1. Introduction
Diabetes and diabetic-induced complications are the leading causes of major healthcare problems in the world. Recent data show that an estimated 530 million people will die of diabetes and diabetes-associated complications by the year 2035. More than 50% of the people are unaware of their diabetic status. In India by 2045, 700 million DM and 548 million pre-DM cases are expected to be found {1} . This is a 51% increase compared to the Year 2019. In addition, the conversion to DM from pre-DM is also much higher in the population. Seventy-five per cent of DM cases are in low and middle-income countries. {2,3}.
The prolonged untreated diabetic condition leads to two types of complications, acute and chronic. Diabetic ketoacis, diabetic hyperosmotic coma, fungal diseases and many other infectious diseases are acute complications. Chronic complications include diabetic retinopathy, diabetic nephropathy, diabetic neuropathy, and diabetic foot and these are irreversible often. Diabetic retinopathy is a highly specific vascular complication, and its prevalence is related to the duration of diabetes and the level of glycemic control {4}. Diabetic Retinopathy is a microvascular complication affecting 15-20% of the population. Undiagnosed people also get DR. Almost 50% of DR are affected by sight -threatening DR (STDR). As of today in India, roughly 3 million people are at risk of developing STDR. DR is a progressive disease, progressing from mild to severe non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy (NPDR) to proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR). Early detection will have a better chance of treatment and control. Diabetes also affects the onset of glaucoma, cataract and other eye disorders. Apart from vascular complications, neurodegeneration is an early development {5} and is responsible for microangiopathy. Because of this, the American Diabetes Association defines Diabetic retinopathy as a highly specific neurovascular complication of both type1 and type2 diabetes. {4}
Most DM cases are type 2 diabetic cases forming roughly 80% of all DM cases. About 80% of the cases of DM live in low and middle-income countries where managing diabetes and preventing diabetic-induced complications is a challenge and difficult. Among the complications of diabetes, diabetic retinopathy is the major cause of blindness. An estimated one-fifth of DM cases will develop some form of DR in a span of 5 to 10 years if the DM condition is not controlled. Among the DR cases (STDR) is the common cause of loss of sight. Timely intervention by screening the DR among DM is an urgent but unmet need. {6}. Diabetic Macular Edema (ME) cases are the worst cases of blindness along with proliferative diabetic retinopathy condition, and DME can develop at any stage of diabetic retinopathy.
2. Biomarkers for disease onset and progression of diabetic retinopathy.
The availability of one or more markers well before the appearance of clinical symptoms allows lifestyle modification and preventive management. In a recent multi-centric study {6} we evaluated several circulatory biomarkers for predicting sight-threatening diabetic retinopathy. The study was conducted in three ophthalmic clinics one in the UK and two centres in India. Patients older than 40 years of age were divided into four groups, (1) no history of diabetes, (2) type 2 diabetes of at least 5 years duration with no evidence of DR,(3) non-proliferative DR with diabetic macular oedema, or (4) proliferative DR. STDR comprised groups 3 and 4. Previous studies reported 14 specific proteins as candidate biomarkers of DR among DM-patients in different populations. Including the new markers discovered during our discovery phase analysis of a small population, a total of 57 proteins were shortlisted for further studies. Among the selected proteins an equal number of proteins we up or downregulated. Among the proteins showing altered expression levels, a total of 12 proteins, including Cystatin C, were taken for validation using ELISA. Results clearly demonstrated the increase in the Cystatin C level in the NPDR & PDR and follow disease progression from DM to DR. Among the 12 markers examined in the Indian and UK cohorts Cystatin C and Leucine _rich alpha 2 glycoprotein1 (LRG 1) are the markers that performed well. People with these markers unregulated can be prioritized for further screening. In the Indian population, Cystatin C itself is doing well as a predictor of onset. In both populations and the addition of LRG1 marginally improves prediction potential. The inclusion of Extracellular Vehicles (EVs) as biomarkers will greatly improve the predictive ability {7}and the same is discussed below.
3. Extracellular Vesicles and DR.
There are several types of EVs produced by all living cells. There are several reviews describing the heterogeneous populations of EVs. EVs include apoptotic bodies, exosomes, microvesicles, migrasomes, exophers, and exomeres {8}. Apoptotic bodies, exomeres , and midbody remnants {9}all are extracellular vesicles of biological significance. These are discussed in detail in the references given {10,11}. In this article, we will call exosomes and microvesicles together Extracellular Vesicles (EVs). These are produced by two different pathways and structurally also differ. The endosomal pathway produces predominantly small exosomes and blebbing or pinching of the plasma membrane gives rise to larger microvesicles. They carry proteins, DNA, RNA, lipids and metabolites and their composition reflects the physiological state of the parent cell producing the EVs. EVs circulate in the blood and can cross the blood-retinal barrier {12}. The production of EVs from the cell occurs non-uniformly across the cell surface. The plasticity of the membrane surface and the micro domains of distinct composition predisposes the release of EVs to certain locations {13}. The predominant locations of EV shedding are membrane protrusions. Platelets, enterocytes, endothelia, melanocytes, stem cells, osteoblast tumor cells, fibroblasts and neuron and dendritic cells all have different types of membrane protrusions {14}. The actin-based membrane protrusions clearly show there are multiple mechanisms that exist for the formation of these protrusions and consequently for the formation of EVs. It has been shown that EVs are produced from cells without any external mechanical force. However, the movement of cells generates adequate mechanical stress for the formation of membrane blebs and hence the formation of EVs. It has been shown that the blebbing of the EVs from the tip of the filopodia is energetically more favourable than the plain plasma membrane and hence higher the plasma membrane curvature less is the energy requirement {14}. However, there are other routes by which the EVs could be generated and as of now, we do not have a clear picture of the relative contribution of each of these pathways of generation EVs. Further, a recent report shows the intriguing result that exosomes of endothelial cells could be encapsulated in the microvesicles and undergo another exocytosis event to get released from the microvesicles {13}.
The interest in EVs and their role in DR is a very active field of study. EVs could be signal transducers, cell-cell communication messengers, modifiers of the biological functions of the target cells and could be excellent biomarkers. The cargo inside the EVs, DNA, RNA, protein and lipids all could be used as biomarkers due to the cell-specific nature of the packaged cargo. In a recent report (Jeya Maheswari et al., in pess) , we observed that the cargo of plasma-derived EVs coupled with proteins from the total serum can increase the number of biomarkers for the progression of diabetic retinopathy. We have used serum from the following six groups of patients: (1) no history of diabetes, (2) type 2 diabetes of at least 5 years duration with no evidence of DR,(3) non-proliferative DR with diabetic macular oedema (DME), (4) non-proliferative DR without diabetic macular oedema (DME),(5 ) proliferative DR, (6) PDR withe DME . EVs isolated from the serum of all the patients and the differential expression of we six proteins was examined. The ROC curve shows the biomarkers, vitronectin and Serum fibronectin along with clinical features can discriminate stage of DR. The following four proteins , CD/61, peroxiredoxin, thrombospondin, fibronectin are found differentially expressed in the serum EVs . This data clearly shows that the combination of serum and serum EV cargo is the best approach for biomarker discovery in DR.
4. Neurovascular Unit, Diabetic Retinopathy and Extracellular Vesicles
DR is a complex and progressive disorder. Neurodegeneration, and at late stages, vascular complications lead to a severe form of the disease. Retinal homeostasis in the retinal microenvironment is maintained by pericytes, endothelial cells, astrocytes, muller cells, bipolar cells, amacrine cells, macrophages, neurons, basement membrane and retinal pigment epithelium {
15}. They are collectively called Neurovascular Units (NVU) {
16}. The interaction among the cells in the NVU is the crucial factor that decides the health of the retina. Diabetic conditions lead to the activation of multiple pathways which ultimately induce oxidative stress. Oxidative stress at the NVU leads to inflammation and finally new abnormal vessel formation. Many components, and in particular the molecular pathways, involved in inflammation and neovascularization have been worked out. These are reviewed in recent articles {
17 18}. The physical interaction between the multiple cell types is not well understood. More than ten years ago {
19} it has been shown that the exosomes from B6 mice can be injected through the periocular route and these exosomes reach the retina in 15 minutes. This study clearly shows that the exosomes could be excellent delivery vehicles of their cargo into the retina, without resorting to intravitreal injection. Recent studies focus on the effect of diabetic conditions on the role of EVs of the NVU cells and the information transfer mediated by the EVs secreted by the cells. The different cell types in the NVU produce distinct EVs and the EVs also differ in their composition under diabetic conditions. Interestingly the NVU cells are producers of EVs and targets of EVs from other cells at the same time. The EVs could be from the NVU cells and also from extraocular sources such as blood and vitreous. Since the EVs can cross the inner and outer blood-retinal barrier{
20,21,
22} the extraocular EVs also play a major role in regulating the NVU cells and alter the outcome of diabetic retinopathy.
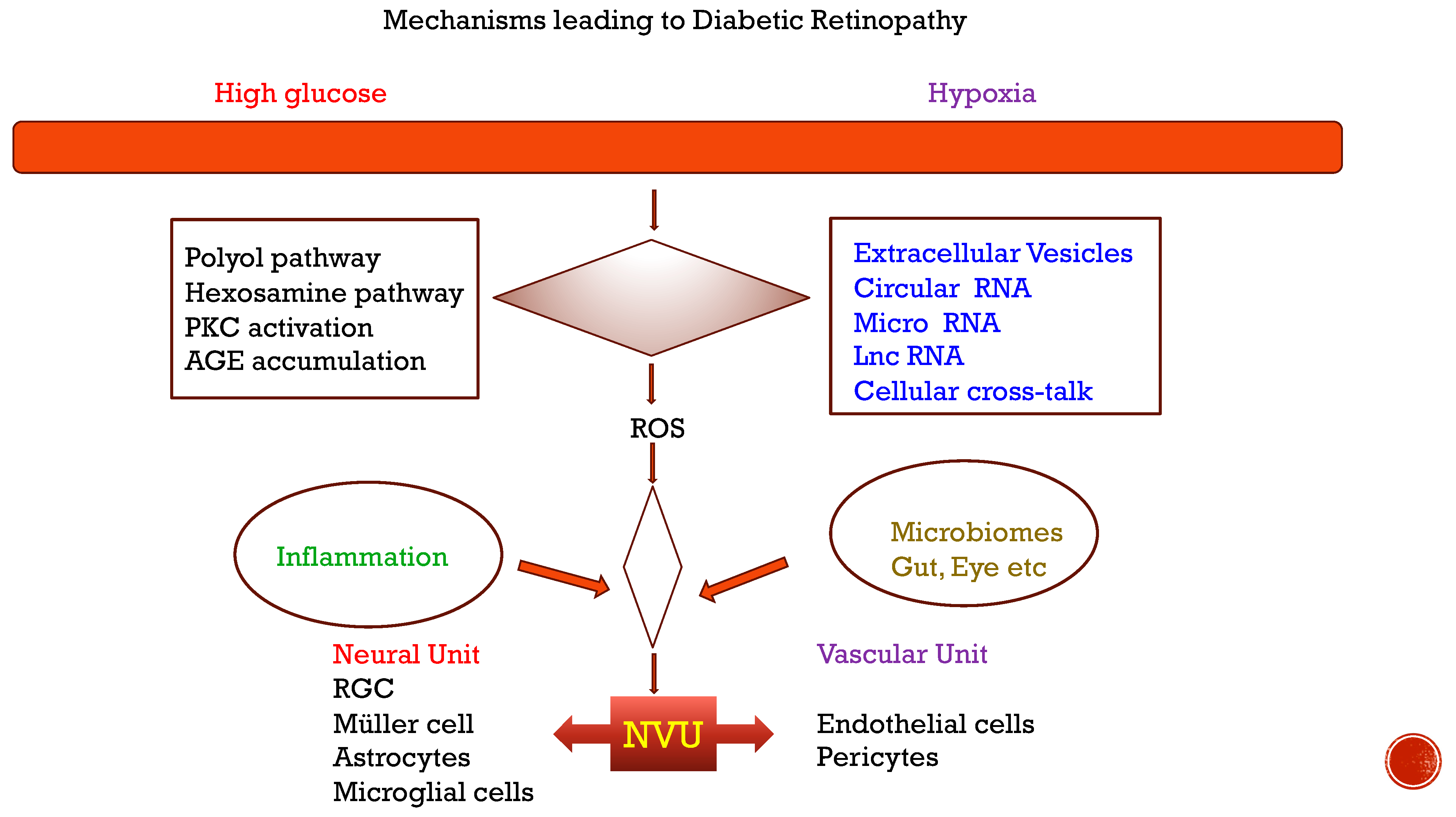
Figure 1.
Mechanisms leading to diabetic retinopathy.
Figure 1.
Mechanisms leading to diabetic retinopathy.
Figure 2.
Retinal capillary and the cells associated.
Figure 2.
Retinal capillary and the cells associated.
5. Mechanism of Angiogenesis.
The stages of the DR progression are well understood, and the clinical characteristics are well characterized. Early stages of DR are called mild, moderate and severe NPDR and microaneurysms, cotton wool spots and minor bleeding may occur. The severe stages are characterized by vascular rupture, severe bleeding, retinal detachment and neovascularization {17}. Late stage shows basement membrane thickness, pericyte apoptosis, endotheliocyte dysfunction, increased vascular permeability and vascular occlusion. The early event in DR development is the abnormal interactions of pericytes and endothelial cells. Pericytes are contractile mesenchymal cells which are responsible for the homeostasis of microvessels in conjunction with endothelial cells. Early loss of pericytes that occur in PDR leads to disruption of its interaction with endothelium and eventually leads to endothelial migration and new abnormal vessel formation {23} Early DR namely NPDR does not show any symptoms and the symptoms become apparent only in late NPDR and PDR conditions. There are several interconnected biochemical pathways involved in neovascularization in PDR. The reader is directed to excellent reviews for the information. {18}. We will be focusing on the EVs and their cargo and their role in DR. The role of EVs from these two cell types along with the EVs of Muller cells and astrocytes play a major role in diabetes-induced microvascular complications in the retina.
6. EVs from the NVU.
In a recent article, the authors { 24} isolated the EVs from primary ex vivo cultures of Retina from cadaver eyes and examined the changes in the cargo of the EVs in control and DR patient retina. Interestingly, the authors also compared the EVs from DR patients’ urine. The proteome of the EVs from the control retina explant-conditioned media and DR explant-conditioned media showed clear changes in the profile of proteomes under these conditions. The DR explant derived EVs were enriched for proteins in epithelial junction remodeling proteins which are related to epithelial migration and permeability. Among the 57 proteins found in both the EVs from the retinal tissue and urine of DR patients. The study shows that urine could be a good source of biomarkers. Gurudas et all { 6} have shown plasma EVS could be a good source of biomarkers for DR. This study shows urine of DR patients also can be used as a biomarker. The identification of junction plakoglobin only in the urine of DR patients is interesting and will be useful to confirm as a biomarker for DR onset in a large sample population.
The Evs were isolated from the neural retina, vitreous humour, retinal astrocytes, endothelial cells, pericytes, retinal pigment epithelium, and Muller cells. We will be examining the EVs produced by these cells of the NVU in the following sections. Recent studies show cells of the extraocular tissue also contribute the vascular health through the secretion of exosomes and perhaps other molecules. The role of extraocular EVs and their involvement in the disease process is described in subsequent sections.
7. Pericytes- derived EVs in DR
Pericytes line the capillaries and are in close contact with the endothelial cells and they both share the basement membrane and hence are in close contact. They are contractile and also have the properties of stem cells. In the capillaries, the exosomes produced by pericytes are taken up by the EC and the EVs of pericytes reduce the pathological changes of the capillaries. { 21}. In the retina, pericytes contribute to the inner blood-retinal barrier also. Pericyte loss is an early event in angiogenesis in PDR. The close association of endothelial cells and pericytes in the microvessels of the retina imply the interaction of these two cell types via the EVs. The primary retina-specific, microvascular co-culture system developed by Eyre et al. {25} will be a good model system to examine the role of pericytes exposed to DM-like conditions. Pericyte expresses MiR126 and the expression of this MiR126 is downregulated by the exosomes derived from human bone marrow-derived MSC exposed to hypoxia. Downregulation of this microRNA leads to up-regulation of expression of VEGF and HiF and both these are involved in Neo vascularization {26}. It is important to know the mechanistic aspect of this pathway. Interestingly the Ang-2 which is also involved in pericyte destabilization is not altered in this experimental system. This result indicates the specificity of the action of the exososmes on the biochemical pathways. Further, the health of the pericytes is essential for the capillary function which is affected in PDR due to pericyte loss. In another experimental system involving spinal cord injury, it was shown that the pericyte-derived exosome can improve the endothelial function, protect the blood-spinal cord barrier and alleviate apoptosis. All these are affected by hypoxic condition induced by diabetes and the onset of PDR also leads to similar pathologies. It will be interesting to examine the role of pericytes EVS of the retinal capillaries in the prevention of endothelial defects. Presumably diabetic stress affects the EVs of pericytes and prevents their protective role in the PDR condition {21}. Even though the role of pericytes in endothelial heath in particular and micro vessel health in general the role of exosomes in the pericyte function is just emerging. The role of pericyte exosomes in the endothelial cross talk is discussed in the subsequent section. Circular RNA {27} are another class of regulators of diabetic retinopathy stress. The Circular RNA CircEhMT1{28} is present in the exosomes of pericytes and the hypoxia-induced pericytes produce EVs that carry this circular RNA to the endothelial cells and alter the functions of Endothelial cells toward tube formation and also induce various function found in diabetic stress exposed endothelial cells. EVs produced by other cells of the NVU are discussed in the subsequent sections.
8. Endothelial cells
Sirtuin 1 (SIRTI) is implicated in the regulation of several cellular functions. In the retinal endothelial cell culture model, high glucose induces angiogenesis and this h29ypoxia-induced angiogenesis is reduced if SIRTI is over-expressed {29}. Under these conditions mi-R30 is unregulated and this microRNA inhibits the expression of SIRT1. This mechanistic insight shows the regulation of Hypoxia i-induced activation of angiogenesis. Endothelial cell and Pericyte crosstalk is essential for vascular health. In diabetic conditions, the cross-talk is affected leading to vessel damage. Circular RNA cPWWP2A {23} is produced by pericytes but not by endothelial cells. Diabetic related stress up-regulates the circular RNA cPWWP2A in pericytes. The circular RNA is encapsulated in exosomes and transferred to endothelial cells. The RNA functions as a sponge of Mir 579 and this inhibition increases the expression of angiopoietin 1, occludin, and SIRT1. Consequently, vascular health is altered by the dysregulation of this system. Other cells in the NVU also transfer the exosomes to endothelial cells. MCSC-released exosomes can alter the function of HUVEC and promote angiogenesis. {30}. These results imply that more than one microRNA might be involved in the regulation of SIRT1 and angiogenesis.
9. Retinal pigment epithelial EVs in DR
Retinal pigment epithelium is the monolayer of cells which are responsible for the health of photoreceptors, and they also form the feeder layer of rods and cones. The RPE cells and their tight junctions along with the basement membrane form the outer blood retinal barrier. As discussed before EVs can cross this barrier as well. RPE are susceptible to oxidative stress and the reactive oxygen species several functions of RPE. In diabetic retinopathy ROS generation and the consequent changes in the NVU is the hallmark of the disease. ARPE-19 cells were used as models to study RPE function in this system. It has been shown {31} that the induction of ROS leads to an almost twofold increase in the number of EVs produced. Further, the cargo in the EVs produced by the ROS-induced cells is different compared to the untreated control cells. VEGFR2 is found in the treated cells but not in the EV of control cells. The EVs from ROS induced cells also induce tube formation in co-culture experiments with Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial (HUVE) cells. This clearly shows conditions mimicking DR activate the tube formation through he EVs produced from RPE cells and transmitted to endothelial cells through the EVs. The RPE which is in close contact with choriocapillaris and photoreceptors use EVs as communication molecules. This study also shows that the autophagy induced by ROS is essential for the release of EVs in stressed ARPE-19 cells. Another observation, which is clinically relevant is the non-involvement of VEGF in the EV-induced tube formation in this in vitro experimental system { 32}. The entry of the EVs into RPE has been studied and shown that the entry of EVs is predominantly through Clathrin-dependent engulfment. Further, protein-ligand interaction is the main pathway of entry and lipid-mediated entry is not involved in the EV transport. Interestingly in ROS-induced RPE cells, the ligands for the entry increased, unlike the control cell EVs. Further, the cargo in the ARPE and porcine primary RPEs produced EVs have enough cargo to reduce the barrier function (transepithelial resistance). However, the role of other cargo of the ROS-induced RPE is yet to be studied. The polarized release of EVs from the apical and basal side of the monolayers of RPE shows the functional importance for the EVs for the crucial disease state of DR {33}. This property also is important when interpreting the EVs produced using the ARPE cells cultured in vitro.
RPE has the potential to transdifferentiate into mesenchymal cells. The exosome from the in vitro induced transdifferentiated RPE cells of the cell line ARPE 19 have altered exosome and microRNA profile. These EVs can induce differentiation of the normal ARPE19 cells through the mi-R 534 {34}. This leads to the formation of myofibroblasts and the pathogenic conditions could alter the differentiation of RPE and lead to this abnormal activity.
Another important cargo carried by the EVs of RPE is αβcrystalline. Being a heat shock protein crystallins are shown to be important for the health of photoreceptors. In RPE polarized monolayers crystalline is secreted from the apical side toward the photoreceptors. The secretion of αβcrystalline are not thought the regular secretion systems but they are secreted as cargo of EVs. In Human RPE cells the EV secretion is dependent on lipid rafts. Under pathological conditions, the EVs are secreted through the basolateral side toward the choroid also. The role of this αβcrystalline in DR is yet to be analyzed { 35}.
10. Muller glial cells
Muller glial cells are the primary producers of VEGF and high glucose and hypoxia regulate the production of VEGF by MH cells {36,37}. In the earlier report by Eichler { 37} it has been shown that hypoxia-induced enhancement of VEGF production is prevented by high glucose in the medium, This is an interesting observation implying that hypoxia and hyperglycemia have a combined role in the outcome of VEGF production and new vessel formation. In a very interesting study { 36} Yu Liu and his coworkers have shown the miR-9-3p produced by MH cells is responsible for the activation of tube formation in endothelial cells. Mir-9-3p is produced when the MH cells are cultured in high glucose or hypoxic conditions and the micro–RNA is packaged into the exosome produced by the MH cells. The number of EVs produced are not altered by high glucose conditions but high glucose increases the expression of miR- 9-3p. Interestingly the authors examine the vitreous from PDR and MH patients for the exosome containing miRNA and found the up regulation of this miRNA in PDR patients. Human retinal endothelial cells-, human microglial cells, ARPE19 cells, and human Muller glial cells were examined and only Muller cells produced miR-9-3p under high glucose conditions.
11. Retinal Astrocytes
Retinal astrocytes (RAC) are distributed in the NVU and are in contact with the capillaries and neural cells. In the mice model of laser-induced choroidal neovascularization {19} astrocyte-derived exosomes can prevent vascularization whereas the exosomes from RPE cells are ineffective in inhibiting angiogenesis. However, in the RPE experiment, the exosomes are prepared from cell cultures and hence the polarized release of exosomes could not be achieved. It is likely the exosomes from the apical or basal side may have different effects on angiogenesis. The study also identified the following up-regulated proteins in RAC-derived exosomes, endostatin, PEDF, and TIMP-1, and these are antiangiogenic factors. These proteins are not upregulated in RPE cells. In a cell culture model using a human astrocyte cell line shows that the induction of oxidative stress using tert-butylhydroperoxide lead to alterations in the EVs of astrocytes {21}. The induced cell produced EVs can induce tube formation in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) indicating the role of EVs produced by astrocytes exposed to diabetic conditions in vascularisation vascularization. The EVs of uninduced RACs can inhibit tube formation by endothelial cells supporting the results of the animal model experiemnts described above.
12. Blood retinal barrier
The human body has mechanisms that restrict the free flow of cells and large materials from blood to other parts. These are the blood-brain barrier (BBB), blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier (BCSFB), blood–lymph barrier (BlyB), blood–air barrier (BAB), stromal barrier (SB), blood–labyrinth barrier (BLaB), blood-retinal barrier (BRB), and placental barrier (PB)
In the retina, the inner and outer blood-retinal barriers prevent free exchange of cells and larger material from blood to the retina to prevent pathological changes. The blood retinal barrier also is affected in diabetic retinopathy. The question remained whether the EVs can cross the Weissman barrier which prevents the changes in the somatic tissue affecting the germ cells.
The mechanistic aspects of the blood-retinal barrier have been studied in the context of the migration of EVs produced by the cells of the NVU as well as the extraocular EVs from vitreous and blood. Their entry has been studied in detail and the use of this property of the EVs has been instrumental in the development of drug delivery using native and engineered EVs. The inner blood-retinal barrier is formed by the endothelial cells and their tight junctions between the endothelial cells and basal lamina and the muller cells cell astrocytes and pericytes complete the iBRB organization. The outer blood-retinal barrier is formed of retinal pigment epithelium tightly bound to Bruch’s membrane and tightly bound by tight junctions. The structure and dynamics of the tight junctions are reviewed recently {20}. The exosomes of retinal cells as well as other cells play a crucial role in the organization and functional integrity of the BRB. The breakdown of the BRB leads to serious consequences in diabetic conditions and the EVs play a crucial role in this process. The details are being worked out now.
Charles Darwin proposed that throughout the life of an organism, all organisms produce gemmules, and the gemmules encapsulated the nature of the organ producing it. A strong muscle produced gemmules for strong muscles, and a weak one produced gemmules for weak muscles. The gemmules are released from the place of origin and circulated in the body, not necessarily through the blood, and aggregated in the gametes. They would then be passed on to the offspring and control the offspring’s development. These gemmules are considered analogous to the exosomes and in many ways, they resemble the exosomes. Exosomes enter epididymis and the cargo of the EVs can alter and ultimately can influence intergenerational transmission of characters. The barrier to somatic changes affecting the gametes is called the Weissman barrier and recent studies point out that exosomes can cross the Weissman barrier as well. {38}.
13. EVs from extraocular cells
The extraocular cells produce EVs and the production of these EVs are affected by diabetic conditions. The EVs from these cells travel through the system and cross blood retinal barrier and enter the NVU. This led to the onset and progression of DR.
14. Mesenchymal stem cell EVs and DR
MSC-derived EVs have both protective and deleterious effects on the retina. The cargo differs in the EVs of MSC when exposed to hyperglycemic stress and the EVs produced from stressed EVs actually accelerate the vascular disorder in DR {39}. On the other hand, the MSC derived EVS from normal cells and prevent DR progression by over-expressing miR192. The MSVs also produce miR 126 which inhibits inflammation. Consequently, the status of the MSC in vivo needs to be examined carefully before using the EVs as therapeutic options. A major shortcoming of the studies is the lack of confirmatory evidence from appropriate model systems.
15. Lymphocytes
Muller cell proliferation and tube formation are prevented by the EVs derived from lymphocytes. MirR 181a, a micro RNA enriched in lymphocytes can block VEGF signaling and avoid neovascularisation {40}. An earlier study showed the mechanism of the entry of EVs from lymphocytes {41}.
16. EVs and Engineered EVs in Precision medicine.
Precision medicine depends on the use of patient-specific information, including genetic, as well as environmental factors contributing to the disease. EVs are being used in precision medicine increasingly. This is beyond the scope of the present review and a recent review describes the field elaborately {42}.
The utility of naturally produced EVs for drug delivery and other application has several problems, including the problem of large-scale production. One of the alternative approaches is the production of cell-derived nanovesicles. These can be produced easily and in large amounts and they have properties similar to the EVs. One of the early approaches was to load the vesicles with the compound of interest and use them as adjuvants for antibiotics or immune modulators. Loading the CDNs is relatively simple. There are multiple methods available and the passive entry is enough in many cases to load the vesicles. The two major methods are active loading and passive loading. Both methods offer efficient loading of molecules, and one has to try various options such as electroporation, passive diffusion, transfection, sonication, freeze-thaw cycles. One another option is to express the target protein by recombinant expression route and the expressed proteins are sorted into the EVs. This allows one to modify the target protein as well {43} . The other way of engineering EVs is to modify the EV surface so that the EVs can be targeted to specific cell carrying corresponding receptors.
Inability to design EVs is the main reason for their broader application. In a recent report,{43} several surface proteins of EVs were used to generate fusion proteins that could be displayed on the membrane surface of the EVs. One such protein PTGFRN which is present on the EVs but not essential for the EV biogenesis has been used to generate fusion proteins which then shown to be displayed on the surface of EVs from HEK293 cells Using this protein scaffold the authors have generated fusion protein from 12 kDa tp 170 kDa in size. They also used another protein BASP1 that sorts normally into the lumen of the EVs , in this study the authors and fused Cas9 and showed that Cas9 is now in the lumen of the EV and they demonstrated the functional status of Cas9 prtein. The important observation is that unlike the naked protein molecule the EV encapsulated protein is not degraded in circulation and delivered into the cells and hence is stable for much longer.
17. Conclusions
The emerging role of EVs as signal transducers and modulators is becoming clear in diabetic complications. The ten cell types found in the NVU each produce EVs with distinct cargo and have both anti and proangiogenic components. Therefore the outcome of DR depends on the balance between the EVs produced by these cells. Careful characterization of the EVs is a first requirement. The second difficulty is the control of integrity and functional competency of the isolated EVs. Both these issues are being addressed in several systems. The use of the in vitro systems has limited potential. Therefore, an appropriate model system that reflects the in vivo EV population in the altered functional state is important. Multiple cells produced EVs and the same cell is a producer and responder to the signal and this aspect needs to be considered carefully in interpreting the in vitro data obtained using cell culture models.
References
- Mathur, P., Leburu, S. & Kulothungan, V. Prevalence, Awareness, Treatment and Control of Diabetes in India From the Countrywide National NCD Monitoring Survey. Frontiers Public Heal 10, 748157 (2022).
- Teo, Z. L. et al. Global Prevalence of Diabetic Retinopathy and Projection of Burden through 2045 Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Ophthalmology 128, 1580–1591 (2021).
- Raman, R. et al. Prevalence of diabetic retinopathy in India stratified by known and undiagnosed diabetes, urban–rural locations, and socioeconomic indices: results from the SMART India population-based cross-sectional screening study. Lancet Global Heal 10, e1764–e1773 (2022).
- Solomon, S. D. et al. Diabetic Retinopathy: A Position Statement by the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 40, 412–418 (2017).
- Simó, R., Hernández, C. & (EUROCONDOR), E. C. for the E. T. of D. R. Neurodegeneration in the diabetic eye: new insights and therapeutic perspectives. Trends Endocrinol Metabolism 25, 23–33 (2014).
- Gurudas, S. et al. Multicenter Evaluation of Diagnostic Circulating Biomarkers to Detect Sight-Threatening Diabetic Retinopathy. Jama Ophthalmol 140, 587–597 (2022).
- Ren, J. et al. Diabetic retinopathy: Involved cells, biomarkers, and treatments. Front Pharmacol 13, 953691 (2022).
- Aafreen, S., Feng, J., Wang, W. & Liu, G. Theranostic extracellular vesicles: a concise review of current imaging technologies and labeling strategies. Extracell Vesicles Circulating Nucleic Acids 4, 107–132 (2023).
- Rai, A. et al. Secreted midbody remnants are a class of extracellular vesicles molecularly distinct from exosomes and microparticles. Commun. Biology 4, 400 (2021).
- Ghanam, J. et al. DNA in extracellular vesicles: from evolution to its current application in health and disease. Cell Biosci 12, 37 (2022).
- 2022_WAUBEN_EVS_ENCYC CELL BIOL.pdf.
- Salimi, L. et al. Physiological and pathological consequences of exosomes at the blood–brain-barrier interface. Cell Commun Signal 21, 118 (2023).
- Petersen, J. D., Mekhedov, E., Kaur, S., Roberts, D. D. & Zimmerberg, J. Endothelial cells release microvesicles that harbour multivesicular bodies and secrete exosomes. J Extracell Biology 2, (2023).
- Rilla, K. Diverse plasma membrane protrusions act as platforms for extracellular vesicle shedding. J Extracell Vesicles 10, e12148 (2021).
- Casciano, F. et al. The role of the mTOR pathway in diabetic retinopathy. Frontiers Medicine 9, 973856 (2022).
- Yang, S., Zhang, J. & Chen, L. The cells involved in the pathological process of diabetic retinopathy. Biomed Pharmacother 132, 110818 (2020).
- Lechner, J., O’Leary, O. E. & Stitt, A. W. The pathology associated with diabetic retinopathy. Vision Res 139, 7–14 (2017).
- Wei, L. et al. The pathophysiological mechanisms underlying diabetic retinopathy. Frontiers Cell Dev Biology 10, 963615 (2022).
- Hajrasouliha, A. R. et al. Exosomes from Retinal Astrocytes Contain Antiangiogenic Components That Inhibit Laser-induced Choroidal Neovascularization*. J Biol Chem 288, 28058–28067 (2013).
- Nagymihály, R. et al. Tissue Barriers in Disease, Injury and Regeneration. 115–146 (2021) doi:10.1016/b978-0-12-818561-2.00003-5.
- Yuan, X. et al. Exosomes Derived From Pericytes Improve Microcirculation and Protect Blood–Spinal Cord Barrier After Spinal Cord Injury in Mice. Front Neurosci-switz 13, 319 (2019).
- Elliott, R. O. & He, M. Unlocking the Power of Exosomes for Crossing Biological Barriers in Drug Delivery. Pharm 13, 122 (2021).
- Liu, C. et al. Targeting pericyte–endothelial cell crosstalk by circular RNA-cPWWP2A inhibition aggravates diabetes-induced microvascular dysfunction. Proc National Acad Sci 116, 7455–7464 (2019).
- Mighty, J. et al. Extracellular vesicles of human diabetic retinopathy retinal tissue and urine of diabetic retinopathy patients are enriched for the junction plakoglo bin protein. Front Endocrinol 13, 1077644 (2023).
- J.Eyre, J. & Levis, R. L. W. and H. J. A human retinal microvascular endothelial-pericyte co-culture model to study diabetic retinopathy in vitro. Experimental Eye Research.
- Mazzeo, A., Beltramo, E., Iavello, A., Carpanetto, A. & Porta, M. Molecular mechanisms of extracellular vesicle-induced vessel destabilization in diabetic retinopathy. Acta Diabetol 52, 1113–1119 (2015).
- Yang, Q., Li, F., He, A. T. & Yang, B. B. Circular RNAs: Expression, localization, and therapeutic potentials. Mol Ther 29, 1683–1702 (2021).
- Ye, L. Exosomal circEhmt1 Released from Hypoxia-Pretreated Pericytes Regulates High Glucose-Induced Microvascular Dysfunction via the NFIA/NLRP3 Pathway. Oxidative Medicine Cell. Longev. 2021, 8833098 (2021).
- Wang, P. et al. Effect of plasma-derived extracellular vesicles on angiogenesis and the ensuing proliferative diabetic retinopathy through a miR-30b-dependent mechanism. Diabetol Metab Syndr 14, 188 (2022).
- Gu, C., Zhang, H. & Gao, Y. Adipose mesenchymal stem cells-secreted extracellular vesicles containing microRNA-192 delays diabetic retinopathy by targeting ITGA1. J. Cell. Physiol. 236, 5036–5051 (2021).
- Atienzar-Aroca, S. et al. Role of retinal pigment epithelium-derived exosomes and autophagy in new blood vessel formation. J Cell Mol Med 22, 5244–5256 (2018).
- Nicholson1, C. et al. Mechanisms of extracellular vesicle uptake in stressed retinal pigment epithelial cell monolayers. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis (2019).
- Klingeborn, M., Stamer, W. D. & Rickman, C. B. Retinal Degenerative Diseases, Mechanisms and Experimental Therapy. Adv Exp Med Biol 1074, 539–544 (2018).
- Zhang, Y. et al. Exosomes mediate an epithelial-mesenchymal transition cascade in retinal pigment epithelial cells: Implications for proliferative vitreoretinopathy. J Cell Mol Med 24, 13324–13335 (2020).
- Sreekumar, P. G. et al. αB Crystallin Is Apically Secreted within Exosomes by Polarized Human Retinal Pigment Epithelium and Provides Neuroprotection to Adjacent Cells. Plos One 5, e12578 (2010).
- Liu, Y. et al. Müller glia-derived exosomal miR-9-3p promotes angiogenesis by restricting sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor S1P1 in diabetic retinopathy. Mol Ther - Nucleic Acids 27, 491–504 (2022).
- Eichler, W., Kuhrt, H., Hoffmann, S., Wiedemann, P. & Reichenbach, A. VEGF release by retinal glia depends on both oxygen and glucose supply. NeuroReport 11, 3533–3537 (2000).
- Noble, D. Exosomes. 487–501 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Gu, C., Zhang, H. & Gao, Y. Adipose mesenchymal stem cells-secreted extracellular vesicles containing microRNA-192 delays diabetic retinopathy by targeting ITGA1. J. Cell. Physiol. 236, 5036–5051 (2021).
- Cai, C. et al. Lymphocytic microparticles suppress retinal angiogenesis via targeting Müller cells in the ischemic retinopathy mouse model. Exp. Cell Res. 399, 112470 (2021).
- Yang, C. et al. Role of receptor-mediated endocytosis in the antiangiogenic effects of human T lymphoblastic cell-derived microparticles. Am. J. Physiol. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 302, R941–R949 (2012).
- Beetler, D. J. et al. Extracellular vesicles as personalized medicine. Mol. Aspects Medicine 91, 101155 (2023).
- Dooley, K. et al. A versatile platform for generating engineered extracellular vesicles with defined therapeutic properties. Mol Ther 29, 1729–1743 (2021).
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).