1. Introduction
The rabbit is a widely accepted translational animal model used in a growing number of experimental orthopedic surgical interventions for humans. It is considered optimal for translational investigations, given the numerous pathophysiological similarities between humans and rabbits [1]. Effective multimodal analgesia regimens are required to maximize animal welfare and reproducibility of the performed investigations [2].
Locoregional anesthesia techniques are widely used to allow effective perioperative pain management in humans and animals, both in clinical and experimental settings. In humans, the incorporation of locoregional anesthesia techniques in balanced anesthetic protocols has been shown to promote better perioperative outcomes, reduced opioid consumption, morbidity, mortality, hospitalization time and avoid the neediness for general anesthesia and intubation [3,4]. Similarly, animals benefit from locoregional anesthesia techniques [5,6].
In veterinary medicine, the neuraxial administration of local anesthetics and or opioids is a common method for regional anesthesia and analgesia at the hind limb during orthopedic surgery. Although this administration promotes clinically effective locoregional anesthesia, in some circumstances, side effects from neuraxial injection such as urinary retention, hypotension, contralateral pelvic limb paralysis may discourage the use of neuraxial techniques during pelvic limb procedures. Compared to neuraxial analgesia techniques, a PNB bypasses the mentioned side-effects and allows a more selective blockade, promoting a comfortable recovery phase while the animal can still be ambulatory on 3 limbs during the early postoperative period. In dogs undergoing pelvic limb orthopedic procedures, locoregional anesthesia using femoral nerve (FN) and sciatic nerve (ScN) PNBs has been associated with improved quality of recovery and reduced perioperative levels of biomarkers indicating stress, i.e., cortisol and glycemia [7].
Local anesthetics injected into the interfascial space containing the target nerve or nerve bundle lead to an interruption of the transduction in peripheral nerves resulting in analgesia in a specific area of the body. These techniques are used for pre-emptive and multimodal pain control, e.g., to alleviate peri- and postoperative pain in both humans and animals [8,9] providing cost-effective analgesia and minimization of considerable adverse effects even in rabbits [10,11]. However, compared to dogs and cats [12-14], studies on peripheral nerve blocks (PNBs) in rabbits are scarce.
The sciatic and the femoral nerves are the main nerves of the hind limb. A peripheral block of the sciatic and the femoral nerves leads to desensitization of the pelvic limb distal to the mid-femur. Therefore, the technique is popular in human and small animal medicine [8,15]. Sonographic guidance is the state-of-the-art method to perform such locoregional anesthesia techniques [16]. With the introduction of this technique to perform PNBs the success rate has increased. Moreover, onset of the block as well as duration of action have been increased while the quantity of local anesthetic (LA) could be reduced. This allowed a reduction of the risk for LA-induced intoxication [17-21].
To date, no ultrasound-guided technique to block the femoral and sciatic nerve has been described in rabbits. In contrast, many techniques to block the same nerves have been described in dogs and cats.
Aim of the study was to describe a technique to block the femoral and the sciatic nerves in rabbits under sonographic guidance. According to our hypothesis, the technique of the ultrasound guided injection to/at the sciatic and femoral nerves performed in dogs and cats can be extrapolated to the rabbit due to anatomical similarities of the hindlimb innervation.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Design
The study was designed as a prospective, experimental, descriptive study divided into two phases. In the first phase, explorative ultrasonographic scans and a gross anatomical dissection of the ScN and FN were performed in 2 fresh cadavers (4 limbs) of female New Zealand White rabbits (90-120 days of age; 3 and 3,1 kg). In the second phase, an US-guided perineural injection to the ScN and FNs with a 1:1 solution of one methylene blue (MethyleneBlue1%w/vaq.soln, AlfaAesar, Thermo FischerGmbH, Germany) and lidocaine (Xylanest purum 2%, Gebro Pharm GmbH, Austria) (L-NMB) was performed in 10 fresh cadavers (20 limbs) of New Zealand White rabbits (90-120 days of age; median body weight of 3,1 kg (range 2,9–3,4). All rabbits had been obtained from a non-survival study (BMBWF-66.009/0281-V/3b/2018) unrelated to this project. The lumbosacral area and the pelvic limbs had remained intact when they had been humanely euthanized at the end of this study.
2.2. Phase 1: Explorative ultrasonographic scans and anatomical study.
Prior to sonographic evaluation of the nerves the animals were clipped. To scan the ScN the animal was placed in lateral recumbency. The greater trochanter of the femur and the sciatic tuber of the pelvis were palpated. Then the transducer was placed in transverse position distal to these two anatomical landmarks. Once the sciatic nerve was identified, it was scanned in distal direction until it separated into two branches (tibial and fibular branch). Prior to sonographic evaluation of the FN, the animals were placed in dorsal recumbency with the leg extended caudally. To scan the FN, the transducer was placed over the hypaxial muscles at the level of the projection of the iliac crest and moved in caudal direction until the FN could be clearly detected in the substance of the iliopsoas muscle (IPM). Then the trace of the FN inside the IPM was followed until it left the IPM to enter the leg. The ideal windows to approach both nerves were determined, and regional anatomy was examined by gross- anatomical dissection as described in dogs. The structures (nerves, muscles, bones) were compared with the structures previously identified by ultrasound, and landmarks for transducer placement were determined.
2.3. Phase 2: Ultrasound-guided sciatic and femoral nerve injection
In this phase, 10 fresh rabbit cadavers (20 limbs) were included.
2.3.1. Sciatic nerve injection
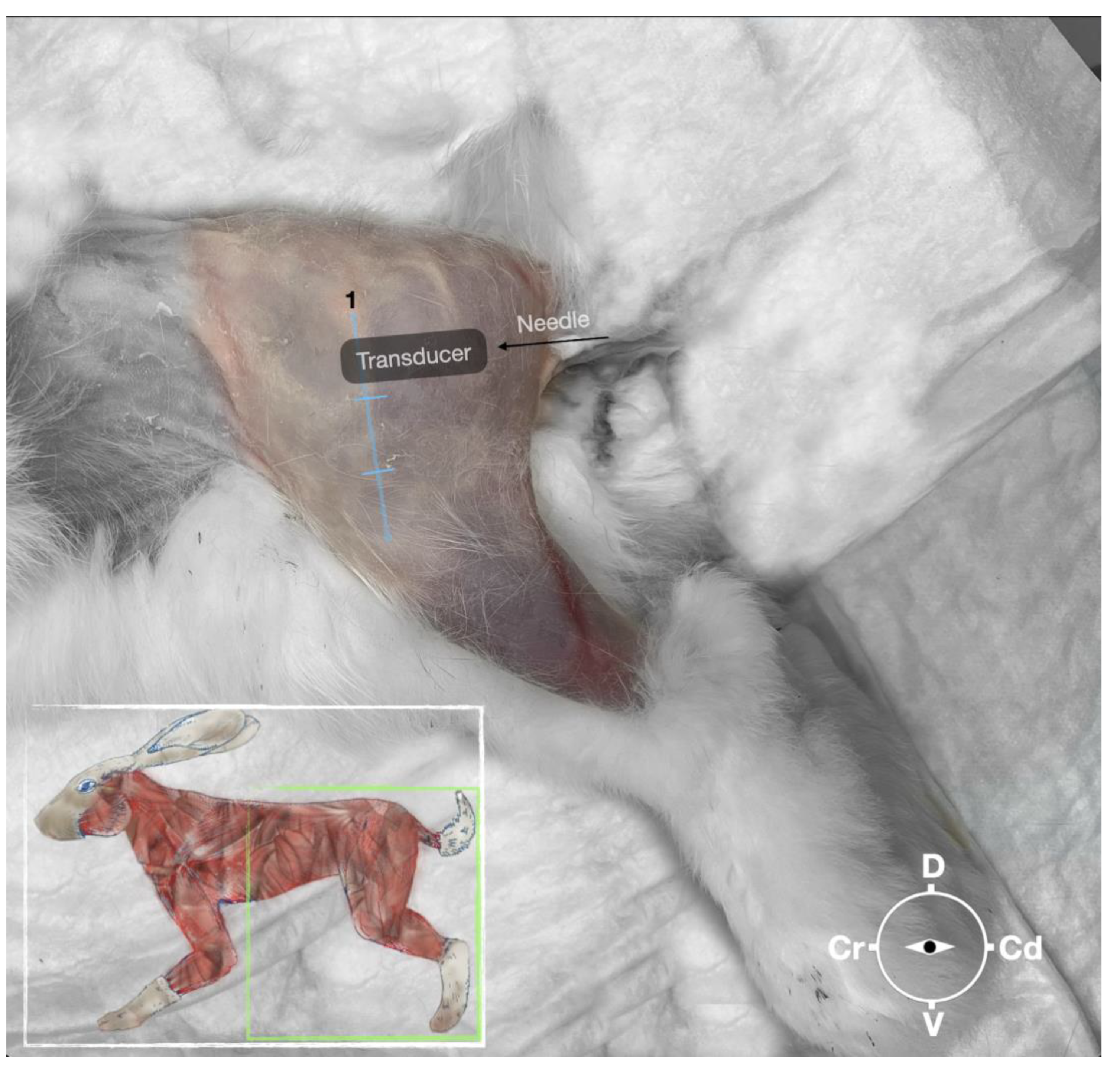
First, the cadaver was positioned in lateral recumbency. Then, the area of interest was clipped, and the hair was removed. A 18-4 MHz linear transducer (L 18-4,Konica Minolta, USA) attached to an ultrasound machine (HS1, Konica Minolta, USA) was used and ultrasound gel (Softa-Man, ViscoRub, B. Braun, Austria) was applied to facilitate acoustic coupling. The transducer was placed in transverse position, at the level of the proximal third of the femur but caudal to the bone with a window of interest set at a depth of 3 cm to optimize the image. Then, the transducer was slightly rotated clock or anticlockwise to obtain a transverse image of the sciatic nerve (
Figure 1). A 50 mm 22 gauge insulated needle (Sonoplex Stim Cannula, Pajunk Medical Produkte GmbH, Germany) prefilled with a 1:1 solution of new methylene blue (MethyleneBlue1%w/vaq.soln, AlfaAesar, Thermo FischerGmbH, Germany) and lidocaine (Xylanest purum 2%, Gebro Pharm GmbH, Austria) (L-NMB) was inserted using an in-plane approach. The needle was inserted at the caudal end of the transducer and advanced in-plane under sonographic guidance through the biceps femoris muscle in a cranio-medial direction towards the sciatic nerve (
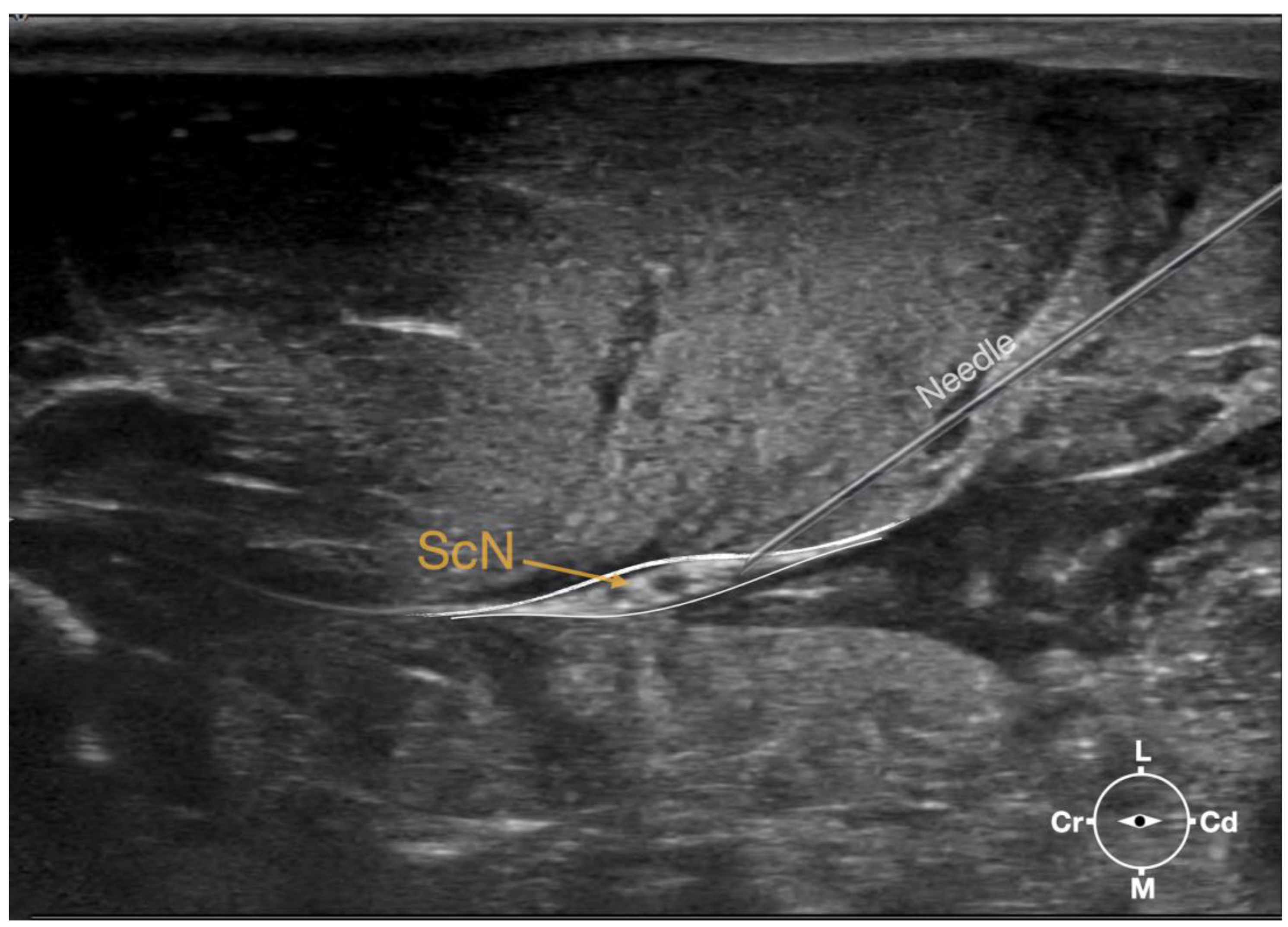
Figure 2). The needle was advanced until its tip punctured the muscular fascia enveloping the sciatic nerve (
Figure 3). A test volume of 0.05 ml of L-NMB was injected to confirm adequate distribution inside the interfascial space that contained the sciatic nerve. The remaining volume of 0.15ml/kg was then injected perineurally around the sciatic nerve.
2.3.2. Femoral nerve injection
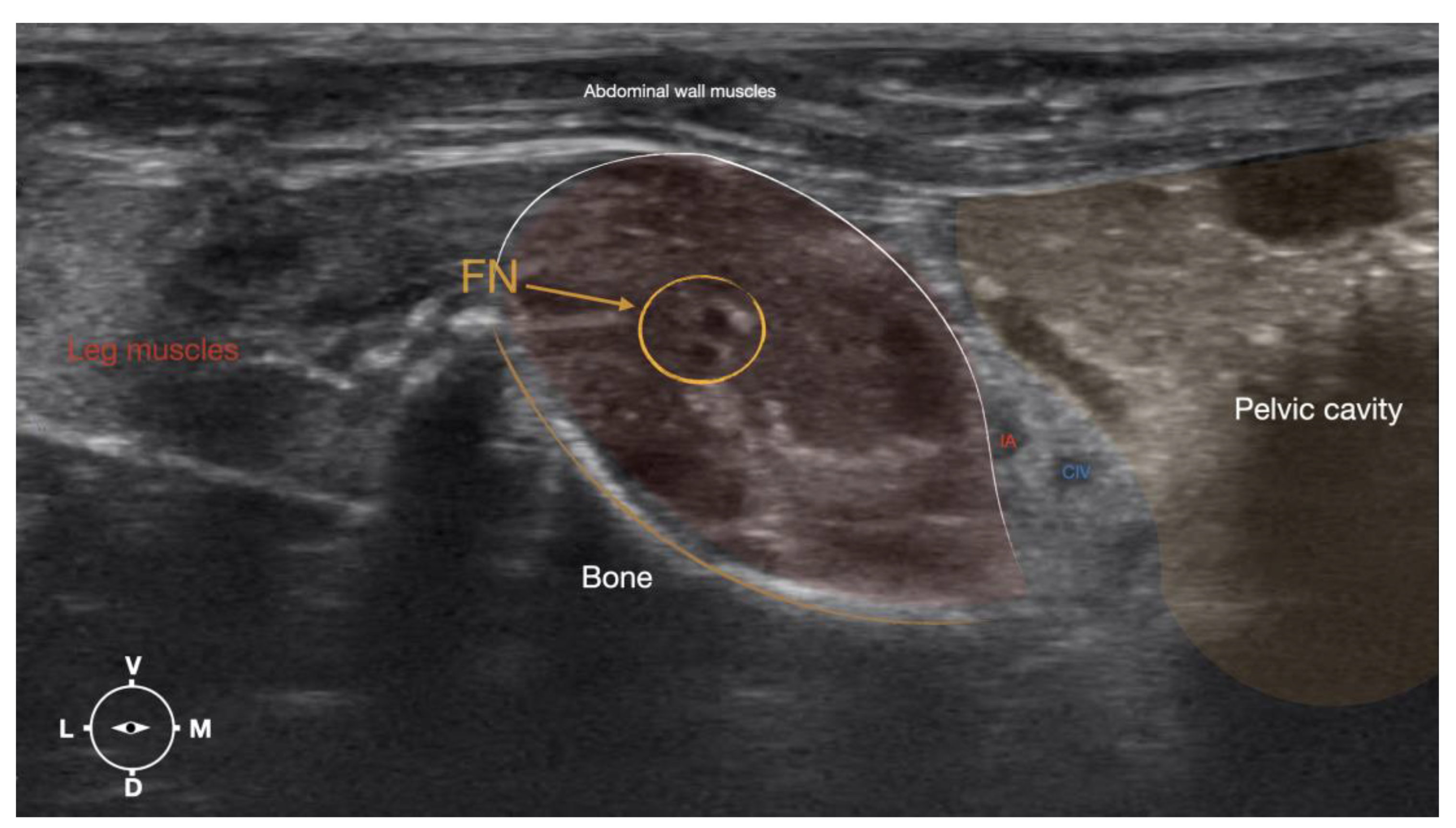
The cadaver was positioned in dorsal recumbency before the leg was extended caudally. The transducer was placed over the hypaxial muscles, transverse to the long-axis of the spine, and at the level of the projection of the iliac crest. Then, the transducer was moved in caudal direction along the IPM until the femoral nerve was clearly seen in the substance of the IP (
Figure 4). A 50mm 22 gauge insulated needle (Sonoplex Stim Cannula, Pajunk Medical Produkte GmbH, Germany) prefilled with a 1:1 solution of new methylene blue (MethyleneBlue1%w/vaq.soln, AlfaAesar, Thermo FischerGmbH, Germany) and lidocaine (Xylanest purum 2%, Gebro Pharm GmbH, Austria) (L-NMB) was inserted using an in-plane approach. The needle was inserted at the lateral edge of the transducer, and advanced in-plane under sonographic guidance through the iliac fascia and IPM in a dorso-medial direction towards the femoral nerve (
Figure 5 and
Figure 6). The needle was advanced until its tip was located in vicinity to the femoral nerve. A test volume of 0.05 ml of L-NMB was injected to confirm adequate distribution. The remaining volume of 0.15ml/kg was then injected extraepineurally around the femoral nerve.
The procedure was repeated in the contralateral limb. All cadavers were dissected immediately after the injections and the distribution pattern of injectate and nerve staining was evaluated. The presence of L-NMB staining of the nerves around their entire circumference for a length of at least two centimeters was considered successful [22] . Additionally, the presence of dye in the surrounding muscle as well as vascular damage or intraneural staining were noted.
3. Results
This study included a total of twelve, 90-120 days old female fresh rabbit (24 pelvic limbs) cadavers, with a median body weight of 3,09 (range 2,9-3,4 kg).
3.1. Phase 1: US- scanning and Anatomical Dissection Helped Define a Suitable US Window for sciatic and femoral nerve Injections.
3.1.1. Sciatic nerve
The ScN emerged between the greater trochanter of the femur and the sciatic tuber where it its proximal muscular branch was detached to the hamstring muscles. The nerve continued in distal direction to separate at the level of the distal third of the femur into the tibial and the peroneal nerve. Based on the anatomical dissection and US scans performed in this phase, the best level for injection was determined to be the in the proximal third of the femur. At the level of the proximal femur, the sciatic nerve was located caudally to the femur, medially to the biceps femoris muscle, cranially to the semimembranosus, and lateral to the adductor muscles (
Figure 7).
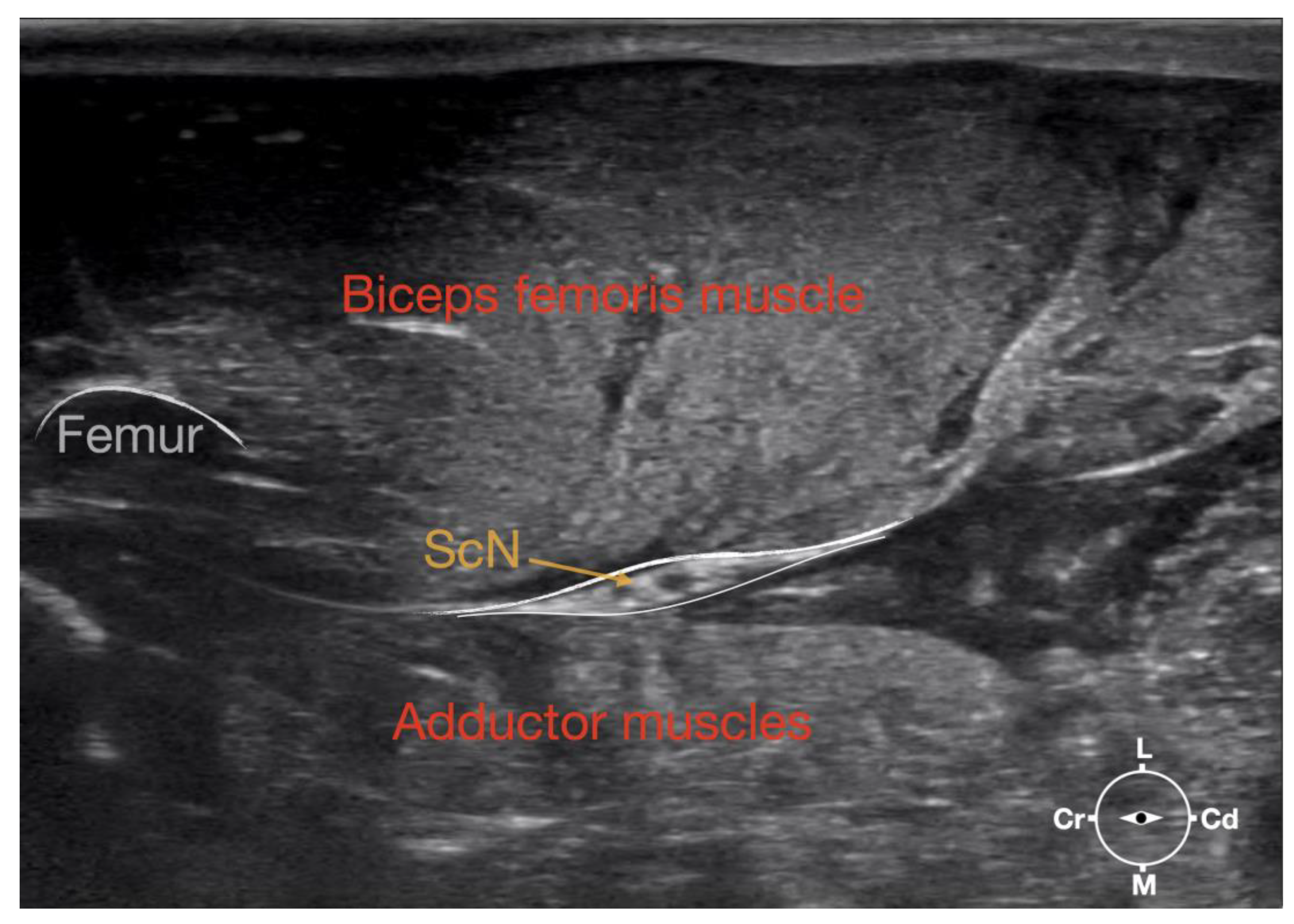
Ultrasonographically, the sciatic nerve appeared as a binocular structure with a hyperechoic rim surrounded by the muscular fascias of the biceps femoris and adductor muscles at this level. All muscles were displayed as structures with heterogeneous echogenicity. The biceps femoris muscle was lying lateral to the ScN while the adductor muscle was medial to the ScN. The femur was displayed as a hyperechoic structure with acoustic shadow and located cranial to the ScN nerve.
3.1.2. Femoral nerve
The femoral nerve was found in the substance of the IPM with a dorso-ventral trace (
Figure 8). It was divided into branches before it left the substance of the IPM to enter the leg through the vascular and muscular lacuna.
Based on the anatomical dissection and the US scans performed in this phase, the best way to locate and inject the FN was achieved by scanning the IPM from the projection of the iliac crest in caudal direction. Ultrasonographically, the femoral nerve appeared as a hypoechoic structure in the dorsal part of the IPM, becoming hyperechoic/honey-comb-like in the ventral part of the mentioned muscle. The IPM was displayed as structures with heterogeneous echogenicity. The ilium and the vertebrae were displayed as a hyperechoic structure with acoustic shadow and located lateral and dorsal to the femoral nerve, respectively.
3.2. Phase II: Sciatic and femoral nerve injection
In the second phase the targeted acoustic windows using the landmarks as described in the anatomical study could be identified in all hind-limbs (22).
In all 20 hind limbs the US-guided ScN and FN injections were performed at the first attempt. Duration to successful injection was around 2 minutes for one leg. During needle advancement, the shaft of the needle was always visible. During injection, an anechoic area appeared around the nerves, which slightly pushed the nerve away from the needle in all cases.
3.2.1. Anatomical Dissection following US-Guided ScN and FN injections
Methylene blue dye was injected into the interfascial space containing the ScN, and in the vicinity of the FN. Staining was successfull in both ScN and FN in all cases (20/20). The length of staining was >2 cm in all ScN and FN nerves in their entire circumference. The distribution of the injectate from the injection site was observed to occur interfascially for SCN, and intramuscularly in the vicinity of the FN for FNB (
Figure 9). A small amount (in traces) of dye was found in the biceps femoris muscle for ScN injection, most likely caused by the needle removal and leakage. There were no signs of vascular damage, intramuscular (ScN) or intraneural injection for both nerves.
4. Discussion
4.1. General outcome
Concerns about pain management in pets are increasing. However, locoregional anaesthesia techniques in rabbits have only been described in very few studies[10,23,24]. This study aimed to describe the gross anatomical and ultrasonographic appearance of the ScN and the FN in this species. The information further served to develop an US-guided approach for injecting a defined volume of methylene blue dye in direct proximity to the ScN and the FN. Methodological feasibility and accuracy were assessed by means of bilateral injections in 10 rabbits. To our knowledge, this is the first study investigating the use of US for localization and perineural injection of the ScN and the FN in rabbits.
4.2. Peri-op fatalities in rabbits
Trauma and surgery are potent triggers of a neuro- humoral stress response in all animals [7] . Anyway, compared to dogs and cats the incidence (38%) of non-fatal gastrointestinal complications is higher in rabbits undergoing general anaesthesia [25]. No specific risk factors have been associated with the higher peri-operative mortality rate recorded in rabbits which are most likely multifactorial (e.g., dietary changes, pain, disease, and medication side effects) [26]. Moreover, stress can predispose to prolonged ileus and determine systemic inflammatory responses [27] in humans, which, can be fatal in rabbits due to their GI physiology.
4.3. Perianaesthetic drugs in rabbits
Opioids are commonly used to provide perioperative analgesia in rabbits [28] . However, in rabbits, these drugs are associated with several side effects as bradycardia, hypotension, hypoventilation, ileus, nausea and reduced postoperative food intake [1]. Rabbits are reluctant to show signs of discomfort, making them particularly challenging for early detection of pain as well as the evaluation of the efficacy of an analgesic treatment if this is based on behavioural changes [25,29] . Therefore, adequate peri-operative analgesia plays a vital role in the outcome. Regional anaesthesia may be an excellent way to block the neuroendocrine stress response in rabbits undergoing orthopaedic surgeries on the hindlimb, consequently improving the outcome in rabbits.
4.4. LRA in animals
The importance of locoregional anaesthesia is rapidly growing in veterinary medicine. When implemented in an anaesthetic protocol, peripheral nerve blocks provide regional surgical anaesthesia allowing a reduction of depth of anesthesia leading to better cardiorespiratory stability compared to opioid-based general anaesthesia or central neuro-axial anaesthesia [7] . Due to the high anaesthesia-related mortality risk in rabbits this fact could be of enormous importance. Moreover, many analgesics are not allowed to be used in certain studies due to their influence on the bone healing process. The implementation of regional anaesthesia in this protocol will elevate the well-being of the experimental animals through its excellent analgesic effects, and hopefully improve the current high mortality rate in rabbit anaesthesia. In human medicine, the scope of anesthesia for patients undergoing isolated limb surgery has changed from general anesthesia to central neuraxial blockade to peripheral nerve blocks with the advent of ultrasound and peripheral nerve stimulation [15,30] . However, in veterinary small animal medicine, regional anesthesia is always combined with deep sedation or light plane of anaesthesia to secure patients safety. Today, a large spectrum of surgical and pain-related cases are managed with peripheral nerve blocks and a light plane of anaesthesia in veterinary medicine [31].
4.5. Ultrasound guided LRA
4.5.1. Anatomy
The anatomical study was useful in establishing an adequate acoustic window for subsequent injections. The anatomical landmarks defined to localize the ScN was the long-axis of the femur. Placing the probe perpendicular over the lateral thigh at level of the prox-femur and caudal to it, was found to be an excellent way to localize the ScN and successful in 100% of cases. These findings corresponds with small animals literature [8].
The landmarks for FN location were the iliac crest and hypaxial muscles. The transducer was placed over and perpendicular to the hypaxial muscles at the level of the ventral projection of the iliac crest and slid caudally until the FN was visualized on the screen as a structure with different echogenicity on its dorso-ventral pattern. The FN was seen as a hypoechoic structure in the dorsal part of the IPM, becoming a honey-comb like structure in the ventral part of the IPM. This result deviates slightly from the information in the small animal literature, where the FN is described as a hypoechoic structure with a hyperechoic rim. With the approach defined, it was feasible to identify the FN in 100% of cases. Another finding was that caudal sliding the transducer over the hypaxial (IPM) helped distinguish the FN from other structures with similar echogenicity inside the IPM. Due to the lack of distinct fascia inside the IPM and around the nerves located there, it is very likely that the injected LA will reach the nerve, even if the tip of the needle cannot be advanced in direct proximity to the nerve. For this reason, this block is usually very effective in small animals [8] . However, this has to be evaluated in another study on rabbits.
Ultrasonography allows a direct visualization of peripheral nerves so that, the needle can be kept away from vulnerable organs and distribution of local anaesthetics can be monitored in real time [32]. This imaging modality has proven highly useful to guide targeted drug injections and catheter placement. The last several years have witnessed a tremendous increase in the use of ultrasound guidance for regional anaesthesia [33,34, 35] . The most important prerequisites for the use of peripheral nerve blocks and regional anaesthesia in the daily clinical practice are success rates and safety, as well as standardized approaches or techniques for a PNB. Both issues are closely related to the administered volumes of local anaesthetics. During the past decades, large volumes of local anaesthetics have been used for peripheral regional anaesthetic techniques to compensate for morphometric methods of nerve identification. Pure landmark-based or nerve stimulation techniques are examples of indirect methods of identification of peripheral nerves. One of the main advantages of ultrasonographic guidance for nerve blocks is the possibility to reduce the volumes of local anaesthetics, mainly due to the direct observation of the needle tip and spread of local anaesthetic in the correct place. With the approaches presented, it was possible to observe the needle and the nerve in the same plane, which is a significant advantage. The visualization of the needle shaft has been considered necessary to accomplish a safer approach to a peripheral nerve [32] . In addition, the visualization of the target nerve in a gross-sectional view further allows detailed observation of the distribution of the anaesthetic solution around the nerve [36] .
4.5.2. Sciatic/femoral nerve block
The length of the nerve in contact with the LA is a major factor in determining the success of a PNB. In myelinated nerves, at least three nodes of Ranvier must be exposed to local anaesthetic to ensure that nerve conduction is blocked, which corresponds to 3–4 mm of nerve. An in vitro study suggested that staining of ≥2 cm along a peripheral nerve should be considered sufficient to produce a clinically effective nerve blockade [22] . The volume we used (0.15mL/kg) was sufficient to stain the ScB and FN successfully in all cadavers. Accordingly, a volume reduction could be considered.
When the ScN block was performed in humans, using an NS-guided technique, a higher failure rate was reported compared to US-guided technique [37] . This fact is probably because NS tell us only the nerve-needle distance, and not whether the tip of the needle is placed in the correct space, namely the interfascial space that contains the nerve. Moreover, the needle may be positioned inside the nerve without eliciting any motor response, despite substantial electrical current (>1,5 mA) [38,39]. US allows us to be away from the nerve and vulnerable structures like vessels but in the correct space, so when injecting the local anaesthetic, the nerve is only touched by the local anaesthetic. This impact the safety, time efficacy and efficacy of peripheral nerve blocks. A strong evidence base has shown that ultrasound guidance improves differentiation between an extra and intraneural injection [40-42], intra- and extravascular injection [43], raises the success rate of locoregional blocks [18], shortens the speed of block onset and enhances duration [44], allows shorter procedure times [45,46], decreases the quantity of local anaesthetic used and their local and systemic complications [47,48], and enhances block success even in difficult situations[49,50]. In our study, using ultrasound guidance, perineural injection of the ScN and FN was successful in 100% of cases. Our findings corresponded to the findings when similar studies were performed in dogs[12].
4.6. Limitations of the study
The present study has some limitations that need to be addressed. This cadaveric study only allows us to speculate on the clinical efficacy of the conducted perineural ScN and FN injections. The results from this study showed, however, that the US-guided perineural ScN and FN injection in rabbits produced an adequate methylene blue dye distribution, so that an adequate nerve block can be assumed when using a LA. Due to the lack of distinct fascia between the muscles of the iliopsoas compartment, and around the nerves located there, it is very likely that the injected LA will reach the perineural space, even if the tip of the needle cannot be advanced in the direct proximity to the nerve. For this reason, this block is usually very effective in small animals. The echogenicity of fascial planes, muscles, and vascular structures may be altered in the early postmortem phase and may not accurately reflect the sono-anatomy of the live rabbit. It is recognized that the spread of dye solutions within an interfascial plane may be unpredictable in cadavers due to differences in tissue integrity [51]. This may also influence the resistance to injection, which, if increased, could promote a wider spread of the dye solution when compared to live animals.
5. Conclusions
In this study, evidence of intraneural, intraperitoneal, retroperitoneal, or intravascular injection of methylene blue dye was not seen in any case. A similar study in cats (FN) showed a small amount of LA in the retroperitoneal space in 3 out of four cases [14] . Cadaveric studies allow us to speculate on the clinical efficacy of the study conducted. However, the results from this study showed that the US-guided perineural ScN and FN injection in rabbits produced an adequate methylene blue dye distribution so that an adequate nerve block can be assumed when using a LA.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization R.T.; methodology R.T. and H.R.; investigation R.T. and H.R.; data curation R.T. and H.R.; formal analysis R.T.; writing—original draft preparation R.T.; writing—review and editing H.R and H.R.; supervision H.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study did not require ethical approval.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available upon request (robertrujanovic@hotmail.com).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Dr. Miriam Szameitat and Ms. Anja Angerer for their assistance and support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Andronowski, J.M.; Schuller, A.J.; Cole, M.E.; LaMarca, A.R.; Davis, R.A.; Tubo, G.R. Rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus) as a Model System for Longitudinal Experimental Opioid Treatments: Implications for Orthopedic and Biomedical Research. Osteology 2021, 1, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auer, J.A.; Goodship, A.; Arnoczky, S.; Pearce, S.; Price, J.; Claes, L; von Rechenberg, B. ; Hofmann-Amtenbrinck, M.; Schneider, E.; Müller-Terpitz, R.; Thiele, F.; Rippe, K.P.; Grainger, D.W. Refining animal models in fracture research: seeking consensus in optimising both animal welfare and scientific validity for appropriate biomedical use. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2007, 8, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stundner, O.; Memtsoudis, S.G. Regional anesthesia and analgesia in critically ill patients: a systematic review. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2012, 37, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugada, D.; Ghisi, D.; Mariano, ER. Continuous regional anesthesia: a review of perioperative outcome benefits. Minerva Anestesiol. 2017, 83, 1089–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosing, M.; Reich, H.; Moens, Y. Clinical evaluation of the anaesthetic sparing effect of brachial plexus block in cats. Vet Anaesth Analg. 2010, 37, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Congdon, J.M.; Boscan, P.; Goh, C.S.S.; Rezende, M. Psoas compartment and sacral plexus block via electrostimulation for pelvic limb amputation in dogs. Vet Anaesth Analg. 2017, 44, 915–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romano, M.; Portela, D.A.; Breghi, G.; Otero, PE. Stress-related biomarkers in dogs administered regional anaesthesia or fentanyl for analgesia during stifle surgery. Vet Anaesth Analg. 2016, 43, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portela, D.A.; Fuensalida, S.E.; Verdier, N. Peripheral nerve blocks of the pelvic limb. In Small Animal Regional Anesthesia, 2nd ed.; Otero, P.E., Portela, D.A., Eds.; Inter-Medica: Buenos Aires, Argentina, 2018; pp. 135–218. [Google Scholar]
- Albrecht, E.; Chin, K.J. Advances in regional anaesthesia and acute pain management: A narrative review. Anaesthesia 2020, 75, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felisberto, R.; Flaherty, D.; Tayari, H. Ultrasound-Guided Saphenous Nerve Block in Rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus): A Cadaveric Study Comparing Two Injectate Volumes. Animals 2022, 12, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- d’Ovidio, D.; Rota, S.; Noviello, E.; Briganti, A.; Adami, C. Nerve Stimulator-guided sciatic and femoral block in pet rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus) undergoing hindlimb surgery: A case series. J. Exot. Pet. Med. 2014, 23, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campoy, L.; Bezuidenhout, A.J.; Gleed, R.D.; Martin-Flores, M.; Raw, R.M.; Santare, C.L.; Jay, A.R.; Wang, A.L. Ultrasound-guided approach for axillary brachial plexus, femoral nerve, and sciatic nerve blocks in dogs. Vet Anaesth Analg. 2010, 37, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Echeverry, D.F.; Laredo, F.G.; Gil, F.; Belda, E.; Soler, M.; Agut, A. Ventral ultrasound-guided suprainguinal approach to block the femoral nerve in the dog. Vet J. 2012, 192, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haro, P.; Laredo, F.; Gil, F.; Belda, E.; Ayala, M.D.; Soler, M.; Agut, A. Ultrasound-guided dorsal approach for femoral nerve blockade in cats: an imaging study. J Feline Med Surg. 2013, 15, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, L.; Attri, J.P.; Verma, P. Lower limb surgeries under combined femoral and sciatic nerve block. Anesth Essays Res. 2016, 10, 432–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marhofer, P.; Fritsch, G. Safe performance of peripheral regional anaesthesia: the significance of ultrasound guidance. Anaesthesia. 2017, 72, 431–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrahams, M.S.; Aziz, M.F.; Fu, R.F.; Horn, J.L. Ultrasound guidance compared with electrical neurostimulation for peripheral nerve block: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Br. J. Anaesth. 2009, 102, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, V.W.S.; Perlas, A.; McCartney, C.J.L.; Brull, R.; Xu, D.; Abbas, S. Ultrasounds guidance improves success rate of axillary brachial plexus block. Can. J. Anesth. 2007, 54, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mogicato, G.; Layssol-Lamour, C.; Mahler, S.; Charrouin, M.; Boyer, G.; Verwaerde, P.; Jourdan, G. Anatomical and ultrasonographic study of the femoral nerve within the iliopsoas muscle in beagle dogs and cats. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2015, 42, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auroy, Y.; Benhamou, D.; Bargues, L.; Ecoffey, C.; Falissard, B.; Mercier, F.; Bouaziz, H.; Samii, K. Major complications of regional anesthesia in France: The SOS Regional Anesthesia Hotline Service. Anesthesiology 2002, 97, 1274–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koscielniak-Nielsen, Z.J. Ultrasound-guided peripheral nerve blocks: What are the benefits? Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2008, 52, 727–737. [Google Scholar]
- Raymond, S.A.; Steffensen, S.C.; Gugino, L.D.; Strichartz, G.R. The role of length of nerve exposed to local anesthetics in impulse blocking action. Anesth Analg. 1989, 68, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluge, K.; Larenza Menzies, M.P.; Kloeppel, H.; Pearce, S.G.; Bettschart-Wolfensberger, R.; Kutter, A.P. ; Femoral and sciatic nerve blockades and incision site infiltration in rabbits undergoing stifle joint arthrotomy. Lab Anim. 2017, 51, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, C.; Server, A.; Esteves, M.; Barastegui, D.; Rosal, M.; Fontecha, C.G.; Soldado, F. An ultrasound-guided technique for axillary brachial plexus nerve block in rabbits. Lab Anim 2015, 4, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.W.; Machin, H.; Adami, C. Peri-anaesthetic mortality and nonfatal gastrointestinal complications in pet rabbits: a retrospective study on 210 cases. Vet Anaesth Analg. 2018, 45, 520–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnellbacher, R.W.; Divers, S.J.; Comolli, J.R.; Beaufrère, H.; Maglaras, C.H.; Andrade, N.; Barbur. L,A.; Rosselli, D.D.; Stejskal, M.; Barletta, M.; Mayer, J.; Rodriguez, P.; Quandt, J.E. Effects of intravenous administration of lidocaine and buprenorphine on gastrointestinal tract motility and signs of pain in New Zealand White rabbits after ovariohysterectomy. Am J Vet Res. 2017, 78, 1359–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, L.A.; Blaze, C.A.; Linder, D.E.; Andrutis, K.A.; Karas, A.Z. A model for clinical evaluation of perioperative analgesia in rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus). J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 2010, 49, 845–851. [Google Scholar]
- Benato, L.; Rooney, N.J.; Murrell, J.C. Pain and analgesia in pet rabbits within the veterinary environment: a review. Vet Anaesth Analg. 2019, 46, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashokka, B.; Chakraborty, A.; Subramanian, B.J.; Karmakar, M.K.; Chan, V. Reconfiguring the scope and practice of regional anesthesia in a pandemic: the COVID-19 perspective. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2020, 45, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, L.A.; Bukoski, A.D.; Zelaya-Nunez, C.; Dodam, J.R.; Varner, K.M.; Torres, B.T. Pelvic limb anesthesia and analgesia in dogs undergoing tibial plateau leveling osteotomy (TPLO): A survey of board-certified anesthesiologists. Vet Surg. 2023, 52, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marhofer, P.; Harrop-Griffiths, W.; Kettner, S.C.; Kirchmair, L. Fifteen years of ultrasound guidance in regional anaesthesia: part 1. Br J Anaesth. 2010, 104, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guay, J.; Suresh, S.; Kopp, S. The use of ultrasound guidance for perioperative neuraxial and peripheral nerve blocks in children. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2019, Issue 2. Art. No.: CD011436. [CrossRef]
- Behera, S.K.; Gunupuru, B.; Sahu, L.; Das, S. Peripheral Nerve Stimulator Versus Ultrasound-Guided Femoral Nerve Block for Knee Arthroscopy Procedures: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Cureus. 2022, 14, 32043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forouzan, A.; Masoumi, K.; Motamed, H.; Gousheh, M.R.; Rohani, A. Nerve Stimulator versus Ultrasound-Guided Femoral Nerve Block; a Randomized Clinical Trial. Emerg (Tehran). 2017, 5, 54. [Google Scholar]
- Marhofer, P.; Greher, M.; Kapral, S. Ultrasound guidance in regional anaesthesia. Br. J. Anaesth. 2005, 94, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Zhao, X.; Xu, J.; Liu, Z.; Li, Q. Ultrasound-guided technology versus neurostimulation for sciatic nerver block: a meta-analysis. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015, 8, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tsai, T.P.; Vuckovic, I.; Dilberovic, F.; Obhodzas, M.; Kapur, E.; Divanovic, K.A.; Hadzic, A. Intensity of the stimulating current may not be a reliable indicator of intraneural needle placement. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2008, 33, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robards, C.; Hadzic, A.; Somasundaram, L.; Iwata, T.; Gadsden, J.; Xu. ;, Sala-Blanch, X. Intraneural injection with low-current stimulation during popliteal sciatic nerve block. Anesth Analg. 2009, 109, 673–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bigeleisen, P.E. Nerve puncture and apparent intraneural injection during ultrasound-guided axillary block does not invariably result in neurologic injury. Anesthesiology. 2006, 105, 779–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, V.W.; Brull, R.; McCartney, C.J.; Xu, D.; Abbas, S.; Shannon, P. An ultrasonographic and histological study of intraneural injection and electrical stimulation in pigs. Anesth Analg. 2007, 104, 1281–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigeleisen, P.E.; Moayeri, N.; Groen, G.J. Extraneural versus intraneural stimulation thresholds during ultrasound-guided supraclavicular block. Anesthesiology. 2009, 110, 1235–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VadeBoncouer, T.R.; Weinberg, G.L.; Oswald, S.; Angelov, F. Early detection of intravascular injection during ultrasound-guided supraclavicular brachial plexus block. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2008, 33, 278–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marhofer, P.; Schrögendorfer, K.; Koinig. ; Kapral, S.; Weinstabl, C.; Mayer, N. Ultrasonographic guidance improves sensory block and onset time of three-in-one blocks. Anesth Analg. 1997, 85, 854–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredrickson, M.J.; Ball, C.M.; Dalgleish, A.J.; Stewart, A.W.; Short, T.G. A prospective randomized comparison of ultrasound and neurostimulation as needle end points for interscalene catheter placement. Anesth Analg. 2009, 108, 1695–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brull, R.; Lupu, M.; Perlas, A.; Chan, V.W.; McCartney, C.J. Compared with dual nerve stimulation, ultrasound guidance shortens the time for infraclavicular block performance. Can J Anaesth. 2009, 56, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casati, A. , Baciarello, M.; Di Cianni, S.; Danelli, G.; De Marco, G.; Leone, S.; Rossi, M.; Fanelli, G. Effects of ultrasound guidance on the minimum effective anaesthetic volume required to block the femoral nerve. Br J Anaesth. 2007, 98, 823–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danelli, G.; Ghisi, D.; Fanelli, A.; Ortu, A.; Moschini, E.; Berti, M.; Ziegler, S.; Fanelli, G. The effects of ultrasound guidance and neurostimulation on the minimum effective anesthetic volume of mepivacaine 1.5% required to block the sciatic nerve using the subgluteal approach. Anesth Analg. 2009, 109, 1674–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plunkett, A.R.; Brown, D.S.; Rogers, J.M.; Buckenmaier, C. C 3rd. Supraclavicular continuous peripheral nerve block in a wounded soldier: when ultrasound is the only option. Br J Anaesth. 2006, 97, 715–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assmann, N.; McCartney, C.J.; Tumber, P.S.; Chan, V.W. Ultrasound guidance for brachial plexus localization and catheter insertion after complete forearm amputation. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2007, 32, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dautzenberg, K.H.W.; Zegers, M.J.; Bleeker, C.P.; Tan, E.C.H.; Vissers, K.C.P.; van Geffen, G.J.; van derWal, S.E.I. Unpredictable injectate spread of the erector spinae block in human cadavers. Anesth. Analg. 2019, 129, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Corresponding transverse ultrasound image to the figure 2. The ultrasound image shows the sciatic nerve and related structures. The white lines indicate the muscular fascias enveloping the sciatic nerve. Cr, cranial, Cd, caudal; L, lateral; M, medial.
Figure 1.
Corresponding transverse ultrasound image to the figure 2. The ultrasound image shows the sciatic nerve and related structures. The white lines indicate the muscular fascias enveloping the sciatic nerve. Cr, cranial, Cd, caudal; L, lateral; M, medial.
Figure 2.
Position of the cadaver, anatomical landmarks for initial ultrasound transducer placement and the needle insertion for the perineural sciatic nerve injection. The blue line indicates the long-axis of the femur. 1, Major trochanter of the femur, Cr, cranial; Cd, caudal; D, dorsal, V, ventral.
Figure 2.
Position of the cadaver, anatomical landmarks for initial ultrasound transducer placement and the needle insertion for the perineural sciatic nerve injection. The blue line indicates the long-axis of the femur. 1, Major trochanter of the femur, Cr, cranial; Cd, caudal; D, dorsal, V, ventral.
Figure 3.
Ultrasonographic image showing the approach of the needle towards the sciatic nerve. ScN, sciatic nerve; Cr, cranial; Cd, caudal; L, lateral; M, medial.
Figure 3.
Ultrasonographic image showing the approach of the needle towards the sciatic nerve. ScN, sciatic nerve; Cr, cranial; Cd, caudal; L, lateral; M, medial.
Figure 4.
Corresponding transverse ultrasound image to the figure 5. The ultrasound image shows the FN and related structures. IA, iliac artery, CV, common iliac vein; FN, femoral nerve; Dm dorsal; L, lateral; M, medial; V, ventral.
Figure 4.
Corresponding transverse ultrasound image to the figure 5. The ultrasound image shows the FN and related structures. IA, iliac artery, CV, common iliac vein; FN, femoral nerve; Dm dorsal; L, lateral; M, medial; V, ventral.
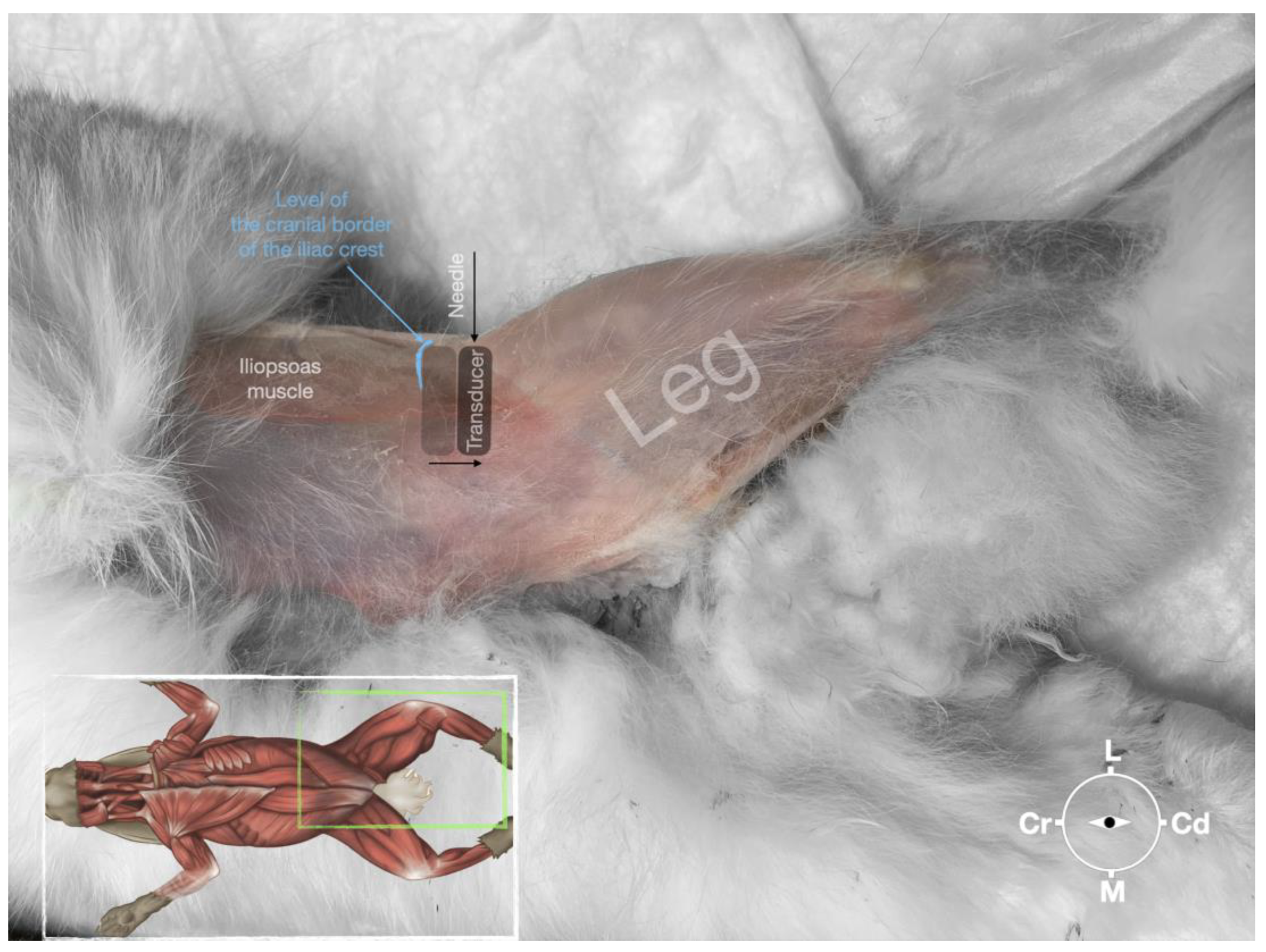
Figure 5.
Position of the cadaver, anatomical landmarks for initial ultrasound transducer placement and the needle insertion for the perineural femoral nerve injection.
Figure 5.
Position of the cadaver, anatomical landmarks for initial ultrasound transducer placement and the needle insertion for the perineural femoral nerve injection.
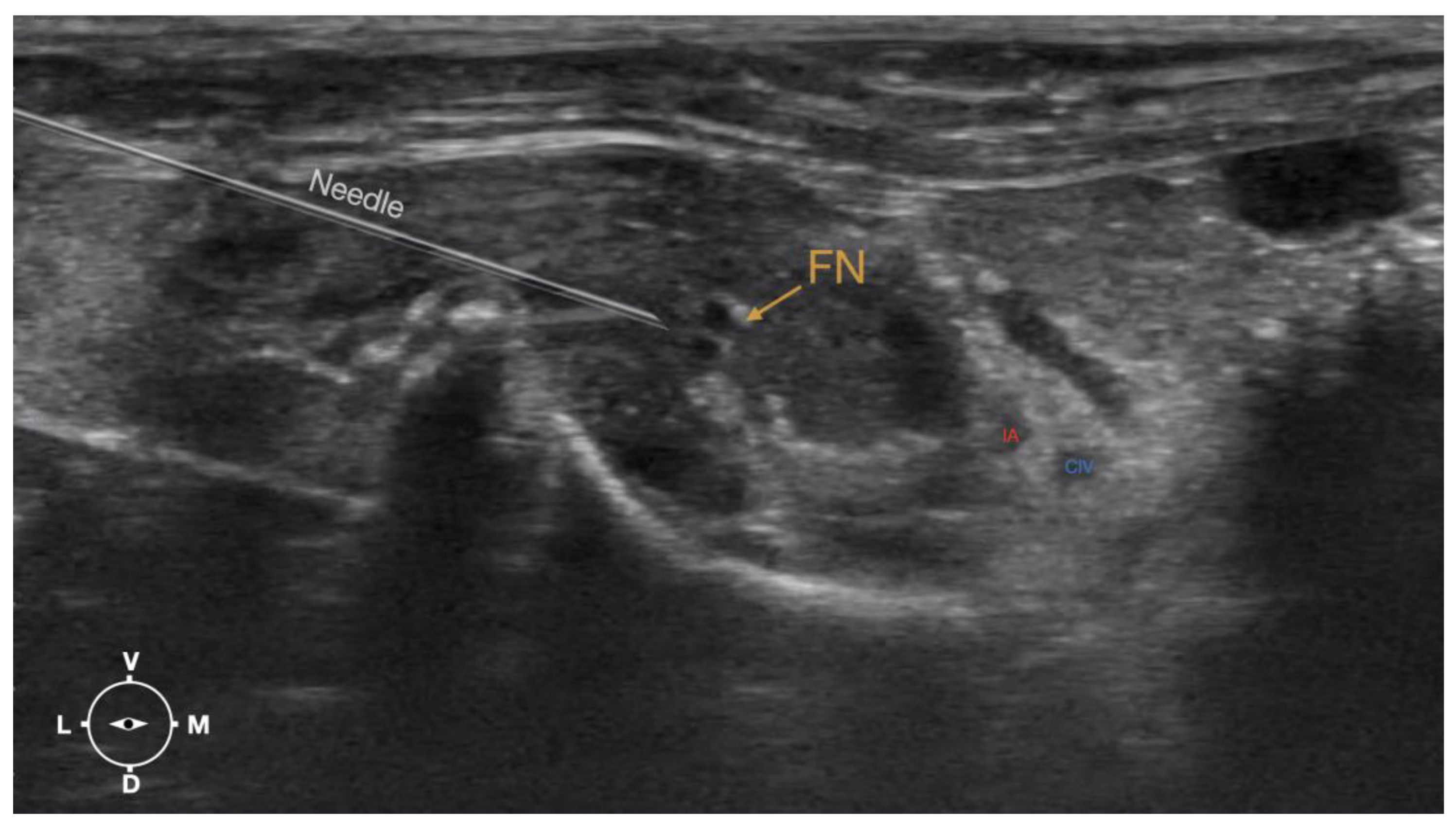
Figure 6.
Ultrasonographic image showing the approach of the needle towards the femoral nerve. IA, iliac artery, CIV, common iliac vein; FN, femoral nerve; D, dorsal; L, lateral; M, medial; V, ventral.
Figure 6.
Ultrasonographic image showing the approach of the needle towards the femoral nerve. IA, iliac artery, CIV, common iliac vein; FN, femoral nerve; D, dorsal; L, lateral; M, medial; V, ventral.
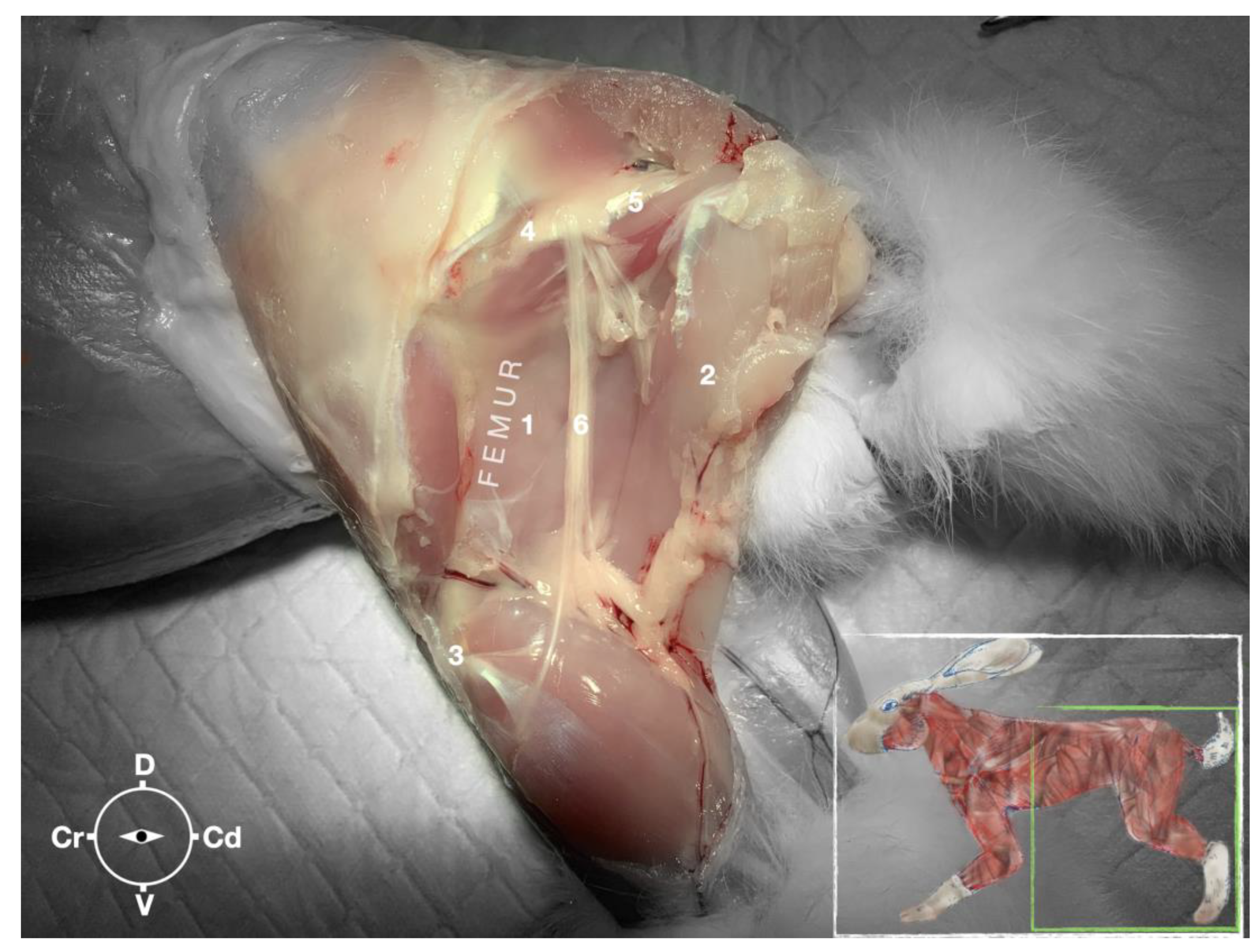
Figure 7.
Dissection of the sciatic nerve at the lateral thigh. The biceps femoris muscle has been removed in order to expose the sciatic nerve. Picture in the insert shows the dissection area. 1, Adductor muscle; 2, Semimembranosus muscle; 3, Stifle joint; 4, Major trochanter of the femur; 5, Ischiatic tuber; 6, sciatic nerve; Cr, cranial; Cd, caudal; D, dorsal; V, ventral.
Figure 7.
Dissection of the sciatic nerve at the lateral thigh. The biceps femoris muscle has been removed in order to expose the sciatic nerve. Picture in the insert shows the dissection area. 1, Adductor muscle; 2, Semimembranosus muscle; 3, Stifle joint; 4, Major trochanter of the femur; 5, Ischiatic tuber; 6, sciatic nerve; Cr, cranial; Cd, caudal; D, dorsal; V, ventral.
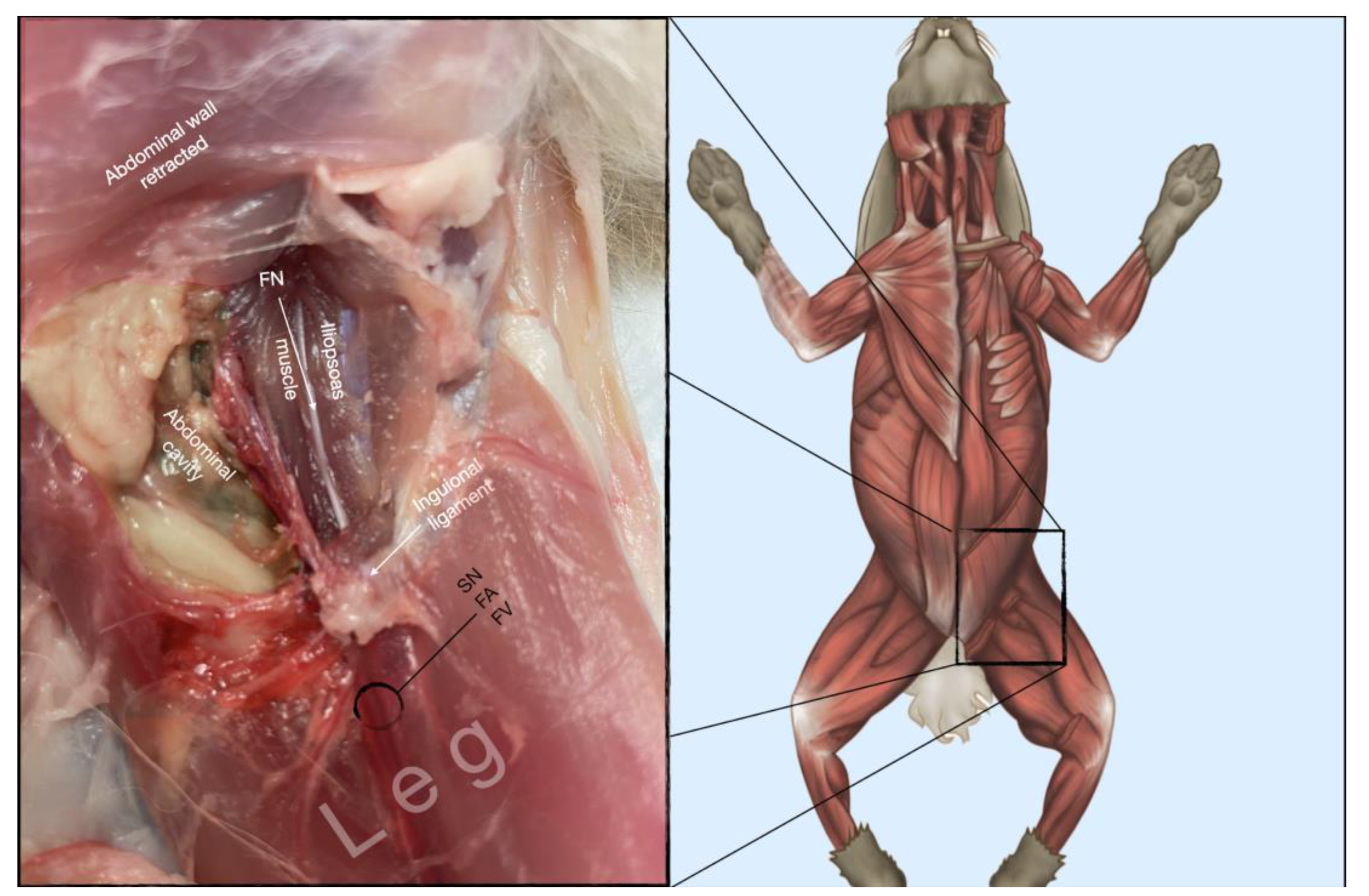
Figure 8.
Dissection of the femoral nerve within the iliopsoas. Picture in the insert shows the dissection area. FA, femoral artery; FN, femoral nerve; FV, femoral vein.
Figure 8.
Dissection of the femoral nerve within the iliopsoas. Picture in the insert shows the dissection area. FA, femoral artery; FN, femoral nerve; FV, femoral vein.
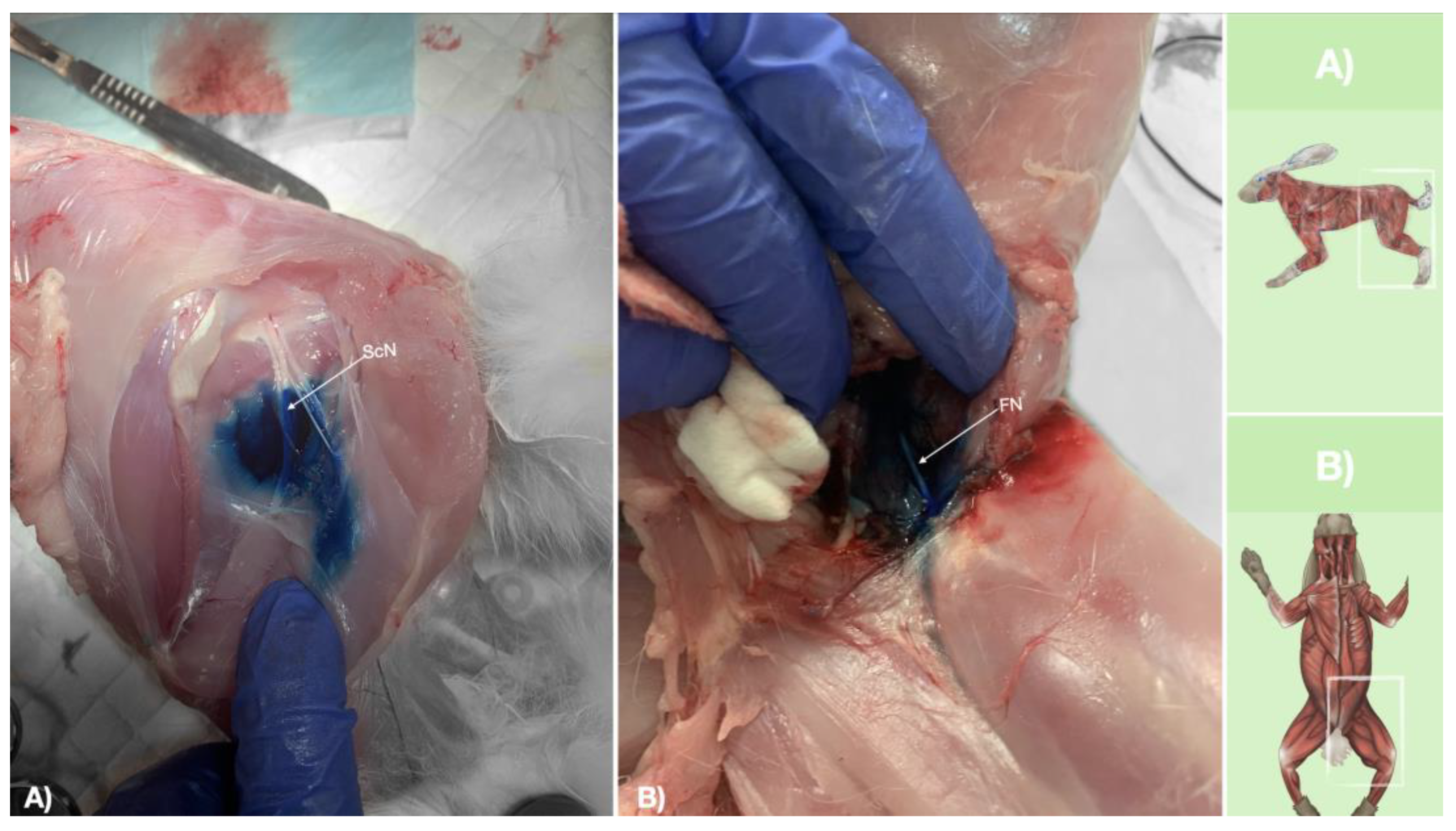
Figure 9.
Dissection of successfully stained femoral and sciatic nerves after perineural injection. A) The biceps femoris muscle reflected to expose the sciatic nerve. B) The iliopsoas muscle dissected and retracted laterally to expose the femoral nerve. FN, femoral nerve; ScN, sciatic nerve.
Figure 9.
Dissection of successfully stained femoral and sciatic nerves after perineural injection. A) The biceps femoris muscle reflected to expose the sciatic nerve. B) The iliopsoas muscle dissected and retracted laterally to expose the femoral nerve. FN, femoral nerve; ScN, sciatic nerve.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).