Submitted:
15 June 2023
Posted:
16 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study groups and DNA isolation
2.2. HPV: detection and genotyping)
2.3. Phylogenetic analysis
2.4. Analysis of selective pressures
2.5. Predicted protein structure modeling
2.6. T-cell and B-cell epitopes prediction
2.7. Plasmid constructs
2.8. Transfection of the C33A cells with recombinant expression vectors
2.9. Evaluation of E7 gene expression in transfected C33A cells
2.10. Statistical analysis
3. Results
3.1. HPV detection and typing
3.2. E7 HPV58 sequence variations
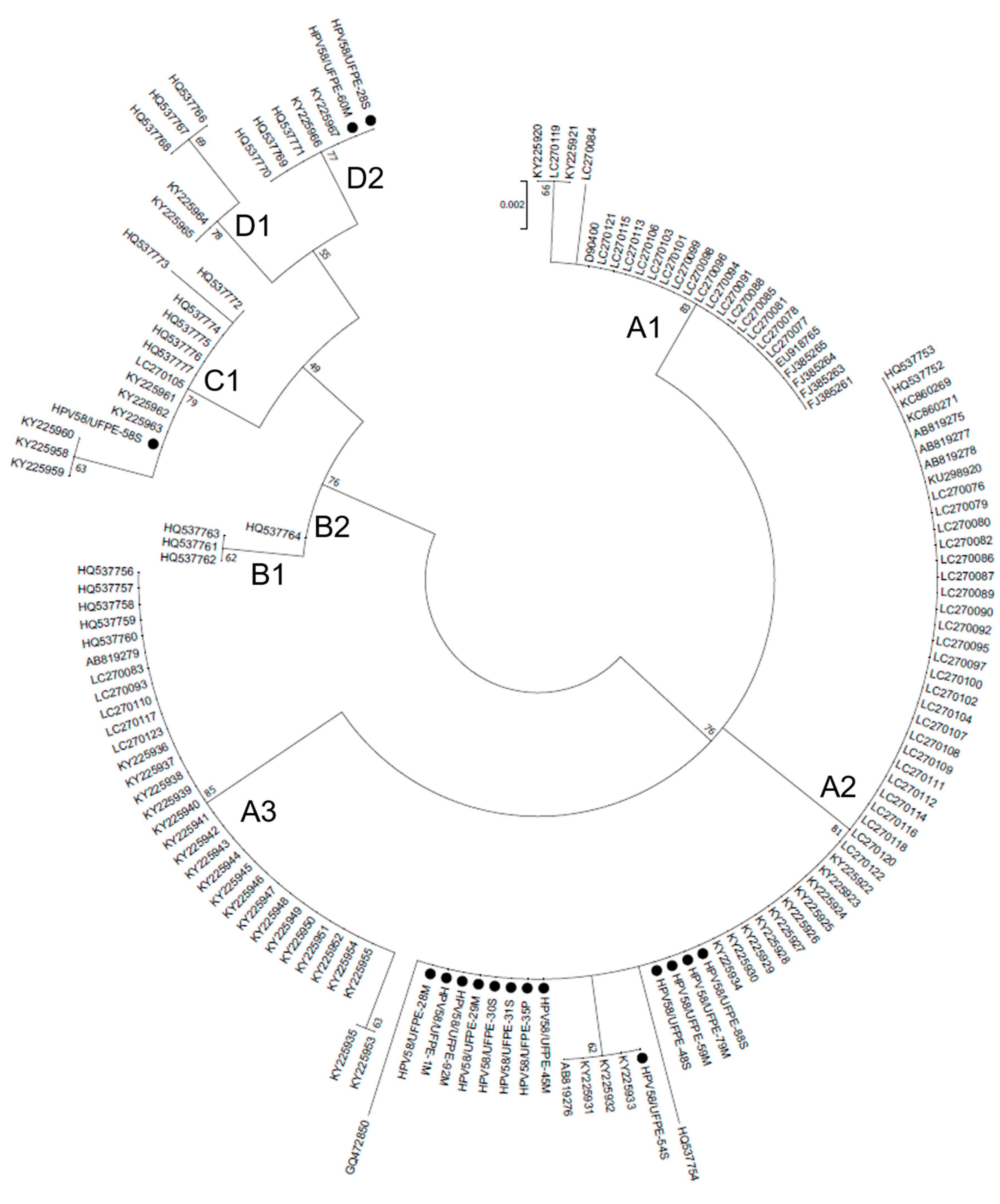
3.3. Phylogenetic analysis
3.4. Selective pressure analysis
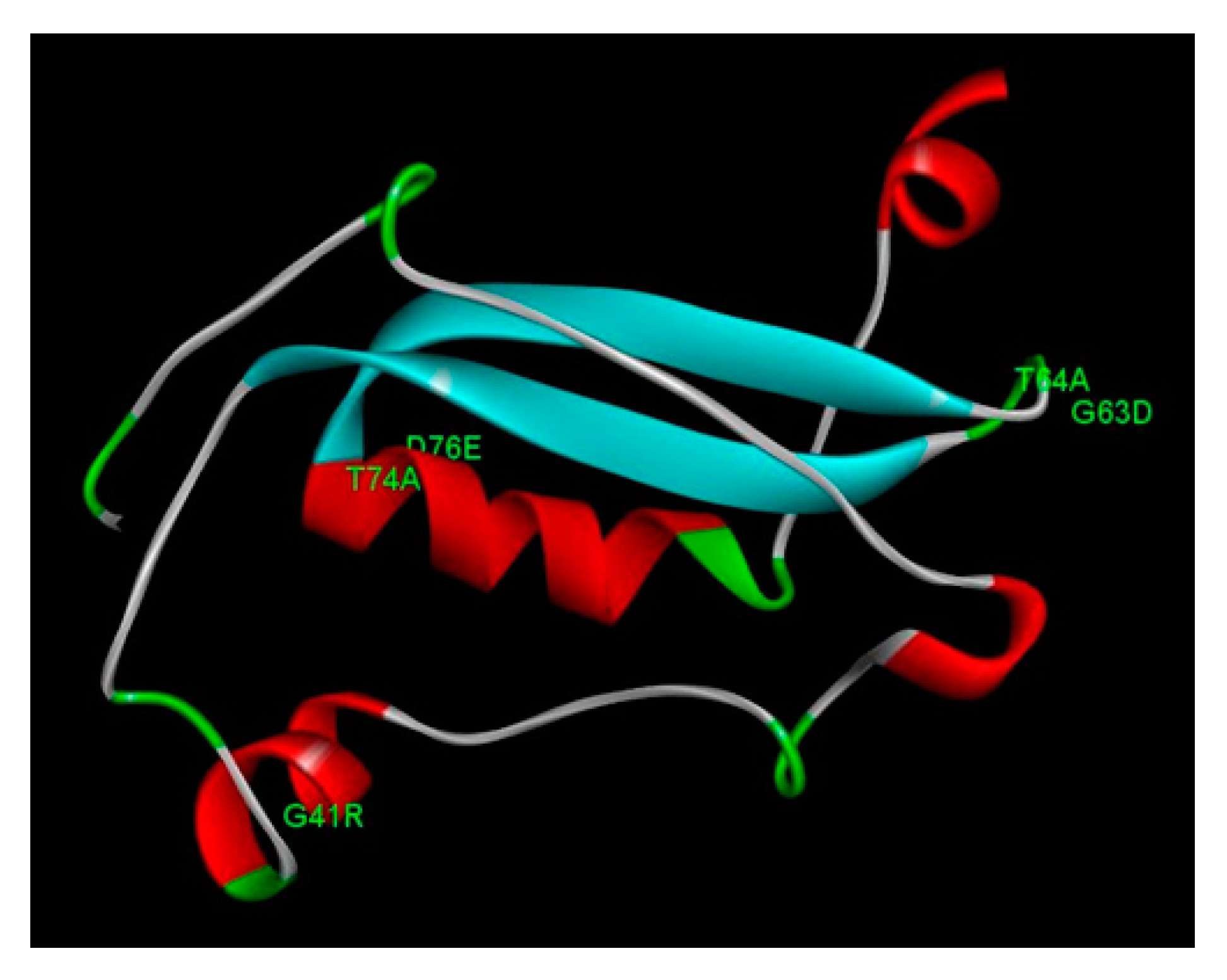
3.5. Structural analysis of E7 mutations
3.6. T-cell and B-cell epitopes prediction
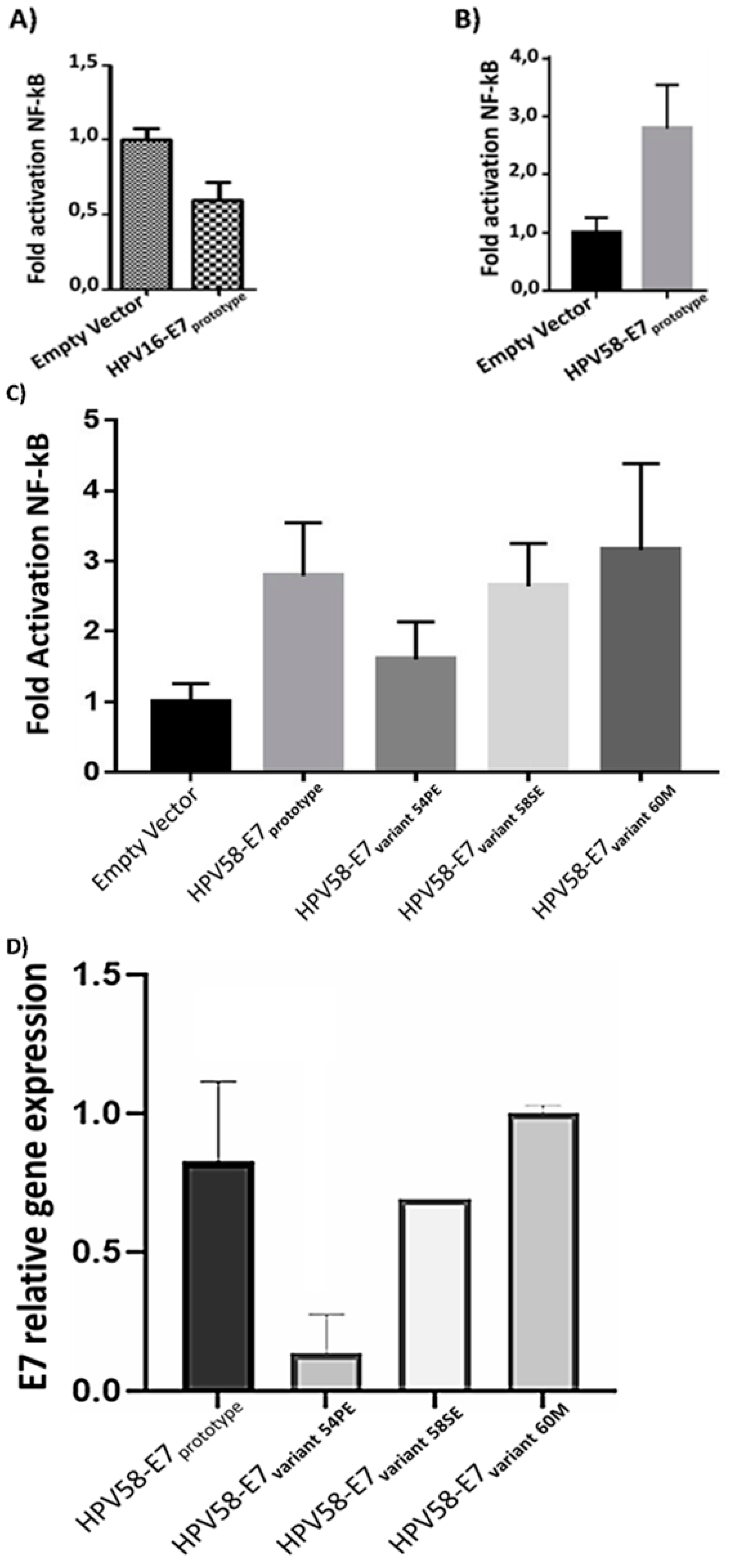
3.7. Effect of E7 polymorphic variants on the NF-kB pathway
3.8. E7 oncoproteingene expression in C33A transfected cells with HPV-58 E7 variants
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- zur Hausen, H. Papillomaviruses in the Causation of Human Cancers - a Brief Historical Account. Virology 2009, 384, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raiol, T.; Wyant, P.S.; de Amorim, R.M.S.; Cerqueira, D.M.; Milanezi, N. von G.; Brígido, M. de M.; Sichero, L.; Martins, C.R.F. Genetic Variability and Phylogeny of the High-Risk {HPV}-31, -33, -35, -52, and -58 in Central {Brazil}. J. Med. Virol. 2009, 81, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arbyn, M.; Weiderpass, E.; Bruni, L.; de Sanjosé, S.; Saraiya, M.; Ferlay, J.; Bray, F. Estimates of Incidence and Mortality of Cervical Cancer in 2018: A Worldwide Analysis. Lancet. Glob. Heal. 2020, 8, e191–e203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global Cancer Statistics 2018: {GLOBOCAN} Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA. Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurgel, A.P.A.D.; Chagas, B.S.; do Amaral, C.M.; Nascimento, K.C.G.; Leal, L.R.S.; Silva Neto, J. da C.; Cartaxo Muniz, M.T.; de Freitas, A.C. Prevalence of Human Papillomavirus Variants and Genetic Diversity in the {L1} Gene and Long Control Region of {HPV16}, {HPV31}, and {HPV58} Found in {North}-{East} {Brazil}. Biomed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 130828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, J.; Carvalho, M.; de Fernandes, T.; Araújo, J.; Azevedo, P.; Azevedo, J.; Meissner, R. Prevalence of Human Papillomavirus Type 58 in Women with or without Cervical Lesions in Northeast {Brazil}. Ann. Med. Health Sci. Res. 2013, 3, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, P.K.S.; Zhang, C.; Park, J.-S.; Smith-McCune, K.K.; Palefsky, J.M.; Giovannelli, L.; Coutlée, F.; Hibbitts, S.; Konno, R.; Settheetham-Ishida, W.; et al. Geographical Distribution and Oncogenic Risk Association of Human Papillomavirus Type 58 {E6} and {E7} Sequence Variations. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 132, 2528–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chagas, B.S.; Batista, M.V.A.; Guimarães, V.; Balbino, V.Q.; Crovella, S.; Freitas, A.C. New Variants of {E6} and {E7} Oncogenes of Human Papillomavirus Type 31 Identified in {Northeastern} {Brazil}. Gynecol. Oncol. 2011, 123, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boon, S.S.; Xia, C.; Lim, J.Y.; Chen, Z.; Law, P.T.Y.; Yeung, A.C.M.; Thomas, M.; Banks, L.; Chan, P.K.S. Human {Papillomavirus} 58 {E7} {T20I}/{G63S} {Variant} {Isolated} from an {East} {Asian} {Population} {Possesses} {High} {Oncogenicity}. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e00090–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, L.F.; Koutsky, L.A.; Hildesheim, A.; Galloway, D.A.; Wheeler, C.M.; Winer, R.L.; Ho, J.; Kiviat, N.B. Risk for High-Grade Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia Associated with Variants of Human Papillomavirus Types 16 and 18. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers \& Prev. A Publ. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. Cosponsored by Am. Soc. Prev. Oncol. 2007, 16, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Boer, M.A.; Peters, L.A.W.; Aziz, M.F.; Siregar, B.; Cornain, S.; Vrede, M.A.; Jordanova, E.S.; Fleuren, G.J. Human Papillomavirus Type 18 Variants: Histopathology and {E6}/{E7} Polymorphisms in Three Countries. Int. J. Cancer 2005, 114, 422–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, P.T.; Boon, S.S.; Hu, C.; Lung, R.W.; Cheung, G.P.; Ho, W.C.; Chen, Z.; Massimi, P.; Thomas, M.; Pim, D.; et al. Oncogenic Comparison of Human Papillomavirus Type 58 {E7} Variants. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 1517–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, T.; Wang, X.; Ye, F.; Cheng, X.; Lu, W.; Xie, X. Distribution of Human Papillomavirus 16 {E6}/{E7} Variants in Cervical Cancer and Intraepithelial Neoplasia in {Chinese} Women. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer Off. J. Int. Gynecol. Cancer Soc. 2010, 20, 1391–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Y.; Bao, S.; Zhao, Y.; Ding, X. Identification of Variants and Therapeutic Epitopes in {HPV}-33/{HPV}-58 {E6} and {E7} in {Southwest} {China}. Virol. J. 2019, 16, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barros, M.R.; de Oliveira, T.H.A.; de Melo, C.M.L.; Venuti, A.; de Freitas, A.C. Viral {Modulation} of {TLRs} and {Cytokines} and the {Related} {Immunotherapies} for {HPV}-{Associated} {Cancers}. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 2912671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, M.R.; de Melo, C.M.L.; Barros, M.L.C.M.G.R.; de Cássia Pereira de Lima, R.; de Freitas, A.C.; Venuti, A. Activities of Stromal and Immune Cells in {HPV}-Related Cancers. J. Exp. \& Clin. cancer Res. CR 2018, 37, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Freitas, A.C.; Gurgel, A.P.A.D.; Chagas, B.S.; Coimbra, E.C.; do Amaral, C.M.M. Susceptibility to Cervical Cancer: An Overview. Gynecol. Oncol. 2012, 126, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staden, R. The {Staden} Sequence Analysis Package. Mol. Biotechnol. 1996, 5, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic Local Alignment Search Tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. {MEGA7}: {Molecular} {Evolutionary} {Genetics} {Analysis} {Version} 7.0 for {Bigger} {Datasets}. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. {MEGA11}: {Molecular} {Evolutionary} {Genetics} {Analysis} {Version} 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. {jModelTest} 2: More Models, New Heuristics and Parallel Computing. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z. Likelihood Ratio Tests for Detecting Positive Selection and Application to Primate Lysozyme Evolution. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1998, 15, 568–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Nielsen, R. Synonymous and Nonsynonymous Rate Variation in Nuclear Genes of Mammals. J. Mol. Evol. 1998, 46, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z. Complexity of the Simplest Phylogenetic Estimation Problem. Proceedings. Biol. Sci. 2000, 267, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.E.; Chivian, D.; Baker, D. Protein Structure Prediction and Analysis Using the {Robetta} Server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, W526–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharya, D.; Nowotny, J.; Cao, R.; Cheng, J. {3Drefine}: An Interactive Web Server for Efficient Protein Structure Refinement. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W406–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laskowski, R.A.; MacArthur, M.W.; Moss, D.S.; Thornton, J.M. {PROCHECK}: A Program to Check the Stereochemical Quality of Protein Structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1993, 26, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, V.B.; Arendall, W.B.; Headd, J.J.; Keedy, D.A.; Immormino, R.M.; Kapral, G.J.; Murray, L.W.; Richardson, J.S.; Richardson, D.C. {MolProbity}: All-Atom Structure Validation for Macromolecular Crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. D. Biol. Crystallogr. 2010, 66, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkert, P.; Biasini, M.; Schwede, T. Toward the Estimation of the Absolute Quality of Individual Protein Structure Models. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Skolnick, J. {TM}-Align: A Protein Structure Alignment Algorithm Based on the {TM}-Score. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 2302–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauck, F.; Smith, C.A.; Friedland, G.F.; Humphris, E.L.; Kortemme, T. {RosettaBackrub}--a Web Server for Flexible Backbone Protein Structure Modeling and Design. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, W569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worth, C.L.; Preissner, R.; Blundell, T.L. {SDM}--a Server for Predicting Effects of Mutations on Protein Stability and Malfunction. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, W215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, H.; Raghava, G.P.S. {ProPred1}: Prediction of Promiscuous {MHC} {Class}-{I} Binding Sites. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 1009–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Raghava, G.P. {ProPred}: Prediction of {HLA}-{DR} Binding Sites. Bioinformatics 2001, 17, 1236–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Raghava, G.P.S. {AlgPred}: Prediction of Allergenic Proteins and Mapping of {IgE} Epitopes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, W202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, A.; Munger, K. The Papillomavirus {E7} Proteins. Virology 2013, 445, 138–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramas, V.; Mirazo, S.; Bonilla, S.; Ruchansky, D.; Arbiza, J. Analysis of Human Papillomavirus 16 {E6}, {E7} Genes and {Long} {Control} {Region} in Cervical Samples from {Uruguayan} Women. Gene 2018, 654, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.-H.; Shi, W.-W.; Zhou, M.-Y.; Liu, J.-M.; Han, Q.-Y.; Xu, H.-H. Genetic Variability and Oncogenic Risk Association of Human Papillomavirus Type 58 {E6} and {E7} Genes in {Taizhou} Area, {China}. Gene 2019, 686, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molano, M.; Buitrago, O.; Moreno-Acosta, P.; Garland, S.M.; Morales, N.; Huertas, A.; Martinez, T.; Gamboa, O.; Tabrizi, S.N.; Cornall, A.; et al. Follow-up Study of {HPV58} Variants in Women with Incident {HPV58} Infection from a {Colombian} Cohort. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 2511–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, J.; Chen, J.; Xu, M.; Yang, H.; Wen, S.; Pan, Y.; Wang, X.; Ye, C.; Qiu, L.; Sun, Q. The Polymorphisms of {LCR}, {E6}, and {E7} of {HPV}-58 Isolates in {Yunnan}, {Southwest} {China}. Virol. J. 2018, 15, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Yang, H.; Yang, L.; Yao, Y.; Dai, S.; Shi, L.; Li, C.; Yang, L.; Yan, Z.; Yao, Y. Human Papillomavirus Type 16 {E6} and {E7} Gene Variations Associated with Cervical Cancer in a {Han} {Chinese} Population. Infect. Genet. Evol. J. Mol. Epidemiol. Evol. Genet. Infect. Dis. 2019, 73, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conde-Ferraez, L.; Pacheco-Arjona, R.; Novelo Canul, C.; Gomez-Carballo, J.; Ramirez-Prado, J.H.; Ayora-Talavera, G.; González-Losa, M.D.R. Genetic {Variability} in {E6} and {E7} {Oncogenes} from {Human} {Papillomavirus} {Type} 58 in {Mexican} {Women}. Intervirology 2017, 60, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenjimbayashi, Y.; Onuki, M.; Hirose, Y.; Mori, S.; Ishii, Y.; Takeuchi, T.; Tasaka, N.; Satoh, T.; Morisada, T.; Iwata, T.; et al. Whole-Genome Analysis of Human Papillomavirus Genotypes 52 and 58 Isolated from {Japanese} Women with Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia and Invasive Cervical Cancer. Infect. Agent. Cancer 2017, 12, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berumen, J.; Ordoñez, R.M.; Lazcano, E.; Salmeron, J.; Galvan, S.C.; Estrada, R.A.; Yunes, E.; Garcia-Carranca, A.; Gonzalez-Lira, G.; la Campa, A. Asian-{American} Variants of Human Papillomavirus 16 and Risk for Cervical Cancer: A Case-Control Study. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2001, 93, 1325–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuna, R.E.; Moore, W.E.; Shanesmith, R.P.; Dunn, S.T.; Wang, S.S.; Schiffman, M.; Blakey, G.L.; Teel, T. Association of {HPV16} {E6} Variants with Diagnostic Severity in Cervical Cytology Samples of 354 Women in a {US} Population. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 125, 2609–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornet, I.; Gheit, T.; Iannacone, M.R.; Vignat, J.; Sylla, B.S.; Del Mistro, A.; Franceschi, S.; Tommasino, M.; Clifford, G.M. {HPV16} Genetic Variation and the Development of Cervical Cancer Worldwide. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 108, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burk, R.D.; Harari, A.; Chen, Z. Human Papillomavirus Genome Variants. Virology 2013, 445, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, P.K.S.; Luk, A.C.S.; Park, J.-S.; Smith-McCune, K.K.; Palefsky, J.M.; Konno, R.; Giovannelli, L.; Coutlée, F.; Hibbitts, S.; Chu, T.-Y.; et al. Identification of Human Papillomavirus Type 58 Lineages and the Distribution Worldwide. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 203, 1565–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dearlove, B.; Lewitus, E.; Bai, H.; Li, Y.; Reeves, D.B.; Joyce, M.G.; Scott, P.T.; Amare, M.F.; Vasan, S.; Michael, N.L.; et al. A {SARS}-{CoV}-2 Vaccine Candidate Would Likely Match All Currently Circulating Variants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2020, 117, 23652–23662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, E.L.; Cheng, A.N.; Sankaran, V.G. The Genetics of Human Hematopoiesis and Its Disruption in Disease. EMBO Mol. Med. 2019, 11, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Luo, P.; Ye, M.; Gong, Q.; Mei, B. Genetic Variability of {E6} and {E7} Genes of Human Papillomavirus Type 58 in {Jingzhou}, {Hubei} {Province} of Central {China}. Virol. J. 2022, 19, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodily, J.M.; Mehta, K.P.M.; Laimins, L.A. Human Papillomavirus {E7} Enhances Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1-Mediated Transcription by Inhibiting Binding of Histone Deacetylases. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 1187–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honegger, A.; Schilling, D.; Bastian, S.; Sponagel, J.; Kuryshev, V.; Sültmann, H.; Scheffner, M.; Hoppe-Seyler, K.; Hoppe-Seyler, F. Dependence of Intracellular and Exosomal {microRNAs} on Viral {E6}/{E7} Oncogene Expression in {HPV}-Positive Tumor Cells. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, E.A.; Sowa, M.E.; Tan, M.J.A.; Jeudy, S.; Hayes, S.D.; Santha, S.; Münger, K.; Harper, J.W.; Howley, P.M. Systematic Identification of Interactions between Host Cell Proteins and {E7} Oncoproteins from Diverse Human Papillomaviruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2012, 109, E260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, H.; Boland, J.F.; Li, H.; Burk, R.; Yeager, M.; Anderson, S.K.; Wentzensen, N.; Schiffman, M.; Mirabello, L.; Dean, M. {HPV16} {E7} {Nucleotide} {Variants} {Found} in {Cancer}-{Free} {Subjects} {Affect} {E7} {Protein} {Expression} and {Transformation}. Cancers (Basel). 2022, 14, 4895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, E.M.; Talpe-Nunes, V.; Sobrinho, J.S.; Ferreira, S.; Lino, V. de S.; Termini, L.; Silva, G.Á.F.; Boccardo, E.; Villa, L.L.; Sichero, L. E6/{E7} {Functional} {Differences} among {Two} {Natural} {Human} {Papillomavirus} 18 {Variants} in {Human} {Keratinocytes}. Viruses 2021, 13, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandermark, E.R.; Deluca, K.A.; Gardner, C.R.; Marker, D.F.; Schreiner, C.N.; Strickland, D.A.; Wilton, K.M.; Mondal, S.; Woodworth, C.D. Human Papillomavirus Type 16 {E6} and {E} 7 Proteins Alter {NF}-{kB} in Cultured Cervical Epithelial Cells and Inhibition of {NF}-{kB} Promotes Cell Growth and Immortalization. Virology 2012, 425, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitkovsky, D.; Hehner, S.P.; Hofmann, T.G.; Möller, A.; Schmitz, M.L. The Human Papillomavirus Oncoprotein {E7} Attenuates {NF}-Kappa {B} Activation by Targeting the {Ikappa} {B} Kinase Complex. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 25576–25582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byg, L.M.; Vidlund, J.; Vasiljevic, N.; Clausen, D.; Forslund, O.; Norrild, B. {NF}-Κ{B} Signalling Is Attenuated by the {E7} Protein from Cutaneous Human Papillomaviruses. Virus Res. 2012, 169, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, R.C. de O.; da Silva Júnior, A.H.P.; Gurgel, A.P.A.D.; Barros Junior, M.R.; Santos, D.L.; de Lima, R. de C.P.; Batista, M.V.A.; Pena, L.J.; Chagas, B.S.; Freitas, A.C. Structural and Functional Impacts of {E5} Genetic Variants of Human Papillomavirus Type 31. Virus Res. 2020, 290, 198143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLaughlin-Drubin, M.E.; Münger, K. Oncogenic Activities of Human Papillomaviruses. Virus Res. 2009, 143, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, M.A.; Azoitei, N.; Baumann, B.; Grünert, S.; Sommer, A.; Pehamberger, H.; Kraut, N.; Beug, H.; Wirth, T. {NF}-{kappaB} Is Essential for Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Metastasis in a Model of Breast Cancer Progression. J. Clin. Invest. 2004, 114, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Pang, T.; Guo, Z.; Pontén, J.; Nistér, M.; Bernard Afink, G. Oncogene Lineages of Human Papillomavirus Type 16 {E6}, {E7} and {E5} in Preinvasive and Invasive Cervical Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Pathol. 2001, 195, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharjee, B.; Mandal, N.R.; Roy, S.; Sengupta, S. Characterization of Sequence Variations within {HPV16} Isolates among {Indian} Women: Prediction of Causal Role of Rare Non-Synonymous Variations within Intact Isolates in Cervical Cancer Pathogenesis. Virology 2008, 377, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makowsky, R.; Lhaki, P.; Wiener, H.W.; Bhatta, M.P.; Cullen, M.; Johnson, D.C.; Perry, R.T.; Lama, M.; Boland, J.F.; Yeager, M.; et al. Genomic Diversity and Phylogenetic Relationships of Human Papillomavirus 16 ({HPV16}) in {Nepal}. Infect. Genet. Evol. J. Mol. Epidemiol. Evol. Genet. Infect. Dis. 2016, 46, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicknell, A.A.; Ricci, E.P. When {mRNA} Translation Meets Decay. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2017, 45, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, G.; Coller, J. Codon Optimality, Bias and Usage in Translation and {mRNA} Decay. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Mao, Y.; Ji, Q.; Dersh, D.; Yewdell, J.W.; Qian, S.-B. Decoding {mRNA} Translatability and Stability from the 5′ {UTR}. Nat. Struct. \& Mol. Biol. 2020, 27, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Samples | Pathological diagnosis |
|---|---|
| HPV58/UFPE-58S | LSIL |
| HPV58/UFPE-30S | HSIL |
| HPV58/UFPE-31S | HSIL |
| HPV58/UFPE-54S | HSIL |
| HPV58/UFPE-88S | LSIL |
| HPV58/UFPE-60M | LSIL |
| HPV58/UFPE-59M | HSIL |
| HPV58/UFPE-1M | HSIL |
| HPV58/UFPE-29M | Without lesion |
| HPV58/UFPE-35P | Without lesion |
| HPV58/UFPE-45M | HSIL |
| HPV58/UFPE-79M | HSIL |
| HPV58/UFPE-92M | HSIL |
| HPV58/UFPE-28M | LSIL |
| HPV58/UFPE-28S | HSIL |
| HPV58/UFPE-48S | HSIL |
| E7 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nt | 694 | 744 | 756 | 761 | 763 | 793 | 798 | 801 | 840 | 852 |
| Reference | G | T | T | G | A | A | C | C | C | T |
| HPV58/UFPE-58S | . | G | . | . | . | G | T | A | T | C |
| HPV58/UFPE-30S | A | G | . | A | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| HPV58/UFPE-31S | A | G | . | A | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| HPV58/UFPE-54S | A | G | C | A | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| HPV58/UFPE-88S | A | G | . | A | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| HPV58/UFPE-60M | . | G | . | A | G | G | T | A | T | . |
| HPV58/UFPE-59M | A | G | . | A | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| HPV58/UFPE-1M | A | G | . | A | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| HPV58/UFPE-29M | A | G | . | A | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| HPV58/UFPE-35P | A | G | . | A | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| HPV58/UFPE-45M | A | G | . | A | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| HPV58/UFPE-79M | A | G | . | A | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| HPV58/UFPE-92M | A | G | . | A | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| HPV58/UFPE-28M | A | G | . | A | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| HPV58/UFPE-28S | . | G | . | A | G | G | T | A | T | . |
| HPV58/UFPE-48S | A | G | . | A | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| Reference amino acid | G | G | T | T | D | |||||
| Amino acid position | 41 | 63 | 64 | 74 | 76 | |||||
| Amino changed | R | D | A | A | E | |||||
| Model 1 | Model 2 | LRT | Positively selected sites |
|---|---|---|---|
| M0 | M3 | 48.63069 | - |
| M1 |
M2 |
31.954069 |
41G (0.979*) 63G (1.000**) 64T (0.826) 74T (0.976*) 76D (0.997**) |
| M1 |
M3 |
31.954662 |
41G (0.997**) 63G (1.000**) 64T (0.893) 74T (0.997**) 76D (1.000**) |
| M7 |
M8 |
32.308663 |
41G (0.987*) 63G (1.000**) 64T (0.857) 74T (0.985*) 76D (0.999**) |
| Protein | Mutation | Predicted ΔΔG | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| E7 | G41R | -0.14 | Reduced stability |
| G63D | -2.48 | Reduced stability | |
| T64A | -0.12 | Reduced stability | |
| T74A | 1.26 | Increased stability | |
| D76E | 1.25 | Increased stability |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





