Submitted:
19 June 2023
Posted:
20 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effect of age on the phenotypic parameters in WT and 5xFAD mice
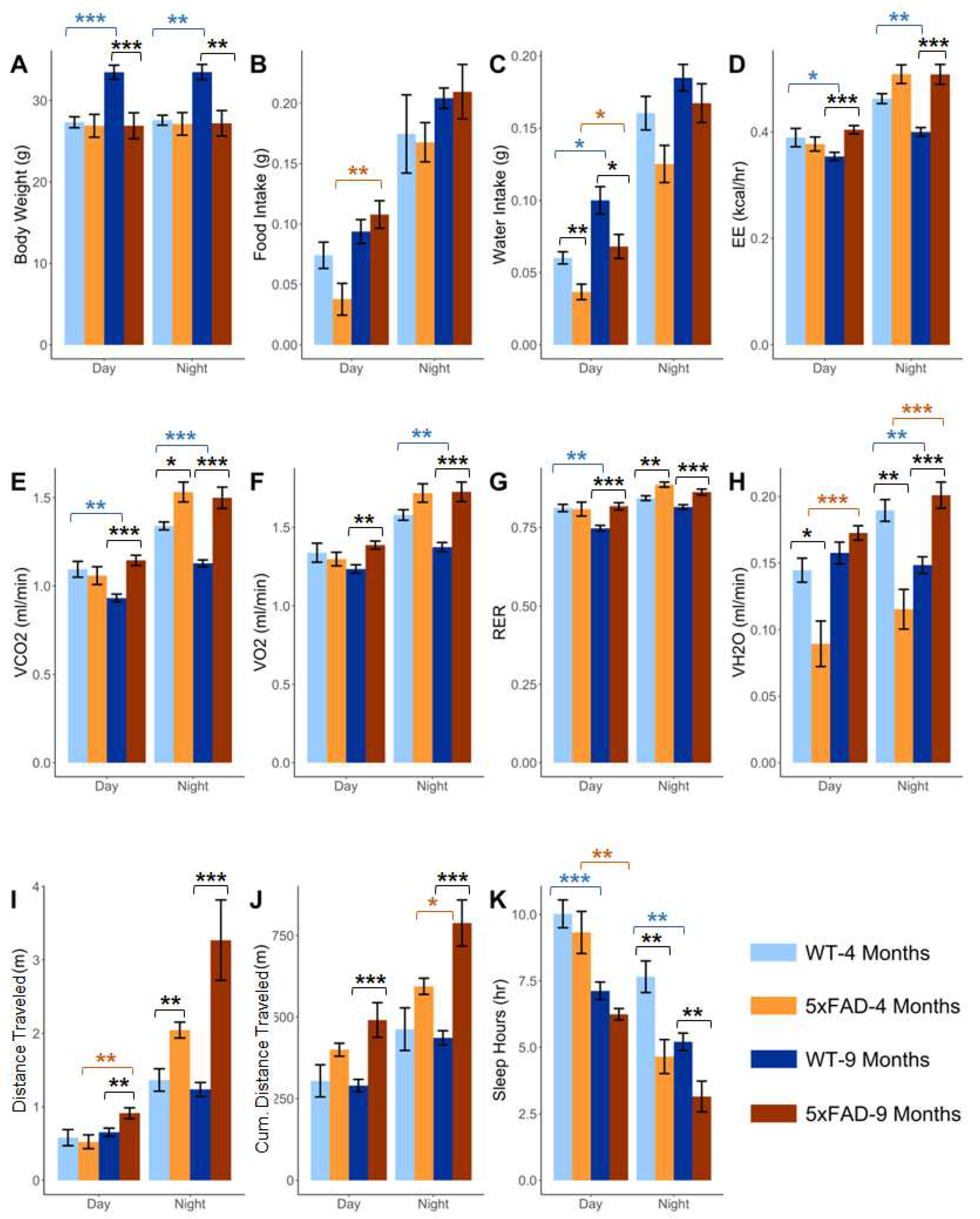
2.2. Effect of pathology on the phenotypic parameters at 4 and 9 months in 5xFAD
2.3. Effect of age and pathology on sleep pattern in WT and 5xFAD mice
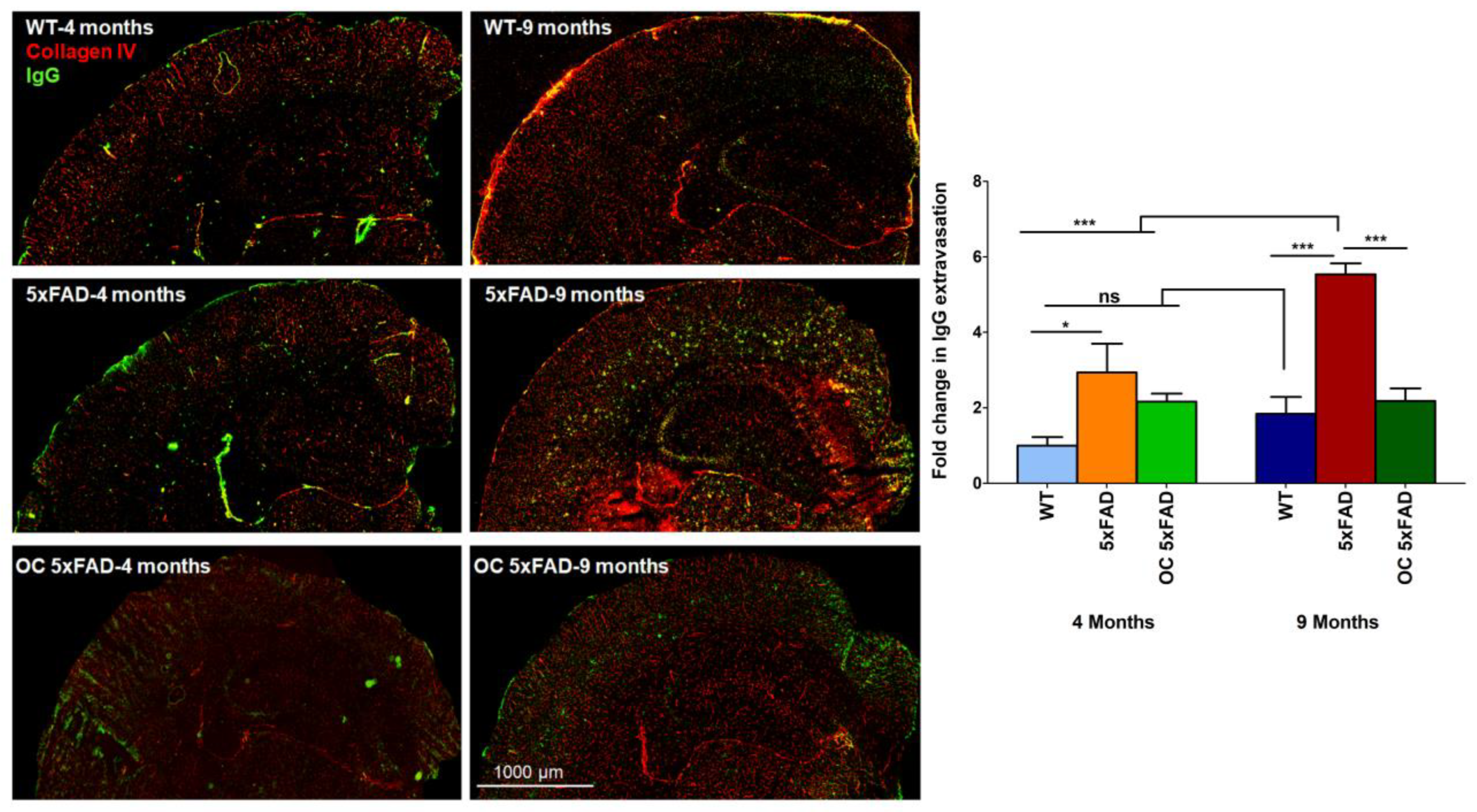
2.4. Effect of age and pathology on BBB function
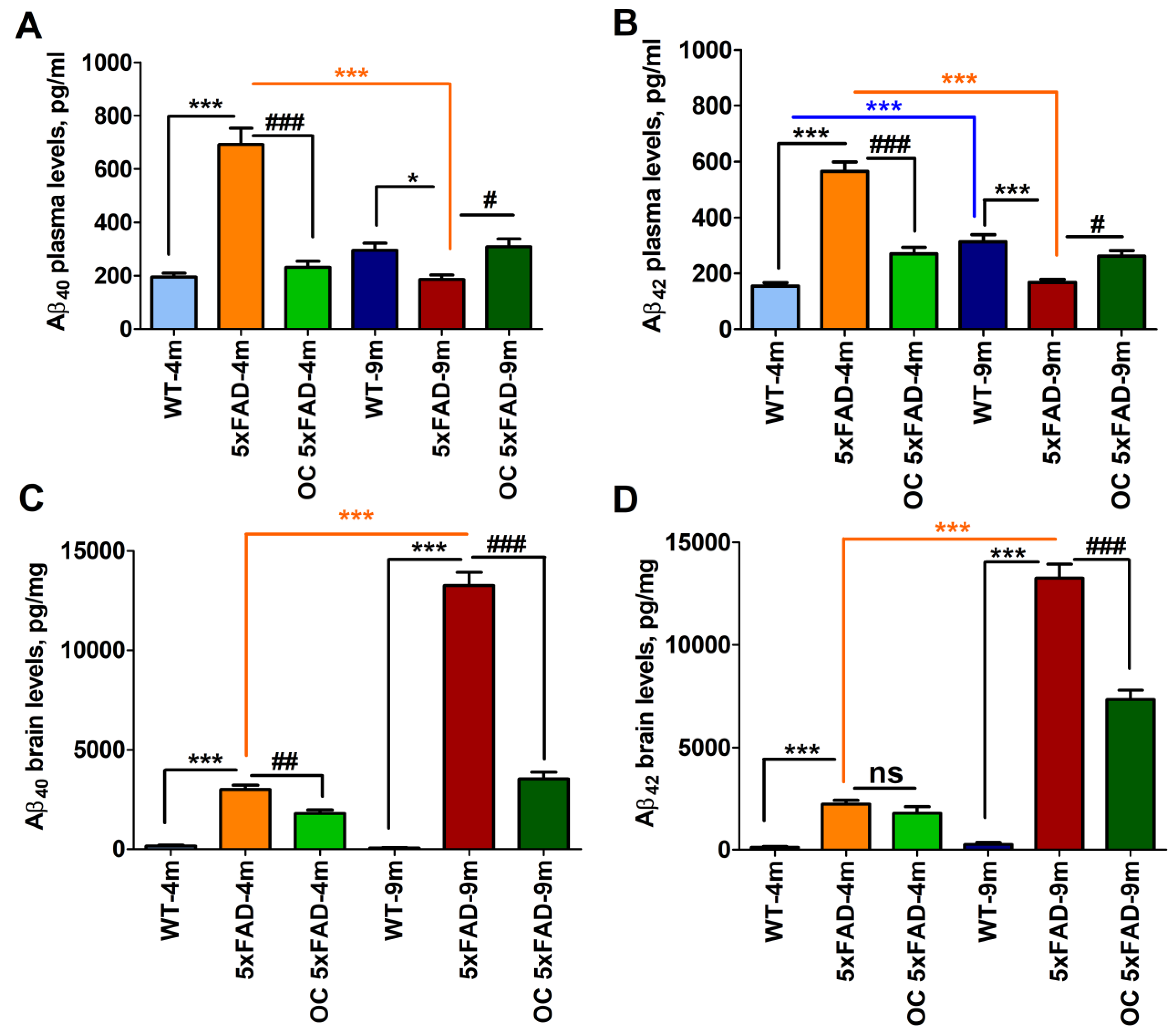
2.5. Effect of age and pathology on plasma and brain Aβ levels in WT and 5xFAD mice
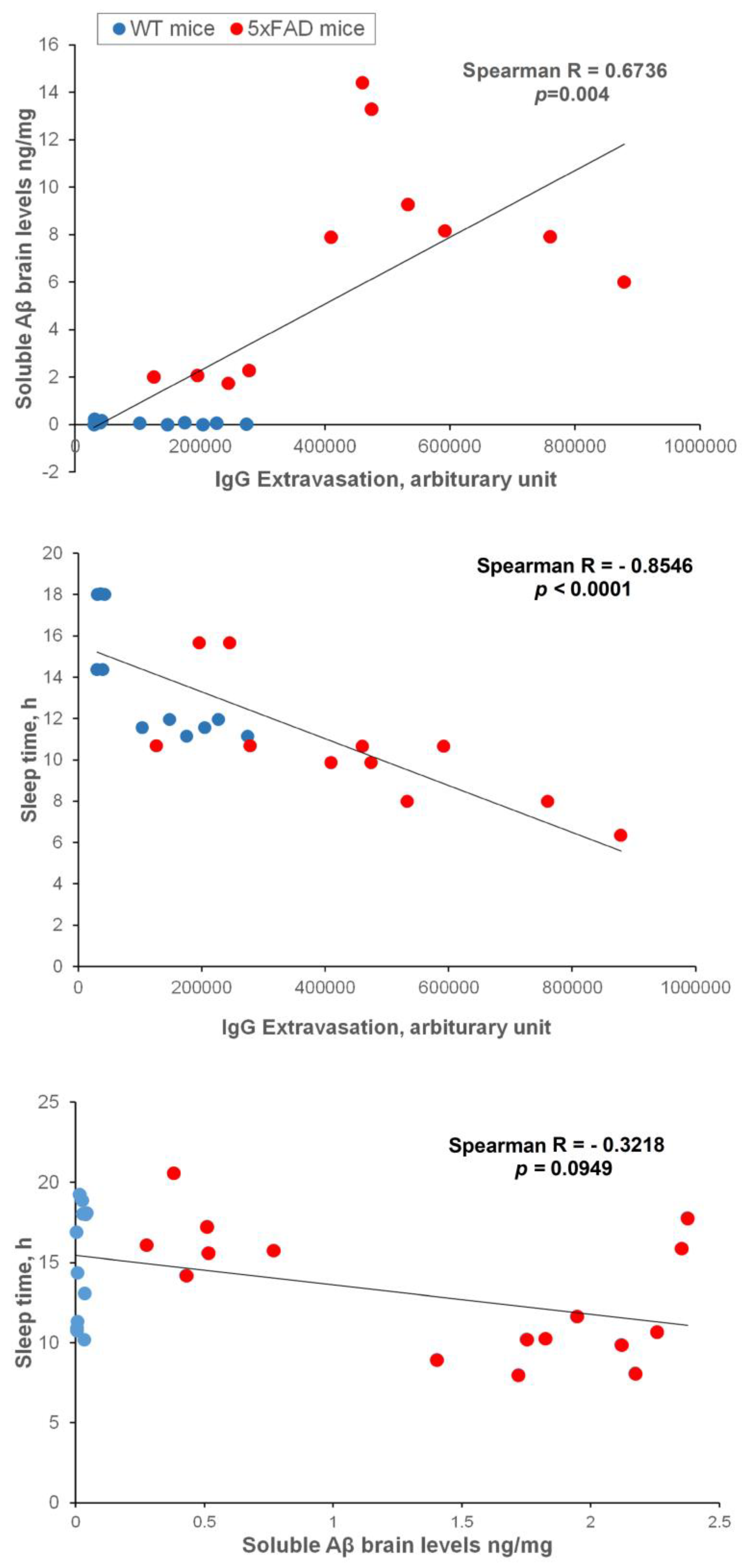
2.6. Brain soluble Aβ, IgG extravasation, and sleep correlation
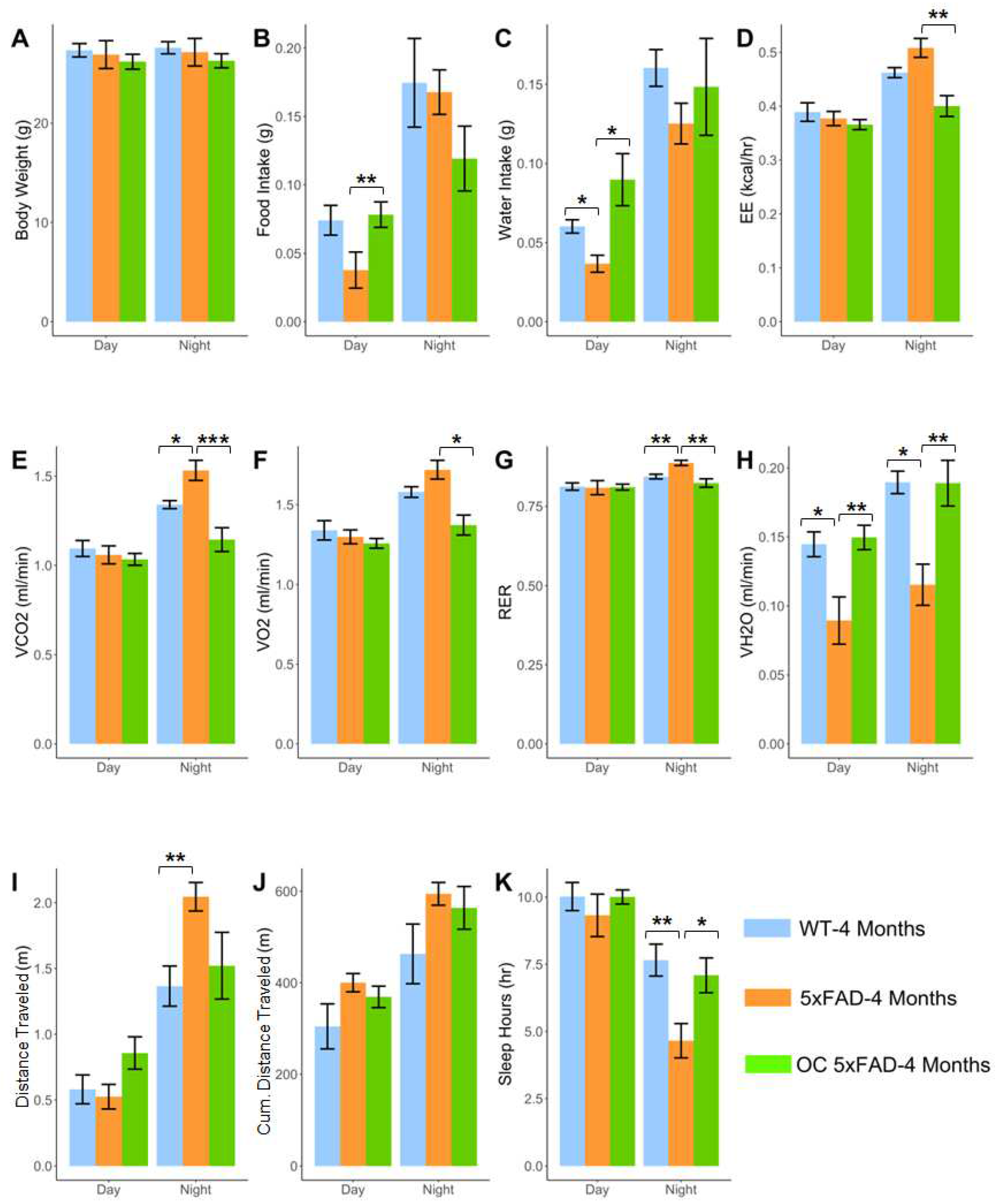
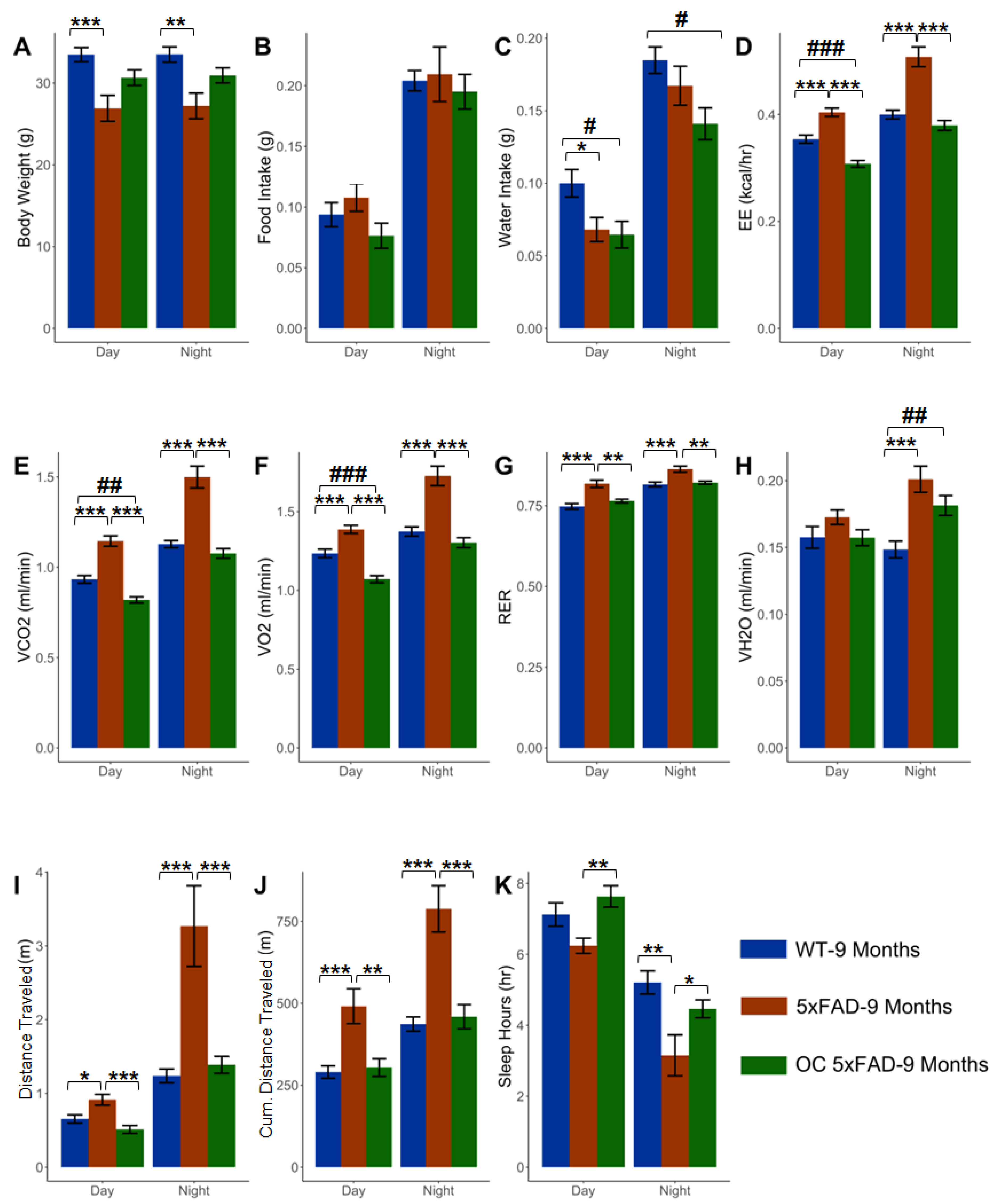
2.7. Effect of OC treatment on metabolic phenotypes, Aβ, and related pathology
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
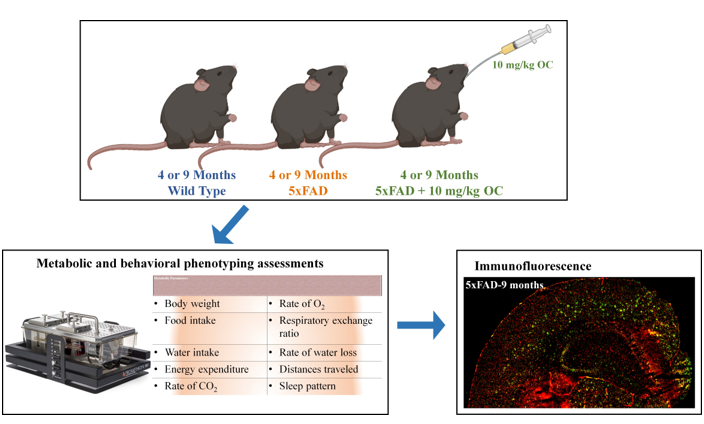
4.1. Animals
4.2. Metabolic and behavioral phenotyping assessments
4.3. Immunofluorescence staining
4.4. Measurements of brain and plasma Aβ by ELISA
4.5. Statistical analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- JafariNasabian, P.; Inglis, J. E.; Reilly, W.; Kelly, O. J.; Ilich, J. Z., Aging human body: changes in bone, muscle and body fat with consequent changes in nutrient intake. J Endocrinol 2017, 234, (1), R37-R51. [CrossRef]
- Holmes, E.; Loo, R. L.; Stamler, J.; Bictash, M.; Yap, I. K.; Chan, Q.; Ebbels, T.; De Iorio, M.; Brown, I. J.; Veselkov, K. A.; Daviglus, M. L.; Kesteloot, H.; Ueshima, H.; Zhao, L.; Nicholson, J. K.; Elliott, P., Human metabolic phenotype diversity and its association with diet and blood pressure. Nature 2008, 453, (7193), 396-400. [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Burrington, C. M.; Graff, E. C.; Zhang, J.; Judd, R. L.; Suksaranjit, P.; Kaewpoowat, Q.; Davenport, S. K.; O'Neill, A. M.; Greene, M. W., Metabolic phenotype and adipose and liver features in a high-fat Western diet-induced mouse model of obesity-linked NAFLD. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2016, 310, (6), E418-39. [CrossRef]
- Di Iulio, F.; Palmer, K.; Blundo, C.; Casini, A. R.; Gianni, W.; Caltagirone, C.; Spalletta, G., Occurrence of neuropsychiatric symptoms and psychiatric disorders in mild Alzheimer's disease and mild cognitive impairment subtypes. Int Psychogeriatr 2010, 22, (4), 629-40. [CrossRef]
- Suma, S.; Watanabe, Y.; Hirano, H.; Kimura, A.; Edahiro, A.; Awata, S.; Yamashita, Y.; Matsushita, K.; Arai, H.; Sakurai, T., Factors affecting the appetites of persons with Alzheimer's disease and mild cognitive impairment. Geriatr Gerontol Int 2018, 18, (8), 1236-1243. [CrossRef]
- Grundman, M.; Corey-Bloom, J.; Jernigan, T.; Archibald, S.; Thal, L. J., Low body weight in Alzheimer's disease is associated with mesial temporal cortex atrophy. Neurology 1996, 46, (6), 1585-91. [CrossRef]
- Westerterp, K. R., Control of energy expenditure in humans. Eur J Clin Nutr 2017, 71, (3), 340-344. [CrossRef]
- Brzecka, A.; Leszek, J.; Ashraf, G. M.; Ejma, M.; Avila-Rodriguez, M. F.; Yarla, N. S.; Tarasov, V. V.; Chubarev, V. N.; Samsonova, A. N.; Barreto, G. E.; Aliev, G., Sleep Disorders Associated With Alzheimer's Disease: A Perspective. Front Neurosci 2018, 12, 330. [CrossRef]
- Krueger, J. M.; Frank, M. G.; Wisor, J. P.; Roy, S., Sleep function: Toward elucidating an enigma. Sleep Med Rev 2016, 28, 46-54. [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Xie, L.; Yu, M.; Kang, H.; Feng, T.; Deane, R.; Logan, J.; Nedergaard, M.; Benveniste, H., The Effect of Body Posture on Brain Glymphatic Transport. J Neurosci 2015, 35, (31), 11034-44. [CrossRef]
- Mendelsohn, A. R.; Larrick, J. W., Sleep facilitates clearance of metabolites from the brain: glymphatic function in aging and neurodegenerative diseases. Rejuvenation Res 2013, 16, (6), 518-23. [CrossRef]
- O'Donnell, J.; Ding, F.; Nedergaard, M., Distinct functional states of astrocytes during sleep and wakefulness: Is norepinephrine the master regulator? Curr Sleep Med Rep 2015, 1, (1), 1-8. [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Kang, H.; Xu, Q.; Chen, M. J.; Liao, Y.; Thiyagarajan, M.; O'Donnell, J.; Christensen, D. J.; Nicholson, C.; Iliff, J. J.; Takano, T.; Deane, R.; Nedergaard, M., Sleep drives metabolite clearance from the adult brain. Science 2013, 342, (6156), 373-7. [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, D. Z.; St Louis, E. K.; Knopman, D. S.; Boeve, B. F.; Lowe, V. J.; Roberts, R. O.; Mielke, M. M.; Przybelski, S. A.; Machulda, M. M.; Petersen, R. C.; Jack, C. R., Jr.; Vemuri, P., Association of Excessive Daytime Sleepiness With Longitudinal beta-Amyloid Accumulation in Elderly Persons Without Dementia. JAMA Neurol 2018, 75, (6), 672-680. [CrossRef]
- Ju, Y. E.; McLeland, J. S.; Toedebusch, C. D.; Xiong, C.; Fagan, A. M.; Duntley, S. P.; Morris, J. C.; Holtzman, D. M., Sleep quality and preclinical Alzheimer disease. JAMA Neurol 2013, 70, (5), 587-93. [CrossRef]
- Masule, M. V.; Rathod, S.; Agrawal, Y.; Patil, C. R.; Nakhate, K. T.; Ojha, S.; Goyal, S. N.; Mahajan, U. B., Ghrelin mediated regulation of neurosynaptic transmitters in depressive disorders. Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov 2022, 3, 100113. [CrossRef]
- Gimson, A.; Schlosser, M.; Huntley, J. D.; Marchant, N. L., Support for midlife anxiety diagnosis as an independent risk factor for dementia: a systematic review. BMJ Open 2018, 8, (4), e019399. [CrossRef]
- Pentkowski, N. S.; Rogge-Obando, K. K.; Donaldson, T. N.; Bouquin, S. J.; Clark, B. J., Anxiety and Alzheimer's disease: Behavioral analysis and neural basis in rodent models of Alzheimer's-related neuropathology. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 2021, 127, 647-658. [CrossRef]
- Bobba, A.; Amadoro, G.; Valenti, D.; Corsetti, V.; Lassandro, R.; Atlante, A., Mitochondrial respiratory chain Complexes I and IV are impaired by β-amyloid via direct interaction and through Complex I-dependent ROS production, respectively. Mitochondrion 2013, 13, (4), 298-311. [CrossRef]
- Ferrer, I., Altered mitochondria, energy metabolism, voltage-dependent anion channel, and lipid rafts converge to exhaust neurons in Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of bioenergetics and biomembranes 2009, 41, (5), 425-431. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Gao, M.; Huang, H.; Gao, S.-H.; Liao, L.-Y.; Tao, Y.; Cheng, H.; Gao, C.-Y., p75NTR Ectodomain Ameliorates Cognitive Deficits and Pathologies in a Rapid Eye Movement Sleep Deprivation Mice Model. Neuroscience 2022, 496, 27-37. [CrossRef]
- Han, S. M.; Jang, Y. J.; Kim, E. Y.; Park, S. A., The Change in Circadian Rhythms in P301S Transgenic Mice is Linked to Variability in Hsp70-related Tau Disaggregation. Experimental Neurobiology 2022, 31, (3), 196. [CrossRef]
- Holth, J. K.; Mahan, T. E.; Robinson, G. O.; Rocha, A.; Holtzman, D. M., Altered sleep and EEG power in the P301S Tau transgenic mouse model. Annals of clinical and translational neurology 2017, 4, (3), 180-190. [CrossRef]
- Beauchamp, G. K.; Keast, R. S.; Morel, D.; Lin, J.; Pika, J.; Han, Q.; Lee, C.-H.; Smith, A. B.; Breslin, P. A., Ibuprofen-like activity in extra-virgin olive oil. Nature 2005, 437, (7055), 45-46. [CrossRef]
- Batarseh, Y. S.; Mohamed, L. A.; Al Rihani, S. B.; Mousa, Y. M.; Siddique, A. B.; El Sayed, K. A.; Kaddoumi, A., Oleocanthal ameliorates amyloid-beta oligomers' toxicity on astrocytes and neuronal cells: In vitro studies. Neuroscience 2017, 352, 204-215. [CrossRef]
- Qosa, H.; Batarseh, Y. S.; Mohyeldin, M. M.; El Sayed, K. A.; Keller, J. N.; Kaddoumi, A., Oleocanthal enhances amyloid-beta clearance from the brains of TgSwDI mice and in vitro across a human blood-brain barrier model. ACS Chem Neurosci 2015, 6, (11), 1849-59. [CrossRef]
- Batarseh, Y. S.; Kaddoumi, A., Oleocanthal-rich extra-virgin olive oil enhances donepezil effect by reducing amyloid-beta load and related toxicity in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. J Nutr Biochem 2018, 55, 113-123. [CrossRef]
- Al Rihani, S. B.; Darakjian, L. I.; Kaddoumi, A., Oleocanthal-Rich Extra-Virgin Olive Oil Restores the Blood-Brain Barrier Function through NLRP3 Inflammasome Inhibition Simultaneously with Autophagy Induction in TgSwDI Mice. ACS Chem Neurosci 2019, 10, (8), 3543-3554. [CrossRef]
- Mehta, R. I.; Carpenter, J. S.; Mehta, R. I.; Haut, M. W.; Ranjan, M.; Najib, U.; Lockman, P.; Wang, P.; D'Haese P, F.; Rezai, A. R., Blood-Brain Barrier Opening with MRI-guided Focused Ultrasound Elicits Meningeal Venous Permeability in Humans with Early Alzheimer Disease. Radiology 2021, 298, (3), 654-662. [CrossRef]
- Baum, J. I.; Kim, I. Y.; Wolfe, R. R., Protein Consumption and the Elderly: What Is the Optimal Level of Intake? Nutrients 2016, 8, (6). [CrossRef]
- Pilgrim, A. L.; Robinson, S. M.; Sayer, A. A.; Roberts, H. C., An overview of appetite decline in older people. Nurs Older People 2015, 27, (5), 29-35. [CrossRef]
- Wang, P. N.; Yang, C. L.; Lin, K. N.; Chen, W. T.; Chwang, L. C.; Liu, H. C., Weight loss, nutritional status and physical activity in patients with Alzheimer's disease. A controlled study. J Neurol 2004, 251, (3), 314-20. [CrossRef]
- Albert, S. G.; Nakra, B. R.; Grossberg, G. T.; Caminal, E. R., Vasopressin response to dehydration in Alzheimer's disease. J Am Geriatr Soc 1989, 37, (9), 843-7. [CrossRef]
- Arendash, G. W.; Gordon, M. N.; Diamond, D. M.; Austin, L. A.; Hatcher, J. M.; Jantzen, P.; DiCarlo, G.; Wilcock, D.; Morgan, D., Behavioral assessment of Alzheimer's transgenic mice following long-term Abeta vaccination: task specificity and correlations between Abeta deposition and spatial memory. DNA Cell Biol 2001, 20, (11), 737-44. [CrossRef]
- Jawhar, S.; Trawicka, A.; Jenneckens, C.; Bayer, T. A.; Wirths, O., Motor deficits, neuron loss, and reduced anxiety coinciding with axonal degeneration and intraneuronal Abeta aggregation in the 5XFAD mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging 2012, 33, (1), 196 e29-40. [CrossRef]
- Radde, R.; Bolmont, T.; Kaeser, S. A.; Coomaraswamy, J.; Lindau, D.; Stoltze, L.; Calhoun, M. E.; Jaggi, F.; Wolburg, H.; Gengler, S.; Haass, C.; Ghetti, B.; Czech, C.; Holscher, C.; Mathews, P. M.; Jucker, M., Abeta42-driven cerebral amyloidosis in transgenic mice reveals early and robust pathology. EMBO Rep 2006, 7, (9), 940-6. [CrossRef]
- Flanigan, T. J.; Xue, Y.; Kishan Rao, S.; Dhanushkodi, A.; McDonald, M. P., Abnormal vibrissa-related behavior and loss of barrel field inhibitory neurons in 5xFAD transgenics. Genes Brain Behav 2014, 13, (5), 488-500. [CrossRef]
- Lippi, S. L. P.; Smith, M. L.; Flinn, J. M., A Novel hAPP/htau Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease: Inclusion of APP With Tau Exacerbates Behavioral Deficits and Zinc Administration Heightens Tangle Pathology. Front Aging Neurosci 2018, 10, 382. [CrossRef]
- Sterniczuk, R.; Antle, M. C.; Laferla, F. M.; Dyck, R. H., Characterization of the 3xTg-AD mouse model of Alzheimer's disease: part 2. Behavioral and cognitive changes. Brain Res 2010, 1348, 149-55. [CrossRef]
- Gulia, K. K.; Kumar, V. M., Sleep disorders in the elderly: a growing challenge. Psychogeriatrics 2018, 18, (3), 155-165. [CrossRef]
- Bliwise, D. L., Sleep disorders in Alzheimer's disease and other dementias. Clin Cornerstone 2004, 6 Suppl 1A, S16-28. [CrossRef]
- Van Erum, J.; Van Dam, D.; De Deyn, P. P., Sleep and Alzheimer's disease: A pivotal role for the suprachiasmatic nucleus. Sleep Med Rev 2018, 40, 17-27. [CrossRef]
- Brown, B. M.; Rainey-Smith, S. R.; Bucks, R. S.; Weinborn, M.; Martins, R. N., Exploring the bi-directional relationship between sleep and beta-amyloid. Curr Opin Psychiatry 2016, 29, (6), 397-401. [CrossRef]
- Brown, B. M.; Rainey-Smith, S. R.; Villemagne, V. L.; Weinborn, M.; Bucks, R. S.; Sohrabi, H. R.; Laws, S. M.; Taddei, K.; Macaulay, S. L.; Ames, D.; Fowler, C.; Maruff, P.; Masters, C. L.; Rowe, C. C.; Martins, R. N.; Group, A. R., The Relationship between Sleep Quality and Brain Amyloid Burden. Sleep 2016, 39, (5), 1063-8. [CrossRef]
- Cordone, S.; Annarumma, L.; Rossini, P. M.; De Gennaro, L., Sleep and beta-Amyloid Deposition in Alzheimer Disease: Insights on Mechanisms and Possible Innovative Treatments. Front Pharmacol 2019, 10, 695. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, F.; Tang, M.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, X., Amyloid beta and tau are involved in sleep disorder in Alzheimer's disease by orexin A and adenosine A(1) receptor. Int J Mol Med 2019, 43, (1), 435-442. [CrossRef]
- Soltani, S.; Chauvette, S.; Bukhtiyarova, O.; Lina, J. M.; Dube, J.; Seigneur, J.; Carrier, J.; Timofeev, I., Sleep-Wake Cycle in Young and Older Mice. Front Syst Neurosci 2019, 13, 51. [CrossRef]
- Lopez, O. L.; Kuller, L. H.; Mehta, P. D.; Becker, J. T.; Gach, H. M.; Sweet, R. A.; Chang, Y. F.; Tracy, R.; DeKosky, S. T., Plasma amyloid levels and the risk of AD in normal subjects in the Cardiovascular Health Study. Neurology 2008, 70, (19), 1664-71. [CrossRef]
- Deane, R.; Bell, R. D.; Sagare, A.; Zlokovic, B. V., Clearance of amyloid-beta peptide across the blood-brain barrier: implication for therapies in Alzheimer's disease. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 2009, 8, (1), 16-30. [CrossRef]
- Abuznait, A. H.; Qosa, H.; Busnena, B. A.; El Sayed, K. A.; Kaddoumi, A., Olive-oil-derived oleocanthal enhances beta-amyloid clearance as a potential neuroprotective mechanism against Alzheimer's disease: in vitro and in vivo studies. ACS Chem Neurosci 2013, 4, (6), 973-82. [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, L. A.; Keller, J. N.; Kaddoumi, A., Role of P-glycoprotein in mediating rivastigmine effect on amyloid-beta brain load and related pathology in Alzheimer's disease mouse model. Biochim Biophys Acta 2016, 1862, (4), 778-787. [CrossRef]
- Darakjian, L. I.; Rigakou, A.; Brannen, A.; Qusa, M. H.; Tasiakou, N.; Diamantakos, P.; Reed, M. N.; Panizzi, P.; Boersma, M. D.; Melliou, E., Spontaneous In Vitro and In Vivo Interaction of (−)-Oleocanthal with Glycine in Biological Fluids: Novel Pharmacokinetic Markers. ACS Pharmacology & Translational Science 2021, 4, (1), 179-192. [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, I. M.; Al-Shami, K. M.; Alkhalifa, A. E.; Al-Ghraiybah, N. F.; Guillaume, C.; Kaddoumi, A., Comparison of Oleocanthal-Low EVOO and Oleocanthal against Amyloid-β and Related Pathology in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Molecules 2023, 28, (3), 1249. [CrossRef]
- Siddique, A. B.; Ebrahim, H.; Mohyeldin, M.; Qusa, M.; Batarseh, Y.; Fayyad, A.; Tajmim, A.; Nazzal, S.; Kaddoumi, A.; El Sayed, K., Novel liquid-liquid extraction and self-emulsion methods for simplified isolation of extra-virgin olive oil phenolics with emphasis on (-)-oleocanthal and its oral anti-breast cancer activity. PloS one 2019, 14, (4), e0214798. [CrossRef]
- Oakley, H.; Cole, S. L.; Logan, S.; Maus, E.; Shao, P.; Craft, J.; Guillozet-Bongaarts, A.; Ohno, M.; Disterhoft, J.; Van Eldik, L., Intraneuronal β-amyloid aggregates, neurodegeneration, and neuron loss in transgenic mice with five familial Alzheimer's disease mutations: potential factors in amyloid plaque formation. Journal of Neuroscience 2006, 26, (40), 10129-10140. [CrossRef]
- Yanai, S.; Endo, S., Functional Aging in Male C57BL/6J Mice Across the Life-Span: A Systematic Behavioral Analysis of Motor, Emotional, and Memory Function to Define an Aging Phenotype. Front Aging Neurosci 2021, 13, 697621. [CrossRef]
- Kaiyala, K.J.; Spiekerman, C.F.; Podolsky, R.H.; McGuinness, O. MMPC Energy Expenditure Analysis Page. Available online: https://www.mmpc.org/shared/regression.aspx.
| Parameters | Definition |
|---|---|
| Body weight | Mean Body mass of the animal, in grams (g) |
| Food intake | Mass of food consumed by animal, in gram (g) |
| Water intake | Mass of water consumed by animal, in gram (g) |
| EE | Mean energy expenditure, in kcal/h |
| VCO2 | Mean rate of carbon dioxide emission, in ml/min |
| VO2 | Mean rate of oxygen consumption in ml/min |
| RER | Respiratory exchange ratio, VCO2/VO2, unit-less |
| VH2O | Mean rate of water vapor loss, in ml/min |
| Distance travelled | Sum of all distances traveled, in meters |
| Cumulative distance | Sum of cultivating distance traveled, in meters |
| Sleep | Sleep time (h) = Quiet for > 40 seconds |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





