1. Introduction
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) is an increasingly utilized intervention that provides emergency respiratory and circulatory support to patients with refractory pulmonary and cardiac failure [
1]. Despite the demonstrated survival benefits of ECMO compared to standard care, the survival rate among ECMO patients remains suboptimal, with a reported 58% survival rate [
2]. One of the leading causes of morbidity and mortality among ECMO patients is acute brain injury (ABI), which has been reported to occur in up to 20% of adult ECMO patients and confers a two-fold increase in mortality risk [
3,
4]. Common neurological complications of ECMO include intracranial hemorrhage, ischemic stroke, seizures, hypoxic-ischemic brain injury, and cerebral edema [
5]. However, given the abundance of patients on heavy sedation with unreliable neurological examination, early diagnosis of ABI is challenging. As ECMO patients are often too unstable to transport for neuroimaging studies out of the intensive care unit (ICU), there is a clinical need for bedside blood-based biomarkers that can reliably predict ABIs [
6]. Additionally, while studies have explored these biomarkers for children on ECMO, there is little data exploring the utility of these biomarkers for adult patients on ECMO [
7].
Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), neurofilament light chain (NFL), and Tau are three sensitive and specific markers for neuronal injury. Their early elevation predicted unfavorable neurological outcomes in patients with cardiac arrest as well as neurodegenerative diseases [
8,
9]. Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) is a cytoskeletal protein that is specifically expressed in astrocytes [
10]. Elevated levels of GFAP in the blood have been shown to be a marker of astroglial activation and can be used to assess brain injury [
10]. GFAP levels are higher in patients with intracranial hemorrhage than in patients with ischemic events, which have a longer duration before peak GFAP is reached [
11]. This suggests that GFAP may be a useful marker for identifying acute brain injuries. Neurofilaments confer structural stability to neurons and are present in dendrites, neuronal soma, and axons [
12]. Elevated levels of NFL in blood and cerebrospinal fluid indicate axonal injury [
13,
14]. Similarly, NFL levels were significantly higher in unfavorable neurological outcome (vs. favorable) after hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in OHCA, especially at 1-3 days with high sensitivity and specificity for 6-month neurological outcomes [
8,
9]. Serum tau stabilizes microtubules and is found in neurons [
14]. Tau protein at 72 hours was accurate in predicting 6-month neurological outcome with the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) of 0.91 in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA) patients [
8,
9]. Despite the promising results of their accuracy in predicting ABIs and neurological outcomes in OHCA, these plasma biomarkers have not been tested in adult patients on ECMO support.
Herein, we conducted a pilot prospective observational study on three brain-specific blood-based biomarkers (GFAP, NFL, and Tau) in adult patients with ECMO support.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Protocol
This is a prospective observational pilot study on a series of ECMO patients admitted to a tertiary care academic hospital between June 2018 and May 2019. We analyzed 20 patients who were consented within 24 hours and underwent plasma sampling once daily over the course of their ECMO duration. We have previously described our standard neuromonitoring protocol as delineated by Cho et. al and Ong et. al. which consists of baseline neurologic examinations including Glasgow Coma Scores (GCS), Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II (APACHE II), and Sepsis-related Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) scores, and protocols for serial imaging by transcranial doppler, electroencephalography, somatosensory evoked potentials and head CT or MRI [
15,
16]. This study was approved by the Johns Hopkins institutional review board.
2.2. Sample Collection, Processing, and Storage Protocol
Standard clinical care for patients placed on ECMO was followed, including physical examination at bedside on the first day of ECMO and close follow-up until hospital discharge or death. After the patient was placed on ECMO, there was a 24-hour window for the patient's family to provide consent. The first blood draws occurred within 24 hours after ECMO cannulation, and then once daily thereafter. All samples were centrifuged at 3000 RPM for 8 minutes and divided into four aliquots, with the first aliquot containing 250 µL, the second aliquot containing 500 µL, and the remainder evenly split into the other two aliquots. These tubes were labeled based on patient number, sample number, and aliquot number – along with the date that the samples were collected. Plasma was extracted from the samples, taking care not to extract red blood cells. The exact amounts extracted were recorded, and each tube was again labeled based on patient number, sample number, and aliquot number. These samples were stored in a -80 °C freezer. GFAP, NFL and Tau were assayed using a commercial multiplex assay (Meso Scale Discovery, Gaithersburg, MD) using the assay protocol and quantified using a SECTOR Imager 6000 plate reader (Meso Scale Discovery). All three analytes were quantifiable in each sample.
2.3. Definitions and Outcomes
A comprehensive collection of pre-ECMO patient history, including demographics, past medical history, ECMO and laboratory variables (creatine, platelet count, lactate, and transaminase values) were recorded for each patient. The primary outcome for this study was any ABI, consisting of subdural hemorrhage, subarachnoid hemorrhage, intracerebral hemorrhage, ischemic stroke, hypoxic-ischemic brain injury, and brain death. We utilized our institution’s existing prospectively collected ECMO database for baseline and in-hospital data [
15,
16]. Patient charts were manually reviewed and validated for the timing of an ABI following ECMO cannulation. Favorable neurological outcome was defined as modified Rankin Scale (mRS) ≤ 3 and unfavorable neurological outcome as mRS ≥ 4 at discharge.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
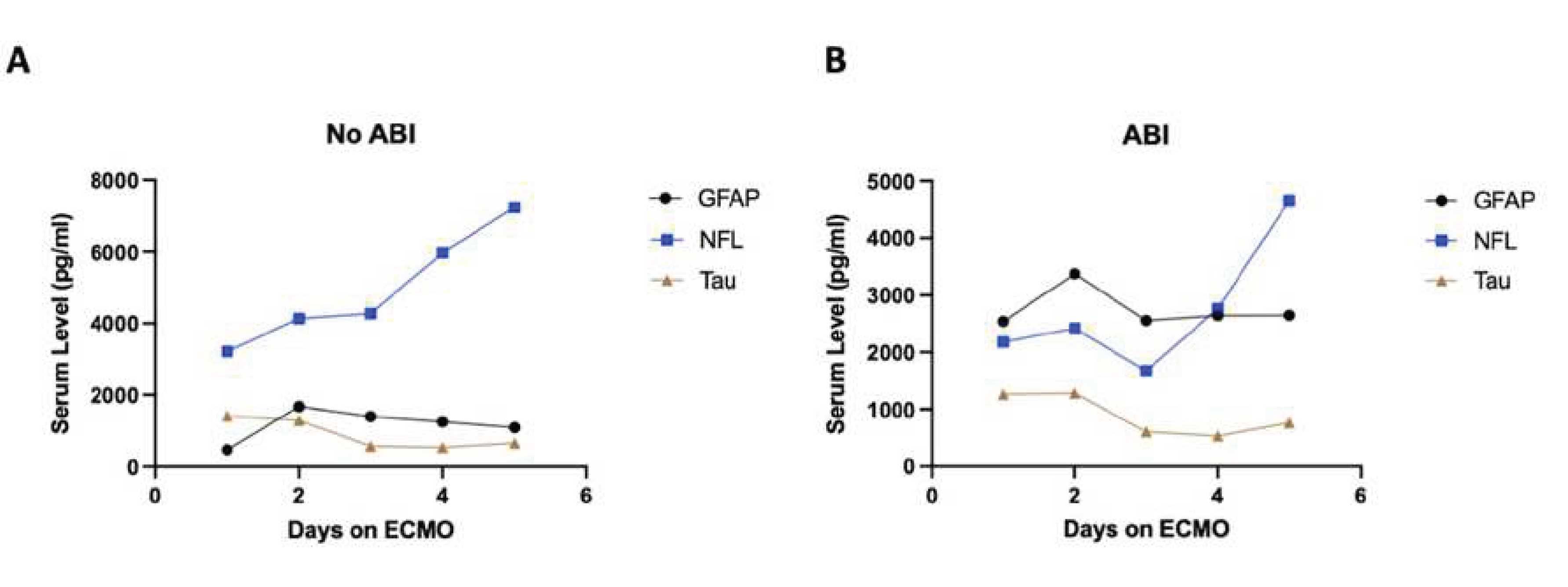
Baseline patient characteristics, patient demographics, and neurologic outcomes were compared between patients with ABI vs. without using Chi-squared tests and Fischer’s exact texts for categorical variables. Mann-Whitney U test was used for continuous variables. Statistical significance level was set at p<0.05, and analyses were performed using Stata 17 (College Station, TX, USA). Serum biomarker peaks were plotted for each patient during ECMO support. Boxplots were created to visualize the differences in peak biomarker concentrations between patients with and without ABI. Sensitivity and specificity analyses were conducted. C-statistics, also known as the area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve, were computed for ABI and unfavorable neurologic outcome. These curves were pictographically demonstrated using GraphPad Prism version 9.0 (San Diego, CA, USA). To examine temporal changes in each biomarker concentration and the ABI timing, peak biomarker values were plotted for each day following ECMO cannulation for six out of eight ABI patients (
Figure 3). Two patients were excluded due to rapid patient mortality after cannulation, yielding no insight into biomarker fluctuation over time. Time-series analyses were performed to characterize the time of diagnosis of ABI in relation to biomarker levels, and the results were displayed using Microsoft Excel 2019 (Redmond, WA, USA).
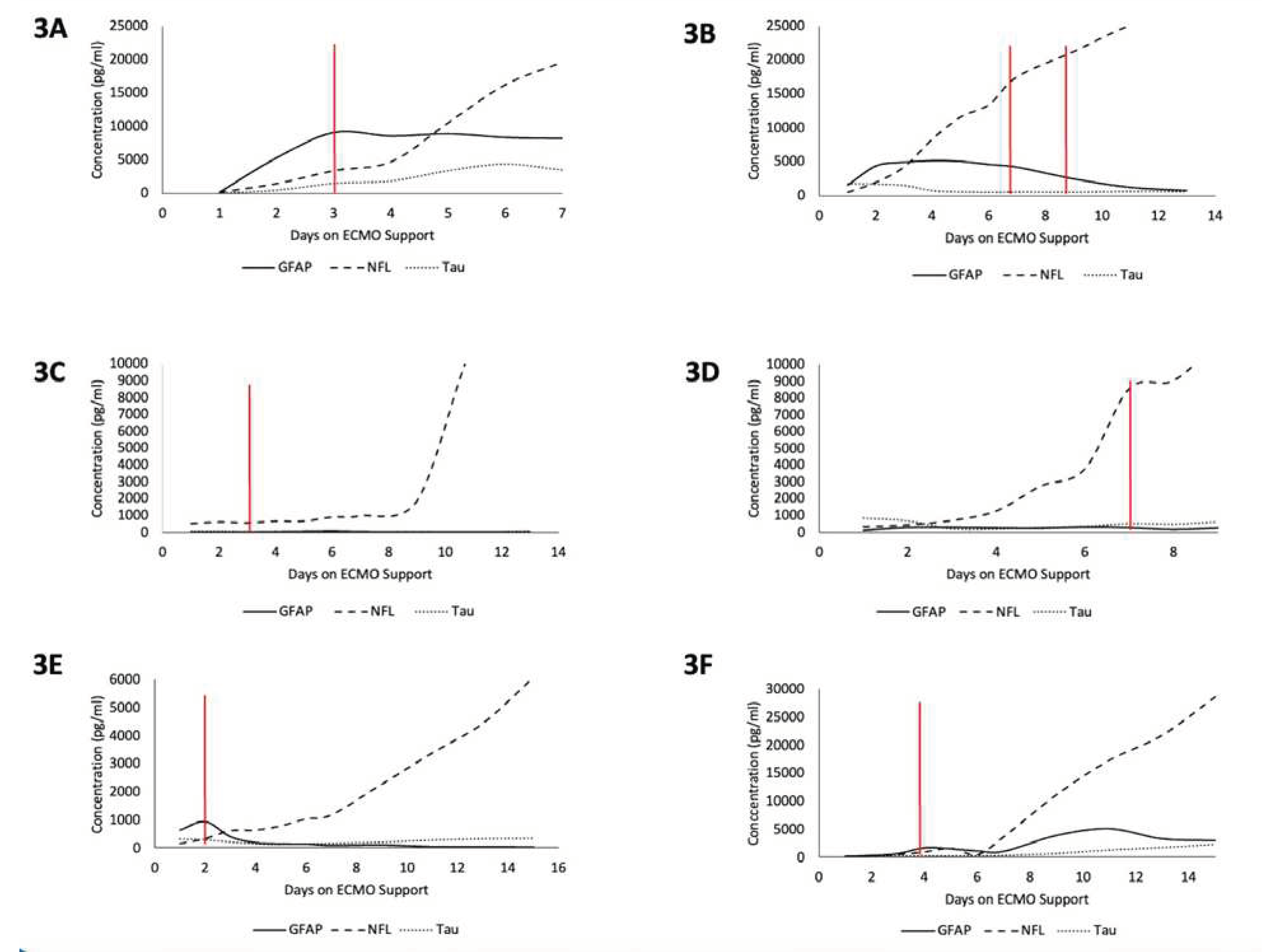
Figure 3.
Time-series plots of peak biomarker levels for six different patients over the course of ECMO cannulation. Red line indicates diagnosis of an ABI. 3A) Patient with ABI on Day 3. 3B) Patient with an ABI on Day 7 and Day 9. 3C) Patient with ABI on Day 3. 3D) Patient with ABI on Day 7. 3E) Patient with ABI on Day 2. 3F) Patient with ABI on Day 4.
Figure 3.
Time-series plots of peak biomarker levels for six different patients over the course of ECMO cannulation. Red line indicates diagnosis of an ABI. 3A) Patient with ABI on Day 3. 3B) Patient with an ABI on Day 7 and Day 9. 3C) Patient with ABI on Day 3. 3D) Patient with ABI on Day 7. 3E) Patient with ABI on Day 2. 3F) Patient with ABI on Day 4.
3. Results
Our pilot study included a patient cohort consisting of 20 patients (median age=48.5 years, 41.5-62.0), with 55% (n=11) being female. All 20 patients were supported with venoarterial ECMO (VA-ECMO) with 10 patients (50%) with central cannulation (50% peripheral VA-ECMO). The primary indications for ECMO were medical cardiogenic shock (55%, n=10), post-cardiotomy shock (35%, n=9), and ECPR (5%, n=1). The median duration on ECMO was 4.5 days (IQR: 2.5-9.5). Of the 20 patients, 15 patients (75%) had a head CT performed. ABI occurred in 40% (n=8) of the patients during ECMO support. The remaining patient characteristics are displayed in
Table 1, stratified by the presence of ABI.
3.1. Brain Injury Biomarkers and ABI
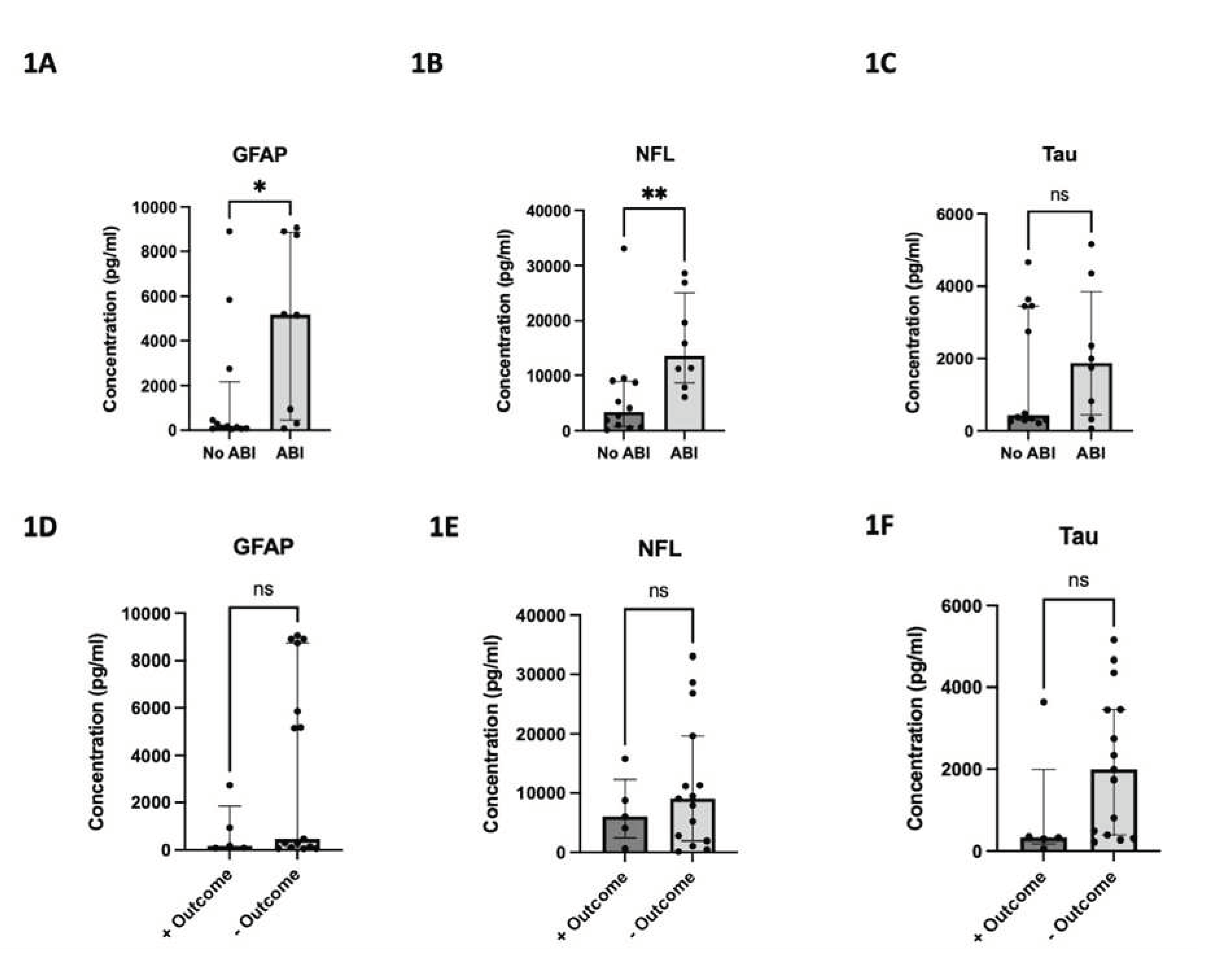
The median peak concentration values and their interquartile ranges for GFAP, NFL, and Tau were 382.3 pg/ml (100.8-5,516.4), 8,306.7 pg/ml (2,338.9-13,577.2), and 1,278.4 pg/ml (318.7-3,447.4), respectively. The median time to peak concentration was 3 days (IQR: 2.0–6.3), 7 days (IQR: 2.0-10.0), and 2 days (IQR: 1.0-6.8), respectively. Median peak GFAP and NFL concentrations were significantly higher for patients who developed ABI vs. without (5167 pg/ml vs. 160.9 pg/ml, p=0.047; 13577 pg/ml vs. 3424 pg/ml, p=0.007), respectively. Although the difference in median peak Tau concentrations did not reach statistical significance, a trend favored higher median peak Tau concentrations in patients with ABI vs. without (1871 pg/ml vs. 439.7 pg/ml, p=0.62) (
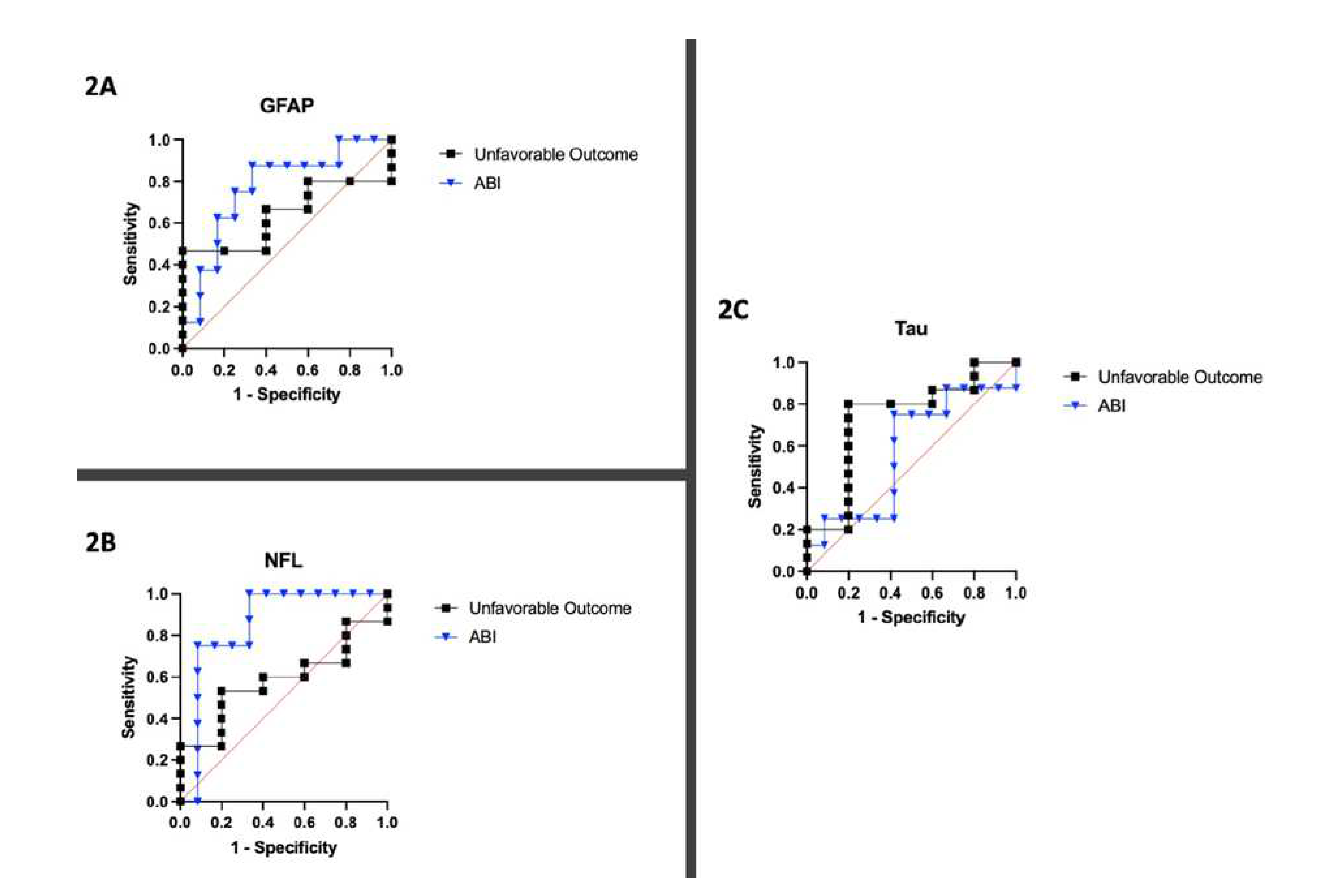
Figure 1). The C-statistics calculated by plotting sensitivity and specificity for each biomarker yielded AUCs of 0.77, 0.85, and 0.57 for GFAP, NFL, and Tau, respectively (
Figure 2).
Figure 1.
125 samples collected for each biomarker. 1A) Peak GFAP concentration for patients with and without ABI. 1B) Peak NFL concentration for patients with and without ABI. 1C) Peak Tau concentration for patients with and without ABI. 1D) Peak GFAP concentration for patients with and without favorable neurologic outcome. 1E) Peak NFL concentration for patients with and without favorable neurologic outcome. 1F) Peak Tau concentration for patients with and without favorable neurologic outcome. Unfavorable neurologic outcome status as assessed by mRS score>3. * denotes p < 0.05. ** denotes p <0.01. ns denotes not significant.
Figure 1.
125 samples collected for each biomarker. 1A) Peak GFAP concentration for patients with and without ABI. 1B) Peak NFL concentration for patients with and without ABI. 1C) Peak Tau concentration for patients with and without ABI. 1D) Peak GFAP concentration for patients with and without favorable neurologic outcome. 1E) Peak NFL concentration for patients with and without favorable neurologic outcome. 1F) Peak Tau concentration for patients with and without favorable neurologic outcome. Unfavorable neurologic outcome status as assessed by mRS score>3. * denotes p < 0.05. ** denotes p <0.01. ns denotes not significant.
Figure 2.
Sensitivity and specificity analysis displayed as Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) Curves for 20 patients for each biomarker. 2A) ROC curve for GFAP with respect to unfavorable neurologic outcome and ABI. 2B) ROC curve for NFL with respect to unfavorable neurologic outcome and ABI. 2C) ROC curve for Tau with respect to unfavorable neurologic outcome and ABI.
Figure 2.
Sensitivity and specificity analysis displayed as Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) Curves for 20 patients for each biomarker. 2A) ROC curve for GFAP with respect to unfavorable neurologic outcome and ABI. 2B) ROC curve for NFL with respect to unfavorable neurologic outcome and ABI. 2C) ROC curve for Tau with respect to unfavorable neurologic outcome and ABI.
3.2. Brain Injury Biomarkers and Neurological Outcomes
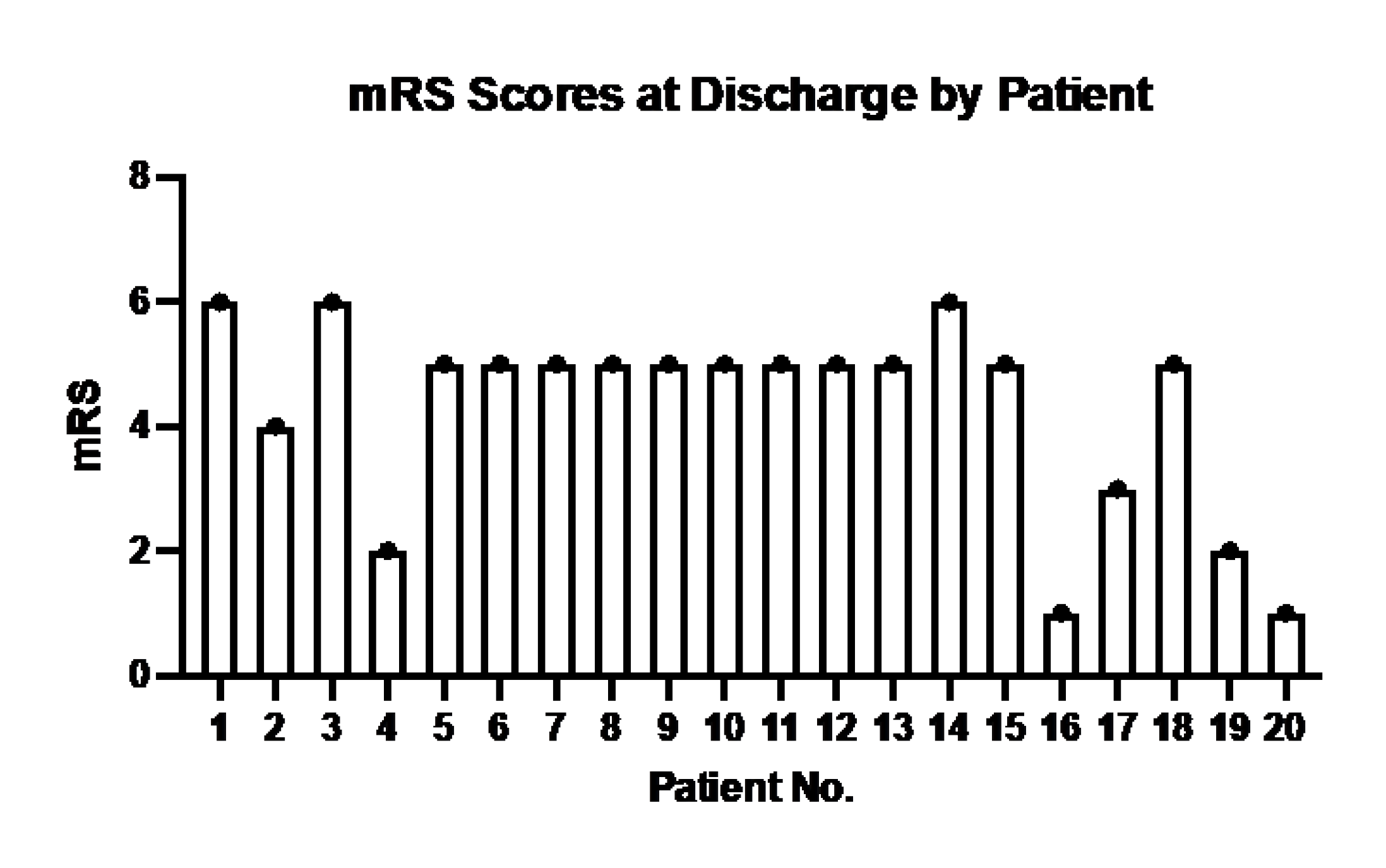
The distribution of mRS is shown in
Figure A1. Overall, 15/20 patients (75%) had unfavorable neurological outcomes at discharge. The difference in median peak concentrations did not reach statistical significance for any biomarker with respect to unfavorable vs. unfavorable neurological outcome. However, trends did show higher biomarker levels in the unfavorable neurological outcome group vs. favorable group (GFAP: 462.6 pg/ml vs. 178.5 pg/ml, p=0.39; NFL: 9048 pg/ml vs. 6090 pg/ml, p=0.61; Tau: 1999 pg/ml vs. 327.8 pg/ml, p=0.14) also shown in
Figure 1. The C-statistics calculated by plotting sensitivity and specificity for each biomarker yielded AUCs of 0.64, 0.59, and 0.73 for GFAP, NFL, and Tau, respectively (
Figure 2).
3.3. Timing of Injury and Biomarker Peak
A total of 125 blood samples were collected over a median of 4.5 days (IQR: 2.5 -9.5) per patient. Notable findings from graphing the temporal relationship of biomarkers with individual patients are as follows (
Figure 3). For patient A, GFAP levels rose prior to the diagnosis of the injury, peaked on the day of diagnosis (Day 3), and continued to stay elevated thereafter. Patient B had 2 instances of ABI (Day 7 and 9) during ECMO, and GFAP and NFL levels began to rise immediately upon cannulation, with GFAP plateauing around the day of first ABI diagnosis and NFL continuing to rise throughout ECMO duration. Patient C had an ABI diagnosis on Day 3 and had no change in GFAP or Tau but around day 7 saw a rapid rise in NFL levels that grew exponentially until day 11. Patient D saw rising NFL levels starting from cannulation that saw a relative peak on day of diagnosis (Day 7) and continued to rise at a lower rate until Day 9. Patient E saw a spike in GFAP levels upon cannulation that peaked on the day of diagnosis of ABI (Day 2) and the values of GFAP fell shortly thereafter and remained low until Day 16, while NFL levels started to rise immediately at cannulation and rapidly rose following injury on Day 2 until Day 16. Patient F saw a relative peak of GFAP and NFL on day of ABI diagnosis (Day 4) which then decreased until around Day 6 and then began to rise again until Day 14, with NFL levels seeing the highest rise between the 3 biomarkers.
Overall, GFAP typically elevated first, NFL elevated to the highest degree, and Tau showed limited change throughout the ECMO process regardless of ABI. The diagnosis of ABI co-occurred with a spike in either GFAP or NFL in five out of six cases analyzed. NFL levels increased starting from ECMO cannulation until day 5 even in the non-ABI group but grew at a faster rate between days 3 and 5 for patients that developed an ABI (
Figure A2). GFAP levels were on aggregate higher in the ABI group than in the non-ABI group and Tau showed no differences across cohorts (
Figure A2).
4. Discussion
ECMO is a life-saving cardiopulmonary intervention that carries risk for ABI such as hypoxic-ischemic brain injury, intracranial thromboembolic or hemorrhagic events, and brain death [
3,
4]. Early diagnosis of ABI can guide clinicians on timely intervention, including cessation and judicious resumption of anticoagulation. However, the means for assessing neurological status in ECMO is limited due to the routine use of sedation and limited ability for patient transport. Currently, no brain injury biomarkers are routinely used in clinical practice despite ongoing concerted efforts [
17,
18,
19,
20]. Blood biomarkers have a series of advantages including low costs, ease of access, quick processing times, and minimal technical expertise necessary for accurate and precise quantification. Serial measurements of GFAP, NFL, and Tau may therefore augment clinical neuromonitoring, assist in earlier diagnosis of ABI, and facilitate appropriate interventions.
The principal findings of this pilot study in adult VA-ECMO patients are that GFAP, NFL, and Tau are markedly elevated in patients with an ABI vs. without. Similarly, the levels of these biomarkers were higher in patients with unfavorable neurological outcomes vs. favorable neurological outcome at discharge. This prospective pilot study builds upon previous research using these biomarkers in patients with cardiac arrest for their utility in neurological prognostication [
8,
9,
17]. To our knowledge, our study is the first to investigate these biomarkers in the context of adult ECMO patients.
4.1. GFAP
Median peak GFAP concentrations were significantly higher for patients who developed ABI vs. without. This corroborates prior research on GFAP outside of ECMO setting, which demonstrates correlation between GFAP levels and the severity of neurologic deficits in ischemic stroke patients [
21]. Upon analysis of GFAP levels, our data revealed a notable trend: for three patients out of the six that developed ABI, GFAP levels exhibited a relative peak on the same day as their brain injury diagnosis. Additionally, GFAP levels were markedly higher earlier (between days 1-5) of ABI patients than their non-ABI counterparts. This is consistent with prior findings with respect to TBI, as GFAP has repeatedly shown to rise 1 hour after injury and peak 20-24 hours after injury [
22,
23,
24]. This trend could be mechanistically explained by the elevation of GFAP in response to astrocyte-mediated repair processes following ABI [
10]. These repair processes might have already been initiated prior to the clinical diagnosis of ABI, accounting for the earlier observed increase in GFAP levels leading up to a peak at the time of clinically diagnosed ABI. Given GFAPs biological role, as well as the findings of previous studies showing that GFAP is elevated following brain injury, it has potential for being a useful biomarker for brain injury occurrence and severity [
25,
26].
4.2. NFL
Median peak NFL concentrations were significantly higher for patients who developed ABI vs. without. NFL levels increased starting from ECMO cannulation until day 5 even in the non-ABI group but grew at a faster rate between days 3 and 5 for patients that developed an ABI (
Figure A2). One of the major causes of ABI is right neck vessel cannulation that can causes disturbances to cerebral blood flow [
27,
28]. Rising NFL levels for all patients, even those that did not develop an ABI, may be an indication of the severity of altered cerebral blood flow and may be explained by the release of NFL in the context of neuronal death and axonal damage [
14]. However, patients with ABI saw a more rapid increase in NFL levels and saw a greater peak at the time of diagnosis, which could aid clinicians towards a quicker and more accurate diagnosis of ABI. These findings corroborate previous research on cardiac arrest patients which indicate that NFL levels are associated with hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in children and worsening outcomes in adults [
8,
29]. Further research with sufficient sample size is warranted to investigate clinically useful cutoffs and better understand temporal associations between peak NFL levels and the severity of ABI, as well as its impact on neurological outcomes.
4.3. Tau
Although the difference in median peak Tau concentrations did not reach statistical significance, a trend favored higher median peak Tau concentrations in patients with ABI vs. without. While tau has been most heavily studied in its misfolded aggregate form in Alzheimer’s disease and other forms of dementia, tau protein release can potentially be used as a biomarker indicating axonal damage [
30]. Tau has demonstrated potential significance for neuro-prognostication after cardiac arrest, but there is a paucity of data in ECPR and ECMO [
9]. Our results indicate Tau protein having poorer sensitivity and specificity in association to ABI than GFAP and NFL. After acute brain injury, GFAP and NFL may be released into the bloodstream more rapidly compared to tau protein. This early release allows for prompt detection and measurement of these biomarkers, enabling their potential use in early prognostication. In contrast, tau protein release may occur later in the injury cascade, reducing its immediate predictive value.
4.4. Limitations
The are several limitations of our study. The study only has 20 patients and therefore, caution should be taken interpreting the findings as this is a pilot study from a single academic center. Secondly, we do not have control non-ECMO groups or blood samples prior to ECMO cannulation. As VA-ECMO is mostly an emergent cannulation, obtaining blood from these patients is not usually possible. Thirdly, although our center has a standardized neuromonitoring protocol that provides better ABI diagnosis ability, performing neuroimaging in a timely manner poses a challenge in ECMO patients with multiple vasoactive medications and often with open chest [
15,
16]. For this, our institution currently is performing a study using a portable brain MRI at bedside (SAFE MRI ECMO study) for ECMO patients, which will improve our current study [
31,
32]. Lastly, the mortality is high in VA-ECMO patients, and thus, mRS is skewed towards unfavorable neurological outcome, limiting discrimination from favorable outcomes. Our ongoing efforts to conduct a multicenter study on this topic can address this limitation.
5. Conclusions
GFAP, NFL, and Tau represent promising novel biomarkers at bedside for predicting ABI and neurological outcomes in adult ECMO patients where accurate neurological examination is limited. Our findings from this pilot study provide valuable insights into the dynamic and temporal changes of these biomarker levels in relation to ABI. Further research is crucial to refine the clinical applications of these promising biomarkers and determine their utility and prognostic values in adult ECMO patients.
Author Contributions
Concept/design: SK, AE, SMC; Data Collection: SK, SMC; Data analysis: SK, AA, SM; Data interpretation: SK, AG, SMC; Drafting: SK, AA, SM; Critical revision: Mela; Approval: all authors.
Funding
This study is supported by the ELSO. SMC is supported by NHLBI (1K23HL157610).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Review Board of Johns Hopkins University (protocol code: IRB00152962 and date of approval: May 15th, 2018).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The de-identified data presented in this study are not publicly available due to PHI privacy considerations.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Appendix A
Figure A1.
mRS Scores of each of the 20 patients in the study at hospital discharge.
Figure A1.
mRS Scores of each of the 20 patients in the study at hospital discharge.
Figure A2.
Average value of biomarkers across 20 patients within each day following ECMO cannulation for the first 5 days. A) Patients that did not develop an ABI. B) Patients that did develop an ABI.
Figure A2.
Average value of biomarkers across 20 patients within each day following ECMO cannulation for the first 5 days. A) Patients that did not develop an ABI. B) Patients that did develop an ABI.
References
- Makdisi G, Wang IW. Extra Corporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO) review of a lifesaving technology. J Thorac Dis. 2015;7(7):E166-176. [CrossRef]
- Thiagarajan RR, Barbaro RP, Rycus PT, et al. Extracorporeal Life Support Organization Registry International Report 2016. ASAIO J. 2017;63(1):60-67. [CrossRef]
- Cho SM, Canner J, Chiarini G, et al. Modifiable Risk Factors and Mortality From Ischemic and Hemorrhagic Strokes in Patients Receiving Venoarterial Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation: Results From the Extracorporeal Life Support Organization Registry. Crit Care Med. 2020;48(10):e897-e905. [CrossRef]
- Cho SM, Farrokh S, Whitman G, Bleck TP, Geocadin RG. Neurocritical Care for Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Patients. Crit Care Med. 2019;47(12):1773-1781. [CrossRef]
- Chiarini G, Cho SM, Whitman G, Rasulo F, Lorusso R. Brain Injury in Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation: A Multidisciplinary Approach. Semin Neurol. 2021;41(4):422-436. [CrossRef]
- Gilje P, Gidlöf O, Rundgren M, et al. The brain-enriched microRNA miR-124 in plasma predicts neurological outcome after cardiac arrest. Crit Care. 2014;18(2):R40. [CrossRef]
- Wilcox C, Choi CW, Cho SM. Brain injury in extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation: translational to clinical research. J Neurocrit Care. 2021;14(2):63-77. [CrossRef]
- Moseby-Knappe M, Mattsson N, Nielsen N, et al. Serum Neurofilament Light Chain for Prognosis of Outcome After Cardiac Arrest. JAMA Neurol. 2019;76(1):64-71. [CrossRef]
- Mattsson N, Zetterberg H, Nielsen N, et al. Serum tau and neurological outcome in cardiac arrest: Serum Tau in Cardiac Arrest. Ann Neurol. 2017;82(5):665-675. [CrossRef]
- Abdelhak A, Foschi M, Abu-Rumeileh S, et al. Blood GFAP as an emerging biomarker in brain and spinal cord disorders. Nat Rev Neurol. 2022;18(3):158-172. [CrossRef]
- Mayer CA, Brunkhorst R, Niessner M, Pfeilschifter W, Steinmetz H, Foerch C. Blood levels of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) in patients with neurological diseases. PLoS One. 2013;8(4):e62101. [CrossRef]
- Shahim P, Gren M, Liman V, et al. Serum neurofilament light protein predicts clinical outcome in traumatic brain injury. Sci Rep. 2016;6(1):36791. [CrossRef]
- Mattsson N, Andreasson U, Zetterberg H, Blennow K, for the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Association of Plasma Neurofilament Light With Neurodegeneration in Patients With Alzheimer Disease. JAMA Neurol. 2017;74(5):557. [CrossRef]
- Mandelkow EM, Mandelkow E. Biochemistry and cell biology of tau protein in neurofibrillary degeneration. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2012;2(7):a006247. [CrossRef]
- Cho SM, Ziai W, Mayasi Y, et al. Noninvasive Neurological Monitoring in Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation. ASAIO J. 2020;66(4):388-393. [CrossRef]
- Ong CS, Etchill E, Dong J, et al. Neuromonitoring detects brain injury in patients receiving extracorporeal membrane oxygenation support. The Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery. Published online 21:S0022522321015087. 20 October. [CrossRef]
- Oh SH, Kim HS, Park KN, et al. The Levels of Circulating MicroRNAs at 6-Hour Cardiac Arrest Can Predict 6-Month Poor Neurological Outcome. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021;11(10):1905. [CrossRef]
- Bembea MM, Savage W, Strouse JJ, et al. Glial fibrillary acidic protein as a brain injury biomarker in children undergoing extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2011;12(5):572-579. [CrossRef]
- Floerchinger B, Philipp A, Foltan M, et al. Neuron-specific enolase serum levels predict severe neuronal injury after extracorporeal life support in resuscitation. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2014;45(3):496-501. [CrossRef]
- Laskowitz DT, Kasner SE, Saver J, Remmel KS, Jauch EC, BRAIN Study Group. Clinical usefulness of a biomarker-based diagnostic test for acute stroke: the Biomarker Rapid Assessment in Ischemic Injury (BRAIN) study. Stroke. 2009;40(1):77-85. [CrossRef]
- Amalia, L. Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein (GFAP): Neuroinflammation Biomarker in Acute Ischemic Stroke. J Inflamm Res. 2021;14:7501-7506. [CrossRef]
- Welch RD, Ellis M, Lewis LM, et al. Modeling the Kinetics of Serum Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein, Ubiquitin Carboxyl-Terminal Hydrolase-L1, and S100B Concentrations in Patients with Traumatic Brain Injury. Journal of Neurotrauma. 2017;34(11):1957-1971. [CrossRef]
- Papa L, Brophy GM, Welch RD, et al. Time Course and Diagnostic Accuracy of Glial and Neuronal Blood Biomarkers GFAP and UCH-L1 in a Large Cohort of Trauma Patients With and Without Mild Traumatic Brain Injury. JAMA Neurol. 2016;73(5):551. [CrossRef]
- Papa L, Zonfrillo MR, Ramirez J, et al. Performance of Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein in Detecting Traumatic Intracranial Lesions on Computed Tomography in Children and Youth With Mild Head Trauma. Macy M, ed. Acad Emerg Med. 2015;22(11):1274-1282. [CrossRef]
- Gazzolo D, Masetti P, Meli M, Grutzfeld D, Michetti F. Elevated S100B protein as an early indicator of intracranial haemorrhage in infants subjected to extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Acta Paediatr. 2002;91(2):218-221. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen DN, Huyghens L, Wellens F, Schiettecatte J, Smitz J, Vincent JL. Serum S100B protein could help to detect cerebral complications associated with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO). Neurocrit Care. 2014;20(3):367-374. [CrossRef]
- Hunter CJ, Blood AB, Bishai JM, et al. Cerebral blood flow and oxygenation during venoarterial and venovenous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in the newborn lamb. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2004;5(5):475-481. [CrossRef]
- Van Heijst A, Liem D, Hopman J, Van Der Staak F, Sengers R. Oxygenation and hemodynamics in left and right cerebral hemispheres during induction of veno-arterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. J Pediatr. 2004;144(2):223-228. [CrossRef]
- Kirschen MP, Yehya N, Graham K, et al. Circulating Neurofilament Light Chain Is Associated With Survival After Pediatric Cardiac Arrest. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2020;21(7):656-661. [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Ortiz F, Turton M, Kac PR, et al. Brain-derived tau: a novel blood-based biomarker for Alzheimer’s disease-type neurodegeneration. Brain. 2023;146(3):1152-1165. [CrossRef]
- Cho SM, Wilcox C, Keller S, et al. Assessing the SAfety and FEasibility of bedside portable low-field brain Magnetic Resonance Imaging in patients on ECMO (SAFE-MRI ECMO study): study protocol and first case series experience. Crit Care. 2022;26(1):119. [CrossRef]
- Wilcox C, Acton M, Rando H, et al. Safety of Bedside Portable Low-Field Brain MRI in ECMO Patients Supported on Intra-Aortic Balloon Pump. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022;12(11):2871. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).