Submitted:
25 June 2023
Posted:
26 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
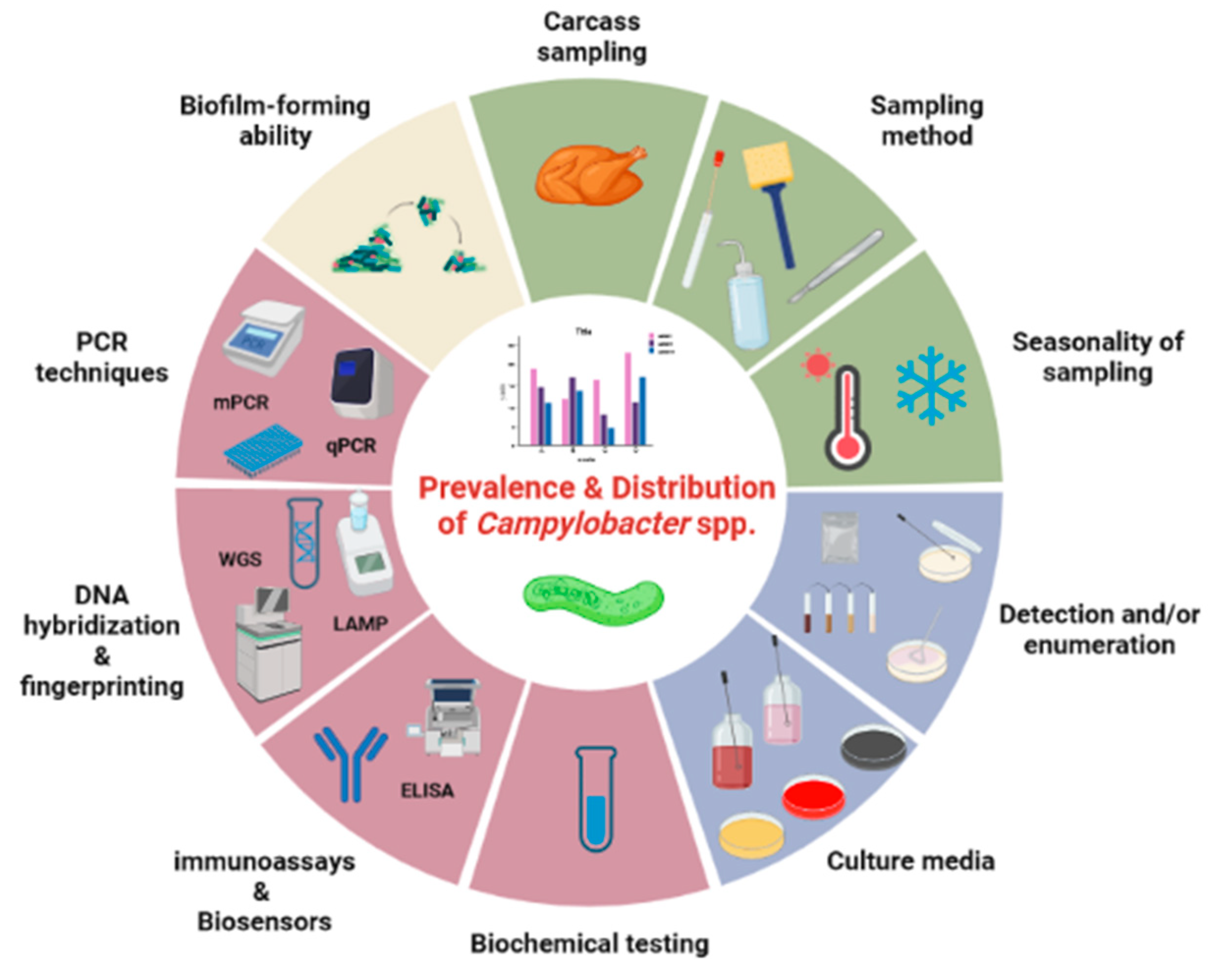
1. Introduction
2. Sampling of Poultry
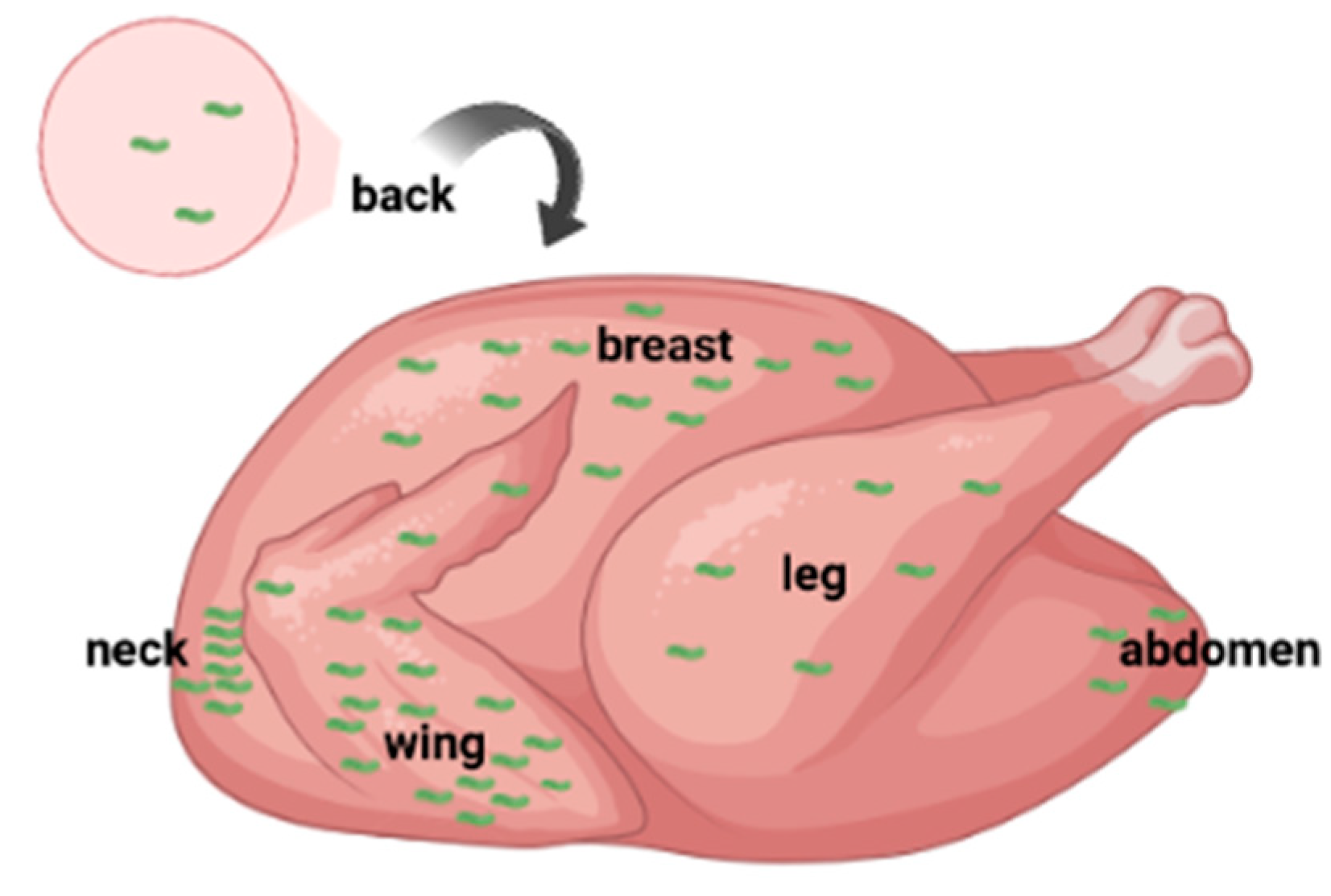
2.1. Carcass Sampling
2.2. Sampling Method, Type of Product and Refrigerated Storage
2.3. Seasonality of Sampling and Environmental Conditions
3. Isolation of Campylobacter spp.
3.1. Detection and/or Enumeration Procedure
3.1.1. Composition of Culture Media for Detection/Enumeration
4. Confirmation and Identification of Campylobacter spp.
4.1. Biochemical Differentiation of Campylobacter species
4.2. Molecular Methods for Differentiating Campylobacter species
4.2.1. PCR-Based Methods and Techniques
5. Biofilm-forming ability of Campylobacter spp.
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- EFSA (European Food Safety Authority); ECDC (European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control). The European Union one health 2021 zoonoses report. ESFA J. 2022, 20, e07666. [CrossRef]
- Kumagai, Y.; Pires, S.M.; Kubota, K.; Asakura, H. Attributing human foodborne diseases to food sources and water in Japan using analysis of outbreak surveillance data. J. Food Prot. 2020, 83, 2087–2094. [CrossRef]
- Scallan, E.; Hoekstra, R.M.; Angulo, F.J.; Tauxe, R.V.; Widdowson, M.-A.; Roy, S.L.; Jones, J.L.; Grifiin, P.M. Foodborne illness acquired in the United States – Major pathogens, Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 7–15. [CrossRef]
- Walter, E.J.S.; Griffin, P.M.; Bruce, B.B.; Hoekstra, R.M. Estimating the number of illnesses caused by agents transmitted commonly through food: A scoping review. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2021, 18, 841–858. [CrossRef]
- Bisht, A.; Kamble, M.P.; Choudhary, P.; Chaturvedi, K.; Kohli, G.; Juneja, V.K.; Sehgal, S.; Taneja, N.K. A surveillance of food borne disease outbreaks in India: 2009–2018. Food Control 2021, 121, 107630. [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Pires, S.M.; Liu, Z.; Ma, X.; Liang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, J.; Liang, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Meng, C.; Huo, X.; Lan, Z.; Lai, S.; Liu, C.; Han, H.; Liu, J. Fu, P.; Guo, Y. Surveillance of foodborne disease outbreaks in China, 2003–2017. Food Control 2020, 118, 107359. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Cheng, H.; Wang, Z.; Fu, P.; Guo, Y.; Yang, S. Attribution analysis of foodborne disease outbreaks related to meat and meat products in China, 2002–2017. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2022, 19, 839–847. [CrossRef]
- Batz, M.B.; Hoffmann, S.; Morris, Jr., J.G. Ranking the disease burden of 14 pathogens in food sources in the United States using attribution data from outbreak investigations and expert elicitation. J. Food Prot. 2012, 75, 1278–1291. [CrossRef]
- Batz, M.B.; Richardson, L.C.; Bazaco, M.C.; Parker, C.C.; Chirtel, S.J.; Cole, D.; Golden, N.J.; Griffin, P.M.; Gu, W.; Schmitt, S.K.; Wolpert, B.J.; Kufel, J.S.Z.; Hoekstra, R.M. Recency-weighted statistical modeling approach to attribute illnesses caused by 4 pathogens to food sources using outbreak data, United States. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 214–222. [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.; Leite, D.; Fernandes, M.; Mena, C.; Gibbs, P.A.; Teixeira, P. Campylobacter spp. as a foodborne pathogen: a review. Front. Microbiol. 2011, 2, 200. [CrossRef]
- Stern, N.J.; Hernandez, M.P.; Blankenship, L.; Deibel, K.E.; Doores, S.; Doyle, M.P.; Ng, H.; Pierson, M.D.; Sofos, J.N.; Sveum, W.H.; Westhoff, D.C. Prevalence and distribution of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli in retail meats. J. Food Prot. 1985, 48, 595–599. [CrossRef]
- Mataragas, M.; Skandamis, P.N.; Drosinos, E.H. Risk profiles of pork and poultry meat and risk ratings of various pathogen/product combinations. Int. J. Food. Microbiol. 2008, 126, 1–12. [CrossRef]
- Scharff, R.L. Food attribution and economic cost estimates for meat- and poultry-related illnesses. J. Food Prot. 2020, 80, 959–967. [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, J.S.; Boras, V.F.; Hetman, B.J.; Taboada, E.N.; Inglis, G.D. Molecular epidemiological evidence implicates cattle as a primary reservoir of Campylobacter jejuni infecting people via contaminated chickens. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1366. [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, H.; Rosado, P.; Roser, M. Our World in Data: Meat and Dairy Production. 2017, Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/meat-production#citation (accessed on 12 April 2023).
- Parte, A.C.; Sardà Carbasse, J.; Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Reimer, L.C.; Göker, M. List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN) moves to the DSMZ. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2022, 70, 5607–5612. [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.bacterio.net/genus/campylobacter (accessed on 7 May 2023).
- Aydin, F.; Abay, S.; Kayman, T.; Karakaya, E.; Mustak, H.K.; Mustak, I.B.; Bilgen, N.; Goncuoglu, M.; Duzler, A.; Guran, O.; Sahin, O.; Saticioglu, I.B. Campylobacter anatolicus sp. nov., a novel member of the genus Campylobacter isolated from feces of Anatolian Ground Squirrel (Spermophilus xanthoprymnus) in Turkey. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 44, 126265. [CrossRef]
- Boukerb, A.M.; Penny, C.; Serghine, J.; Walczak, C.; Cauchie, H.M.; Miller, W.G.; Losch, S.; Ragimbeau, C.; Mossong, J.; Mégraud, F.; Lehours, P.; Bénéjat, L.; Gourmelot, M. Campylobacter armoricus sp. nov., a novel member of the Campylobacter lari group isolated from surface water and stools from humans with enteric infection. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 3969–3979. [CrossRef]
- Bryant, E.; Shen, Z.; Mannion, A.; Patterson, M.; Buczek, J.; Fox, J.G. Campylobacter taeniopygiae sp. nov., Campylobacter aviculae sp. nov., and Campylobacter estrildidarum sp. nov., novel species isolated from laboratory-maintained zebra finches. Avian Dis. 2020, 64, 457–466. [CrossRef]
- Rossi, M.; Debruyne, L.; Zanoni, R.G.; Manfreda, G.; Revez, J.; Vandamme, P. Campylobacter avium sp. nov., a hippurate-positive species isolated from poultry. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2009, 59, 2364–2369. [CrossRef]
- Phung, C.; Scott, P.C.; Dekiwadia, C.; Moore, R.J.; Van T.T.H. Campylobacter bilis sp. nov., isolated from chickens with spotty liver disease. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2022, 72, 5314. [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, M.J.; Zomer, A.L.; Timmerman, A.J.; Spaninks, M.P.; Rubio-Garcia, A.; Rossen, J.W.; Duim, B.; Wagenaar, J.A. Campylobacter blaseri sp. nov., isolated from common seals (Phoca vitulina). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 1787–1794. [CrossRef]
- Inglis, G.D.; Hoar, B.M.; Whiteside, D.P.; Morck, D.W. Campylobacter canadensis sp. nov., from captive whooping cranes in Canada. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 2636–2644. [CrossRef]
- Véron, M.; Chatelain, R. Taxonomic study of the genus Campylobacter Sebald and Véron and designation of the neotype strain for the type species, Campylobacter fetus (Smith and Taylor) Sebald and Véron. Int. J. Syst. Bact. 1973, 23:122–134. [CrossRef]
- Tanner, A.C.R.; Badger, S.; Lai, C.H.; Listgarten, M.A.; Visconti, R.A.; Socransky, S.S. Wolinella gen. nov., Wolinella succinogenes (Vibrio succinogenes Wolin et al.) comb. nov., and description of Bacteroides gracilis sp. nov., Wolinella recta sp. nov., Campylobacter concisus sp. nov., and Eikenella corrodens from humans with periodontal disease. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1981, 31, 432–445. [CrossRef]
- Koziel, M.; O'Doherty, P.; Vandamme, P.; Corcoran, G.D.; Sleator R.D.; Lucey, B. Campylobacter corcagiensis sp. nov., isolated from faeces of captive lion-tailed macaques (Macaca silenus). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2014; 64, 2878–2883. [CrossRef]
- Zanoni, R.G.; Debruyne, L.; Rossi, M.; Revez, J.; Vandamme, P. Campylobacter cuniculorum sp. nov., from rabbits. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2009, 59, 1666–1671. [CrossRef]
- Vandamme, P.; Falsen, E.; Rossau, R.; Hoste, B.; Segers, P.; Tytgat, R.; De Ley, J. Revision of Campylobacter, Helicobacter, and Wolinella taxonomy: emendation of generic descriptions and proposal of Arcobacter gen. nov. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1991, 41, 88–103. [CrossRef]
- Sebald, M.; Veron, M. [BASE DNA CONTENT AND CLASSIFICATION OF VIBRIOS]. Ann. Inst. Pasteur (Paris) 1963, 105, 897–910.
- Piccirillo, A.; Nier,o G.; Calleros, L.; Perez, R.; Naya, H.; Iraola, G. Campylobacter geochelonis sp. nov. isolated from the western Hermann's tortoise (Testudo hermanni hermanni). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016 66, 3468–3476. [CrossRef]
- Vandamme, P.; Daneshvar, M.I.; Dewhirst, F.E.; Paster, B.J.; Kersters, K.; Goossens, H.; Moss, C.W. Chemotaxonomic analyses of Bacteroides gracilis and Bacteroides ureolyticus and reclassification of B. gracilis as Campylobacter gracilis comb. nov. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1995, 45, 145–152. [CrossRef]
- Stanley, J.; Burnens, A.P.; Linton, D.; On, S.L.; Costas, M.; Owen, R.J. Campylobacter helveticus sp. nov., a new thermophilic species from domestic animals: characterization, and cloning of a species-specific DNA probe. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1992, 138, 2293–2303. [CrossRef]
- Van, T.T.; Elshagmani, E.; Gor, M.C.; Scott, P.C.; Moore, R.J. Campylobacter hepaticus sp. nov., isolated from chickens with spotty liver disease. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 4518–4524. [CrossRef]
- Lawson, A.J.; On, S.L.; Logan, J.M.; Stanley, J. Campylobacter hominis sp. nov., from the human gastrointestinal tract. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2001, 51, 651–660. [CrossRef]
- Gebhart, C.J.; Edmonds, P.; Ward, G.E.; Kurtz, H.J.; Brenner, D.J. "Campylobacter hyointestinalis" sp. nov.: a new species of Campylobacter found in the intestines of pigs and other animals. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1985, 21, 715–720. [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, M.J.; Kik, M.; Miller, W.G.; Duim, B.; Wagenaar, J.A. Campylobacter iguaniorum sp. nov., isolated from reptiles. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 975–982. [CrossRef]
- Foster, G.; Holmes, B.; Steigerwalt, A.G.; Lawson, P.A.; Thorne, P.; Byrer, D.E.; Ross, H.M.; Xerry, J.; Thompson, P.M.; Collins, M.D. Campylobacter insulaenigrae sp. nov., isolated from marine mammals. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2004, 54, 2369–2373. [CrossRef]
- Logan, J.M.; Burnens, A.; Linton, D.; Lawson, A.J.; Stanley, J. Campylobacter lanienae sp. nov., a new species isolated from workers in an abattoir. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2000, 50, 865–872. [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, J.; Leaper, S.; Owen, R.J.; Skirrow, M.B. Description of Campylobacter laridis, a new species comprising the nalidixic acid resistant thermophilic Campylobacter (NARTC) group. Curr. Microbiol. 1983, 8, 231–238. [CrossRef]
- Lynch, C.; Peeters, C.; Walsh, N.; McCarthy, C.; Coffey, A.; Lucey, B.; Vandamme, P. Campylobacter majalis sp. nov. and Campylobacter suis sp. nov., novel Campylobacter species isolated from porcine gastrointestinal mucosa. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2022, 72,5510. [CrossRef]
- Antezack, A.; Boxberger, M.; Rolland, C.; Ben Khedher, M.; Monnet-Corti, V.; La Scola, B. Isolation and characterization of Campylobacter massiliensis sp. nov., a novel Campylobacter species detected in a gingivitis subject. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2021, 71, 5039. [CrossRef]
- Roop Ii, R.M.; Smibert, R.M.; Johnson, J.L.; Krieg, N.R. Campylobacter mucosalis (Lawson, Leaver, Pettigrew, and Rowland 1981) comb. nov.: emended description. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1985, 35, 189–192. [CrossRef]
- Bloomfield, S.; Wilkinson, D.; Rogers, L.; Biggs, P.; French, N.; Mohan, V.; Savoian, M.; Venter, P.; Midwinter, A. Campylobacter novaezeelandiae sp. nov., isolated from birds and water in New Zealand. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 3775–3784. [CrossRef]
- Caceres, A.; Munoz, I.; Iraola, G.; Diaz-Viraque, F.; Collado, L. Campylobacter ornithocola sp. nov., a novel member of the Campylobacter lari group isolated from wild bird faecal samples. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 1643–1649. [CrossRef]
- Debruyne, L.; On, S.L.; De Brandt, E.; Vandamme, P. Novel Campylobacter lari-like bacteria from humans and molluscs: description of Campylobacter peloridis sp. nov., Campylobacter lari subsp. concheus subsp. nov. and Campylobacter lari subsp. lari subsp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2009, 59, 1126–1132. [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, M.J.; Miller, W.G.; Leger, J.S.; Chapman, M.H.; Timmerman, A.J.; Duim, B.; Foster, G.; Wagenaar, J.A. Campylobacter pinnipediorum sp. nov., isolated from pinnipeds, comprising Campylobacter pinnipediorum subsp. pinnipediorum subsp. nov. and Campylobacter pinnipediorum subsp. caledonicus subsp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 1961–1968. [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.F.; Pereira, G.; Carneiro, C.; Hemphill, A.; Mateus, L.; Lopes-da-Costa, L.; Silva, E. Campylobacter portucalensis sp. nov., a new species of Campylobacter isolated from the preputial mucosa of bulls. PLoS One 2020, 15, e0227500. [CrossRef]
- Etoh, Y.; Dewhirst, F.E.; Paster, B.J.; Yamamoto, A.; Goto, N. Campylobacter showae sp. nov., isolated from the human oral cavity. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1993, 43, 631–639. [CrossRef]
- Debruyne, L.; Broman, T.; Bergstrom, S.; Olsen, B.; On, S.L.; Vandamme, P. Campylobacter subantarcticus sp. nov., isolated from birds in the sub-Antarctic region. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2010, 60, 815–819. [CrossRef]
- Sandstedt, K.; Ursing, J. Description of Campylobacter upsaliensis sp. nov. previously known as the CNW group. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 1991, 14, 39–45. [CrossRef]
- Vandamme, P.; Debruyne, L.; De Brandt, E.; Falsen, E. Reclassification of Bacteroides ureolyticus as Campylobacter ureolyticus comb. nov., and emended description of the genus Campylobacter. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2010, 60, 2016–2022. [CrossRef]
- Debruyne, L.; Broman, T.; Bergstrom, S.; Olsen, B.; On, S.L.; Vandamme, P. Campylobacter volucris sp. nov., isolated from black-headed gulls (Larus ridibundus). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2010, 60, 1870–1875. [CrossRef]
- Parisi, A.; Chiara, M.; Caffara, M.; Mion, D.; Miller, W.G.; Caruso, M.; Manzari, C.; Florio, D.; Capozzi, L.; D'Erchia, A.M.; Manzulli, V.; Zanoni, R.G. Campylobacter vulpis sp. nov. isolated from wild red foxes. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 44, 126204. [CrossRef]
- Ghafir, Y.; China, B.; Dierick, K.; De Zutter, L.; Daube, G. A seven-year survey of Campylobacter contamination in meat at different production stages in Belgium. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 116, 111–120. [CrossRef]
- Wagenaar, J.A.; van der Graaf-van Blools, L. Chapter 3.10.4. Infection with Campylobacter jejuni and C. coli. In Manual of Diagnostic Tests and Vaccines for Terrestrial Animals, OIE; World Organization for Animal Health, 2018; pp. 1669–1677. Available online: https://www.woah.org/en/what-we-do/standards/codes-and-manuals/terrestrial-manual-online-access/ (accessed on 11 April 2023).
- Jorgensen, F.; Ellis-Iversen, J.; Rushton, S.; Bull, S.A.; Harris; S.A.; Bryan, S.J.; Gonzalez, A.; Humphrey, T.J. Influence of season and geography on Campylobacter jejuni and C. coli subtypes in housed broiler flocks reared in Great Britain. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 3741–3748. [CrossRef]
- Habib, I.; Mohamed, M.-Y.I.; Lakshmi, G.B.; Khan, M.; Li, D. Quantification of Campylobacter contamination on chicken carcasses sold in retail markets in the United Arab Emirates. Int. J. Food Contam. 2022, 9, 9. [CrossRef]
- Manfreda, G.; De Cesare, A.; Bondioli, V.; Stern, J.N.; Franchini, A. Enumeration and identity of Campylobacter spp. in Italian broilers. Poult. Sci. 2006, 85, 556–562. [CrossRef]
- Repérant, E.; Laisney, M.J.; Nagard, B.; Quesne, S.; Rouxel, S.; Le Gall, F.; Chemaly, M.; Denis, M. Influence of enrichment and isolation media on the detection of Campylobacter spp. in naturally contaminated chicken samples. J. Microbiol. Methods 2016, 128, 42–47. [CrossRef]
- Wieczorek, K.; Bocian, Ł.; Osek, J. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of Campylobacter isolated from carcasses of chickens slaughtered in Poland – a retrospective study. Food Control 2020, 112, 107159. [CrossRef]
- Wieczorek, K.; Szewczyk, R.; Osek, J. Prevalence, antimicrobial resistance, and molecular characterization of Campylobacter jejuni and C. coli isolated from retail raw meat in Poland. Vet. Med. 2012, 57, 293–299.
- Andritsos, N.D.; Tzimotoudis, N.; Mataragas, M. Estimating the performance of four culture media used for enumeration and detection of Campylobacter species in chicken meat. LWT 2020, 118, 108808. [CrossRef]
- Marinou, I.; Bersimis, S.; Ioannidis, A.; Nicolau, C.; Mitroussia-Ziouva, A.; Legakis, N.J.; Chatzipanagiotou, S. Identification and antimicrobial resistance of Campylobacter species isolated from animal sources. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 58. [CrossRef]
- Jeffrey, J.S.; Tonooka, K.H.; Lozano, J. (2001). Prevalence of Campylobacter spp. from skin, crop, and intestine of commercial broiler chicken carcasses at processing. Poult. Sci. 2001, 80, 1390–1392. [CrossRef]
- Buhr, R.J.; Berrang, M.E.; Cason, J.A. Bacterial recovery from breast skin of genetically feathered and featherless broiler carcasses immediately following scalding and picking. Poult. Sci. 2003, 82, 1641–1647.
- Cason, J.A.; Hinton, Jr., A.;Buhr, R.J. Impact of feathers and feather follicles on broiler carcass bacteria. Poult. Sci. 2004, 83, 1452–1455. [CrossRef]
- Habib, I.; Sampers, I.; Uyttendaelle, M.; Berkvens, D.; De Zutter, L. Baseline data from a Belgium-wide survey of Campylobacter species contamination in chicken meat preparations and considerations for a reliable monitoring program. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 5483–5489. [CrossRef]
- Kinde, H.; Genigeorgis, C.A.; Pappaioanou, M. Prevalence of Campylobacter jejuni in chicken wings. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1983, 45, 1116–1118. [CrossRef]
- Rayes, H.M.; Genigeorgis, C.A.; Farver, T.B. Prevalence of Campylobacter jejuni on turkey wings at the supermarket level. J. Food Prot. 1983, 46, 292–294. [CrossRef]
- Baré, J.; Uyttendaele, M.; Depraetere, O.; Houf, K.; De Zutter, L. Variation in Campylobacter distribution on different sites of broiler carcasses. Food Control 2013, 32, 279–282. [CrossRef]
- Russell, S.M.; Cox, N.A.; Bailey, J.S. Sampling poultry carcasses and parts to determine bacterial levels. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 1997, 6, 234–237. [CrossRef]
- Sproston, E.L.; Carrillo, C.D.; Boulter-Bitzer, J. The quantitative and qualitative recovery of Campylobacter from raw poultry using USDA and Health Canada methods. Food Microbiol. 2014, 44, 258–263. [CrossRef]
- Commission Regulation (EC) 2073/2005. Microbiological criteria for foodstuffs. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/ALL/?uri=CELEX%3A32005R2073 (accessed on 12 April 2023).
- Commission Regulation (EU) 2017/1495. Amending Regulation (EC) No 2073/2005 as regards Campylobacter in broiler carcasses. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A32017R1495 (accessed on 12 April 2023).
- Gill, C.O.; Badoni, M.; Moza, L.F.; Barbut, S.; Griffiths, M.W. Microbiological sampling of poultry carcass portions by excision, rinsing, or swabbing. J. Food Prot. 2005, 68, 2718–2720. [CrossRef]
- Bishop. H.; Evans, J.; Eze, J.I.; Webster, C.; Humphry, R.W.; Beattie, R.; White, J.; Couper, J.; Allison, L.; Brown, D.; Tongue, S.C. Bacteriological survey of fresh minced beef on sale at retail outlets in Scotland in 2019: Three foodborne pathogens, hygiene process indicators, and phenotypic antimicrobial resistance. J. Food Prot. 2022, 85, 1370–1379. [CrossRef]
- Stella, S.; Soncini, G.; Ziino, G.; Panebianco, A.; Pedonese, F.; Nuvoloni, R.; Di Giannatale, E.; Colavita, G.; Alberghini, L.; Giaccone, V. Prevalence and quantification of thermophilic Campylobacter spp. in Italian retail poultry meat: Analysis of influencing factors. Food Microbiol. 2017, 62, 232–238. [CrossRef]
- Beterams, A.; Tolksdorf, T.; Martin, A.; Stingl, K.; Bandick, N.; Reich, F. Change of Campylobacter, Escherichia coli and Salmonella counts in packaged broiler breast meat stored under modified atmosphere and vacuum conditions at 4 and 10 °C based on cultural and molecular biological quantification. Food Control 2023, 145, 109337. [CrossRef]
- Proietti, P.C.; Pergola, S.; Bellucci, S.; Menchetti, L.; Miraglia, D.; Franciosini, M.P. Occurrence and antimicrobial susceptibility of Campylobacter spp. on fresh and refrigerated chicken meat products in central Italy. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 2895–2901. [CrossRef]
- Andritsos, N.D.; Paramithiotis, S.; Mataragas, M.; Drosinos, E.H. Listeria monocytogenes serogroup 1/2 strains have a competitive growth advantage over serotype 4b during refrigerated storage of an artificially contaminated ready-to-eat pork meat product. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6096. [CrossRef]
- Djennad, A.; Lo lacono, G.; Sarran, C.; Lane, C.; Elson, R.; Höser, C.; Lake, I.R.; Colón-González, F.J.; Kovats, S.; Semenza, J.C.; Bailey, T.C.; Kessel, A.; Fleming, L.E.; Nichols, G.L. Seasonality and the effects of weather on Campylobacter infections. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 255. [CrossRef]
- Guerrin, M.T.; Sir, C.; Sargeant, J.M.; Wadell, L.; O’Connor, A.M.; Wills, R.M.; Bailey, R.H.; Byrd, J.A. The change in prevalence of Campylobacter on chicken carcasses during processing. Poult. Sci. 2010, 89, 1070–1084. [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, F.; Ellis-Iversen, J.; Rushton, S.; Bull, S.A.; Harris, S.A.; Bryan, S.J.; Gonzalez, A.; Humphrey, T.J. Influence of season and geography on Campylobacter jejuni and C. coli subtypes in housed broiler flocks reared in Great Britain. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 3741–3748. [CrossRef]
- Mäesaar, M.; Praakle, K.; Meremäe, K.; Kramarenko, T.; Sõgel, J.; Viltrop, A.; Muutra, K.; Kovalenko, K.; Matt, D.; Hörman, A.; Hänninen, M.-L.; Roasto, M. Prevalence and counts of Campylobacter spp. in poultry meat at retail level in Estonia. Food Control 2014, 44, 72–77. [CrossRef]
- Kalupahana, R.S.; Mughini-Gras, L.; Kottawatta, S.A.; Somarathne, S.; Gamage, C.; Wagenaar, J.A. Weather correlates of Campylobacter prevalence in broilers at slaughter under tropical conditions in Sri Lanka. Epidemiol. Infect. 2018, 146, 972–979. [CrossRef]
- Prachantasena, S.; Charununtakorn, P.; Muangnoicharoen, S.; Hankla, L.; Techawal, N.; Chaveerach, P.; Tuitemwong, P.; Chokesajjawatee, N.; Williams, N.; Humphrey, T.; Luangtongkum, T. Climatic factors and prevalence of Campylobacter in commercial broiler flocks in Thailand. Poult. Sci. 2017, 96, 980–985. [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, M.E.; Chriél, M.; Norström, M.; Hofshagen, M. Effect of climate and farm environment on Campylobacter spp. colonization in Norwegian broiler flocks. Prev. Vet. Med. 2012, 107, 95–104. [CrossRef]
- Nylen, G.; Dunstan, F.; Palmer, S.R.; Andersson, Y.; Bager, F.; Cowden, J.; Feierl, G.; Galloway, Y.; Kapperud, G.; Megraud, F.; Molbak, K.; Petersen, L.R.; Ruutu, P. The seasonal distribution of campylobacter infection in nine European countries and New Zealand. Epidemiol. Infect. 2002, 128, 383–390. [CrossRef]
- Urdaneta, S.; Lorca-Oró, C.; Dolz, R.; López-Soria, S.; Cerdà-Cuéllar, M. In a warm climate, ventilation, indoor temperature and outdoor relative humidity have significant effects on Campylobacter spp. colonization in chicken broiler farms which can occur in only 2 days. Food Microbiol. 2023, 109, 104118. [CrossRef]
- Smith, O.M.; Cornell, K.A.; Crossley, M.S.; Crespo, R.; Jones, M.S.; Snyder, W.E.; Owen, J.P. Wind speed and landscape context mediate Campylobacter risk among poultry reared in open environments. Animals 2023, 13, 492. [CrossRef]
- Sommer, H.M.; Borck Høg, B.; Larsen, L.S.; Sørensen, A.I.V.; Williams, N.; Merga, J.Y.; Cerdà-Cuéllae, M.; Urdaneta, S.; Dolz, R.; Wieczorek, K.; Osek, J.; David, B.; Hofshagen, M.; Jonsson, M.; Wagenaar, J.A.; Bolder, N.; Rosenquist, H. Analysis of farm specific risk factors for Campylobacter colonization of broilers in six European countries. Microb. Risk Anal. 2016, 2–3, 16–26. [CrossRef]
- Wong, T.L.; Hollis, L.; Cornelius, A.; Nicol, C.; Cook, R.; Hudson, J.A. Prevalence, numbers, and subtypes of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli in uncooked retail meat samples. J. Food. Prot. 2007, 70, 566–573. [CrossRef]
- Baylis, C.L.; MacPhee, S.; Martin, K.W.; Humphrey, T.J.; Betts, R.P. Comparison of three enrichment media for the isolation of Campylobacter spp. from foods. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2000, 89, 884–891. [CrossRef]
- Carrillo, C.D.; Plante, D.; Iugovaz, I.; Kenwell, R.; Bélanger, G.; Boucher, F.; Poulin, N.; Trottier, Y.-L. Method-dependent variability in determination of prevalence of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli in Canadian retail poultry. J. Food Prot. 2014, 77, 1682–1688. [CrossRef]
- Habib, I.; Uyttendaele, M.; De Zutter, L. Evaluation of ISO 10272:2006 standard versus alternative enrichment and plating combinations for enumeration and detection of Campylobacter in chicken meat. Food Microbiol. 2011, 28, 1117–1123. [CrossRef]
- Jasson, V.; Sampers, I.; Botteldoorn, N.; López-Gálvez, F.; Baert, L.; Denayer, S.; Rajkovic, A.; Habib, I.; De Zutter, L.; Debevere, J.; Uyttendaele, M. Characterization of Escherichia coli from raw poultry in Belgium and impact on the detection of Campylobacter jejuni using Bolton broth. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2009, 135, 248–253. [CrossRef]
- Repérant, E.; Laisney, M.J.; Nagard, B.; Quesne, S.; Rouxel, S.; Le Gall, F.; Chemaly, M.; Denis, M. Influence of enrichment and isolation media on the detection of Campylobacter spp. in naturally contaminated chicken meat samples. J. Microbiol. Methods 2016, 128, 42–47. [CrossRef]
- Seliwiorstow, T.; De Zutter, L.; Houf, K.; Botteldoorn, N.; Baré, J.; Van Damme, I. Comparative performance of isolation methods using Preston broth, Bolton broth and their modifications for the detection of Campylobacter spp. from naturally contaminated fresh and frozen raw poultry meat. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 234, 60–64. [CrossRef]
- Stern, N.J.; Line, J.E. Comparison of three methods for recovery of Campylobacter spp. from broiler carcasses. J. Food Prot. 1992, 55, 663–666. [CrossRef]
- Williams, L.K.; Jørgensen, F.; Grogono-Thomas, R.; Humphrey, T.J. Enrichment culture for the isolation of Campylobacter spp.: Effects of incubation conditions and the inclusion of blood in selective broths. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2009, 130, 131–134. [CrossRef]
- ISO 10272-1, G: Food Chain–Horizontal Method for Detection and Enumeration of Campylobacter spp.–Part 1: Detection Method. ISO (International Organization for Standardization), 2017.
- Hayashi, M.; Kubota-Hayashi, S.; Natori, T.; Mizuno, T.; Miyata, M.; Yoshida, S.; Zhang, J.; Kawamoto, K.; Ohkusu, K.; Makino, S.; Ezaki, T. Use of blood-free enrichment broth in the development of a rapid protocol to detect Campylobacter in twenty-five grams of chicken meat. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 163, 41–46. [CrossRef]
- Hinton, A.; Cox, N.A.; Selective medium for aerobic incubation of Campylobacter. J. Food Microbiol. Saf. Hyg. 2018, 3, 131. [CrossRef]
- Seliwiorstow, T.; De Zutter, L.; Houf, K.; Botteldoorn, N.; Baré, J.; Van Damme, I. Comparative performance of isolation methods using Preston broth, Bolton broth and their modifications for the detection of Campylobacter spp. from naturally contaminated fresh and frozen raw poultry meat. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 234, 60–64. [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.-H.; Choi, N.-Y.; Bae, Y.-M.; Lee, J.-S.; Lee, S.-Y. Development of a selective agar plate for the detection of Campylobacter spp. in fresh produce. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 189, 67–74. [CrossRef]
- ISO 10272-2, G: Food Chain–Horizontal Method for Detection and Enumeration of Campylobacter spp.–Part 2: Enumeration Method. ISO (International Organization for Standardization), 2017.
- Ahmed, León-Velarde, C.G.; Odumeru, J.A. Evaluation of novel agars for the enumeration of Campylobacter spp. in poultry retail samples. J. Microbiol. Methods 2012, 88, 304–310. [CrossRef]
- Le Bars, H.; Kayal, S.; Bonnaure-Mallet, M.; Minet, J. CASA chromogenic medium for enteric Campylobacter species. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 3675–3677. [CrossRef]
- Levican, A.; Hinton, Jr., A. CAMPYAIR, a new selective, differential medium for Campylobacter spp. isolation without the need for microaerobic atmosphere. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1403. [CrossRef]
- Seliwiorstow, T.; Baré, J.; Verhaegen, B.; Uyttendaele, M.; De Zutter, L. Evaluation of a new chromogenic medium for direct enumeration of Campylobacter in poultry meat samples. J. Food Prot. 2014, 77, 2111–2114. [CrossRef]
- Teramura, H.; Iwasaki, M.; Ogihara, H. Development of a novel chromogenic medium for improved Campylobacter detection from poultry samples. J. Food Prot. 2015, 78, 1750–1755. [CrossRef]
- Lanzl, M.I.; van Mastrigt, O.; Zwietering, M.H.; Abee, T.; den Besten, H.M.W. Role of substrate availability in the growth of Campylobacter co-cultured with extended spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli in Bolton broth. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2022, 363, 109518. [CrossRef]
- Chon, J.-W.; Hyeon, J.-Y.; Yim, J.-H.; Kim, J.-H.; Song, K.-Y.; Seo, K.-H. Improvement of modified charcoal-cefoperazone-deoxycholate agar by supplementation with a high concentration of polymyxin B for detection of Campylobacter jejuni and C. coli in chicken carcass rinses. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 1624–1626. [CrossRef]
- Chon, J.-W.; Kim, H.; Kim, H.-S.; Seo, K.-H. Improvement of modified charcoal-cefoperazone-deoxycholate agar by addition of potassium clavulanate for detecting Campylobacter spp. in chicken carcass rinse. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 165, 7–10. [CrossRef]
- Chon, J.-W.; Kim, H.; Yim, J.-H.; Song, K.-Y.; Moon, J.-S.; Kim, Y.-J.; Seo, K.-H. Improvement of Karmali agar by addition of polymyxin B for the detection of Campylobacter jejuni and C. coli in whole-chicken carcass rinse. J. Food Sci. 2013, 78, 752–755. [CrossRef]
- Chon, J.-W.; Kim, H.-S.; Kim, D.-H.; Kim, H.; Choi, I.-S.; Oh, D.-H.; Seo, K.-H. Modification of Karmali agar by supplementation with potassium clavulanate for the isolation of Campylobacter from chicken carcass rinses. J. Food Prot. 2014, 77, 1207–1211. [CrossRef]
- Chon, J.-W.; Kim, Y.-J.; Kim, H.-S.; Kim, D.-H.; Kim, H.; Song, K.-W.; Seo, K.-H. Supplementation of Bolton broth with triclosan improves detection of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli in chicken carcass rinse. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 181, 37–39. [CrossRef]
- Chon, J.-W.; Kim, Y.-J.; Kim, Y.-J.; Jung, J.Y.; Bae, D.; Khan, S.; Seo, K.-H.; Sung, K. Addition of rifampicin to Bolton broth to inhibit extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli for the detection of Campylobacter. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 1688–1692. [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-J.; Whan, C.-J.; Kim, H.-S.; Kim, K.-Y.; Yim, J.-H.; Cho, S.-H.; Seo, K.-H. Improvement of Karmali agar by supplementation with tazobactam for detecting Campylobacter in raw poultry. J. Food Prot. 2016, 79, 1982–1985. [CrossRef]
- Moran, L.; Kelly, C.; Cormican, M.; McGettrick, S.; Madden, R.H. Restoring the selectivity of Bolton broth during enrichment for Campylobacter spp. from raw chicken. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 52, 614–618. [CrossRef]
- Rautelin, H.; Jusufovic, J.; Hänninen, M.-L. Identification of hippurate-negative thermophilic campylobacters. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 1999, 35, 9–12. [CrossRef]
- Totten, P.A.; Patton, C.M.; Tenover, F.C.; Barrett, T.J.; Stamm, W.E.; Steigerwalt, A.G.; Lin, J.Y.; Holmes, K.K.; Brenner, D.J. Prevalence and characterization of hippurate-negative Campylobacter jejuni in King County, Washington. J. Clin. Microbiol.1987, 25, 1747–1752. [CrossRef]
- Bessède, E.; Asselineau, J.; Perez, P.; Valdenaire, G.; Richer, O.; Lehours, P.; Mégraud, F. Evaluation of the diagnostic accuracy of two immunochromatographic tests detecting campylobacter in stools and their role in campylobacter infection diagnosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, e01567-17. [CrossRef]
- Franco, J.; Bénejat, L.; Ducournau, A.; Mégraud, F.; Lehours, P.; Bessède, E. Evaluation of CAMPYLOBACTER QUIK CHEK™ rapid membrane enzyme immunoassay to detect Campylobacter spp. antigen in stool samples. Gut Pathog. 2021, 13, 4. [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Chen, X.; Wen, R.; Ma, P.; Gu, K.; Li, C.; Zhou, C.; Lei, C.; Tang, Y.; Wang, H. Immunocapture magnetic beads enhanced the LAMP-CRISP/Cas12a method for the sensitive, specific, and visual detection of Campylobacter jejuni. Biosensors 2022, 12, 154. [CrossRef]
- Muralidharan, C.; Anwar, A.; Wilson, T.B.; Scott, P.C.; Moore, R.J.; Van, T.T.H. Development of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detecting Campylobacter hepaticus specific antibodies in chicken sera – a key tool in spotty liver disease screening and vaccine development. Avian Pathol. 2020, 49, 658–665. [CrossRef]
- Schnee, A.E.; Haque, R.; Taniuchi, M.; Uddin, J.; Petri, W.A., Jr. Evaluation of two new membrane-based and microtiter plate enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays for detection of Campylobacter jejuni in stools of Bangladeshi children. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, e00702-18. [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Du, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xu, E.; Jin, Z.; Wu, Z. Quantitative detection of Campylobacter jejuni with a core-satellite assemblies-based dual-modular aptasensor. Food Control 2022, 135, 108828. [CrossRef]
- Quintela, I.A.; Vasse, T.; Lin, C.-S.; Wu, V.C.H. Advances, applications, and limitations of portable and rapid detection technologies for routinely encountered foodborne pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1054782. [CrossRef]
- Babu, U.S.; Harrison, L.M.; Mammel, M.K.; Bigley III, E.C.; Hiett, K.L.; Balan, K.V. A loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assay for the consensus detection of human pathogenic Campylobacter species. J. Microbiol. Methods 2020, 176, 106009. [CrossRef]
- Phaneuf, C.R.; Mangadu, B.; Tran, H.M.; Light, Y.K.; Sinha, A.; Charbonier, F.W.; Eckles, T.P.; Singh, A.K.; Koh, C.-Y. Integrated LAMP and immunoassay platform for diarrheal disease detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 120, 93–101. [CrossRef]
- Asakura, H.; Yamamoto, S.; Kazuhiro, Y.; Kawase, J.; Nakamura, H.; Abe, K.; Sasaki, Y.; Ikeda, T.; Nomoto, R. Quantitative detection and genetic characterization of thermotolerant Campylobacter spp. in fresh chicken meats at retail in Japan. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1014212. [CrossRef]
- Aydin, F.; Kayman, T.; Abay, S.; Hizlisoy, H.; Saticioğlu, I.B.; Karakaya, E.; Sahin, O. MLST genotypes and quinolone resistance profiles of Campylobacter jejuni isolates from various sources in Turkey. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2023, 391-393, 110137. [CrossRef]
- Joseph, L.A.; Griswold, T.; Vidyaprakash, E.; Im, S.B.; Williams, G.M.; Pouseele, H.A.; Hise, K.B.; Carleton, H.A. Evaluation of core genome and whole genome multilocus sequence typing schemes for Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli outbreak detection in the USA. Microb. Genom. 2023, 9, 001012. [CrossRef]
- Bakhshi, B.; Kalantar, M.; Rastegar-Lari, A.; Fallah, F. PFGE genotyping and molecular characterization of Campylobacter spp. isolated from chicken meat. Iran J. Vet. Res. 2016, 17, 177–183.
- Davedow, T.; Carleton, H.; Kubota, K.; Palm, D.; Schroeder, M.; Gerner-Smidt, P.; Al-Jardani, A.; Chinen, I.; Kam, K.M.; Smith, A.M.; Nadon, C. PulseNet international survey on the implementation of whole genome sequencing in low and middle-income countries for foodborne disease surveillance. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2022, 19, 332–340. [CrossRef]
- Hodges, L.M.; Taboada, E.N.; Koziol, A.; Mutschall, S.; Blais, B.W.; Inglis, G.D.; Leclair, D.; Carrillo, C.D. Systematic evaluation of whole-genome sequencing based prediction of antimicrobial resistance in Campylobacter jejuni and C. coli. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 776967. [CrossRef]
- Lakicevic, B.; Jankovic, V.; Pietzka, A.; Ruppitsch, W. Wholegenome sequencing as the gold standard approach for control of Listeria monocytogenes in the food chain. J. Food Prot. 2023, 86, 100003. [CrossRef]
- Natsos, G.; Mouttotou, N.K.; Ahmad, S.; Kamran, Z.; Ioannidis, A.; Koutoulis, K.C. The genus Campylobacter: detection and isolation methods, species identification & typing techniques. J. Hellenic Vet. Med. Soc. 2019, 70, 1327–1338. [CrossRef]
- Al Amri, A.; Senok, A.C.; Ismaeel, A.Y.; Al-Mahmeed, A.E.; Botta, G.A. Multiplex PCR for direct identification of Campylobacter spp. in human and chicken stools. J. Med. Microbiol. 2007, 56, 1350–1355. [CrossRef]
- Linton, D.; Lawson, A.J.; Owen, R.J.; Stanley, J. PCR detection, identification to species level, and fingerprinting of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli direct from diarrheic samples. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1997, 35, 2568–2572. [CrossRef]
- Persson, S.; Olsen, K.E.P. Multiplex PCR for identification of Campylobacter coli and Campylobacter jejuni from pure cultures and directly on stool samples. J. Med. Microbiol. 2005, 54, 1043–1047. [CrossRef]
- Lanzl, M.I.; Zwietering, M.H.; Abee, T.; den Besten, H.M.W. Combining enrichment with multiplex real-time PCR leads to faster detection and identification of Campylobacter spp. in food compared to ISO 10272-1:2017. Food Microbiol. 2022, 108, 104117. [CrossRef]
- Hetman, B.M.; Mutschall, S.K.; Carrillo, C.D.; Thomas, J.E.; Gannon, V.P.J.; Inglis, G.D.; Taboada, E.N. “These aren’t the strains you’re looking for”: Recovery bias of common Campylobacter jejuni subtypes in mixed cultures. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 541. [CrossRef]
- Nayak, R.; Stewart, T.M.; Nawaz, M.S. PCR identification of Campylobacter coli and Campylobacter jejuni by partial sequencing of virulence genes. Moll. Cell. Probes 2005, 19, 187–193. [CrossRef]
- Commission Regulation (EU) 2017/1495. Campylobacter in broiler carcasses. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A32017R1495 (accessed on 18 June 2023).
- Dawson, P.; Buyukyavuz, A.; Ionita, C.; Northcutt, J. Effects of DNA extraction methods on the real time PCR quantification of Campylobacter jejuni, Campylobacter coli, and Campylobacter lari in chicken feces and ceca contents. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102369. [CrossRef]
- Dubovitskaya, O.; Seinige, D.; Valero, A.; Reich, F.; Kehrenberg, C. Quantitative assessment of Campylobacter spp. levels with real-time PCR methods at different stages of the broiler food chain. Food Microbiol. 2023, 110, 104152. [CrossRef]
- Ito, S.; Kishimoto, M. Development of a sampling and real-time PCR method for the quantitative detection of Campylobacter spp. in retail chicken meat without DNA extraction. J. Food Prot. 2023, 86, 100028. [CrossRef]
- Reese, K.R.; Elkins, K.M. Simultaneous detection of foodborne pathogens using real-time PCR triplex high-resolution melt assay. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 2, 453–459. [CrossRef]
- Pacholewicz, E.; Buhler, C.; Wulsten, I.F.; Kraushaar, B.; Luu, H.Q.; Iwobi, A.N.; Huber, I.; Stingl, K. Internal sampling process control improves cultivation-independent quantification of thermotolerant Campylobacter. Food Microbiol. 2019, 78, 53–61. [CrossRef]
- Stingl, K.; Heise, J.; Thieck, M.; Wulsten, I.F.; Pacholewicz, E.; Iwobi, A.N.; Govindaswamy, J.; Zeller-Pérronet, V.; Scheuring, S.; Luu, H.Q.; Fridriksdottir, V.; Gölz, G.; Priller, F.; Gruntar, I.; Jorgensen, F.; Koene, M.; Kovac, J.; Lick, S.; Répérant, E.; Rohlfing, A.; Zawilak-Pawlik, A.; Rossow, M.; Schlierf, A.; Frost, K.; Simon, K.; Uhlig, S.; Huber, I. Challenging the “gold standard” of colony-forming units – Validation of a multiplex real-time PCR for quantification of viable Campylobacter spp. in meat rinses. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 359, 109417. [CrossRef]
- Wulsten, I.F.; Galeev, A.; Stingl, K. Underestimated survival of Campylobacter in raw milk highlighted by viability real-time PCR and growth recovery. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1107. [CrossRef]
- Wulsten, I.F.; Thieck, M.; Göhler, A.; Schuh, E.; Stingl, K. Chicken skin decontamination of thermotolerant Campylobacter spp. and hygiene indicator Escherichia coli assessed by viability real-time PCR. Pathogens 2022, 11, 706. [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Feng, J.; Zhang, J.; Lu, X. Campylobacter biofilms. Microbiol. Res. 2022, 264, 127149. [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-H.; Park, C.; Lee, E.-J.; Bang, W.-S.; Kim, Y.-J.; Kim, J.-S. Biofilm formation of Campylobacter strains isolated from raw chickens and its reduction with DNase I treatment. Food Control 2017, 71, 94–100. [CrossRef]
- Laconi, A.; Tolosi, R.; Drigo, I.; Bano, L.; Piccirillo, A. Association between ability to form biofilm and virulence factors of poultry extra-intestinal Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. Vet Microbiol. 2023, 282, 109770. [CrossRef]
- Gunther IV, N.W.; Chen, C.-Y. The biofilm forming potential of bacterial species in the genus Campylobacter. Food Microbiol. 2009, 26, 44–51. [CrossRef]
- Kostoglou, D.; Mucka, E.; Andritsos, N.; Giaouris, E. A Combined Study on the Antibiotic Resistance and Biofilm-Forming Abilities of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli Isolates from Retail Raw Chicken Samples. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Biofilms (Asia-Pacific Biofilms 2022), Guangzhou, China, 18–23 October 2022.
- Sulaeman, S.; Le Bihan, G.; Rossero, A.; Federighi, M.; Dé, E.; Tresse, O. Comparison between the biofilm initiation of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli strains to an inert surface using BioFilm Ring Test. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 108, 1303–1312. [CrossRef]
- Karki, A.B.; Ballard, K.; Harper, C.; Sheaff, R.J.; Fakhr, M.K. Staphylococcus aureus enhances biofilm formation, aerotolerance, and survival of Campylobacter strains isolated from retail meats. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13837. [CrossRef]
- Klančnik, A.; Gobin, I.; Jeršek, B.; Možina, S.S.; Vučkovic, D.; Žnidarič, M.T.; Abram, M. Adhesion of Campylobacter jejuni is increased in association with foodborne bacteria. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 201. [CrossRef]
- Ramić, D.; Klančnik, A.; Možina, S.S.; Dogsa, I. Elucidation of the AI-2 communication system in the food-borne pathogen Campylobacter jejuni by whole-cell-based biosensor quantification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 212, 114439. [CrossRef]
- The, K.H.; Flint, S.; French, N. Biofilm formation by Campylobacter jejuni in controlled mixed-microbial populations. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 143, 118–124. [CrossRef]
- Ica, T.; Caner, V.; Istanbullu, O.; Nguyen, H.D.; Ahmed, B.; Call, D.R.; Beyenal, H. Characterization of mono- and mixed-culture Campylobacter jejuni biofilms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 1033–1038. [CrossRef]
- Sterniša, M.; Centa, U.G.; Drnovšek, A.; Remškar, M.; Možina, S.S. Pseudomonas fragi biofilm on stainless steel 9at low temperatures) affects the survival of Campylobacter jejuni and Listeria monocytogenes and their control by a polymer molybdenum oxide nanocomposite coating. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2023, 394, 110159. [CrossRef]
| Characteristic | C. jejuni | C. coli | C. lari | C. upsaliensis |
| Catalase activity | + 1 | + | + | - 2 or weak |
| Hippurate hydrolysis | + 3 | - | - | - |
| Indoxyl acetate hydrolysis | + | + | - | + |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





