Submitted:
12 June 2023
Posted:
13 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. GC-MS analysis
2.2. Antimicrobial activity
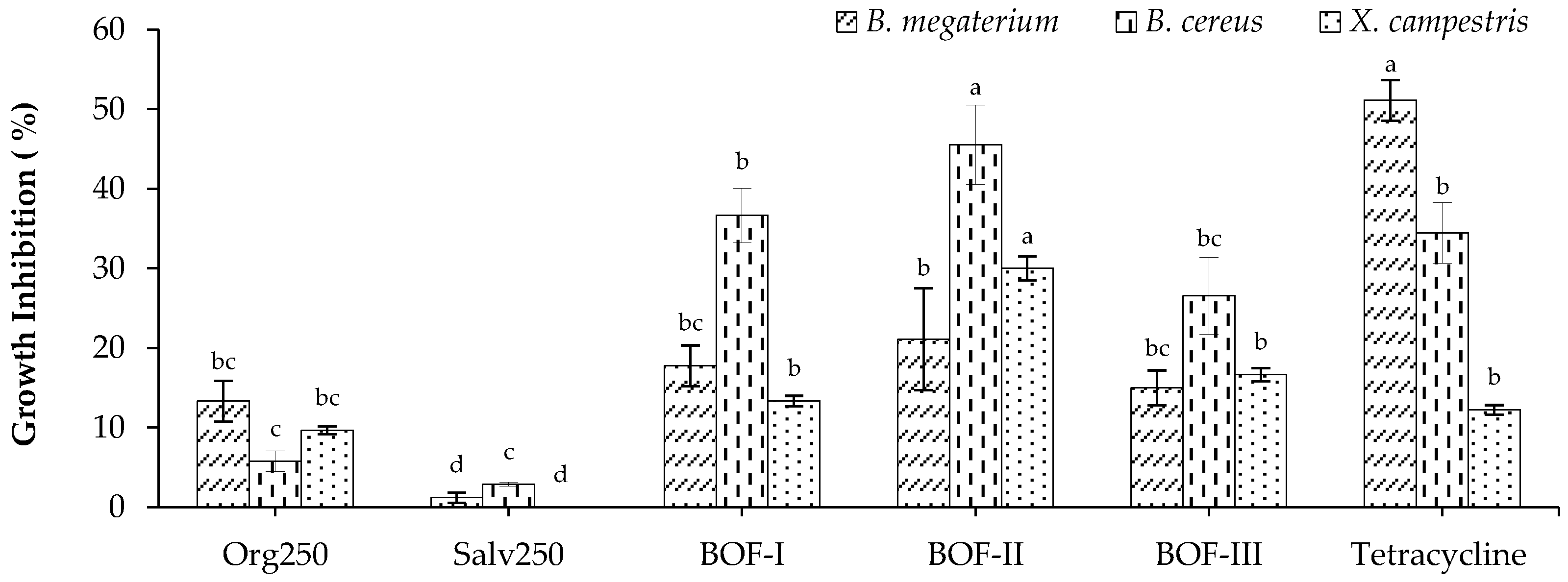
2.2.1. Bactericidal activity
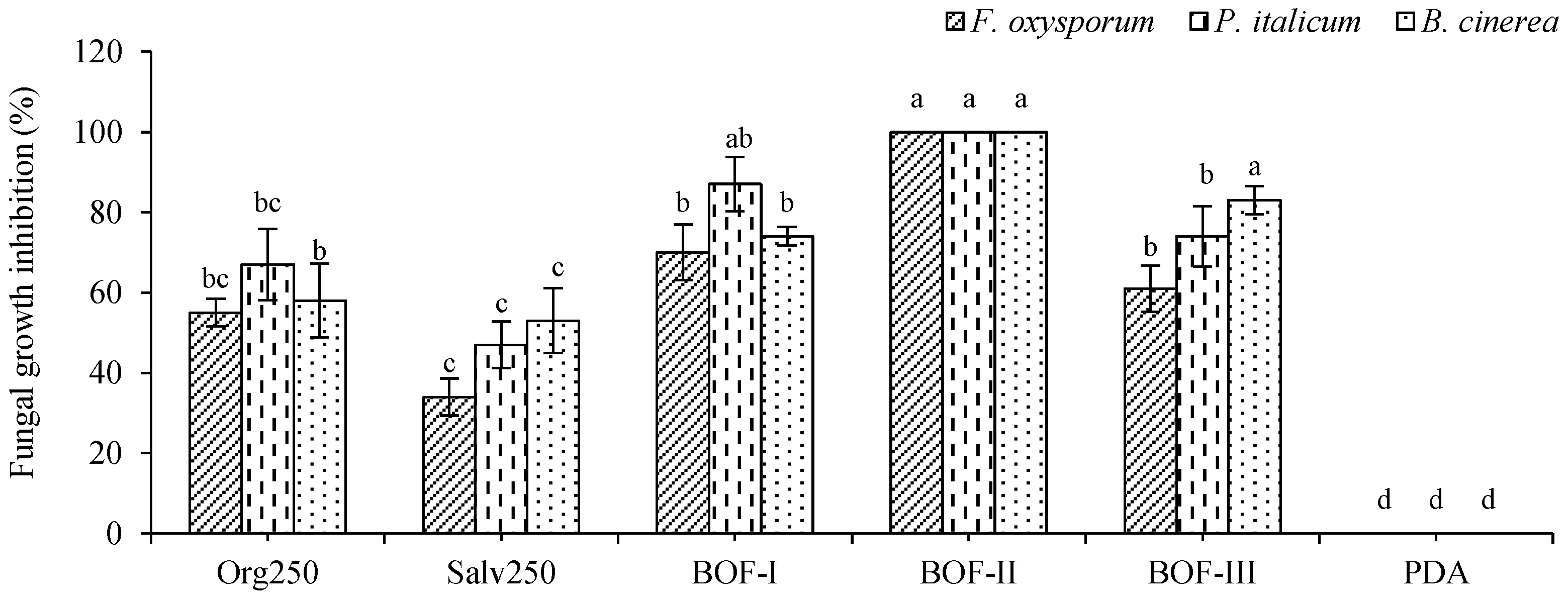
2.2.2. Fungicidal activity
2.3. Phytotoxic activity
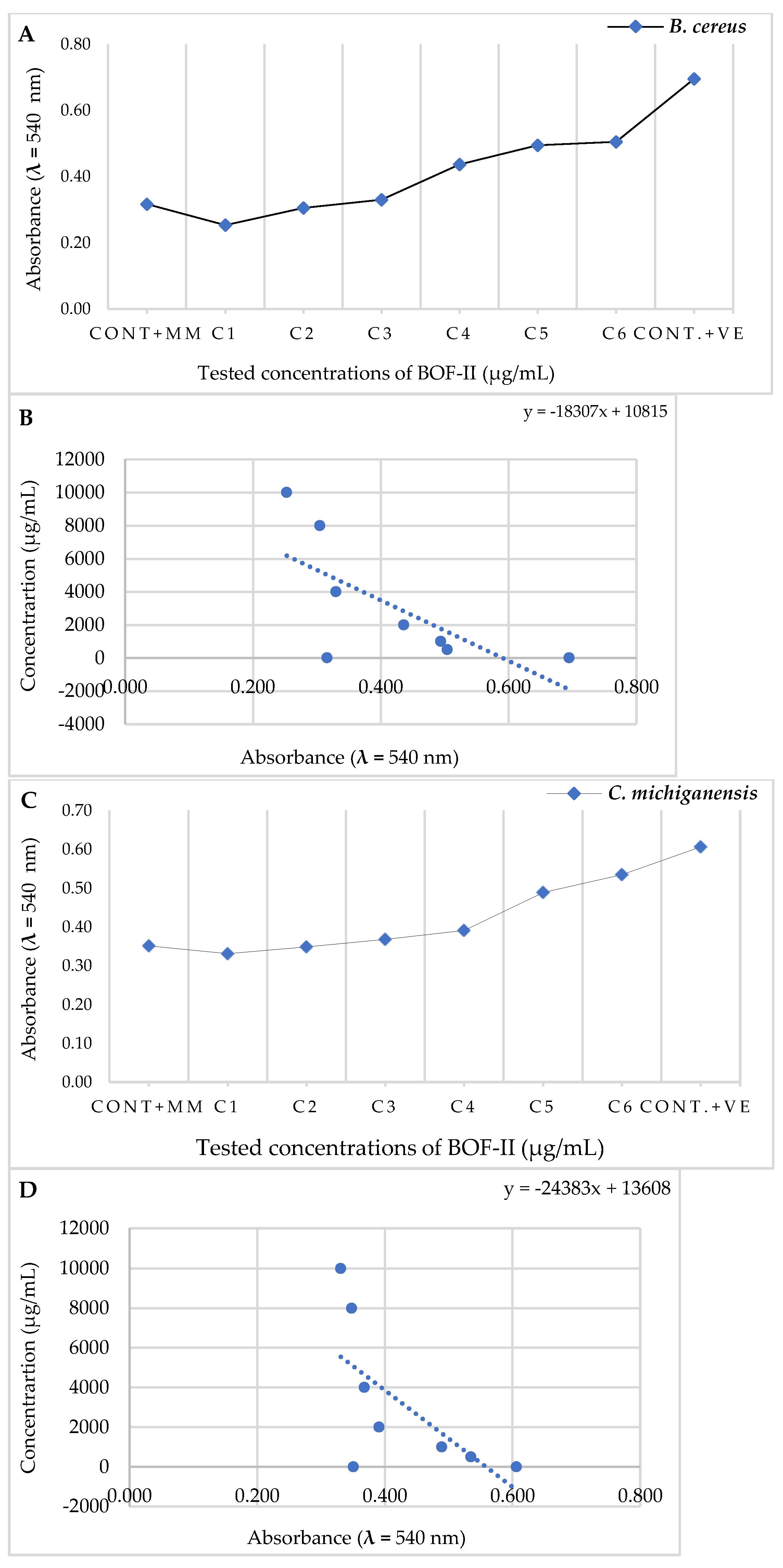
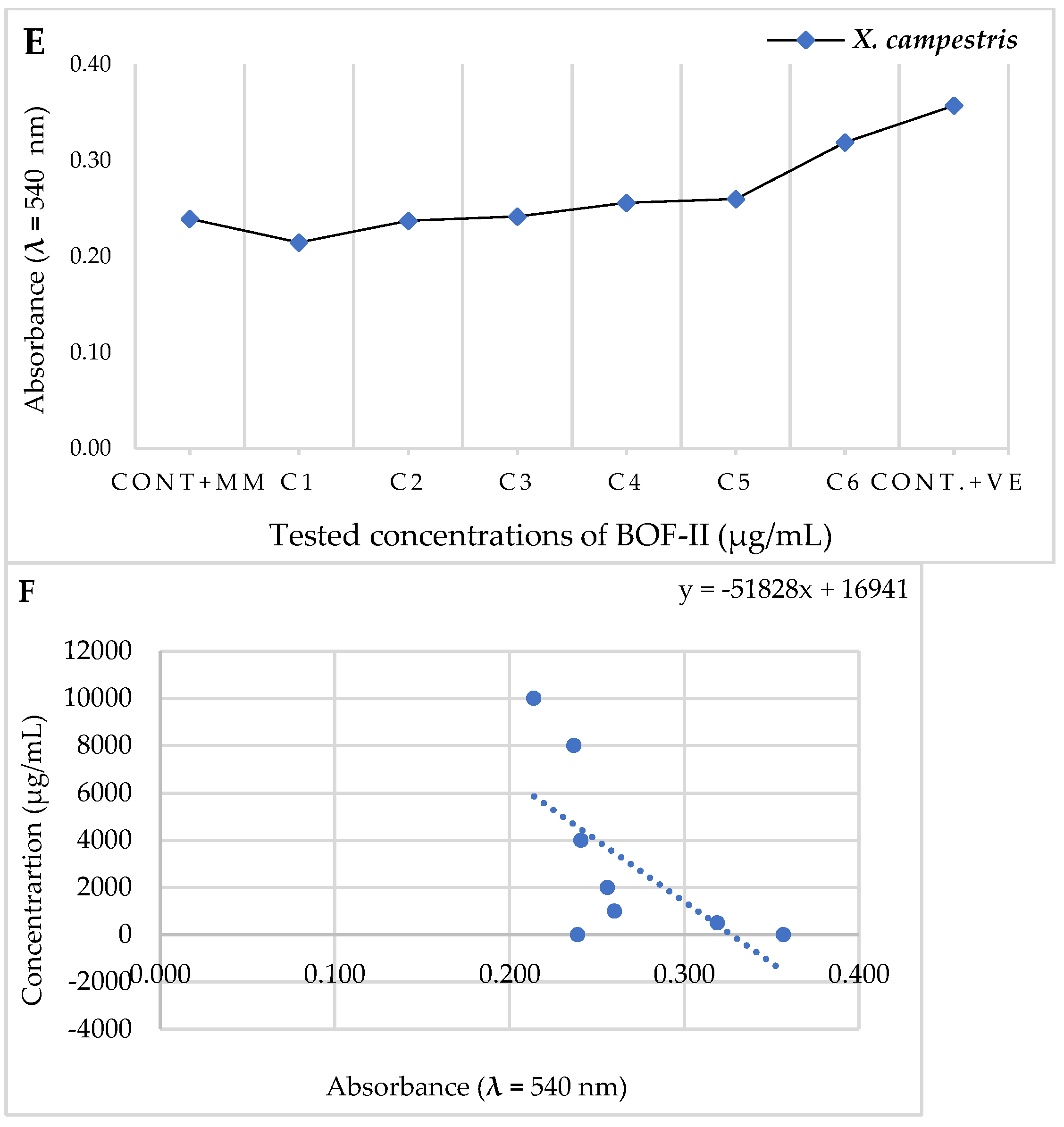
2.4. MBC analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant materials, extraction EOs and formulation
4.2. GC-MS analysis
4.3. Antimicrobial activity
4.3.1. Bactericidal assay
4.3.2. Fungicidal assay
4.4. Miminum bactericidal concentration (MBC)
4.5. Phytotoxic assay
4.6. Statistical analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Duke, S.O. Why have no new herbicide modes of action appeared in recent years? Pest Manag. Sci. 2012, 68, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolopoulou-Stamati, P.; Maipas, S.; Kotampasi, C.; Stamatis, P.; Hens, L. Chemical Pesticides and Human Health: The Urgent Need for a New Concept in Agriculture. Front. Public Health 2016, 4, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruľová, D.; Caputo, L.; Elshafie, H.S.; Baranová, B.; De Martino, L.; Sedlák, V.; Camele, I.; De Feo, V. Thymol Chemotype Origanum vulgare L. Essential Oil as a Potential Selective Bio-Based Herbicide on Monocot Plant Species. Molecules 2020, 25, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Pepa, T.; Elshafie, H.S.; Capasso, R.; De Feo, V.; Camele, I.; Nazzaro, F.; Scognamiglio, M.R.; Caputo, L. Antimicrobial and phytotoxic activity of Origanum heracleoticum and O. majorana essential oils growing in Cilento (Southern Italy). Molecules 2019, 24, 2576. [Google Scholar]
- Anyanwu, M.U.; Okoye, R.C. Antimicrobial activity of Nigerian medicinal plants. J. Intercult. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 6, 240–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazella Luciane, N.; Glamoclija, J.; Soković, M.; Gonçalves, J.E.; Linde, G.A.; Colauto, N.B.; Gazim, Z.C. Antimicrobial Activity of Essential Oil of Baccharis dracunculifolia DC (Asteraceae) Aerial Parts at Flowering Period. Frontiers Plant Sci. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Camele, I.; Elshafie, H.S.; Caputo, L.; Sakr, S.H.; De Feo, V. Bacillus mojavensis: Biofilm formation and biochemical investigation of its bioactive metabolites. J. Biol. Res. 2019, 92, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossolini, G.M.; Arena, F.; Pecile, P.; Pollini, S. Update on the antibiotic resistance crisis. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2014, 18, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshafie, H.S.; Racioppi, R.; Bufo, S.A.; Camele, I. In vitro study of biological activity of four strains of Burkholderia gladioli pv. agaricicola and identification of their bioactive metabolites using GC–MS. Saudia J. Biol Sci. 2017, 24, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filho, J.G.; Silva, G.; de Aguiar, A.C.; Cipriano, L.; de Azeredo, H.M.C.; Junior, S.B.; Ferreira, M.D. Chemical composition and antifungal activity of essential oils and their combinations against Botrytis cinerea in strawberries. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2021, 15, 1815–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camele, I.; Elshafie, H.S.; De Feo, V.; Caputo, L. Anti-quorum Sensing and Antimicrobial Effect of Mediterranean Plant Essential Oils Against Phytopathogenic Bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elshafie, H.S.; Camele, I. An overview of The Biological Effects of Some Mediterranean Essential Oils on Human Health (Review article). Biomed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, Article ID 9268468, pp. 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshafie, H.S.; Caputo, L.; De Martino, L.; Gruľová, D.; Zheljazkov, V.D.; De Feo, V.; Camele, I. Biological investigations of essential oils extracted from three Juniperus species and evaluation of their antimicrobial, antioxidant and cytotoxic activities. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 129, 1261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomazoni, E.Z.; Pauletti, G.F.; da Silvaibeiro, R.T.; Moura, S.; Schwambach, J. In vitro and in vivo activity of essential oils extracted from Eucalyptus staigeriana, Eucalyptus globulus and Cinnamomum camphora against Alternaria solani Sorauer causing early blight in tomato. Sci. Hortic. 2017, 223, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshafie, H.S.; Ghanney; N. ; Mang, S.M.; Ferchichi, A.; Camele, I. 'An in vitro attempt for controlling severe phyto and human pathogens using essential oils from Mediterranean plants of genus Schinus. J. Med. Food 2016, 19, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshafie, H.S.; Camele, I.; Mohamed, A.A. A Comprehensive Review on the Biological, Agricultural and Pharmaceutical Properties of Secondary Metabolites Based-Plant Origin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, E.; Camele, I.; Elshafie, H.S.; De Martino, L.; Pellegrino, C.; Grulova, D.; Vincenzo De Feo. Chemical Composition and Biological Activity of the Essential Oil of Origanum vulgare ssp. hirtum from Different Areas in the Southern Apennines (Italy). Chem. Biodiver. 2014, 11, 639–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camele, I.; Grul’ová, D.; Elshafie, H.S. Chemical Composition and Antimicrobial Properties of Mentha _ piperita cv. ‘Kristinka’ Essential Oil. Plants 2021, 10, 1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardakani, M.S.; Mosadeggh, M.; Shafaati, A. Volatile constituents from the aerial parts of Verbena officinalis L (Vervain). Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2003, 2, 39–42. [Google Scholar]
- Elshafie, S.S.; Elshafie, H.S.; El Bayomi, R.M.; Camele, I.; Morshdy, A.E.M. Evaluation of the Antimicrobial Activity of Four Plant Essential Oils against Some Food and Phytopathogens Isolated from Processed Meat Products in Egypt. Foods 2022, 11, 1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshafie, H.S.; Sakr, S.; Mang, S.M.; De Feo, V.; Camele, I. Antimicrobial activity and chemical composition of three essential oils extracted from Mediterranean aromatic plants. J. Med. Food. 2016, 19, 1096–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tundis, R.; Leporini, M.; Bonesi, M.; Rovito, S.; Passalacqua, N.G. Salvia officinalis L. from Italy: A Comparative Chemical and Biological Study of Its Essential Oil in the Mediterranean Context. Molecules 2020, 10, 25–5826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A´cimovi´c, M.; Pezo, L.; Cabarkapa, I.; Trudi´c, A.; Stankovi´c ˇ Jeremi´c, J.; Varga, A.; Lonˇcar, B.; Šovljanski, O.; Teševi´c, V. Variation of Salvia officinalis L. Essential Oil and Hydrolate Composition and Their Antimicrobial Activity. Processes 2022, 10, 1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glisic, S.; Ivanovic, J.; Ristic, M.; Skala, D. Extraction of sage (Salvia officinalis L.) by supercritical CO2: Kinetic data, chemical composition and selectivity of diterpenes. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2010, 52, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatma, Ebru, K. ; Ayse, A.; Caglar, K. Extraction and HPLC Analysis of Sage (Salvia officinalis) Plant. Nat. Prod. Chem. Res. 2017, 5, 298. [Google Scholar]
- Keifer, M.C.; Firestone, J. Neurotoxicity of pesticides. J. Agromed. 2007, 12, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirmostafaee, S.; Azizi, M.; Fujii, Y. Study of Allelopathic Interaction of Essential Oils from Medicinal and Aromatic Plants on Seed Germination and Seedling Growth of Lettuce. Agronomy 2020, 10, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Lee, S.Y. Application of food-grade natural antimicrobials for the control of crop disease caused by phytopathogens. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2022, 31, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakkali., F.; Averbeck., S.; Averbeck., D.; Idaomar, M. Biological effects of essential oils—a review. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 446–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camele, I.; De Feo, V.; Altieri, L.; Mancini, E.; De Martino, L.; Rana, G.L. An attempt of postharvest orange fruit rot control using essential oils from Mediterranean plants. J. Med. Food 2010, 13, 1515–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buriani, A; Fortinguerra, S; Sorrenti, V; Caudullo, G; Carrara, M. Essential Oil Phytocomplex Activity, a Review with a Focus on Multivariate Analysis for a Network Pharmacology-Informed Phytogenomic Approach. Molecules 2020, 16, 25–1833. [Google Scholar]
- Bouyahya, A.; Abrini, J.; Dakka, N.; Bakri, Y. Essential oils of Origanum compactum increase membrane permeability, disturb cell membrane integrity, and suppress quorum-sensing phenotype in bacteria. J. Pharmaceut. Anal. 2019, 9, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhifi W; Bellili S. ; Jazi S.; Bahloul N.; Mnif W. Essential Oils' Chemical Characterization and Investigation of Some Biological Activities: A Critical Review. Medicines 2016, 22, 3–25. [Google Scholar]
- Lak, F.; Zandi-Sohani, N.; Ghodoum Parizipour, M.H.; Ebadollahi, A. Synergic effects of some plant-derived essential oils and Iranian isolates of entomopathogenic fungus Metarhizium anisopliae Sorokin to control Acanthoscelides obtectus (Say) (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae). Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1075761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, Á.; Varona, S.; Navarrete, A.; Cocero, M.J. Encapsulation and co-precipitation processes with supercritical fluids: applications with essential oils. Open Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 4, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basavegowda, N.; Baek, K.H. Synergistic Antioxidant and Antibacterial Advantages of Essential Oils for Food Packaging Applications. Biomolecules 2021, 2, 1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-García, R.; López-Malo, A.; Palou, E. Bactericidal action of binary and ternary mixtures of carvacrol, thymol, and eugenol against Listeria innocua. J. Food Sci. 2011, 76, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Council of Europe. European Pharmacopoeia, 5th ed. Council of Europe: Strasbourg Cedex, France, I, 2004, 217.
- Wiley Registry of Mass Spectral Data, with NIST Spectral Data CD Rom, 7th ed. John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1998.
- King, E.O.; Ward, M.K.; Raney, D.E. Two simple media for demonstration of pyocyanin and fluorescin. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 1954, 44, 301–307. [Google Scholar]
- Elshafie, H.S.; Camele, I.; Racioppi, R.; Scrano, L.; Iacobellis, N.S.; Bufo, S.A. In vitro antifungal activity of Burkholderia gladioli pv. agaricicola against some Phytopathogenic fungi. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 16291–16302. [Google Scholar]
- Elshafie, H.S.; Viggiani, L.; Mostafa, M.S.; El-Hashash, M.A.; Bufo, S.A.; Camele, I. Biological activity and chemical identification of ornithine lipid produced by Burkholderia gladioli pv. agaricicola ICMP 11096 using LC-MS and NMR analyses. J. Biol. Res. 2017, 90, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshafie, H.S.; Sakr, S.H.; Sadeek, S.A.; Camele, I. Biological investigations and spectroscopic studies of new Moxifloxacin/Glycine-Metal complexes. Chem. Biodivers. 2019, 16, e1800633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofo, A.; Elshafie, H.S.; Scopa, A.; Mang, S.M.; Camele, I. Impact of airborne zinc pollution on the antimicrobial activity of olive oil and the microbial metabolic profiles of Zn-contaminated soils in an Italian olive orchard. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2018, 49, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zygadlo, J.A.; Guzman, C.A.; Grosso, N.R. Antifungal properties of the leaf oils of Tagetes minuta L. and Tagetes filifolia Lag. J. Essent. Oil Res. 1994, 6, 617–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceglie, F.; Elshafie, H.S.; Verrastro, V.; Tittarelli, F. Evaluation of Olive Pomace and Green Waste Composts as Peat Substitutes for Organic Tomato Seedling Production. Compost Sci. Util. 2011, 19, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallik, E.; Klein, J.; Grinberg, S.; Lomaniee, E.; Lurie, S.; Lalazar, A. Effect of postharvest heat treatment of tomatoes on fruit ripening and decay caused by Botrytis cinerea. Plant Dis. 1993, 77, 985–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Name of Compound | KI exp | KI Lit | % | Identif. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α-pinene | 938 | 936 | 0.2 | KI, MS, S | M |
| camphene | 951 | 950 | 0.2 | KI, MS | M |
| sabinene | 976 | 973 | 0.1 | KI, MS | M |
| β-pinene | 980 | 978 | 0.3 | KI, MS, S | M |
| α-terpinene | 1016 | 1013 | 0.7 | KI, MS, S | M |
| p-cymene | 1020 | 1015 | 5.7 | KI, MS, S | M |
| 1,8-cineole | 1033 | 1024 | 0.6 | KI, MS, S | MO |
| (Z)-β-ocimene | 1035 | 1029 | T | KI, MS, S | M |
| γ-terpinene | 1060 | 1051 | 2.5 | KI, MS, S | M |
| terpinolene | 1088 | 1082 | T | KI, MS, S | M |
| linalool | 1098 | 1086 | 2.6 | KI, MS, S | MO |
| camphor | 1121 | 1123 | 0.7 | KI, MS, S | MO |
| L-trans-pinocarveol | 1130 | 1125 | T | KI, MS | MO |
| borneol | 1152 | 1150 | 0.8 | KI, MS, S | MO |
| terpinen-4-ol | 1160 | 1164 | 0.7 | KI, MS | MO |
| α-terpineol | 1178 | 1176 | 0.4 | KI, MS | MO |
| carvone | 1217 | 1214 | T | KI, MS, S | MO |
| carvotanacetone | 1230 | 1220 | T | KI, MS | MO |
| thymol | 1270 | 1267 | 76.0 | KI, MS, S | MO |
| carvacrol | 1282 | 1278 | 3.2 | KI, MS, S | MO |
| eugenol | 1333 | 1331 | 0.1 | KI, MS | MO |
| α-cubebene | 1354 | 1355 | 0.3 | KI, MS | S |
| α-gurjunene | 1411 | 1413 | T | KI, MS | S |
| α-himachalene | 1449 | 1450 | 0.1 | KI, MS | S |
| humulene | 1454 | 1455 | T | KI, MS | S |
| allo-aromadendrene | 1461 | 1462 | T | KI, MS | S |
| β-guaiene | 1490 | 1488 | T | KI, MS | S |
| valencene | 1494 | 1494 | 0.1 | KI, MS | S |
| α-muurolene | 1495 | 1496 | T | KI, MS | S |
| γ-cadinene | 1512 | 1507 | 0.1 | KI, MS | S |
| calamenene | 1513 | 1517 | T | KI, MS | S |
| β-cadinene | 1520 | 1526 | 0.4 | KI, MS | S |
| α-calacorene | 1534 | 1527 | 0.1 | KI, MS | S |
| elemol | 1539 | 1541 | T | KI, MS | SO |
| caryophyllene oxide | 1580 | 1578 | 0.4 | KI, MS | SO |
| globulol | 1583 | 1589 | T | KI, MS | SO |
| cedrol | 1598 | 1603 | T | KI, MS | SO |
| γ-eudesmol | 1620 | 1618 | T | KI, MS | SO |
| allo-aromadendrene epoxide | 1621 | 1623 | 0.1 | KI, MS | SO |
| tau.cadinol | 1634 | 1633 | T | KI, MS | SO |
| tau.muurolol | 1635 | 1633 | T | KI, MS | SO |
| cubenol | 1636 | 1630 | T | KI, MS | SO |
| Total Identified (%) | 96.4 | ||||
| Compound | Kia | Kib | Percentagec | Identificationd |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| α-Thujene | 930 | 1,035 | 0.4 ± 0.0 | 1, 2 |
| α-Pinene | 936 | 1,032 | 4.4 ± 0.3 | 1, 2, 3 |
| (-)-Camphene | 953 | 1,076 | 4.1 ± 0.0 | 1, 2, 3 |
| Sabinene | 972 | 1,132 | 0.4 ± 0.3 | 1, 2 |
| Hepten-3-one | 975 | - | 1, 2 | |
| β-Pinene | 977 | 1,118 | 2.5 ± 0.0 | 1, 2, 3 |
| Verbenene | 981 | T | 1, 2 | |
| Myrcene | 993 | 1,174 | 0.5 ± 0.3 | 1, 2, 3 |
| α-Phellandrene | 995 | 1,176 | T | 1, 2, 3 |
| Δ3-Carene | 997 | 1,153 | - | 1, 2, 3 |
| α-Terpinene | 1,011 | 1,188 | T | 1, 2 |
| O-Cymene | 1,020 | 1,187 | 2.5 ± 0.3 | 1, 2, 3 |
| ρ-Cymene | 1,023 | 1,280 | 1.2 ± 0.3 | 1, 2, 3 |
| β-Phellandrene | 1,028 | 1,218 | 1.0 | 1, 2, 3 |
| Limonene | 1,031 | 1,203 | 1.4 ± 0.0 | 1, 2, 3 |
| 1,8-Cineole | 1,033 | 1,213 | 4.2 ± 0.0 | 1, 2 |
| (Z)-β-Ocimene | 1,038 | 1,246 | T | 1, 2, 3 |
| (E)-β-Ocimene | 1,049 | 1,280 | T | 1, 2 |
| γ-Terpinene | 1,057 | 1,255 | 0.1 ± 0.1 | 1, 2, 3 |
| Cis-Sabinene hydrate | 1,063 | 1,556 | 0.1 ± 0.0 | 1, 2, 3 |
| Terpinolene | 1,086 | 1,265 | T | 1, 2 |
| Linalol | 1,096 | 1,553 | 1.1 ± 0.3 | 1, 2, 3 |
| trans-Thujone | 1,116 | 1,449 | 37.9 ± 0.0 | 1, 2, 3 |
| trans-Pinocarveol | 1,139 | 1,654 | 0.2 ± 0.3 | 1, 2 |
| (-)-Citronellal | 1,143 | 1,491 | 0.2 ± 0.3 | 1, 2, 3 |
| iso-Borneol | 1,143 | 1,633 | - | 1, 2, 3 |
| Camphor | 1,144 | 1,532 | 13.9 ± 0.0 | 1, 2, 3 |
| iso-Pinocamphone | 1,153 | 1,566 | 0.1 ± 0.0 | 1, 2 |
| trans-Pinocamphone | 1,159 | 0.3 ± 0.3 | 1, 2, 3 | |
| Pinocarvone | 1,166 | 1,587 | T | 1, 2, 3 |
| Borneol | 1,167 | 1,719 | 7.6 ± 0.3 | 1, 2, 3 |
| Terpinen-4-ol | 1,177 | 1,611 | 0.5 ± 0.0 | 1, 2, 3 |
| Dihydrocarveol | 1,177 | 0.2 ± 0.0 | 1, 2, 3 | |
| ρ-Cymen-8-ol | 1,186 | 1,864 | 0.1 ± 0.1 | 1, 2 |
| α-Terpineol | 1,188 | 1,706 | 0.3 ± 0.2 | 1, 2, 3 |
| Myrtenal | 1,193 | 1,648 | 0.2 ± 0.0 | 1, 2, 3 |
| Estragole | 1,196 | 1,670 | T | 1, 2, 3 |
| Myrtenol | 1,196 | 1,804 | 0.2 ± 0.0 | 1, 2, 3 |
| Isobornyl formate | 1,227 | - | 1, 2, 3 | |
| Linalyl acetate | 1,248 | 1,565 | 1.5 ± 0.2 | 1, 2, 3 |
| Geraniol | 1,256 | 1,857 | 0.3 ± 0.2 | 1, 2 |
| cis-Anethole | 1,262 | - | 1, 2, 3 | |
| (E)-Citral | 1,271 | 1,727 | - | 1, 2, 3 |
| Isobornyl acetate | 1,277 | 0.7 ± 0.3 | 1, 2, 3 | |
| Bornyl acetate | 1,284 | 1,591 | 0.9 ± 0.3 | 1, 2, 3 |
| Thymol | 1,291 | 1,298 | T | 1, 2, 3 |
| Carvacrol | 1,297 | 2,239 | 0.3 ± 0.2 | 1, 2, 3 |
| Myrtenyl acetate | 1,313 | T | 1, 2 | |
| Terpinyl acetate | 1,334 | - | 1, 2, 3 | |
| Methyl eugenol | 1,369 | 2,023 | - | 1, 2 |
| α-Copaene | 1,377 | 1,497 | T | 1, 2, 3 |
| Isoledene | 1,383 | T | 1, 2, 3 | |
| β-Elemene | 1,387 | 1,600 | - | 1, 2, 3 |
| Longifolene | 1,412 | 1,576 | T | 1, 2, 3 |
| β-Caryophyllene | 1,418 | 1,612 | 1.3 ± 0.3 | 1, 2, 3 |
| β-Cedrene | 1,424 | 1,638 | 1.0 ± 0.2 | 1, 2, 3 |
| Aromadendrene | 1,437 | 1,628 | 0.1 ± 0.3 | 1, 2, 3 |
| α-Humulene | 1,456 | 1,689 | 5.9 ± 0.3 | 1, 2, 3 |
| allo-Aromadendrene | 1,463 | 1,661 | 0.1 ± 0.2 | 1, 2 |
| γ-Gurjunene | 1,474 | 1,687 | 0.1 ± 0.2 | 1, 2 |
| Bicyclogermacrene | 1,491 | 1,756 | - | 1, 2, 3 |
| cis-Muurola-4(14),5-diene | 1,510 | 1,675 | T | 1, 2, 3 |
| α-7-epi-Selinene | 1,519 | 1,740 | 0.1 ± 0.3 | 1, 2 |
| Caryophyllene oxide | 1,581 | 2,008 | 0.8 ± 0.3 | 1, 2, 3 |
| Total identified (%) | 98.7 | |||
| EOs formulations | Seed germinationa (%) |
Radical elongationb (cm) | Growth indexc (%) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L. sativum | Org250 | 4,3±0,8b | 0,8±0,6ab | 1,4±0,0b |
| Salv250 | 80,0±1,8d | 7,4±0,5bc | 43,1±6,1d | |
| BOF-I | 0,0±0,0a | 0,0±0,0a | 0,0±0,0a | |
| BOF-II | 6,7±0,5b | 1,8±0,5b | 1,0±0,1b | |
| BOF-III | 53,3±0,5c | 5,4±0,7bc | 17,9±2,6c | |
| Cont. H2O | 100,0±0,0d | 14,7±1,3d | 97,5±3,9e | |
| S. lycopersicum | Org250 | 3,0±0,4a | 4,6±0,3b | 8,9±0,0bc |
| Salv250 | 73,3±1,0c | 9,9±0,4b | 56, 2±7,7d | |
| BOF-I | 6,7±0,5a | 0,0±0,0a | 0,0±0,0a | |
| BOF-II | 13,3±0,5b | 0,7±0,2a | 1,1±0,6b | |
| BOF-III | 60,0±1,4c | 6,3±1,4b | 22,2±8,2c | |
| Cont. H2O | 100,0±0,0d | 11,6±0,5bc | 100,0±0,0e | |
| L. sativa | Org250 | 2,0±0,4b | 0,8±0,5ab | 0,9±0,2ab |
| Salv250 | 12,4±1,0bc | 5,2±0,4c | 33,4±7,7c | |
| BOF-I | 0,0±0,0a | 0,0±0,0a | 0,0±0,0a | |
| BOF-II | 0,0±0,0a | 0,0±0,0a | 0,0±0,0a | |
| BOF-III | 0,0±0,0a | 0,0±0,0a | 0,0±0,0a | |
| Cont. H2O | 100,0±0,0d | 10.5±0,3d | 100,0±0,0d | |
| Tested bacteria | Abs. (540 nm) | MIC (µg/mL) | 50% Colony Inhibition | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cont. MM | BOF-II | Abs. (540 nm) | IC50 (µg/mL) | ||
| B. cereus | 0,316 | 0,330 | 4000 | 0,347 | 4462,5 |
| C. michiganensis | 0,351 | 0,368 | 2000 | 0,41 | 6219,9 |
| X. campestris | 0,239 | 0,260 | 1000 | 0,231 | 7715,6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





