Submitted:
22 June 2023
Posted:
23 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Protein Construct Design, Expression, and Purification
2.3. Development and Optimization of the ELISA-Based Protocol
2.4. Validation of the ELISA-Based Protocol
- Accuracy: Low, medium, and high titers of National Institute of Health-provided standard serum were serially diluted 2-fold from 1:200 to 1:6,400. All experiments were performed in duplicate for each concentration. The average optical density values were plotted against the antiserum concentrations, and the r2 values were derived by correlating the calculated antibody titers against the three RSV antigens.
- Precision: One sample was used from each age group. A total of five samples was diluted 2-fold from 1:200 to 1:25,600. The experiment was performed six times for each sample concentration, and the coefficient of variation (CV) was calculated.
- Specificity: All 150 samples were adsorbed with each of the three homologous/heterologous RSV antigens (10 μg/mL of DS-Cav1, SC-TM, and G protein) for an hour with gentle shaking (300 rpm) at RT following which the antibody titers were measured. Post-adsorption titers were compared with pre-adsorption titers. Cross-reactivity was determined based on whether the antibody titers were significantly lower after adsorption. Because RSV infection is mainly prevalent in young children, and also because antibody specificity might be affected by the difference in the duration of time elapsed since the last RSV infection among the age groups studied, we investigated whether there was a difference in the antibody specificity based on age.
2.5. Correlation of Antibody Titers Determined by ELISA with Neutralizing Antibody Titers
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Development and Optimization of ELISA-Based Protocol
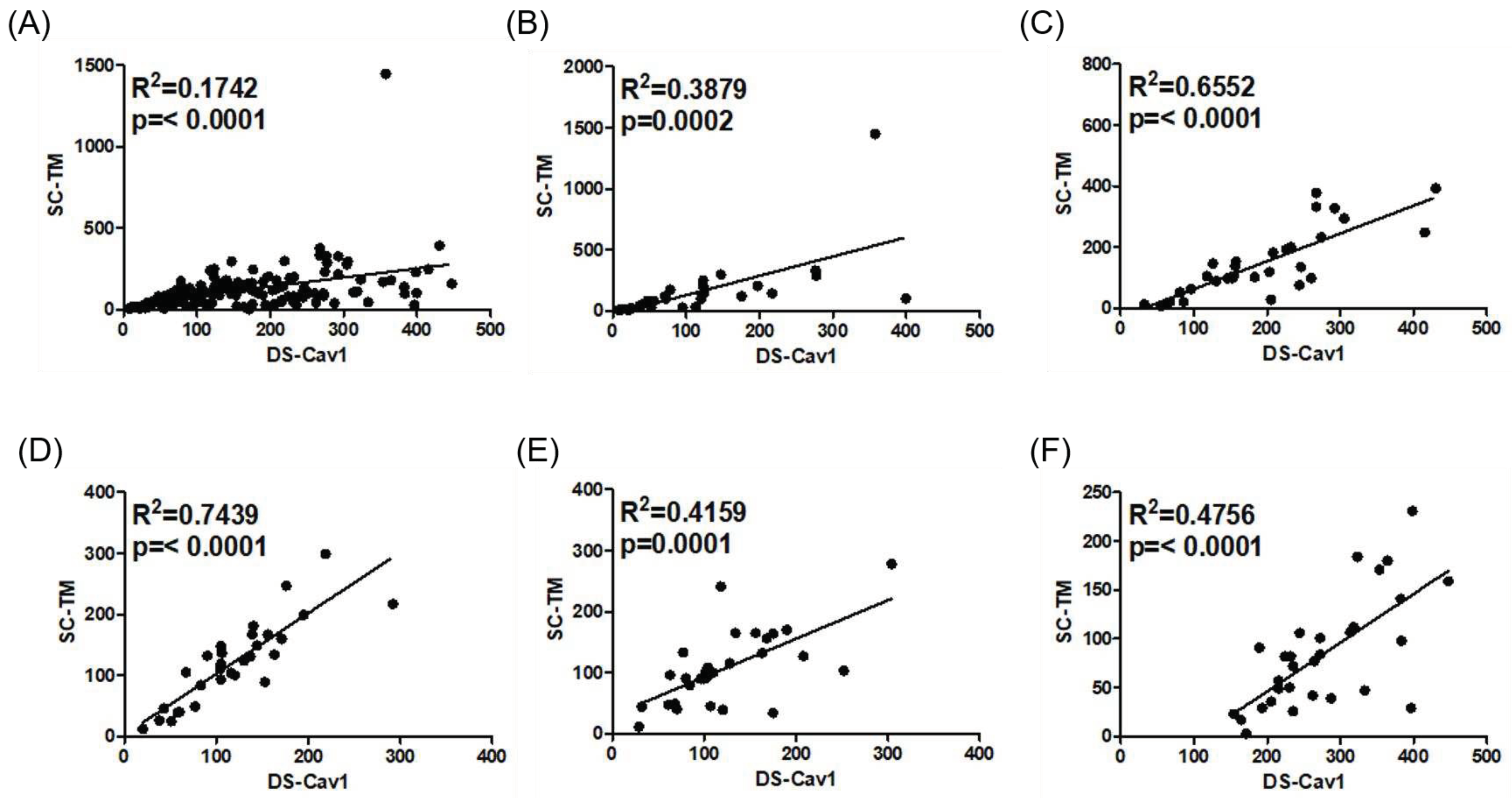
3.2. Validation of the ELISA-Based Protocol
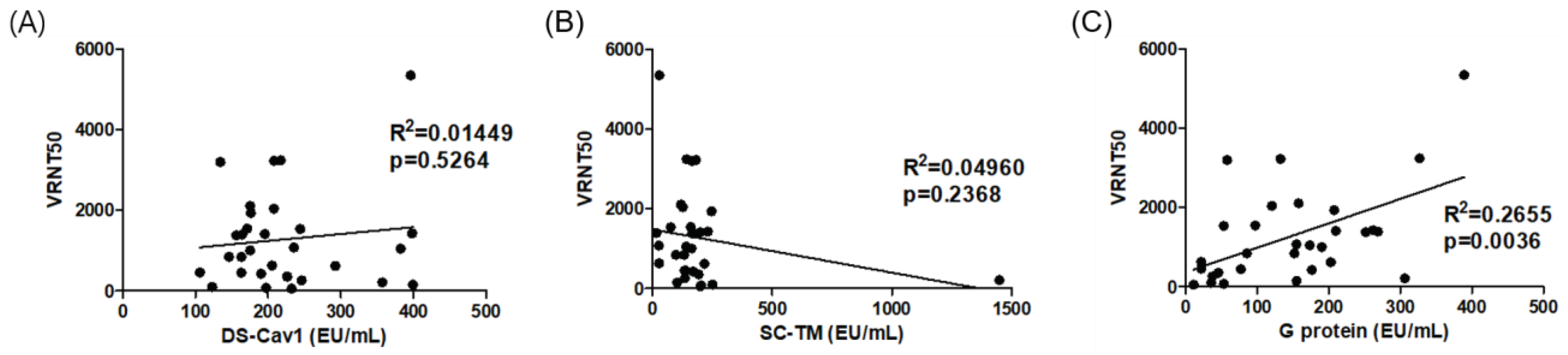
3.3. Correlation with Neutralizing Antibody Titers
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shi, T.; McAllister, D.A.; O'Brien, K.L.; Simoes, E.A.F.; Madhi, S.A.; Gessner, B.D.; Polack, F.P.; Balsells, E.; Acacio, S.; Aguayo, C.; et al. Global, regional, and national disease burden estimates of acute lower respiratory infections due to respiratory syncytial virus in young children in 2015: A systematic review and modelling study. Lancet 2017, 390, 946–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falsey, A.R.; Walsh, E.E. Respiratory syncytial virus infection in adults. Clin Microbiol Rev 2000, 13, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, N.; Lui, G.C.; Wong, K.T.; Li, T.C.; Tse, E.C.; Chan, J.Y.; Yu, J.; Wong, S.S.; Choi, K.W.; Wong, R.Y.; et al. High morbidity and mortality in adults hospitalized for respiratory syncytial virus infections. Clin Infect Dis 2013, 57, 1069–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.G.; Noh, J.Y.; Choi, W.S.; Park, J.J.; Suh, Y.B.; Song, J.Y.; Cheong, H.J.; Kim, W.J. Clinical characteristics and disease burden of respiratory syncytial virus infection among hospitalized adults. Scientific Reports 2020, 10, 12106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. RSV Vaccine Research and Development Technology Roadmap. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-IVB-17.12 (accessed on 19 February 2023).
- PATH. RSV Vaccine and mAb Snapshot. Available online: https://www.path.org/resources/rsv-vaccine-and-mab-snapshot/ (accessed on 19 February 2023).
- Mejias, A.; Rodríguez-Fernández, R.; Oliva, S.; Peeples, M.E.; Ramilo, O. The journey to a respiratory syncytial virus vaccine. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 2020, 125, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, K.A.; Settembre, E.C.; Shaw, C.A.; Dey, A.K.; Rappuoli, R.; Mandl, C.W.; Dormitzer, P.R.; Carfi, A. Structural basis for immunization with postfusion respiratory syncytial virus fusion F glycoprotein (RSV F) to elicit high neutralizing antibody titers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2011, 108, 9619–9624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLellan, J.S.; Chen, M.; Joyce, M.G.; Sastry, M.; Stewart-Jones, G.B.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Chen, L.; Srivatsan, S.; Zheng, A.; et al. Structure-based design of a fusion glycoprotein vaccine for respiratory syncytial virus. Science 2013, 342, 592–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krarup, A.; Truan, D.; Furmanova-Hollenstein, P.; Bogaert, L.; Bouchier, P.; Bisschop, I.J.M.; Widjojoatmodjo, M.N.; Zahn, R.; Schuitemaker, H.; McLellan, J.S.; et al. A highly stable prefusion RSV F vaccine derived from structural analysis of the fusion mechanism. Nat Commun 2015, 6, 8143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flynn, J.A.; Durr, E.; Swoyer, R.; Cejas, P.J.; Horton, M.S.; Galli, J.D.; Cosmi, S.A.; Espeseth, A.S.; Bett, A.J.; Zhang, L. Stability Characterization of a Vaccine Antigen Based on the Respiratory Syncytial Virus Fusion Glycoprotein. PLoS One 2016, 11, e0164789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jounai, N.; Yoshioka, M.; Tozuka, M.; Inoue, K.; Oka, T.; Miyaji, K.; Ishida, K.; Kawai, N.; Ikematsu, H.; Kawakami, C.; et al. Age-Specific Profiles of Antibody Responses against Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection. EBioMedicine 2017, 16, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegrist, C.-A. 2 - Vaccine immunology. In Vaccines (Sixth Edition), Plotkin, S.A., Orenstein, W.A., Offit, P.A., Eds. W.B. Saunders: London, 2013; pp. 14-32. [CrossRef]
- Cullen, L.M.; Schmidt, M.R.; Torres, G.M.; Capoferri, A.A.; Morrison, T.G. Comparison of Immune Responses to Different Versions of VLP Associated Stabilized RSV Pre-Fusion F Protein. Vaccines (Basel) 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, H.H.; Ison, M.G. Respiratory syncytial virus infection in adults. Bmj 2019, 366, l5021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papi, A.; Ison, M.G.; Langley, J.M.; Lee, D.G.; Leroux-Roels, I.; Martinon-Torres, F.; Schwarz, T.F.; van Zyl-Smit, R.N.; Campora, L.; Dezutter, N.; et al. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Prefusion F Protein Vaccine in Older Adults. N Engl J Med 2023, 388, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, E.E.; Pérez Marc, G.; Zareba, A.M.; Falsey, A.R.; Jiang, Q.; Patton, M.; Polack, F.P.; Llapur, C.; Doreski, P.A.; Ilangovan, K.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of a Bivalent RSV Prefusion F Vaccine in Older Adults. N Engl J Med 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moderna. Moderna Announces MRNA-1345, An Investigational Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Vaccine, Has Met Primary Efficacy Endpoints in Phase 3 Trial IN Older Adults. Updated Jan 17, 2023. Available online: https://investors.modernatx.com/news/news-details/2023/Moderna-Announces-mRNA-1345-an-Investigational-Respiratory-Syncytial-Virus-RSV-Vaccine-Has-Met-Primary-Efficacy-Endpoints-in-Phase-3-Trial-in-Older-Adults/default.aspx.
- Kampmann, B.; Madhi, S.A.; Munjal, I.; Simões, E.A.F.; Pahud, B.A.; Llapur, C.; Baker, J.; Pérez Marc, G.; Radley, D.; Shittu, E.; et al. Bivalent Prefusion F Vaccine in Pregnancy to Prevent RSV Illness in Infants. N Engl J Med 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-H.; Kim, H.Y.; Lee, M.; Ahn, J.G.; Baek, J.Y.; Kim, M.Y.; Huh, K.; Jung, J.; Kang, J.-M. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Outbreak Without Influenza in the Second Year of the Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic: A National Sentinel Surveillance in Korea, 2021–2022 Season. J Korean Med Sci 2022, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ujiie, M.; Tsuzuki, S.; Nakamoto, T.; Iwamoto, N. Resurgence of Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infections during COVID-19 Pandemic, Tokyo, Japan. Emerg Infect Dis 2021, 27, 2969–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ECDC. Risk of severe pressure on healthcare systems due to RSV, flu and COVID-19 co-circulation. 2022.
| DS-Cav1 (5 μg/ml) | |||||||
| Dilution factor | r2 | ||||||
| 1:200 | 1:400 | 1:800 | 1:1600 | 1:3200 | 1:6400 | ||
| Reference sera | 2.519 | 1.9658 | 1.4659 | 0.9846 | 0.7047 | 0.42405 | 0.9045 |
| Low titer sera | 2.2103 | 1.5678 | 1.0532 | 0.6568 | 0.46605 | 0.3265 | 0.9603 |
| Medium titer sera | 2.3991 | 1.70445 | 1.161 | 0.73195 | 0.4868 | 0.43985 | 0.9629 |
| High titer sera | 2.6452 | 2.1615 | 1.70685 | 1.21075 | 0.84935 | 0.56785 | 0.87 |
| SC-TM (2.5 μg/ml) | |||||||
| Dilution factor | R2 | ||||||
| 1:200 | 1:400 | 1:800 | 1:1600 | 1:3200 | 1:6400 | ||
| Reference sera | 2.83735 | 2.38555 | 1.8442 | 1.2892 | 0.85635 | 0.63475 | 0.8603 |
| Low titer sera | 2.34215 | 1.73725 | 1.2267 | 0.82085 | 0.4996 | 0.37665 | 0.9355 |
| Medium titer sera | 2.64995 | 2.1299 | 1.50995 | 1.037 | 0.66725 | 0.5086 | 0.9051 |
| High titer sera | 2.8413 | 2.41785 | 1.90155 | 1.34495 | 0.966 | 0.6745 | 0.8514 |
| G protein (5 μg/ml) | |||||||
| Dilution factor | R2 | ||||||
| 1:200 | 1:400 | 1:800 | 1:1600 | 1:3200 | 1:6400 | ||
| Reference sera | 1.01015 | 0.70585 | 0.4602 | 0.2764 | 0.16345 | 0.10335 | 0.9777 |
| Low titer sera | 1.14245 | 0.86765 | 0.6395 | 0.40675 | 0.2446 | 0.13945 | 0.9512 |
| Medium titer sera | 0.81455 | 0.5709 | 0.34935 | 0.2087 | 0.12385 | 0.0763 | 0.9797 |
| High titer sera | 0.97235 | 0.68775 | 0.44775 | 0.2775 | 0.1618 | 0.10215 | 0.9760 |
| Aged < 5 years | Aged 5–18 years | Aged 19–49 years | Aged 50–64 years | Aged ≥ 65 years | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antigen | DF | OD (mean ± SD) |
CV (%) | OD (mean ± SD) |
CV (%) | OD (mean ± SD) |
CV (%) | OD (mean ± SD) |
CV (%) | OD (mean ± SD) |
CV (%) |
| DS-Cav1 | 1:200 | 1.105 ± 0.005 | 0.443 | 1.177 ± 0.020 | 1.685 | 1.230 ± 0.015 | 1.251 | 0.807 ± 0.012 | 1.505 | 1.187 ± 0.015 | 1.258 |
| 1:400 | 0.704 ± 0.009 | 1.218 | 0.894 ± 0.020 | 2.235 | 0.959 ± 0.012 | 1.247 | 0.542 ± 0.011 | 2.1 | 0.897 ± 0.021 | 2.291 | |
| 1:800 | 0.454 ± 0.010 | 2.196 | 0.690 ± 0.010 | 1.498 | 0.724 ± 0.009 | 1.223 | 0.353 ± 0.008 | 2.206 | 0.671 ± 0.014 | 2.016 | |
| 1:1600 | 0.278 ± 0.002 | 0.864 | 0.478 ± 0.012 | 2.567 | 0.514 ± 0.014 | 2.811 | 0.220 ± 0.005 | 2.241 | 0.502 ± 0.016 | 3.137 | |
| 1:3200 | 0.169 ± 0.004 | 2.623 | 0.317 ± 0.010 | 3.106 | 0.347 ± 0.012 | 3.548 | 0.138 ± 0.002 | 1.805 | 0.360 ± 0.005 | 1.414 | |
| 1:6400 | 0.108 ±0.003 | 3.046 | 0.200 ± 0.006 | 3.129 | 0.228 ± 0.007 | 2.892 | 0.090 ± 0.003 | 2.933 | 0.243 ± 0.006 | 2.506 | |
| 1:12800 | 0.072 ± 0.002 | 2.749 | 0.125 ± 0.005 | 3.881 | 0.145 ± 0.008 | 5.202 | 0.063 ± 0.002 | 3.014 | 0.159 ± 0.006 | 3.559 | |
| 1:25600 | 0.058 ± 0.002 | 3.354 | 0.088 ± 0.004 | 4.634 | 0.103 ± 0.005 | 4.526 | 0.052 ± 0.003 | 6.283 | 0.109 ± 0.004 | 3.751 | |
| SC-TM | 1:200 | 1.167 ± 0.011 | 0.982 | 1.343 ± 0.008 | 0.571 | 1.298 ± 0.027 | 2.069 | 0.962 ± 0.012 | 1.296 | 0.779 ± 0.012 | 1.567 |
| 1:400 | 0.731 ± 0.021 | 2.877 | 1.088 ± 0.014 | 1.259 | 0.983 ± 0.019 | 1.938 | 0.666 ± 0.006 | 0.918 | 0.439 ± 0.011 | 2.484 | |
| 1:800 | 0.484 ± 0.006 | 1.304 | 0.870 ± 0.020 | 2.276 | 0.728 ± 0.020 | 2.747 | 0.449 ± 0.005 | 1.004 | 0.288 ± 0.005 | 1.670 | |
| 1:1600 | 0.304 ± 0.009 | 2.857 | 0.644 ± 0.010 | 1.604 | 0.530 ± 0.008 | 1.585 | 0.291 ± 0.009 | 3.104 | 0.185 ± 0.006 | 3.237 | |
| 1:3200 | 0.188 ± 0.005 | 2.417 | 0.430 ± 0.013 | 2.980 | 0.353 ± 0.008 | 2.318 | 0.185 ± 0.007 | 3.829 | 0.121 ± 0.001 | 1.030 | |
| 1:6400 | 0.120 ± 0.007 | 6.035 | 0.273 ± 0.006 | 2.282 | 0.236 ± 0.003 | 1.061 | 0.117 ± 0.005 | 4.240 | 0.083 ± 0.001 | 1.438 | |
| 1:12800 | 0.080 ± 0.004 | 4.865 | 0.166 ± 0.006 | 3.481 | 0.151 ± 0.004 | 2.600 | 0.081 ± 0.005 | 5.856 | 0.062 ± 0.001 | 2.237 | |
| 1:25600 | 0.061 ± 0.003 | 5.454 | 0.111 ± 0.003 | 2.761 | 0.105 ± 0.003 | 3.007 | 0.062 ± 0.007 | 10.717 | 0.052 ± 0.002 | 3.524 | |
| G protein | 1:200 | 0.657 ± 0.020 | 2.987 | 0.199 ± 0.016 | 8.001 | 0.964 ± 0.032 | 3.355 | 0.746 ± 0.031 | 4.172 | 1.490 ± 0.028 | 1.904 |
| 1:400 | 0.394 ± 0.010 | 2.508 | 0.107 ± 0.010 | 9.189 | 0.600 ± 0.023 | 3.852 | 0.434 ± 0.002 | 5.154 | 1.262 ± 0.038 | 2.985 | |
| 1:800 | 0.236 ± 0.008 | 3.227 | 0.071 ± 0.007 | 9.943 | 0.430 ± 0.015 | 3.424 | 0.285 ± 0.025 | 8.754 | 1.036 ± 0.044 | 4.230 | |
| 1:1600 | 0.136 ± 0.003 | 2.274 | 0.050 ± 0.003 | 6.295 | 0.267 ± 0.009 | 3.284 | 0.170 ± 0.014 | 8.251 | 0.821 ± 0.046 | 5.596 | |
| 1:3200 | 0.086 ± 0.005 | 6.356 | 0.039 ± 0.001 | 2.807 | 0.156 ± 0.006 | 4.006 | 0.105 ± 0.008 | 8.026 | 0.579 ± 0.038 | 6.544 | |
| 1:6400 | 0.061 ± 0.003 | 4.572 | 0.035 ± 0.001 | 2.674 | 0.098 ± 0.002 | 2.385 | 0.069 ± 0.004 | 5.475 | 0.363 ± 0.034 | 9.427 | |
| 1:12800 | 0.051 ± 0.006 | 11.501 | 0.033 ± 0.001 | 2.646 | 0.065 ± 0.002 | 2.849 | 0.049 ± 0.002 | 3.124 | 0.219 ± 0.020 | 8.971 | |
| 1:25600 | 0.041 ± 0.002 | 5.743 | 0.034 ± 0.001 | 2.795 | 0.047 ± 0.002 | 3.347 | 0.040 ± 0.001 | 3.521 | 0.134 ± 0.012 | 9.003 | |
| Coated protein | DS-Cav1 | SC-TM | G protein | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitor (10 μg/mL) |
None | DS-Cav1 | SC-TM | G protein | None | DS-Cav1 | SC-TM | G protein | None | DS-Cav1 | SC-TM | G protein | |
| Aged < 5 years | EU/ml | 115.0 | 83.3 | 78.2 | 122.9 | 153.3 | 35.8 | 30.8 | 113.7 | 117.3 | 53.5 | 49.2 | 22.4 |
| % | - | 72.5 | 68.0 | 106.9 | - | 23.3 | 20.1 | 74.2 | - | 45.6 | 42.0 | 19.1 | |
| Aged 5–18 years | EU/ml | 193.8 | 73.0 | 67.3 | 121.6 | 148.4 | 69.3 | 65.7 | 122.5 | 78.8 | 44.1 | 41.9 | 17.3 |
| % | - | 37.7 | 34.7 | 62.8 | - | 46.7 | 44.2 | 82.5 | - | 56.0 | 53.2 | 22.0 | |
| Aged 19–49 years | EU/ml | 118.8 | 45.2 | 60.5 | 114.0 | 121.1 | 73.4 | 60.6 | 130.7 | 101.9 | 89.0 | 77.3 | 28.2 |
| % | - | 38.1 | 51.0 | 96.0 | - | 60.6 | 50.0 | 108.0 | - | 87.4 | 75.9 | 27.6 | |
| Aged 50–64 years | EU/ml | 122.7 | 65.7 | 84.0 | 107.7 | 107.0 | 88.0 | 61.1 | 120.4 | 134.3 | 145.8 | 132.1 | 42.3 |
| % | - | 53.5 | 68.5 | 87.8 | - | 82.3 | 57.1 | 112.6 | - | 108.6 | 98.4 | 31.5 | |
| Aged ≥ 65 years | EU/ml | 113.7 | 62.2 | 75.6 | 127.2 | 84.1 | 71.4 | 43.5 | 95.2 | 165.8 | 172.4 | 157.0 | 36.1 |
| % | - | 54.7 | 66.5 | 111.9 | - | 84.8 | 51.8 | 113.2 | - | 104.0 | 94.7 | 21.8 | |
| Average | EU/ml | 132.8 | 65.9 | 73.1 | 118.7 | 122.8 | 67.6 | 52.3 | 116.5 | 119.6 | 101.0 | 91.5 | 29.3 |
| % | - | 49.6 | 55.1 | 89.4 | - | 55.0 | 42.6 | 94.9 | - | 84.4 | 76.5 | 24.5 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





