Submitted:
12 June 2023
Posted:
12 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
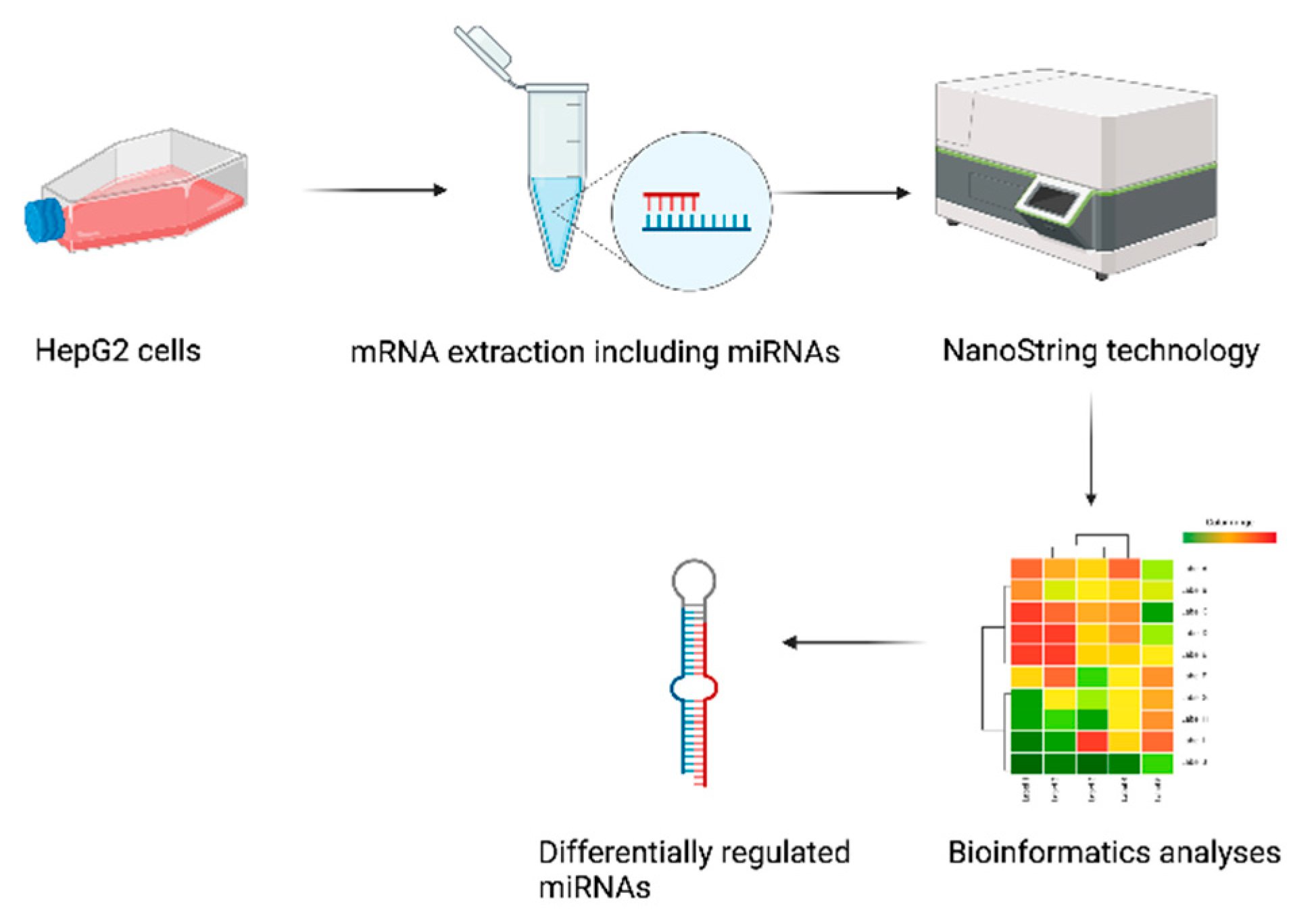
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Exendin-4 Reduces OA-Induced Lipid Accumulation in HepG2
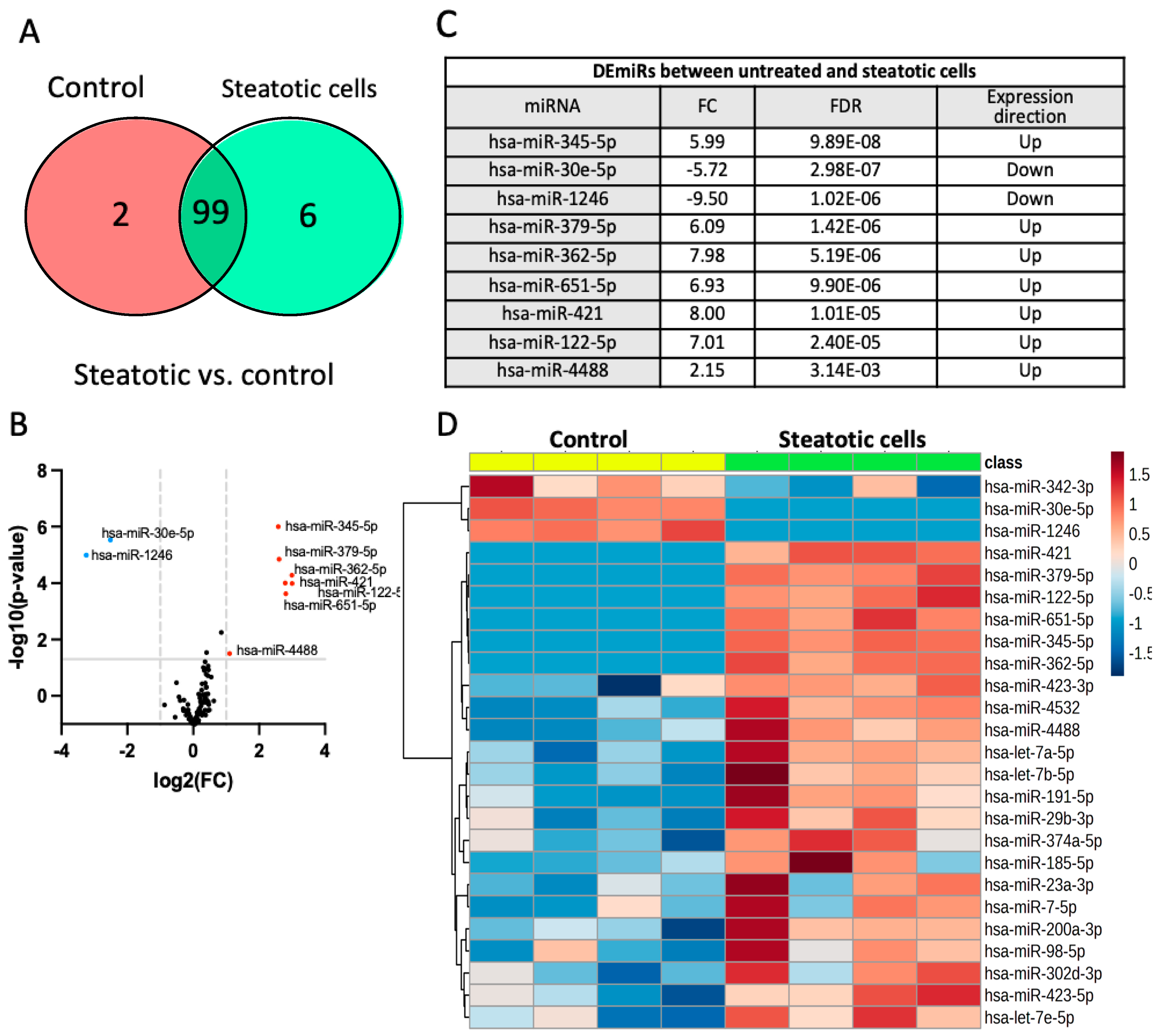
2.3. Identification of Differentially Expressed miRNAs
- a)
- Differentially expressed miRNAs in steatotic versus control cells
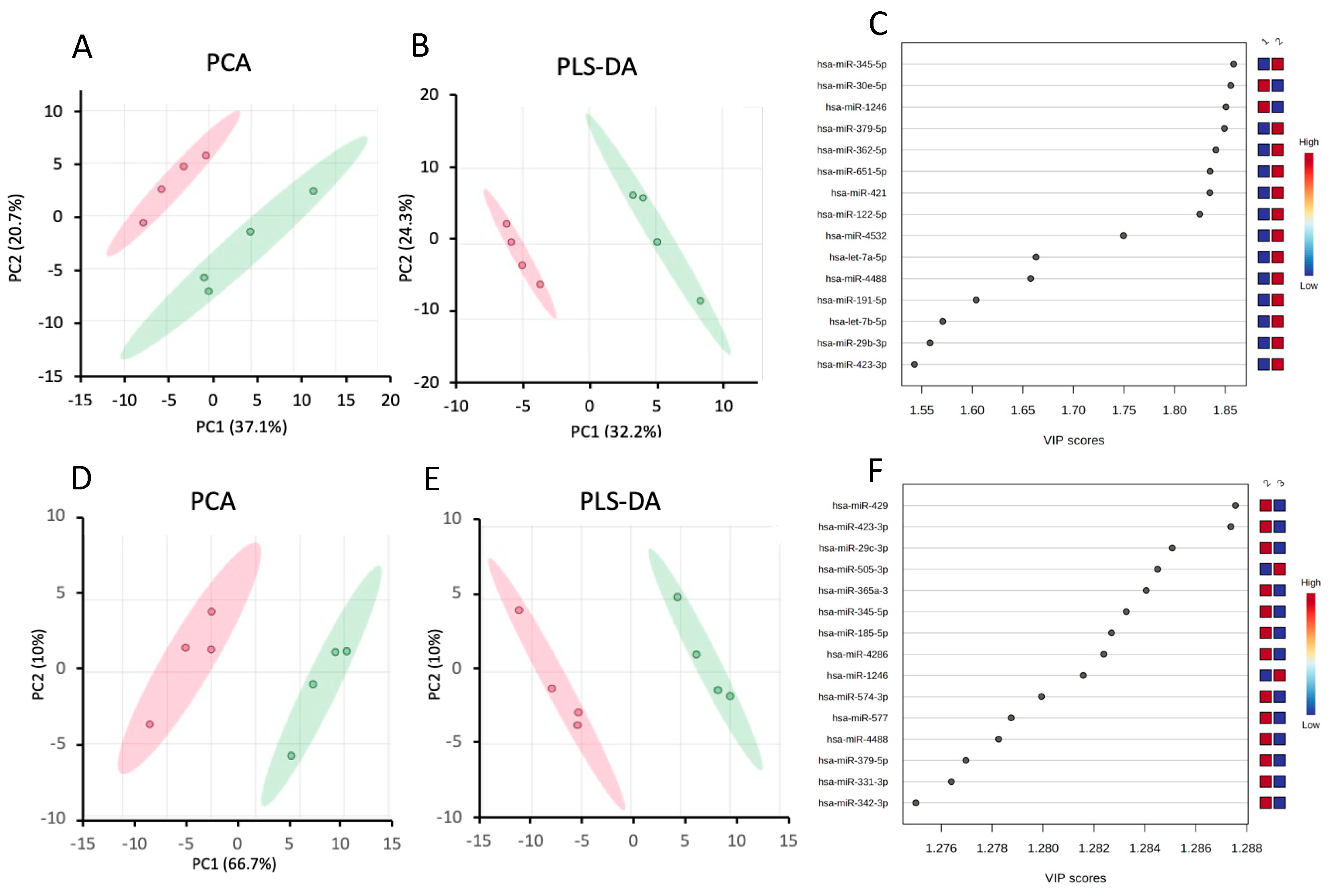
Chemometric Analysis
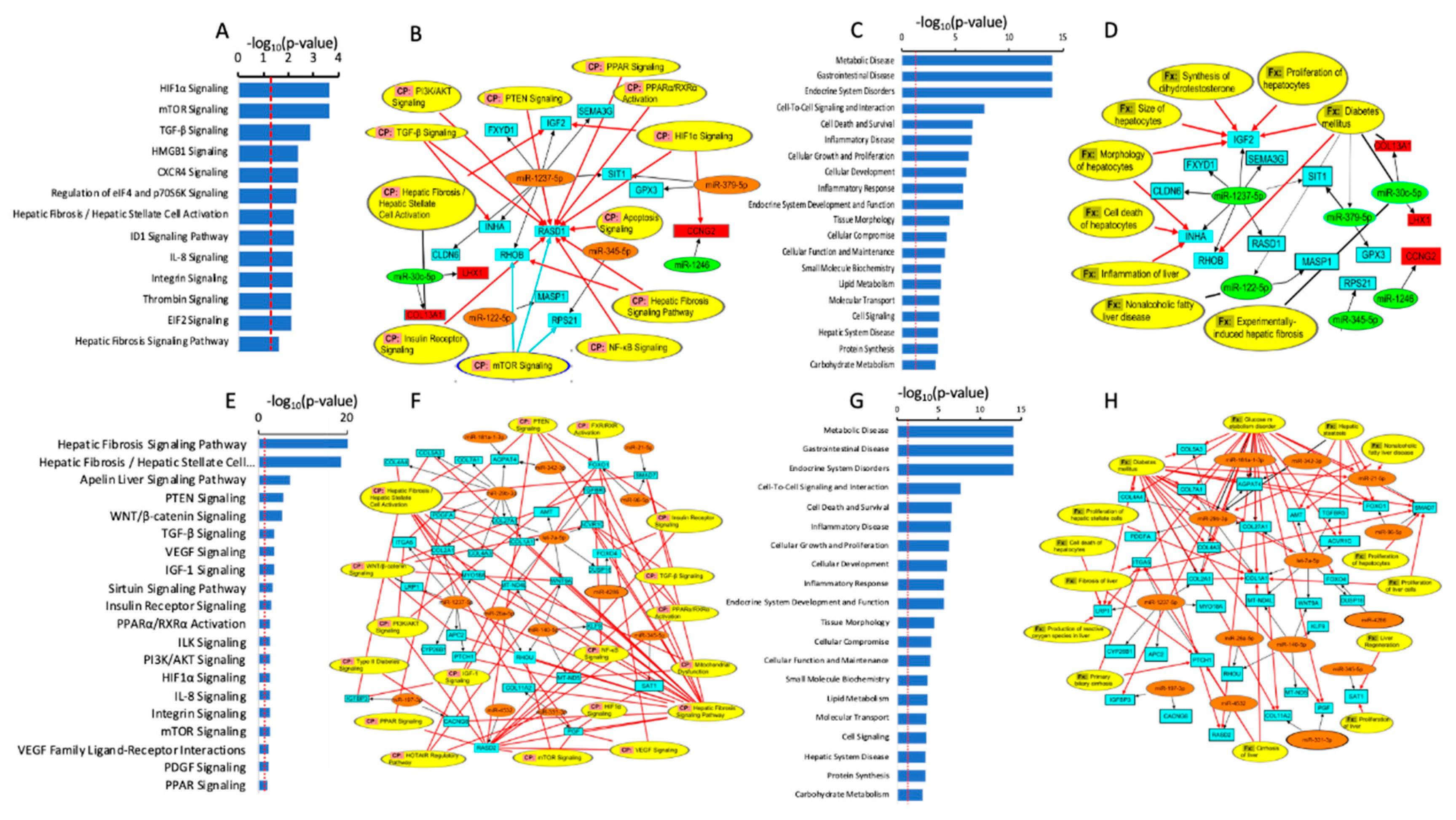
Pathway Enrichment Analysis
- b)
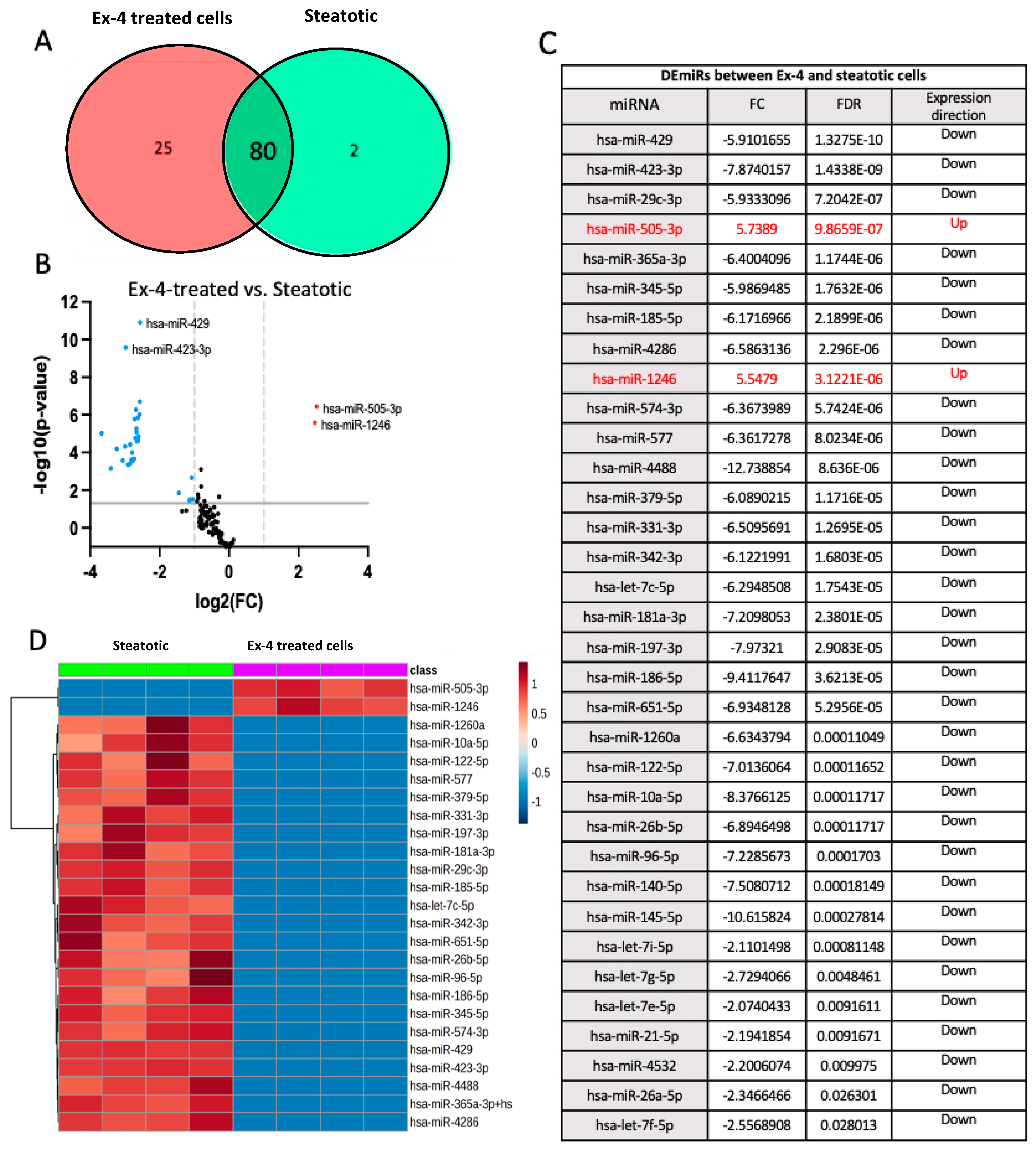
- Differentially expressed miRNAs in Ex-4-treated versus steatotic cells
Chemometric Analysis
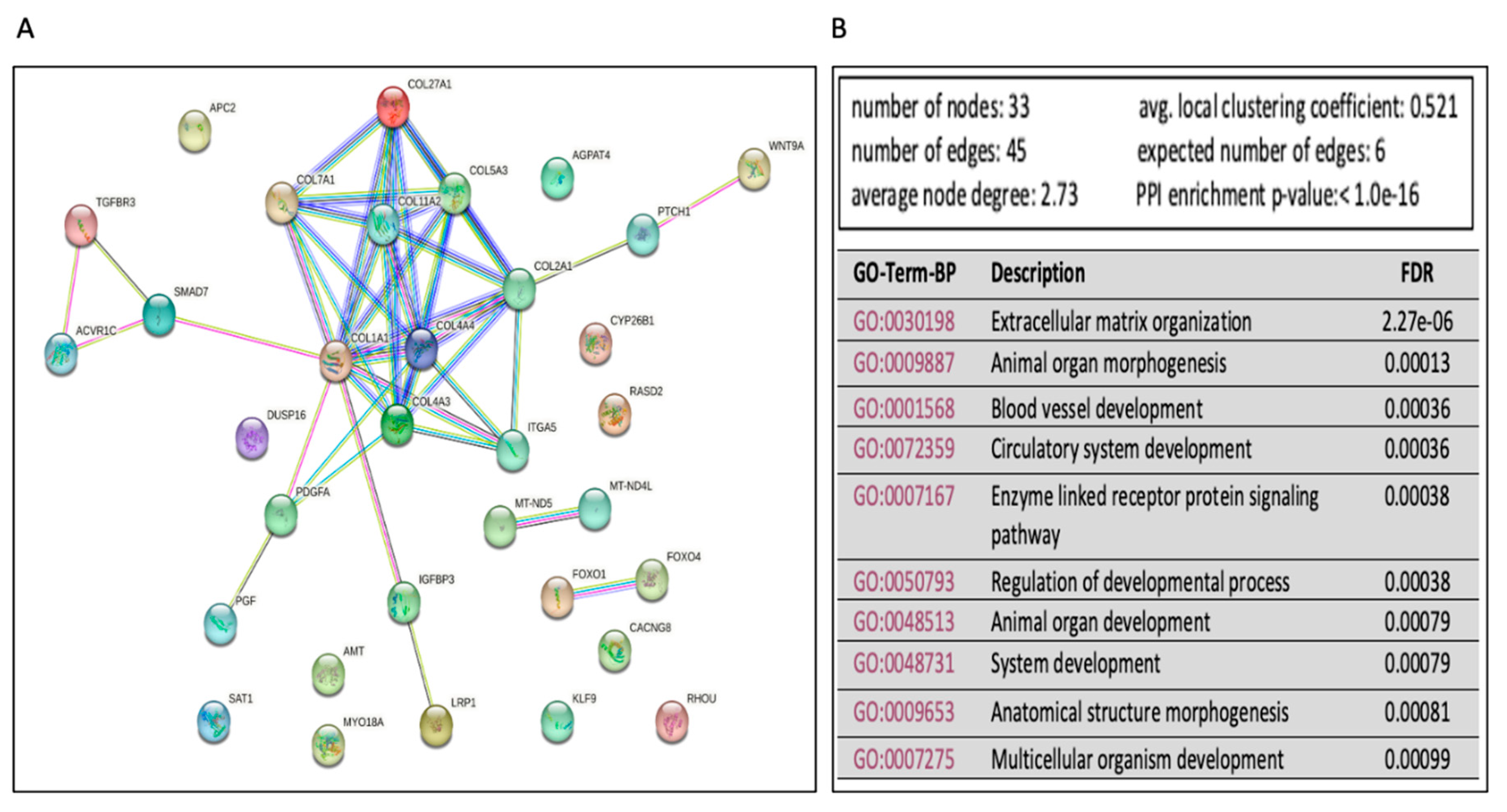
Pathway Enrichment Analysis
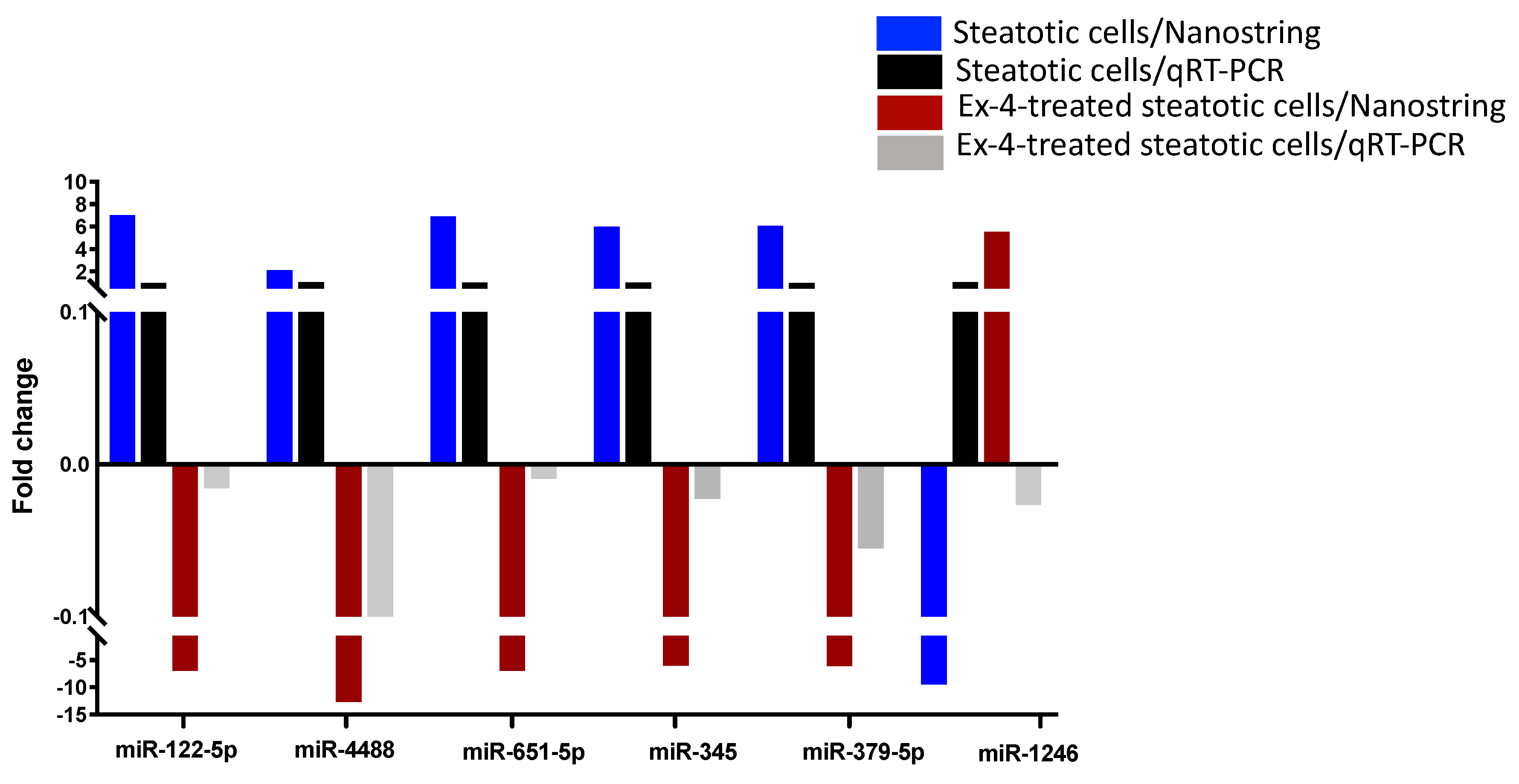
2.4. Validation of miRNA Differential Expression with qRT-PCR
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. HepG2 Culture and OA Preparation
4.2. Induction of Steatosis and Treatment with Exendin-4
4.3. Quantification of Steatosis
4.4. Total RNA Isolation
4.5. NanoString Analysis Platform and miRNA Profiling
4.6. Quantification Reverse Transcriptase PCR (qRT-PCR)
4.7. Statistical Analyses
4.8. Functional, Biological Pathway, and Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Perumpail, B.J., et al., Clinical epidemiology and disease burden of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol, 2017. 23(47): p. 8263-8276. [CrossRef]
- Pouwels, S., et al., Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): a review of pathophysiology, clinical management and effects of weight loss. BMC Endocr Disord, 2022. 22(1): p. 63. [CrossRef]
- Vieira Barbosa, J. and M. Lai, Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Screening in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients in the Primary Care Setting. Hepatol Commun, 2021. 5(2): p. 158-167. [CrossRef]
- Kitade, H., et al., Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Insulin Resistance: New Insights and Potential New Treatments. Nutrients, 2017. 9(4). [CrossRef]
- Noureddin, M., et al., NASH Leading Cause of Liver Transplant in Women: Updated Analysis of Indications For Liver Transplant and Ethnic and Gender Variances. Am J Gastroenterol, 2018. 113(11): p. 1649-1659. [CrossRef]
- Francque, S.M., et al., Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A patient guideline. JHEP Rep, 2021. 3(5): p. 100322. [CrossRef]
- Shaker, M., et al., Liver transplantation for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: new challenges and new opportunities. World J Gastroenterol, 2014. 20(18): p. 5320-30. [CrossRef]
- Pais, R., et al., NAFLD and liver transplantation: Current burden and expected challenges. J Hepatol, 2016. 65(6): p. 1245-1257. [CrossRef]
- Lazarus, J.V., et al., Advancing the global public health agenda for NAFLD: a consensus statement. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2022. 19(1): p. 60-78. [CrossRef]
- Yoo, E.R., et al., When to Initiate Weight Loss Medications in the NAFLD Population. Diseases, 2018. 6(4). [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.C., E. Ness, and K.V. Kowdley, Nutritional Approaches to Achieve Weight Loss in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Adv Nutr, 2017. 8(2): p. 253-265. [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A. and A. Dalbeni, Treatments for NAFLD: State of Art. Int J Mol Sci, 2021. 22(5). [CrossRef]
- van der Windt, D.J., et al., The Effects of Physical Exercise on Fatty Liver Disease. Gene Expr, 2018. 18(2): p. 89-101.
- Hung, C.K. and H.C. Bodenheimer, Jr., Current Treatment of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease/Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Clin Liver Dis, 2018. 22(1): p. 175-187. [CrossRef]
- Vilar-Gomez, E., et al., Weight Loss Through Lifestyle Modification Significantly Reduces Features of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology, 2015. 149(2): p. 367-78.e5; quiz e14-5. [CrossRef]
- Brunner, K.T., et al., Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Obesity Treatment. Curr Obes Rep, 2019. 8(3): p. 220-228. [CrossRef]
- Nauck, M.A., et al., GLP-1 receptor agonists in the treatment of type 2 diabetes - state-of-the-art. Mol Metab, 2021. 46: p. 101102. [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, O., et al., Exendin-4 alleviates steatosis in an in vitro cell model by lowering FABP1 and FOXA1 expression via the Wnt/-catenin signaling pathway. Sci Rep, 2022. 12(1): p. 2226. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F., et al., Recombinant human GLP-1 beinaglutide regulates lipid metabolism of adipose tissues in diet-induced obese mice. iScience, 2021. 24(12): p. 103382. [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.C., R.L. Feinbaum, and V. Ambros, The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell, 1993. 75(5): p. 843-54. [CrossRef]
- Smith-Vikos, T. and F.J. Slack, MicroRNAs and their roles in aging. J Cell Sci, 2012. 125(Pt 1): p. 7-17. [CrossRef]
- Aryal, B., et al., MicroRNAs and lipid metabolism. Curr Opin Lipidol, 2017. 28(3): p. 273-280. [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z., G. Dou, and L. Wang, MicroRNAs in the Pathogenesis of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Int J Biol Sci, 2021. 17(7): p. 1851-1863. [CrossRef]
- Leti, F., et al., High-throughput sequencing reveals altered expression of hepatic microRNAs in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-related fibrosis. Transl Res, 2015. 166(3): p. 304-14. [CrossRef]
- Di Mauro, S., et al., Intracellular and extracellular miRNome deregulation in cellular models of NAFLD or NASH: Clinical implications. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis, 2016. 26(12): p. 1129-1139. [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, K., et al., A Series of microRNA in the Chromosome 14q32.2 Maternally Imprinted Region Related to Progression of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in a Mouse Model. PLoS One, 2016. 11(5): p. e0154676. [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, Y., S. Tanaka, and Y. Haga, Enhanced GLUT2 gene expression in an oleic acid-induced in vitro fatty liver model. Hepatol Res, 2002. 23(2): p. 138-144. [CrossRef]
- Errafii, K., et al., Comparative Transcriptome Analysis Reveals That Exendin-4 Improves Steatosis in HepG2 Cells by Modulating Signaling Pathways Related to Lipid Metabolism. Biomedicines, 2022. 10(5). [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, O., et al., Investigation of the Effect of Exendin-4 on Oleic Acid-Induced Steatosis in HepG2 Cells Using Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy. Biomedicines, 2022. 10(10). [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D., et al., The STRING database in 2021: customizable protein-protein networks, and functional characterization of user-uploaded gene/measurement sets. Nucleic Acids Res, 2021. 49(D1): p. D605-d612.
- Sarwar, R., N. Pierce, and S. Koppe, Obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: current perspectives. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes, 2018. 11: p. 533-542. [CrossRef]
- Seghieri, M., et al., Future Perspectives on GLP-1 Receptor Agonists and GLP-1/glucagon Receptor Co-agonists in the Treatment of NAFLD. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), 2018. 9: p. 649.
- Wong, C., et al., Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists for Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Type 2 Diabetes: A Meta-Analysis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), 2021. 12: p. 609110. [CrossRef]
- Patel Chavez, C., K. Cusi, and S. Kadiyala, The Emerging Role of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists for the Management of NAFLD. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2022. 107(1): p. 29-38. [CrossRef]
- Dougherty, J.A., E. Guirguis, and K.A. Thornby, A Systematic Review of Newer Antidiabetic Agents in the Treatment of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Ann Pharmacother, 2021. 55(1): p. 65-79. [CrossRef]
- Zafar, Y., et al., Effect of novel glucose lowering agents on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol, 2022. 46(7): p. 101970. [CrossRef]
- Rowlands, J., et al., Pleiotropic Effects of GLP-1 and Analogs on Cell Signaling, Metabolism, and Function. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), 2018. 9: p. 672. [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.A., et al., Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor is present on human hepatocytes and has a direct role in decreasing hepatic steatosis in vitro by modulating elements of the insulin signaling pathway. Hepatology, 2010. 51(5): p. 1584-92. [CrossRef]
- Yokomori, H. and W. Ando, Spatial expression of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor and caveolin-1 in hepatocytes with macrovesicular steatosis in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. BMJ Open Gastroenterol, 2020. 7(1). [CrossRef]
- Körner, M., et al., GLP-1 receptor expression in human tumors and human normal tissues: potential for in vivo targeting. J Nucl Med, 2007. 48(5): p. 736-43. [CrossRef]
- López-Pastor, A.R., et al., miRNA Dysregulation in the Development of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and the Related Disorders Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Cardiovascular Disease. Front Med (Lausanne), 2020. 7: p. 527059. [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.Y., et al., The Emerging Role of MicroRNAs in NAFLD: Highlight of MicroRNA-29a in Modulating Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Beyond. Cells, 2020. 9(4). [CrossRef]
- Gjorgjieva, M., et al., miRNAs and NAFLD: from pathophysiology to therapy. Gut, 2019. 68(11): p. 2065-2079. [CrossRef]
- Kazeminasab, F., M. Baharlooie, and K. Ghaedi, Noncoding RNAs Associated with PPARs in Etiology of MAFLD as a Novel Approach for Therapeutics Targets. PPAR Res, 2022. 2022: p. 6161694. [CrossRef]
- Jansson, M.D. and A.H. Lund, MicroRNA and cancer. Mol Oncol, 2012. 6(6): p. 590-610.
- Khalifa, O., et al., Noncoding RNAs in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Potential Diagnosis and Prognosis Biomarkers. Dis Markers, 2020. 2020: p. 8822859. [CrossRef]
- Long, J.K., et al., miR-122 promotes hepatic lipogenesis via inhibiting the LKB1/AMPK pathway by targeting Sirt1 in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Mol Med, 2019. 25(1): p. 26.
- Inomata, Y., et al., Downregulation of miR-122-5p Activates Glycolysis via PKM2 in Kupffer Cells of Rat and Mouse Models of Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis. Int J Mol Sci, 2022. 23(9). [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y., et al., MicroRNA-122-5p Inhibition Improves Inflammation and Oxidative Stress Damage in Dietary-Induced Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Through Targeting FOXO3. Front Physiol, 2022. 13: p. 803445. [CrossRef]
- Yamada, H., et al., Associations between circulating microRNAs (miR-21, miR-34a, miR-122 and miR-451) and non-alcoholic fatty liver. Clin Chim Acta, 2013. 424: p. 99-103. [CrossRef]
- Nakao, K., H. Miyaaki, and T. Ichikawa, Antitumor function of microRNA-122 against hepatocellular carcinoma. Journal of gastroenterology, 2014. 49(4): p. 589-593. [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.J., et al., Complements are involved in alcoholic fatty liver disease, hepatitis and fibrosis. World J Hepatol, 2018. 10(10): p. 662-669. [CrossRef]
- Wang, P., et al., miR-345-5p curbs hepatic stellate cell activation and liver fibrosis progression by suppressing hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha expression. Toxicol Lett, 2022. 370: p. 42-52. [CrossRef]
- Feng, J., et al., mTOR: A Potential New Target in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Int J Mol Sci, 2022. 23(16). [CrossRef]
- Arora, M., N. Kutinová Canová, and H. Farghali, mTOR as an eligible molecular target for possible pharmacological treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Eur J Pharmacol, 2022. 921: p. 174857. [CrossRef]
- Mesarwi, O.A., et al., Hepatocyte Hypoxia Inducible Factor-1 Mediates the Development of Liver Fibrosis in a Mouse Model of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. PLoS One, 2016. 11(12): p. e0168572. [CrossRef]
- Han, J., et al., Hypoxia inducible factor-1 promotes liver fibrosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by activating PTEN/p65 signaling pathway. J Cell Biochem, 2019. 120(9): p. 14735-14744. [CrossRef]
- Holzner, L.M.W. and A.J. Murray, Hypoxia-Inducible Factors as Key Players in the Pathogenesis of Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis. Front Med (Lausanne), 2021. 8: p. 753268. [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, K., et al., Serum miR-379 expression is related to the development and progression of hypercholesterolemia in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. PLoS One, 2020. 15(2): p. e0219412. [CrossRef]
- de Guia, R.M., et al., microRNA-379 couples glucocorticoid hormones to dysfunctional lipid homeostasis. Embo j, 2015. 34(3): p. 344-60.
- Cao, C., et al., Lack of miR-379/miR-544 Cluster Resists High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity and Prevents Hepatic Triglyceride Accumulation in Mice. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2021. 9: p. 720900.
- Dong, Y., et al., MicroRNA-379-5p regulates free cholesterol accumulation and relieves diet induced-liver damage in db/db mice via STAT1/HMGCS1 axis. Mol Biomed, 2022. 3(1): p. 25.
- Wang, C.H., et al., Losartan Prevents Hepatic Steatosis and Macrophage Polarization by Inhibiting HIF-1α in a Murine Model of NAFLD. Int J Mol Sci, 2021. 22(15). [CrossRef]
- Mesarwi, O.A., et al., Hepatocyte HIF-1 and Intermittent Hypoxia Independently Impact Liver Fibrosis in Murine Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol, 2021. 65(4): p. 390-402. [CrossRef]
- He, Y., et al., Silencing HIF-1α aggravates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in vitro through inhibiting PPAR-α/ANGPTL4 singling pathway. Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2021. 44(5): p. 355-365.
- Seo, M.H., et al., Exendin-4 Inhibits Hepatic Lipogenesis by Increasing β-Catenin Signaling. PLoS One, 2016. 11(12): p. e0166913. [CrossRef]
- Meyer, G., et al., A potential role of progestin-induced laminin-5/α6-integrin signaling in the formation of side branches in the mammary gland. Endocrinology, 2012. 153(10): p. 4990-5001.
- Nair, B. and L.R. Nath, Inevitable role of TGF-β1 in progression of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Recept Signal Transduct Res, 2020. 40(3): p. 195-200.
- Fougerat, A., et al., Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors and Their Novel Ligands as Candidates for the Treatment of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Cells, 2020. 9(7). [CrossRef]
- Hardwick, J.P., et al., PPAR/RXR Regulation of Fatty Acid Metabolism and Fatty Acid omega-Hydroxylase (CYP4) Isozymes: Implications for Prevention of Lipotoxicity in Fatty Liver Disease. PPAR Res, 2009. 2009: p. 952734.
- Daniel, P.V., et al., NF-κB p65 regulates hepatic lipogenesis by promoting nuclear entry of ChREBP in response to a high carbohydrate diet. J Biol Chem, 2021. 296: p. 100714.
- Dongiovanni, P., et al., Genetic variants regulating insulin receptor signalling are associated with the severity of liver damage in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Gut, 2010. 59(2): p. 267-73. [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, S., M. Kobayashi, and Y. Kitagishi, Roles for PI3K/AKT/PTEN Pathway in Cell Signaling of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. ISRN Endocrinol, 2013. 2013: p. 472432. [CrossRef]
- Yang, P., et al., Liraglutide ameliorates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in diabetic mice via the IRS2/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes, 2019. 12: p. 1013-1021.
- Vinciguerra, M., et al., PTEN down-regulation by unsaturated fatty acids triggers hepatic steatosis via an NF-kappaBp65/mTOR-dependent mechanism. Gastroenterology, 2008. 134(1): p. 268-80.
- Dattaroy, D., et al., Micro-RNA 21 inhibition of SMAD7 enhances fibrogenesis via leptin-mediated NADPH oxidase in experimental and human nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 2015. 308(4): p. G298-312. [CrossRef]
- Wree, A., et al., NLRP3 inflammasome activation results in hepatocyte pyroptosis, liver inflammation, and fibrosis in mice. Hepatology, 2014. 59(3): p. 898-910. [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Gea, V. and S.L. Friedman, Pathogenesis of liver fibrosis. Annu Rev Pathol, 2011. 6: p. 425-56. [CrossRef]
- Miura, K., et al., Hepatic recruitment of macrophages promotes nonalcoholic steatohepatitis through CCR2. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 2012. 302(11): p. G1310-21. [CrossRef]
- Marra, F. and G. Svegliati-Baroni, Lipotoxicity and the gut-liver axis in NASH pathogenesis. J Hepatol, 2018. 68(2): p. 280-295. [CrossRef]
- Alkhatatbeh, M.J., L.F. Lincz, and R.F. Thorne, Low simvastatin concentrations reduce oleic acid-induced steatosis in HepG(2) cells: An in vitro model of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Exp Ther Med, 2016. 11(4): p. 1487-1492. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




