4.2. Hydrogen atom content and the symmetries
In this section, we examine the hydrogen atom content in each one of the symmetry cases summarized in
Section 2: Rumer’s symmetry (
Section 2.1), the 3
rd base symmetry (
Section 2.2) and the weak/strong, purine/pyrimidine and keto/amino symmetries (
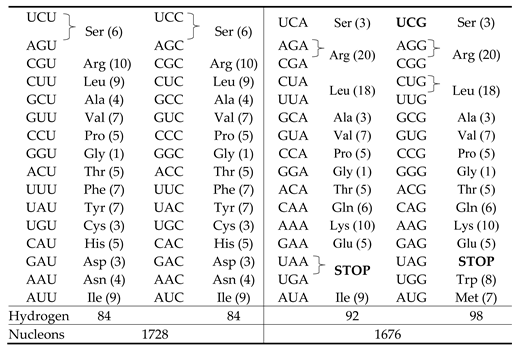
Section 2.3). Before developing these topics, let us consider, first, the hydrogen atom content in the 61 amino acids side chains, as partitioned by the degeneracy. (Please note that when we say, here and below, “61 amino acids”, we are of course taking into account the degeneracy of each one of the 20 amino acids.) From the table in the
Appendix A, we have that the total number of hydrogen atoms in the 61 amino acids side chains is equal to
. Let us note from the start that in this count, we take for the (singular)
imino acid proline, as a special case, 5 hydrogen atoms in its side chain. We will return to this important point later, in
Section 5, with brand new results. A quick look at
Table 4 of our Fibonacci-like sequences, reveals that the number of hydrogen atoms, mentioned above, is showing itself in multiple instances. First, ostensibly, as the ninth member of the sequence
(
Second, from the relation (viii) in Equ.(2) which, we recall, is valid for any n, in particular for
:
. Third, from the recurence relation of the sequence
. Fourth, from the sum
This last equation will be considered in detail below as it has a great importance concerning the computation of the degeneracy of the genetic code, in various formats. By isolating the last term
, we have
This relation is important and will play a prominent role is this section, and later (in
Section 6); it gives the number of hydrogen atoms in the amino acids side chains, distributed into two parts: 139 hydrogen atoms in 23 amino acids (17 amino acids with no “degeneracy” at the
first base position and the six entities
,
and
), on the one hand, and
hydrogen atoms in the 38 remaining amino acids corresponding to the
degenerate codons, on the other (see the introduction, below and also the
Appendix A for the calculations). This is the pattern “
”. Now, as we have
from the recurrence relation of the sequence
, we can cast the relation above as follows
This is the hydrogen atom in the usual pattern “
(20 amino acids and 41 degenerate codons). Note that 22 is the number of hydrogen atoms in serine, arginine and leucine, corresponding to one codon for each one of them (see the table in
Appendix A). By restricting the sum in Equ.(10) as shown below, we have
This pattern corresponds to Rakocevic’s
Cyclic Invariant Periodic System (CIPS) classification of the 20 amino acids where there are 133 (225) hydrogen atoms in the amino acids side chains in the secondary superclass (primary superclass), see [
12] and [
13]. The above hydrogen atom pattern,
, is only one unit from another one which is twice relevant. By transferring the all first member of the sequence,
, from the sum to the other factor, we get
First, this hydrogen atom pattern corresponds to 132 hydrogen atoms in the 3 sextets, on the one hand, and 226 hydrogen atoms in the remaining 17 amino acids, on the other (see below). Here, we see, the 3 sextets are set apart and this has, we think, a link with the subject of this section, see below. Second, this pattern describes also the partition of the 20 amino acids into 10 amino acids in the Class-I aminoacyl t-RNA synthetases (226 hydrogen atoms) and 10 amino acids in the Class-II aminoacyl t-RNA synthetases (132 hydrogen atoms), see [
14]. Here, of course, the degeneracy is taken into account.
Now, in the following, we consider the hydrogen atom content for the three symmetry cases mentioned in
Section 2.1, 2.2 and 2.3. As the case of
Section 2.3, the “ideal” symmetry classification scheme, [
6], occupies an important place in this work, inasmuch as it has a tight relation with our “seeds” of Fibonacci-like series, we begin by considering it, first. As mentioned and promised in the introduction, it is here the right place to explain and justify the choice of the “seeds”, or “initial conditions” of our Fibonacci-like sequences defined in
Section 3, more precisely those of the sequences
and
. Concerning the former, the “seeds” are
and
(see
Table 4). These are, respectively the number of hydrogen atoms in serine and arginine (
) and in leucine (9) and their sum, that is the recurrence relation,
is the number of hydrogen atoms in the side chains of these three amino acids. As for the latter, the “seeds” are
and
, respectively the number of atoms in the side chains of arginine and leucine (
) and in the side chain of serine (
). Here also, as for hydrogen,
is the number of atoms in the side chains of these three amino acids. We show, below in this paper, using all the resources offered by our Fibonacci-like series and their properties, that these 3 sextets, more precisely, their hydrogen and atoms numbers, as “seeds”, will create the entire hydrogen atom, atom and even nucleon content of the whole set of amino acids, including the degeneracy, much like the creation of the 64 codons from the three sextets in the “ideal” symmetry scheme mentioned above, [
6]. Let us, here in this section, begin with the hydrogen atom content. First, using the relation (v)
in Equ.(2), we can derive the hydrogen atom content in the two sets: the “leading” group and the “nonleading” group. As a matter of fact, for
(see
Table 4), we have
It could be seen, from
Table 3 and computed from the data in the table in
Appendix A, that there are
and
hydrogen atoms in the”leading” group and in the “nonleading” group, respectively. Moreover, concerning the latter, we have that there are
hydrogen atoms in the amino acids the codons of which have the same first two bases UU, CC, AA and GG (in the four corners of
Table 3) and
hydrogen atoms in the amino acids located in the four boxes in the center of the table which have as first two (different) bases UG, GU, AC and CA. The equation (14) above describes therefore, faithfully, this pattern. Now, we move further to describe accurately the hydrogen atom content involving the amino acids of the “core” comprising serine, arginine and leucine. To see this, we invoke the following two relations
It could be easily verified that they give the same result and both hold for any n. They can also be transformed into each other, using the relation (viii) in Equ.(2),
. Now, for
, they give
and
, respectively, with common value 358, the total number of hydrogen atoms in the 61 amino acids side chains. These are very interesting results for what follows. In the first case, as we have seen above,
is the number of hydrogen atoms in the “leading” group and
is the number of hydrogen atoms in the “nonleading” group. In the second case,
is the number of hydrogen atoms in the part of the “core” belonging to the “leading” group (
,
) and
is the number of hydrogen atoms in the rest, comprising, in particular, the part of the “core” belonging to the “nonleading” group, that is,
. The authors write in their paper “the sextets as initial building blocks for creation of their new scheme of the genetic code generate by themselves the patterns of A+U rich/C+G rich, purine/pyrimidine, weak-strong and amino-keto symmetries.” They also add that, in their approach, “the symmetries are a consequence of sextet’s dynamics”. Here, below, we can use our Fibonacci-like sequences to reveal the exact hydrogen atom content of the “core”, constituted by the 3 sextets. As mentioned above, the “core” has two parts: the one which belongs to the “leading” group and the other belonging to the “nonleading” group. Let us consider the former with 114 hydrogen atoms. Using Euler’s totient function ϕ and also so-called “reduced” totient function or Carmichael’s function λ(n), see
Appendix B, we have for the number 114
and
. Subtracting these from the number 114, we get
and, rearranging, we get
This is the correct content of the part of the “core” in the “leading” group:
hydrogen atoms (
) in arginine (
), 36 hydrogen atoms
in leucine (
) and 18 hydrogen atoms (
) in serine (
). Let us, alternatively, add the above mentioned two functions to the number 114. We get
This is the number of hydrogen atoms in the “nonleading” group where the isolated number 18 is now
re-interpreted as the number of hydrogen atoms
in the “seed” of the “nonleading” group, that is,
(see above). We have thus established the exact hydrogen atom content of the “ideal” symmetry scheme of the genetic code where the sextets play a prominent role. Note, finally, that, as
has been used two times, one time as the number of hydrogen atoms in
and one time as as the number of hydrogen atoms in
, we can summarize all what has been said above by adding
=18 to Equ.(17) and write the exact hydrogen atom structure of the entire “core”
constituted by
and
, respectively. (The
codons of the “core” are undelined in
Table 3.) Of course, subtracting the number
from the total sum
, in Equ.(14) above, we are left with
which is the number of hydrogen atoms in the other part of the 17 amino acids outside the “core”. We have seen above that the “seeds” of the sequences
and
are capable of creating the hydrogen atom structure of the “ideal” symmetry classification scheme. Now, what about the other sequences of
Table 4 in this respect, that is the link to the “ideal” symmetry scheme? In fact, in turns out that they also house something interesting. Here, we consider only the sequence
but more will be said later in
Section 4.3 (Equs.(34-35)), concerning the sequence
, defined below in Equ.(26). We have for the sequence
, using Equ.(6):
. First, from the Fibonacci relation
with
, we have
or
. Second, it could be easily shown that the sequence
, in Equ.(4), is related to the Lucas sequence,
so that, for
, we have
. Finally, we call, exceptionally, the term
which also obeys the recurrence relation
, that is
or, equivalently,
. Putting together all these results, we end up with
. The last four terms could be easily interpreted as 1 triplet, 2 singlets, 5 quartets and 9 doublets, that is the 17 amino acids outside the “core”. As for the first two terms, in the parenthesis, they are just enough to describe the 5 entities
and
forming the part of the “core” belonging to the “leading” group, on the one hand, and 1 for
, the part of the “core” belonging to the “nonleading” group, on the other.
As an interesting by-product of the results in this section, we have found, unexpectedly, a way to derive from the number of hydrogen atoms in the part of the “core” in the “leading” group,
and in the rest,
comprising the part of the “core” in the “nonleading” group (see above), and only from these, the very chemical structure of the building blocks of RNA; the four ribonucleotides
uridine monophosphate (UMP),
cytidine monophosphate (CMP),
adenosine monophosphate (AMP) and
guanosine monophosphate (GMP). As a matter of fact, using the functions
and λ (see
Appendix B), we have
,
and
(see
Appendix B where the details of the computations are given as examples). First, we have from these three quantities
This is the total number of atoms in the four ribonucleotides, 56 in the four nucleotides U (12 atoms), C (13 atoms), A (15 atoms) and G (16 atoms) and 88 in the four identical “blocks” each with 22 atoms (see [
12], for the details of the calculation, which includes also a mathematical derivation of the number 22 above which is part of the “
condensation” equation for the assembly of a ribonucleotide from the three units a nucleotide, a ribose and a phosphate group with the release of two water molecules, also derived). Now, as there are 30 codons in the “leading” group (two stop codons not counted) and 31 codons in the “nonleading” group (one stop codon also not counted), see
Table 3, we can use this decomposition for the number 61 above and finally write the relations above in the form
. Note that the above decomposition of the number 61 could also be obtained another way, by using directly the properties of the sequence
, see
Table 4. We have
,
and
so that by combining them, we get
. The above computed quantities
,
,
and
are respectively the number of atoms in the four ribonucleotides UMP, CMP, AMP and GMP (see [
14]).
Now, we return to the symmetries and examine the second case, Rumer’s symmetry (
Section 2.1). Let us reconsider Equ.(10) and write it in the form
where we have used the recurrence relation of the sequence
, to write the number
as
(see
Table 4). Now, we have already mentioned in the examples following Equ.(5) that, for
, one has
or
. Inserting, this quantity in the above equation results in
This is the hydrogen atom content in Rumer’s division: 186 hydrogen atoms in
and 172 hydrogen atoms in
where, in this latter, we have the correct partition into 84 hydrogen atoms
in the 5 quartets and 88 hydrogen atoms
in the 3 quartets of the 3 sextets. To get the details concerning the number of hydrogen atoms in
, 186, we first isolate the sum of the first four numbers in the sum in Equ.(19), that is
This is equal to the number of hydrogen atoms in the triplet isoleucine (see below). We are left, in the sum, with the three terms
. Writing one time the number
as
from the relation (viii) in Equ.(2) with n=5 and two times as
from the recurrence relation of the sequence
we obtain finally
Here,
and
from the recurrence relation of the sequence
. We have therefore, in the detail, the correct number of hydrogen atoms in
:
in the 9 doublets,
in the doublets of the 3 sextets,
in the triplet,
in the singlet methionine and
in the singlet tryptophane. Below, we consider the third and last case of symmetry. In
Section 2.2, we explained that the authors extracted an inherent basic symmetry linked to the third base by portioning the 64-codons set into four pair-wise sub-sets where each one of them contains only codons having the same third base. In this way, a one-to-one correspondence between one member of a doubly degenerate codon pair to the other member. Here also, for this symmetry, we could describe the hydrogen atom content, using our Fibonacci-like series. Take the relation (v) in Equ.(2), the one we already considered above in Equ.(14)
This relation,
as it is, is the pattern shown in
Table 2 for the gross third-base division UC/AG. Here, we note that this relation already describes, nicely, the equality of the number of hydrogen atoms in the columns 3
rd base U and 3
rd base C where the amino acids are exactly the same (see the penultimate row in
Table 2). In fact, we can do better by invoking two more relations. First, the relation (x) in Equ.(2):
which, for
, gives
. Second, the relation
, which also holds and gives, for
,
. Inserting the number
, from the relation just above, in the second one, results in
. Collecting these results in Equ.(22) above gives, finally
This last relation describes, therefore, completely, the hydrogen atom content pattern of
Table 2. It is interesting that the 3
rd base classification mentioned above can be supported by the following calculation. We know, from
Section 2.2, that the doubly degenerate codons (group-II) obey a fundamental symmetry, so they must play a basic role including, we will show, in the hydrogen atom content too. As a matter of fact, we have, using the sequence
Subtracting this sum from Equ.(22) above, which gives the total number of hydrogen atoms in the 61 amino acids, we get by arranging
This is quite interesting as
and
are respectively the number of hydrogen atoms in the 9 doublets, on the one hand, and in the remaining 11 amino acids (5 quartets, 3 sextets, two singlets and 1 triplet), on the other, see below Equ.(21). In fact, this same relation could also be obtained, another way, from the relation mentioned in
Section 4.1,
and noting that the sum in Equ.(24) above is equal, in fact, to
(recall
, with k=9), we get back to our result:
. Note also that
and
or
which is nothing but the hydrogen atoms pattern of the present classification (see Equ.(22) and
Table 2). (The function
is defined in
Appendix B and the factor 2 which has been introduced is for “doubly” degenerate codons.)
4.3. The atom content and degeneracy
In the course of writing this paper, we have discovered one more Fibonacci-like sequence, tailor-made for the description of the number of atoms in the 61 amino acids (see Equ.(29) below). It is defined as follows
The first few terms are shown below
This sequence is related to the sequences
and
as follows
which holds for any n. The case
is particularly interesting. As a matter of fact, we have
and we see that it gives the total number of atoms in the 61 amino acids distributed into 358 hydrogen atoms (see above) and 236 atoms (C/N/O/S), see the table in
Appendix A (180 carbon atoms and 56 N/O/S atoms). Now, from the relation
which holds for any
and is the analog relation for the sum of the first k Fibonacci numbers. For
it gives
or
and, by inserting this latter in the above equation, we obtain
We have here the number of atoms in 23 amino acids,
(the sextets with 35 atoms are counted two times) and
is the number of atoms in the 38 amino acids corresponding to the 38 degenerate codons (see the table in
Appendix A). Let us, at this stage, remember the sequence
, especially its “seeds”
and
with sum
. Let us also remember that these “seeds” were chosen, intentionally, as the sum of the number of atoms in
and
, on the one hand, and the number of atoms in
, on the other. They are therefore, together, exactly the right thing to add and subtract from Equ.(31) above to obtain
which is the correct partition of the number of atoms:
atoms in the 20 amino acids, on the one hand, and 390 atoms in the 41 amino acids corresponding to the 41 degenerate codons (see the table in
Appendix A). Now, the use of the above sum in Equ(30), for
, gives
which number appears also doubly significant, see below. By subtracting this latter number from the total sum,
, and arranging, we have
This partition of the number of atoms is interesting as
is equal to the number of atoms in the six amino acids (sextets)
and
and
is the number of atoms in the remaining 17 amino acids, of course, taking into account the degeneracy. It is striking that the first two recurrence relations of the sequence
and
, together, lead to the relation
which is in line with the above result for the atom numbers and also with the “ideal” symmetry scheme (as depicted below):
Finally, we could also derive the partition of the number of atoms for Rumer’s sets
and
. Consider, again, the equation above,
, more precisely, the number 384 which was calculated from Equ.(30) with
. By partitioning this sum in two parts, for
and
, we have
, on the one hand, and
, on the other. By gathering both terms in Equ.(33) and arranging, we obtain
This is the content of atoms 264 in
and 330 in
, see the table in
Appendix A. We can also go to the details for the multiplets. Considering, first,
, let us present the following (new) relation connecting the sequences
and
:
which, for
gives
. Using the recurrence relation for
, we have
and, by combining the above two relations, we get
or
. Multiplying this latter equality by any number does not change it, in particular by 4, having in mind that the 8 quartets composing the set
have each 4 codons, and we have
This is exactly the number of atoms in
:
in the 5 quartets and
in the 3 quartet parts of the three sextets (see the table in
Appendix A). The above equality,
, which was used as an intermediate of the calculation above, could also be exploited for the set
. As a matter of fact, consider Equ.(5),
, for
:
. Inserting this difference in the above equality gives
. Now, the following relation linking Fibonacci and Lucas numbers:
is interesting as, for
it gives
. If, moreover, we use the recurrence relation for the Lucas number
as
, we get
. This matches perfectly the number of atoms in the triplet isoleucine (
), in the singlet methionine (11) and in the other singlet tryptophane (18), see the table in
Appendix A. We showed above that there are
atoms in the set
. Subtracting the above number of atoms, 68, in the triplet and in the two singlets, we have
atoms left. To get the right partition of these, it suffices to take the sum of the three first members of the sequence
which appears to be the right number of atoms in the doublet parts of the three singlets. Adding and subtracting this latter from
gives
which is the number of atoms in the nine doublets,
(see the table in
Appendix A). In summary, we have
which is the very precise partition. Finally, let us note that the number
, mentioned above (see below Equ.(32)), has also another relevant interpretation. As a matter of fact, it is equal to the number of atoms in the 20 amino acids, this time including to their side chains their 20 identical “blocks” with 9 atoms each:
4.4. Derivation of several nucleon number patterns
In this section, we use our Fibonacci-like series to derive several interesting patterns for the nucleon number (or integer molecular mass) content in the 61 amino acids. Before starting, let us make an important remark about the sequence
(see
Table 4).. In fact, there is a simple relation between the sequences
and
, the latter is simply five times the former:
. One may wonder how the use of
would bring something significant as it is simply related to
? In fact, it does and we will show that below. First, let us consider the following sum
It appears that this number,
, is the number of nucleons, or integer molecular mass, contained in the 61 amino acids (see the table in
Appendix A). This is nice but we could do more. Consider the “seeds” of the sequence
30 and 5 with sum 35, the number of atoms in the 3 sextets serine (5), arginine (17) and leucine (13). (It is not difficult to show, using the Zekendorf representation[1] of the number 30 (
) in terms of Fibonacci numbers and the fact that
, that the sum of the “seeds” takes the form
, i.e., the correct atom numbers in the three sextets, mentioned above.) Now, by isolating the sum of the above two “seeds” of
from the third sum in Equ.(39) and include it in the two other sums, we get
Here also, we have another interesting result: there are
nucleons in the 20 amino acids (see the table in
Appendix A) and 2149 nucleons in the 41 amino acids corresponding to 41 degenerate codons. Let us now exploit the relation between the two sequences
and
(
, mentioned above, and write the sum in Equ(39) as follows
Now, recall the sum
, mentioned in Equ.(6) of
Section 4.1. In our present case for its use in Equ.(41), we have
for
. By considering this latter relation in
only one such sum in the first bracket of the above equation and transfer the unit,
1, to the second bracket, we obtain
One recognizes here the nucleon number in the pattern “
(see above and
Appendix A):
nucleons in the
amino acids side chains and
nucleons in the 38 amino acids side chains corresponding to the 38 degenerate codons (see above). As another, also interesting finding, we can, from the above relations, make contact with the “ideal” symmetry mentioned above in
Section 4.2, at the level of the nucleon numbers. To do this, let us, first, remark that the number
appears
two times, one time as the number of hydrogen atoms in the “core” of the “ideal” symmetry scheme (see above) and one time as the number of nucleons in
, see the table in
Appendix A). This will prove significant in the following. Consider now the sum
The number
by itself, is not very interesting but its ϕ-function is. As a matter of fact, we have
and, adding to it two times the number
gives
This is the number of nucleons in the “core”:
. Isolating one time the number 114 in the sum, that is
gives us the partition of the nucleon numbers between the two parts of the “core”,
in the “leading” group, on the one hand, and
in the “nonleading” group, on the other:
In the following, we can also derive three more results by “watering three plants with one hose”, so to speak. As a matter of fact, consider again the sum in Equ.(39) and cut it as follows
Here, we have the nucleon number pattern of the 3
rd-base classification of
Section 2.2:
nucleons in the U/C third-base division and
nucleons in the A/G third-base division (see
Table 2, last row). Now, by borrowing from the first bracket above the sum of the first three members of the sequence
, the one we used earlier (see above Equ.(38)), to the benefit of the second bracket, we get[2]
Here, we recognize the number of nucleons in the “leading”group/”nonleading” group,
and
, respectively. Finally, we could also establish the nucleon number pattern corresponding to Rumer’s division. Consider again Equ.(39) by partitioning it as follows
It suffices now, analogously to what we did in Equ. (40) above, to subtract,
one time, the sum of the “seeds” of the sequence
in the bracket, that is,
, and add it to the three terms in the parenthesis to obtain
We have, as promised above,
nucleons in
and 2072 nucleons in
(see the table in
Appendix A).