Submitted:
15 June 2023
Posted:
16 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Epidemiology
2. Genetic predisposition for prostate cancer
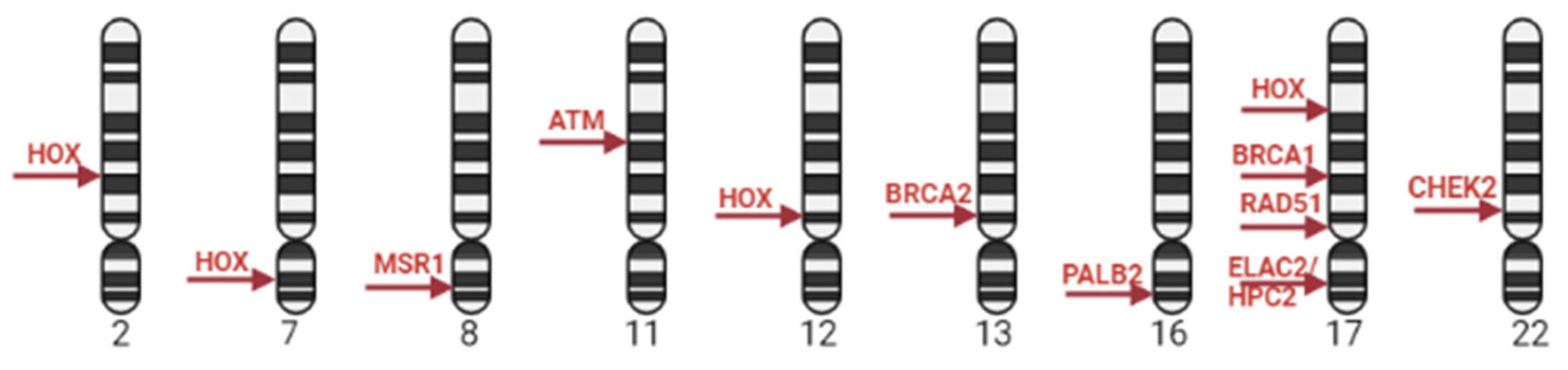
2.1. Genetic markers of PCa
2.2. GWAS in PCa
2.3. GWAS and PCa aggressiveness
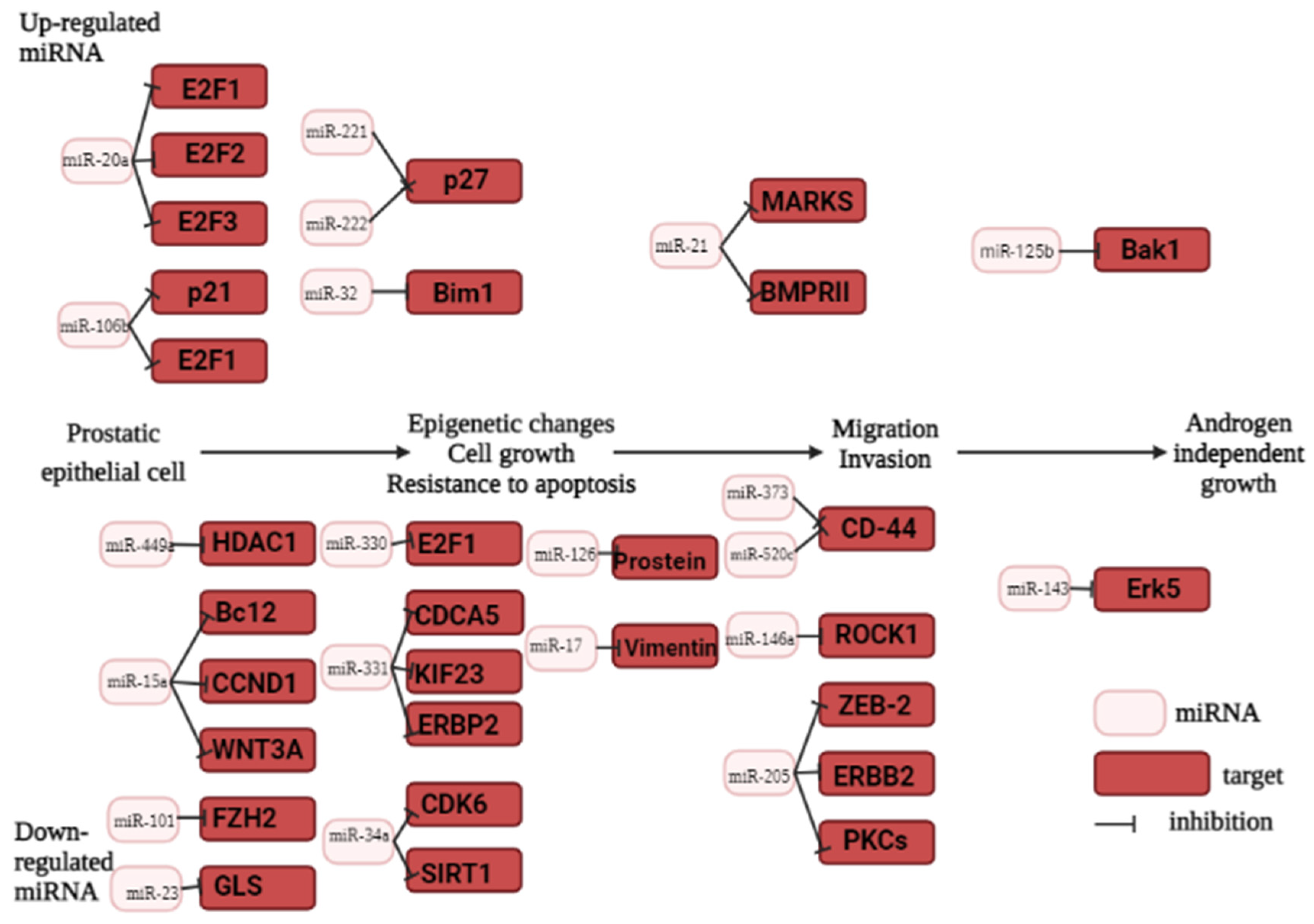
3. MiRNA as prostate cancer biomarker
3.1. MicroRNA biogenesis
3.2. The role of miRNA in prostate carcinogenesis
3.3. Oncogenic miRNAs in prostate cancer
3.4. Tumor suppressor miRNAs in prostate cancer
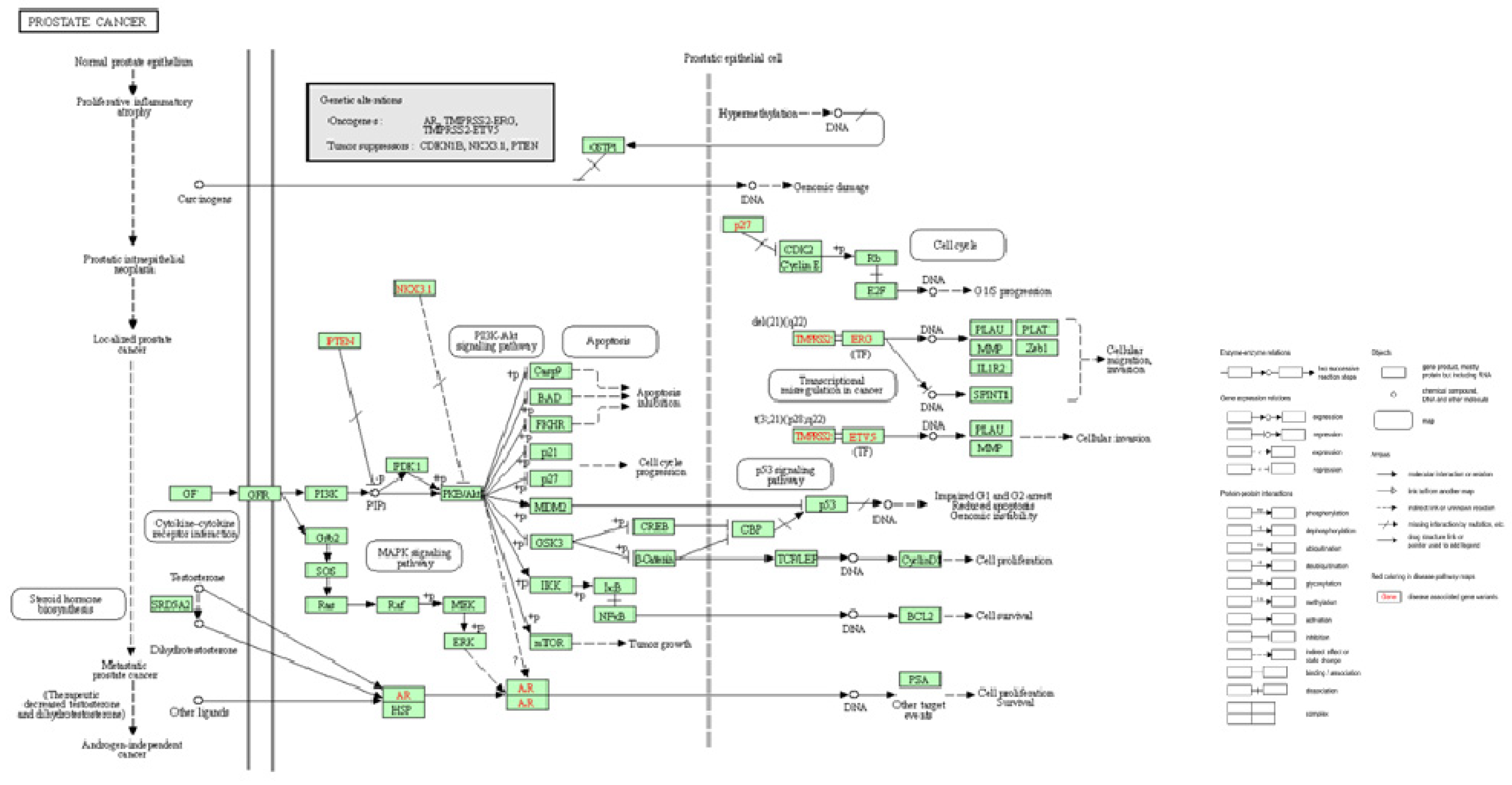
4. Pathogenesis and staging
5. Methods for diagnosing prostate cancer.
5.1. Currently used diagnostic approaches
- digital rectal examination (DRE)
- and/or transrectal ultrasound (TRUS)
- serum PSA (prostate-specific antigen): total PSA and the ratio of free PSA to total PSA.
- biopsy confirmation.
5.2. Necessity of early screening
5.3. Biopsy examination and how TAMs can help
5.4. State-of-the art imaging for staging and metastasis detection
5.5. Raman spectroscopy
6. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- F. Bray, J. Ferlay, I. Soerjomataram, R. L. Siegel, L. A. Torre, и A. Jemal, «Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries», CA. Cancer J. Clin., 68, pp. 394–424, . 2018. [CrossRef]
- T. I. A. for R. on Cancer (IARC), «Global Cancer Observatory». https://gco.iarc.fr/ (accessed 9 march 2023 ).
- T. R. Rebbeck, «Prostate Cancer Genetics: Variation by Race, Ethnicity, and Geography», Semin. Radiat. Oncol., 27, 1, pp. 3–10, 2017. [CrossRef]
- A. J. Vickers, A. Elfiky, V. L. Freeman, и M. Roach, «Race, Biology, Disparities, and Prostate Cancer», Eur. Urol., 81, 5, pp. 463–465, 2022. [CrossRef]
- T. M. Ma et all, «Comparison of Response to Definitive Radiotherapy for Localized Prostate Cancer in Black and White Men: A Meta-analysis», JAMA Netw. Open, 4, 12, с. e2139769, 2021. [CrossRef]
- M. Koscuiszka et all, «Impact of race on survival in patients with clinically nonmetastatic prostate cancer who deferred primary treatment: Race and Survival in PCa Patients», Cancer, 118, 12, pp. 3145–3152, 2012. [CrossRef]
- G. Wang, D. Zhao, D. J. Spring, и R. A. DePinho, «Genetics and biology of prostate cancer», Genes Dev., 32, 17–18, pp. 1105–1140, 2018. [CrossRef]
- J. L. Jahn, E. L. Giovannucci, и M. J. Stampfer, «The high prevalence of undiagnosed prostate cancer at autopsy: implications for epidemiology and treatment of prostate cancer in the Prostate-specific Antigen-era: High prostate cancer prevalence: Research implications in the PSA-ERA», Int. J. Cancer, 137, 12, pp. 2795–2802, 2015. [CrossRef]
- S. Wasim, S.-Y. Lee, и J. Kim, «Complexities of Prostate Cancer», Int. J. Mol. Sci., 23, 22, с. 14257, 2022. [CrossRef]
- B. Turanli et all, «Drug Repositioning for Effective Prostate Cancer Treatment», Front. Physiol., 9, с. 500, 2018. [CrossRef]
- H. Han et all, «Characteristics of BRCA2 Mutated Prostate Cancer at Presentation», Int. J. Mol. Sci., 23, 21, с. 13426, 2022. [CrossRef]
- M. D. Bardis et all, «Applications of Artificial Intelligence to Prostate Multiparametric MRI (mpMRI): Current and Emerging Trends», Cancers, 12, 5, с. 1204, 2020. [CrossRef]
- J. M. Santos-Pereira и A. Aguilera, «R loops: new modulators of genome dynamics and function», Nat. Rev. Genet., 16, 10, pp. 583–597, 2015. [CrossRef]
- A. Abeshouse et all, «The Molecular Taxonomy of Primary Prostate Cancer», Cell, 163, 4, pp. 1011–1025, 2015. [CrossRef]
- C. Kumar-Sinha, S. Kalyana-Sundaram, и A. M. Chinnaiyan, «Landscape of gene fusions in epithelial cancers: seq and ye shall find», Genome Med., 7, 1, с. 129, 2015. [CrossRef]
- L. F. van Dessel et all, «The genomic landscape of metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancers reveals multiple distinct genotypes with potential clinical impact», Nat. Commun., 10, 1, с. 5251, 2019. [CrossRef]
- D. Tong, «Unravelling the molecular mechanisms of prostate cancer evolution from genotype to phenotype», Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol., 163, с. 103370, 2021. [CrossRef]
- M. Adamaki и V. Zoumpourlis, «Prostate Cancer Biomarkers: From diagnosis to prognosis and precision-guided therapeutics», Pharmacol. Ther., 228, с. 107932, 2021. [CrossRef]
- D.-P. Kong et all, «Prevalence and clinical application of TMPRSS2-ERG fusion in Asian prostate cancer patients: a large-sample study in Chinese people and a systematic review», Asian J. Androl., 22, 2, с. 200, 2020. [CrossRef]
- J. St. John, K. Powell, и M. K. C. -LaComb, «TMPRSS2-ERG Fusion Gene Expression in Prostate Tumor Cells and Its Clinical and Biological Significance in Prostate Cancer Progression», J. Cancer Sci. Ther., 04, 04, 2012. [CrossRef]
- U. Testa, G. Castelli, и E. Pelosi, «Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Prostate Cancer Development: Therapeutic Implications», Medicines, 6, 3, с. 82, 2019. [CrossRef]
- S. Stelloo et all, «Integrative epigenetic taxonomy of primary prostate cancer», Nat. Commun., 9, 1, с. 4900, 2018. [CrossRef]
- I. Dudka et all, «Comprehensive metabolomics analysis of prostate cancer tissue in relation to tumor aggressiveness and TMPRSS2-ERG fusion status», BMC Cancer, 20, 1, с. 437, 2020. [CrossRef]
- H. Koide et all, «Comparison of ERG and SPINK1 expression among incidental and metastatic prostate cancer in Japanese men», The Prostate, 79, 1, pp. 3–8, 2019. [CrossRef]
- R. D. Webster, J. L. Ross, и B. K. Arun, «The changing landscape of hereditary cancer genetic testing: Hereditary Cancer Genetic Testing», Cancer, 124, 4, pp. 664–666, 2018. [CrossRef]
- E. Dathathri et all, «Liquid Biopsy Based Circulating Biomarkers in Metastatic Prostate Cancer», Front. Oncol., 12, с. 863472, 2022. [CrossRef]
- P. Tian, M. Zhong, и G.-H. Wei, «Mechanistic insights into genetic susceptibility to prostate cancer», Cancer Lett., 522, pp. 155–163, 2021. [CrossRef]
- The COGS–Cancer Research UK GWAS–ELLIPSE (part of GAME-ON) Initiative et all, «Identification of 23 new prostate cancer susceptibility loci using the iCOGS custom genotyping array», Nat. Genet., 45, 4, pp. 385–391, 2013. [CrossRef]
- S. Benafif, Z. Kote-Jarai, и R. A. Eeles, «A Review of Prostate Cancer Genome-Wide Association Studies (GWAS)», Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev., 27, 8, pp. 845–857, 2018. [CrossRef]
- The Profile Study et all, «Association analyses of more than 140,000 men identify 63 new prostate cancer susceptibility loci», Nat. Genet., 50, 7, pp. 928–936, 2018. [CrossRef]
- The UKGPCS Collaborators et all, «Frequent germline deleterious mutations in DNA repair genes in familial prostate cancer cases are associated with advanced disease», Br. J. Cancer, 110, 6, pp. 1663–1672, 2014. [CrossRef]
- M. Wang et all, «Large-scale association analysis in Asians identifies new susceptibility loci for prostate cancer», Nat. Commun., 6, 1, с. 8469, 2015. [CrossRef]
- D. V. Conti et all, «Trans-ancestry genome-wide association meta-analysis of prostate cancer identifies new susceptibility loci and informs genetic risk prediction», Nat. Genet., 53, 1, pp. 65–75, 2021. [CrossRef]
- C. Sipeky, T. L. J. Tammela, A. Auvinen, и J. Schleutker, «Novel prostate cancer susceptibility gene SP6 predisposes patients to aggressive disease», Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis., 24, 4, pp. 1158–1166, 2021. [CrossRef]
- C. Amarasekera, V. Wong, E. Yura, A. Manjunath, E. Schaeffer, и S. Kundu, «Prostate cancer in sexual minorities and the influence of HIV status», Nat. Rev. Urol., 16, 7, pp. 404–421, 2019. [CrossRef]
- D. Duggan et all, «Two Genome-wide Association Studies of Aggressive Prostate Cancer Implicate Putative Prostate Tumor Suppressor Gene DAB2IP», JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst., 99, 24, pp. 1836–1844, 2007. [CrossRef]
- J. Sun et all, «Sequence Variants at 22q13 Are Associated with Prostate Cancer Risk», Cancer Res., 69, 1, pp. 10–15, 2009. [CrossRef]
- J. Xu et all, «Inherited genetic variant predisposes to aggressive but not indolent prostate cancer», Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., 107, 5, pp. 2136–2140, 2010. [CrossRef]
- L. M. FitzGerald et all, «Genome-wide Association Study Identifies a Genetic Variant Associated with Risk for More Aggressive Prostate Cancer», Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev., 20, 6, pp. 1196–1203, 2011. [CrossRef]
- R. K. Nam et all, «New variants at 10q26 and 15q21 are associated with aggressive prostate cancer in a genome-wide association study from a prostate biopsy screening cohort», Cancer Biol. Ther., 12, 11, pp. 997–1004, 2011. [CrossRef]
- F. R. Schumacher et all, «Genome-wide association study identifies new prostate cancer susceptibility loci», Hum. Mol. Genet., 20, 19, pp. 3867–3875, 2011. [CrossRef]
- A. Amin Al Olama et all, «A meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies to identify prostate cancer susceptibility loci associated with aggressive and non-aggressive disease», Hum. Mol. Genet., 22, 2, pp. 408–415, 2013. [CrossRef]
- S. I. Berndt et all, «Two susceptibility loci identified for prostate cancer aggressiveness», Nat. Commun., 6, 1, с. 6889, 2015. [CrossRef]
- C. C. Teerlink et all, «Genome-wide association of familial prostate cancer cases identifies evidence for a rare segregating haplotype at 8q24.21», Hum. Genet., 135, 8, pp. 923–938, 2016. [CrossRef]
- I. M. Shui et all, «Prostate cancer (PCa) risk variants and risk of fatal PCa in the National Cancer Institute Breast and Prostate Cancer Cohort Consortium», Eur. Urol., 65, 6, pp. 1069–1075, 2014. [CrossRef]
- J.-H. Xia и G.-H. Wei, «Oncogenic regulatory circuits driven by 19q13 rs11672691 underlies prostate cancer aggressiveness», Mol. Cell. Oncol., 5, 6, с. e1516451, 2018. [CrossRef]
- P. Gao et all, «Biology and Clinical Implications of the 19q13 Aggressive Prostate Cancer Susceptibility Locus», Cell, 174, 3, pp. 576-589.e18, 2018. [CrossRef]
- B. T. Helfand et all, «Associations of prostate cancer risk variants with disease aggressiveness: results of the NCI-SPORE Genetics Working Group analysis of 18,343 cases», Hum. Genet., 134, 4, pp. 439–450, 2015. [CrossRef]
- D. Vanacore et all, «Micrornas in prostate cancer: an overview», Oncotarget, 8, 30, pp. 50240–50251, 2017. [CrossRef]
- G. Cochetti, G. Poli, G. Guelfi, A. Boni, M. G. Egidi, и E. Mearini, «Different levels of serum microRNAs in prostate cancer and benign prostatic hyperplasia: evaluation of potential diagnostic and prognostic role», OncoTargets Ther., Volume 9, pp. 7545–7553, 2016. [CrossRef]
- H. S. Zhou, T. Zhao, X. M. Rao, и A. L. Beaudet, «Production of helper-dependent adenovirus vector relies on helper virus structure and complementing», J. Gene Med., 4, 5, pp. 498–509, 2002. [CrossRef]
- K. Kasomva et all, «Roles of microRNA in prostate cancer cell metabolism», Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol., 102, pp. 109–116, 2018. [CrossRef]
- N. Sharma и M. M. Baruah, «The microRNA signatures: aberrantly expressed miRNAs in prostate cancer», Clin. Transl. Oncol., 21, 2, pp. 126–144, 2019. [CrossRef]
- M. Hill и N. Tran, «miRNA interplay: mechanisms and consequences in cancer», Dis. Model. Mech., 14, 4, с. dmm047662, 2021. [CrossRef]
- S. Khan, H. Ayub, T. Khan, и F. Wahid, «MicroRNA biogenesis, gene silencing mechanisms and role in breast, ovarian and prostate cancer», Biochimie, 167, pp. 12–24, 2019. [CrossRef]
- C. Massillo, G. N. Dalton, P. L. Farré, P. De Luca, и A. De Siervi, «Implications of microRNA dysregulation in the development of prostate cancer», Reproduction, 154, 4, pp. R81–R97, 2017. [CrossRef]
- D. Trümbach и N. Prakash, «The conserved miR-8/miR-200 microRNA family and their role in invertebrate and vertebrate neurogenesis», Cell Tissue Res., 359, 1, pp. 161–177, 2015. [CrossRef]
- M. Majidinia et all, «MicroRNAs, DNA damage response and ageing», Biogerontology, 21, 3, pp. 275–291, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Rawat et all, «MicroRNA in Pancreatic Cancer: From Biology to Therapeutic Potential», Genes, 10, 10, с. 752, 2019. [CrossRef]
- T. Takahashi et all, «LGP2 virus sensor regulates gene expression network mediated by TRBP-bound microRNAs», Nucleic Acids Res., 46, 17, pp. 9134–9147, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Y.-K. Kim, B. Kim, и V. N. Kim, «Re-evaluation of the roles of DROSHA , Exportin 5 , and DICER in microRNA biogenesis», Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., 113, 13, 2016. [CrossRef]
- C. Stavast и S. Erkeland, «The Non-Canonical Aspects of MicroRNAs: Many Roads to Gene Regulation», Cells, 8, 11, с. 1465, 2019. [CrossRef]
- A. Khan, E. Ahmed, N. Elareer, K. Junejo, M. Steinhoff, и S. Uddin, «Role of miRNA-Regulated Cancer Stem Cells in the Pathogenesis of Human Malignancies», Cells, 8, 8, с. 840, 2019. [CrossRef]
- K. P. Porkka, M. J. Pfeiffer, K. K. Waltering, R. L. Vessella, T. L. J. Tammela, и T. Visakorpi, «MicroRNA Expression Profiling in Prostate Cancer», Cancer Res., 67, 13, pp. 6130–6135, 2007. [CrossRef]
- «KEGG PATHWAY: MicroRNAs in cancer - Reference pathway». https://www.kegg.jp/pathway/map=map05206&keyword=prostate%20cancer (accessed 13 march 2023 ).
- W. Wittling и M. Pflüger, «Neuroendocrine hemisphere asymmetries: Salivary cortisol secretion during lateralized viewing of emotion-related and neutral films», Brain Cogn., 14, 2, pp. 243–265, 1990. [CrossRef]
- A. R. Rhodes et all, «The malignant potential of small congenital nevocellular nevi», J. Am. Acad. Dermatol., 6, 2, pp. 230–241, 1982. [CrossRef]
- K. R. M. Leite et all, «Controlling RECK miR21 Promotes Tumor Cell Invasion and Is Related to Biochemical Recurrence in Prostate Cancer», J. Cancer, 6, 3, pp. 292–301, 2015. [CrossRef]
- T. Li, D. Li, J. Sha, P. Sun, и Y. Huang, «MicroRNA-21 directly targets MARCKS and promotes apoptosis resistance and invasion in prostate cancer cells», Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 383, 3, pp. 280–285, 2009. [CrossRef]
- K. Schramedei et all, «MicroRNA-21 targets tumor suppressor genes ANP32A and SMARCA4», Oncogene, 30, 26, pp. 2975–2985, 2011. [CrossRef]
- M. Rizzo, «Mechanisms of docetaxel resistance in prostate cancer: The key role played by miRNAs», Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA - Rev. Cancer, 1875, 1, с. 188481, 2021. [CrossRef]
- K. Seputra, B. Purnomo, H. Susianti, H. Kalim, и A. Purnomo, «miRNA-21 as Reliable Serum Diagnostic Biomarker Candidate for Metastatic Progressive Prostate Cancer: Meta-analysis Approach», Med. Arch., 75, 5, с. 347, 2021. [CrossRef]
- K. Seputra, B. Purnomo, H. Susianti, H. Kalim, и A. Purnomo, «miRNA-21 Serum Evaluation in BPH, Hormone Sensitive Prostate Cancer, and Castrate Resistant Prostate Cancer: Attempt for Diagnostic Biomarker Evaluation», Acta Inform. Medica, 29, 4, с. 266, 2021. [CrossRef]
- N. H. Ibrahim, M. S. Abdellateif, S. H. Kassem, M. A. Abd El Salam, и M. M. El Gammal, «Diagnostic significance of miR-21, miR-141, miR-18a and miR-221 as novel biomarkers in prostate cancer among Egyptian patients», Andrologia, 51, 10, 2019. [CrossRef]
- D. Mehlich, F. Garbicz, и P. K. Włodarski, «The emerging roles of the polycistronic miR-106b∼25 cluster in cancer – A comprehensive review», Biomed. Pharmacother., 107, pp. 1183–1195, 2018. [CrossRef]
- R. S. Hudson et all, «MicroRNA-106b-25 cluster expression is associated with early disease recurrence and targets caspase-7 and focal adhesion in human prostate cancer», Oncogene, 32, 35, pp. 4139–4147, 2013. [CrossRef]
- S. Rezaei, M. Mahjoubin Tehran, A. Sahebkar, A. Jalili, и S. H. Aghaee-Bakhtiari, «Androgen receptor-related micro RNAs in prostate cancer and their role in antiandrogen drug resistance», J. Cell. Physiol., 235, 4, pp. 3222–3234, 2020. [CrossRef]
- J. Fredsøe et all, «Diagnostic and Prognostic MicroRNA Biomarkers for Prostate Cancer in Cell-free Urine», Eur. Urol. Focus, 4, 6, pp. 825–833, 2018. [CrossRef]
- A. A. Svoronos, S. G. Campbell, и D. M. Engelman, «MicroRNA function can be reversed by altering target gene expression levels», iScience, 24, 10, с. 103208, 2021. [CrossRef]
- H. Nip et all, «Oncogenic microRNA-4534 regulates PTEN pathway in prostate cancer», Oncotarget, 7, 42, pp. 68371–68384, 2016. [CrossRef]
- H. E. Zidan, R. S. Abdul-Maksoud, W. S. H. Elsayed, и E. A. M. Desoky, «Diagnostic and prognostic value of serum miR-15a and miR-16-1 expression among egyptian patients with prostate cancer: SERUM MIR-15A AND MIR-16-1 IN PROSTATE CANCER», IUBMB Life, 70, 5, pp. 437–444, 2018. [CrossRef]
- G. Deng et all, «Targeting androgen receptor (AR) with antiandrogen Enzalutamide increases prostate cancer cell invasion yet decreases bladder cancer cell invasion via differentially altering the AR/circRNA-ARC1/miR-125b-2-3p or miR-4736/PPARγ/MMP-9 signals», Cell Death Differ., 28, 7, pp. 2145–2159, 2021. [CrossRef]
- H. Liang, L. Studach, R. L. Hullinger, J. Xie, и O. M. Andrisani, «Down-regulation of RE-1 silencing transcription factor (REST) in advanced prostate cancer by hypoxia-induced miR-106b~25», Exp. Cell Res., 320, 2, pp. 188–199, 2014. [CrossRef]
- S. J. Oh-Hohenhorst и T. Lange, «Role of Metastasis-Related microRNAs in Prostate Cancer Progression and Treatment», Cancers, 13, 17, с. 4492, 2021. [CrossRef]
- X. Yang et all, «Down-Regulation of mir-221 and mir-222 Restrain Prostate Cancer Cell Proliferation and Migration That Is Partly Mediated by Activation of SIRT1», PLoS ONE, 9, 6, с. e98833, 2014. [CrossRef]
- Z.-H. Zuo et all, «Oncogenic Activity of miR-650 in Prostate Cancer Is Mediated by Suppression of CSR1 Expression», Am. J. Pathol., 185, 7, pp. 1991–1999, 2015. [CrossRef]
- R. J. Bryant et all, «Changes in circulating microRNA levels associated with prostate cancer», Br. J. Cancer, 106, 4, pp. 768–774, 2012. [CrossRef]
- J. C. Brase et all, «Circulating miRNAs are correlated with tumor progression in prostate cancer», Int. J. Cancer, 128, 3, pp. 608–616, 2011. [CrossRef]
- L. A. Selth et all, «Discovery of circulating microRNAs associated with human prostate cancer using a mouse model of disease», Int. J. Cancer, 131, 3, pp. 652–661, 2012. [CrossRef]
- P. Porzycki, E. Ciszkowicz, M. Semik, и M. Tyrka, «Combination of three miRNA (miR-141, miR-21, and miR-375) as potential diagnostic tool for prostate cancer recognition», Int. Urol. Nephrol., 50, 9, pp. 1619–1626, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Z. Li et all, «Exosomal microRNA-141 is upregulated in the serum of prostate cancer patients», OncoTargets Ther., 9, pp. 139–148, 2016. [CrossRef]
- M. Rodríguez et all, «Identification of non-invasive miRNAs biomarkers for prostate cancer by deep sequencing analysis of urinary exosomes», Mol. Cancer, 16, 1, с. 156, 2017. [CrossRef]
- Z. Li, L.-X. Li, Y.-J. Diao, J. Wang, Y. Ye, и X.-K. Hao, «Identification of Urinary Exosomal miRNAs for the Non-Invasive Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer», Cancer Manag. Res., 13, pp. 25–35, 2021. [CrossRef]
- T. Guo et all, «The Identification of Plasma Exosomal miR-423-3p as a Potential Predictive Biomarker for Prostate Cancer Castration-Resistance Development by Plasma Exosomal miRNA Sequencing», Front. Cell Dev. Biol., 8, с. 602493, 2020. [CrossRef]
- C. Alix-Panabières, «Circulating Tumor Cells: Finding Rare Events for a Huge Knowledge of Cancer Dissemination», Cells, 9, 3, с. 661, 2020. [CrossRef]
- J. Chisholm, S. Haas-Neill, P. Margetts, и K. Al-Nedawi, «Characterization of proteins, mRNAs, and miRNAs of circulating extracellular vesicles from prostate cancer patients compared to healthy subjects», Front. Oncol., 12, с. 895555, 2022. [CrossRef]
- M. Worthington et all, «A Study to Investigate the Role of Noncoding RNA miR146 Alpha as a Potential Biomarker in Prostate Cancer», J. Anal. Oncol., 11, pp. 21–23, 2022. [CrossRef]
- J. Juracek et all, «A tissue miRNA expression pattern is associated with disease aggressiveness of localized prostate cancer», The Prostate, 83, 4, pp. 340–351, 2023. [CrossRef]
- L. K. Dennis, C. F. Lynch, и J. C. Torner, «Epidemiologic association between prostatitis and prostate cancer», Urology, 60, 1, pp. 78–83, 2002. [CrossRef]
- G. S. Palapattu et all, «Prostate carcinogenesis and inflammation: emerging insights», Carcinogenesis, 26, 7, pp. 1170–1181, 2005. [CrossRef]
- R. O. Roberts, E. J. Bergstralh, S. E. Bass, M. M. Lieber, и S. J. Jacobsen, «Prostatitis as a Risk Factor for Prostate Cancer»:, Epidemiology, 15, 1, pp. 93–99, 2004. [CrossRef]
- G. Jung, J. K. Kim, H. Kim, J. Lee, и S. K. Hong, «The association between prostatitis and risk of prostate cancer: a National Health Insurance Database study», World J. Urol., 40, 11, pp. 2781–2787, 2022. [CrossRef]
- M. Murata, «Inflammation and cancer», Environ. Health Prev. Med., 23, с. 50, 2018. [CrossRef]
- «Chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome and prostate cancer: study of immune cells and cytokines - Liu - 2020 - Fundamental & Clinical Pharmacology - Wiley Online Library». https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/fcp.12517 (accessed 19 march 2023 ).
- H. M. Wise, M. A. Hermida, и N. R. Leslie, «Prostate cancer, PI3K, PTEN and prognosis», Clin. Sci., 131, 3, pp. 197–210, 2017. [CrossRef]
- W. G. Nelson, A. M. De Marzo, и W. B. Isaacs, «Prostate Cancer», N. Engl. J. Med., 349, 4, pp. 366–381, 2003. [CrossRef]
- V. T. DeVita, T. S. Lawrence, и S. A. Rosenberg, Ред., DeVita, Hellman, and Rosenberg’s cancer: principles & practice of oncology, 11th edition. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer, 2019.
- J. L. Mohler et all, «Prostate Cancer, Version 2.2019, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology», J. Natl. Compr. Canc. Netw., 17, 5, pp. 479–505, 2019. [CrossRef]
- C. Parker et all, «Prostate cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up», Ann. Oncol., 31, 9, pp. 1119–1134, 2020. [CrossRef]
- C. De Nunzio et all, «The Controversial Relationship Between Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia and Prostate Cancer: The Role of Inflammation», Eur. Urol., 60, 1, pp. 106–117, 2011. [CrossRef]
- M. Patysheva et all, «Effect of Early-Stage Human Breast Carcinoma on Monocyte Programming», Front. Oncol., 11, с. 800235, 2022. [CrossRef]
- I. Larionova et all, «PFKFB3 overexpression in monocytes of patients with colon but not rectal cancer programs pro-tumor macrophages and is indicative for higher risk of tumor relapse», Front. Immunol., 13, с. 1080501, 2023. [CrossRef]
- M. Patysheva et all, «Monocyte programming by cancer therapy», Front. Immunol., 13, с. 994319, 2022. [CrossRef]
- J. Kzhyshkowska, C. Neyen, и S. Gordon, «Role of macrophage scavenger receptors in atherosclerosis», Immunobiology, 217, 5, pp. 492–502, 2012. [CrossRef]
- S. Mosig et all, «Different functions of monocyte subsets in familial hypercholesterolemia: potential function of CD14 + CD16 + monocytes in detoxification of oxidized LDL», FASEB J., 23, 3, pp. 866–874, 2009. [CrossRef]
- L. Willemsen и M. P. Winther, «Macrophage subsets in atherosclerosis as defined by single-cell technologies», J. Pathol., 250, 5, pp. 705–714, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Д. А. Нoсoв et all, «Практические рекoмендации пo лечению рака предстательнoй железы», Malig. Tumours, 12, 3s2-1, pp. 607–626, 2022. [CrossRef]
- H. G. Welch и P. C. Albertsen, «Reconsidering Prostate Cancer Mortality — The Future of PSA Screening», N. Engl. J. Med., 382, 16, pp. 1557–1563, 2020. [CrossRef]
- P. Rawla, «Epidemiology of Prostate Cancer», World J. Oncol., 10, 2, pp. 63–89, 2019. [CrossRef]
- D. W. Donnelly et all, «Quality of life among symptomatic compared to PSA-detected prostate cancer survivors - results from a UK wide patient-reported outcomes study», BMC Cancer, 19, 1, с. 947, 2019. [CrossRef]
- P. C. Sotomayor et all, «Active Surveillance in Prostate Cancer: Current and Potentially Emerging Biomarkers for Patient Selection Criteria», Urol. Int., 106, 12, pp. 1201–1213, 2022. [CrossRef]
- J. Andersson et all, «Digital Rectal Examination in Stockholm3 Biomarker-based Prostate Cancer Screening», Eur. Urol. Open Sci., 44, pp. 69–75, 2022. [CrossRef]
- M. Bilal, A. Javaid, F. Amjad, T. A. Youssif, и S. Afzal, «An overview of prostate cancer (PCa) diagnosis: Potential role of miRNAs», Transl. Oncol., 26, с. 101542, 2022. [CrossRef]
- D. Ilic et all, «Prostate cancer screening with prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test: a systematic review and meta-analysis», BMJ, с. k3519, 2018. [CrossRef]
- S. V. Carlsson и A. J. Vickers, «Screening for Prostate Cancer», Med. Clin. North Am., 104, 6, pp. 1051–1062, 2020. [CrossRef]
- F. H. Schröder et all, «Screening and Prostate-Cancer Mortality in a Randomized European Study», N. Engl. J. Med., 360, 13, pp. 1320–1328, 2009. [CrossRef]
- F. H. Schröder et all, «Prostate-Cancer Mortality at 11 Years of Follow-up», N. Engl. J. Med., 366, 11, pp. 981–990, 2012. [CrossRef]
- G. L. Andriole et all, «Mortality Results from a Randomized Prostate-Cancer Screening Trial», N. Engl. J. Med., 360, 13, pp. 1310–1319, 2009. [CrossRef]
- «A 16-yr Follow-up of the European Randomized study of Screening for Prostate Cancer». [CrossRef]
- M. Noureldin et all, «Review article: MRI-targeted biopsies for prostate cancer diagnosis and management», World J. Urol., 39, 1, pp. 57–63, 2021. [CrossRef]
- T. B. J. Murray, «The Pathogenesis of Prostate Cancer», в Prostate Cancer, Urology Department, Frimley Park Hospital, Portsmouth Rd, Frimley, Camberley GU16 7UJ, UK, S. R. Bott, и K. Lim Ng, Ред., Exon Publications, 2021, pp. 29–42. [CrossRef]
- G. J. L. H. Van Leenders et all, «The 2019 International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) Consensus Conference on Grading of Prostatic Carcinoma», Am. J. Surg. Pathol., 44, 8, pp. e87–e99, 2020. [CrossRef]
- G. Sauter et all, «Clinical Utility of Quantitative Gleason Grading in Prostate Biopsies and Prostatectomy Specimens», Eur. Urol., 69, 4, pp. 592–598, 2016. [CrossRef]
- J. I. Epstein et all, «The 2019 Genitourinary Pathology Society (GUPS) White Paper on Contemporary Grading of Prostate Cancer», Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med., 145, 4, pp. 461–493, 2021. [CrossRef]
- A. V. Alford, J. M. Brito, K. K. Yadav, S. S. Yadav, A. K. Tewari, и J. Renzulli, «The Use of Biomarkers in Prostate Cancer Screening and Treatment», Rev. Urol., 19, 4, pp. 221–234, 2017. [CrossRef]
- Y. Naya и K. Okihara, «Role of Complexed PSA in the Early Detection of Prostate Cancer», J. Natl. Compr. Canc. Netw., 2, 3, pp. 209–212, 2004. [CrossRef]
- A. christensson et all, «Serum Prostate Specific Antigen Complexed to α 1-Antichymotrypsin as an Indicator of Prostate Cancer», J. Urol., 150, 1, pp. 100–105, 1993. [CrossRef]
- M. F. Darson et all, «Human glandular kallikrein 2 (hK2) expression in prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and adenocarcinoma: A novel prostate cancer marker», Urology, 49, 6, pp. 857–862, 1997. [CrossRef]
- Y.-H. Fan et all, «Prostate Health Index outperforms other PSA derivatives in predicting a positive biopsy in men with tPSA <10 ng/mL: Largest prospective cohort in Taiwan», J. Chin. Med. Assoc., 82, 10, pp. 772–777, 2019. [CrossRef]
- P. Nurmikko, K. Pettersson, T. Piironen, J. Hugosson, и H. Lilja, «Discrimination of Prostate Cancer from Benign Disease by Plasma Measurement of Intact, Free Prostate-specific Antigen Lacking an Internal Cleavage Site at Lys145-Lys146», Clin. Chem., 47, 8, pp. 1415–1423, 2001. [CrossRef]
- «Modern biomarkers in prostate cancer diagnosis», Cent. Eur. J. Urol., 73, 2020. [CrossRef]
- N. A. Deebel, J. P. Morin, R. Autorino, R. Vince, B. Grob, и L. J. Hampton, «Prostate Cancer in Transgender Women: Incidence, Etiopathogenesis, and Management Challenges», Urology, 110, pp. 166–171, 2017. [CrossRef]
- M. D. Ingham, R. J. Lee, D. MacDermed, и A. F. Olumi, «Prostate cancer in transgender women», Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig., 36, 12, pp. 518–525, 2018. [CrossRef]
- I. Larionova et all, «Tumor-Associated Macrophages in Human Breast, Colorectal, Lung, Ovarian and Prostate Cancers», Front. Oncol., 10, с. 566511, 2020. [CrossRef]
- I. Mitrofanova et all, «Tumor-associated macrophages in human breast cancer parenchyma negatively correlate with lymphatic metastasis after neoadjuvant chemotherapy», Immunobiology, 222, 1, pp. 101–109, 2017. [CrossRef]
- T. Cavalleri et all, «Tumor-associated macrophages and risk of recurrence in stage III colorectal cancer», J. Pathol. Clin. Res., 8, 4, pp. 307–312, 2022. [CrossRef]
- E. Kazakova, P. Iamshchikov, I. Larionova, и J. Kzhyshkowska, «Macrophage scavenger receptors: Tumor support and tumor inhibition», Front. Oncol., 12, с. 1096897, 2023. [CrossRef]
- J. Kzhyshkowska, S. Yin, T. Liu, V. Riabov, и I. Mitrofanova, «Role of chitinase-like proteins in cancer», Biol. Chem., 397, 3, pp. 231–247, 2016. [CrossRef]
- I. Larionova, E. Kazakova, T. Gerashchenko, и J. Kzhyshkowska, «New Angiogenic Regulators Produced by TAMs: Perspective for Targeting Tumor Angiogenesis», Cancers, 13, 13, с. 3253, 2021. [CrossRef]
- K. V. Danilko et all, «Morphological heterogeneity of intratumoral macrophages in prostate tumors», Sib. J. Oncol., 21, 6, pp. 81–90, 2022. [CrossRef]
- J.-L. Descotes, «Diagnosis of prostate cancer», Asian J. Urol., 6, 2, pp. 129–136, 2019. [CrossRef]
- L. Naji et all, «Digital Rectal Examination for Prostate Cancer Screening in Primary Care: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis», Ann. Fam. Med., 16, 2, pp. 149–154, 2018. [CrossRef]
- A. M. D. Wolf et all, «American Cancer Society Guideline for the Early Detection of Prostate Cancer: Update 2010», CA. Cancer J. Clin., 60, 2, pp. 70–98, 2010. [CrossRef]
- K. A. O. Tikkinen et all, «Prostate cancer screening with prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test: a clinical practice guideline», BMJ, с. k3581, 2018. [CrossRef]
- M. Shiva, C. Wei, H. Molana, и G. Nabi, «Cost-Effectiveness of Prostate Cancer Detection in Biopsy-Naïve Men: Ultrasound Shear Wave Elastography vs. Multiparametric Diagnostic Magnetic Resonance Imaging», Healthcare, 10, 2, с. 254, 2022. [CrossRef]
- O. Derin, L. Fonseca, R. Sanchez-Salas, и M. J. Roberts, «Infectious complications of prostate biopsy: winning battles but not war», World J. Urol., 38, 11, pp. 2743–2753, 2020. [CrossRef]
- F.-J. H. Drost et all, «Prostate MRI, with or without MRI-targeted biopsy, and systematic biopsy for detecting prostate cancer», Cochrane Database Syst. Rev., 2019, 4, 2019. [CrossRef]
- J. S. Quon, B. Moosavi, M. Khanna, T. A. Flood, C. S. Lim, и N. Schieda, «False positive and false negative diagnoses of prostate cancer at multi-parametric prostate MRI in active surveillance», Insights Imaging, 6, 4, pp. 449–463, 2015. [CrossRef]
- H. U. Ahmed et all, «Diagnostic accuracy of multi-parametric MRI and TRUS biopsy in prostate cancer (PROMIS): a paired validating confirmatory study», The Lancet, 389, 10071, pp. 815–822, 2017. [CrossRef]
- A. O’Shea и M. Harisinghani, «PI-RADS: multiparametric MRI in prostate cancer», Magn. Reson. Mater. Phys. Biol. Med., 35, 4, pp. 523–532, 2022. [CrossRef]
- V. V. Rafalsky, A. Yu. Zyubin, E. M. Moiseeva, и I. G. Samusev, «Prospects for Raman spectroscopy in cardiology», Cardiovasc. Ther. Prev., 19, 1, pp. 70–77, 2020. [CrossRef]
- K. Aubertin et all, «Mesoscopic characterization of prostate cancer using Raman spectroscopy: potential for diagnostics and therapeutics», BJU Int., 122, 2, pp. 326–336, 2018. [CrossRef]
- M. Pinto et all, «Integration of a Raman spectroscopy system to a robotic-assisted surgical system for real-time tissue characterization during radical prostatectomy procedures», J. Biomed. Opt., 24, 02, с. 1, 2019. [CrossRef]
- D. K. R. Medipally et all, «Vibrational spectroscopy of liquid biopsies for prostate cancer diagnosis», Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol., 12, с. 175883592091849, 2020. [CrossRef]
- R. Patel et all, «Sprouty2 loss-induced IL 6 drives castration-resistant prostate cancer through scavenger receptor B1», EMBO Mol. Med., 10, 4, 2018. [CrossRef]
- S. Yue et all, «Cholesteryl Ester Accumulation Induced by PTEN Loss and PI3K/AKT Activation Underlies Human Prostate Cancer Aggressiveness», Cell Metab., 19, 3, pp. 393–406, 2014. [CrossRef]
- G. Del Mistro et all, «Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy of urine for prostate cancer detection: a preliminary study», Anal. Bioanal. Chem., 407, 12, pp. 3271–3275, 2015. [CrossRef]
- Y. Ma, J. Chi, Z. Zheng, A. Attygalle, I. Y. Kim, и H. Du, «Therapeutic prognosis of prostate cancer using surface-enhanced Raman scattering of patient urine and multivariate statistical analysis», J. Biophotonics, 14, 1, 2021. [CrossRef]
- S. Chen et all, «Raman Spectroscopy Reveals Abnormal Changes in the Urine Composition of Prostate Cancer: An Application of an Intelligent Diagnostic Model with a Deep Learning Algorithm», Adv. Intell. Syst., 3, 4, с. 2000090, 2021. [CrossRef]
- N. Chen et all, «Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy of serum accurately detects prostate cancer in patients with prostate-specific antigen levels of 4–10 ng/mL», Int. J. Nanomedicine, Volume 12, pp. 5399–5407, 2017. [CrossRef]
- I. Larionova, E. Kazakova, M. Patysheva, и J. Kzhyshkowska, «Transcriptional, Epigenetic and Metabolic Programming of Tumor-Associated Macrophages», Cancers, 12, 6, с. 1411, 2020. [CrossRef]
| Region | Incidence | Deaths | 5-year prevalence (all ages) | |||||
| number | % of all sites | Rank | number | % of all sites | Rank | number | Per 100 000 | |
| World | 1 414 259 | 7.3% | 3 | 375 304 | 3,8% | 8 | 4 956 901 | 126,13 |
| Europe | 473 344 | 10.8% | 3 | 108 088 | 5.5% | 5 | 1 873 814 | 518.11 |
| Northern America | 239 574 | 9.4% | 3 | 37 192 | 5.3% | 5 | 929 921 | - |
| Latin America and the Caribbean | 214 522 | 14.6% | 1 | 57 415 | 8.0% | 3 | 709 119 | 220.48 |
| Asia | 371 225 | 3.9% | 8 | 120 593 | 2,1% | 14 | 1 176 781 | 49.59 |
| Africa | 93 173 | 8,4% | 3 | 47 249 | 6.6% | 4 | 178 197 | 26.60 |
| Oceania | 22 421 | 8.8% | 2 | 4 767 | 6,9 | 4 | 89 069 | 416.92 |
| Russia Federation | 46 454 | 7,9% | 3 | 14 434 | 4,6 | 7 | 169 221 | 250.18 |
| miRNA | Function | Experimental models (Cell lines, animal models) | Patient cohort, size, age, and geographic location, groups of comparison | Reference |
| miR-18a | Increasing cancer progression | - | 160 patients, average age 56.8 ± 12 including stage I, II, and IV presented the National Cancer Institute Cairo compared to 50 normal control healthy male individuals |
[74] |
| miR-21 | Accelerating tumor invasion and inducing castration resistance | - | 170 patient older 45 years from Zagazig University Hospitals, Egypt compared to 70 healthy men | [81] |
| miR-32 | Inhibition of apoptosis and increased proliferation | transgenic mir-32 mice | - | [30] |
| miR-106/miR-25 | Increasing cancer progression | LNCaP cells PC-3 cells |
- |
[31] |
| miR-125b |
Increase in cell proliferation and suppression of apoptosis | The human PCa cell lines: C4-2 CWR22Rv1 BCa cell lines: T24, TCC-SUP, UMUC3, TCC-5637, and 293T |
- | [82] |
| miR-141 | Development of castration resistance | LNCaP cells PC-3 cells |
- | [82,83,84] |
| miR-221/miR-222 | Increased cell proliferation, invasion, cell survival | LNCaP, PC3 | - | [85] |
| miR-375 |
Diagnostics | LNCaP, PC3 | - | [84] |
| miR-650 | Reduced expression of the cellular stress response gene 1 (CSR1). | PC3 | 216 patients from 45 through 79 years from Pittsburgh, USA compared with 77 healthy men | [86] |
| miR-4534 | Downregulating the tumor suppressor PTEN gene | LNCaP, PC3 | [80] |
| Diagnostic method | Principle | Sensitivity (0-1) |
Specificity (0-1) | False-negative cases (%) | False positive cases (%) | Benefits | Limitations | Reference |
| Digital Rectal Examination (DRE) | Palpation of the lower part of the rectum, pelvis and lower abdomen | 0,51 | 0,59 | - | - | availability and affordability non-invasive |
low sensitivity lack specificity More than 60% are identified as asymptomatic |
[118,139,140] |
| Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) | Venous blood sampling for prostate-specific antigen, a glycoprotein expressed in both cancerous and normal columnar prostate epithelial cells. | 0,21-0,5 | 0,91 | 10-15% | - | availability and affordability | lack specificity predictive accuracy of 8% to 10% |
[118,141,142] |
| Transrectal Ultrasound Scan (TRUS) | Ultrasound examination of the prostate with insertion of the sensor into the rectum. | - | - | 11,34-29,31 | 4,61-6,11% | availability and affordability non-invasive |
lack specificity | [123] |
| Transrectal biopsy (TRB) | Tissue sampling with a thin needle that is inserted through the rectum into the prostate. | 0,53 | 1 | 11-46% | - | Availability affordability |
most lesion are small and sometime located in regions that are not identifiable Complications of prostate biopsy (eg, infection, pain, bleeding, urinary obstruction) |
[118,139,143,144,145,146] |
| MRI -guided biopsy | MRI-guided sampling of prostate tumor tissue | 0.77 | 1 | 6% | 4,2% | accuracy | Complications of prostate biopsy (eg, infection, pain, bleeding, urinary obstruction); expensive |
[143,144,145] |
| MRI | Creation of detailed volumetric images of areas using a magnetic tomography | 0.67 | 0.92 | 2,7% | 44,1% | non-invasive |
expensive |
[143,145] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





