Submitted:
12 June 2023
Posted:
13 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Results
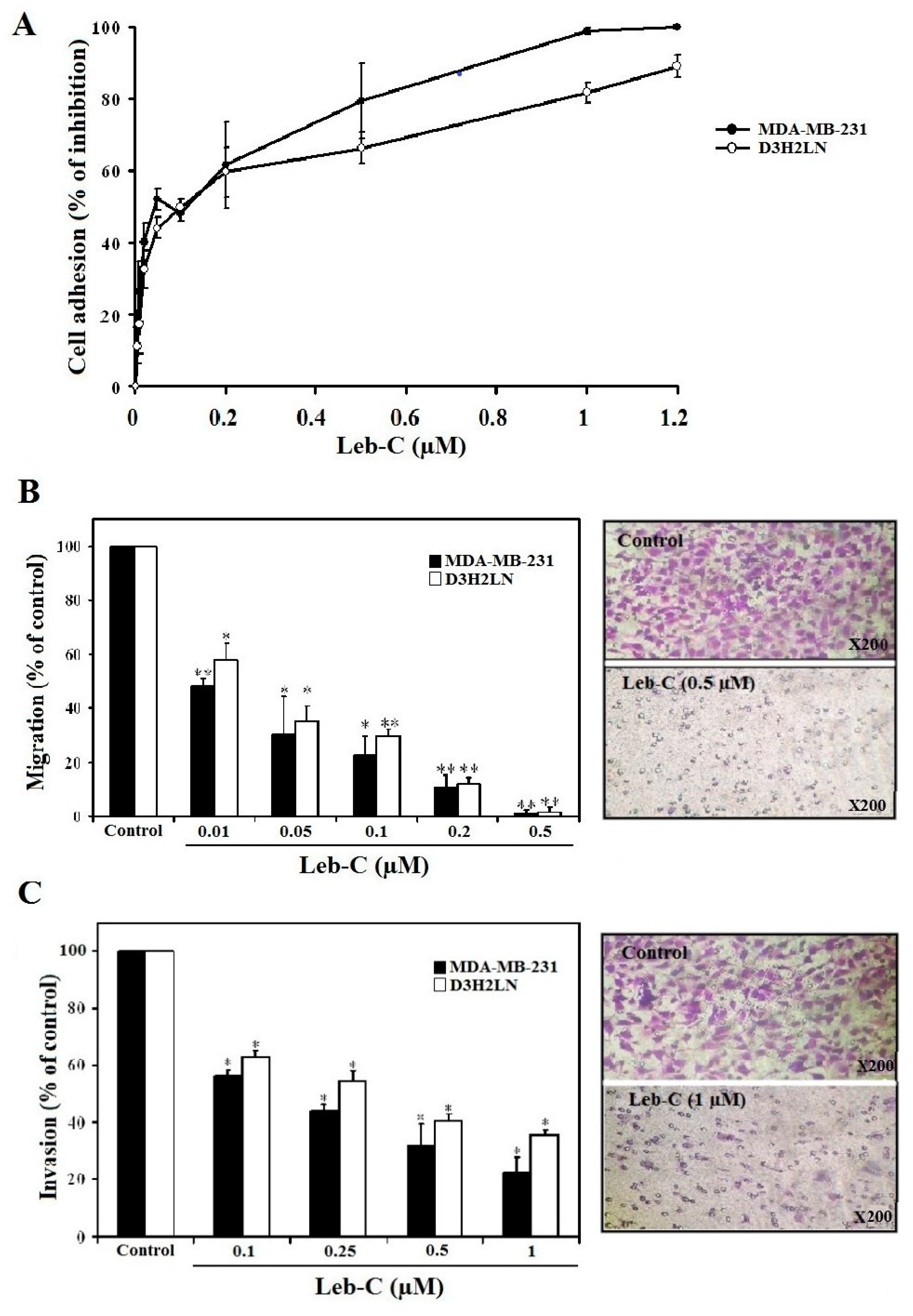
Leb-C inhibited MDA-MB-231 and D3H2LN cell adhesion
Leb-C suppressed MDA-MB-231 and D3H2LN migration, and invasiveness
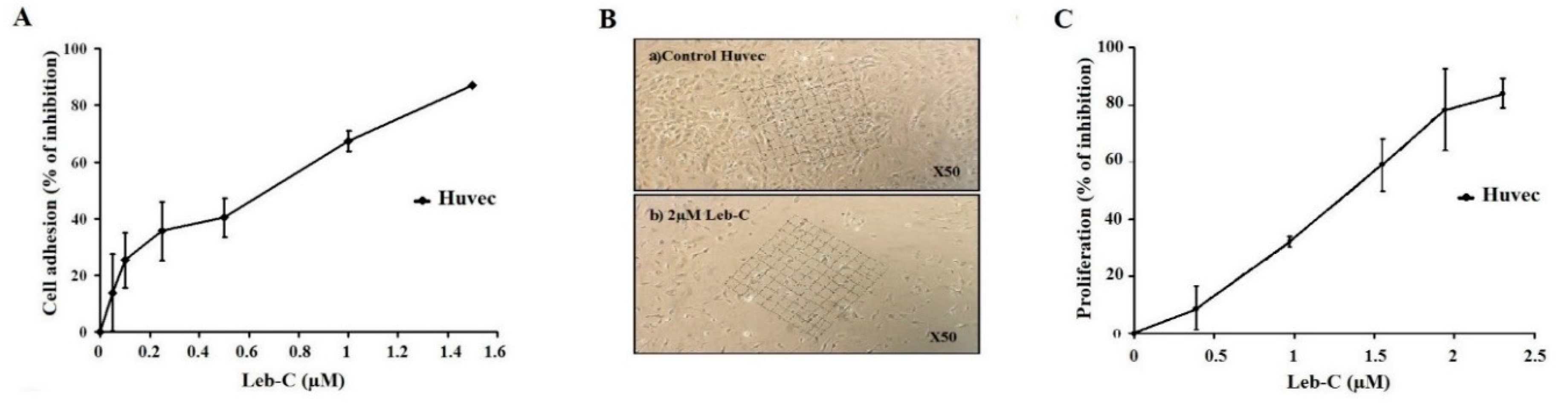
Leb-C inhibited HUVECs adhesion
Leb-C suppressed HUVEC cell growth
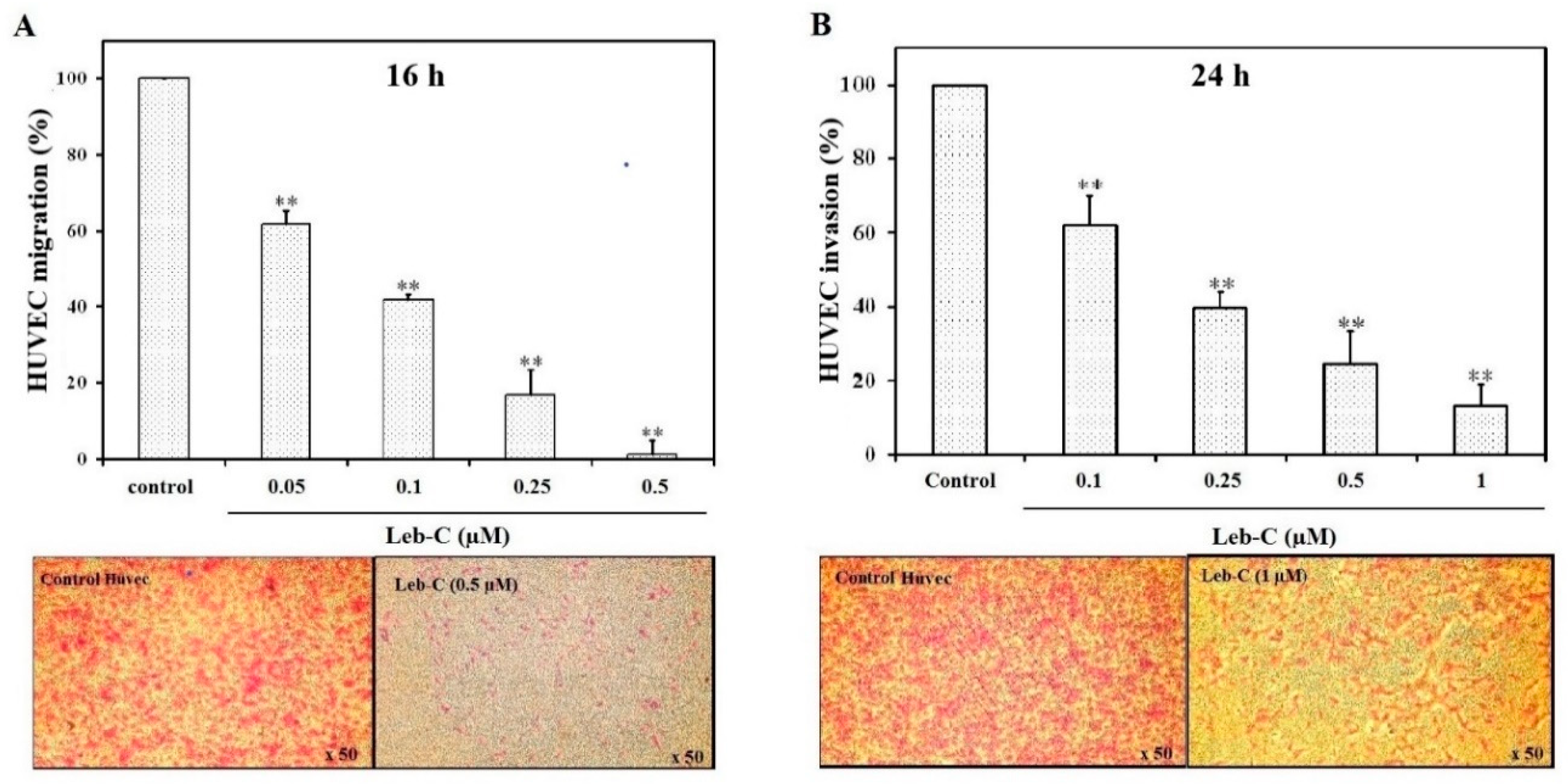
Leb-C exhibited a reduction in HUVEC migration and invasion
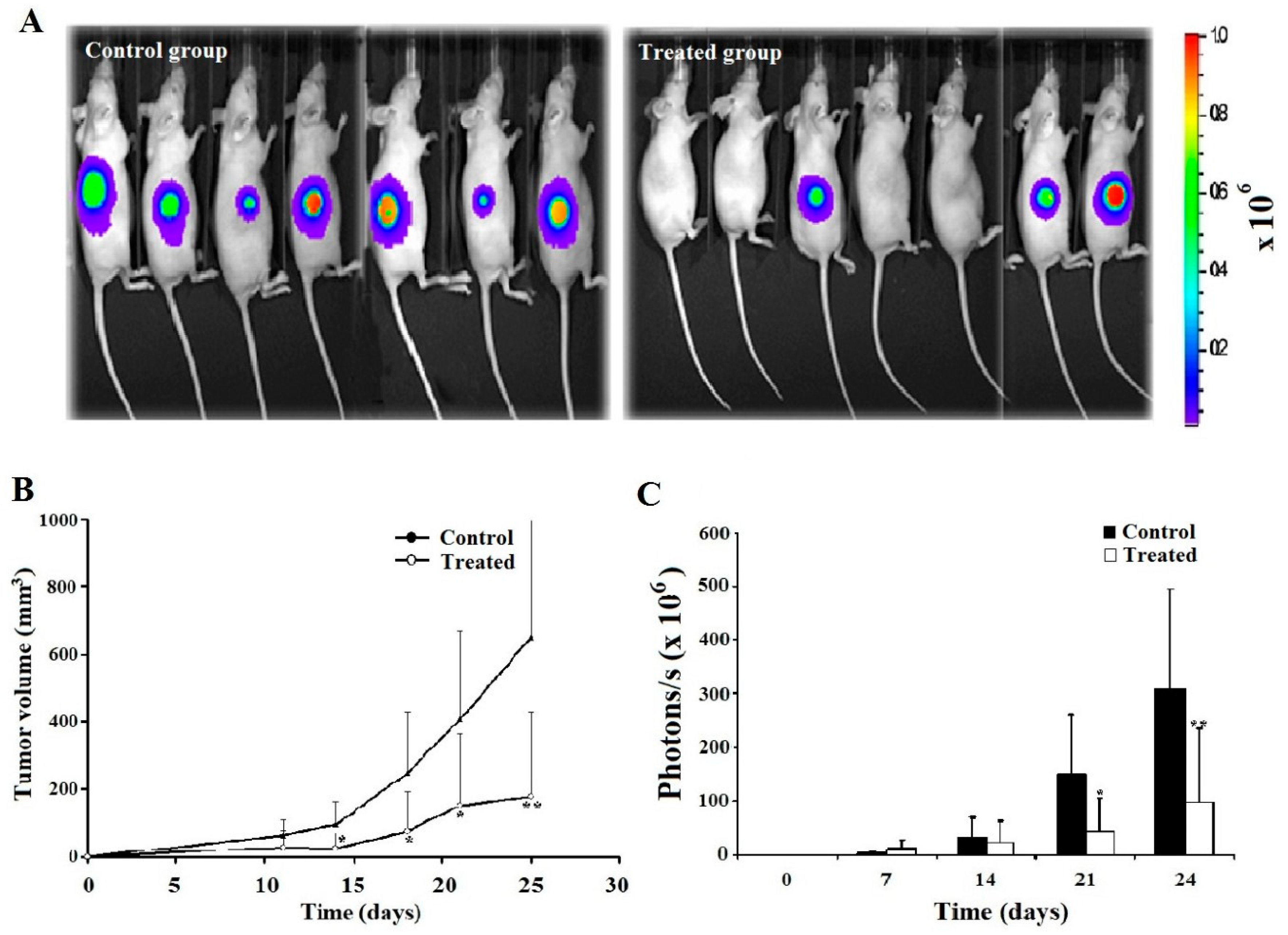
Leb-C decreased D3H2LN Tumor in vivo
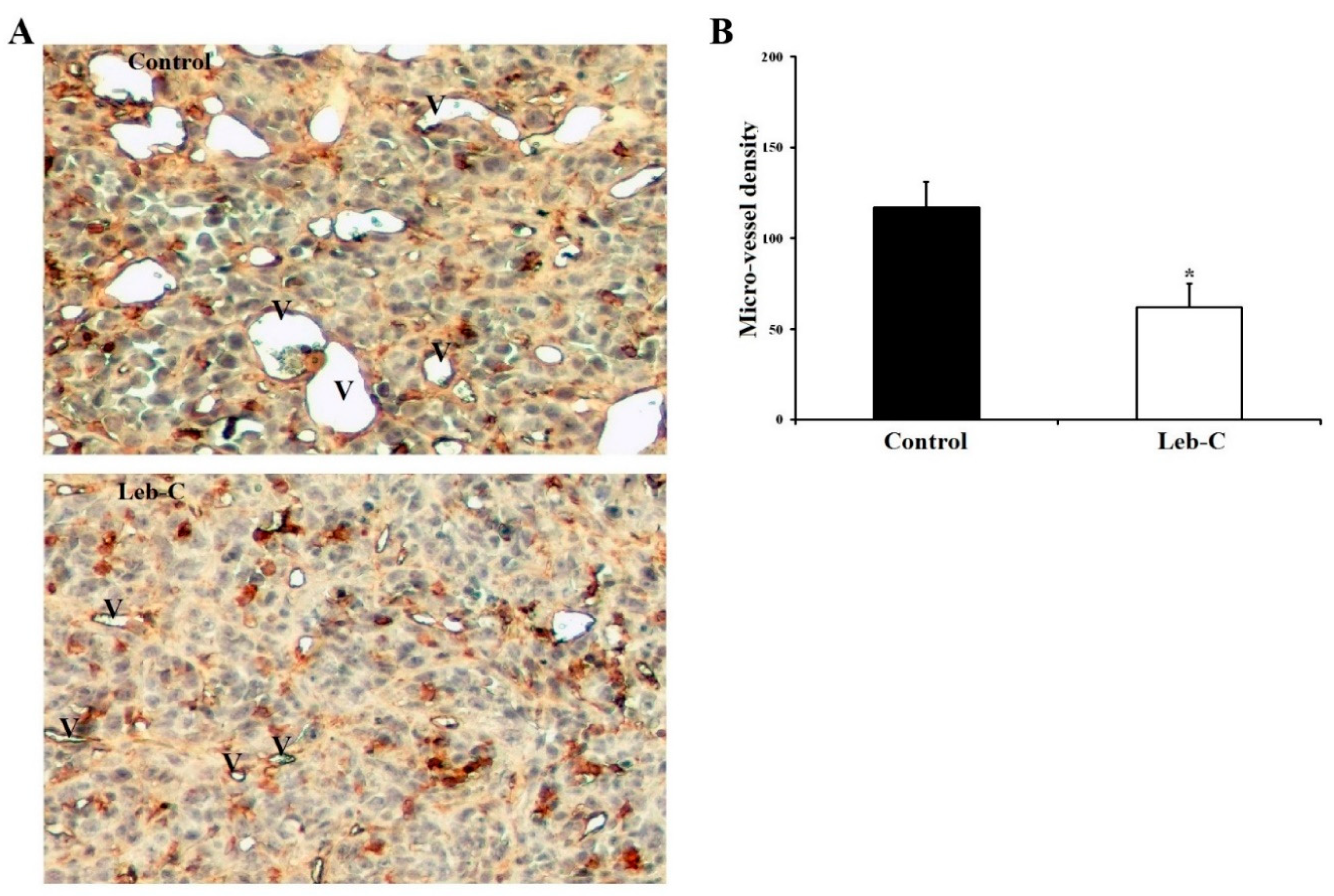
Leb-C reduced tumor angiogenesis in vivo
Discussion
Materials and methods
Compound isolation
Cell lines and cell culture
Cell adhesion assay
Cell migration and invasion assays
Cell proliferation assay
Xenografts in nude mice
Bioluminescent Imaging
Immunohistochemical analysis
Statistical Analysis
Conclusion
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Folkman, J. Angiogenesis: An Organizing Principle for Drug Discovery? Nat Rev Drug Discov 2007, 6, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- di Somma, M.; Vliora, M.; Grillo, E.; Castro, B.; Dakou, E.; Schaafsma, W.; Vanparijs, J.; Corsini, M.; Ravelli, C.; Sakellariou, E.; et al. Role of VEGFs in Metabolic Disorders. Angiogenesis 2020, 23, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribatti, D.; Pezzella, F. Overview on the Different Patterns of Tumor Vascularization. Cells 2021, 10, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melaiu, O.; Vanni, G.; Portarena, I.; Pistolese, C.A.; Anemona, L.; Pomella, S.; Bei, R.; Buonomo, O.C.; Roselli, M.; Mauriello, A.; et al. The Combination of Immune Checkpoint Blockade with Tumor Vessel Normalization as a Promising Therapeutic Strategy for Breast Cancer: An Overview of Preclinical and Clinical Studies. IJMS 2023, 24, 3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viallard, C.; Larrivée, B. Tumor Angiogenesis and Vascular Normalization: Alternative Therapeutic Targets. Angiogenesis 2017, 20, 409–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deryugina, E.I.; Quigley, J.P. Tumor Angiogenesis: MMP-Mediated Induction of Intravasation- and Metastasis-Sustaining Neovasculature. Matrix Biology 2015, 44–46, 94–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duro-Castano, A.; Gallon, E.; Decker, C.; Vicent, M.J. Modulating Angiogenesis with Integrin-Targeted Nanomedicines. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 2017, 119, 101–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhavalikar, P.; Robinson, A.; Lan, Z.; Jenkins, D.; Chwatko, M.; Salhadar, K.; Jose, A.; Kar, R.; Shoga, E.; Kannapiran, A.; et al. Review of Integrin-Targeting Biomaterials in Tissue Engineering. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2020, 9, 2000795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawaetz, M.; Christensen, A.; Juhl, K.; Karnov, K.; Lelkaitis, G.; Kanstrup Fiehn, A.-M.; Kjaer, A.; von Buchwald, C. Potential of UPAR, Avβ6 Integrin, and Tissue Factor as Targets for Molecular Imaging of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Evaluation of Nine Targets in Primary Tumors and Metastases by Immunohistochemistry. IJMS 2023, 24, 3853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avraamides, C.J.; Garmy-Susini, B.; Varner, J.A. Integrins in Angiogenesis and Lymphangiogenesis. Nat Rev Cancer 2008, 8, 604–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergonzini, C.; Kroese, K.; Zweemer, A.J.M.; Danen, E.H.J. Targeting Integrins for Cancer Therapy - Disappointments and Opportunities. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 863850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieberler, M.; Reuning, U.; Reichart, F.; Notni, J.; Wester, H.-J.; Schwaiger, M.; Weinmüller, M.; Räder, A.; Steiger, K.; Kessler, H. Exploring the Role of RGD-Recognizing Integrins in Cancer. Cancers 2017, 9, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.-M.; Chang, W.-J.; Chu, H.-Y.; De Luca, R.; Pedersen, J.Z.; Incerpi, S.; Li, Z.-L.; Shih, Y.-J.; Lin, H.-Y.; Wang, K.; et al. Nano-Strategies Targeting the Integrin Avβ3 Network for Cancer Therapy. Cells 2021, 10, 1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Li, X.; Gao, W.; Jing, J. Integrin Targeting Enhances the Antimelanoma Effect of Annexin V in Mice. IJMS 2023, 24, 3859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somanath, P.R.; Malinin, N.L.; Byzova, T.V. Cooperation between Integrin Aνβ3 and VEGFR2 in Angiogenesis. Angiogenesis 2009, 12, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahra, F.T.; Sajib, Md.S.; Mikelis, C.M. Role of BFGF in Acquired Resistance upon Anti-VEGF Therapy in Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danhier, F.; Le Breton, A.; Préat, V. RGD-Based Strategies To Target Alpha(v) Beta(3) Integrin in Cancer Therapy and Diagnosis. Mol. Pharmaceutics 2012, 9, 2961–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contois, L.W.; Akalu, A.; Caron, J.M.; Tweedie, E.; Cretu, A.; Henderson, T.; Liaw, L.; Friesel, R.; Vary, C.; Brooks, P.C. Inhibition of Tumor-Associated Avβ3 Integrin Regulates the Angiogenic Switch by Enhancing Expression of IGFBP-4 Leading to Reduced Melanoma Growth and Angiogenesis in Vivo. Angiogenesis 2015, 18, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehling, J.; Misiewicz, M.; von Stillfried, S.; Möckel, D.; Bzyl, J.; Pochon, S.; Lederle, W.; Knuechel, R.; Lammers, T.; Palmowski, M.; et al. In Situ Validation of VEGFR-2 and α v ß 3 Integrin as Targets for Breast Lesion Characterization. Angiogenesis 2016, 19, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, B.S.; Kessler, H.; Kossatz, S.; Reuning, U. RGD-Binding Integrins Revisited: How Recently Discovered Functions and Novel Synthetic Ligands (Re-)Shape an Ever-Evolving Field. Cancers 2021, 13, 1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Yan, D.; Liu, Y.; Huang, P.; Cui, H. The Roles of Integrin A5β1 in Human Cancer. OTT 2020, Volume 13, 13329–13344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desgrosellier, J.S.; Cheresh, D.A. Integrins in Cancer: Biological Implications and Therapeutic Opportunities. Nat Rev Cancer 2010, 10, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Benedetto, M.; Toullec, A.; Buteau-Lozano, H.; Abdelkarim, M.; Vacher, S.; Velasco, G.; Christofari, M.; Pocard, M.; Bieche, I.; Perrot-Applanat, M. MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells Overexpressing Single VEGF Isoforms Display Distinct Colonisation Characteristics. Br J Cancer 2015, 113, 773–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeltz, C.; Primac, I.; Erusappan, P.; Alam, J.; Noel, A.; Gullberg, D. Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts in Desmoplastic Tumors: Emerging Role of Integrins. Seminars in Cancer Biology 2020, 62, 166–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limam, I.; Abdelkarim, M.; Essid, R.; Chahbi, A.; Fathallah, M.; Elkahoui, S.; Ben Aissa-Fennira, F. Olea Europaea L. Cv. Chetoui Leaf and Stem Hydromethanolic Extracts Suppress Proliferation and Promote Apoptosis via Caspase Signaling on Human Multiple Myeloma Cells. European Journal of Integrative Medicine 2020, 37, 101145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trabalzini, L.; Ercoli, J.; Trezza, A.; Schiavo, I.; Macrì, G.; Moglia, A.; Spiga, O.; Finetti, F. Pharmacological and In Silico Analysis of Oat Avenanthramides as EGFR Inhibitors: Effects on EGF-Induced Lung Cancer Cell Growth and Migration. IJMS 2022, 23, 8534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasconcelos, A.A.; Estrada, J.C.; David, V.; Wermelinger, L.S.; Almeida, F.C.L.; Zingali, R.B. Structure-Function Relationship of the Disintegrin Family: Sequence Signature and Integrin Interaction. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 783301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schönthal, A.H.; Swenson, S.D.; Chen, T.C.; Markland, F.S. Preclinical Studies of a Novel Snake Venom-Derived Recombinant Disintegrin with Antitumor Activity: A Review. Biochemical Pharmacology 2020, 181, 114149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaoba, O.T.; Karina dos Santos, P.; Selistre-de-Araujo, H.S.; Ferreira de Souza, D.H. Snake Venom Metalloproteinases (SVMPs): A Structure-Function Update. Toxicon: X 2020, 7, 100052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limam, I.; El Ayeb, M.; Marrakchi, N. [Snake venom metalloproteinases: Structure, biosynthesis and function(s)]. Arch Inst Pasteur Tunis 2010, 87, 3–15. [Google Scholar]
- Rabelo, L.F.G.; Ferreira, B.A.; Deconte, S.R.; Tomiosso, T.C.; dos Santos, P.K.; Andrade, S.P.; Selistre de Araújo, H.S.; Araújo, F. de A. Alternagin-C, a Disintegrin-like Protein from Bothrops Alternatus Venom, Attenuates Inflammation and Angiogenesis and Stimulates Collagen Deposition of Sponge-Induced Fibrovascular Tissue in Mice. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2019, 140, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, D.A.; Almeida, M.C.; Barros, C.C.; Sanchez, E.F.; Pesquero, P.R.; Lang, E.A.S.; Samaan, M.; Araujo, R.C.; Pesquero, J.B.; Pesquero, J.L. Leucurogin, a New Recombinant Disintegrin Cloned from Bothrops Leucurus (White-Tailed-Jararaca) with Potent Activity upon Platelet Aggregation and Tumor Growth. Toxicon 2011, 58, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limam, I.; Bazaa, A.; Srairi-Abid, N.; Taboubi, S.; Jebali, J.; Zouari-Kessentini, R.; Kallech-Ziri, O.; Mejdoub, H.; Hammami, A.; El Ayeb, M.; et al. Leberagin-C, A Disintegrin-like/Cysteine-Rich Protein from Macrovipera Lebetina Transmediterranea Venom, Inhibits Alphavbeta3 Integrin-Mediated Cell Adhesion. Matrix Biology 2010, 29, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentile, M.; Centonza, A.; Lovero, D.; Palmirotta, R.; Porta, C.; Silvestris, F.; D’Oronzo, S. Application of “Omics” Sciences to the Prediction of Bone Metastases from Breast Cancer: State of the Art. Journal of Bone Oncology 2021, 26, 100337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosentino, G.; Plantamura, I.; Tagliabue, E.; Iorio, M.V.; Cataldo, A. Breast Cancer Drug Resistance: Overcoming the Challenge by Capitalizing on MicroRNA and Tumor Microenvironment Interplay. Cancers 2021, 13, 3691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denkert, C.; Liedtke, C.; Tutt, A.; von Minckwitz, G. Molecular Alterations in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer—The Road to New Treatment Strategies. The Lancet 2017, 389, 2430–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foulkes, W.D.; Smith, I.E.; Reis-Filho, J.S. Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. N Engl J Med 2010, 363, 1938–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Chen, W.; Yin, J.; Sun, J.; Xie, Q.; Wu, M.; Zeng, F.; Ren, H. RIPK1 Is a Negative Mediator in Aquaporin 1-Driven Triple-Negative Breast Carcinoma Progression and Metastasis. npj Breast Cancer 2021, 7, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fillmore, C.M.; Kuperwasser, C. Human Breast Cancer Cell Lines Contain Stem-like Cells That Self-Renew, Give Rise to Phenotypically Diverse Progeny and Survive Chemotherapy. Breast Cancer Res 2008, 10, R25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, D.E.; Hornig, Y.S.; Oei, Y.; Dusich, J.; Purchio, T. Bioluminescent Human Breast Cancer Cell Lines That Permit Rapid and Sensitive in Vivodetection of Mammary Tumors and Multiple Metastases in Immune Deficient Mice. Breast Cancer Res 2005, 7, R444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desgrosellier, J.S.; Barnes, L.A.; Shields, D.J.; Huang, M.; Lau, S.K.; Prévost, N.; Tarin, D.; Shattil, S.J.; Cheresh, D.A. An Integrin Avβ3–c-Src Oncogenic Unit Promotes Anchorage-Independence and Tumor Progression. Nat Med 2009, 15, 1163–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagati, A.; Kumar, S.; Jiang, P.; Pyrdol, J.; Zou, A.E.; Godicelj, A.; Mathewson, N.D.; Cartwright, A.N.R.; Cejas, P.; Brown, M.; et al. Integrin Avβ6–TGFβ–SOX4 Pathway Drives Immune Evasion in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 54–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barney, L.E.; Hall, C.L.; Schwartz, A.D.; Parks, A.N.; Sparages, C.; Galarza, S.; Platt, M.O.; Mercurio, A.M.; Peyton, S.R. Tumor Cell–Organized Fibronectin Maintenance of a Dormant Breast Cancer Population. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaz4157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moritz, M.N. de O.; Casali, B.C.; Stotzer, U.S.; Karina dos Santos, P.; Selistre-de-Araujo, H.S. Alternagin-C, an Alpha2beta1 Integrin Ligand, Attenuates Collagen-Based Adhesion, Stimulating the Metastasis Suppressor 1 Expression in Triple-Negative Breast Tumor Cells. Toxicon 2022, 210, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, C.-H.; Chiang, T.-B.; Wang, W.-J. Inhibition of Integrins Av/A5-Dependent Functions in Melanoma Cells by an ECD-Disintegrin Acurhagin-C. Matrix Biology 2013, 32, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Shen, L.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Pan, J.; Ni, C.; Chen, Z. Antiangiogenic Therapy Reverses the Immunosuppressive Breast Cancer Microenvironment. Biomark Res 2021, 9, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, L.; Fidler, I. Angiogenesis and Breast Cancer Metastasis. The Lancet 1995, 346, 388–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulous, F.E.; Carnevale, J.C.; Al-Yafeai, Z.; Pearson, B.H.; Hamilton, J.A.G.; Henry, C.J.; Orr, A.W.; Petrich, B.G. Talin-Dependent Integrin Activation Is Required for Endothelial Proliferation and Postnatal Angiogenesis. Angiogenesis 2021, 24, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, T.; Vaganay, E.; Carpentier, G.; Coudert, P.; Guzman-Gonzales, V.; Manuel, R.; Eymin, B.; Coll, J.-L.; Ruggiero, F. A Collagen Vα1-Derived Fragment Inhibits FGF-2 Induced-Angiogenesis by Modulating Endothelial Cells Plasticity through Its Heparin-Binding Site. Matrix Biology 2020, 94, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-J. Acurhagin-C, an ECD Disintegrin, Inhibits Integrin Avβ3-Mediated Human Endothelial Cell Functions by Inducing Apoptosis via Caspase-3 Activation: Acurhagin-C Is a Novel Angiostatic Agent. British Journal of Pharmacology 2010, 160, 1338–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, M.C.; Santos, I.C.; Paschoalin, T.; Travassos, L.R.; Mauch, C.; Zigrino, P.; Pesquero, J.B.; Pesquero, J.L.; Higuchi, D.A. Leucurogin and Melanoma Therapy. Toxicon 2019, 159, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, P.K.; Altei, W.F.; Danilucci, T.M.; Lino, R.L.B.; Pachane, B.C.; Nunes, A.C.C.; Selistre-de-Araujo, H.S. Alternagin-C (ALT-C), a Disintegrin-like Protein, Attenuates Alpha2beta1 Integrin and VEGF Receptor 2 Signaling Resulting in Angiogenesis Inhibition. Biochimie 2020, 174, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itatani, Y.; Kawada, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Sakai, Y. Resistance to Anti-Angiogenic Therapy in Cancer—Alterations to Anti-VEGF Pathway. IJMS 2018, 19, 1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Kim, J. Regulation of IL-6 Signaling by MiR-125a and Let-7e in Endothelial Cells Controls Vasculogenic Mimicry Formation of Breast Cancer Cells. BMB Rep. 2019, 52, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, E.; Luna, I.; Persad, K.L.; Agopsowicz, K.; Jay, D.A.; West, F.G.; Hitt, M.M.; Persad, S. Inhibition of Triple Negative Breast Cancer Metastasis and Invasiveness by Novel Drugs That Target Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition. Sci Rep 2021, 11, 11757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subhan, M.A.; Parveen, F.; Shah, H.; Yalamarty, S.S.K.; Ataide, J.A.; Torchilin, V.P. Recent Advances with Precision Medicine Treatment for Breast Cancer Including Triple-Negative Sub-Type. Cancers 2023, 15, 2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelkarim, M.; Guenin, E.; Sainte-Catherine, O.; Vintonenko, N.; Peyri, N.; Perret, G.Y.; Crepin, M.; Khatib, A.-M.; Lecouvey, M.; Di Benedetto, M. New Symmetrically Esterified M-Bromobenzyl Non-Aminobisphosphonates Inhibited Breast Cancer Growth and Metastases. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaffe, E.A.; Nachman, R.L.; Becker, C.G.; Minick, C.R. Culture of Human Endothelial Cells Derived from Umbilical Veins. Identification by Morphologic and Immunologic Criteria. J Clin Invest 1973, 52, 2745–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloane, B.F.; Honn, K.V. Cysteine Proteinases and Metastasis. Cancer Metast Rev 1984, 3, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelkarim, M.; Vintonenko, N.; Starzec, A.; Robles, A.; Aubert, J.; Martin, M.-L.; Mourah, S.; Podgorniak, M.-P.; Rodrigues-Ferreira, S.; Nahmias, C.; et al. Invading Basement Membrane Matrix Is Sufficient for MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells to Develop a Stable In Vivo Metastatic Phenotype. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelkarim, M.; Ben Younes, K.; Limam, I.; Guermazi, R.; ElGaaied, A.B.A.; Aissa-Fennira, F.B. 3,6-Dichloro-1,2,4,5-Tetrazine Assayed at High Doses in the Metastatic Breast Cancer Cell Line MDA-MB-231 Reduces Cell Numbers and Induces Apoptosis. CBC 2020, 16, 546–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limam, I.; Ben Aissa-Fennira, F.; Essid, R.; Chahbi, A.; Kefi, S.; Mkadmini, K.; Elkahoui, S.; Abdelkarim, M. Hydromethanolic Root and Aerial Part Extracts from Echium Arenarium Guss Suppress Proliferation and Induce Apoptosis of Multiple Myeloma Cells through Mitochondrial Pathway. Environmental Toxicology 2021, 36, 874–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weidner, N.; Semple, J.P.; Welch, W.R.; Folkman, J. Tumor Angiogenesis and Metastasis — Correlation in Invasive Breast Carcinoma. N Engl J Med 1991, 324, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




