Submitted:
13 June 2023
Posted:
16 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
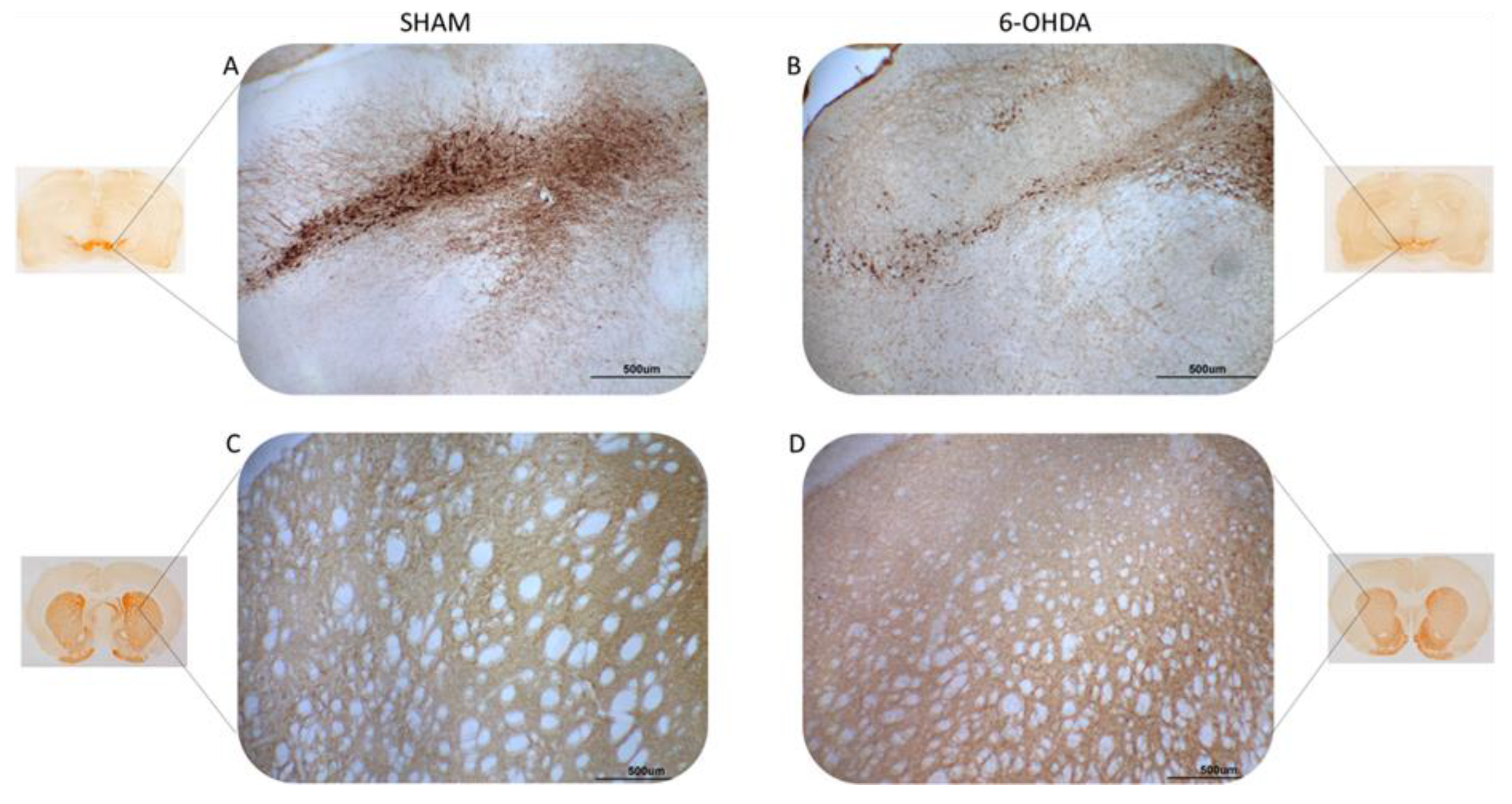
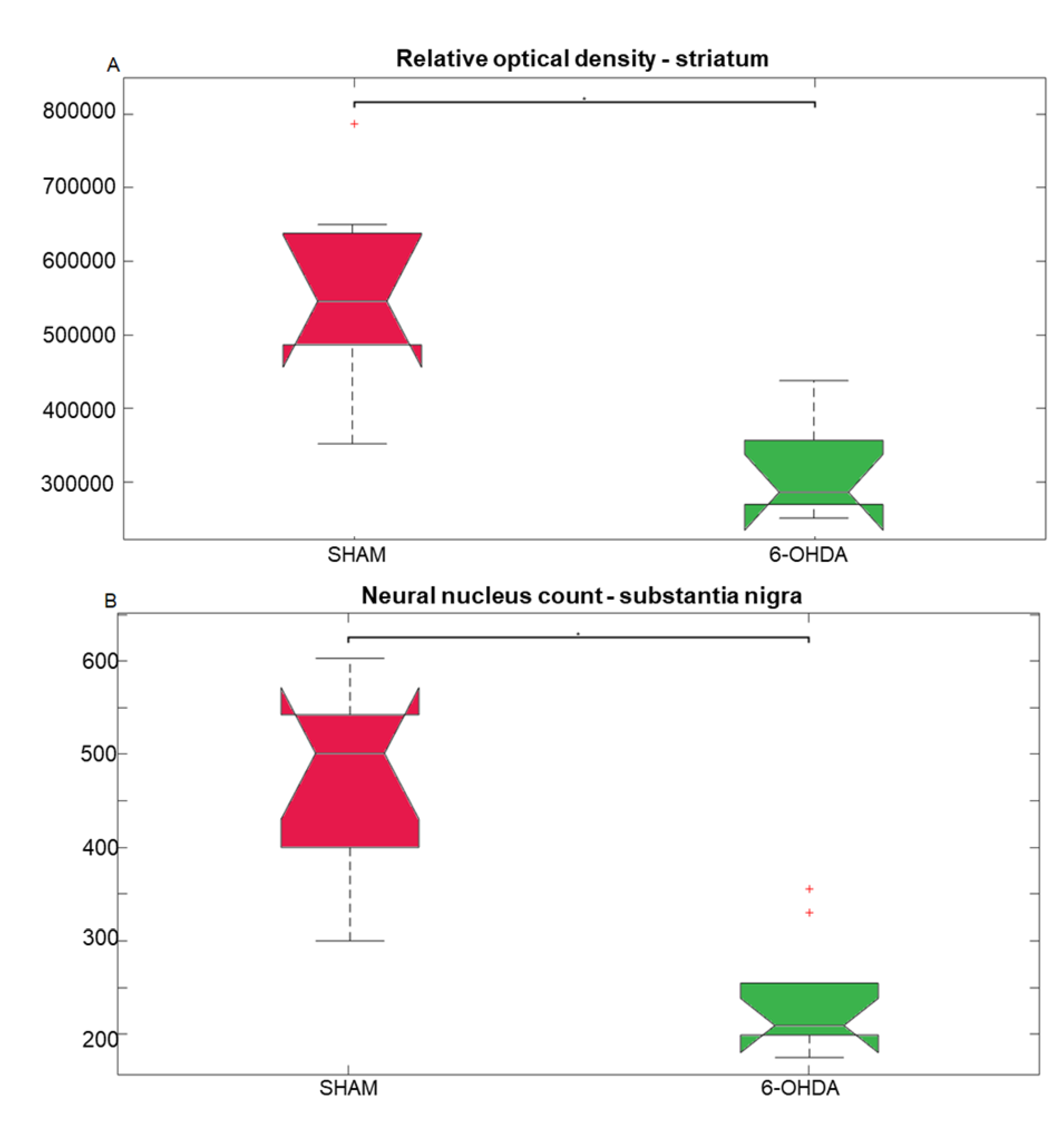
2.1. Tyrosine hydroxylase immunohistochemistry
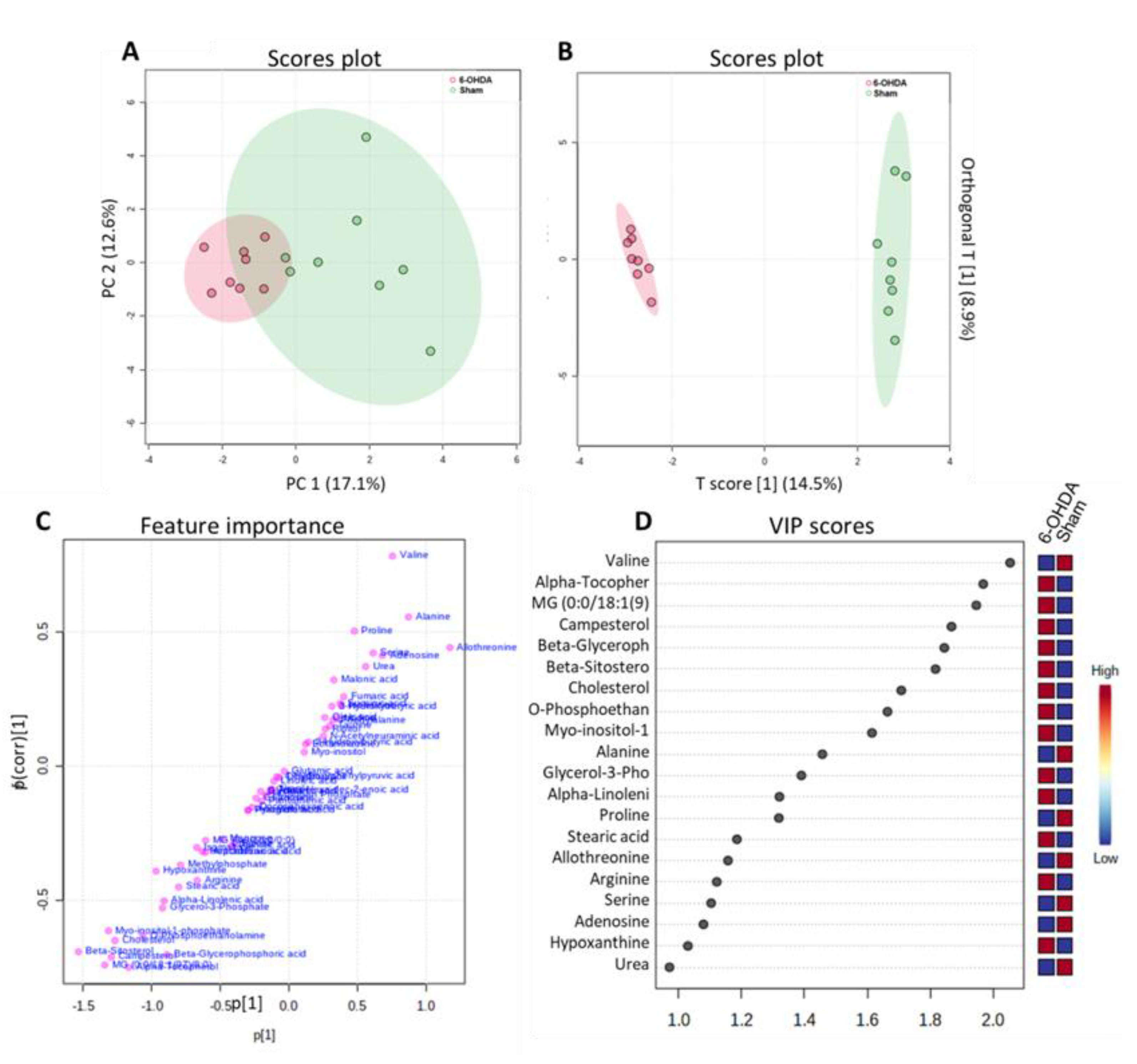
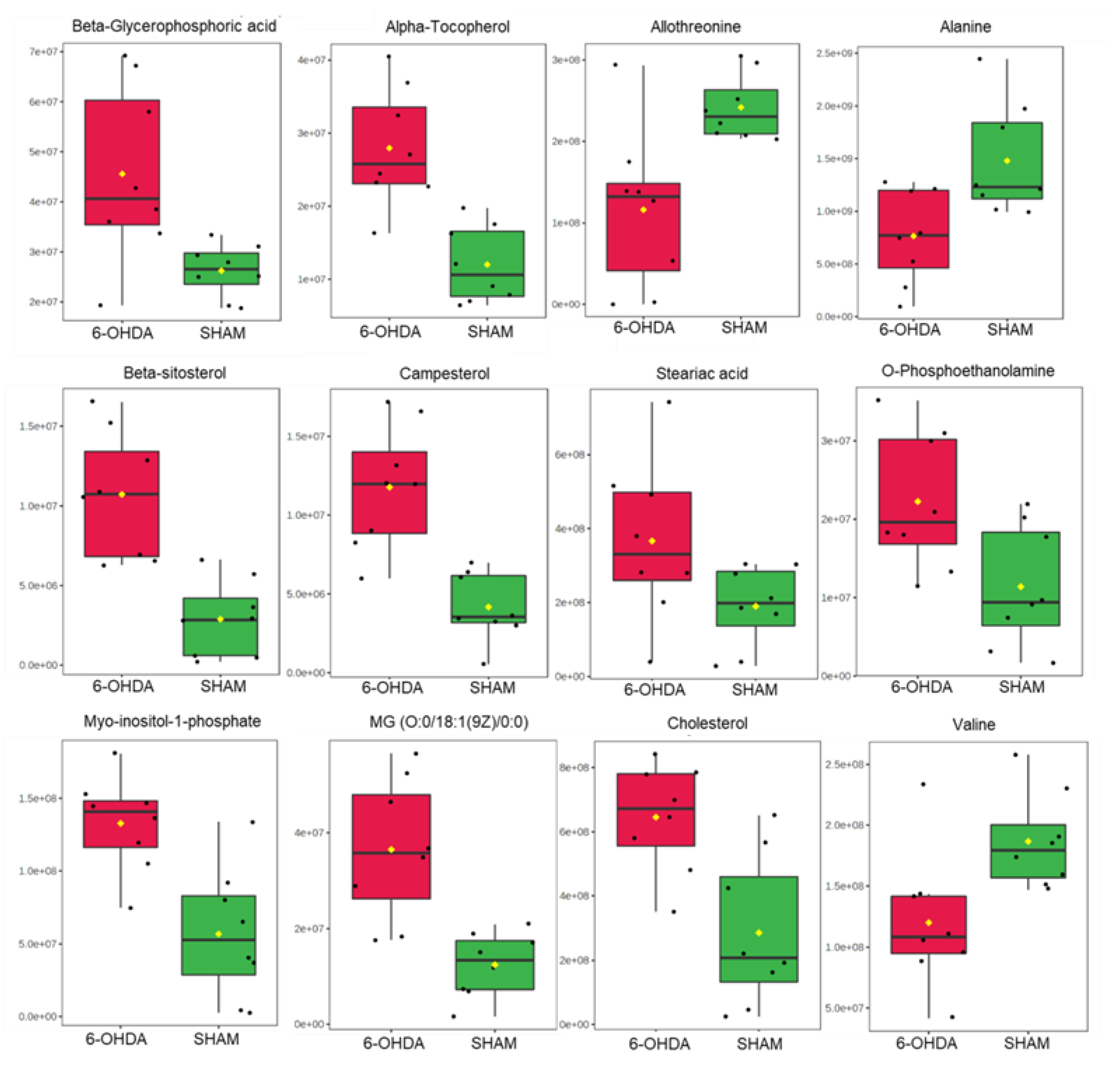
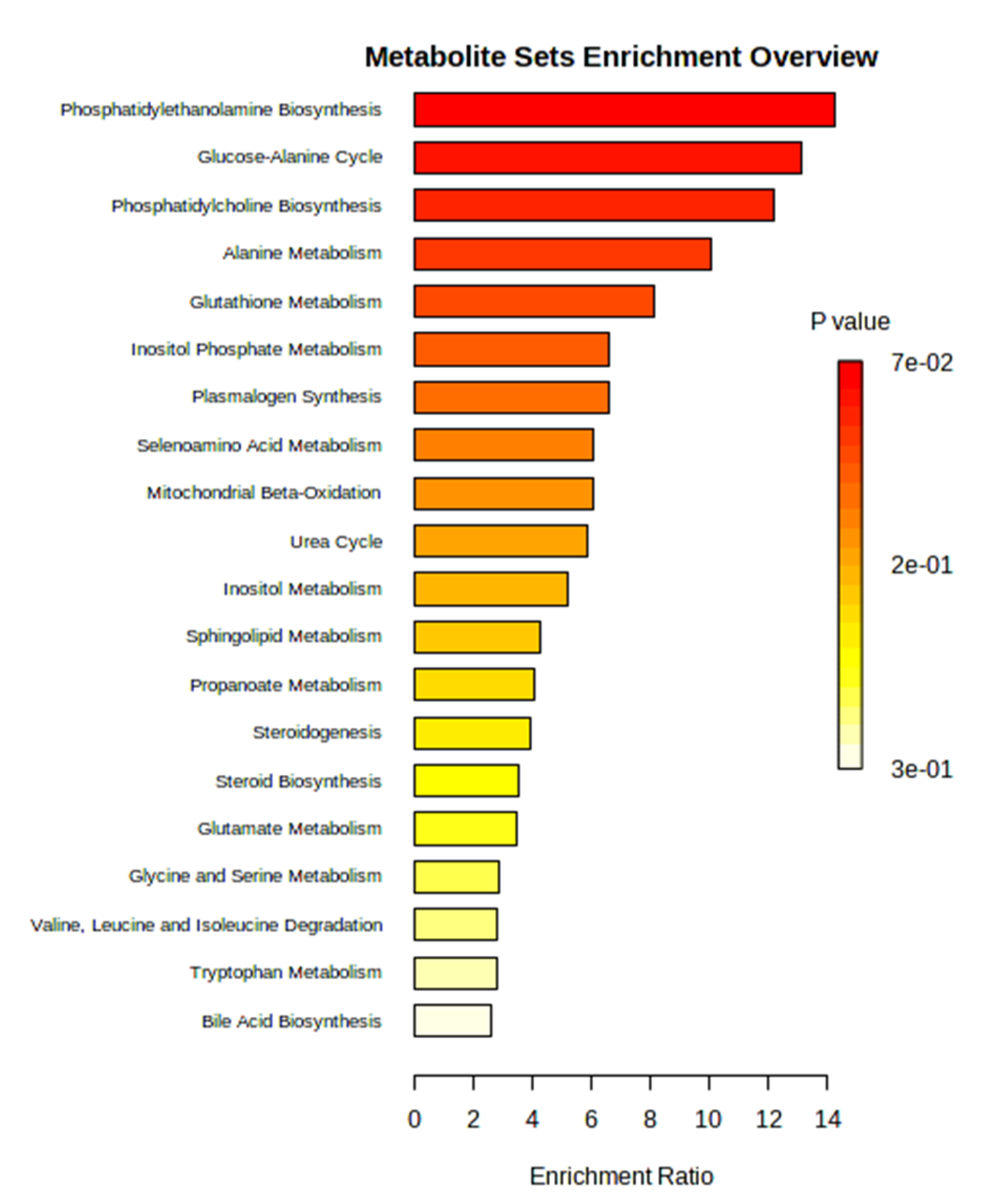
3.2. Untargeted metabolomics
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Study Design
4.4. Immunohistochemistry
4.5. Metabolomics
4.6. Statistics
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hou, Y.; Dan, X.; Babbar, M.; Wei, Y.; Hasselbalch, S.G.; Croteau, D.L.; Bohr, V.A. Ageing as a risk factor for neurodegenerative disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 15, 565–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, Z. , Pan, J., Tang, S., Duan, D., Yu, D., Nong, H., Wang, Z. 2021. Global trends in the incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability of Parkinson's disease in 204 countries/territories from 1990 to 2019. Frontiers in public health 9: 776847.
- Değirmenci, H. , Bakirci, E.M., Hamur, H. 2020. Cardiac Effects of Parkinson’s Disease. Open Journal of Parkinson's Disease and Treatment 3(1): 006-007.
- Park, T.-S.; Yamashita, H.; Blaner, W.S.; Goldberg, I.J. Lipids in the heart: a source of fuel and a source of toxins. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 18, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, A.; Kristensen, K.K.; Ploug, M.; Winther, A.L.-M. The Importance of Lipoprotein Lipase Regulation in Atherosclerosis. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, I.J.; Trent, C.M.; Schulze, P.C. Lipid Metabolism and Toxicity in the Heart. Cell Metab. 2012, 15, 805–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual, F.; Coleman, R.A. Fuel availability and fate in cardiac metabolism: A tale of two substrates. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) - Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2016, 1861, 1425–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toczylowska, B.; Zieminska, E.; Michałowska, M.; Chalimoniuk, M.; Fiszer, U. Changes in the metabolic profiles of the serum and putamen in Parkinson’s disease patients – In vitro and in vivo NMR spectroscopy studies. Brain Res. 2020, 1748, 147118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanning, S.; Selkoe, D.; Dettmer, U. Parkinson’s disease: proteinopathy or lipidopathy? npj Park. Dis. 2020, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xicoy, H.; Brouwers, J.F.; Kalnytska, O.; Wieringa, B.; Martens, G.J.M. Lipid Analysis of the 6-Hydroxydopamine-Treated SH-SY5Y Cell Model for Parkinson’s Disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 57, 848–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Y.; Le, W. Recent advances and perspectives of metabolomics-based investigations in Parkinson’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2019, 14, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poli, A. , Marangoni, F., Corsini, A., Manzato, E., Marrocco, W., Martini, D., Medea, G., Visioli, F. 2021. Phytosterols, Cholesterol Control, and Cardiovascular Disease. Nutrients 13(8), 2810.
- Ge, H.; Liu, G.; Yamawaki, T.M.; Tao, C.; Alexander, S.T.; Ly, K.; Fordstrom, P.; Shkumatov, A.A.; Li, C.-M.; Rajamani, S.; et al. Phytosterol accumulation results in ventricular arrhythmia, impaired cardiac function and death in mice. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhmudova, U.; Schulze, P.C.; Lütjohann, D.; Weingärtner, O. Phytosterols and Cardiovascular Disease. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2021, 23, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz, M. , Horn, K., Pott, J., Gross, A., Kleber, M.E., Delgado, G.E., Mishra, P.P., Kirsten, H., Gieger, C., Müller-Nurasyid, M., Tönjes, A., Kovacs, P., Lehtimäki, T., Raitakari, O., Kähönen, M., Gylling, H., Baber, R., Isermann, B., Stumvoll, M., Loeffler, M., März, W., Meitinger, T., Peters, A., Thiery, J., Teupser, D., Ceglarek, U. 2022. Genome-wide meta-analysis of phytosterols reveals five novel loci and a detrimental effect on coronary atherosclerosis. Nature communications 13(1), 143.
- Sudhop, T.; Gottwald, B.M.; von Bergmann, K. Serum plant sterols as a potential risk factor for coronary heart disease. Metabolism 2002, 51, 1519–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Othman, R.; Moghadasian, M.H. Beyond cholesterol-lowering effects of plant sterols: clinical and experimental evidence of anti-inflammatory properties. Nutr. Rev. 2011, 69, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanasila, L.; Marques-Vidal, P. Serum Phytosterols Are Not Associated with Inflammatory Markers in Two Cross-Sectional, Swiss Population-Based Studies (The CoLaus|PsyCoLaus Study). Nutrients 2022, 14, 2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fakih, O.; Sanver, D.; Kane, D.; Thorne, J.L. Exploring the biophysical properties of phytosterols in the plasma membrane for novel cancer prevention strategies. Biochimie 2018, 153, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hah, Y.-S.; Lee, W.K.; Lee, S.; Kim, E.J.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, S.-J.; Ji, Y.H.; Kim, S.G.; Lee, H.-H.; Hong, S.Y.; et al. β-Sitosterol Attenuates Dexamethasone-Induced Muscle Atrophy via Regulating FoxO1-Dependent Signaling in C2C12 Cell and Mice Model. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.; Nath, N.; Rauf, A.; Bin Emran, T.; Mitra, S.; Islam, F.; Chandran, D.; Barua, J.; Khandaker, M.U.; Idris, A.M.; et al. Multifunctional roles and pharmacological potential of β-sitosterol: Emerging evidence toward clinical applications. Chem. Interactions 2022, 365, 110117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xicoy, H.; Wieringa, B.; Martens, G.J.M. The Role of Lipids in Parkinson’s Disease. Cells 2019, 8, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, F.A.; Flores, R.A.; Bruxel, M.A.; da Silva, F.N.; Moreira, E.L.G.; Zoccal, D.B.; Prediger, R.D.; Rafacho, A. Glucose Homeostasis Is Not Affected in a Murine Model of Parkinson’s Disease Induced by 6-OHDA. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 12, 1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Peng, G.; Tang, Y.; Li, S.; Liu, Z.; Zheng, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Wei, L.; Su, Y.; et al. Lipid profiles in the cerebrospinal fluid of rats with 6-hydroxydopamine-induced lesions as a model of Parkinson’s disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2023, 14, 1077738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Wang, Y.; He, X.; Li, H.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X. A systematic review and meta-analysis of serum cholesterol and triglyceride levels in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Lipids Heal. Dis. 2020, 19, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurh, K.; Park, M.; Jang, S.-I.; Park, E.-C.; Jang, S.-Y. Association between serum lipid levels over time and risk of Parkinson’s disease. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.; Han, P.; Wong, M.-Y.; Chang, R.C.-C.; Legido-Quigley, C. Palmitate and Stearate are Increased in the Plasma in a 6-OHDA Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Metabolites 2019, 9, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Loo, B.; Labugger, R.; Aebischer, C.P.; Skepper, J.N.; Bachschmid, M.; Spitzer, V.; Kilo, J.; Altwegg, L.; Ullrich, V.; Lüscher, T.F.; et al. Cardiovascular aging is associated with vitamin E increase. Circulation 2002, 105, 1635–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heim, C.; Kolasiewicz, W.; Kurz, T.; Sontag, K.H. Behavioral alterations after unilateral 6-hydroxydopamine lesions of the striatum. Effect of alpha-tocopherol. Pol. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 53. [Google Scholar]
- Roghani, M.; Behzadi, G. Neuroprotective effect of vitamin E on the early model of Parkinson’s disease in rat: behavioral and histochemical evidence. Brain Res. 2001, 892, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, H. , Maeda, M., Makita, M. 1991. O-phosphoethanolamine content in mouse tissues during development. Agricultural and biological chemistry 55(1): 289-290.
- Kennergren, C.; Mantovani, V.; Lönnroth, P.; Nyström, B.; Berglin, E.; Hamberger, A. Extracellular Amino Acids as Markers of Myocardial Ischemia during Cardioplegic Heart Arrest. Cardiology 1999, 91, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, B.M. , Mamalias, N., Moszczynska, A., Rajput, A.H., Kish, S.J. 2001. Elevated activity of phospholipid biosynthetic enzymes in substantia nigra of patients with Parkinson's disease. Neuroscience 102(4), 899–904.
- Hayakawa, T. , Chang, M.C., Bell, J.M., Seeman, R., Rapoport, S.I., Appel, N.M. 1998. Fatty acid incorporation depicts brain activity in a rat model of Parkinson's disease. Brain research 807(1-2), 177–181.
- Alesutan, I.; Moritz, F.; Haider, T.; Shouxuan, S.; Gollmann-Tepeköylü, C.; Holfeld, J.; Pieske, B.; Lang, F.; Eckardt, K.-U.; Heinzmann, S.S.; et al. Impact of β-glycerophosphate on the bioenergetic profile of vascular smooth muscle cells. J. Mol. Med. 2020, 98, 985–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, H.P.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Wood, L.; Wang, G. Obesity-Associated Metabolic Signatures Correlate to Clinical and Inflammatory Profiles of Asthma: A Pilot Study. Allergy, Asthma Immunol. Res. 2018, 10, 628–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, G.; Yin, C.; Tian, Z.; Wang, T.; Sun, W.; Xiang, Q.; Guo, G. Metabolomic Analysis of Plasma From Patients With Acute Mountain Sickness Using Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry. Medicine 2015, 94, e1988–e1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- She, J.; Guo, M.; Li, H.; Liu, J.; Liang, X.; Liu, P.; Zhou, B.; Liu, S.; Deng, Y.; Lou, B.; et al. Targeting amino acids metabolic profile to identify novel metabolic characteristics in atrial fibrillation. Clin. Sci. 2018, 132, 2135–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoaib, M.; Choudhary, R.C.; Choi, J.; Kim, N.; Hayashida, K.; Yagi, T.; Yin, T.; Nishikimi, M.; Stevens, J.F.; Becker, L.B.; et al. Plasma metabolomics supports the use of long-duration cardiac arrest rodent model to study human disease by demonstrating similar metabolic alterations. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Le, S.; Ojanen, X.; Tan, X.; Wiklund, P.; Cheng, S. Effects of exercise and dietary interventions on serum metabolites in men with insomnia symptoms: A 6-month randomized controlled trial. Sports Med. Heal. Sci. 2020, 2, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, S.K.; Novak, J.E.; Agranoff, B.W. Inositol and higher inositol phosphates in neural tissues: homeostasis, metabolism and functional significance. J. Neurochem. 2002, 82, 736–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhetri, D.R. Myo-Inositol and Its Derivatives: Their Emerging Role in the Treatment of Human Diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Uarquin, F.; Rodehutscord, M.; Huber, K. Myo-inositol: its metabolism and potential implications for poultry nutrition—a review. Poult. Sci. 2019, 99, 893–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calzada, E.; Onguka, O.; Claypool, S.M. Phosphatidylethanolamine Metabolism in Health and Disease. 2015, 321, 29–88. [CrossRef]
- van der Veen, J.N.; Lingrell, S.; da Silva, R.P.; Jacobs, R.L.; Vance, D.E. The Concentration of Phosphatidylethanolamine in Mitochondria Can Modulate ATP Production and Glucose Metabolism in Mice. Diabetes 2014, 63, 2620–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, D.; Witt, S.N. Ethanolamine and Phosphatidylethanolamine: Partners in Health and Disease. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavasoli, M.; Lahire, S.; Reid, T.; Brodovsky, M.; McMaster, C.R. Genetic diseases of the Kennedy pathways for membrane synthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 17877–17886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozelli, J.C.; Azher, S.; Epand, R.M. Plasmalogens and Chronic Inflammatory Diseases. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarabhai, T.; Roden, M. Hungry for your alanine: when liver depends on muscle proteolysis. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 4563–4566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, S.; Kumaran, S.S.; Goyal, V.; Bose, S.; Jain, S.; Dwivedi, S.N.; Srivastava, A.K.; Jagannathan, N.R. Metabolomic analysis of serum using proton NMR in 6-OHDA experimental PD model and patients with PD. Neurochem. Int. 2020, 134, 104670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachhawat, A.K.; Yadav, S. The glutathione cycle: Glutathione metabolism beyond the γ-glutamyl cycle. IUBMB Life 2018, 70, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lushchak, V.I. Glutathione Homeostasis and Functions: Potential Targets for Medical Interventions. J. Amino Acids 2012, 2012, 736837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjørklund, G.; Peana, M.; Maes, M.; Dadar, M.; Severin, B. The glutathione system in Parkinson’s disease and its progression. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2020, 120, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatree, S.; Thongmaen, N.; Tantivejkul, K.; Sitticharoon, C.; Vucenik, I. Role of Inositols and Inositol Phosphates in Energy Metabolism. Molecules 2020, 25, 5079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schantl, A.E.; Verhulst, A.; Neven, E.; Behets, G.J.; D’haese, P.C.; Maillard, M.; Mordasini, D.; Phan, O.; Burnier, M.; Spaggiari, D.; et al. Inhibition of vascular calcification by inositol phosphates derivatized with ethylene glycol oligomers. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, S.E.; Sun, L.Y.; Yang, A.L.; Liao, J.; Yang, G.Y. Overview of Inositol and Inositol Phosphates on Chemoprevention of Colitis-Induced Carcinogenesis. Molecules 2020, 26, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wundenberg, T.; Mayr, G.W. Synthesis and biological actions of diphosphoinositol phosphates (inositol pyrophosphates), regulators of cell homeostasis. Biol. Chem. 2012, 393, 979–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paxinos, G.; Watson, C. The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 6th ed.; Elsevier Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; London, UK, 2007; ISBN 9780123919496. [Google Scholar]
- Shimohama, S. , Sawada, H., Kitamura, Y., Taniguchi, T. 2003. Disease model: Parkinson's disease. Trends in molecular medicine 9(8), 360–365.
- Perlbarg, V.; Lambert, J.; Butler, B.; Felfli, M.; Valabrègue, R.; Privat, A.-L.; Lehéricy, S.; Petiet, A. Alterations of the nigrostriatal pathway in a 6-OHDA rat model of Parkinson’s disease evaluated with multimodal MRI. PLOS ONE 2018, 13, e0202597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrangelo, A.; Ferrarini, A.; Rey-Stolle, F.; García, A.; Barbas, C. From sample treatment to biomarker discovery: A tutorial for untargeted metabolomics based on GC-(EI)-Q-MS. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 900, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




