nelson, M., Eds.; Oxford University Press: New York, USA, 1997; pp. 241–272. [Google Scholar]
- U. S. Department of Agriculture. FoodData Central. FoodData Central. 2019; (April).
- Bland, J.M.; Altman, D.G. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet 1986, 1, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cade, J.E. Measuring diet in the 21st century: Use of new technologies. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2017, 76, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, J.S.; Oh, K.; Kim, H.C. Dietary assessment methods in epidemiologic studies. Epidemiol. Health. 2014, 36, e2014009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, C.A.; Oluwagbemigun, K.; Nöthlings, U. Advances in dietary pattern analysis in nutritional epidemiology. Eur. J. Nutr. 2021, 60, 4115–4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buitenhuis, H.; Soute, B.; Vermeer, C. Comparison of the vitamins K1, K2 and K3 as cofactors for the hepatic vitamin K-dependent carboxylase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1990, 1034, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hara, K.; Akiyama, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Murota, S.; Morita, I. The inhibitory effect of vitamin K2 (menatetrenone) on bone resorption may be related to its side chain. Bone 1995, 16, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrożewicz, E.; Muszyńska, M.; Tokajuk, G.; Grynkiewicz, G.; Žarković, N.; Skrzydlewska, E. Beneficial Effects of Vitamins K and D3 on Redox Balance of Human Osteoblasts Cultured with Hydroxypatite-Based Biomaterials. Cells 2019, 8, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lev, M.; Milford, A. The 3-Ketodihydrosphingosine melaninogenicus: Synthetase of Bacteroides melaninogenicus: Induction by Vitamin K. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1973, 157, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundaram, K.S.; Lev, M. Regulation of sulfotransferase activity by vitamin k in mouse brain. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1990, 277, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xv, F.; Chen, J.; Duan, L.; Li, S. Research progress on the anticancer effects of vitamin K2. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 8926–8934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thijssen, H.; Drittij-Reijnders, M. Vitamin K status in human tissues: Tissue-specific accumulation of phylloquinone and menaquinone-4. Br. J. Nutr. 1996, 75, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thijssen, H.H.; Drittij, M.J.; Vermeer, C.; Schoffelen, E. Menaquinone-4 in breast milk is derived from dietary phylloquinone. Br. J. Nutr. 2002, 87, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, S.L.; Sokoll, L.J.; O’Brien, M.E.; Tucker, K.; Dawson-Hughes, B.; Sadowski, J.A. Assessment of dietary phylloquinone intake and vitamin K status in postmenopausal women. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 1995, 49, 832–841. [Google Scholar]
- Booth, S.L.; Tucker, K.L.; McKeown, N.M.; Davidson, K.W.; Dallal, G.E.; Sadowski, J.A. Relationships between Dietary Intakes and Fasting Plasma Concentrations of Fat-Soluble Vitamins in Humans. J. Nutr. 1997, 127, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pritchard, J.M.; Seechurn, T.; Atkinson, S.A. A food frequency questionnaire for the assessment of calcium, vitamin D and vitamin K: A pilot validation study. Nutrients 2010, 2, 805–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couris, R.R.; Tataronis, G.R.; Booth, S.L.; Dallal, G.E.; Blumberg, J.B.; Dwyer, J.T. Development of a self-assessment instrument to determine daily intake and variability of dietary vitamin K. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2000, 19, 801–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cade, J.E.; Burley, V.J.; Warm, D.L.; Thompson, R.L.; Margetts, B.M. Food-frequency questionnaires: A review of their design, validation and utilisation. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2004, 17, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantin, J.; Latour, E.; Ferland-Verry, R.; Morales Salgado, S.; Lambert, J.; Faraj, M.; Nigam, A. Validity and reproducibility of a food frequency questionnaire focused on the Mediterranean diet for the Quebec population. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2016, 26, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwakenberg, S.R.; Engelen, A.I.P.; Dalmeijer, G.W.; Booth, S.L.; Vermeer, C.; Drijvers, J.J.M.M.; Ocke, M.C.; Feskens, E.J.M.; van der Schouw, Y.T.; Beulens, J.W.J. Reproducibility and relative validity of a food frequency questionnaire to estimate intake of dietary phylloquinone and menaquinones. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 71, 1423–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, S.Y.; Choi, M.K.; Jin So, E. Validity and Reliability of a Self-administered Food Frequency Questionnaire to Assess Vitamin K Intake in Korean Adults. Clin. Nutr. Res. 2016, 5, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thane, C.W.; Paul, A.A.; Bates, C.J.; Bolton-Smith, C.; Prentice, A.; Shearer, M.J. Intake and sources of phylloquinone (vitamin K1): Variation with socio-demographic and lifestyle factors in a national sample of British elderly people. Br. J. Nutr. 2002, 87, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).