Submitted:
24 June 2023
Posted:
26 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
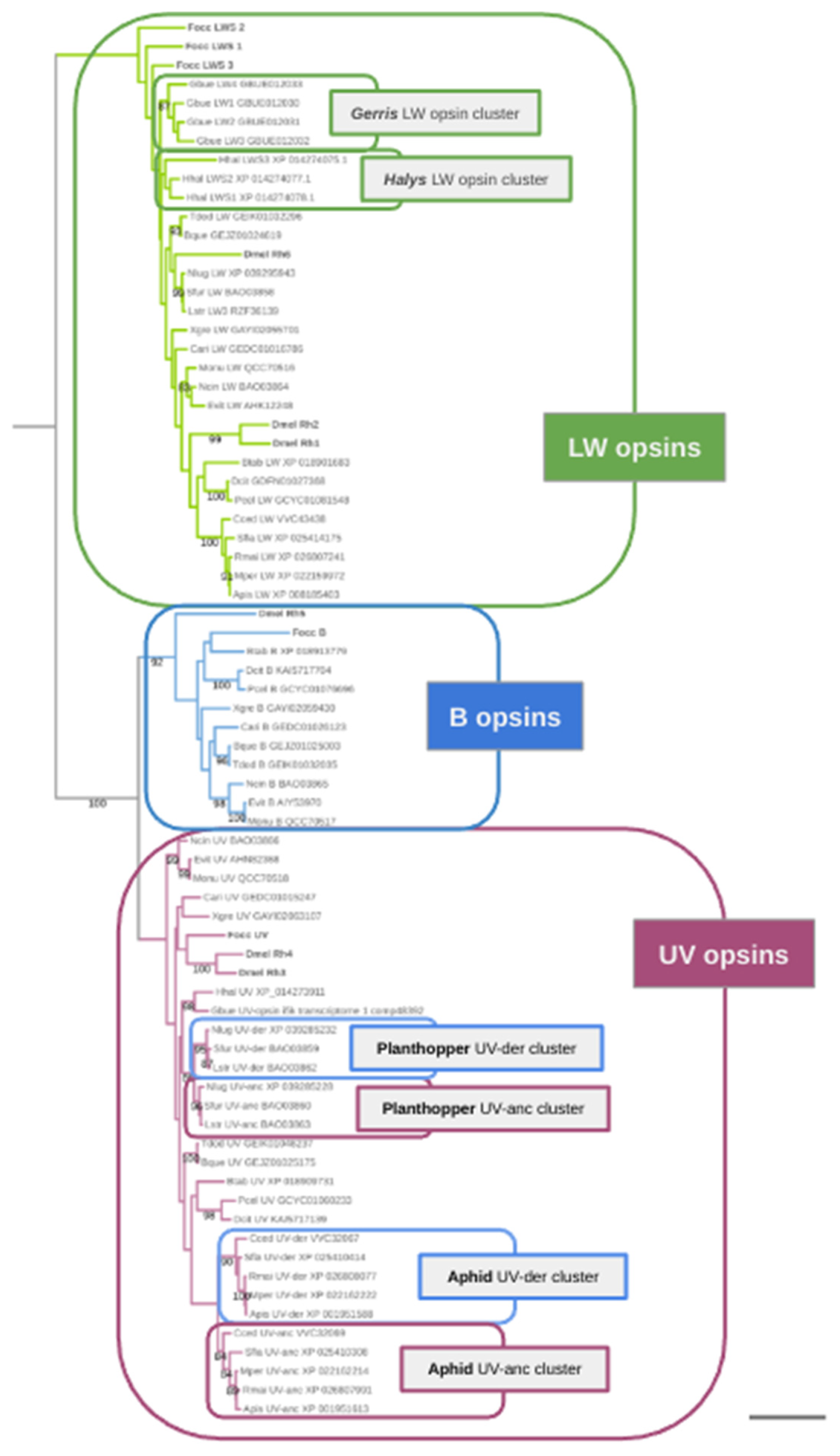
2. Results
Singleton B-opsin homologs in Sternorrhyncha, Auchenorrhyncha, and Coleorrhyncha
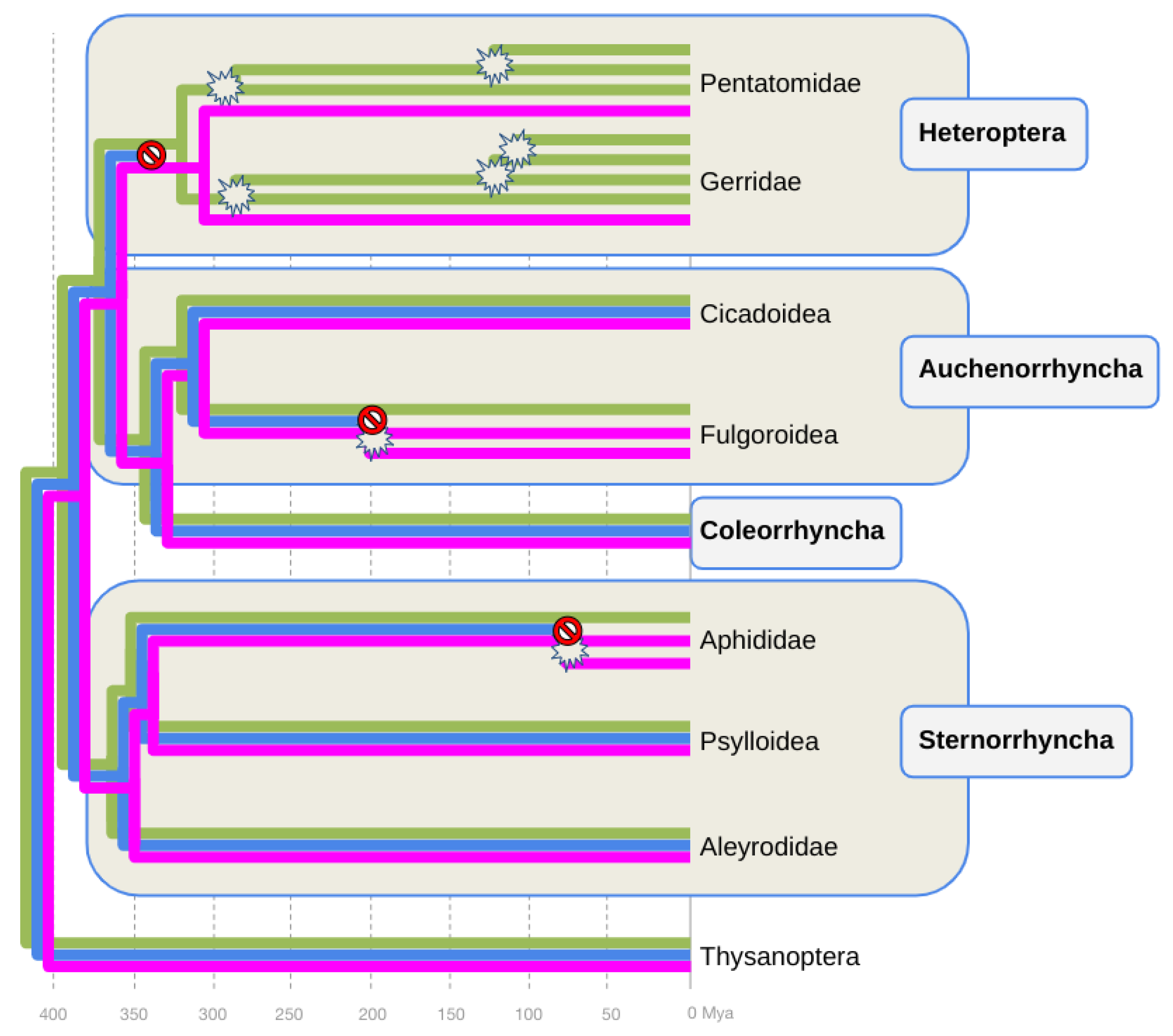
Parallel losses of B-opsin in the Heteroptera, Auchenorrhyncha, and Sternorrhyncha
B-opsin losses correlate with UV-opsin duplications in the aphids and planthoppers
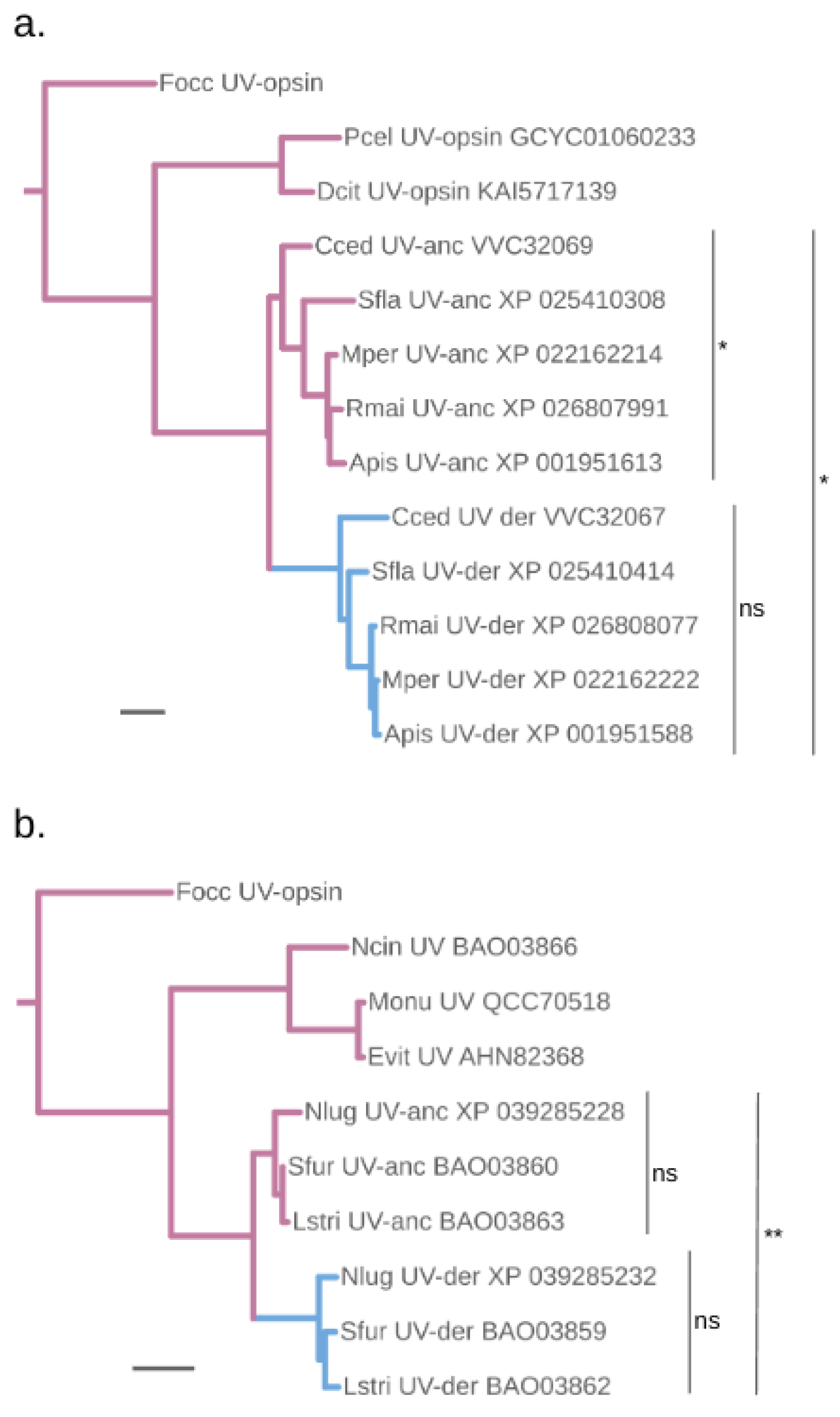
Accelerated protein sequence evolution rates in the putatively blue-shifted UV-opsin paralogs of aphids and planthoppers
Protein sequence change at documented tuning sites
Parallel vs diversified protein sequence changes
3. Discussion
At least three B-opsin losses during hemipteran diversification
Timing B-opsin losses and UV-opsin duplications in planthoppers and aphids
Combined evidence of B-opsin loss compensation through parallel UV-opsin neofunctionalization in aphids and planthoppers
Parallel vs convergent events leading to the compensatory replacements of B-opsin with peak sensitivity shifted UV-opsins in aphids and planthoppers
4. Materials & methods
Homolog compilation
Sequence analyses
Gene tree reconstruction
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
References
- Benoit, J.B.; Adelman, Z.N.; Reinhardt, K.; Dolan, A.; Poelchau, M.; Jennings, E.C.; Szuter, E.M.; Hagan, R.W.; Gujar, H.; Shukla, J.N.; et al. Unique Features of a Global Human Ectoparasite Identified through Sequencing of the Bed Bug Genome. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesquita, R.D.; Vionette-Amaral, R.J.; Lowenberger, C.; Rivera-Pomar, R.; Monteiro, F.A.; Minx, P.; Spieth, J.; Carvalho, A.B.; Panzera, F.; Lawson, D.; et al. Genome of Rhodnius Prolixus, an Insect Vector of Chagas Disease, Reveals Unique Adaptations to Hematophagy and Parasite Infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2015, 112, 14936–14941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, W.; Li, Y.; Zhu, D.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, J.; Chen, N.; Zhou, X.-N. A Chromosomal-Level Genome Assembly for the Insect Vector for Chagas Disease, Triatoma Rubrofasciata. Gigascience 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panfilio, K.A.; Angelini, D.R. By Land, Air, and Sea: Hemipteran Diversity through the Genomic Lens. Curr Opin Insect Sci 2018, 25, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Condamine, F.L.; Clapham, M.E.; Kergoat, G.J. Global Patterns of Insect Diversification: Towards a Reconciliation of Fossil and Molecular Evidence? Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, K.P.; Dietrich, C.H.; Friedrich, F.; Beutel, R.G.; Wipfler, B.; Peters, R.S.; Allen, J.M.; Petersen, M.; Donath, A.; Walden, K.K.O.; et al. Phylogenomics and the Evolution of Hemipteroid Insects. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2018, 115, 12775–12780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kieran, T.J.; Gordon, E.R.L.; Forthman, M.; Hoey-Chamberlain, R.; Kimball, R.T.; Faircloth, B.C.; Weirauch, C.; Glenn, T.C. Insight from an Ultraconserved Element Bait Set Designed for Hemipteran Phylogenetics Integrated with Genomic Resources. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2019, 130, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Leavengood, J.M., Jr.; Chapman, E.G.; Burkhardt, D.; Song, F.; Jiang, P.; Liu, J.; Zhou, X.; Cai, W. Mitochondrial Phylogenomics of Hemiptera Reveals Adaptive Innovations Driving the Diversification of True Bugs. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2017, 284, 20171223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Aphid Genomics Consortium. Genome Sequence of the Pea Aphid Acyrthosiphon Pisum. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armisen, D.; Rajakumar, R.; Friedrich, M.; Benoit, J.B.; Robertson, H.M.; Panfilio, K.A.; Ahn, S.-J.; Poelchau, M.F.; Chao, H.; Dinh, H.; et al. The Genome of the Water Strider Gerris Buenoi Reveals Expansions of Gene Repertoires Associated with Adaptations to Life on the Water. BMC Genomics 2018, 19, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panfilio, K.A.; Vargas Jentzsch, I.M.; Benoit, J.B.; Erezyilmaz, D.; Suzuki, Y.; Colella, S.; Robertson, H.M.; Poelchau, M.F.; Waterhouse, R.M.; Ioannidis, P.; et al. Molecular Evolutionary Trends and Feeding Ecology Diversification in the Hemiptera, Anchored by the Milkweed Bug Genome. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, M.E.; Bansal, R.; Benoit, J.B.; Blackburn, M.B.; Chao, H.; Chen, M.; Cheng, S.; Childers, C.; Dinh, H.; Doddapaneni, H.V.; et al. Brown Marmorated Stink Bug, Halyomorpha Halys (Stål), Genome: Putative Underpinnings of Polyphagy, Insecticide Resistance Potential and Biology of a Top Worldwide Pest. BMC Genomics 2020, 21, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pruitt, K.D.; Tatusova, T.; Maglott, D.R. NCBI Reference Sequence (RefSeq): A Curated Non-Redundant Sequence Database of Genomes, Transcripts and Proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, D501–D504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCulloch, K.J.; Macias-Muñoz, A.; Briscoe, A.D. Insect Opsins and Evo-Devo: What Have We Learned in 25 Years? Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2022, 377, 20210288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henze, M.J.; Oakley, T.H. The Dynamic Evolutionary History of Pancrustacean Eyes and Opsins. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2015, 55, 830–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, N.S.; Hagen, J.F.D.; Johnston, R.J., Jr. The Diversity of Invertebrate Visual Opsins Spanning Protostomia, Deuterostomia, and Cnidaria. Dev. Biol. 2022, 492, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, M.L.; Cronin, T.W.; McClellan, D.A.; Crandall, K.A. Molecular Characterization of Crustacean Visual Pigments and the Evolution of Pancrustacean Opsins. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 253–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briscoe, A.D.; Chittka, L. The Evolution of Color Vision in Insects. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2001, 46, 471–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collantes-Alegre, J.M.; Mattenberger, F.; Barberà, M.; Martínez-Torres, D. Characterisation, Analysis of Expression and Localisation of the Opsin Gene Repertoire from the Perspective of Photoperiodism in the Aphid Acyrthosiphon Pisum. J. Insect Physiol. 2018, 104, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Lu, B.; Chao, J.; Holdbrook, R.; Liang, G.; Lu, Y. The Evolution of Opsin Genes in Five Species of Mirid Bugs: Duplication of Long-Wavelength Opsins and Loss of Blue-Sensitive Opsins. BMC Ecol Evol 2021, 21, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, Y.; Wakakuwa, M.; Yukuhiro, F.; Arikawa, K.; Hiroaki, N. Attraction to Different Wavelength Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs), the Compound Eye Structure, and Opsin Genes in Nilaparvata Lugens. Jap. J. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2014, 58, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Tian, F.; Lin, T.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J.; Zeng, X. The Expression and Function of Opsin Genes Related to the Phototactic Behavior of Asian Citrus Psyllid. Pest Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 1578–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharkey, C.R.; Fujimoto, M.S.; Lord, N.P.; Shin, S.; McKenna, D.D.; Suvorov, A.; Martin, G.J.; Bybee, S.M. Overcoming the Loss of Blue Sensitivity through Opsin Duplication in the Largest Animal Group, Beetles. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liénard, M.A.; Bernard, G.D.; Allen, A.; Lassance, J.-M.; Song, S.; Childers, R.R.; Yu, N.; Ye, D.; Stephenson, A.; Valencia-Montoya, W.A.; et al. The Evolution of Red Color Vision Is Linked to Coordinated Rhodopsin Tuning in Lycaenid Butterflies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2021, 118, e2008986118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCulloch, K.J.; Macias-Muñoz, A.; Mortazavi, A.; Briscoe, A.D. Multiple Mechanisms of Photoreceptor Spectral Tuning in Heliconius Butterflies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2022, 39, msac067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernet, M.F.; Perry, M.W.; Desplan, C. The Evolutionary Diversity of Insect Retinal Mosaics: Common Design Principles and Emerging Molecular Logic. Trends Genet. 2015, 31, 316–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feuda, R.; Goulty, M.; Zadra, N.; Gasparetti, T.; Rosato, E.; Pisani, D.; Rizzoli, A.; Segata, N.; Ometto, L.; Stabelli, O.R. Phylogenomics of Opsin Genes in Diptera Reveals Lineage-Specific Events and Contrasting Evolutionary Dynamics in Anopheles and Drosophila. Genome Biol. Evol. 2021, 13, evab170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakakuwa, M.; Terakita, A.; Koyanagi, M.; Stavenga, D.G.; Shichida, Y.; Arikawa, K. Evolution and Mechanism of Spectral Tuning of Blue-Absorbing Visual Pigments in Butterflies. PLoS One 2010, 5, e15015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Kooi, C.J.; Stavenga, D.G.; Arikawa, K.; Belušič, G.; Kelber, A. Evolution of Insect Color Vision: From Spectral Sensitivity to Visual Ecology. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2021, 66, 435–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, M.; Czelusniak, J.; Moore, G.W.; Romero-Herrera, A.E.; Matsuda, G. Fitting the Gene Lineage into Its Species Lineage, a Parsimony Strategy Illustrated by Cladograms Constructed from Clobin Sequences. Syst. Biol. 1979, 28, 132–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharkey, C.R.; Blanco, J.; Lord, N.P.; Wardill, T.J. Jewel Beetle Opsin Duplication and Divergence Is the Mechanism for Diverse Spectral Sensitivities. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2023, 40, msad023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirchner, S.M.; Döring, T.F.; Saucke, H. Evidence for Trichromacy in the Green Peach Aphid, Myzus Persicae (Sulz.) (Hemiptera: Aphididae). J. Insect Physiol. 2005, 51, 1255–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lord, N.P.; Plimpton, R.L.; Sharkey, C.R.; Suvorov, A.; Lelito, J.P.; Willardson, B.M.; Bybee, S.M. A Cure for the Blues: Opsin Duplication and Subfunctionalization for Short-Wavelength Sensitivity in Jewel Beetles (Coleoptera: Buprestidae). BMC Evol. Biol. 2016, 16, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salcedo, E.; Zheng, L.; Phistry, M.; Bagg, E.E.; Britt, S.G. Molecular Basis for Ultraviolet Vision in Invertebrates. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 10873–10878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biello, R.; Singh, A.; Godfrey, C.J.; Fernández, F.F.; Mugford, S.T.; Powell, G.; Hogenhout, S.A.; Mathers, T.C. A Chromosome-Level Genome Assembly of the Woolly Apple Aphid, Eriosoma Lanigerum Hausmann (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2021, 21, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nováková, E.; Hypša, V.; Klein, J.; Foottit, R.G.; von Dohlen, C.D.; Moran, N.A. Reconstructing the Phylogeny of Aphids (Hemiptera: Aphididae) Using DNA of the Obligate Symbiont Buchnera Aphidicola. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2013, 68, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, C.L.; Miller, G.L. Phylogenomics of the Aphididae: Deep Relationships between Subfamilies Clouded by Gene Tree Discordance, Introgression and the Gene Tree Anomaly Zone. Syst. Entomol. 2022, 47, 470–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Rivas, B.; Martínez-Torres, D. Combination of Molecular Data Support the Existence of Three Main Lineages in the Phylogeny of Aphids (Hemiptera: Aphididae) and the Basal Position of the Subfamily Lachninae. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2010, 55, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Qiao, G. Mitochondrial Genome Sequences Effectively Reveal Deep Branching Events in Aphids (Insecta: Hemiptera: Aphididae). Zool. Scr. 2017, 46, 706–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Chen, X.; Bashir, N.H.; Lu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Ling, X.; Ding, W.; Chen, H. High-Resolution Lac Insect Genome Assembly Provides Genetic Insights into Lac Synthesis and Evolution of Scale Insects. bioRxiv 2023, 2023.02.05.526168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmin, E.; Taylor, J.S.; Boone, C. Retention of Duplicated Genes in Evolution. Trends Genet. 2022, 38, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weadick, C.J.; Chang, B.S.W. Complex Patterns of Divergence among Green-Sensitive (RH2a) African Cichlid Opsins Revealed by Clade Model Analyses. BMC Evol. Biol. 2012, 12, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liénard, M.A.; Valencia-Montoya, W.A.; Pierce, N.E. Molecular Advances to Study the Function, Evolution and Spectral Tuning of Arthropod Visual Opsins. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2022, 377, 20210279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stukenberg, N.; Poehling, H.-M. Blue–green Opponency and Trichromatic Vision in the Greenhouse Whitefly ( Trialeurodes Vaporariorum ) Explored Using Light Emitting Diodes. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2019, 175, 146–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döring, T.F.; Kirchner, S.M.; Skorupski, P.; Hardie, J. Spectral Sensitivity of the Green Photoreceptor of Winged Pea Aphids. Physiol. Entomol. 2011, 36, 392–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellor, H.E.; Bellingham, J.; Anderson, M. Spectral Efficiency of the Glasshouse Whitefly Trialeurodes Vaporariorum and Encarsia Formosa Its Hymenopteran Parasitoid. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 1997, 83, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakakuwa, M.; Stewart, F.; Matsumoto, Y.; Matsunaga, S.; Arikawa, K. Physiological Basis of Phototaxis to near-Infrared Light in Nephotettix Cincticeps. J. Comp. Physiol. A Neuroethol. Sens. Neural Behav. Physiol. 2014, 200, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Park, H.; Smith, T.E.; Moran, N.A. Gene Family Evolution in the Pea Aphid Based on Chromosome-Level Genome Assembly. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2019, 36, 2143–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Shen, G.; Guo, D.; Wang, S.; Ma, X.; Xiao, H.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; et al. InsectBase: A Resource for Insect Genomes and Transcriptomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D801–D807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Xu, L.; Hua, H.; Chen, M.; Guo, M.; He, K.; Zhao, J.; Li, F. Chromosomal-Level Genomes of Three Rice Planthoppers Provide New Insights into Sex Chromosome Evolution. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2021, 21, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Jiang, F.; Wang, X.; Yang, P.; Bao, Y.; Zhao, W.; Wang, W.; Lu, H.; Wang, Q.; Cui, N.; et al. Genome Sequence of the Small Brown Planthopper, Laodelphax Striatellus. Gigascience 2017, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, B.; Yu, X.; Dai, R.; Li, Z.; Yang, M. Chromosome-Level Genome Assembly of Nephotettix Cincticeps (Uhler, 1896) (Hemiptera: Cicadellidae: Deltocephalinae). Genome Biol. Evol. 2021, 13, evab236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julca, I.; Marcet-Houben, M.; Cruz, F.; Vargas-Chavez, C.; Johnston, J.S.; Gómez-Garrido, J.; Frias, L.; Corvelo, A.; Loska, D.; Cámara, F.; et al. Phylogenomics Identifies an Ancestral Burst of Gene Duplications Predating the Diversification of Aphidomorpha. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 730–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shippy, T.D.; Miller, S.; Massimino, C.; Vosburg, C.; Hosmani, P.S.; Flores-Gonzalez, M.; Mueller, L.A.; Hunter, W.B.; Benoit, J.B.; Brown, S.J.; et al. Annotating Genes in Diaphorina Citri Genome Version 3. protocols. io 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Hasegawa, D.K.; Kaur, N.; Kliot, A.; Pinheiro, P.V.; Luan, J.; Stensmyr, M.C.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, W.; Sun, H.; et al. The Draft Genome of Whitefly Bemisia Tabaci MEAM1, a Global Crop Pest, Provides Novel Insights into Virus Transmission, Host Adaptation, and Insecticide Resistance. BMC Biol. 2016, 14, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.F.; Koonin, E.V. Iterated Profile Searches with PSI-BLAST—a Tool for Discovery in Protein Databases. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1998, 23, 444–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGinnis, S.; Madden, T.L. BLAST: At the Core of a Powerful and Diverse Set of Sequence Analysis Tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, W20–W25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artimo, P.; Jonnalagedda, M.; Arnold, K.; Baratin, D.; Csardi, G.; de Castro, E.; Duvaud, S.; Flegel, V.; Fortier, A.; Gasteiger, E.; et al. ExPASy: SIB Bioinformatics Resource Portal. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajima, F. Simple Methods for Testing the Molecular Evolutionary Clock Hypothesis. Genetics 1993, 135, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notredame, C.; Higgins, D.G.; Heringa, J. T-Coffee: A Novel Method for Fast and Accurate Multiple Sequence Alignment. J. Mol. Biol. 2000, 302, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capella-Gutiérrez, S.; Silla-Martínez, J.M.; Gabaldón, T. trimAL: A Tool for Automated Alignment Trimming in Large-Scale Phylogenetic Analyses. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1972–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML Version 8: A Tool for Phylogenetic Analysis and Post-Analysis of Large Phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.A.; Pfeiffer, W.; Schwartz, T. Creating the CIPRES Science Gateway for Inference of Large Phylogenetic Trees. In Proceedings of the 2010 Gateway Computing Environments Workshop (GCE); IEEE, 2010; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talavera, G.; Castresana, J. Improvement of Phylogenies after Removing Divergent and Ambiguously Aligned Blocks from Protein Sequence Alignments. Syst. Biol. 2007, 56, 564–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Species | Diaphorina citri | Superfamily | Family | LW Opsins | B Opsins | UV Opsins | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nilaparvata lugens | Auchenorrhyncha | Fulgoroidea | Delphacidae | XP_039295943 | - | XP_039285232 XP_039285228 |
Matsumoto et al.(2014) Ma et al. (2021) |
| Laodelphax striatellus | Auchenorrhyncha | Fulgoroidea | Delphacidae | RZF36139 | - | BAO03863 BAO03862 |
Ma et al. (2021) Zhu et al. (2017) Matsumoto et al.(2014) |
| Sogatella furcifera | Auchenorrhyncha | Fulgoroidea | Delphacidae | BAO03858 | - | BAO03860 BAO03859 |
Matsumoto et al.(2014) Ma et al. (2021) |
| Clastoptera arizonana | Auchenorrhyncha | Cercopoidea | Clastopteridae | GEDC01016786 | GEDC01026123 | GEDC01015247 | BioProject: PRJNA303152 |
| Tamasa doddi | Auchenorrhyncha | Cicadoidea | Cicadidae | GEIK01032296 | GEIK01032035 | GEIK01048237 | Johnson et al. (2018) |
| Burbunga queenslandica | Auchenorrhyncha | Cicadoidea | Cicadidae | GEJZ01024619 | GEJZ01025003 | GEJZ01025175 | Johnson et al. (2018) |
| Nephotettix cincticeps | Auchenorrhyncha | Membracoidea | Cicadellidae | BAO03864 | BAO03865 | BAO03866 | Matsumoto et al.(2014) |
| Empoasca vitis | Auchenorrhyncha | Membracoidea | Cicadellidae | AHK12248 | AIY53970 | AHN82368 | unpublished |
| Matsumurasca onukii | Auchenorrhyncha | Membracoidea | Cicadellidae | QCC70516 | QCC70517 | QCC70518 | unpublished |
| Xenophysella greensladeae | Coleorrhyncha | - | Peloridiidae | GAYI02055701 | GAYI02059430 | GAYI02063107 | Misof et al. (2014) |
| Gerris buenoi | Heteroptera | Gerroidea | Gerridae | LW1 GBUE012030 LW2 GBUE012031 LW3 GBUE012032 LW4 GBUE012033 |
- | GBUE021384 | Armisen et al. (2018) |
| Halyomorpha halys | Heteroptera | Pentatomoidea | Pentatomidae | XP_014274078 XP_014274077 XP_014274075 |
- | XP_014273911 | Sparks et al. (2020) |
| Acyrthosiphon pisum | Sternorrhyncha | Aphidoidea | Aphididae | XP_008185403 | - | XP_001951588 XP_001951613 |
Li Y et al. (2019) |
| Myzus persicae | Sternorrhyncha | Aphidoidea | Aphididae | XP_022159972 | - | XP_022162222 XP_022162214 |
Rispe et al. (2008) |
| Sipha flava | Sternorrhyncha | Aphidoidea | Aphididae | XP_025414175 | - | XP_025410308 XP_025410414 |
BioProject PRJNA479456 |
| Cinara cedri | Sternorrhyncha | Aphidoidea | Aphididae | LW_VVC43438 | - | VVC32069 VVC32067 |
Julca et al. (2020) |
| Rhopalosiphum maidis | Sternorrhyncha | Aphidoidea | Aphididae | XP_026807241 | - | XP_026808077 XP_026807991 |
BioProject PRJNA503266 |
| Bemisia tabaci | Sternorrhyncha | Aleyrodoidea | Aleyrodidae | XP_018901683 | XP_018913779 | XP_018909731 | Chen et al. (2016) |
| Pachypsylla celtidismamma | Sternorrhyncha | Psylloidea | Aphalaridae | GCYC01060233 | GCYC01076696 | GCYC01081548 | Johnson et al. (2018) |
| Diaphorina | Sternorrhyncha | Psylloidea | Liviidae | GDFN01027368 | XP_008487287 | KAI5717139 | Johnson et al. (2018) |
| Genus | UV-Opsins | Locus ID | Linkage Group | start (bp) | end (bp) | interlocus distance (bp) | # intervening genes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nilaparvata lugens | XP_039285228 | LOC111058697 | 5 | 75,381,302 | 75,410,087 | ||
| XP_039285232 | LOC111051439 | 5 | 75,416,027 | 75,437,887 | 5,940 | 0 | |
| Acyrthosiphon pisum | XP_001951588 | LOC100163348 | A3 | 27,235,720 | 27,247,458 | ||
| XP_001951613 | LOC100161312 | A3 | 27,217,337 | 27,226,019 | 30,121 | 0 | |
| Myzus persicae | XP_022162222 | LOC111028006 | NW_019101158 | 450,218 | 461,548 | ||
| XP_022162214 | LOC111027999 | NW_019101158 | 432,490 | 442,835 | 29,058 | 1 | |
| Rhopalosiphum maidis | XP_026808077 | LOC113550447 | NC_040877 | 46,583,828 | 46,592,054 | ||
| XP_026807991 | LOC113550397 | NC_040878 | 46,570,436 | 46,578,338 | 21,618 | 0 |
| Aphids | Planthoppers | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Site | ancestral | UV-anc | UV-der | ancestral | UV-anc | UV-der |
| 15 | L | L | M | L | L | L |
| 29* | P | A | P | T | T | L |
| 33 | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | H |
| 45* | E | E | E | A | E | A |
| 47* | D | S | R | E | D | E |
| 43 | L | M | S | I/L | L | V |
| 47 | F | F | L | F | F | Y |
| 52 | V/I/L | L | V | L | L | F |
| 63 | L/I | C | C | C | C | S |
| 84 | F | F | F | F | F | L |
| 85 | V/M | V/L/C | S | M/L | M/L | L |
| 87 | M | M | V | M | M | M |
| 90 | K | K | V | K | K | K |
| 94 | F | F | L | F | F | F |
| 102 | G | G | K(T) | G | G | G |
| 105 | Q | Q | P | L | T/S | A |
| 125 | G/S | S | G | A | S | S |
| 183 | Y | Y | F | Y | Y | F |
| 201 | R | R,K | K | R | Q | R |
| 204 | V | L/V | V | V | V | T |
| 244 | (D)S | Q | Q | Q | Q | M |
| 264 | S | S/A | A | S | S | A |
| 273 | L | M | M(L) | L | M | L |
| 286 | G | G | I | G | G | G/V |
| 293 | C | I | V | L | C | L |
| 294 | C,T,A | F | F | T | T | A |
| 295 | C | C | A | C | C | C |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




