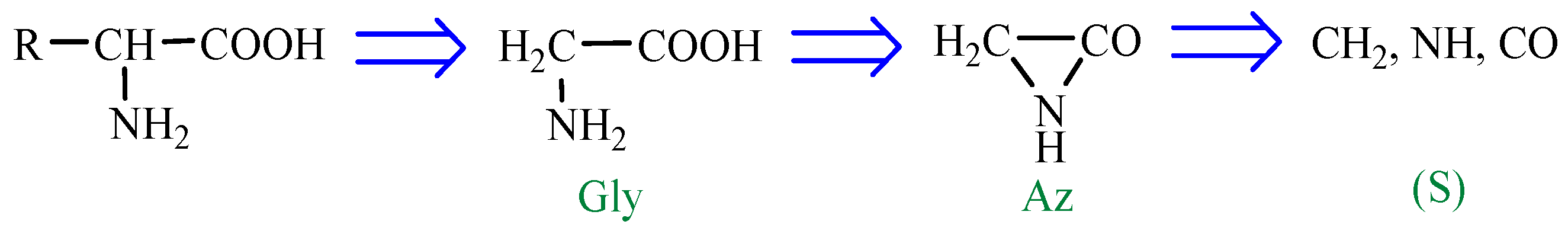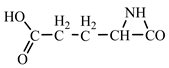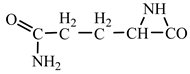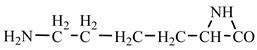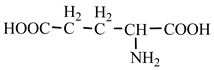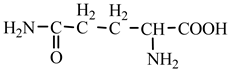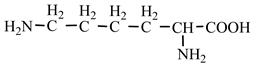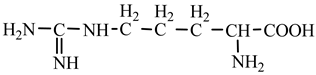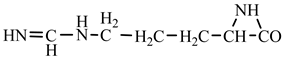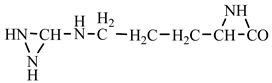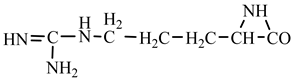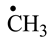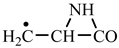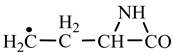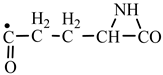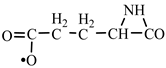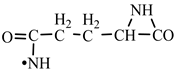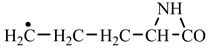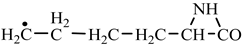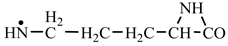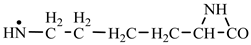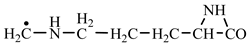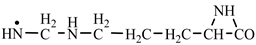1. Introduction
The appearance of life is undoubtedly related to the formation of proteinogenic amino acids and proteins. Researches related to biology, chemistry and biochemistry offers a plethora of information regarding the synthesis of proteinogenic racemic amino acids, starting with simple structure chemical compounds which are constituents of the so called primordial atmosphere and interstellar compounds [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5].
In previous work [
6], we reported that the first precursors of proteinogenic amino acids and their corresponding polypeptides would have been obtained somewhere outside the Earth from three synthons: methylene, nitrene and carbon monoxide. These precursors, carried by a celestial body (comet) in the form of diazomethane, hydrazoic acid and diazocarbonyl, at low temperatures in contact with the components of the primary atmosphere, formed on Earth the first proteinogenic amino acids and the first polypeptides [
1,
7,
8,
9,
10,
11,
12,
13,
14]. It should be noted that the first polypeptides formed from their precursors and not from amino acids [
6]. In previous works [
15,
16,
17,
18] we studied the pathways of formation of 14 proteinogenic amino acids: glycine, alanine, serine, cysteine, aspartic acid, asparagine, threonine, valine, leucine, isoleucine, methionine, proline, phenylanaline and tyrosine. In this paper we extend our studies on the construction of four new proteinogenic amino acids: glutamic acid, glutamine, lysine and arginine. From the beginning we have pursued two important aspects in the conception of our chemical reactivity studies:
a) In the formation of each amino acid precursor, more reaction pathways were researched. From these ones were chosen only the reaction pathways where in the chemical reactions involved, we have to deal only with continuous decreases of the energies of the reaction systems in the passing from the initial states towards the final states;
b) Nitrogen-stabilized synthons and precursors as diazo derivatives, on contact with the components of the primary atmosphere, form a complex mixture of compounds, including proteinogenic amino acids.
2. Computational details
The structures of chemical sample were refined by performing an optimized geometry calculation in mechanic using successively: augmented MM3 parameters, MOPAC AM1 parameters and DGauss with B88-LYP, GGA functional with the DZVP basis sets [
19,
20,
21,
22,
23,
24].
The structure corresponding to the reaction path, with all kinetic energy removed at every step, are calculated also in DGauss using B88-LYP, GGA, functional with DZVP sets.
Specifically, the structures of the reactants and reaction products were established. We explored the whole conformational space between the reactants in all the interradical reactions studied in this paper. From the multiple reaction pathways, for each case, we chose the favored transformations in terms of energy. "Only" for these, we refer to entropies and enthalpies of reaction. The reaction pathways were searched, in which a continuous decrease of energies exists in the passing from reactants to final products. When Gibbs free energies were calculated, we started from intermediate states between reactants and reaction products and the reactions were reconstituted in both directions. Regarding the evaluation of entropies, we mention that we took into account the parameters included in the CacheWork System Library, version 7.5.0.85 [
25].
3. Results and Discussion
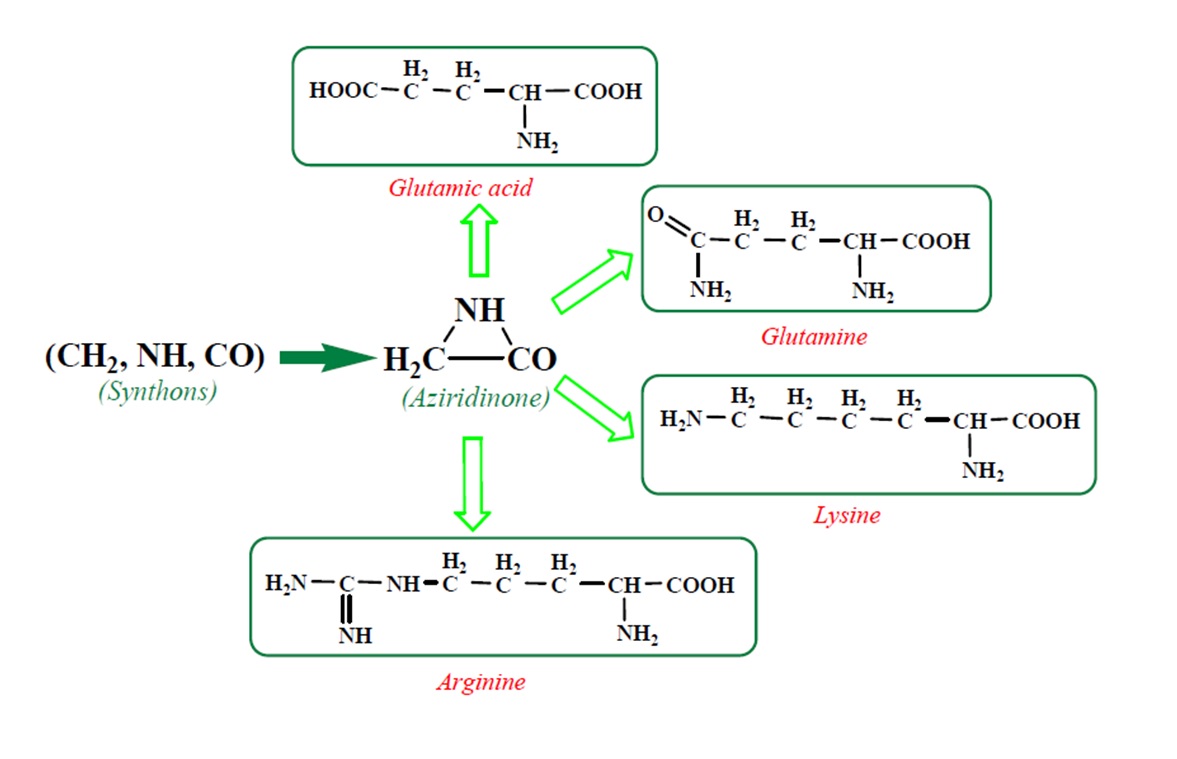
According to a general retrosynthetic scheme (
Scheme 1), three synthons: methylene, nitrene and carbon monoxide first form a key compound, aziridinone. This one, with the same three synthons, would form glycine and amino acid precursors. In contact with the components of the primary atmosphere (H
2O, CO
2, NH
3, H
2S) proteinogenic amino acids would result. This section may be divided by subheadings. It should provide a concise and precise description of the experimental results, their interpretation, as well as the experimental conclusions that can be drawn.
3.1. Thermodynamics
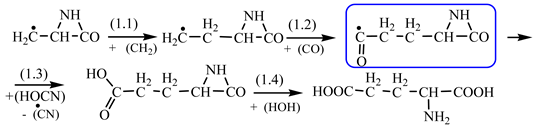
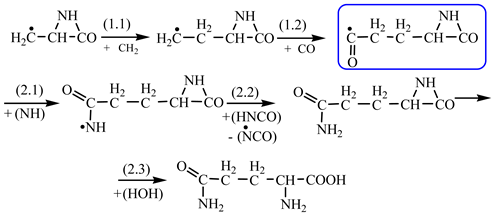
In order to construct the four proteinogenic amino acids: glutamic acid, glutamine, lysine and arginine, the formation enthalpies of all reactants and final products involved in the reactions were first calculated (
Table 1).
Further, in
Table 2 are shown the chemical transformations, considered by us as being the most likely to form proteinogenic amino acids. We mention that the formation of these four proteinogenic amino acids started from the C-methyl-aziridinonyl radical. The conditions under which this radical would form from aziridinone and methylene, have been presented in previous work [
6].
The reactions enthalpies are given in the last column of
Table 2. It can be easily observed that we deal only with exothermic reactions. The only endothermic reaction (reaction 1.4,
Table 2) was chosen in the idea of having such a transformation that could occur at the contact between the radical precursors and the carbon dioxide, a component of the primary atmosphere. In
Table 2, we have highlighted the precursors of proteinogenic acids: glutamic acid, glutamine, lysine and arginine. In the case of proteinogenic acids: glutamic acid, glutamine and lysine, it is possible for the precursors to form these amino acids by reactions with other reaction partners, cyanic acid or isocyanic acid, compounds that can be obtained by reactions between two synthons: CO and NH. We did not consider this type of reactions (noninterradical) that can be endothermic. The main thing for us was that the precursors obtained only by interradical reactions, to be able to form proteinogenic amino acids on contact with the components of the primary atmosphere. We talk about reaction conditions at approximately normal temperatures, where activations are possible.
Concerning the glutamic acid formation, two successive chain reactions with methylene and carbon monoxide (reactions 1.1 and 1.2,
Table 2) are sufficient to form the glutamic acid precursor. Neither reaction 1.4 (
Table 2) is excluded.
Next, glutamine formation is easy to explain. The glutamic acid precursor in reaction with nitrene (reaction 2.1,
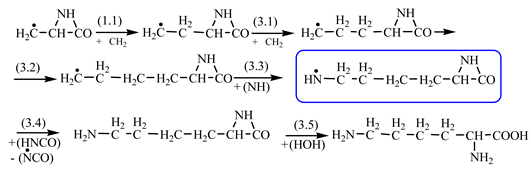
Table 2) leads to glutamine precursor. Upon contact with water, the last one forms glutamine. In this case we can assume that glutamic acid precursor in reaction with ammonia, a component of the primary atmosphere, could lead to glutamine too. Lysine would be formed only by chain reactions starting from aziridinone and methylene to C-butyl-aziridinonyl radical. This one, with nitrene, forms the N-radical precursor of lysine (reaction 3.3,
Table 2). In the case of lysine, we can admit that the C-butyl-aziridinonyl precursor in reaction with ammonia also form lysine.
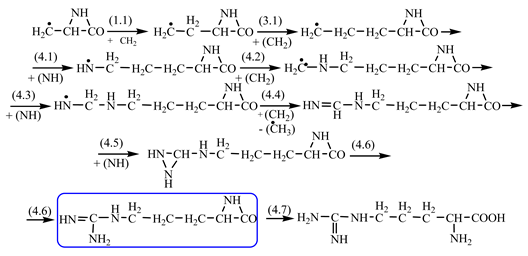
Things are much more complicated in the case of arginine formation. We have studied many possibilities regarding the formation of this proteinogenic amino acid. From all of these, we suppose the variant that seems to us the most probable.
Specifically, by chain reactions, with methylene three times and with nitrene twice times (reactions 1.1, 3.1, 4.1, 4.2 and 4.3,
Table 2) an N-radical would be formed which, by dehydrogenation, would lead to an iminic compound, neutral molecule (reaction 4.4,
Table 2). This one, by cyclization with nitrene (reaction 4.5,
Table 2) followed by isomerization (reaction 4.6,
Table 2), leads to arginine precursor which of course contains the guanidyl residue.
3.2. Pathways of reaction
In
Table 3, the initial and final enthalpies of the reactants and the final states of all intermediates regarding the formation of glutamic acid, glutamine, lysine and arginine are successive presented.
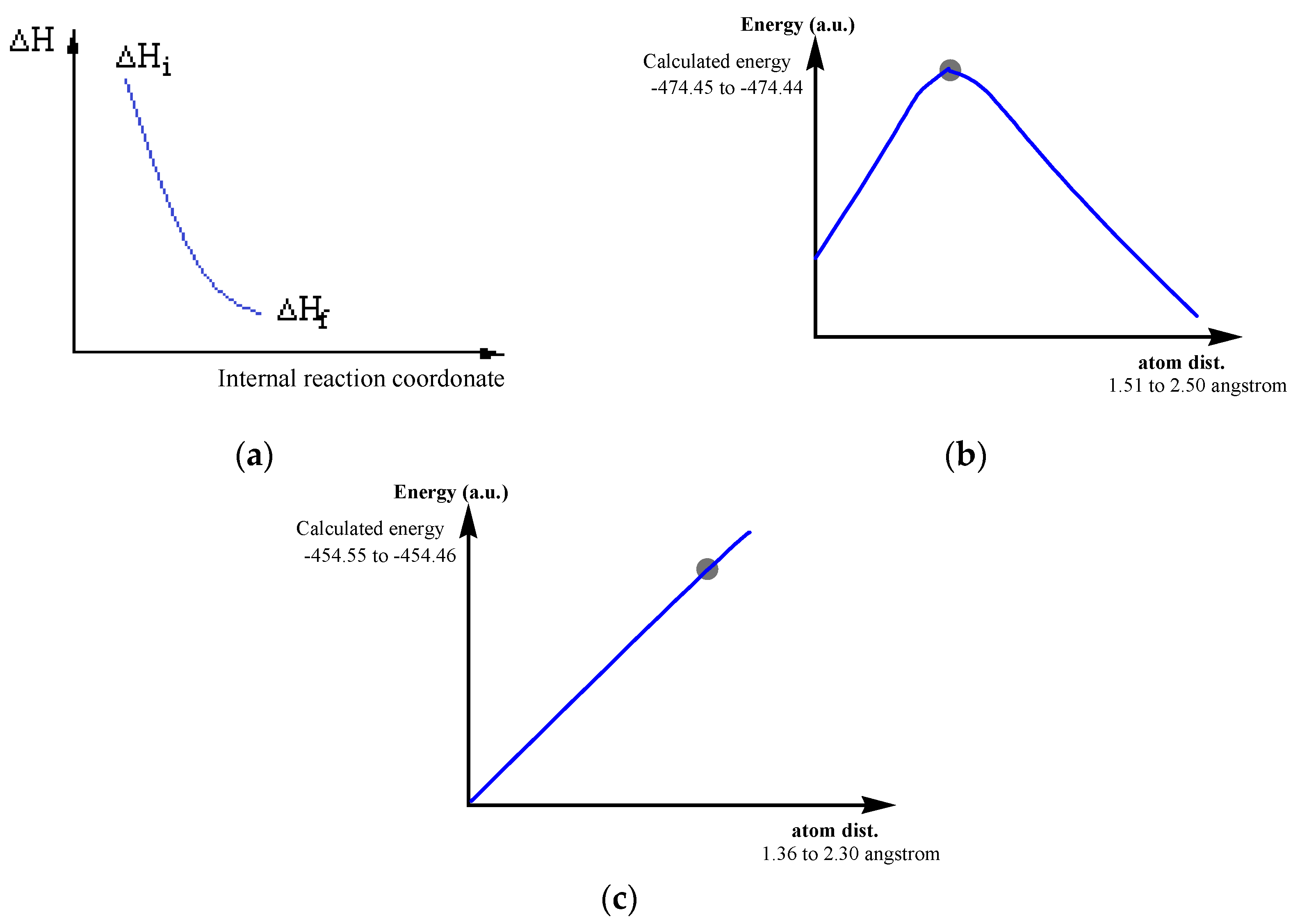
Free energy Gibbs (ΔG) calculations, at two low temperatures, confirm the meaning of the chemical transformations chosen by us.
At the end of this paper we return to the imposed conditions, respecting the decreasing of energies of the reaction systems in the passing from the initial states to final ones (
Figure 1.a).
The reactions studied and presented in
Table 3 are analogous to reaction 2.1 from
Table 2. We chose a single example of a reaction that would occur differently (reaction 1.4,
Table 2), the illustration being shown in
Figure 1.
All map reactions of 1.4 type, were not taken into account in the formation of the precursors of the four proteinogenic amino acids studied. We considered that at low temperatures, only interradical reactions can occur. It is natural to consider that in contact with the components of the primary atmosphere, many reactions can occur, which also include the neutral molecular systems which would lead to the formation of proteinogenic amino acids.
4. Conclusions
Starting from the C-methyl-aziridinonyl radical by chain reactions with methylene, nitrene and carbon monoxide, the precursors of glutamic acid, glutamine, lysine and arginine were obtained. All the formation reactions of the proteinogenic amino acid precursors mentioned above are exothermic. Chemical reactivity studies, free energy Gibbs calculations, ΔG, confirm the possibility of these reactions to be occurred.
We find interesting the cycle of reactions by which the guanidyl residue of arginine would have formed, until the precursors met with the components of the primary atmosphere (so at very low temperatures). Guanidine is easily obtained in the laboratory [
26,
27,
28,
29].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.S.; methodology, G.S.; software, G.S. and N.C.L.; validation, G.S., I.-D.N. and N.C.L.; formal analysis, G.S. and N.C.L.; investigation, G.S. and N.C.L.; resources, G.S.; data curation, G.S. and N.C.L.; writing—original draft preparation, G.S. and A.-M.G.; writing—review and editing, G.S. and A.-M.G.; visualization, G.S., I.-D.N. and A.-M.G; supervision, G.S. and I.-D.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Miller, S.L. A Production of Amino Acids Under Possible Primitive Earth Conditions. Science, 1953, 117, 528-529. [CrossRef]
- Schlesinger, G.; Miller S. L. Prebiotic synthesis in atmospheres containing CH4, CO, and CO2. I. Amino acids. J. Mol. Evol. 1983 19, 376-382, . [CrossRef]
- Sorrell, W. H. Origin of Amino Acids and Organic Sugars in Interstellar Clouds. Astrophys. J. 2001, 555, L129-L132. [CrossRef]
- Takano, Y.; Takahashi, J.; Kaneko, T.; Marumo, K.; Kobayashi K. Asymmetric synthesis of amino acid precursors in interstellar complex organics by circularly polarized light. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2007, 254, 106-114. [CrossRef]
- Elsina, J.E.; Glavin, D.P.; Dworkin, J.P. Cometary glycine detected in samples returned by Stardust, Meteorit. Planet Sci. 2009, 44, 1323-1330. [CrossRef]
- Surpateanu, G. Syntone chemistry and prebiotic stage in life evolution 1. Aziridinone, a key compound in formation of the first proteinogenic amino acids and polypeptides. Int. J. Astrobiology 2018, 17, 361-379. [CrossRef]
- Lopez, A.; Fiore, M. Investigating Prebiotic Protocells for a Comprehensive Understanding of the Origins of Life: A Prebiotic Systems Chemistry Perspective. Life 2019, 9, 49. [CrossRef]
- Miyakawa, S.; Yamanashi, H.; Kobayashi, K.; Cleaves, H.J.; Miller S.L. Prebiotic synthesis from CO atmospheres: Implications for origins of life. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2002, 99, 23, 14628-14631. [CrossRef]
- Parker, E.T.; Zhou, M.; Burton, A.S.; Glavin, D.P.; Dworkin, J.P.; Krishnamurthy, R.; Fernández, F.M.; Bada, J.L. A plausible simultaneous synthesis of amino acids and simple peptides on the primordial Earth. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2014 Jul 28; 53(31):8132-6. [CrossRef]
- Cleaves, H.J., II. Prebiotic Chemistry: Geochemical Context and Reaction Screening. Life 2013, 3, 331-345. [CrossRef]
- Nagahama, M.; Kawamura, K. A new approach for the cooperative chemical evolution of nucleic acids and proteins under the primitive earth environment. Nucleic Acids Res. Suppl. 2002; (2):279-80. [CrossRef]
- Bizzarri, B.M.; Saladino, R.; Delfino, I.; García-Ruiz, J.M.; Di Mauro, E. Prebiotic Organic Chemistry of Formamide and the Origin of Life in Planetary Conditions: What We Know and What Is the Future. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021 Jan 18; 22(2):917. [CrossRef]
- Saha, A.; Yi, R.; Fahrenbach, A.C.; Wang, A.; Jia, T.Z. A Physicochemical Consideration of Prebiotic Microenvironments for Self-Assembly and Prebiotic Chemistry. Life 2022, 12, 1595. [CrossRef]
- Micca Longo, G.; Vialetto, L.; Diomede, P.; Longo, S.; Laporta, V. Plasma Modeling and Prebiotic Chemistry: A Review of the State-of-the-Art and Perspectives. Molecules. 2021 Jun 16;26(12):3663. [CrossRef]
- Surpateanu, G.; Nistor, I.D.; Georgescu, A.M.; Lungu, N.C. Syntone chemistry. Theoretical study on the formation of glycine, alanine and serine. Rev. Chim., 2019 70, 1707-1711. [CrossRef]
- Surpateanu, G.; Georgescu, A.M.; Nistor, I.D.; Lungu, N.C. Synthon Chemistry. Theoretical study on the formation of valine, leucine, isoleucine and methionine. Rev. Chim. 2020, 71, 95-100. [CrossRef]
- Surpateanu, G; Nistor, I.D.; Georgescu, A.M.; Lungu, N.C. Syntone chemistry. Theoretical study on the formation of cysteine, aspartic acid, asparagine and threonine. Rev. Chim. 2020 71 (7), p. 278-283. [CrossRef]
- Surpateanu, G.; Georgescu, A.M.; Nistor, I.D.; Lungu, N.C., Synthon chemistry: theoretical study on the formation of proline, phenylanaline and tyrosine, Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2021, 20, 7, 1111-1117.
- Kumeda, Y.; Wales, D. J.; Munro, L. J. Transition states and rearrangements mechanisms from hybrid eigenvector – following and density functional theory. Application to C10H10 and defect migration, Chem. Phys. Lett. 2001, 341, 185-194. [CrossRef]
- Li, J, Jiang WY, Han KL, He GZ, Li C., Density functional study on the mechanism of bicyclic guanidine-catalyzed Strecker reaction. J Org Chem. 2003; 68 (23):8786-9. [CrossRef]
- Zhou. L.-X., Ab initio and density functional theory studies of the structure, gas-phase acidity and aromaticity of tetraselenosquaric acid, Chin. J. Chem. 2010, 18, Issue 6 p. 808-814. [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, Y. S.; Ihee, H. Density functional and ab initio studies on structures and energies of the ground state of CrCO, Properties, Dynamics, and Electronic Structure of Atoms and Molecules, Int. J. Quantum Chem. 2006, 107, 2, 458-463. [CrossRef]
- Atkins, P.; Paula, J.D. Physical Chemistry, 8th Edition; W.H. Freeman and Company, New York, 2006.
- Solomons, T.W.G.; Fryhle C.B. Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition; John Wiley & Sons, Inc., Hoboken, New York; 2004.
- Cache Worksystem Library, version 7.5.0.85 Fujitsu, Poland (2006).
- Sfecci, E.; Lacour, T.; Amade, P.; Mehiri, M. Polycyclic Guanidine Alkaloids from Poecilosclerida Marine Sponges. Mar Drugs. 2016, 14(4):77. [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, T. P.; Dener, J.M.; Boldi, A.M. Solid-Phase Synthesis of Trisubsituted Guanidines. J. Comb. Chem. 2002, 4 (2), 167-174. [CrossRef]
- Katritzky, A. R.; Khashab, N.M.; Bobrov, S. The preparation of 1, 2, 3 – Trisubstituted Guanidines. Helv. Chim. Acta 2005, 88, 7, 1664-1675. [CrossRef]
- Armitage, I.; Fu, M.; Hicks, F.; Kattuboina, A.; Li, J.S.N.; McCarron, A.; Zhu, L. The Use of Chloroformamidine Hydrochloride as a Reagent for the Synthesis of Guanidines from Electron Deficient Aromatic Amines. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2015, 54, 1, 728-734. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).