Introduction
Staphylococcus aureus is an important gram-positive bacteria that lives in the human body in a commensal manner, however, under certain conditions (immunosuppression states, diabetes mellitus, elderly individuals), this microorganism causes superficial or deep infections, such as contaminated ulcers on the skin, pneumonia and sepsis. As the same way as other microorganisms,
S. aureus has powerful tools to cause infection diseases successfully, that are called virulence factors [
1]. Virulence factors are cellular structures, molecules and regulatory systems that assist the bacterium to colonize the host tissue. The biofilm living form of the microorganisms is considered an important virulence factor that helps them to establish a highly structured microbial community. Biofilm is a complex microbial organization, where the microorganisms are embebbed in a self-produced extra-celular matrix (ECM) that protects them from chemical agents and physical stress. The biofilm formation is an endless process, and this life cycle is divided in the following steps: (I) Adhesion: microorganisms are reversibly adsorbed to a biotic or abiotic surface; (II) Colonization: microorganisms are irreversibly attached to the surface; (III) Development: the multilayered cells proliferate and the ECM is produced and secreted; (IV) Maturation: formation of a three-dimensional stable community that contains channels to efficiently distribute nutrients and signaling molecules (quorum sensing) within the biofilm; (V) Dispersal: detachment of microbial cells to disseminate and, subsequently, colonize other sites. The presence of the ECM that protects the cells, the quorum sensing molecules that are produced and the architecture of the biofilm turn this community more resistant to the antimicrobial therapies than the planktonic counterparts. Moreover, around 70% of the infectious diseases are caused by microorganisms organized as biofilms, increasing to 85% when considering the chronic infections; for this reason, the management of biofilms is the main challenge for microbial control [
2].
The need to develop new antimicrobial treatments to combat microbial biofilms is unquestionable. In this context, Antimicrobial Photodynamic Therapy (PDT) is a powerful treatment that has been studied and proposed worldwide and its effectiveness against bacteria, fungi and virus has been demonstrated in a series of
in vitro,
in vivo and clinical studies. The PDT is based on the combination of three compounds: a photosensitizer (PS), a light source at appropriate wavelength to excite the PS and molecular oxygen in the target tissue. The mechanisms involved in the PDT action are very well known and described. When the PS molecule in its singlet ground state is illuminated, it absorbs energy, enters in a high-energy state and remains activated. During the PS relaxation process, highly cytotoxic reactive oxygen species (ROS) are generated by two reactions: type I and type II. In a type I reaction, when the PS can transfer a proton or an electron to the substrate to form a radical anion or radical cation; these radicals may react with oxygen to produce ROS. In a type 2 reaction, the PS can directly transfer energy to molecular oxygen producing the excited state singlet oxygen (
1O
2). Both type 1 and 2 reaction occurs simultaneously, but depending on the PS chemical structure, one of the reactions will be preferential. The efficiency of the PDT is often related to the
1O
2 quantum yield of the PS [
3,
4,
5,
6,
7].
Interestingly, it has been verified that many of the available clinically-used photosensitizers can be also activated by ultrasound (US), even though the exact mechanism(s) by which this occurs remain(s) unknown. This antimicrobial strategy is called Sonodynamic Therapy (SDT). The advantage of using the US is that, besides adding another activation mechanism, the ultrasonic waves can penetrate deeper into the sample, resulting in an improved cytotoxic effect. Possible mechanisms of SDT include generation of sonosensitizer derived radicals which initiate chain peroxidation of membrane lipids, the physical destabilization of the cell membrane by cavitation phenomenon, which is able to produce reversible effects, such as transient pores that enhances the drug penetration, or completely cell membrane damage, leading to cell death. It is proposed that the SDT mechanism is probably governed by multiple factors including the nature of the biological model, the sonosensitizer and the ultrasound parameters [
8].
Besides that, a new approach that combines US and light to activate the PS, called Sonophotodynamic Therapy (SPDT), has been assessed to improve microbial inactivation [
9]. This strategy takes advantage of the mechanical effects of US and the ability of light to excite the PS. In the treatment of cancer, this modality is currently being evaluated and studies have proved that the sensitizers can be effectively excited by both sources (light and US), being the combined treatment (SPDT) more effective than the isolated therapies (PDT or SDT) [
9]. In the microbial field, this pattern of higher effectiveness of SPDT was also verified against
Candida albicans, Enterococcus faecalis, Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans, Porphyromonas gingivalis, Prevotella intermedia [
10,
11,
12,
13,
14].
Recently, our research group proved that aPDT, SDT and SPDT mediated by Curcumin were effective to inactivate S. aureus biofilm, and the highest reduction was achieved with the combined treatment (SPDT), where 7.43 log of inactivation was obtained. In the attempt to better understand the effects and mechanisms involved in the bacteria inactivation, the present work evaluated the effects in the metabolism, adhesion and biofilm formation abilities of the bacteria S. aureus after the treatments, the production of reactive oxygen species by each therapy and the spectrum degradation of the curcumin over the sources of the treatments (light, US and light+US).
Materials and methods
PS, light source and ultrasound
The curcumin (PDT Pharma, Cravinhos, SP, Brazil) was used as photosensitizer. A stock solution of 16 mM was prepared in DMSO, then, diluted in sterile saline to the final concentration of 40 μM (keeping the final concentration of DMSO at 0.025%). For this study, a customized device combining a blue LED and ultrasound was developed at São Carlos Institute of Physics, University of São Paulo. The LED-based source has centered emission at 455 nm, (LXHL-PR09, Luxeon® III Emitter, Lumileds Lighting, San Jose, CA, USA) with irradiance of 37 mW/cm2. The ultrasound, coupled in the same device, was used at a frequency of 1 MHz, pulse repetition frequency of 100 Hz, 20% of duty cycle, and 3 W/cm² of intensity.
Treatments
After 48 h of biofilm formation, samples were submitted to SDT, PDT or SPDT. In order to evaluate the effects of the treatments in remaining bacteria, sub-lethal doses of the treatments were applied to recover live cells, and the parameters used were selected based on our previously work. For SDT, 2 mL of curcumin (Cur) at 40 μM was added, and the plates were incubated in the dark for 20 min. Afterwards, the US transducer was applied over the biofilms, at the frequency of 1 MHz, a power density of 3 W/cm², 20% of duty cycle and pulse frequency of 100 Hz for 15 min (SDT group). For PDT, biofilms were incubated for 20 min with 2 mL of the sensitizer, then, plates were irradiated with blue LED light (35 J/cm²) (PDT group). Finally, for SPDT, biofilm samples were incubated for 20 min with Cur and, then, both light and US were applied simultaneously using the same parameters as described previously. Other biofilm samples were treated with the sensitizer (Cur group), US (US group) or LED light only (Light group), or no treatment (Control group).
Confocal microscopy
The effect of the treatments on the biofilm components (bacterial cells and extra cellular matrix) were examined under Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy (LSM780, Carl Zeiss, Germany). For this, after the treatments, Cur solution was removed and the biofilm washed twice with saline. First, the fluorescent LIVE/DEAD Baclight Bacterial Viability Kit (Life Technologies GmbH) was used according to the manufacturer's protocol. This kit is based on a mixture of SYTO 9 and Propidium Iodide (PI). The first fluorochrome is a green fluorescent nucleic acid, staining viable bacterial cells, while PI is a fluorescent red nucleic acid that marks nonviable bacterial cells. The mixture of both dyes was added to the biofilms and incubated for 15 min. After this, the biofilms were whashed twice with sterile saline and then, the ECM were stained with the blue fluorescent dye Calcofluor White (Sigma Aldrich®) that binds to glycans and can be used to detect extracellular polysaccharides. Biofilms were incubated with 50 μg/mL of Calcofluor during 10 min. The stained biofilms were imaged, using as excitation/emission wavelengths at 480/500 nm for SYTO-9 stain, 490/635 nm for PI and 405/433 nm for Calcofluor, as recommended by the manufacturers.
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
The OCT imaging was performed to visualize the effect of each treatment on the biofilm structure. For this, after treatments, the Cur was removed, biofilms were carefully washed twice with saline solution and, then, samples were observed in the OCT equipment (ThorLabs, Model Tel300, Telesto series, Probe.uni, nominal center length of 1310 nm). Images were obtained with medium sensitivity, speed of 76 kHz, with field image correction, subsampling filter, scanning pattern of 400 x 400 x 512 pixels (X, Y, Z) and pixel size of 5 x 5 x 2.49 μm (X, Y, Z). Transversal images of the biofilms were obtained to evaluate the cell density, thickness and topography of the biofilm.
Reactive oxygen species generation
To evaluate the production of oxygen singlet species and hydroxyl radicals by SDT, PDT and SPDT mediated by Curcumin, it was used the fluorescent probes APF (Hydroxyl Radical, Hypochlorite or Peroxynitrite Sensor, which exhibits bright green fluorescence, excitation/ emission maxima ∼490/515 nm), and SOSG (Singlet Oxygen Sensor Green Reagent, that in the presence of singlet oxygen, it emits a green fluorescence, excitation/emission maxima ~504/525 nm), both from Thermo Fisher. The stock solution of each probe was diluted in phosphate buffer according to the manufacturer's instructions at the final concentration of 3 μM. The treatments were applied at the presence of the probes, individually. Control groups consisted of the US, light, US+light and Cur only. The fluorescence was measured at the Cary Eclipse Fluorescence spectrophotometer at the appropriated wavelength for each probe.
Curcumin degradation over treatments
To evaluate the Cur degradation over each treatment, the absorbance spectrum of Cur was monitored in spectrophotometer (Varian Cary® 50 UV-Vis Spectrophotometer - Agilent, Santa Clara, California, USA). For this, the Curcumin was prepared at the concentration of 32 μM in DMSO and it was exposed to the sources of each treatment: light (aPDT), US (SDT) and light+US (SPDT), and the absorbance spectrum was obtained every 5 min of exposition, until 30 min.
Statistical analyses
The CFU/mL values were transformed into log10 and the homogeneity of variance and normality of the data were verified by the Levene and Shapiro–Wilk tests, respectively. Data was analyzed statistically by one-way analysis of variance (one-way ANOVA) and, for multiple comparisons, the post-hoc Tukey test was applied (α = 0.05). These analyses were performed using a SPSS software package (IBM® SPSS® Statistics, version 20, Chicago, IL, USA).
Results and discussion
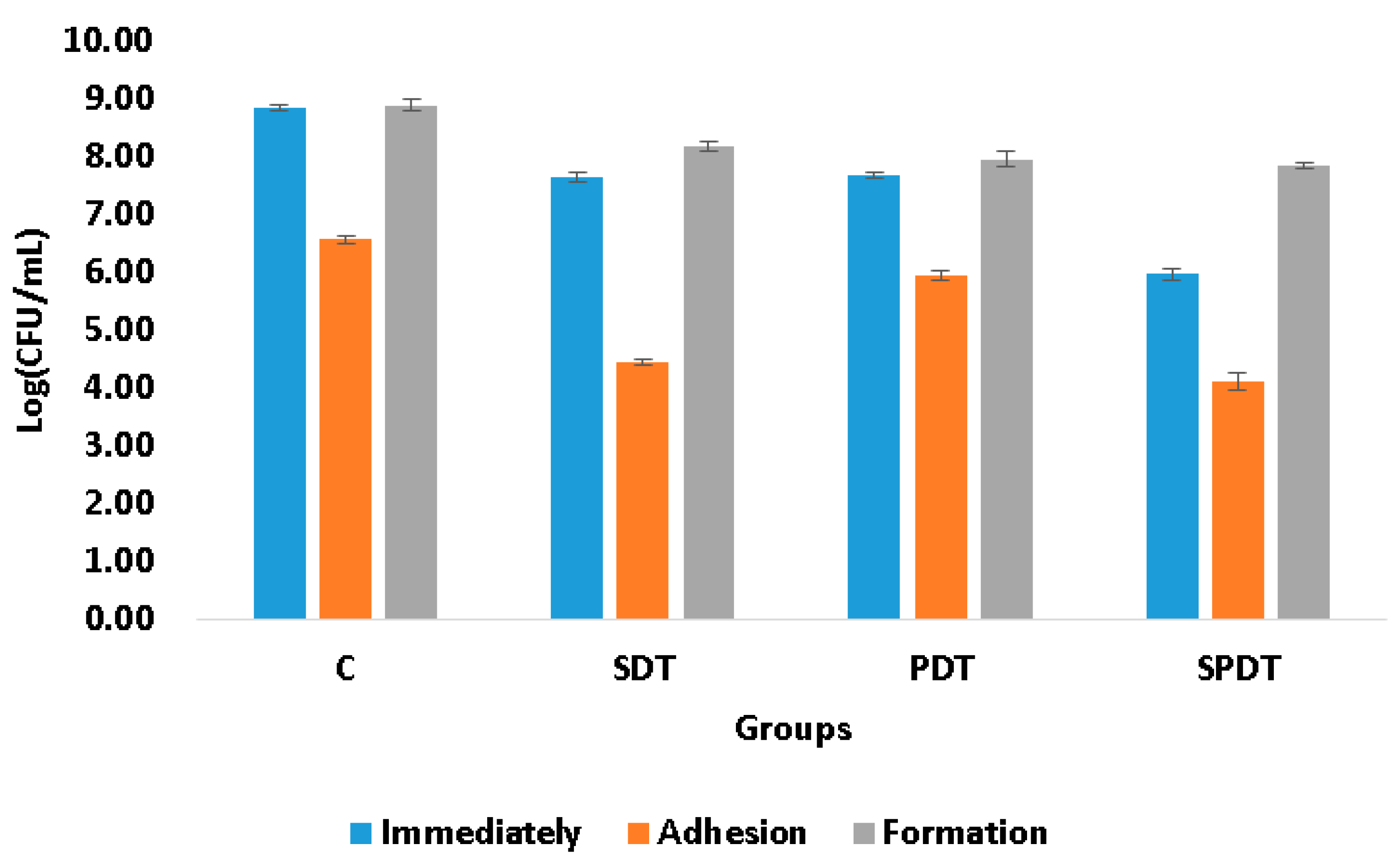
The adhesion ability of the microorganisms to biotic or abiotic surfaces, such as mucosa, ulcer, prostheses, dental implants, catheters; is of great importance, since it is the first step of the free cells to form the biofilm community and, consequently, establish a successful microbial community, and infection. The complexity of the bacterial tools used for cell adhesion and invasion ranges from single monomeric proteins to intricate multimeric macromolecules that perform highly sophisticated functions. The surface organelles and toxins secreted allow the pathogenic bacteria to invade many different niches throughout the course of an infection. In the present study the effect of PDT, SDT and SPDT on the ability of the bacteria to attach (adhere) to an abiotic surface was evaluated. According to the viability assay (CFU/mL), it was observed that the sub-lethal dose of the treatments were able to decrease the adhesion ability of
S. aureus (
Figure 1). Analyzing the treatments individually, from the survived cells of the SPDT group, 58% of the bacteria were able to adhere to the polystyrene plate, so 42% of the surviving cells were not able to attach to the surface. For the SDT group, also 58% of the bacteria had capacity for adherence. In the PDT group, 71% of the bacteria attached to the plate surface. In the control group (that did not receive any treatment), 21% of the cells were not able to adhere to the polystyrene plate. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study that evaluated the action of SDT and SPDT on the adhesion ability, other studies investigated only the PDT effects. The work of Xin Li et al. evaluated the effects of toluidine blue O (TBO)-mediated photodynamic therapy on
Staphylococcus epidermidis adherence and biofilm formation, using confocal laser scanning microscopy. The results of the adhesion assay indicated that the control groups exhibited significant bacterial adherence compared with the TBO-PDT groups. Analysis of the biofilm formation revealed significant light dose-dependent differences between the TBO-PDT groups and the control groups [
15]. Alves et al. evaluated the interference of PDT mediated by Photodithazine on the adhesion ability of
Candida albicans biofilm. Authors did not verify significant difference in the capacity for adhesion between the cells treated with PDT in comparison with the other groups [
16]. Soares et al., who evaluated the effect of PDT mediated by TBO on the capacity of adhesion of
Candida species to bucco-epithelial cells (BECs), they observed that the greater the effectiveness of PDT against the
Candida species, the greater was the reduction in adhesion of the yeast to BECs [
17].
The biofilm formation ability of some bacteria species is also considered a pathogenicity factor and resistance mechanism that protects the microorganisms of physical, chemical and environmental stress. A biofilm is an organized aggregate of microorganisms living within a self-produced ECM. The ECM is mainly composed of polysaccharides, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids (RNA and extracellular DNA), which form a highly hydrated polar mixture that contributes to the overall scaffold and three-dimensional structure of a biofilm. The biofilm is considered to be one of the most successful modes of life on the Earth, and the most prevalent microbial lifestyle in natural environments. Further studies have also shown that 70-75% of the human infections are related to microorganisms organized as biofilm, being this living-form more resistant to the treatments than the planktonic counterpart [
2]. In the present study, the biofilm formation ability was evaluated after the treatments. For this, the cells that survived to the treatments were re-submitted to the biofilm formation steps and, after 48 h of maturation, the viability assay was performed to quantify the cells in the biofilm. It was observed that none of the therapies were able to alter the biofilm formation ability, since the number of the living cells collected immediately after the treatments were also obtained after 48 h of biofilm formation (
Figure 1), following the same pattern of the control group. In the literature, the biofilm ability was only evaluated after PDT and the results obtained depend on the target microorganism and the PS/light used. Carmello et al. showed that the PDT mediated by chloro-aluminum phthalocyanine encapsulated in cationic nanoemulsion was capable to reduce the biofilm ability of
Candida albicans present on oral candidosis of mice [
18]. In another study,
Candida krusei also exhibited reduction in this virulence factor after being treat by PDT mediated by toluidine blue [
19]. Moreover, PDT mediated by methylene blue reduced the biofilm formation ability of
Serratia marcescens. Finally, sub-lethal doses of PDT mediated by TBO, methylene blue and indocyanine green affected biofilm formation ability and metabolic activity of
Enterococcus faecalis [
20]. However, Alves et al., demonstrated that PDT mediated by Photodithazine did not alter the adherence and biofilm formation ability of fluconazole-susceptible and fluconazole-resistant
C. albicans [
16].
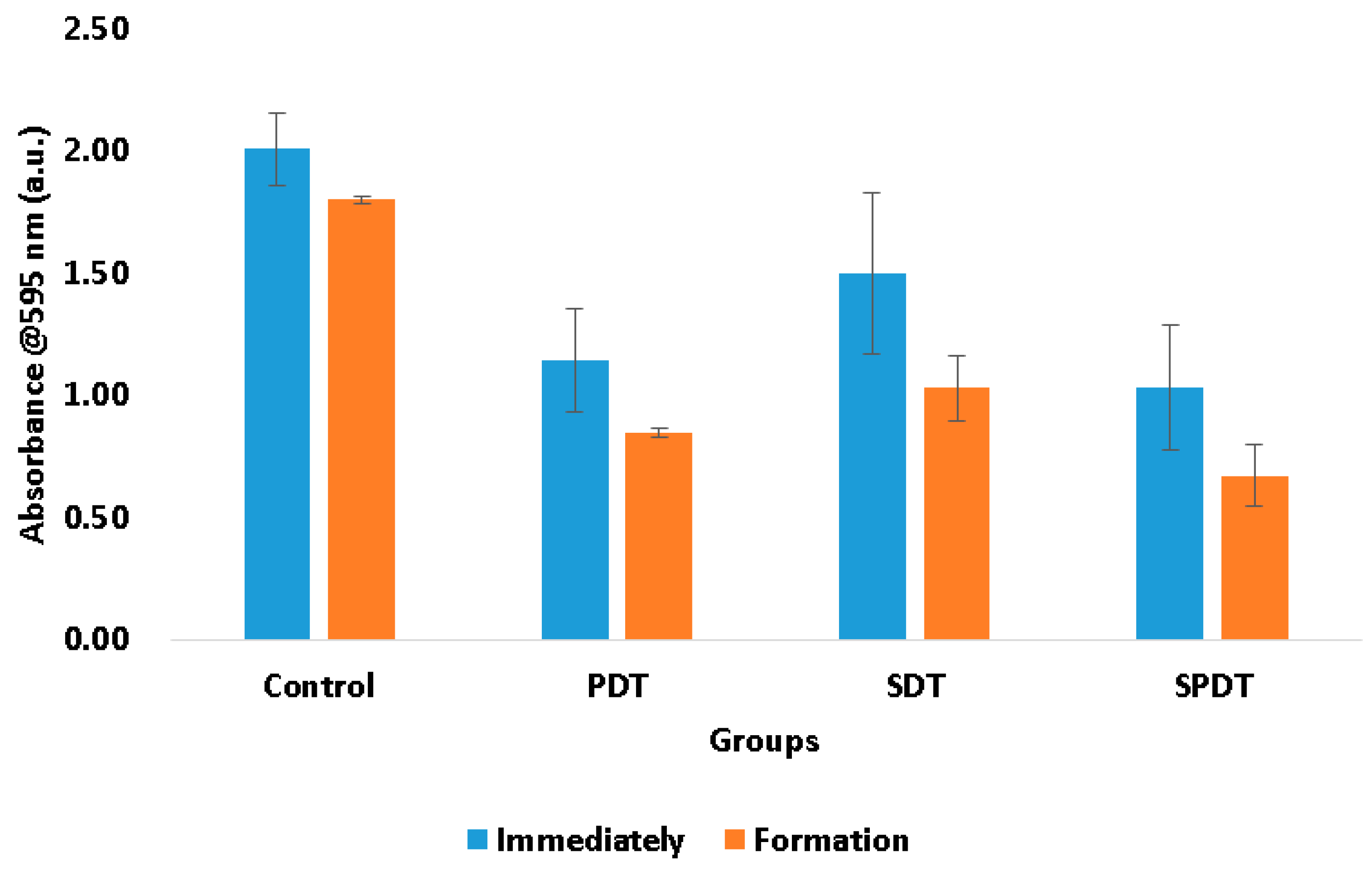
The total biomass of the biofilms at the end of the therapies and after 48 h of biofilm formation were also evaluated by means of crystal violet assay. This measurement represents both bacteria cells and the ECM involving them. In this test, it was observed that the treatments were able to reduce the biomass immediately after in comparison with the control group. The PDT samples exhibited a reduction of the total biomass equivalent to 42.96%, the SDT group 25.36% and the SPDT group 48.73% in comparison with the control group (
Figure 2). After the treatments, the survived cells were re-submitted to the biofilm formation steps and the total biomass was once again evaluated. It was observed that all groups (including the control group) demonstrated a reduction in the total biomass in comparison with those values obtained at the “immediately” period of evaluation (
Figure 2). The control group showed a total biomass 10.39% lower than that found at the immediately period. The PDT group demonstrated a reduction of 26.16%, the SDT 31.31% and the SPDT group 34.92% of the total biomass in comparison with the immediately period of evaluation of each group (
Figure 2). With these results is possible to conclude that PDT, SDT and SPDT treatments were capable to reduce the biomass and the biofilm formed by the survivor cells was thinner. This means that the treatments changed significantly the biofilm characteristics, mainly the SPDT group. Taking the CFU/mL assay in account, it is possible to correlate the total biomass results with those found in the viability test. The CFU/mL assay showed no change in the values in the biofilm formed after the treatments, however, the total biomass was reduced, for this reason, it is possible to conclude that the reduction in the crystal violet measurement was mainly in the extracellular matrix of the biofilm. This is an important result, since a thinner biofilm with lesser amount of ECM involving the cells turns the bacteria more susceptible to a next antimicrobial therapy.
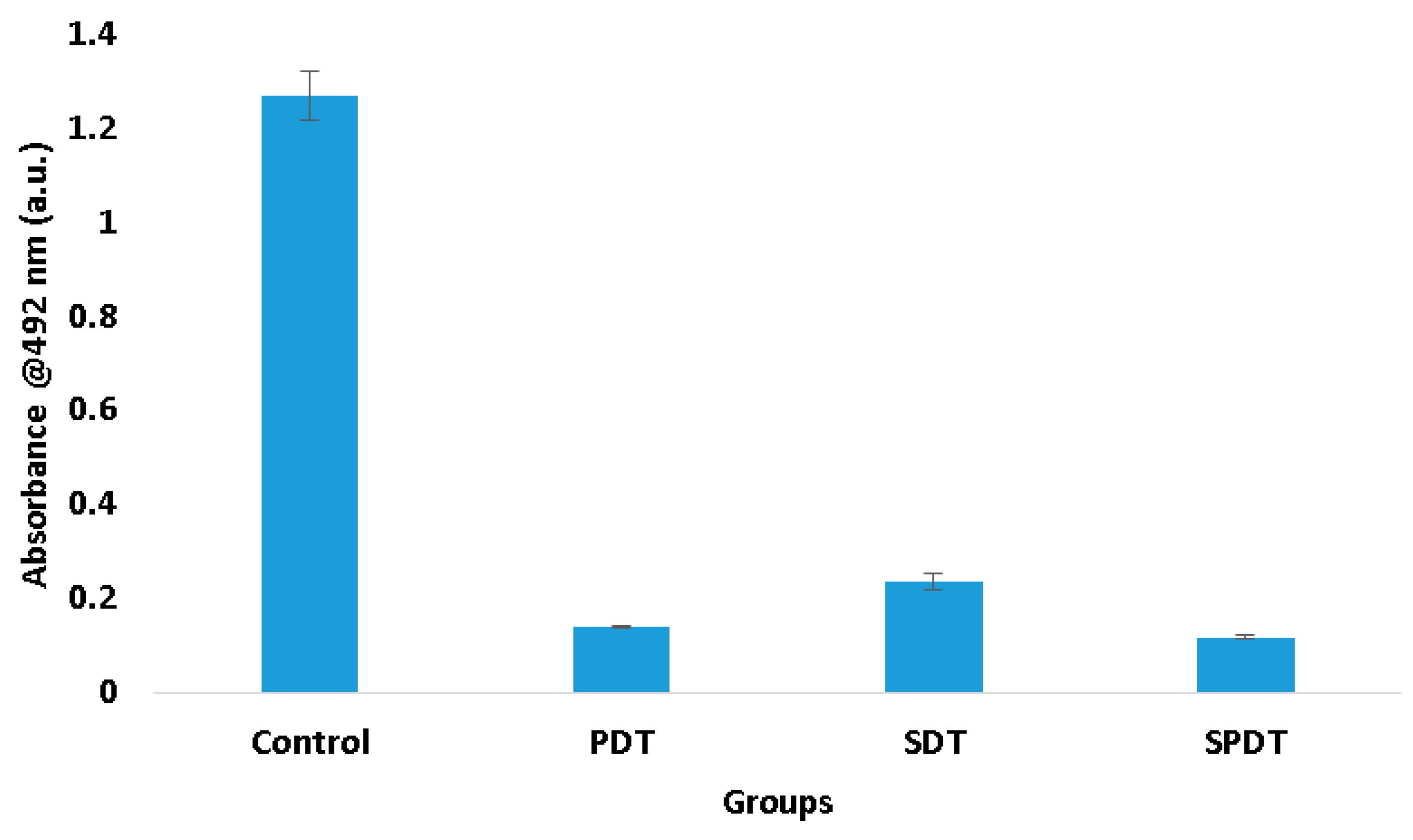
Trying to understand these results of viability and total biomass of the biofilm, it was performed the XTT assay, which evaluates the metabolic activity of the cells. According to the results obtained, it was observed that the three therapies reduced expressively the cell metabolism. The PDT group exhibited a metabolic activity 88.66% lower than the control group, while SDT and SPDT showed 81.71% and 90.48%, respectively (
Figure 3). This reduction influences totally in the biofilm development.
Staphylococcal biofilm development is a complex process that is divided in phases, such as, initial attachment, production of extracellular matrix, cell proliferation, biofilm structuring and cell detachment. In all these steps there are many biological events, such as gene expression, enzyme production and secretion, cell multiplication (grow and division) and cell detachment. All these cell events are dependent on the cell metabolism status. For this reason, cells with low metabolism have a deficient biofilm development. The results of the present study demonstrated that the therapies reduced the metabolism and it is possible to conclude that the biofilm development was hindered, explaining the reduction in the total biomass.
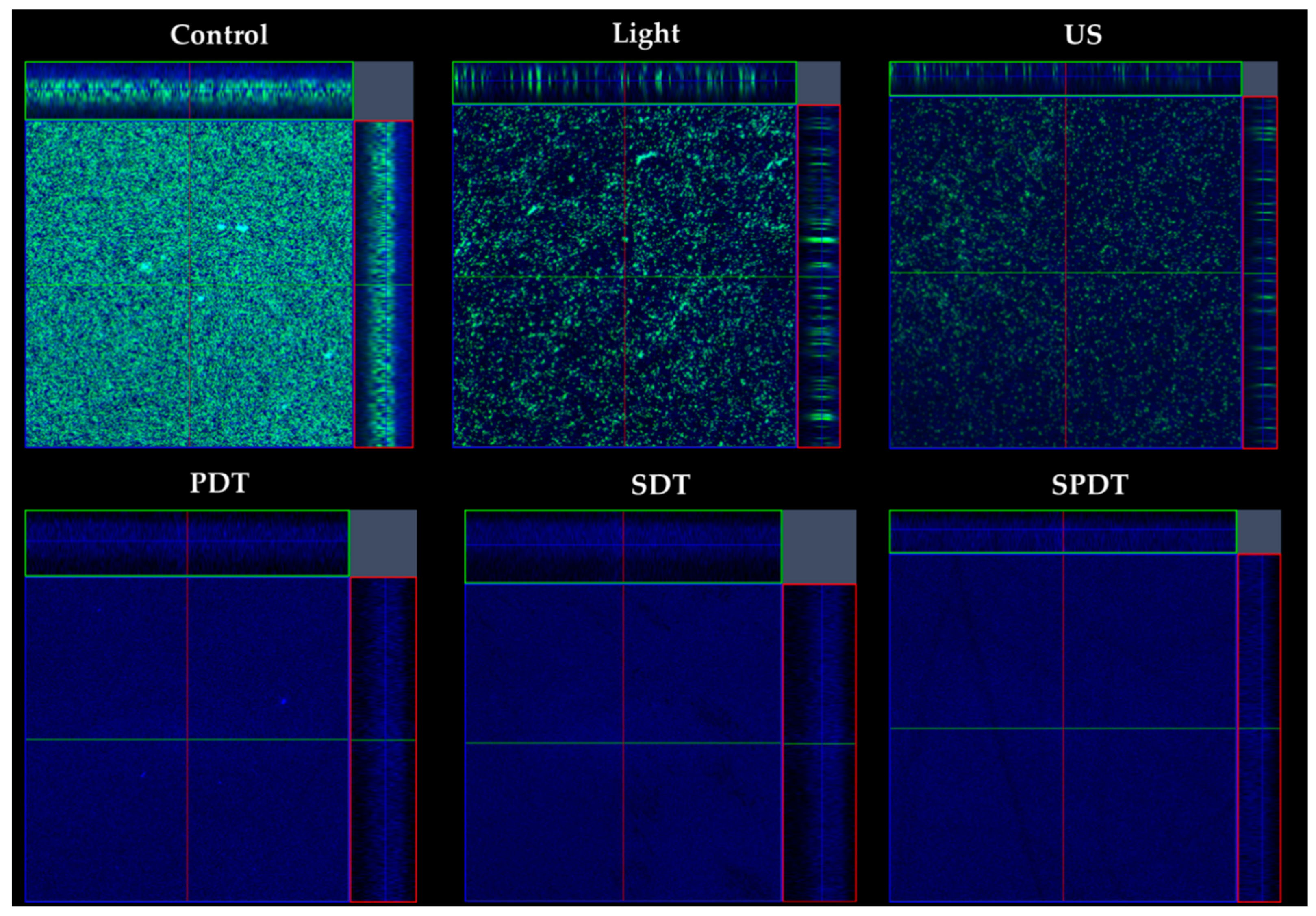
The effects of the treatments on the biofilm components were evaluated under confocal microscopy, where live/dead cells and the ECM were stained after treatments (
Figure 4). According to the images obtained, all treatments caused a high impact on the bacteria cells, where no live or dead cells were detected. Moreover, there was a reduction in the amount of ECM of all treated groups (PDT, SDT and SPDT), when compared with the control group. Regarding the effects of light or ultrasound alone (without Cur), a slighter effect of these sources on the cells and ECM amount was observed, however, a lesser populated biofilm with some defects were observed. Finally, the control group was full of live cells embedded in the ECM, covering all the analyzed area. These results all together show the ability of the dynamic process involved in the treatments (PDT, SDT and SPDT) to cause a significant impact on the biofilm components, reducing the cells and ECM. Additionally, the biofilm structure was assessed by OCT (
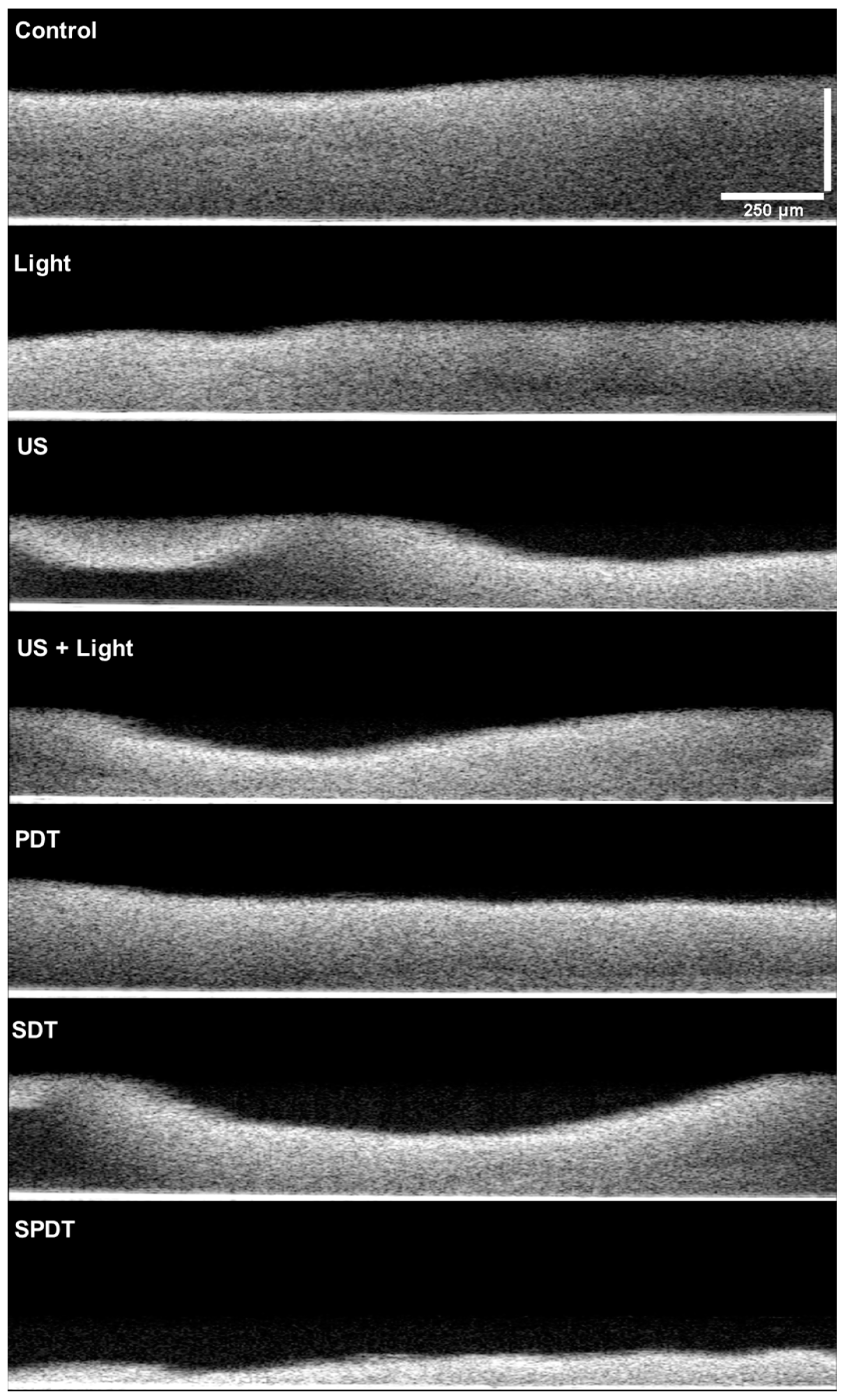
Figure 5). This assay revealed that PDT and Light groups showed very similar characteristics between each other, such as density, topography and exhibited a slighter reduction in the thickness compared to the control. The US, US + light and SDT groups exhibited a more expressive alteration, with lower thickness compared to the control, defects on the topography and some regions with lower biomass density. However, the most impacted biofilm was the SPDT group, where a destructive effect on the structure of the biofilm was observed and a thin layer of biomass was imaged.
These results evidence the mechanical action of the ultrasound on the biofilm by itself, where the US, US + Light and SDT groups exhibited structural alterations, and this effect was extremely enhanced when the three components (sensitizer, ultrasound and light) were applied together (SDPT group). The mechanical effect of US is governed by the dynamic phenomenon called cavitation, where microbubbles with high energy interact with the media [
8]. Depending on the US intensity, cavitation occurs in a different way, being divided in non-inertial cavitation (also known as stable cavitation) and inertial cavitation. The non-inertial cavitation occurs when a low-intensity ultrasound is applied in a liquid media, characterized by the production of bubbles with high energy, that do not firmly collapse and are able to generate radiation force, microstreaming and pull-push. The inertial cavitation bubbles absorb high quantities of energy and release it in a small area, which increases the local temperature and pressure, there is the formation of free radicals, the appearance of strong shock waves and high-speed micro-jets in the media [
8]. All these events interact with the structures that are closed to them, such as the cells and the ECM, being able to cause transient or permanent structural alterations. An advantage of using the US to mediate the treatments is that its mechanical effects are nonspecific, and could be applied for gram-positive or gram-negative bacteria, fungi, susceptible or resistant microorganisms and even to cause severe alterations in biofilms, as demonstrated in the present study.
In the present work the production of oxygen singlet species and hydroxyl radicals by each treatment were also evaluated by the use of fluorescent probes (SOSG and APF, respectively) in the attempt to correlate the inactivation with the ROS production. The production of the reactive oxygen species by PDT, SDT and SPDT were dependent on the source of irradiation. In the groups where the US was applied, there was a predominance of hydroxyl radicals, on the other hand, when the light was used, the production of oxygen singlet species was observed (
Table 1). These results showed that Curcumin reacts differently over the ultrasound and light. Probably, when the ultrasound is applied there is a preference in the type I reaction, so the PS in the T
1 can transfer a proton or an electron to the substrate to form a radical anion or radical cation; these radicals may react with oxygen to produce ROS. On the opposite side, when the light is used, it facilitates the type 2 reaction, then the PS in the T
1 can directly transfer energy to molecular oxygen (a triplet in the ground state) producing the excited state singlet oxygen (
1O
2). It is important to emphasize that the SPDT group generated both singlet oxygen and hydroxyl radicals. Another point that is important to highlight is the fact that, when the US or light were used solely (in the absence of the Cur) but in the presence of the probes, there was a high production of hydroxyl radicals (by the US) and singlet oxygen (by the light), even more than in the treatment groups (PDT, SDT and SPDT). It may be explained by the anti-oxidant property of the Cur that is well known. Besides that, there is a limitation in the use of fluorescent probes to measure reactive oxygen species together with the ultrasound. Depending on the ultrasound parameters (frequency, intensity), it may cause chemical reactions in the molecules present in the media, called sonochemistry. When the media is exposed to the ultrasound waves, microbubbles are formed, catastrophically implode, and then may interact with the molecules surrounding them, such as the Curcumin or the probe, leading to the production of ROS. For this reason, the results obtained in the groups where the ultrasound was applied must be carefully analyzed, since the use of indirect techniques to measure reactive oxygen species have their limitations. The work performed by Pourhajibagher et al., a nanomicelle curcumin was used for sonodynamic therapy against
Streptococcus mutans, and the ROS production was measured by the fluorescent probe 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescein diacetate (H2DCFDA). Authors observed a considerably enhanced ROS generation in the SDT group compared to the control group [
21], however, this probe is not specific for any kind of ROS. For this reason, authors concluded that one of the mechanisms involved in the bacteria inactivation was the ROS production.
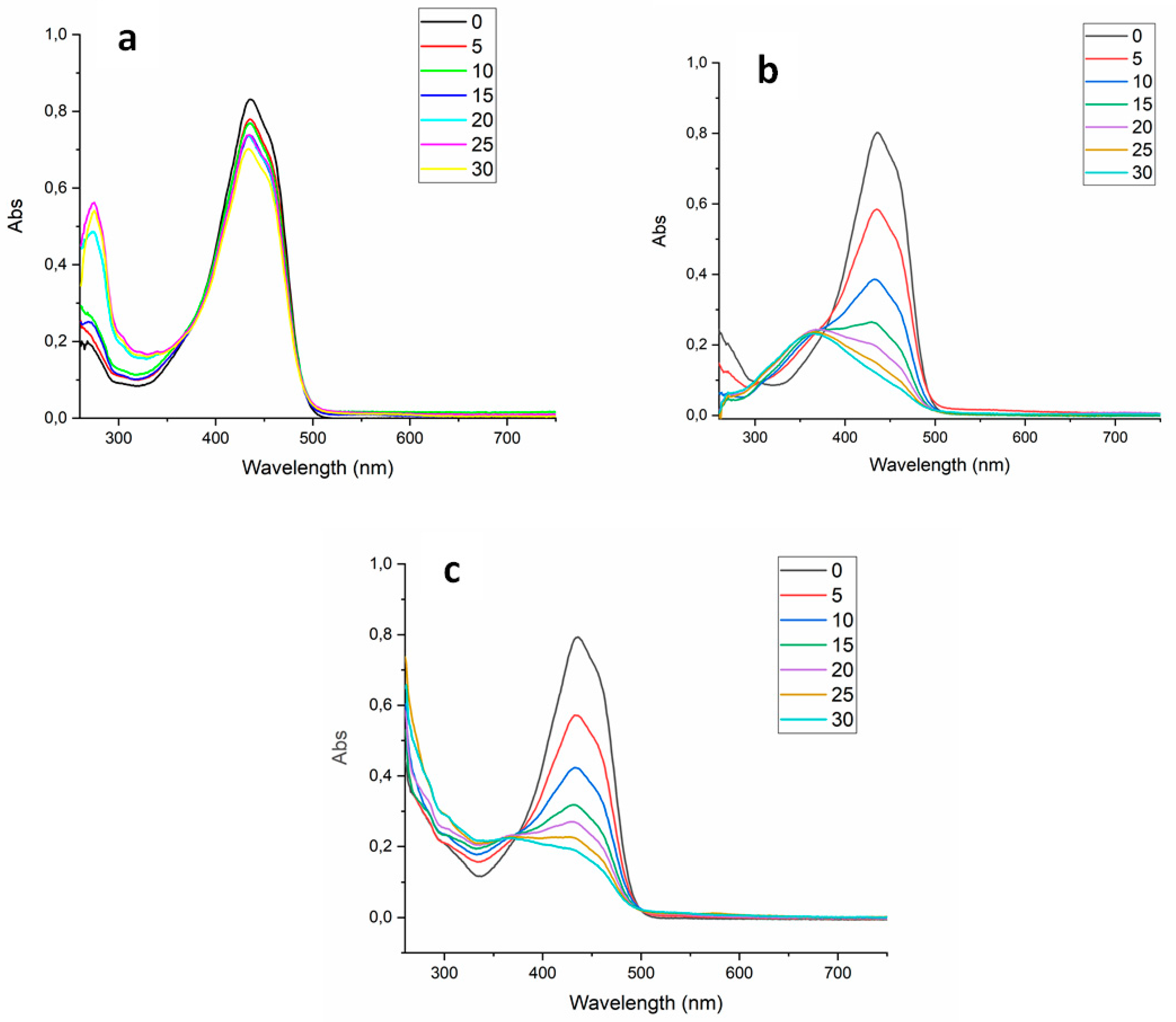
Finally, the absorbance spectrum of the Cur was collected every 5 min during the treatments to verify the PS degradation over each source (light, US and light+US) until 30 min (
Figure 6). The curcumin working solution exhibited absorption maximum around 435 nm and a small shoulder at 460 nm. After light irradiation (PDT and SPDT), the curcumin absorbance decayed significantly at 435 nm. However, a slight decay was observed in the SDT group, demonstrating that the degradation of the curcumin by the US at the parameters used was not expressive as that caused by the light. Additionally, during ultrasound irradiation (SDT and SPDT groups), the absorbance at 250 nm increased with exposure time and this process did not occur during PDT, for this reason, it was considered a sono-product formed during sonication. The ability of the ultrasound to degrade a sensitizer may be related to the sensitizer characteristic (concentration, solvent, molecule), however, the US parameters (intensity, duty cycle and frequency) also influence on it. Ponce et al. perfomed a comprehensive study in sono-photo degradation of the Protoporphyrin IX (PpIX), where a range of light/US intensities and PpIX concentrations where tested and the PS degradation was monitored. Authors verified that PpIX molecules were degraded by US, light and US+light and this process was intensified by increasing the intensity of the excitation sources. Also, the absorption spectra revealed that the PpIX decay rate induced by US+light (combined irradiation) was approximately the sum of those induced by photodynamic and sonodynamic activity. Additionally, authors also observed a sono-product at the region of 250 nm, as the same way as observed in the present work [
22]. Future works should consider to comprehensively evaluate a range of curcumin concentrations, light doses and US intensities to better understand the sonophotochemistry behind SPDT.
Figure 1.
Mean log(CFU/mL) values and standard deviation of the control (C), SDT, PDT and SPDT groups at the different periods of evaluation (immediately after the treatments, after adhesion and post biofilm formation).
Figure 1.
Mean log(CFU/mL) values and standard deviation of the control (C), SDT, PDT and SPDT groups at the different periods of evaluation (immediately after the treatments, after adhesion and post biofilm formation).
Figure 2.
Mean values and standard deviation of the total biomass from the control, SDT, PDT and SPDT groups at the different periods of evaluation (immediately after the treatments and post biofilm formation).
Figure 2.
Mean values and standard deviation of the total biomass from the control, SDT, PDT and SPDT groups at the different periods of evaluation (immediately after the treatments and post biofilm formation).
Figure 3.
Mean values and standard deviation of the metabolic activity from the control, SDT, PDT and SPDT groups immediately after the treatments.
Figure 3.
Mean values and standard deviation of the metabolic activity from the control, SDT, PDT and SPDT groups immediately after the treatments.
Figure 4.
Confocal images obtained of the biofilms from the control, light, US, PDT, SDT and SPDT groups. Biofilms were stained with LIVE/DEAD (SYTO 9 and Propidium Iodide), which mark viable (green color) and nonviable cells (red color). The ECM was stained with Calcofluor White (blue color). The stained biofilms were imaged, using as excitation/emission wavelengths at 480/500 nm for SYTO-9 stain, 490/635 nm for PI and 405/433 nm for Calcofluor, as recommended by the manufacturers.
Figure 4.
Confocal images obtained of the biofilms from the control, light, US, PDT, SDT and SPDT groups. Biofilms were stained with LIVE/DEAD (SYTO 9 and Propidium Iodide), which mark viable (green color) and nonviable cells (red color). The ECM was stained with Calcofluor White (blue color). The stained biofilms were imaged, using as excitation/emission wavelengths at 480/500 nm for SYTO-9 stain, 490/635 nm for PI and 405/433 nm for Calcofluor, as recommended by the manufacturers.
Figure 5.
OCT images obtained from the Control, light US, US+Light, PDT, SDT and SPDT groups. Images were obtained with medium sensitivity, speed of 76 kHz, with field image correction, subsampling filter, scanning pattern of 400 x 400 x 512 pixels (X, Y, Z) and pixel size of 5 x 5 x 2.49 μm (X, Y, Z). Transversal images of the biofilms were obtained to evaluate the cell density, thickness and topography of the biofilm.
Figure 5.
OCT images obtained from the Control, light US, US+Light, PDT, SDT and SPDT groups. Images were obtained with medium sensitivity, speed of 76 kHz, with field image correction, subsampling filter, scanning pattern of 400 x 400 x 512 pixels (X, Y, Z) and pixel size of 5 x 5 x 2.49 μm (X, Y, Z). Transversal images of the biofilms were obtained to evaluate the cell density, thickness and topography of the biofilm.
Figure 6.
UV-VIS absorbance spectrum of the curcumin over different sources used in the treatments (SDT - a, PDT - b, SPDT - c), measured every 5 minutes until 30 minutes.
Figure 6.
UV-VIS absorbance spectrum of the curcumin over different sources used in the treatments (SDT - a, PDT - b, SPDT - c), measured every 5 minutes until 30 minutes.
Table 1.
Mean values of the fluorescence intensities of the test groups immediately after the treatments, equivalent to the production of the hydroxyl radicals (APF probe, 515 nm) and singlet oxygen species (SOSG probe, 525 nm).
Table 1.
Mean values of the fluorescence intensities of the test groups immediately after the treatments, equivalent to the production of the hydroxyl radicals (APF probe, 515 nm) and singlet oxygen species (SOSG probe, 525 nm).
| |
Probe |
Cur |
Light |
US |
PDT |
SDT |
SPDT |
Hydroxyl Radicals
(APF – 515 nm)
|
2.09E+04 |
3.71E+03 |
8.30E+03 |
1.58E+05 |
3.58E+04 |
7.18E+04 |
4.22E+04 |
Singlet Oxygen Species
(SOSG – 525 nm)
|
4.86E+03 |
3.29E+04 |
6.53E+05 |
9.68E+04 |
4.56E+05 |
3.67E+04 |
4.28E+05 |