Submitted:
13 June 2023
Posted:
13 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Fungal Infections
2. Antifungal Agents
3. Cyclic Peptides Development as Antifungal Agents
3.1. Cyclic Peptides Isolated From Cyanobacteria
3.2. Cyclic Peptides Isolated From Other Bacteria
3.3. Cyclic Peptides Isolated From Fungi
3.4. Cyclic Peptides Isolated from Plants
3.5. Synthetic Cyclic Peptides With Antifungal Activity
3.6. Combination Antifungal Activity
4. Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martins, N.; Ferreira, I.C.; Barros, L.; Silva, S.; Henriques, M. Candidiasis: predisposing factors, prevention, diagnosis and alternative treatment. Mycopathologia 2014, 177, 223–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadena, J.; Thompson, G.R., 3rd; Patterson, T.F. Aspergillosis: Epidemiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Infect Dis Clin North Am 2021, 35, 415–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rautenbach, M.; Troskie, A.M.; Vosloo, J.A. Antifungal peptides: To be or not to be membrane active. Biochimie 2016, 130, 132–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
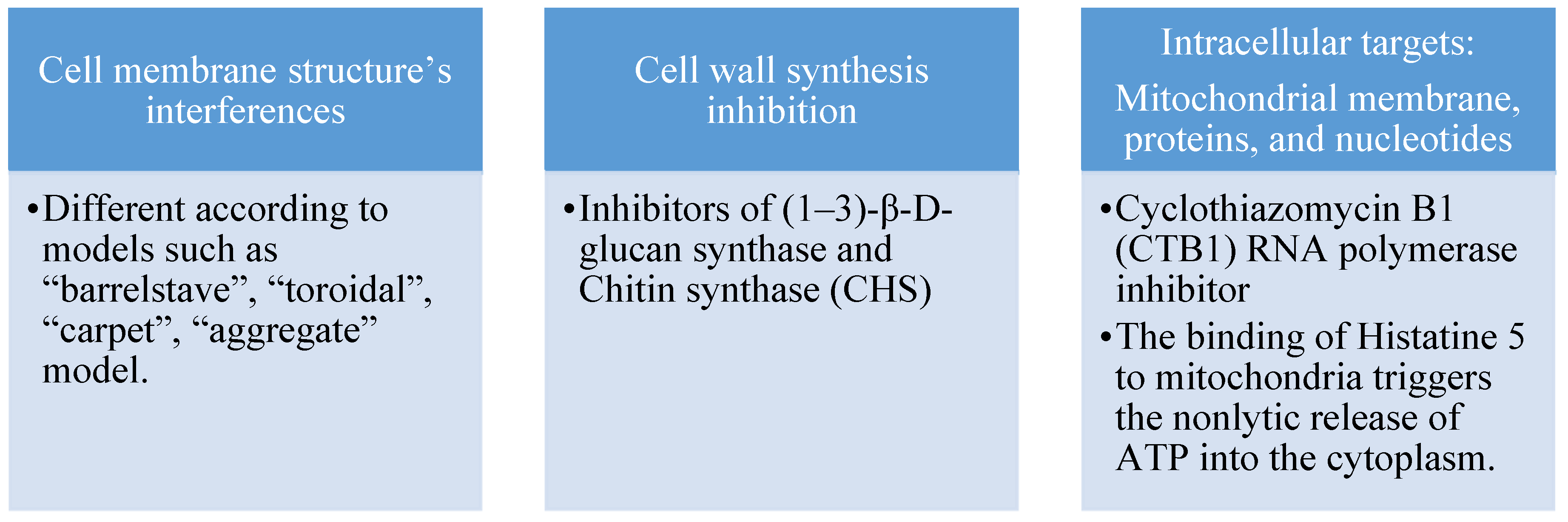
- Zähner, H.; Maas, W.K. Mode of Action. In Biology of Antibiotics; Springer US: New York, NY, 1972; pp. 62–96. [Google Scholar]
- Carrillo-Muñoz, A.J.; Giusiano, G.; Ezkurra, P.A.; Quindós, G. Antifungal agents: mode of action in yeast cells. Rev Esp Quimioter 2006, 19, 130–139. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Lu, Y.; Chen, H.; Wu, C.; Zhang, H.; Chen, L.; Chen, X. Antifungal peptides produced by actinomycetes and their biological activities against plant diseases. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 2020, 73, 265–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramadhani, D.; Maharani, R.; Gazzali, A.M.; Muchtaridi, M. Cyclic Peptides for the Treatment of Cancers: A Review. Molecules 2022, 27, 4428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, B.J.; King, A.T.; Katsifis, A.; Matesic, L.; Jamie, J.F. Methods to Enhance the Metabolic Stability of Peptide-Based PET Radiopharmaceuticals. Molecules 2020, 25, 2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinogradov, A.A.; Yin, Y.; Suga, H. Macrocyclic Peptides as Drug Candidates: Recent Progress and Remaining Challenges. Journal of the American Chemical Society 2019, 141, 4167–4181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
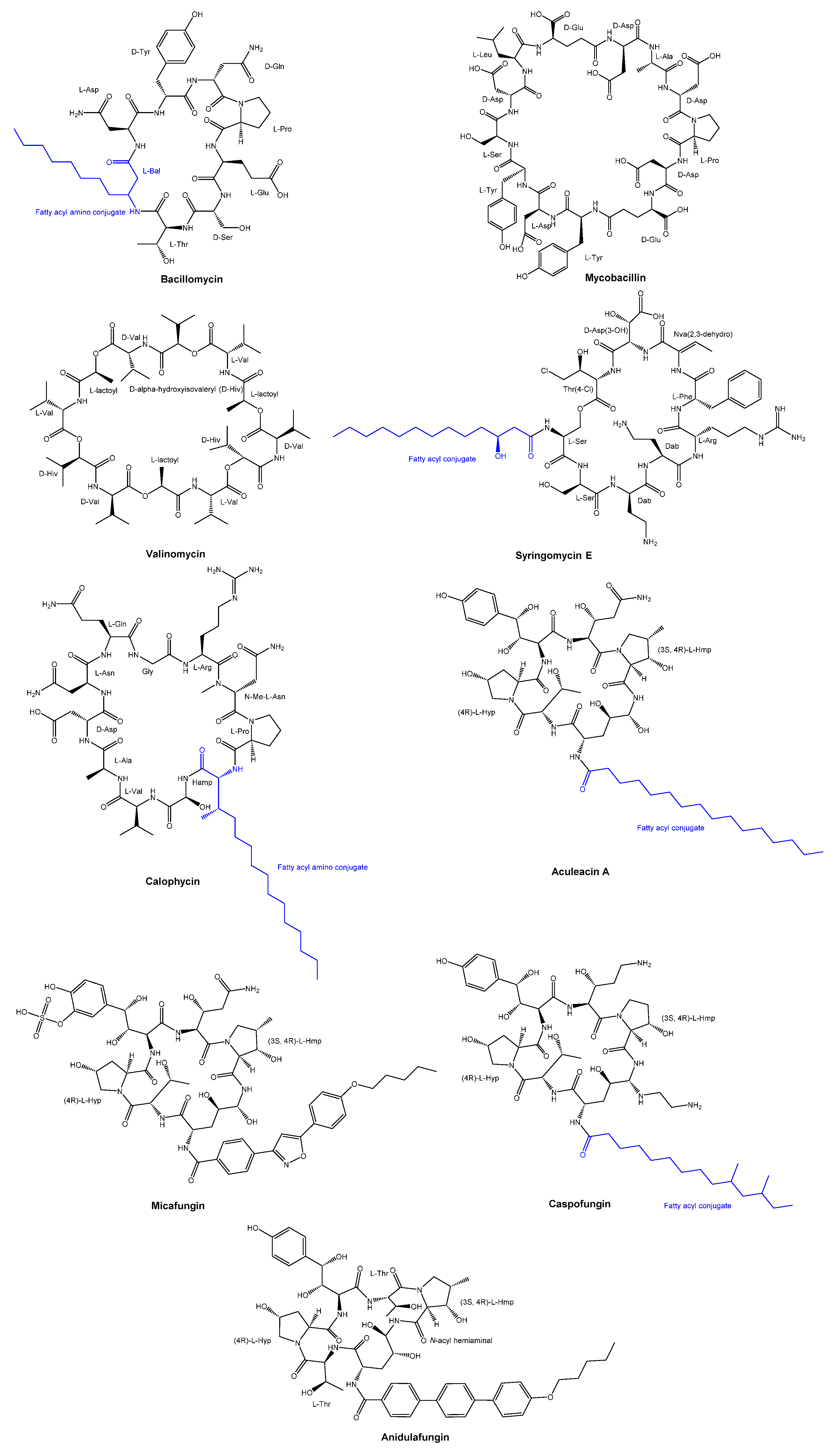
- Landy, M.; Warren, G.H.; RosenmanM, S.B.; Colio, L.G. Bacillomycin: An Antibiotic from Bacillus subtilis Active against Pathogenic Fungi∗. Proceedings of the Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine 1948, 67, 539–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, N.; Bose, S.K. MODE OF ACTION OF MYCOBACILLIN, A NEW ANTIFUNGAL ANTIBIOTIC. J Bacteriol 1963, 86, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, A.H.; Wilkinson, J.F. Advances in Microbial Physiology; Elsevier Science: 1970.
- Segre, A.; Bachmann, R.C.; Ballio, A.; Bossa, F.; Grgurina, I.; Iacobellis, N.S.; Marino, G.; Pucci, P.; Simmaco, M.; Takemoto, J.Y. The structure of syringomycins A1, E and G. FEBS Lett 1989, 255, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takemoto, J.Y.; Zhang, L.; Taguchi, N.; Tachikawa, T.; Miyakawa, T. Mechanism of action of the phytotoxin syringomycin: a resistant mutant of Saccharomyces cerevisiae reveals an involvement of Ca2+ transport. Microbiology 1991, 137, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.S.; Chen, J.L.; Moore, R.E.; Patterson, G.M.L. Calophycin, a fungicidal cyclic decapeptide from the terrestrial blue-green alga Calothrix fusca. The Journal of Organic Chemistry 1992, 57, 1097–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, K.; Yagi, A.; Satoi, S.; Takada, M.; Hayashi, M. Studies on aculeacin. I. Isolation and characterization of aculeacin A. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1977, 30, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordee, R.S.; Zeckner, D.J.; Ellis, L.F.; Thakkar, A.L.; Howard, L.C. In vitro and in vivo anti-Candida activity and toxicology of LY121019. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1984, 37, 1054–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizoguchi, J.; Saito, T.; Mizuno, K.; Hayano, K. On the mode of action of a new antifungal antibiotic, aculeacin A: inhibition of cell wall synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1977, 30, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkovec, J.M.; Hughes, D.L.; Masurekar, P.S.; Sable, C.A.; Schwartz, R.E.; Singh, S.B. Discovery and development of first in class antifungal caspofungin (CANCIDAS®)—A case study. Natural Product Reports 2014, 31, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, S. Cyclic peptide drugs approved in the last two decades (2001-2021). RSC Chem Biol 2022, 3, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, M.A.; McGaw, L.J. Natural Cyclic Peptides as an Attractive Modality for Therapeutics: A Mini Review. Molecules 2018, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashiyama, Y.; Kohno, S. Micafungin: a therapeutic review. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther 2004, 2, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, L.J. Micafungin: a review of its use in the prophylaxis and treatment of invasive Candida infections. Drugs 2012, 72, 2141–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasmann, R.E.; Muilwijk, E.W.; Burger, D.M.; Verweij, P.E.; Knibbe, C.A.; Brüggemann, R.J. Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Micafungin. Clin Pharmacokinet 2018, 57, 267–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kofla, G.; Ruhnke, M. Pharmacology and metabolism of anidulafungin, caspofungin and micafungin in the treatment of invasive candidosis: review of the literature. Eur J Med Res 2011, 16, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gang, D.; Kim, D.W.; Park, H.S. Cyclic Peptides: Promising Scaffolds for Biopharmaceuticals. Genes (Basel) 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, S. Micafungin: a sulfated echinocandin. The Journal of Antibiotics 2009, 62, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, L.; Li, J.; Liu, A.; Chang, Q.; Lin, H.; Chen, D. Efficient bioconversion of echinocandin B to its nucleus by overexpression of deacylase genes in different host strains. Appl Environ Microbiol 2013, 79, 1126–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, S.L.; Vazquez, J.A. Anidulafungin: an evidence-based review of its use in invasive fungal infections. Core Evid 2008, 2, 241–249. [Google Scholar]
- Alarcón-Manoja, E.; Cardozo-Espinola, C.; Puerta-Alcalde, P.; García-Vidal, C. Comments on practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of aspergillosis made by the IDSA in 2016. Rev Esp Quimioter 2017, 30 Suppl 1, 26–29. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, R.E. Cyclic peptides and depsipeptides from cyanobacteria: a review. J Ind Microbiol 1996, 16, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
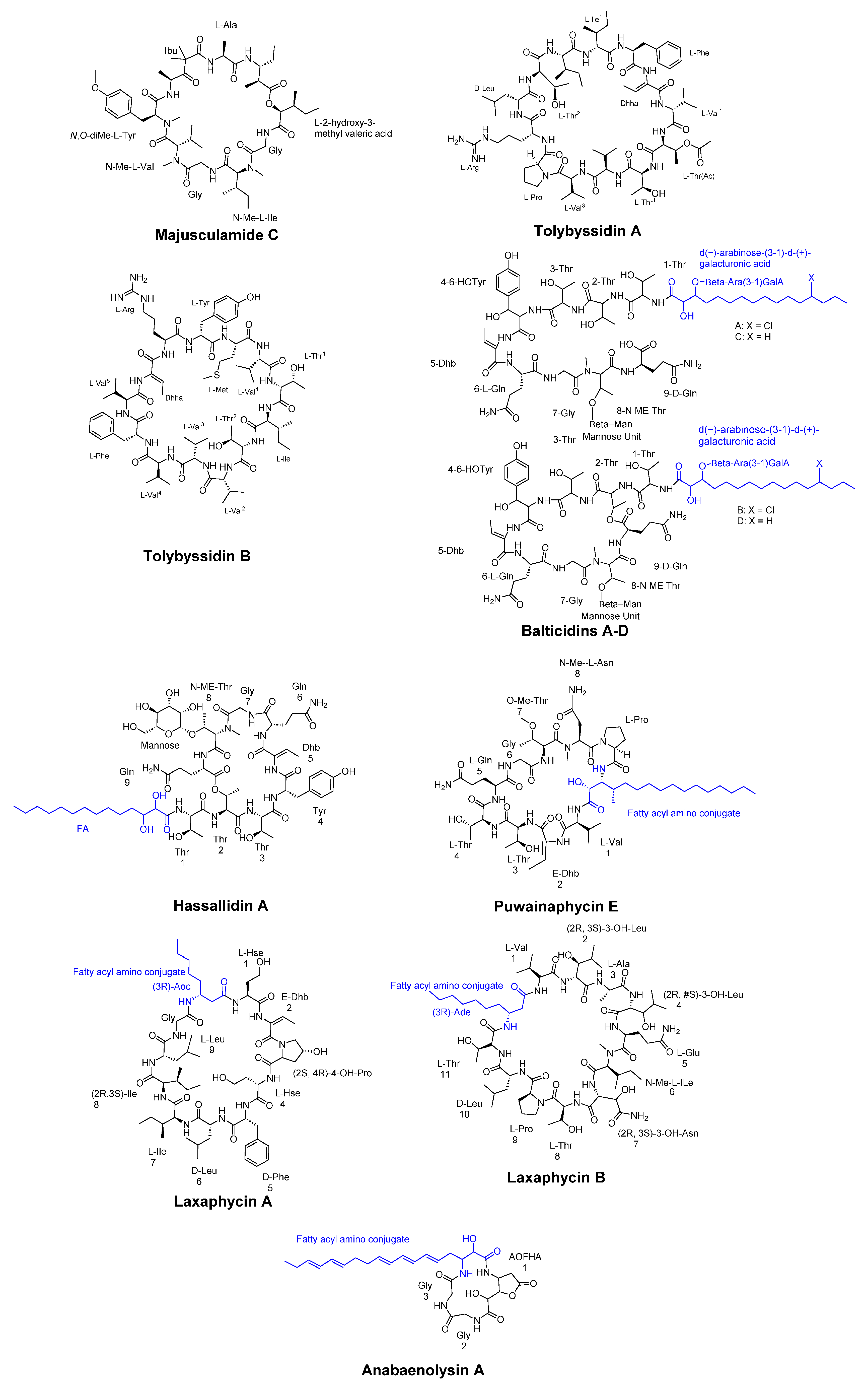
- Jaki, B.; Zerbe, O.; Heilmann, J.; Sticher, O. Two novel cyclic peptides with antifungal activity from the cyanobacterium Tolypothrix byssoidea (EAWAG 195). J Nat Prod 2001, 64, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, T.H.; Wray, V.; Nimtz, M.; Fossen, T.; Preisitsch, M.; Schröder, G.; Wende, K.; Heiden, S.E.; Mundt, S. Balticidins A-D, antifungal hassallidin-like lipopeptides from the Baltic Sea cyanobacterium Anabaena cylindrica Bio33. J Nat Prod 2014, 77, 1287–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
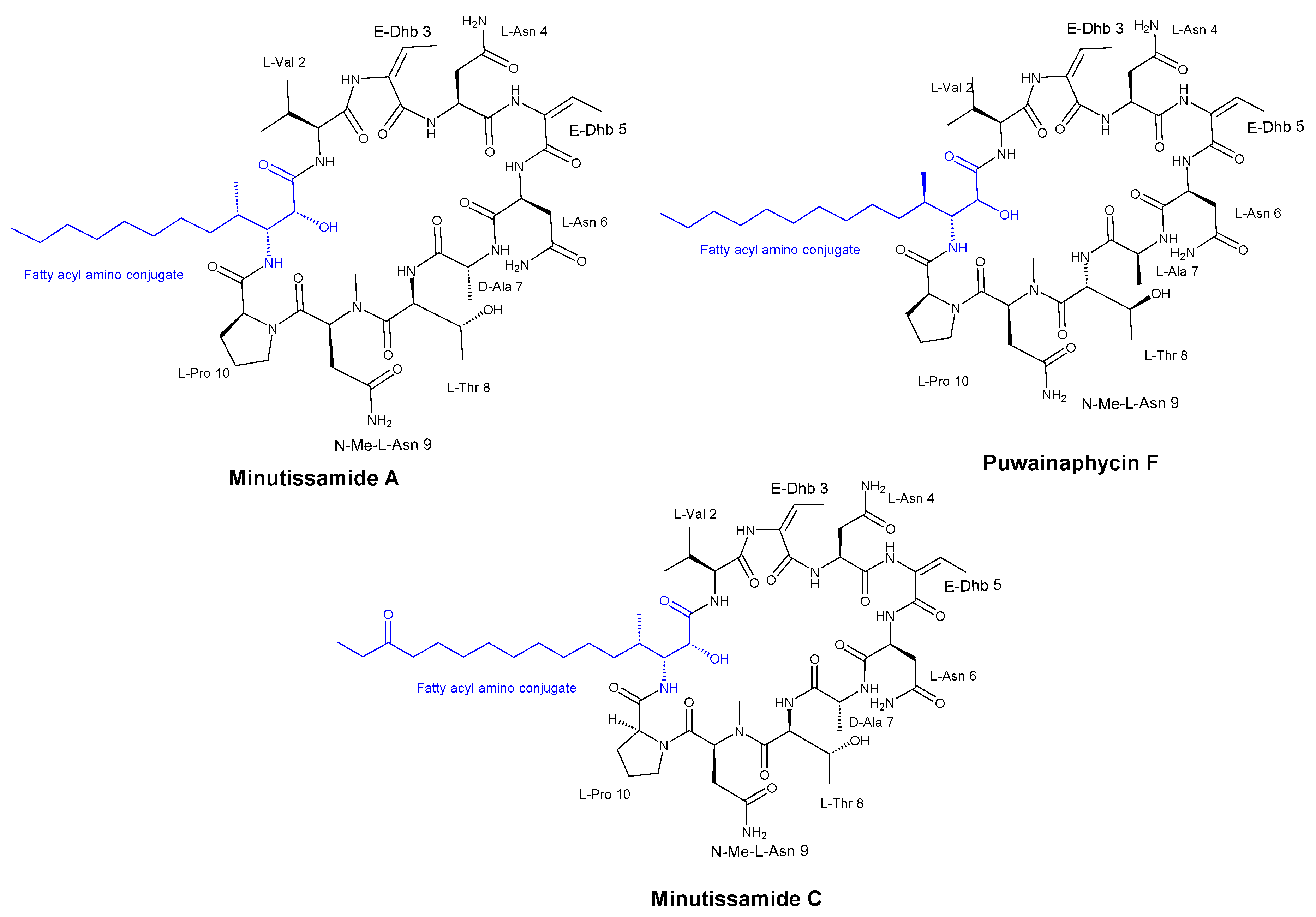
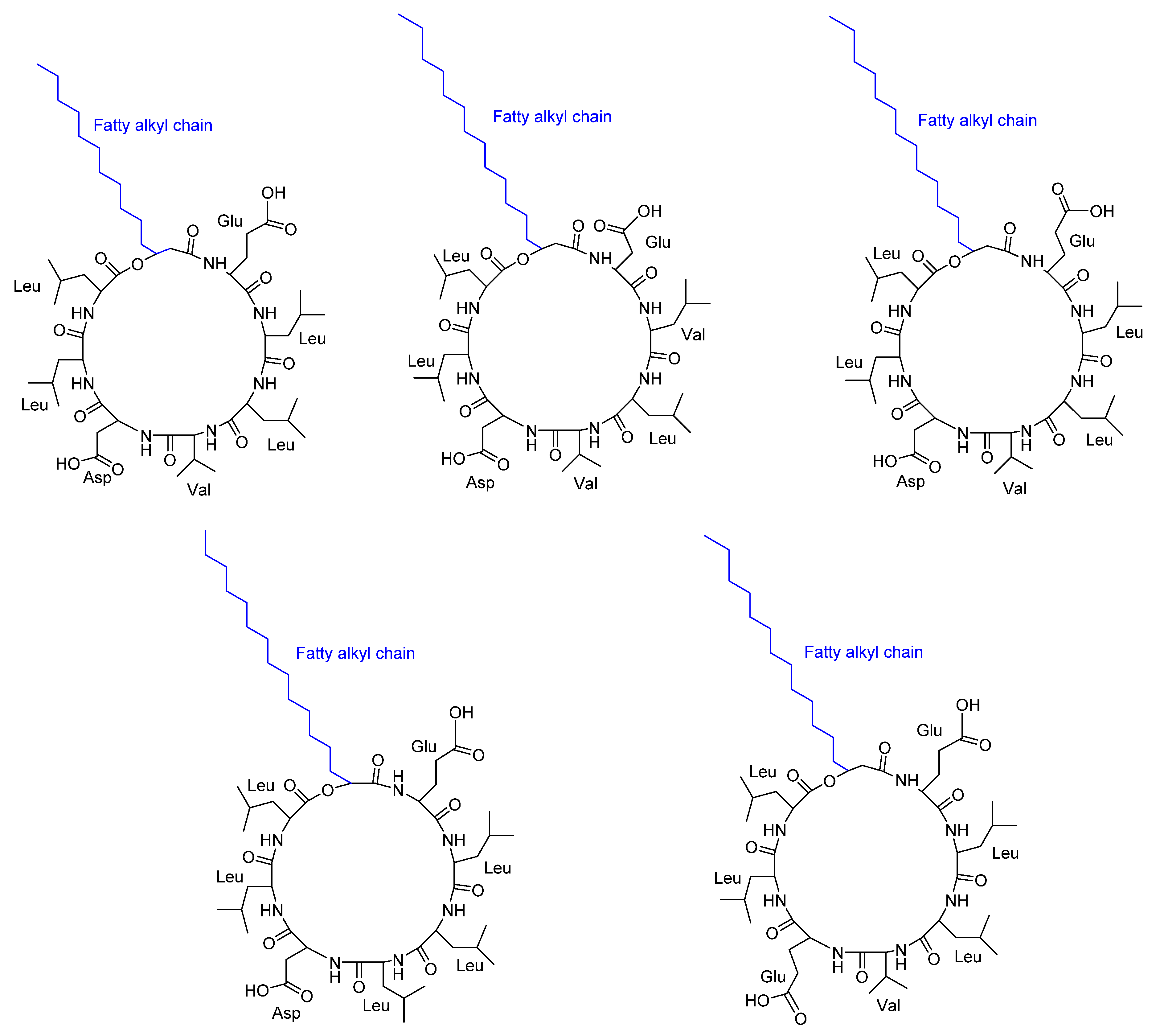
- Fewer, D.P.; Jokela, J.; Heinilä, L.; Aesoy, R.; Sivonen, K.; Galica, T.; Hrouzek, P.; Herfindal, L. Chemical diversity and cellular effects of antifungal cyclic lipopeptides from cyanobacteria. Physiol Plant 2021, 173, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hájek, J.; Bieringer, S.; Voráčová, K.; Macho, M.; Saurav, K.; Delawská, K.; Divoká, P.; Fišer, R.; Mikušová, G.; Cheel, J.; et al. Semi-synthetic puwainaphycin/minutissamide cyclic lipopeptides with improved antifungal activity and limited cytotoxicity. RSC Adv 2021, 11, 30873–30886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
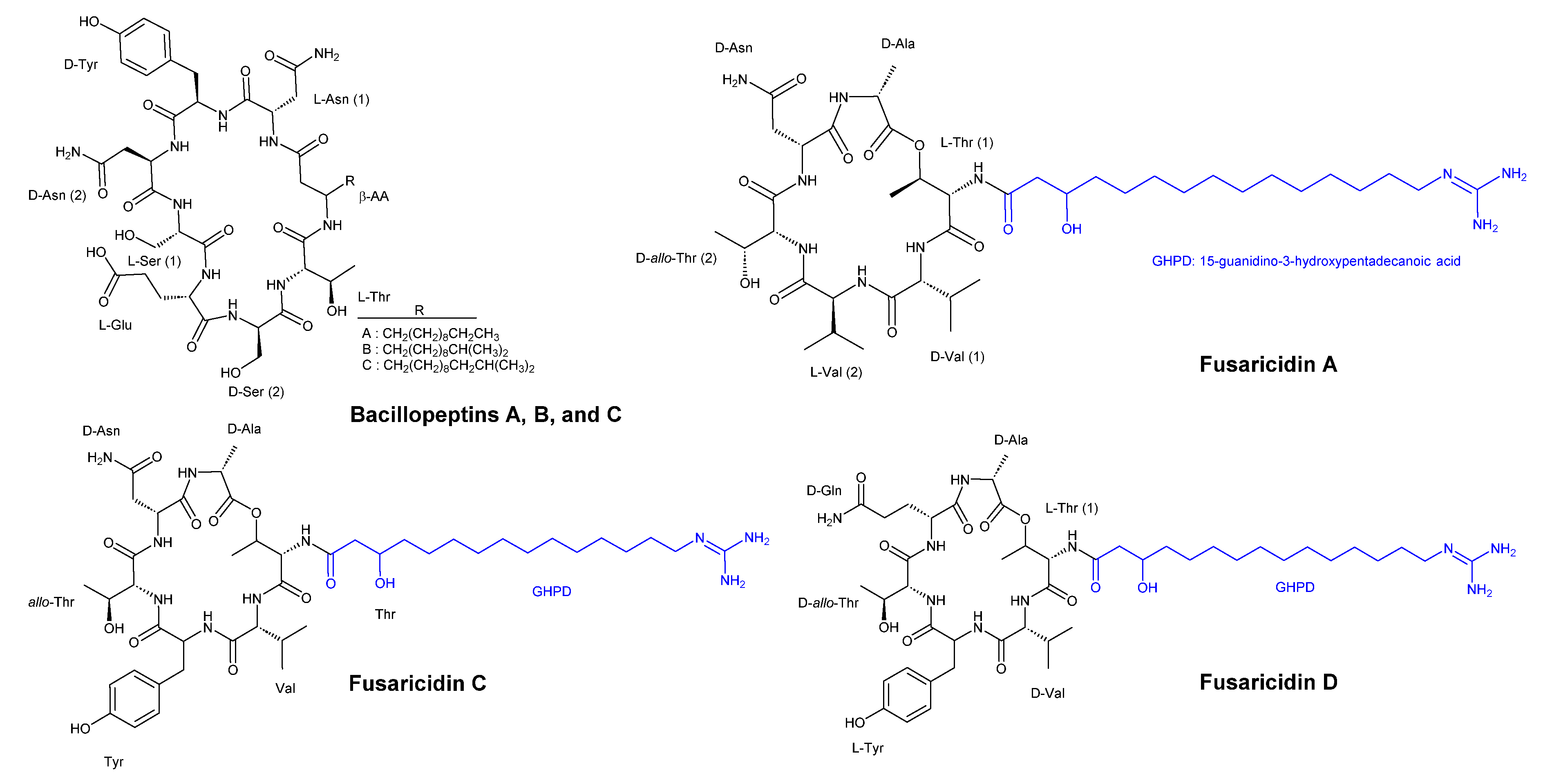
- Kaneda, M.; Kajimura, Y. [New antifungal antibiotics, bacillopeptins and fusaricidins]. Yakugaku Zasshi 2002, 122, 651–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
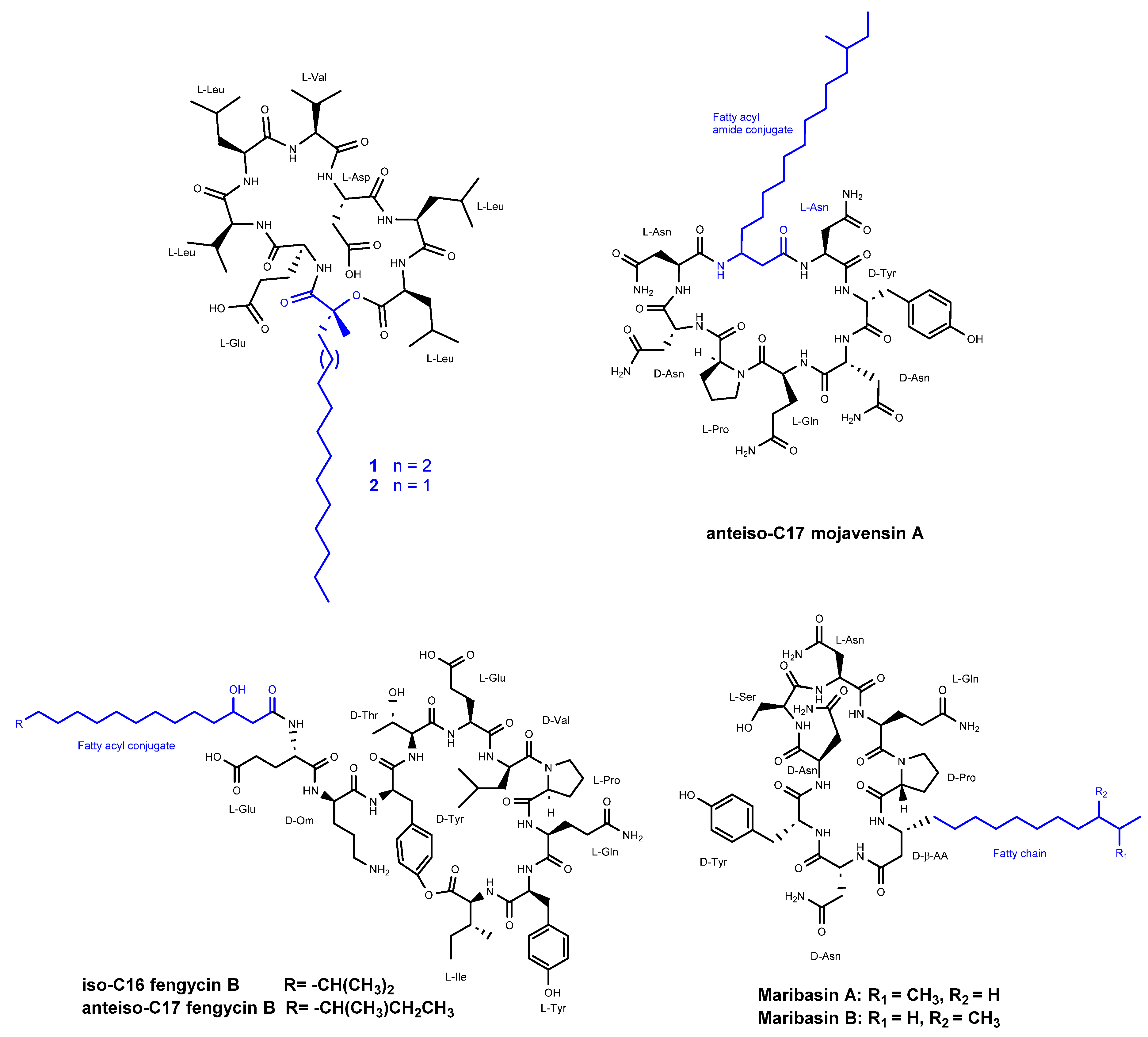
- Romano, A.; Vitullo, D.; Senatore, M.; Lima, G.; Lanzotti, V. Antifungal cyclic lipopeptides from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain BO5A. J Nat Prod 2013, 76, 2019–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Wang, N.; Hu, J.; Wang, S. Isolation and characterization of a new iturinic lipopeptide, mojavensin A produced by a marine-derived bacterium Bacillus mojavensis B0621A. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 2012, 65, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.J.; Liu, R.F.; Li, Y.G.; Tao, L.M.; Tian, L. Two new antifungal cyclic lipopeptides from Bacillus marinus B-9987. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 2010, 58, 1630–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Routhu, S.R.; Ragi, N.C.; Yedla, P.; Shaik, A.B.; Venkataraman, G.; Cheemalamarri, C.; Chityala, G.K.; Amanchy, R.; Sripadi, P.; Kamal, A. Identification, characterization and evaluation of novel antifungal cyclic peptides from Neobacillus drentensis. Bioorg Chem 2021, 115, 105180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konno, H.; Otsuki, Y.; Matsuzaki, K.; Nosaka, K. Synthesis and antifungal activities of cyclic octa-lipopeptide burkholdine analogues. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2013, 23, 4244–4247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troskie, A.M.; Rautenbach, M.; Delattin, N.; Vosloo, J.A.; Dathe, M.; Cammue, B.P.; Thevissen, K. Synergistic activity of the tyrocidines, antimicrobial cyclodecapeptides from Bacillus aneurinolyticus, with amphotericin B and caspofungin against Candida albicans biofilms. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2014, 58, 3697–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
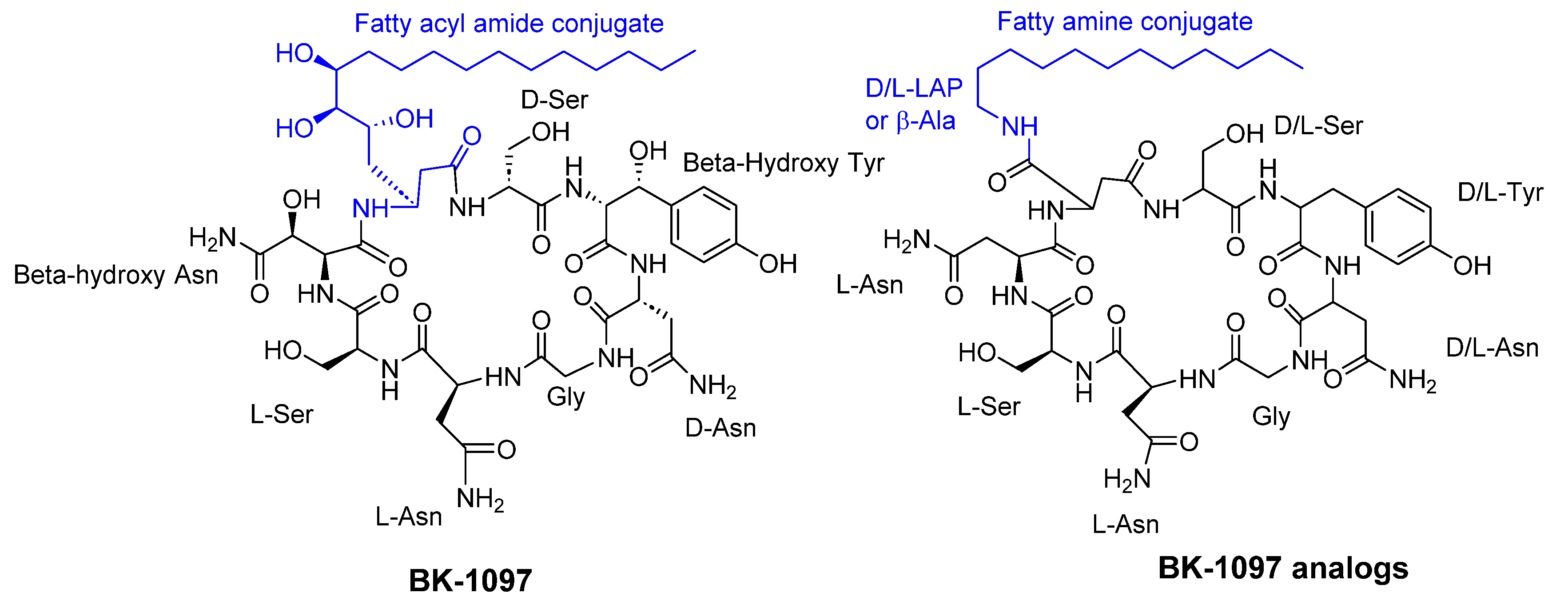
- van Eijk, M.; Boerefijn, S.; Cen, L.; Rosa, M.; Morren, M.J.H.; van der Ent, C.K.; Kraak, B.; Dijksterhuis, J.; Valdes, I.D.; Haagsman, H.P.; et al. Cathelicidin-inspired antimicrobial peptides as novel antifungal compounds. Med Mycol 2020, 58, 1073–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troskie, A.M.; de Beer, A.; Vosloo, J.A.; Jacobs, K.; Rautenbach, M. Inhibition of agronomically relevant fungal phytopathogens by tyrocidines, cyclic antimicrobial peptides isolated from Bacillus aneurinolyticus. Microbiology (Reading) 2014, 160, 2089–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rautenbach, M.; Troskie, A.M.; Vosloo, J.A.; Dathe, M.E. Antifungal membranolytic activity of the tyrocidines against filamentous plant fungi. Biochimie 2016, 130, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
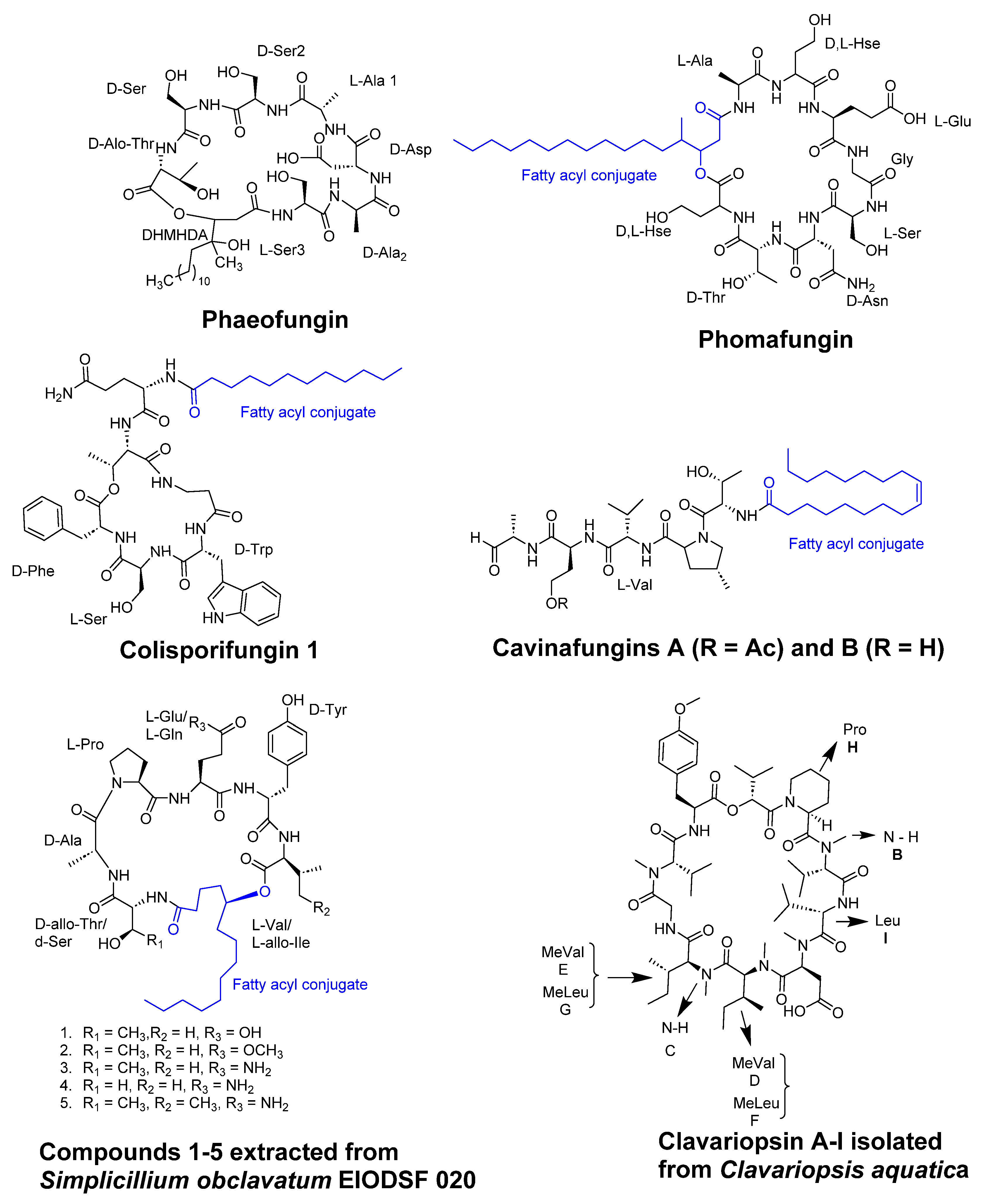
- Singh, S.B.; Ondeyka, J.; Harris, G.; Herath, K.; Zink, D.; Vicente, F.; Bills, G.; Collado, J.; Platas, G.; González del Val, A.; et al. Isolation, structure, and biological activity of Phaeofungin, a cyclic lipodepsipeptide from a Phaeosphaeria sp. Using the Genome-Wide Candida albicans Fitness Test. J Nat Prod 2013, 76, 334–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortíz-López, F.J.; Monteiro, M.C.; González-Menéndez, V.; Tormo, J.R.; Genilloud, O.; Bills, G.F.; Vicente, F.; Zhang, C.; Roemer, T.; Singh, S.B.; et al. Cyclic colisporifungin and linear cavinafungins, antifungal lipopeptides isolated from Colispora cavincola. J Nat Prod 2015, 78, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Nong, X.H.; Huang, Z.H.; Qi, S.H. Antifungal and Antiviral Cyclic Peptides from the Deep-Sea-Derived Fungus Simplicillium obclavatum EIODSF 020. J Agric Food Chem 2017, 65, 5114–5121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firmansyah, K. Bioassay-guided isolation of antifungal cyclopeptides from the deep-sea-derived fungus Simplicillium obclavatum EIODSF 020. Phytochemistry letters 2022, 48, 68–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, F.H.; Liang, X.; Cheng, X.; Ling, J.; Dong, J.D.; Qi, S.H. Antifungal peptides from the marine gorgonian-associated fungus Aspergillus sp. SCSIO41501. Phytochemistry 2021, 192, 112967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soe, T.W.; Han, C.; Fudou, R.; Kaida, K.; Sawaki, Y.; Tomura, T.; Ojika, M. Clavariopsins C-I, Antifungal Cyclic Depsipeptides from the Aquatic Hyphomycete Clavariopsis aquatica. J Nat Prod 2019, 82, 1971–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikai, K.; Takesako, K.; Shiomi, K.; Moriguchi, M.; Umeda, Y.; Yamamoto, J.; Kato, I.; Naganawa, H. Structure of aureobasidin A. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1991, 44, 925–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frankmölle, W.P.; Larsen, L.K.; Caplan, F.R.; Patterson, G.M.; Knübel, G.; Levine, I.A.; Moore, R.E. Antifungal cyclic peptides from the terrestrial blue-green alga Anabaena laxa. I. Isolation and biological properties. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1992, 45, 1451–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
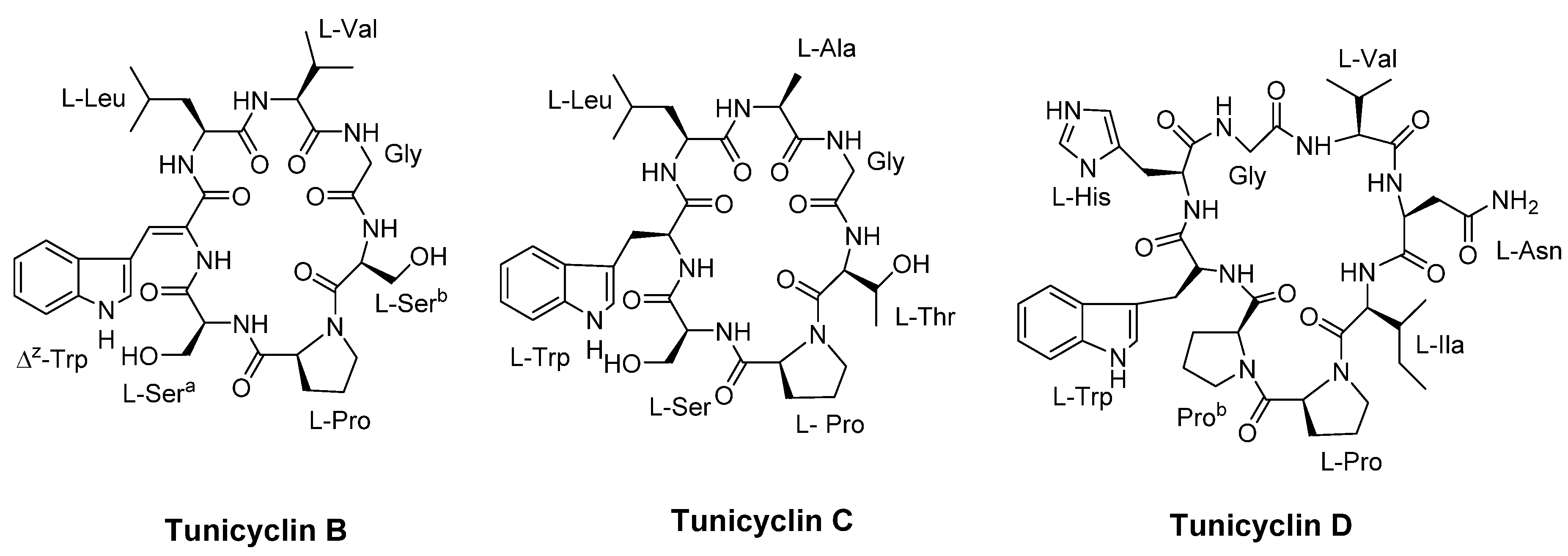
- Tian, J.; Shen, Y.; Yang, X.; Liang, S.; Shan, L.; Li, H.; Liu, R.; Zhang, W. Antifungal cyclic peptides from Psammosilene tunicoides. J Nat Prod 2010, 73, 1987–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thevissen, K.; Ferket, K.K.; François, I.E.; Cammue, B.P. Interactions of antifungal plant defensins with fungal membrane components. Peptides 2003, 24, 1705–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mongkolvisut, W.; Sutthivaiyakit, S.; Leutbecher, H.; Mika, S.; Klaiber, I.; Möller, W.; Rösner, H.; Beifuss, U.; Conrad, J. Integerrimides A and B, cyclic heptapeptides from the latex of Jatropha integerrima. J Nat Prod 2006, 69, 1435–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramalho, S.D.; Pinto, M.E.F.; Ferreira, D.; Bolzani, V.S. Biologically Active Orbitides from the Euphorbiaceae Family. Planta Med 2018, 84, 558–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, T.; Mishra, R.; Bushra; Gulati, P.; Mohanty, A. An insight into biological activities of native cyclotides for potential applications in agriculture and pharmaceutics. Peptides 2021, 135, 170430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strömstedt, A.A.; Park, S.; Burman, R.; Göransson, U. Bactericidal activity of cyclotides where phosphatidylethanolamine-lipid selectivity determines antimicrobial spectra. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr 2017, 1859, 1986–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimaldi, M.; De Rosa, M.; Di Marino, S.; Scrima, M.; Posteraro, B.; Sanguinetti, M.; Fadda, G.; Soriente, A.; D'Ursi, A.M. Synthesis of new antifungal peptides selective against Cryptococcus neoformans. Bioorg Med Chem 2010, 18, 7985–7990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurokawa, N.; Ohfune, Y. Synthetic studies on antifungal cyclic peptides, echinocandins. Stereoselective total synthesis of echinocandin D via a novel peptide coupling. Tetrahedron 1993, 49, 6195–6222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, M.P.; Kruijtzer, J.A.; Breukink, E.J.; Kemmink, J.; Pieters, R.J.; Liskamp, R.M. Synthesis and evaluation of novel macrocyclic antifungal peptides. Bioorg Med Chem 2011, 19, 6505–6517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Hu, H.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, T.; Zou, Y.; Yu, S.; Wu, Q.; Guo, Z. Synthesis and antifungal activities of glycosylated derivatives of the cyclic peptide fungicide caspofungin. ChemMedChem 2012, 7, 1496–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubiczek, D.; Raber, H.; Gonzalez-García, M.; Morales-Vicente, F.; Staendker, L.; Otero-Gonzalez, A.J.; Rosenau, F. Derivates of the Antifungal Peptide Cm-p5 Inhibit Development of Candida auris Biofilms In Vitro. Antibiotics (Basel) 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahiya, R.; Kaur, K. Synthesis and pharmacological investigation of segetalin C as a novel antifungal and cytotoxic agent. Arzneimittelforschung 2008, 58, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pesee, S.; Angkananuwat, C.; Tancharoensukjit, S.; Muanmai, S.; Sirivan, P.; Bubphawas, M.; Tanarerkchai, N. In vitro activity of Caspofungin combined with Fluconazole on mixed Candida albicans and Candida glabrata biofilm. Med Mycol 2016, 54, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez López, A.L.; Lee, M.R.; Wang, N.B.; Dunn, K.K.; Sanchez, H.; Raman, N.; Andes, D.R.; Lynn, D.M.; Palecek, S.P. Small-Molecule Morphogenesis Modulators Enhance the Ability of 14-Helical β-Peptides To Prevent Candida albicans Biofilm Formation. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2019, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhaj, F.F.; George, S.J.; Nguyen, C.D.; Tyring, S.K. Antimicrobials and resistance part II: Antifungals, antivirals, and antiparasitics. J Am Acad Dermatol 2022, 86, 1207–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neoh, C.F.; Jeong, W.; Kong, D.C.; Slavin, M.A. The antifungal pipeline for invasive fungal diseases: what does the future hold? Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther 2023, 21, 577–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kersten, R.D.; Weng, J.K. Gene-guided discovery and engineering of branched cyclic peptides in plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2018, 115, E10961–e10969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlach, S.L.; Göransson, U.; Kaas, Q.; Craik, D.J.; Mondal, D.; Gruber, C.W. A systematic approach to document cyclotide distribution in plant species from genomic, transcriptomic, and peptidomic analysis. Biopolymers 2013, 100, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellinger, R.; Sigurdsson, A.; Wu, W.; Romanova, E.V.; Li, L.; Sweedler, J.V.; Süssmuth, R.D.; Gruber, C.W. Peptidomics. Nature Reviews Methods Primers 2023, 3, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Srivastava, D.; Sahu, M.; Tiwari, S.; Ambasta, R.K.; Kumar, P. Artificial intelligence to deep learning: machine intelligence approach for drug discovery. Mol Divers 2021, 25, 1315–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melo, M.C.R.; Maasch, J.R.M.A.; de la Fuente-Nunez, C. Accelerating antibiotic discovery through artificial intelligence. Communications Biology 2021, 4, 1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ermert, P.; Luther, A.; Zbinden, P.; Obrecht, D. Frontier Between Cyclic Peptides and Macrocycles. Methods Mol Biol 2019, 2001, 147–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulder, M.P.C.; Fodran, P.; Kemmink, J.; Breukink, E.J.; Kruijtzer, J.A.W.; Minnaard, A.J.; Liskamp, R.M.J. Mutual influence of backbone proline substitution and lipophilic tail character on the biological activity of simplified analogues of caspofungin. Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry 2012, 10, 7491–7502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, A.; Wolfe, A.; Williamson, J.C. Antifungal Resistance and the Role of New Therapeutic Agents. Curr Infect Dis Rep 2022, 24, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.D.; MacDougall, C.; Ostrosky-Zeichner, L.; Perfect, J.R.; Rex, J.H. Combination antifungal therapy. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2004, 48, 693–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lignieres, G.; Guitard, J.; Alby-Laurent, F.; Rambaud, J.; Bigot, J.; Morand, K.; Leverger, G.; Tabone, M.D. Antifungal combination therapy for invasive fungal infections in a paediatric oncology and haematology department: A retrospective analysis of practice. J Mycol Med 2022, 32, 101276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Yan, H.; Min, L.; Wang, H.; Chen, X.; Shi, J.; Sun, S. The antifungal activity of caspofungin in combination with antifungals or non-antifungals against Candida species in vitro and in clinical therapy. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther 2022, 20, 161–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chassot, F.; Venturini, T.P.; Piasentin, F.B.; Santurio, J.M.; Svidzinski, T.I.E.; Alves, S.H. Activity of antifungal agents alone and in combination against echinocandin-susceptible and -resistant Candida parapsilosis strains. Revista Iberoamericana de Micología 2019, 36, 44–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatipoglu, N.; Hatipoglu, H. Combination antifungal therapy for invasive fungal infections in children and adults. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther 2013, 11, 523–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yan, H.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Sun, S. Antifungal activity and potential mechanism of action of caspofungin in combination with ribavirin against Candida albicans. Int J Antimicrob Agents 2023, 61, 106709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).