1. Introduction
Staphylococcus aureus has been a key opportunistic pathogen in humans, can cause various infections, and was the first discovery of the staphylococcal disease—in 1880 by surgeon Alexander Ogston in pus from a surgical abscess [
1]. Approximately 40%–60% of the human population is intermittently colonized by
S. aureus, and approximately 20% is persistently colonized [
2]. Individuals colonized with
S. aureus are at increased risk of infection; the rate of colonization is higher in those who inject drugs or with type 1 diabetes, dermatologic conditions, immunodeficiency syndrome, or hemodialysis than in the general population [
3,
4]. After the first appearance of methicillin-resistant
S. aureus (MRSA) in 1961 shortly after methicillin was introduced, MRSA spread globally. It was first documented in Taiwan in the early 1980s and spread rapidly in the 1990s [
5]. In the past two decades, a decline has been observed in health care–associated MRSA and community-acquired MRSA has increased in incidence [
6]. ST239 and ST59 are the major clones of
S. aureus in Taiwan. ST239 is health care–associated, whereas ST59 is community-associated. The reduction in ST239 and increase in ST59 in hospital settings since the 2010s indicates the effective adaptation of ST59 to hospital environments. ST59 appears to be a nosocomial clone capable of causing invasive infection [
7,
8].
Infections are the second most common cause of hospitalization, morbidity, and mortality in hemodialysis patients after cardiovascular events. This population has higher risk of invasive
S. aureus infection than does the nondialysis population [
9].
S. aureus carriers on hemodialysis have 1.8- to 4.7-fold higher risk of vascular access infections (VAIs) and bacteremia compared with noncarriers [
10]. The risk of MRSA infection in hemodialysis patients is 100 times that in the general population [
11]. Patients receiving hemodialysis are highly susceptible to VAIs because of their long-term necessity for vascular access, frequent puncture of vascular access sites, repeated hospitalization, frequent and long-term use of antibiotics, and immunosuppression [
12]. Vascular access type is associated with the risk of infection; the common vascular access types are the tunneled cuffed catheters (TCCs), arteriovenous grafts (AVGs), and arteriovenous fistulas (AVFs), in order of decreasing infection risk [
13]. Although AVFs have the benefit of a high patency rate and low infection rate, they have the disadvantage of a high primary failure rate because of early thrombosis and failure to mature, partly contributing to the higher incidence of catheter use.
Ongoing molecular surveillance is essential for preventing
S. aureus infection in healthcare facilities. During the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, numerous infection control and prevention measures were implemented in response to COVID-19, and these measures brought additional benefits in reducing other infections [
14]. However, patients receiving hemodialysis are especially vulnerable to COVID-19 because of their greater comorbidities and frequent healthcare visits, which are often made using public transportation even under pandemic conditions, further exposing them to the risk of community-transmitted infection. Therefore, this study examined the molecular epidemiology and antibiotic resistance of
S. aureus isolates obtained from VAIs before versus during the pandemic and clarified the correlation between access types, genetic background, and antibiotic resistance.
2. Results
2.1. Distribution of isolates from different VAI types
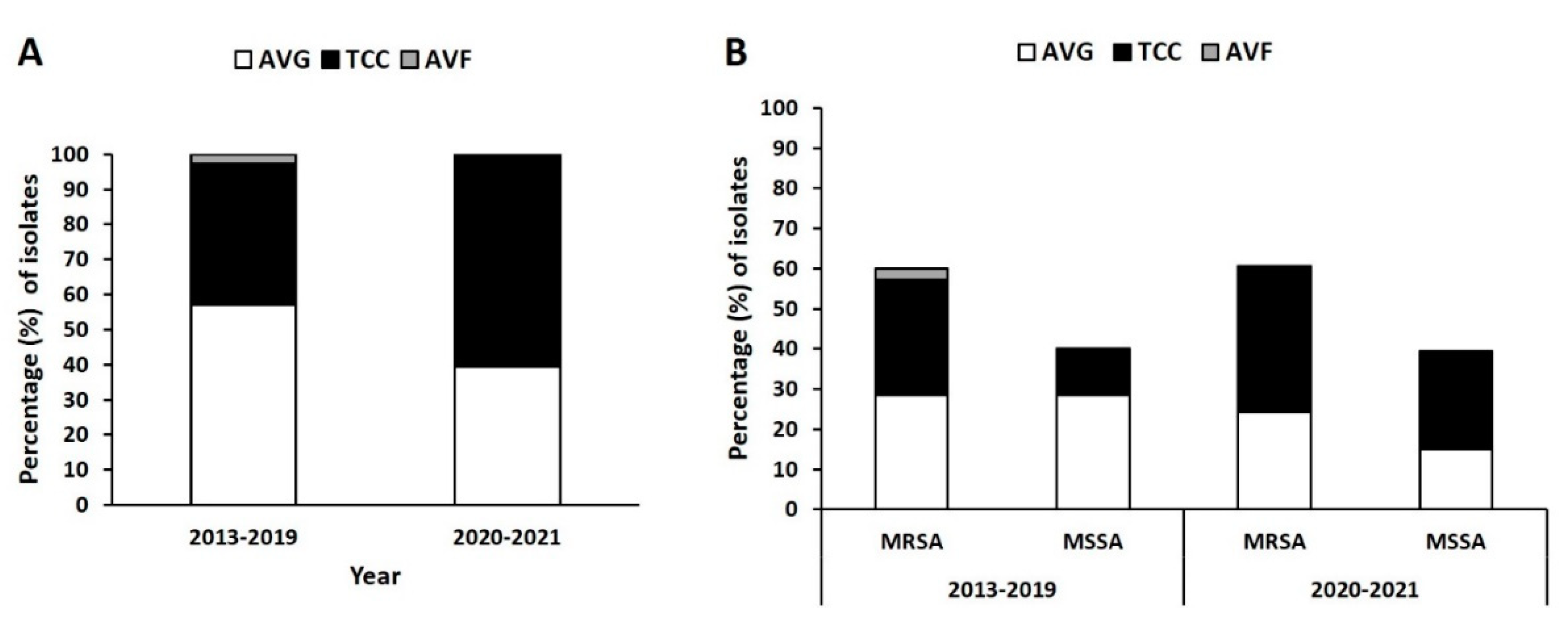
In total, 102 isolates were collected from three types of VAI: those of AVGs (n = 53), TCCs (n = 47), and AVFs (n = 2); 69 isolates were collected before the COVID-19 pandemic (November 2013–November 2019), and 33 isolates were collected during the pandemic (March 2020–December 2021). As depicted in
Figure 1A, the prevalence of AVG, TCC, and AVF infections in the prepandemic period were 58%, 39.1%, and 2.9%, respectively. During the pandemic, the prevalence of AVG infection was lower at 39.4%, whereas that of TCC infection was higher at to 60.6%.
The prevalence of MRSA and that of methicillin-sensitive S. aureus (MSSA) from AVG infection were both 29% before the pandemic but lower at 24.2% and 15.2% during the pandemic, respectively (
Figure 1B). The ratio of AVG-MRSA to AVG-MSSA during the pandemic was 1.6:1 compared with 1:1 before the pandemic, indicating an increase in MRSA in the AVG infection population during the pandemic. By contrast, the prevalence of MRSA and MSSA from TCC infection was 27.5% and 11.6%, respectively, in the prepandemic period and 36.4% and 24.2% during the pandemic, respectively. The ratio of TCC-MRSA to TCC-MSSA was 1.5:1 during the pandemic period compared with 2.4:1 before the pandemic, indicating a decrease in MRSA in the TCC infection population.
2.2. Distribution of SCCmec type in MRSA isolates
Of 102 S. aureus isolates, 61 were identified as MRSA, of which 60 were mecA-positive MRSA and 1 was oxacillin-resistant mecA-negative MRSA.
Of the 61 MRSA isolates, the predominant SCCmec type was SCCmec type IV, followed by SCCmec V. The prevalence of SCCmec type IV was approximately 50% in both periods, whereas the prevalence of type V increased from 19.5% before the pandemic to 30% during it. Conversely, that of SCCmec III decreased from 17.1% to 10%. SCCmec IV and V are present mainly in community-associated MRSA isolates, indicating that VAI isolates tend to be community-associated. The most prevalent SCCmec type of AVG-MRSA was SCCmec IV, with a prevalence of 65% before the pandemic that increased to 75% during the pandemic. By contrast, TCC-MRSA predominantly carried SCCmec III and V elements before the pandemic, whereas SCCmec IV overtook III to become the second predominant type after SCCmec V during the pandemic.
2.3. Distribution of sequence types (STs) in VAI isolates
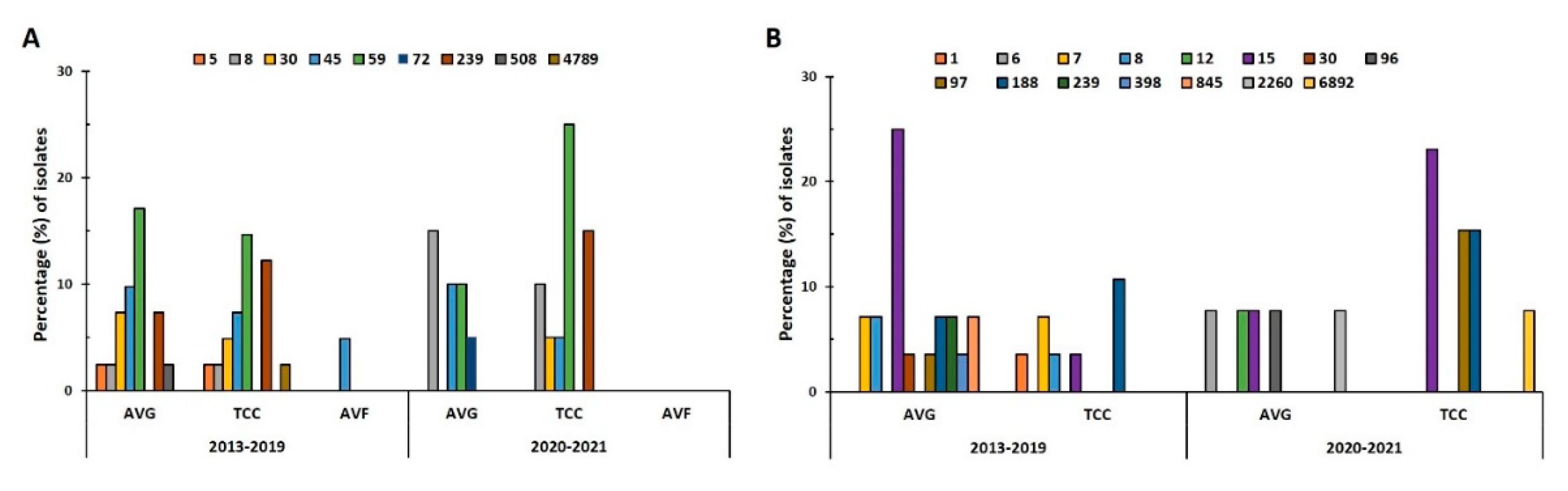
In the prepandemic period, 8 STs were identified in 41 MRSA isolates, and the predominant ST types were ST59 (31.7%, 13/41), ST45 (22%, 9/41), ST239 (19.5%, 8/41), and ST30 (12.2%, 5/41;
Figure 2A). During the pandemic, only 6 STs were identified in 20 MRSA isolates, and the predominant STs were ST59 (35%, 7/20) and ST8 (25%, 5/20). ST59 was the predominant ST in both periods, with its prevalence being slightly higher during the pandemic; AVG-MRSA ST59 (17.1%) was slightly more prevalent than was TCC-MRSA ST59 (14.6%) before the pandemic, whereas TCC-MRSA ST59 (25%) increased remarkably during the pandemic. AVG-MRSA ST30 and ST45 were slightly more prevalent than TCC-MRSA before the pandemic. ST45 levels remained consistent during the pandemic; however, no AVG-MRSA ST30 isolates were detected. ST8 prevalence in AVG-MRSA and TCC-MRSA increased substantially during the pandemic, and ST8 became dominant in AVG-MRSA. Of 41 MSSA isolates, 10 STs were identified in 28 isolates before the pandemic, and 8 STs in 13 isolates during the pandemic (
Figure 2B). ST15 was the predominant ST both before (28.6%) and during (30.8%) the pandemic. Before the pandemic, ST15 was prominent in AVG-MSSA, whereas ST188 was dominant in TCC-MSSA. The distribution of ST changed during the pandemic, as particularly exhibited by the decrease in AVG-MSSA ST15, the absence of AVG-MSSA ST188, the considerable increase in TCC-MSSA ST15, and the presence of TCC-MSSA ST97.
2.4. Prevalence of antibiotic resistance in VAI isolates
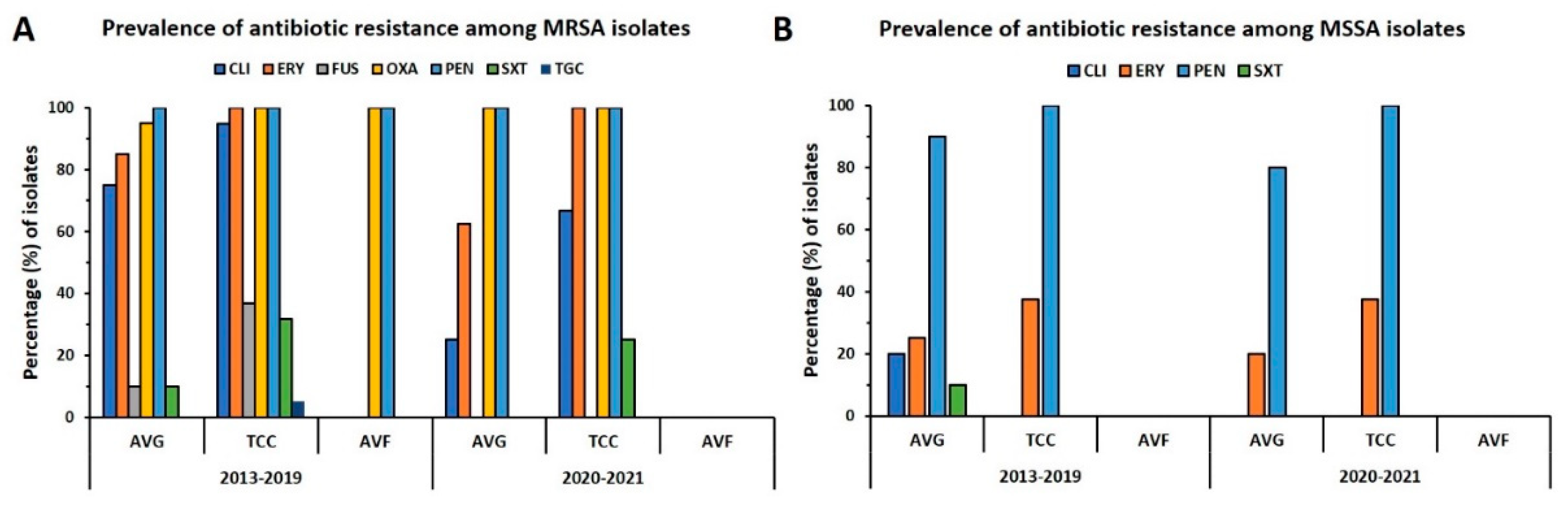
The distribution of antibiotic resistance in MRSA and MSSA isolates from different types of VAI is summarized in
Figure 3. Each of the MRSA isolates was resistant to penicillin, and all but one was oxacillin-resistant. For the prepandemic period, more than 80% of isolates were resistant to clindamycin and erythromycin, wherein 75% of isolates for AVG-MRSA and 94.7% of isolates for TCC-MRSA were clindamycin-resistant and 85% of isolates for AVG-MRSA and 100% of isolates for TCC-MRSA were erythromycin-resistant, respectively. However, the rate of resistance to clindamycin was reduced to 50% during the pandemic, whereas the resistance rate was remarkably reduced to 25% for AVG-MRSA isolates and 66.7% for TCC-MRSA isolates. The rate of resistance to erythromycin for AVG-MRSA decreased to 62.5% during the pandemic; by contrast, the resistance rate of TCC-MRSA was the same as before. The rate of resistance to SXT decreased slightly during the pandemic, especially because none of the AVG-MRSA isolates were resistant to SXT. The MSSA isolates consistently exhibited high resistance to penicillin. The rate of resistance to penicillin and erythromycin in AVG-MSSA decreased slightly during the pandemic, and the AVG-MSSA antibiotic resistance rate was lower than that of TCC-MSSA. Overall, the AVG isolates generally exhibited lower resistance to the tested antibiotics than did the TCC isolates, and this trend was more apparent during the pandemic.
2.5. Correlation of ST with antibiotic resistance
The antibiotic resistance profiles of each ST from different VAIs before and during the pandemic are summarized in
Table 1. ST5, ST45, ST59, and ST239 were the STs mainly associated with clindamycin and erythromycin resistance in AVG-MRSA in the prepandemic period. An absence of ST5 and ST239 isolates and loss of clindamycin and erythromycin resistance in ST45 isolates occurred during the pandemic, indicating that the change in ST distribution in AVG-MRSA during the pandemic led to a reduction in the rate of resistance to clindamycin and erythromycin. A similar phenomenon was observed for clindamycin resistance in TCC-MRSA during the pandemic, suggesting that the distribution of STs was considerably correlated with antibiotic resistance in isolates from different VAIs. The MSSA isolates with different STs were mainly resistant to penicillin and sometimes erythromycin; this was particularly true for ST7, ST12, ST15, and ST188. ST30 and ST239 were the AVG-MSSA isolates exhibiting clindamycin resistance; they exhibited similar resistance patterns to those of MRSA-ST30 and MRSA-ST239.
2.6. Correlation of resistance genotype with phenotype
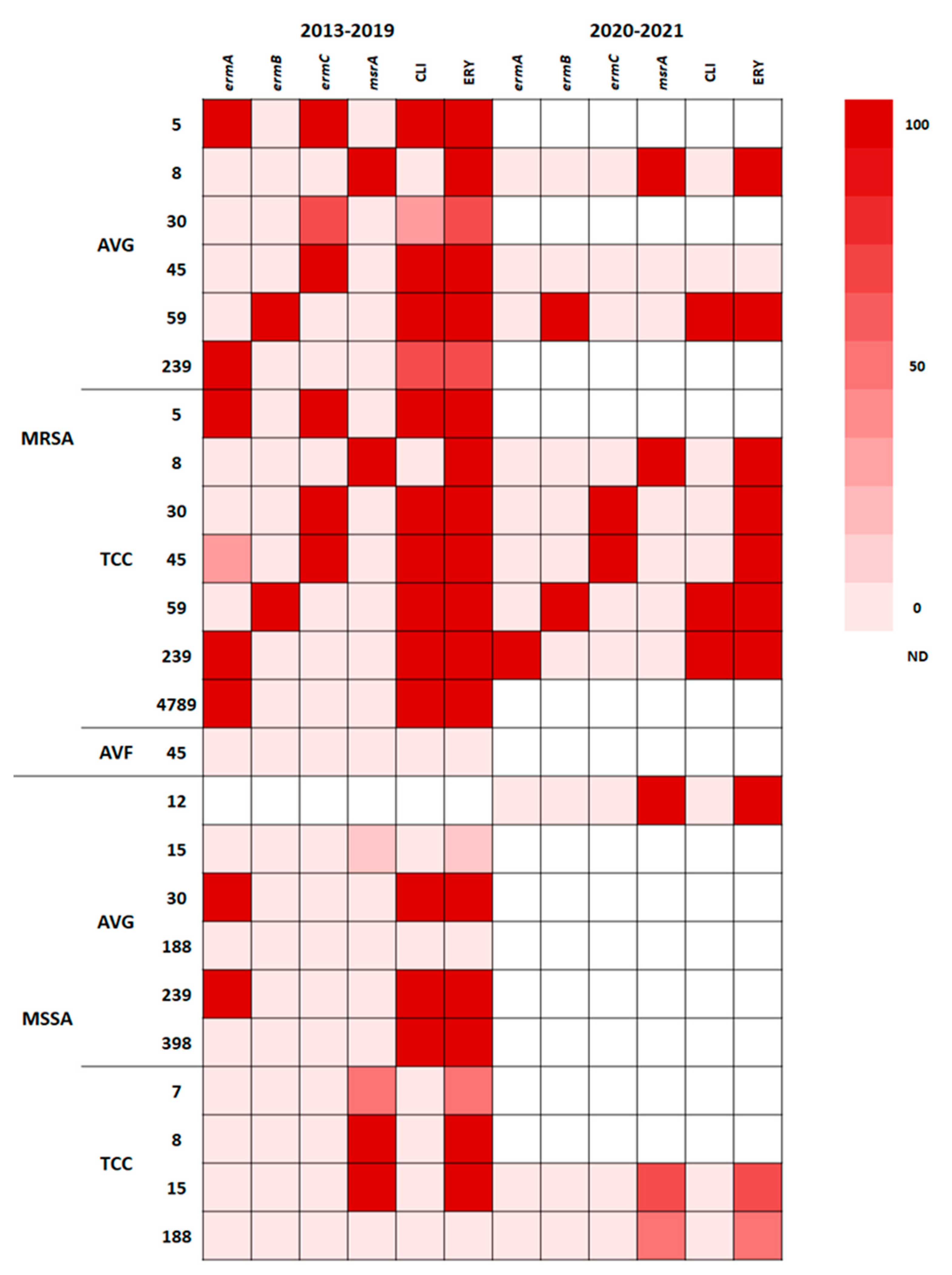
Macrolide (erythromycin)–lincosamide (clindamycin)–streptogramin B resistance is typically mediated by a ribosomal RNA methylase encoded by erm genes through ribosomal target site methylation [
23]. The phenotypic and genotypic resistance traits of isolates with different STs to erythromycin and clindamycin are presented in the heat map shown in
Figure 4. The distribution of erm and msrA genes varied in different STs; 100% of ST5 MRSA and ST59 MRSA isolates from AVG and TCC infections were resistant to clindamycin and erythromycin; ST5 MRSA harbored the ermA + ermC genes, whereas ST59 MRSA harbored the ermB gene. AVG-MRSA ST45 and TCC-MRSA ST45, predominantly carrying the ermC gene, were resistant to clindamycin and erythromycin, but one TCC-MRSA isolate carried the ermA + ermC genes; by contrast, AVF-MRSA ST45 was susceptible to clindamycin and erythromycin and carried no erm genes. MRSA and MSSA ST239 carrying the ermA gene exhibited clindamycin and erythromycin resistance; one AVG-MRSA ST239 isolate carried ermA but did not have clindamycin or erythromycin resistance, suggesting mutation of the ermA gene. ST8 MRSA and MSSA isolates harboring the msrA gene were only resistant to erythromycin. The MSSA isolates of different STs that exhibited erythromycin resistance harbored the msrA gene. Both before and during the pandemic, the distribution of genotypic and phenotypic resistance to erythromycin and clindamycin of S. aureus was closely correlated with the ST.
3. Discussion
Because vascular access provides repeated access to the circulation, effectively functioning vascular access is crucial to efficient hemodialysis [
24]. However, hemodialysis patients appear more vulnerable to S. aureus infection than are others because vascular access can provide a route for S. aureus colonization and transmission; the type of vascular access is also associated with the specific risk of infection. In this single-institution study, S. aureus isolation rates differed considerably by the type of VAI, and the proportion of TCC infections increased and that of AVG infections decreased during the pandemic. The overall proportion of MRSA to MSSA was the same, approximately 3:2, before and during the pandemic. Nevertheless, the ratio of TCC-MRSA to TCC-MSSA declined during the pandemic; the ratio of AVG-MRSA to AVG-MSSA exhibited the opposite trend. The main reason for the increased use of TCCs during the pandemic was that timely maintenance of AVGs was difficult at this time. Once AVG dysfunction occurred, patients were more likely to be administered a TCC for hemodialysis than to receive thrombectomy of the AVG. Additionally, because TCC infections mostly occur in community-based clinics, their resistance to antibiotics is often greater than that of infections contracted in hospitals.
Regarding MLST, the clonal spread in hemodialysis patients and with S. aureus infection was explored before and during the pandemic. In Taiwan, the community-associated ST59 became a major clone in hospital settings in the 2010s [
25]. A surveillance study conducted across 18 provinces of China reported the dominance of ST59 between 2014 and 2019 [
26], and Zhang et al. reported the dominance of ST59 in MRSA isolates in Anhui Province, China, in the 2020s [
27]. Nevertheless, a study performed from 2009 to 2014 in a medical center in Southern Taiwan revealed that ST239 was the most common MLST type in hemodialysis cases (23.9%), followed by ST59 (17.7%) and ST45 (13.5%); however, infections by community-associated genotypes are increasing in the hemodialysis population [
11]. In the present study, ST59 was the most predominant ST in the VAI MRSA population before and even during the pandemic and was especially prevalent in TCC-MRSA during the pandemic. MRSA ST45 and ST239 were also predominant in the prepandemic period. ST45 has been reported as endemic in nursing homes and long-term care facilities in Taiwan [
28,
29] and is the second leading nasal MRSA colonization in emergency department patients and healthcare workers in central Taiwan [
30]. Patients receiving hemodialysis are frequently shuttled between dialysis centers (healthcare facilities) and hospitals for health care may be the inadvertent cause of dissemination of ST59 and ST45 within communities and hospitals. ST8 supplanted ST45 to become the second most prevalent ST after ST59 during the pandemic. The community-associated ST8 was initially the dominant clone in the United States [
31,
32] but gradually spread worldwide; identification of it in Asia, including Taiwan, has not been uncommon since 2010 [
33,
34,
35]. A multicenter MRSA surveillance study conducted between 1995 and 2015 in Taiwan reported that 85% of MRSA ST8 isolates were identified after 2010, with their first identification being in 2005 [
35]. A study conducted between 2016 and 2018 in northern Taiwan indicated that after an abrupt increase in prevalence, ST8 became the most prevalent ST in 2018, even replacing ST59 in community-associated settings [
36]. However, the study indicated a low proportion of ST8 in catheter- and device-related infections; this may explain why ST8 was undetected in VAIs before the pandemic. Whether the high prevalence of ST8 during the pandemic was due to clonal expansion from community to hospital settings and high fitness in the hemodialysis population requires a prolonged observation.
Exploring the contribution of antibiotic resistance over time is essential if appropriate drugs are to be selected for treating infections and the stockpiling of resistant bacteria is to be reduced. The prevalence of antibiotic resistance patterns is highly associated with STs. The overwhelming majority of S. aureus isolates (~97%) from VAIs were resistant to β-lactam penicillin, and approximately 60% of isolates were oxacillin-resistant. Before the pandemic, TCC-MRSA was highly resistant to clindamycin (94.7%) and erythromycin (100%) in addition to penicillin and oxacillin and exhibited a remarkably higher resistance rate than did AVG-MRSA (75% and 85%, respectively). Although the rate of resistance to clindamycin was reduced during the pandemic, TCC-MRSA continued to exhibit higher resistance than that of AVG-MRSA. ST59 and ST239 isolates exhibit high rates of resistance to clindamycin and erythromycin [
25,
37], consistent with the current study’s finding that all ST59 and most ST239 isolates were resistant to both of these antibiotics. Consequently, the prevalence of ST59 and ST239 in TCC-MRSA during the pandemic led to higher clindamycin and erythromycin resistance rates than those for AVG-MRSA. The increase in the clindamycin susceptibility rate in Taiwan is mainly due to the increase in ST8 prevalence [
38]. The increasing rate of ST8 during the pandemic directly reflected the decline in the clindamycin resistance rate because none of the ST8 exhibited clindamycin resistance. Other studies have indicated that the clindamycin resistance rate of ST8 was 7.7%, 66.7%, and 44.6% in northern Taiwan between 2016 and 2018 [
36]; in Anhui Province, China, between 2021 and 2022 [
27]; and in Japan in 2019 [
39], respectively, suggesting geographical variation depending on local antibiotic usage or different genetic distributions.
Both before and during the pandemic, all ST8 isolates, including MRSA and MSSA isolates, harboring the msrA gene exclusively exhibited erythromycin resistance because clindamycin is neither an inducer nor a substrate for the msrA-mediated efflux pump, which is responsible for pumping macrolide and streptogramin B antibiotics out of bacteria [
40]. Nevertheless, a study conducted in Japan reported a high rate of retention of the ermA gene in ST8 isolates with almost the same clindamycin resistance rate [
39], suggesting that the spread of resistance genes is possibly confined geographically. Wang et al. [
41] reported that MRSA ST59 isolates from children in northern Taiwan between 1997 to 2002 were resistant to erythromycin and clindamycin and had the ermB gene, which is similar to our finding. A study conducted in Hangzhou, China [
42], demonstrated that ST59 predominantly carried the ermB gene as dominant and to a lesser extent the ermC gene, wherein the transmissible ermC gene was also exhibited in other STs. In our study, the ermC gene was detected in AVG-MRSA and TCC-MRSA ST5, ST30, and ST45 with clindamycin and erythromycin resistance before the pandemic but in TCC-MRSA ST30 and ST45 with erythromycin resistance during the pandemic, suggesting that the management of antibiotic usage or clonal contraction may confine the spread of resistance genes.
This study provided insight into molecular characteristics and phenotypic and genotypic antibiotic resistance in S. aureus isolates from different types of VAIs before and during the pandemic. Nonetheless, this study has several limitations. This was a single-institution longitudinal study covering an 8-year period; the varying frequency of isolates collected each year and the small sample size may have caused bias; however, the data nonetheless reflect the situation during the study. Furthermore, because of the lack of patients’ demographic data, the impact of changes in STs on the clinical course is unclear. Although our findings may not represent the different STs circulating in the hemodialysis population with S. aureus VAIs in different geographic regions and periods, the data provide insight regarding the distribution of STs and the spreading of antibiotic resistance in infection control and management.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of Chang Gung Memorial Hospital (IRB201508482B and IRB201901354B0).
4.2. Study setting, bacterial isolate collection, and identification
The study was conducted at a tertiary teaching hospital, Chiayi Chang Gung Memorial Hospital in Chiayi, Taiwan, between November 2013 and December 2021. A total of 102 bacterial isolates were collected from hemodialysis patients for whom infected TCCs, AVGs, and AVFs had to be removed. The bacterial isolates were derived from contaminated Hickman catheter tips, wounds, pus, abscesses, and blood. The samples were routinely cultured under laboratory standards. Strains were identified using standard biochemical (phenotypic) procedures. The isolates collected after 2019 were identified using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS).
4.3. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing
The antimicrobial susceptibility of S. aureus isolates was determined using disk diffusion with the following antibiotics: clindamycin, erythromycin, fusidic acid, oxacillin, penicillin, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (SXT), and tigecycline. The results were interpreted in accordance with the standards of the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute [
15].
4.4. Molecular characterization and antibiotic resistance gene detection
4.4.1. Identification of methicillin-resistant S. aureus and staphylococcal chromosomal cassette mec (SCCmec) type
Genomic DNA was extracted using a method previously described [
16]. The isolates were identified as MRSA when they exhibited oxacillin resistance and mecA positivity. The detection of mecA was performed using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) with previously described primer pairs [
17]. This study also categorized the oxacillin-resistant mecA-negative and oxacillin-sensitive mecA-positive isolates as MRSA. SCCmec types I–V were identified using a multiplex PCR assay together with specific primers [
18].
4.4.2. Molecular typing
For 102 isolates, multilocus sequence typing (MLST) was performed by amplifying the internal fragment of seven housekeeping genes through a previously described protocol followed by sequencing [
19]. When the aroE gene could not be amplified, we used alternative primers described by Schuster et al. [
20]. The amplified product sequencing in both directions was performed using Sanger dideoxy DNA sequencing (Mission Biotech, Taipei, Taiwan). The sequence type (ST) of each isolate was determined using BioNumerics 7.6 (Applied Maths, Sint-Martens-Latem, Belgium) in accordance with the MLST database [
21].
4.4.3. Erythromycin-resistant-gene detection
Several antibiotic-resistant genes were identified using multiplex PCR with the 16S rDNA gene as an internal control. The following genes conferring resistance to erythromycin were screened for: ermA, ermB, ermC, and msrA [
22].
5. Conclusions
During the pandemic, AVG-related infections decreased and TCC-related infections increased. The prevalence of various STs differed by VAI type and changed from before the pandemic to during the pandemic. ST8 took over from ST59 as the dominant ST in AVG-MRSA and ST59 increased remarkably in TCC-MRSA during the pandemic. The change in antibiotic resistance rate in different VAIs between the two periods was closely related to the distribution of STs because some STs carry specific resistance genes. The molecular surveillance of S. aureus VAIs is crucial in tracing the expansion/reduction of certain clones for infection management and further delineating an effective therapeutic strategy.
Author Contributions
Author Contributions: Conceptualization, C.C.K. and Y.K.H.; methodology, T.Y.H. and Y.K.H.; validation, C.C.K. and Y.H.T.; formal analysis, M.Y.W., C.H.L., and C.C.K.; investigation, M.Y.W., C.H.L., Y.H.T.; resources, T.Y.H. and Y.K.H.; data curation, M.Y.W., C.H.L., and C.C.K.; writing—original draft preparation, M.Y.W., C.H.L., Y.K.H., and C.C.K.; writing—review and editing, C.C.K., C.H.L., M.Y.W., Y.H.T., T.Y.H., and Y.K.H.; project administration, Y.K.H., and C.C.K.; supervision, Y.K.H.; funding acquisition, Y.K.H., C.C.K. and Y.T.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by grants from the Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Chiayi, Taiwan (Grant numbers: CMRPG6M0101-3 and CMRPG6L0071).
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of Chang Gung Memorial Hospital (IRB201508482B and IRB201901354B0), and this study was performed in accordance with the approved guidelines.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The authors declare that the experimental data published in this paper are made accessible upon request for interested readers.
Acknowledgments
We thank Wallace Academic for editing this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
References
- Ogston, A. Micrococcus poisoning. J. Anat. Physiol. 1882, 16 Pt 4, 526–567. [Google Scholar]
- Kluytmans, J.; van Belkum, A.; Verbrugh, H. Nasal carriage of Staphylococcus aureus: epidemiology, underlying mechanisms, and associated risks. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1997, 10, 505–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, H. F. The changing epidemiology of Staphylococcus aureus? Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2001, 7, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowy, F. D. Staphylococcus aureus infections. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 520–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M. L.; Chang, S. C.; Pan, H. J.; Hsueh, P. R.; Yang, L. S.; Ho, S. W.; Luh, K. T. Longitudinal analysis of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates at a teaching hospital in Taiwan. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 1999, 98, 426–432. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.-C.; Chen, C.-J. Community-associated meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in children in Taiwan, 2000s. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2011, 38, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.-J.; Huang, Y.-C.; Su, L.-H.; Wu, T.-L.; Huang, S.-H.; Chien, C.-C.; Chen, P.-Y.; Lu, M.-C.; Ko, W.-C. Molecular epidemiology and antimicrobial resistance of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bloodstream isolates in Taiwan, 2010. PLoS One 2014, 9, e101184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-Y.; Fang, Y.-P.; Chang, Y.-F.; Wu, T.-H.; Yang, Y.-Y.; Huang, Y.-C. Comparison of molecular epidemiology of bloodstream methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates between a new and an old hospital in central Taiwan. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 79, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerging Infections Program, Healthcare-Associated Infections - Community Interface Surveillance Report, Invasive Staphylococcus aureus; 2019. https://www.cdc.gov/hai/eip/pdf/2019-MRSA-Report-508.pdf.
- Vandecasteele, S. J.; Boelaert, J. R.; De Vriese, A. S. Staphylococcus aureus infections in hemodialysis: what a nephrologist should know. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 4, 1388–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.-Y.; Tu, H.-P.; Chen, T.-C.; Shen, M.-C.; Chiu, Y.-W.; Chen, Y.-H.; Lu, P.-L. Association of bacterial genotypes and epidemiological features with treatment failure in hemodialysis patients with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia. PLoS One 2018, 13, e0198486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Control, C. F. D. & Prevention. Invasive methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections among dialysis pa-tients--United States. MMWR. Morbidity and mortality weekly report 2005, 56, 197–199. [Google Scholar]
- Akoh, J. A. Vascular access infections: epidemiology, diagnosis, and management. Curr. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2011, 13, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.-C.; Chen, S.-Y.; Ko, W.-C.; Hsueh, P.-R. Increased antimicrobial resistance during the COVID-19 pandemic. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2021, 57, 106324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI. <i>CLSI document M100-S27</i>. CLSI Wayne, PA. 15. CLSI. CLSI document M100-S27, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Tseng, Y. H. Molecular characterization of clinical isolates from vascular access infection: A single-institution study. Microbiologyopen, 1: (2020), e1126. https://doi.org, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Pournajaf, A.; Ardebili, A.; Goudarzi, L.; Khodabandeh, M.; Narimani, T.; Abbaszadeh, H. PCR-based identification of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains and their antibiotic resistance profiles. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2014, 4 (Suppl 1), S293–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boye, K.; Bartels, M. D.; Andersen, I. S.; Møller, J. A.; Westh, H. A new multiplex PCR for easy screening of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus SCCmec types I-V. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2007, 13, 725–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enright, M. C.; Day, N. P.; Davies, C. E.; Peacock, S. J.; Spratt, B. G. Multilocus sequence typing for characterization of methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible clones of Staphylococcus aureus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 1008–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruimy, R.; Armand-Lefevre, L.; Barbier, F.; Ruppé, E.; Cocojaru, R.; Mesli, Y.; Maiga, A.; Benkalfat, M.; Benchouk, S.; Hassaine, H.; Dufourcq, J.-B.; Nareth, C.; Sarthou, J.-L.; Andremont, A.; Feil, E. J. Comparisons between geographically diverse samples of carried Staphylococcus aureus. J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 5577–5583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolley, K. A.; Bray, J. E.; Maiden, M. C. J. Open-access bacterial population genomics: BIGSdb Software, the PubMLST.org website and their applications. Wellcome Open Res. 2018, 3, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duran, N.; Ozer, B.; Duran, G. G.; Onlen, Y.; Demir, C. Antibiotic resistance genes & susceptibility patterns in staphylococci. Indian J. Med. Res. 2012, 135, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Weisblum, B. Erythromycin resistance by ribosome modification. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1995, 39, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, D.; Benedetto, F.; Mondello, P.; Pipitò, N.; Barillà, D.; Spinelli, F.; Ricciardi, C. A.; Cernaro, V.; Buemi, M. Vascular access for hemodialysis: current perspectives. Int. J. Nephrol. Renovasc. Dis. 2014, 7, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-J.; Huang, Y.-C. New epidemiology of Staphylococcus aureus infection in Asia. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, 605–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Zhou, W.; Zhan, Q.; Zheng, B.; Chen, Y.; Luo, Q.; Shen, P.; Xiao, Y. Genomic epidemiology and characterization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from bloodstream infections in China. mSystems 2021, 6, e0083721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Cao, J.; He, Z.; Zong, X.; Sun, B. Molecular epidemiology of Staphylococcus aureus in a Tertiary Hospital in Anhui, China: ST59 Remains a Serious Threat. Infect. Drug Resist. 2023, 16, 961–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsao, F.-Y.; Kou, H.-W.; Huang, Y.-C. Dissemination of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus sequence type 45 among nursing home residents and staff in Taiwan. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2015, 21, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.-C.; Chang, C.-J.; Lin, Y.-T.; Huang, K.-Y. A.; Chen, C.-J. A longitudinal survey of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus carriage in nursing homes and the long-term care facility in Taiwan. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2022, 55, 853–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.-H.; Lee, C.-Y.; Yang, H.-J.; Fang, Y.-P.; Chang, Y.-F.; Tzeng, S.-L.; Lu, M.-C. Prevalence and molecular characteristics of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus among nasal carriage strains isolated from emergency department patients and healthcare workers in central Taiwan. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2019, 52, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diekema, D. J.; Richter, S. S.; Heilmann, K. P.; Dohrn, C. L.; Riahi, F.; Tendolkar, S.; McDanel, J. S.; Doern, G. V. Continued emergence of USA300 methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in the United States: results from a nationwide surveillance study. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2014, 35, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrel, M.; Perencevich, E. N.; David, M. Z. USA300 methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, United States, 2000-2013. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 1973–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.; Song, E. H.; Park, S. Y.; Lee, S.-R.; Park, S.-J.; Sung, H.; Kim, M.-N.; Kim, S.-H.; Lee, S.-O.; Choi, S.-H.; Woo, J. H.; Kim, Y. S.; Chong, Y. P. Emergence of panton-valentine leucocidin-positive ST8-methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (USA300 Clone) in Korea causing healthcare-associated and hospital-acquired bacteraemia. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 35, 1323–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagao, M. First outbreak of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus USA300 harboring the Panton-Valentine leukocidin genes among Japanese health care workers and hospitalized patients. Am J Infect Con-trol 2010, 38, e37–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.-C.; Chen, C.-J.; Kuo, C.-C.; Lu, M.-C. Emergence, transmission and phylogeny of meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus sequence type 8 (USA300) in Taiwan. J. Hosp. Infect. 2018, 100, 355–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.-Y.; Chuang, Y.-C.; Wang, J.-T.; Sheng, W.-H.; Chen, Y.-C.; Chang, S.-C. Sequence type 8 as an emerging clone of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus causing bloodstream infections in Taiwan: evolving molecular epidemiology of MRSA bacteraemia. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2021, 10, 1908–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, Y. Y.; Huang, Y. C. Molecular epidemiology of community-associated meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Asia. Lancet Infect Dis 2013, 13, 698–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y. C.; Chen, C. J. USA300 (sequence type 8) has become a major clone of methicillin-resistant Staphy-lococcus aureus in northern Taiwan. Int J Antimicrob Agents 2022, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaku, N.; Sasaki, D.; Ota, K.; Miyazaki, T.; Yanagihara, K. Changing molecular epidemiology and characteristics of MRSA isolated from bloodstream infections: nationwide surveillance in Japan in 2019. J Antimicrob Chemother 2022, 77, 2130–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aktas, Z.; Aridogan, A.; Kayacan, C. B.; Aydin, D. Resistance to macrolide, lincosamide and streptogramin antibiotics in staphylococci isolated in Istanbul, Turkey. J. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 286–290. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.-C.; Lo, W.-T.; Chu, M.-L.; Siu, L. Epidemiological typing of community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates from children in Taiwan. Clinical infectious diseases 2004, 39, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhuang, H.; Ji, S.; Sun, L.; Zhao, F.; Wu, D.; Shen, P.; Jiang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Chen, Y. Distribution of erm genes among MRSA isolates with resistance to clindamycin in a Chinese teaching hospital. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2021, 96, 105127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).