1. Introduction
Uremia is a complex disorder due to the accumulation of the toxic compounds in the body and the lack of the physiological function of the kidney. One of the consequences of that state is the imbalance between the increased oxidant stress and reduced activity of the antioxidants. Correction of uremic anaemia improves the antioxidant capacity of the body, but at the same time, large amounts of the supplemented iron induce oxidative stress [
1]. In uremic patients with a large iron deficit or poor iron absorption from the GI tract, intravenous supplementation is the treatment of choice. However, the effects of such treatment should be considered in patients treated with peritoneal dialysis due to the potential long-term impact of such therapy on peritoneal dialysis efficacy [
2]. Prolonged oxidative stress in peritoneal dialysis patients may accelerate the progression of atherosclerosis, loss of residual renal function and peritoneal fibrosis [
3]. During intravenous infusion of iron-containing compounds in patients treated with peritoneal dialysis, some amount of these drugs can directly diffuse into the peritoneal cavity, where after digestion by macrophages, free iron can be released. Also, transferrin with bound iron can diffuse from the bloodstream into the peritoneal cavity, where at the low pH of the dialysis fluid, free iron can be released [
4]. We found that intravenous iron therapy with iron sucrose or iron isomaltoside induces oxidative stress in the peritoneal mesothelial cells, which changes their functional properties [
5,
6]. Yamaji and coworkers described, in CAPD patients treated with intravenous iron, deposition of that metal in the peritoneum, especially in the area with the advanced fibrotic changes [
4].
Deposition of iron in the peritoneum may accelerate the loss of the properties of that structure as the dialysis membrane. Previously we found that iron-induced changes in the functional properties of the mesothelial cells in in vitro conditions are partially reversible after prolonged culture of these cells in a medium without iron [
7]. However in clinical conditions, patients are repeatedly exposed to iron, and therefore, we cannot exclude the accumulation of that metal in the peritoneum as shown by Yamaji et a. [
4]. Thus there is a need for searching of therapies which can minimize the injurious effect of iron on the peritoneum in patients treated with peritoneal dialysis. Previously we found that N-Acetylcysteine reduces the iron-induced changes in the function of the mesothelial cells [
6].
In the present study, we evaluated the effect of the NF-κβ inhibitor dehyroymethyepoxyquinmicin (DHMEQ) on Iron Isomaltoside (IIS) induced changes in the peritoneal mesothelial cells. We found in our previous study that DHMEQ reduces the inflammatory reactions in the mesothelial cells and slows their proliferation and synthesis of collagen [
8]. Such properties may be beneficial during intravenous iron therapy in peritoneal dialysis patients.
2. Results
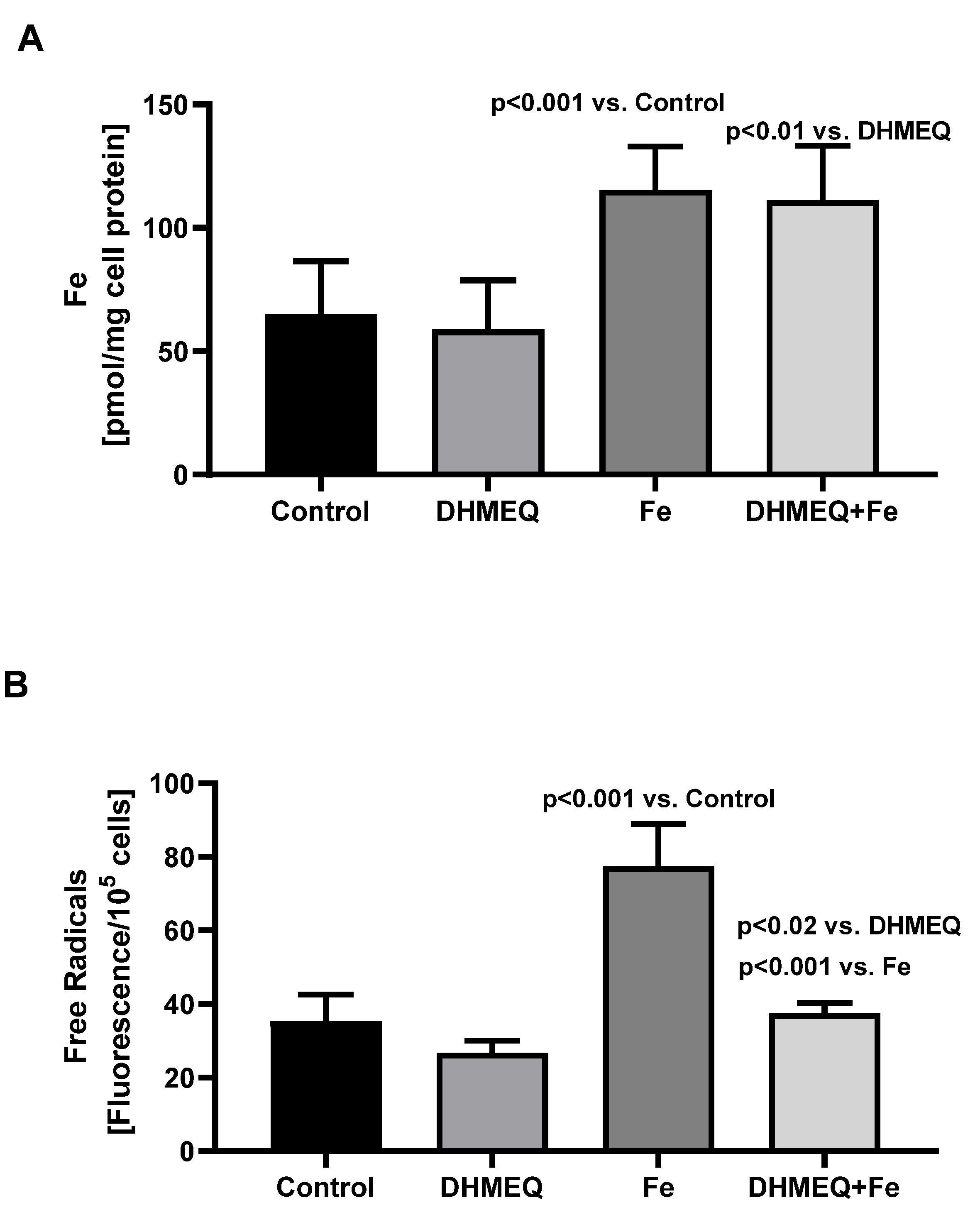
Treatment of the mesothelial cells with the studied media did not affect their viability, as reflected by the results of the MTT test, which were the same as in the control group. In the cells exposed to media supplemented with IIS, at the end of the 24 hours incubation, intracellular iron content was significantly increased as compared to cells not treated with iron (
Figure 1A). Treatment with IIS resulted in increased intracellular oxidative stress (+118%, p<0.001), but when the cells were simultaneously treated with DHMEQ increase of the intracellular free radicals was smaller (+40%, p<0.02) (
Figure 1B).
Exposure of the cells to a medium supplemented with IIS caused changes in the genes expression as compared to the control group: an increase for IL6 (+74%, p<0.001), PAI-1 (+43%, p<0.01) and TGFβ1 (+53%, p<0.001), whereas expression of tPA gene was reduced ( -36%, p<0.01). Simultaneous exposure to DHMEQ significantly reduced iron-induced changes in the expression of the studied genes (
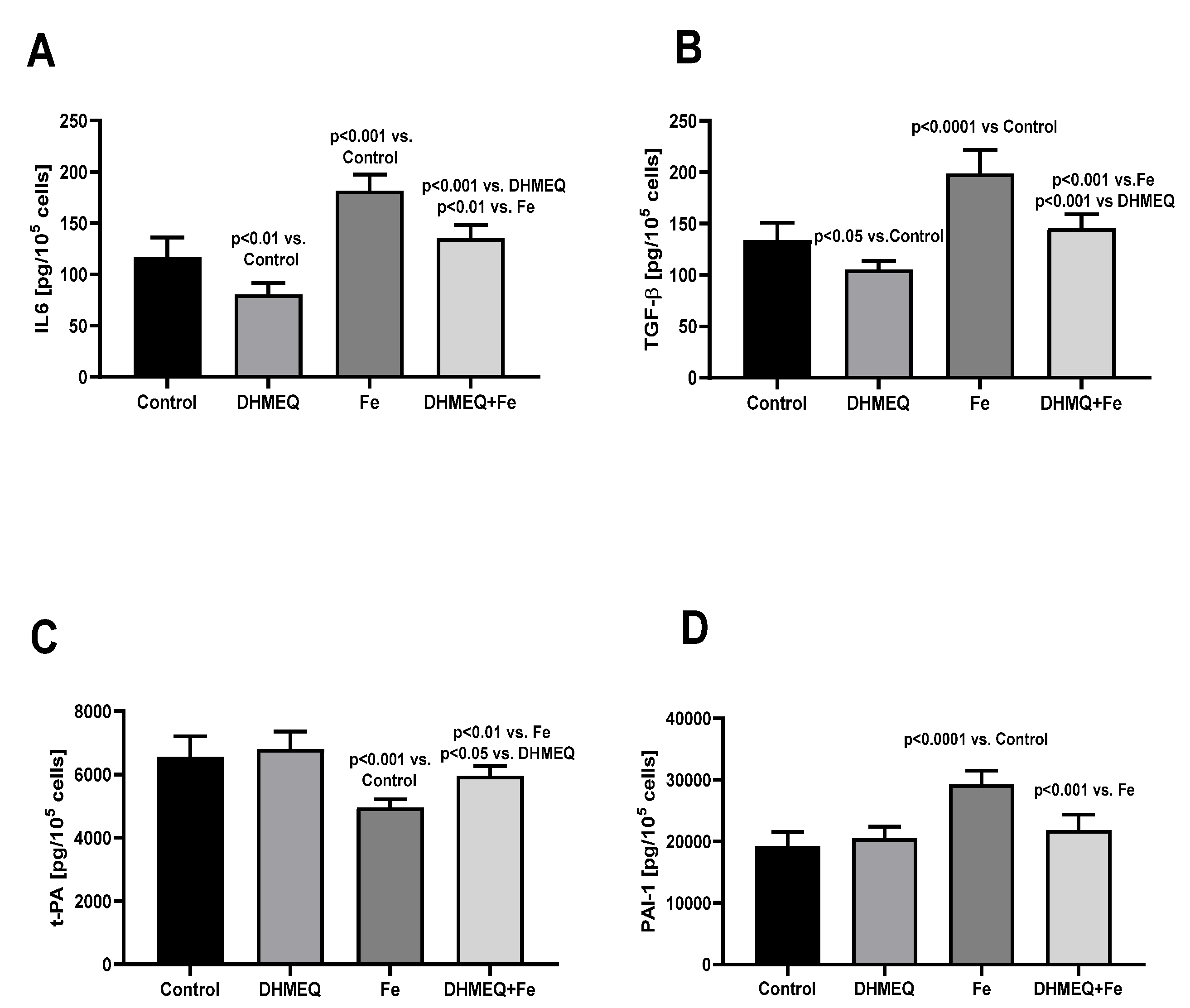
Figure 2). Changes in the genes expression were reflected by the modified cellular secretory activity (
Figure 3). IIS stimulated secretion of IL6 (+56%, p<0.001) but in the presence of DHMEQ, IL6 synthesis was reduced (-32%, p<0.01). Simultaneous exposure of the cells to IIS and DHMEQ resulted in a weaker increase in IL6 secretion (
Figure 3A). IIS stimulated the release of TGFβ1 from the mesothelial cells ( +49%, p<0.001), and that effect was milder (-27%, p<0.05) when the cells were simultaneously treated with DHMEQ. When DHMEQ was used as the only supplement to the culture medium, synthesis of TGFβ1 was lower than in the control group (-21%,p<0.05) (
Figure 3B). Synthesis of t-PA was reduced in cells exposed to IIS (-25%, p<0.001) and that effect was weaker (-12%, p<0.01)when simultaneously DHMEQ was used (
Figure 3C). In the presence of IIS, synthesis of PAI-1 was increased by 51% (p<0.001) as compared to control (p<0.001) and no such effect was seen when DHMEQ was used (
Figure 3D).
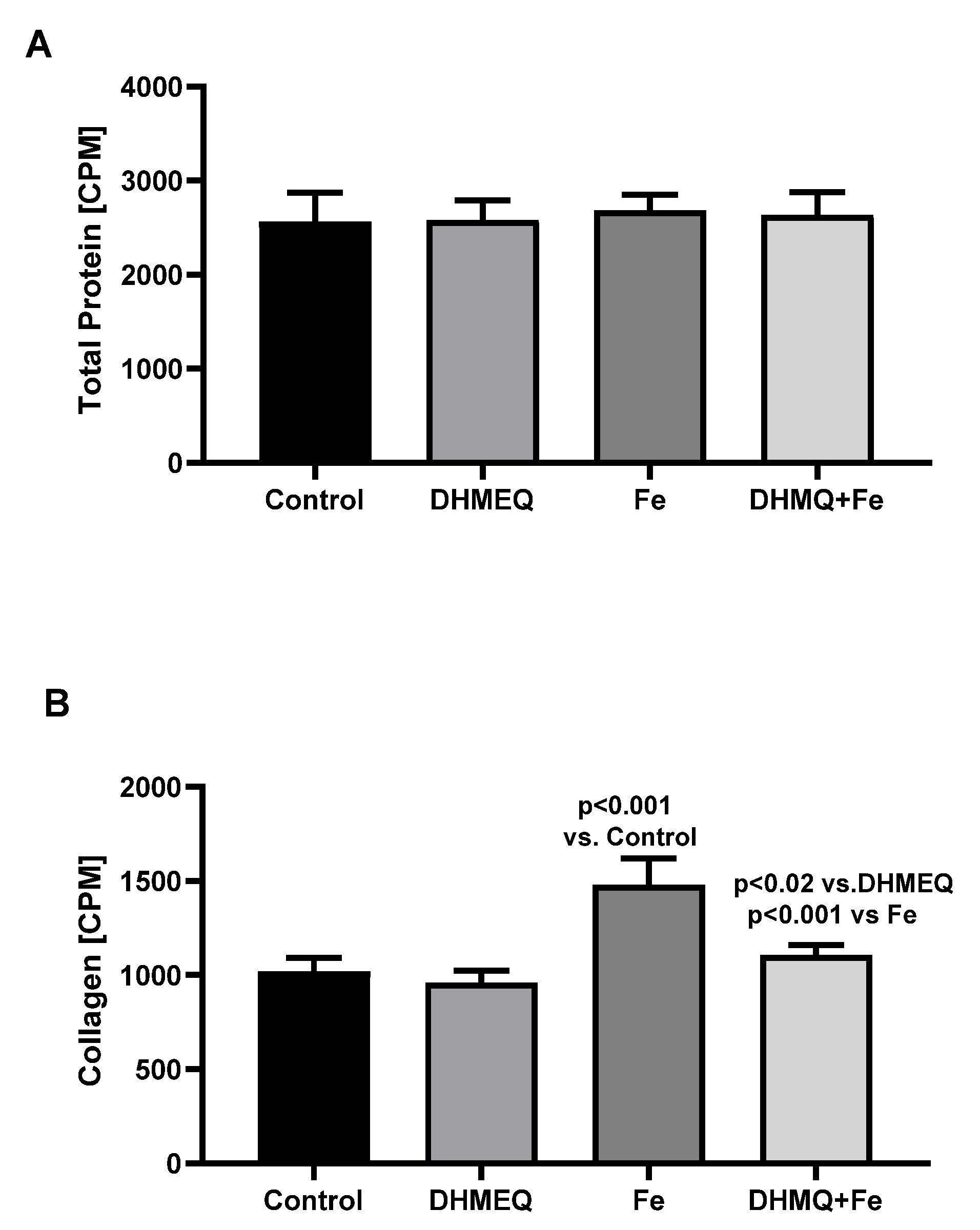
The synthesis of total proteins was comparable in all studied groups (
Figure 4A). However in the presence of IIS, synthesis of collagen was higher (+45%, p<0.001) as compared to the control group. However, when IIS was used together with DHMEQ, collagen synthesis was reduced (-25%, p<0.001) when compared to the effect of IIS alone (
Figure 4B).
3. Discussion
Results of our experiments confirm iron toxicity towards the mesothelial cells which was described in our previous studies [
6,
9] as well by other researchers [
10,
11]. The protective effect of N-Acetylcysteine against iron toxicity in conditions of peritoneal dialysis was observed in in vitro study [
7], but in the clinical scenario effectiveness of N-Acetylcysteine in dialysis patients is not confirmed by all researchers [
12]. There is a need for the effective protection of the mesothelial cells during peritoneal dialysis against iron toxicity. A significant amount of iron infused intravenously diffuses into the peritoneal cavity filled with the dialysis fluid, what can lead to injury of the peritoneal mesothelial cells [
5,
6].
Iron cytotoxicity is mediated via oxidative stress, which starts various processes leading to cells death [
13]. Iron-induced intracellular oxidative stress leads to activation of the NF-κβ system [
14]. Various components of the dialysis fluids stimulate the mesothelial cells via activation of the NF-κβ pathway, which results in their increased inflammatory profile [
8,
15]. Also, iron toxicity towards the peritoneum is linked with the activation of the NF-κβ system [
16]. In the present study, we found that application of the NFκβ inhibitor – DHMEQ reduces iron toxicity towards the peritoneal mesothelial cells
Exposure of the mesothelial cells to IIS in the presence of DHMEQ resulted in a significant decrease in the intracellular generation of free radicals as compared to cells treated only with IIS (
Figure 1B). Also, the proinflammatory pattern of the iron-treated mesothelial cells, reflected by the increased IL6 synthesis, was milder after treatment with DHMEQ (
Figure 2A). The anti-inflammatory effect of the NF-κβ inhibition is well described in various biological models [
17,
18], also in the mesothelial cells [
8,
19]. Exposure of the mesothelial cells to IIS resulted in the decreased synthesis of t-PA and increased synthesis of PAI-1 (
Figure 3 C,D), which consequence was the reduced fibrinolytic activity of these cells. Such an effect may be secondary to the increased inflammatory activity of the cells exposed to iron [
20]. Impaired fibrinolytic activity of the mesothelial cells may result in the increased deposition of fibrin within the peritoneum with the subsequent overgrowth of the connective tissue [
21,
22]. Inhibition of NF-κβ significantly reduced the iron-induced changes of tPA and PAI-1 secretion from the mesothelial cells (
Figure 3C,D).
Iron induces fibrosis in various organs such as the liver, lungs or kidney [
23,
24,
25]. In peritoneal biopsies obtained from patients treated with peritoneal dialysis, iron deposition was found in the parts of the peritoneum with the overgrowth of the fibrotic tissue [
4]. We found in the mesothelial cells exposed to IIS increased expression of TGFβ1 (
Figure 2) and secretion of that cytokine (
Figure 3B). IIS also increased the production of collagen in the mesothelial cells (
Figure 4B). Simultaneous exposure to DHMEQ reduced all these effects. In the experimental study on rats Duan and coworkers found that downregulation of the TGFβ1 expression with sulodexide reduced peritoneal fibrosis caused by chronic peritoneal dialysis [
26]. The antifibrotic effect of DHMEQ was shown in keloid fibroblasts [
27], kidneys[
28] and peritoneal mesothelial cells exposed to the effluent dialysates [
8]. Our results show that the application of DHMEQ may also prevent iron-induced fibrosis in the peritoneum.
Peritoneal dialysis is not a biocompatible procedure because the intraperitoneal infusion of the dialysis fluid induces the inflammatory reaction, leading in long term to peritoneal fibrosis. That process may be additionally enhanced by iron compounds diffusing into the peritoneal cavity from the bloodstream. Inhibition of the NF-κβ pathway within the peritoneal cavity may help to prevent peritoneal damage during long- term peritoneal dialysis.
4. Material and Methods
Experiments were performed on the primary cultures of human peritoneal mesothelial cells harvested from the effluent dialysates collected from patients treated with peritoneal dialysis. Effluents obtained during the first six months of the peritoneal dialysis therapy were used. Study was approved by the Bioethical Committee at the University of Medical Sciences in Poznan.
Mesothelial cells were cultured in medium M199 supplemented with hydrocortisone ( 1 ug/ml), antibiotics (streptomycin 100 ug/ml and penicillin 100 U/ml) and 10% fetal calf serum (FCS). Cells were grown in 24, and 6 wells plates and the experiments were performed on the cell monolayers. We studied the effect of the iron compound: Iron Isomaltoside 1000 (Monover®) on the function of the mesothelial cells in the presence of NF-kappaβ inhibitor: Dehydroxymethylepoxyquinomicin (DHMEQ). DHMEQ was used in concentration of 10 ug/nL, which as we found in our previous study is not toxic towards the mesothelial cells [
8]
The following experimental groups were studied:
Control group – culture medium
IIS group – culture medium plus Iron Isomaltoside 15 ug/dL
DHMEQ group – culture medium plus DHMEQ 10 ug/mL
IIS – DHMEQ group – culture medium plus Iron Isomaltoside 15 ug/dL and DHMEQ 10 ug/mL
In groups 3 & 4, before the start of the experiment, cells were incubated for 6 hours in a culture medium plus DHMEQ 10 ug/mL. Afterwards, in all groups, cells were incubated for 24 hours in the studied media, as listed above. Experiments were repeated nine times on the mesothelial cells from different donors.
Secretory activity: At the end of the incubation, supernatants were collected for measurement of the following substances: interleukin 6 (IL6), Tissue Plasminogen Activator (tPA), Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 (PAI-1), Transforming Growth Factor-β1 (TGFβ1) with the standard ELISA tests (DuoSeT® Immunoassay; R&D Systems, USA). In each group, in triplicate, the number of cells was counted in a hemocytometer, and cell protein and intracellular iron content were measured. Also, the viability of the cells was evaluated, and the intracellular generation of free radicals was measured.
Mesothelial cell parameters: To quantify the cells number, the cells were harvested from the wells with trypsin 0.05% - EDTA0.02% solution and counted in a hemocytometer. Protein concentration in the cells lysates was measured with the Lowry method [
29]. Intracellular iron in the mesothelial cells was measured with a colorimetric ferrozine-based method in the cells lysates and expressed per amount of the cells' protein [
30]. The amount of iron in the cells was expressed per amount of the cellular protein. The viability of the cells' monolayers at the end of the incubation was measured with MTT assay (Abcam, Cambridge, UK). Cells were exposed to MTT salt [3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide] for 3 hours at 37 °C. The generated formazan product was lysed, and its absorbance was measured at 595 nm. Free radicals generated within the cells were measured during their 45 minutes of incubation at 37oC with 2’7’dochlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate probe. Then, after the cells lysis, the fluorescence of the cell lysates was measured in a fluorimeter at wavelength 485 nm for excitation and 535 nm for emission. Intracellular generation of free radicals was expressed per mg of the cells' protein.
Analysis of genes expression: Total RNA from the mesothelial monolayers in 6 wells plates, after their exposition to the studied media ( group 1-4) was isolated with the ReliaPrepTM RNA Cell Miniprep System (Promega, Madison, WI, USA), treated with DNase I using DNA-free DNase Treatment and Removal Reagent (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham MA, USA). Afterwards, RNA was reverse-transcribed to cDNA with the Transcriptor First Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (Roche, Basel, Switzerland).Relative levels of mRNA of 4 genes:
IL6 [F:ATGAACTCCTTCTCCACAAGC; R:GTTTTCTGCCAGTGCCTCTTTG]
t-PA [F:CAGCCAGGAAATCCATGCCC; R:GCCATGACTGATGTTGCTGG]
PAI-1 [F:TGCTGGTGAATGCCCTCTACT;R: CGGTCATTCCCAGGTTCTCTA]
TGF-β1 [F:TGGAAATCAATGGGATCAGTC; R: GAGCAAGTGCTTGGTATGG]
were studied in triplicates from each experiment and normalized to levels of an internal house-keeping gene: Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase (GAPDH) [F:TTCGTCATGGGTGTGAACC; R:GATGATGTTCTGGAGAGCCC]. Relative gene expression was calculated using the 2-∆∆Ct method [
31].
Measurement of total protein and collagen synthesis: Mesothelial monolayers in the 24 wells plates were exposed to the studied media as described above. Additionally, all media were supplemented with β-aminopropionitrile (50 μg/mL), L-ascorbic acid (50 μg/mL) and 3H-Proline (5 μCi/mL). After 24 hours of incubation, the plates were put into the freezer ( -20oC), and then cells were lysed by repeated freezing and thawing. The collected from each well, mixed supernatants and cells lysates were divided into two equal portions ( 2 x 0.5 mL), which were mixed ( 1:1 v/v) with:
A. Hanks solution with N-etylmaleimide (2.5 mM/ml)
B. Hanks solution with N-etylmaleimide (2.5 mM/ml) and collagenase 0.2 mg/ml)
Such prepared mixtures were incubated for 4 hours at 37oC, and afterwards, proteins in each sample were precipitated with 10% trichloroacetic acid (TCA). After spinning and removal of the supernatant, the precipitate was washed twice with 10% TCA and finally lysed overnight at 4oC in 0.1 N NaOH. The radioactivity of the cells lysates was measured in a β-liquid scintillation counter (Wallac, Perkin Elmer, Warsaw, Poland). Radioactivity of the A samples reflected total protein synthesis, and the difference of radioactivity between samples A and B was used as an index of collagen synthesis.
Statistical analysis: Results are presented as mean ± SD. Analysis of the obtained data was performed with a one-way analysis of variance with the post hoc Newman Keuls test. A p value of less than 0.05 was considered significant.
Authors Contributions
AB: conceptualization, methodology, validation, analysis of the results, writing the manuscript. KU: conceptualization, methodology, validation, analysis of the results,
Funding
The study was supported by a grant from the National Science Center Poland: OPUS 2018/31/B/NZ4/00776
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Bioethical Committee of the Poznan University of Medical Sciences.
Informed Consent Statement
Human resources were not involved in this study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in this article
Conflict of Interest
Author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Lahera V, Goicoechea M, de Vinuesa SG, Pilar Oubiña, Victoria Cachofeiro, Francisco Gómez-Campderá, Raquel Amann, José Luño, Oxidative stress in uremia: the role of anemia correction. J Am Soc Nephrol. ;2006: 17(12 Suppl 3): S174-S177. [CrossRef]
- Zager RA, Intravenous iron therapy in peritoneal dialysis patients: short-term efficacy and long-term issues. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 1, 353-355 (2006). [CrossRef]
- Liakopoulos V, Roumeliotis S, Gorny X, Eleftheriadis T, Mertens PR Oxidative Stress in Patients Undergoing Peritoneal Dialysis: A Current Review of the Literature. Oxid Med Cell Longev.2017 :3494867. [CrossRef]
- Yamaji Y, Nakazato Y, Oshima N, Hayashi M, Saruta T, Oxidative stress induced by iron released from transferrin in low pH peritoneal dialysis solution. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2014:19,2592-2597. [CrossRef]
- Bręborowicz A, Połubinska A, Kupczyk M Wanic-Kossowska M, Oreopoulos DG, Intravenous iron sucrose changes the intraperitoneal homeostasis. Blood Purif. 2009:28, 53-58. [CrossRef]
- Misian M, Baum E, Breborowicz A, N-Acetylcysteine modulates effect of the iron isomaltoside on peritoneal mesothelial cells. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2020: 3, 365-371. [CrossRef]
- 7. Jasiński T, Bręborowicz A. Adverse effects of iron toward the peritoneal mesothelial cells are reversible. Ther Apher Dial. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Sosińska P, Baum E, Maćkowiak B, Staniszewski R, Jasinski T, Umezawa K, Breborowicz A, Inhibition of NF-kappaB with Dehydroxymethylepoxyquinomicin modifies the function of human peritoneal mesothelial cells. Am J Transl Res. 2016: 8,5756-5765.
- Breborowicz M, Polubinska A, Tam P, Wu G, Breborowicz A, Effect of iron sucrose on human peritoneal mesothelial cells. Eur J Clin Invest. 2003:33,1038-1044. [CrossRef]
- Okazaki Y, Chew SH, Nagai H, Yamashita Y, Ohara H, Jiang L, Akatsuka S, Takahashi T, Toyokuni S Overexpression of miR-199/214 is a distinctive feature of iron-induced and asbestos-induced sarcomatoid mesothelioma in rats. Cancer Sci. 2020:111, 2016-2027. [CrossRef]
- Nakayama M, Zhu W, Watanabe K, Gibo A, Sherif AM, Kabayama S, Ito S. Dissolved molecular hydrogen (H2) in Peritoneal Dialysis (PD) solutions preserves mesothelial cells and peritoneal membrane integrity. BMC Nephrol. 2017:18, 327. [CrossRef]
- Liakopoulos V, Roumeliotis S, Bozikas A, Eleftheriadis T, Dounousi E. Antioxidant Supplementation in Renal Replacement Therapy Patients: Is There Evidence? Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019. [CrossRef]
- Galaris D, Barbouti A, Pantopoulos K. Iron homeostasis and oxidative stress: An intimate relationship. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2019,1866 (12):11853. [CrossRef]
- Banerjee P, Sahoo A, Anand S, Ganguly A, Righi G, Bovicelli P, Saso L, Chakrabarti S. Multiple mechanisms of iron-induced amyloid beta-peptide accumulation in SHSY5Y cells: protective action of negletein. Neuromolecular Med 2014:16,787-798 (. [CrossRef]
- Nevado J, Peiró C, Vallejo S, El-Assar M, Lafuente N, Matesanz N, Azcutia V, Cercas E, Sánchez-Ferrer CF, Rodríguez-Mañas L. Amadori adducts activate nuclear factor-kappaB-related proinflammatory genes in cultured human peritoneal mesothelial cells. Br J Pharmacol. 2005. 146, 268-279. [CrossRef]
- Defrère S, González-Ramos R, Lousse JC, Colette S, Donnez O, Donnez J, Van Langendonckt A. Insights into iron and nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-kappaB) involvement in chronic inflammatory processes in peritoneal endometriosis. Histol Histopathol. 2011:26,1083-1092. [CrossRef]
- Suzuki E, Sugiyama C, Umezawa K, Inhibition of inflammatory mediator secretion by (-)-DHMEQ in mouse bone marrow-derived macrophages. Biomed. Pharmacother.2009: 63, 351-358. [CrossRef]
- Miyajima A, Kosaka T, Seta K, Asano T, Umezawa K, Hayakawa M Novel nuclear factor kappa B activation inhibitor prevents inflammatory injury in unilateral ureteral obstruction. J Urol. 2003:169,1559-1563. [CrossRef]
- Hams E, Colmont CS, Dioszeghy V, Victoria J Hammond, Fielding CA, Williams AS, Tanaka M, Miyajima A, Taylor PR, Topley N, Jones SA, Oncostatin M receptor-beta signaling limits monocytic cell recruitment in acute inflammation. J Immunol.2018: 181, 2174-2178. [CrossRef]
- Medcalf RL. Fibrinolysis, inflammation, and regulation of the plasminogen activating system. J Thromb Haemost. 2007:5, Suppl 1:132-42. [CrossRef]
- Ruppert C, Markart P, Wygrecka M, Preissner KT, Günther A. A. Role of coagulation and fibrinolysis in lung and renal fibrosis. Hamostaseologie. 2008:28,30-32.
- Dobbie JW, Pathogenesis of peritoneal fibrosing syndromes (sclerosing peritonitis) in peritoneal dialysis. Perit Dial Int 1992:12, 14-27.
- Mehta KJ, Farnaud SJ, Sharp PA, Iron and liver fibrosis: Mechanistic and clinical aspects. World J Gastroenterol. 2019:25, 521-538. [CrossRef]
- Ali MK, Kim RY, Karim R, Mayall JR, Martin KL, Shahandeh A, Abbasian F, Starkey MR, Loustaud-Ratti V, Johnstone D, Milward EA, Hansbro PM, Horvat JC. Role of iron in the pathogenesis of respiratory disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2017: 88,181-195. [CrossRef]
- Naito Y, Fujii A, Sawada H, Oboshi M, Iwasaku T, Okuhara Y, Morisawa D, Eguchi A, Hirotani S, Masuyama T. Association between renal iron accumulation and renal interstitial fibrosis in a rat model of chronic kidney disease. Hypertens Res. 2015. 38, 463-470. [CrossRef]
- Duan Z, Yao J, Duan N, Wang M, Wang S. Sulodexide Prevents Peritoneal Fibrosis by Downregulating the Expression of TGF- β 1 and Its Signaling Pathway Molecules. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021: 2052787. [CrossRef]
- Makino S, Mitsutake N, Nakashima Saenko VA, Ohtsuru A, Umezawa K, Tanaka K, Hirano A, Yamashita S. DHMEQ, a novel NF-kappaB inhibitor, suppresses growth and type I collagen accumulation in keloid fibroblasts. J Dermatol Sc. 2008: 51, 171-180. [CrossRef]
- Morita S, Shinoda K, Yoshida T, Shimoda M, Kanno Y, Mizuno R, Kono H, Asanuma H, Nakagawa K, Umezawa K, Oya M. Dehydroxymethylepoxyquinomicin, a novel nuclear factor-κB inhibitor, prevents the development of cyclosporine A nephrotoxicity in a rat model. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2020: 60. [CrossRef]
- Lowry OH, Rosenbrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall LJ, Protein measurement with the fo-lin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951: 193, 265-275.
- Riemer J, Hoepken HH, Czerwinska H, Robinson SR, Dringen R, Colorimetric fer-rozine-based assay for the quantitation of iron in cultured cells. Anal Biochem 2004: 331,370-375. [CrossRef]
- Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods.2001:25, 402-408. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).