Submitted:
09 June 2023
Posted:
09 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Molecular Regulation of Phosphate Uptake at the Transcriptional, Translational and Post-translational Levels
2.1. Transcription Factors as Regulators of Systemic Responses to Phosphate (Pi) Starvation
2.2. New Insights for Plant Phosphate Starvation Response at the Translational Levels
2.3. Roles of Phosphorylated Proteins and Phospholipids in Pi Homeostasis
3. SPX PP-InsPs in Regulating Cellular Pi Homeostasis in Plants
3.1. Phosphorylated Inositols as Signalling Molecules and Roles of Inositol Polyphosphate Kinases for Cellular Homeostasis of Pi in Plants
3.2. Molecular Mechanism Involving SPX in Regulating Transcriptional Activities of PHR
3.3. Regulatory Mechanism Involving SPX in Controlling Vacuolar Phosphate Transporter (VPT) Activities for Plant Pi Homeostasis
4.0. CRISPR-mediated genome editing for improving phosphorus use efficiency
5. Summary and Future Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflict of Interest
References
- Lynch, J.P., Root phenes for enhanced soil exploration and phosphorus acquisition: tools for future crops. Plant physiology, 2011. 156(3): p. 1041-1049. [CrossRef]
- Shrivastav, P., et al., Role of nutrients in plant growth and development. Contaminants in agriculture: Sources, impacts and management, 2020: p. 43-59.
- Yadav, D.S., et al., Soil acidification and its impact on plants. Plant responses to soil pollution, 2020: p. 1-26.
- Etesami, H., B.R. Jeong, and B.R. Glick, Contribution of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, phosphate–solubilizing bacteria, and silicon to P uptake by plant. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2021. 12: p. 699618. [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, I.I., et al., The dynamic responses of oil palm leaf and root metabolome to phosphorus deficiency. Metabolites, 2021. 11(4): p. 217. [CrossRef]
- Trejo-Téllez, L.I. and F.C. Gómez-Merino, Phosphite as an inductor of adaptive responses to stress and stimulator of better plant performance. Biotic and Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Plants, 2018: p. 203-238.
- Malhotra, H., et al., Phosphorus nutrition: plant growth in response to deficiency and excess. Plant nutrients and abiotic stress tolerance, 2018: p. 171-190. [CrossRef]
- Luan, M., et al., Vacuolar phosphate transporters contribute to systemic phosphate homeostasis vital for reproductive development in Arabidopsis. Plant physiology, 2019. 179(2): p. 640-655. [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo-Orts, L., D. Couto, and M. Hothorn, Identity and functions of inorganic and inositol polyphosphates in plants. New Phytologist, 2020. 225(2): p. 637-652. [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y., et al., The genetic basis of phosphorus utilization efficiency in plants provide new insight into woody perennial plants improvement. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2022. 23(4): p. 2353. [CrossRef]
- Li, H., et al., Molecular mechanism of phosphorous signaling inducing anthocyanin accumulation in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2023. 196: p. 121-129. [CrossRef]
- Verma, L., et al., Phosphate deficiency response and membrane lipid remodeling in plants. Plant Physiology Reports, 2021: p. 1-12. [CrossRef]
- Long, L., et al., Root plasticity and Pi recycling within plants contribute to low-P tolerance in Tibetan wild barley. BMC plant biology, 2019. 19(1): p. 1-13. [CrossRef]
- Gu, M., et al., Complex regulation of plant phosphate transporters and the gap between molecular mechanisms and practical application: what is missing? Molecular Plant, 2016. 9(3): p. 396-416. [CrossRef]
- Kong, S.-L., et al., Comparative transcriptome analysis reveals novel insights into transcriptional responses to phosphorus starvation in oil palm (Elaeis guineensis) root. BMC genomic data, 2021. 22: p. 1-15. [CrossRef]
- Chien, P.-S., et al., Sensing and signaling of phosphate starvation: from local to long distance. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2018. 59(9): p. 1714-1722. [CrossRef]
- Su, T., et al., WRKY42 modulates phosphate homeostasis through regulating phosphate translocation and acquisition in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiology, 2015. 167(4): p. 1579-1591. [CrossRef]
- Chiou, T.-J. and S.-I. Lin, Signaling network in sensing phosphate availability in plants. Annual review of plant biology, 2011. 62: p. 185-206. [CrossRef]
- Devaiah, B.N., V.K. Nagarajan, and K.G. Raghothama, Phosphate homeostasis and root development in Arabidopsis are synchronized by the zinc finger transcription factor ZAT6. Plant Physiology, 2007. 145(1): p. 147-159. [CrossRef]
- Hamzah, M.L., S.N.A. Abdullah, and A.M. Azzeme, Genome-wide molecular characterization of Phosphate Transporter 1 and Phosphate Starvation Response gene families in Elaeis guineensis Jacq. and their transcriptional response under different levels of phosphate starvation. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 2021. 43: p. 1-15. [CrossRef]
- Li, Z., et al., Integrated mRNA and microRNA expression analysis of root response to phosphate deficiency in Medicago sativa. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2022: p. 3444. [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.-B., et al., GmPHR25, a GmPHR member up-regulated by phosphate starvation, controls phosphate homeostasis in soybean. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2017. 68(17): p. 4951-4967. [CrossRef]
- Sun, L., et al., Arabidopsis PHL2 and PHR1 act redundantly as the key components of the central regulatory system controlling transcriptional responses to phosphate starvation. Plant Physiology, 2016. 170(1): p. 499-514. [CrossRef]
- Guo, M., et al., Integrative comparison of the role of the PHOSPHATE RESPONSE1 subfamily in phosphate signaling and homeostasis in rice. Plant Physiology, 2015. 168(4): p. 1762-1776. [CrossRef]
- Dong, J., et al., Inositol pyrophosphate InsP8 acts as an intracellular phosphate signal in Arabidopsis. Molecular plant, 2019. 12(11): p. 1463-1473. [CrossRef]
- Liu, N., et al., Evolution of the SPX gene family in plants and its role in the response mechanism to phosphorus stress. Open biology, 2018. 8(1): p. 170231. [CrossRef]
- Sedeek, K.E., A. Mahas, and M. Mahfouz, Plant genome engineering for targeted improvement of crop traits. Frontiers in plant science, 2019. 10: p. 114. [CrossRef]
- Doudna, J.A. and E. Charpentier, The new frontier of genome engineering with CRISPR-Cas9. Science, 2014. 346(6213): p. 1258096. [CrossRef]
- Moradpour, M. and S.N.A. Abdulah, CRISPR/dC as9 platforms in plants: strategies and applications beyond genome editing. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2020. 18(1): p. 32-44.
- Naumann, C., et al., The local phosphate deficiency response activates endoplasmic reticulum stress-dependent autophagy. Plant physiology, 2019. 179(2): p. 460-476. [CrossRef]
- Pandey, B.K., P. Mehra, and J. Giri, Phosphorus starvation response in plants and opportunities for crop improvement. Climate change and plant abiotic stress tolerance, 2013: p. 991-1012.
- Liu, T.-Y., et al., Identification of plant vacuolar transporters mediating phosphate storage. Nature communications, 2016. 7(1): p. 11095. [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, F., et al., Functional characterization of the gene promoter for an Elaeis guineensis phosphate starvation-inducible, high affinity phosphate transporter in both homologous and heterologous model systems. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2018. 127: p. 320-335. [CrossRef]
- Victor Roch, G., et al., The role of PHT1 family transporters in the acquisition and redistribution of phosphorus in plants. Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences, 2019. 38(3): p. 171-198. [CrossRef]
- Chiou, T.-J., The diverse roles of rice PHO1 in phosphate transport: from root to node to grain. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2020. 61(8): p. 1384-1386. [CrossRef]
- Devaiah, B.N. and K.G. Raghothama, Transcriptional regulation of Pi starvation responses by WRKY75. Plant signaling & behavior, 2007. 2(5): p. 424-425. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A., V. Gahlaut, and M. Nagaraju, Transcription factors and their roles in phosphorus stress tolerance in crop plants, in Transcription factors for abiotic stress tolerance in plants. 2020, Elsevier. p. 201-224.
- Zhang, J.-F., et al., Comprehensive Evolution and Expression anaLysis of PHOSPHATE 1 Gene Family in Allotetraploid Brassica napus and Its Diploid Ancestors. Biochemical Genetics, 2023: p. 1-18. [CrossRef]
- Ambawat, S., et al., MYB transcription factor genes as regulators for plant responses: an overview. Physiology and Molecular Biology of Plants, 2013. 19: p. 307-321. [CrossRef]
- Sega, P. and A. Pacak, Plant PHR transcription factors: put on a map. Genes, 2019. 10(12): p. 1018. [CrossRef]
- Bustos, R., et al., A central regulatory system largely controls transcriptional activation and repression responses to phosphate starvation in Arabidopsis. PLoS genetics, 2010. 6(9): p. e1001102. [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, E., et al., PHOSPHATE TRANSPORTER TRAFFIC FACILITATOR1 is a plant-specific SEC12-related protein that enables the endoplasmic reticulum exit of a high-affinity phosphate transporter in Arabidopsis. The Plant Cell, 2005. 17(12): p. 3500-3512. [CrossRef]
- Mehra, P., B.K. Pandey, and J. Giri, Improvement in phosphate acquisition and utilization by a secretory purple acid phosphatase (OsPAP21b) in rice. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2017. 15(8): p. 1054-1067. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z., et al., Functional characterization of Arabidopsis PHL4 in plant response to phosphate starvation. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2018. 9: p. 1432. [CrossRef]
- Ruan, W., et al., Phosphate starvation induced OsPHR4 mediates Pi-signaling and homeostasis in rice. Plant molecular biology, 2017. 93: p. 327-340. [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y., et al., OsPHR3 affects the traits governing nitrogen homeostasis in rice. BMC plant biology, 2018. 18(1): p. 1-15. [CrossRef]
- Ruan, W., et al., Genetic manipulation of a high-affinity PHR1 target cis-element to improve phosphorous uptake in Oryza sativa L. Plant molecular biology, 2015. 87: p. 429-440. [CrossRef]
- Devaiah, B.N., et al., Phosphate starvation responses and gibberellic acid biosynthesis are regulated by the MYB62 transcription factor in Arabidopsis. Molecular plant, 2009. 2(1): p. 43-58. [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.T., et al., Overexpression of OsMYB4P, an R2R3-type MYB transcriptional activator, increases phosphate acquisition in rice. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2014. 80: p. 259-267. [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.T., et al., Rice OsMYB5P improves plant phosphate acquisition by regulation of phosphate transporter. PLoS One, 2018. 13(3): p. e0194628. [CrossRef]
- Bari, R., et al., PHO2, microRNA399, and PHR1 define a phosphate-signaling pathway in plants. Plant physiology, 2006. 141(3): p. 988-999. [CrossRef]
- Chiou, T.-J., et al., Regulation of phosphate homeostasis by microRNA in Arabidopsis. The Plant Cell, 2006. 18(2): p. 412-421. [CrossRef]
- Hu, B., et al., LEAF TIP NECROSIS1 plays a pivotal role in the regulation of multiple phosphate starvation responses in rice. Plant Physiology, 2011. 156(3): p. 1101-1115. [CrossRef]
- Xu, F., et al., Genome-wide identification of soybean microRNAs and their targets reveals their organ-specificity and responses to phosphate starvation. BMC genomics, 2013. 14: p. 1-30. [CrossRef]
- Baek, D., et al., Regulation of miR399f transcription by AtMYB2 affects phosphate starvation responses in Arabidopsis. Plant physiology, 2013. 161(1): p. 362-373. [CrossRef]
- Qi, X., et al., Arabidopsis G-Protein β Subunit AGB1 Negatively Regulates DNA Binding of MYB62, a Suppressor in the Gibberellin Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2021. 22(15): p. 8270. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-F., et al., The WRKY6 transcription factor modulates PHOSPHATE1 expression in response to low Pi stress in Arabidopsis. The Plant Cell, 2009. 21(11): p. 3554-3566. [CrossRef]
- Li, C., et al., Transcription factor GmWRKY46 enhanced phosphate starvation tolerance and root development in transgenic plants. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2021: p. 1984. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.-H., et al., BHLH32 modulates several biochemical and morphological processes that respond to Pi starvation in Arabidopsis. Biochemical Journal, 2007. 405(1): p. 191-198. [CrossRef]
- Yeh, C.-M., et al., Blue light regulates phosphate deficiency-dependent primary root growth inhibition in Arabidopsis. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2020. 10: p. 1803. [CrossRef]
- Huang, L., et al., Zinc finger protein 5 (ZFP5) associates with ethylene signaling to regulate the phosphate and potassium deficiency-induced root hair development in Arabidopsis. Plant molecular biology, 2020. 102: p. 143-158. [CrossRef]
- Staudinger, C., et al., The wheat secreted root proteome: Implications for phosphorus mobilisation and biotic interactions. Journal of Proteomics, 2022. 252: p. 104450. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y., et al., Abscisic acid facilitates phosphate acquisition through the transcription factor ABA INSENSITIVE5 in Arabidopsis. The Plant Journal, 2022. 111(1): p. 269-281. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y., et al., Proteomic Investigation of Molecular Mechanisms in Response to PEG-Induced Drought Stress in Soybean Roots. Plants, 2022. 11(9): p. 1173. [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L., et al., Quantitative proteomics reveals that GmENO2 proteins are involved in response to phosphate starvation in the leaves of Glycine max L. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2021. 22(2): p. 920. [CrossRef]
- Guo, M., et al., Alternative splicing of REGULATOR OF LEAF INCLINATION 1 modulates phosphate starvation signaling and growth in plants. The Plant Cell, 2022. 34(9): p. 3319-3338. [CrossRef]
- Muneer, S. and B.R. Jeong, Proteomic analysis provides new insights in phosphorus homeostasis subjected to Pi (inorganic phosphate) starvation in tomato plants (Solanum lycopersicum L.). PLoS One, 2015. 10(7): p. e0134103. [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q., et al., Identification of phosphorus stress related proteins in the seedlings of Dongxiang wild rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.) using label-free quantitative proteomic analysis. Genes, 2022. 13(1): p. 108. [CrossRef]
- Roustan, V., et al., Quantitative in vivo phosphoproteomics reveals reversible signaling processes during nitrogen starvation and recovery in the biofuel model organism Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Biotechnology for biofuels, 2017. 10(1): p. 1-24. [CrossRef]
- Hetz, R., et al., Excessive Inorganic Phosphate Burden Perturbed Intracellular Signaling: Quantitative Proteomics and Phosphoproteomics Analyses. Frontiers in Nutrition, 2022: p. 1101. [CrossRef]
- Graham, P.H. and C.P. Vance, Legumes: importance and constraints to greater use. Plant physiology, 2003. 131(3): p. 872-877.
- Madhu, M. and J.L. Hatfield, Interaction of carbon dioxide enrichment and soil moisture on photosynthesis, transpiration, and water use efficiency of soybean. Agricultural Sciences, 2014. 2014. [CrossRef]
- Guo, W., et al., Identification of temporally and spatially phosphate-starvation responsive genes in Glycine max. Plant Science, 2008. 175(4): p. 574-584. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z., et al., GmPTF1 modifies root architecture responses to phosphate starvation primarily through regulating GmEXPB2 expression in soybean. The Plant Journal, 2021. 107(2): p. 525-543. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W., et al., Soybean responds to phosphate starvation through reversible protein phosphorylation. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2021. 167: p. 222-234. [CrossRef]
- Fan, R., et al., Insights into the mechanism of phospholipid hydrolysis by plant non-specific phospholipase C. Nature Communications, 2023. 14(1): p. 1-11. [CrossRef]
- Yang, M., et al., Chloroplastic Sec14-like proteins modulate growth and phosphate deficiency responses in Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Physiology, 2023: p. kiad212. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q., et al., Flavonoids Mediate the Modulation of Phosphate Uptake and Phosphate-Starvation Signaling in Tobacco. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation, 2023: p. 1-11. [CrossRef]
- Li, J., et al., Phosphate deficiency modifies lipid composition and seed oil production in camelina. Plant Science, 2023. 330: p. 111636. [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, Y., K. Takano, and K. Saito, Lipidomic analysis of soybean leaves revealed tissue-dependent difference in lipid remodeling under phosphorus-limited growth conditions. Plant Biotechnology, 2017. 34(1): p. 57-63. [CrossRef]
- Ngo, A.H. and Y. Nakamura, Phosphate starvation-inducible GLYCEROPHOSPHODIESTER PHOSPHODIESTERASE6 is involved in Arabidopsis root growth. Journal of experimental botany, 2022. 73(9): p. 2995-3003. [CrossRef]
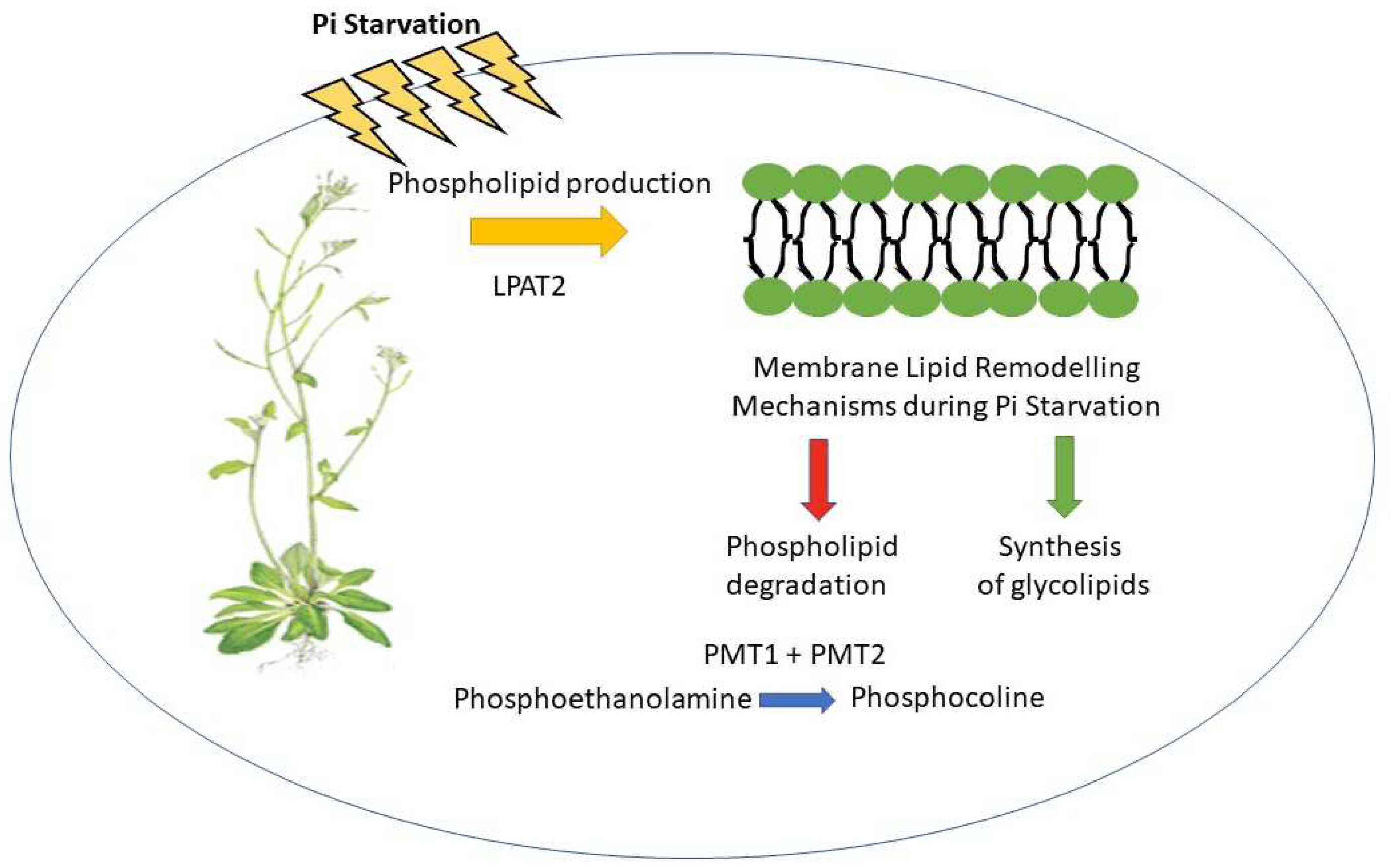
- Angkawijaya, A.E., V.C. Nguyen, and Y. Nakamura, Enhanced root growth in phosphate-starved Arabidopsis by stimulating de novo phospholipid biosynthesis through the overexpression of LYSOPHOSPHATIDIC ACID ACYLTRANSFERASE 2 (LPAT2). Plant, Cell & Environment, 2017. 40(9): p. 1807-1818.
- Ngo, A.H., et al., The phospho-base N-methyltransferases PMT1 and PMT2 produce phosphocholine for leaf growth in phosphorus-starved Arabidopsis. Journal of experimental botany, 2022. 73(9): p. 2985-2994. [CrossRef]
- Shears, S.B., Intimate connections: Inositol pyrophosphates at the interface of metabolic regulation and cell signaling. Journal of Cellular Physiology, 2018. 233(3): p. 1897-1912. [CrossRef]
- Cridland, C. and G. Gillaspy, Inositol pyrophosphate pathways and mechanisms: what can we learn from plants? Molecules, 2020. 25(12): p. 2789. [CrossRef]
- Adepoju, O., et al., Inositol trisphosphate kinase and diphosphoinositol pentakisphosphate kinase enzymes constitute the inositol pyrophosphate synthesis pathway in plants. Biorxiv, 2019: p. 724914.
- Laha, D., et al., Arabidopsis ITPK1 and ITPK2 have an evolutionarily conserved phytic acid kinase activity. ACS chemical biology, 2019. 14(10): p. 2127-2133. [CrossRef]
- Laha, D., et al., Regulation of plant biotic interactions and abiotic stress responses by inositol polyphosphates. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2022: p. 2835. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J., et al., Two bifunctional inositol pyrophosphate kinases/phosphatases control plant phosphate homeostasis. Elife, 2019. 8: p. e43582. [CrossRef]
- Land, E.S., et al., A role for inositol pyrophosphates in the metabolic adaptations to low phosphate in arabidopsis. Metabolites, 2021. 11(9): p. 601. [CrossRef]
- Kuo, H.F., et al., Arabidopsis inositol phosphate kinases IPK 1 and ITPK 1 constitute a metabolic pathway in maintaining phosphate homeostasis. The Plant Journal, 2018. 95(4): p. 613-630. [CrossRef]
- Gulabani, H., et al., Arabidopsis inositol polyphosphate kinases IPK1 and ITPK1 modulate crosstalk between SA-dependent immunity and phosphate-starvation responses. Plant Cell Reports, 2021: p. 1-17. [CrossRef]
- Laha, D., et al., VIH2 regulates the synthesis of inositol pyrophosphate InsP8 and jasmonate-dependent defenses in Arabidopsis. The Plant Cell, 2015. 27(4): p. 1082-1097. [CrossRef]
- Lv, Q., et al., SPX4 negatively regulates phosphate signaling and homeostasis through its interaction with PHR2 in rice. The Plant Cell, 2014. 26(4): p. 1586-1597. [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y., et al., Rice SPX6 negatively regulates the phosphate starvation response through suppression of the transcription factor PHR2. New Phytologist, 2018. 219(1): p. 135-148. [CrossRef]
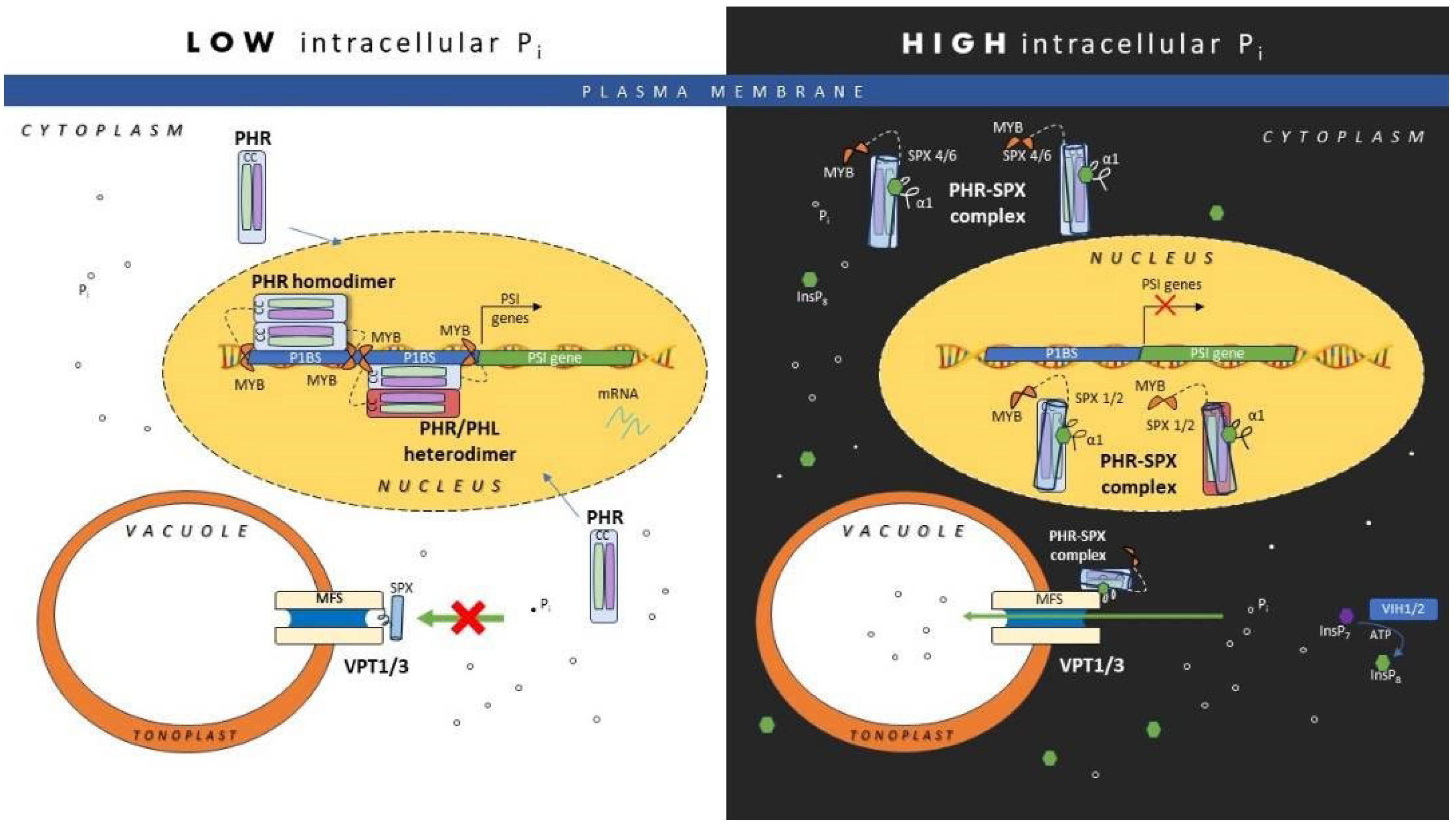
- Puga, M.I., et al., SPX1 is a phosphate-dependent inhibitor of Phosphate Starvation Response 1 in Arabidopsis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2014. 111(41): p. 14947-14952. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-W., et al., CRISPR/Cas9 nuclease cleavage combined with Gibson assembly for seamless cloning. BioTechniques, 2015. 58(4): p. 161-170. [CrossRef]
- Qi, W., et al., AtSPX1 affects the AtPHR1–DNA-binding equilibrium by binding monomeric AtPHR1 in solution. Biochemical Journal, 2017. 474(21): p. 3675-3687. [CrossRef]
- Du, H., et al., Genome-wide identification and characterization of SPX domain-containing members and their responses to phosphate deficiency in Brassica napus. Frontiers in plant science, 2017. 8: p. 35. [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.-Y., et al., Control of plant phosphate homeostasis by inositol pyrophosphates and the SPX domain. Current opinion in biotechnology, 2018. 49: p. 156-162. [CrossRef]
- Ried, M.K., et al., Inositol pyrophosphates promote the interaction of SPX domains with the coiled-coil motif of PHR transcription factors to regulate plant phosphate homeostasis. Nature communications, 2021. 12(1): p. 384. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J., et al., Mechanism of phosphate sensing and signaling revealed by rice SPX1-PHR2 complex structure. Nature communications, 2021. 12(1): p. 7040. [CrossRef]
- He, Y., et al., SPX4 interacts with both PHR1 and PAP1 to regulate critical steps in phosphorus-status-dependent anthocyanin biosynthesis. New Phytologist, 2021. 230(1): p. 205-217. [CrossRef]
- Osorio, M.B., et al., SPX4 acts on PHR1-dependent and-independent regulation of shoot phosphorus status in Arabidopsis. Plant physiology, 2019. 181(1): p. 332-352. [CrossRef]
- Han, B., et al., Identification of vacuolar phosphate influx transporters in Brassica napus. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2022. 45(11): p. 3338-3353. [CrossRef]
- Sun, G., et al., Genetically controlling VACUOLAR PHOSPHATE TRANSPORTER 1 contributes to low-phosphorus seeds in Arabidopsis. Plant Signaling & Behavior, 2023. 18(1): p. 2186641. [CrossRef]
- Diallinas, G., Understanding transporter specificity and the discrete appearance of channel-like gating domains in transporters. Frontiers in pharmacology, 2014. 5: p. 207. [CrossRef]
- Luan, M., et al., A SPX domain vacuolar transporter links phosphate sensing to homeostasis in Arabidopsis. Molecular Plant, 2022. 15(10): p. 1590-1601. [CrossRef]
- Jia, X., et al., Insights of intracellular/intercellular phosphate transport and signaling in unicellular green algae and multicellular land plants. New Phytologist, 2021. 232(4): p. 1566-1571. [CrossRef]
- Kimura, S. and K. Sakaguchi, DNA repair in plants. Chemical reviews, 2006. 106(2): p. 753-766.
- Jinek, M., et al., A programmable dual-RNA–guided DNA endonuclease in adaptive bacterial immunity. science, 2012. 337(6096): p. 816-821. [CrossRef]
- Nacry, P., et al., Major chromosomal rearrangements induced by T-DNA transformation in Arabidopsis. Genetics, 1998. 149(2): p. 641-650. [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K., et al., Decreased expression of a gene caused by a T-DNA insertion in an adjacent gene in arabidopsis. Plos one, 2016. 11(2): p. e0147911. [CrossRef]
- Gu, M., et al., Maintenance of phosphate homeostasis and root development are coordinately regulated by MYB1, an R2R3-type MYB transcription factor in rice. Journal of experimental botany, 2017. 68(13): p. 3603-3615. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P., Q. You, and M. Lei, A CRISPR/Cas9 deletion into the phosphate transporter SlPHO1; 1 reveals its role in phosphate nutrition of tomato seedlings. Physiologia plantarum, 2019. 167(4): p. 556-563. [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Torres, C.-A., et al., Phosphate availability alters lateral root development in Arabidopsis by modulating auxin sensitivity via a mechanism involving the TIR1 auxin receptor. The Plant Cell, 2008. 20(12): p. 3258-3272.
- Williamson, L.C., et al., Phosphate availability regulates root system architecture in Arabidopsis. Plant physiology, 2001. 126(2): p. 875-882. [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.Y., et al., Editing of the OsACS locus alters phosphate deficiency-induced adaptive responses in rice seedlings. Journal of experimental botany, 2019. 70(6): p. 1927-1940. [CrossRef]
- Xu, L., et al., Identification of vacuolar phosphate efflux transporters in land plants. Nature Plants, 2019. 5(1): p. 84-94. [CrossRef]
- Wu, P. and X. Wang, Role of OsPHR2 on phosphorus homoestasis and root hairs development in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant signaling & behavior, 2008. 3(9): p. 674-675. [CrossRef]
- Ueda, Y., T. Kiba, and S. Yanagisawa, Nitrate-inducible NIGT1 proteins modulate phosphate uptake and starvation signalling via transcriptional regulation of SPX genes. The Plant Journal, 2020. 102(3): p. 448-466. [CrossRef]
- Poza-Carrión, C. and J. Paz-Ares, When nitrate and phosphate sensors meet. Nature plants, 2019. 5(4): p. 339-340. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X., et al., The transcription factor NIGT1. 2 modulates both phosphate uptake and nitrate influx during phosphate starvation in Arabidopsis and maize. Plant Cell, 2020. 32(11): p. 3519-3534. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q., et al., Potential high-frequency off-target mutagenesis induced by CRISPR/Cas9 in Arabidopsis and its prevention. Plant molecular biology, 2018. 96: p. 445-456. [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y., et al., CRISPR-P: a web tool for synthetic single-guide RNA design of CRISPR-system in plants. Molecular plant, 2014. 7(9): p. 1494-1496. [CrossRef]
- Xie, K., J. Zhang, and Y. Yang, Genome-wide prediction of highly specific guide RNA spacers for CRISPR–Cas9-mediated genome editing in model plants and major crops. Molecular plant, 2014. 7(5): p. 923-926. [CrossRef]
- Meng, X., et al., Robust genome editing of CRISPR-Cas9 at NAG PAMs in rice. Science China. Life Sciences, 2018. 61(1): p. 122-125. [CrossRef]
- Cong, L., et al., Multiplex genome engineering using CRISPR/Cas systems. Science, 2013. 339(6121): p. 819-823. [CrossRef]
- Engler, C. and S. Marillonnet, Golden gate cloning. DNA cloning and assembly methods, 2014: p. 119-131.
- Van Vu, T., et al., Challenges and perspectives in homology-directed gene targeting in monocot plants. Rice, 2019. 12(1): p. 1-29. [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.B., et al., Increasing the genome-targeting scope and precision of base editing with engineered Cas9-cytidine deaminase fusions. Nature biotechnology, 2017. 35(4): p. 371-376. [CrossRef]
- Komor, A.C., et al., Programmable editing of a target base in genomic DNA without double-stranded DNA cleavage. Nature, 2016. 533(7603): p. 420-424. [CrossRef]
- Rees, H.A., et al., Improving the DNA specificity and applicability of base editing through protein engineering and protein delivery. Nature communications, 2017. 8(1): p. 15790. [CrossRef]
- Bharat, S.S., et al., Base editing in plants: Current status and challenges. The Crop Journal, 2020. 8(3): p. 384-395. [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y. and J.-K. Zhu, Precise editing of a target base in the rice genome using a modified CRISPR/Cas9 system. Molecular plant, 2017. 10(3): p. 523-525. [CrossRef]
- Fontenot, E.B., et al., Increased phosphate transport of A rabidopsis thaliana P ht1; 1 by site-directed mutagenesis of tyrosine 312 may be attributed to the disruption of homomeric interactions. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2015. 38(10): p. 2012-2022.
- Anzalone, A.V., et al., Search-and-replace genome editing without double-strand breaks or donor DNA. Nature, 2019. 576(7785): p. 149-157. [CrossRef]
- Zhan, X., et al., Genome editing for plant research and crop improvement. Journal of integrative plant biology, 2021. 63(1): p. 3-33. [CrossRef]
- Chen, A., et al., Identification of two conserved cis-acting elements, MYCS and P1BS, involved in the regulation of mycorrhiza-activated phosphate transporters in eudicot species. New Phytologist, 2011. 189(4): p. 1157-1169.
- Feng, Z., et al., Efficient genome editing in plants using a CRISPR/Cas system. Cell research, 2013. 23(10): p. 1229-1232. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J., et al., CRISPR-Cas9 based genome editing reveals new insights into microRNA function and regulation in rice. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2017. 8: p. 1598. [CrossRef]
- Liu, P., et al., A putative high affinity phosphate transporter, CmPT1, enhances tolerance to Pi deficiency of chrysanthemum. BMC plant biology, 2014. 14(1): p. 1-9. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z., et al., SPX proteins regulate Pi homeostasis and signaling in different subcellular level. Plant signaling & behavior, 2015. 10(9): p. e1061163. [CrossRef]
| Type of Factor | Transcription | Species | Responses | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MYB Family | MYB-CC (R1-type) - PHL1, PHL2, PHL 3 and PHL4 | Arabidopsis | Pi starvation | Bustos at al., (2010); Sun et al., (2016); Wang et al., (2018) |
| MYB-CC (R2R3-type) -MYB2 | Pi starvation, salt/ABA/drought response | Baek et al., (2013) | ||
| MYB-CC (R2R3-type) - MYB62, | Pi starvation, GA defiency, root development | Devaiah et al., (2009); Qi et al., (2021) | ||
| MYB-CC (R2R3-type) -MYB2P-1, MYB4P | Rice | Pi starvation | Yang et al., (2014); Yang et al., (2018) | |
| W-box and E/G-box, the binding site for PHR | Elaeis guineensis | Pi Starvation, root development | Ahmadi et al., (2018) | |
| WRKY Family | WRKY6 | Arabidopsis | Pi starvation, anthocyanin accumulation and root hair formation | Chen at al., (2009) |
| WRKY42 | Pi starvation | Su et al., (2005) | ||
| WRKY46 | Pi Starvation, root development | Li et al., (2021) | ||
| WRKY75 | Pi starvation | Devaiah et al., (2009) | ||
| bHLH Family | bHLH32 | Arabidopsis | Pi starvation, anthocyanin accumulation, root hair formation | Chen et al., (2007); Yeh et al., (2020) |
| ZFP Family | Zinc Finger (C2H2-type) -ZAT6 | Arabidopsis | Pi starvation | Devaiah et al., (2009) |
| Zinc Finger (C2H2-type) -ZFP5 | Pi starvation, regulation of trichome and root hair development. | Huang et al., (2019) |
| Target | Gene/ protein |
Function | Effects of targeted editing | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SlPHO1;1 | Gene | Regulates root-to-shoot phosphate transport | Decreased shoot fresh weight, increased root biomass, higher root-to-shoot ratio | Zhao et al., (2019) |
| OsACS1 and OsACS2 | Gene | Regulates ethylene biosynthesis during low Pi | Altered root system architecture | Lee et al., (2019) |
| OsVPE1 and OsVPE2 | Transporter | Vacuolar Pi efflux transporters | Higher accumulation of vacuolar Pi content under low Pi stress than the wild type | Xu et al., (2019) |
| NIGT1 and NIGT1.2 | Trancriptional repressor | Negative regulator of SPX to activate PHR expression | Reduced P uptake and improved N under Pi-deficient conditions | Wang et al., (2020b) |
| OsPHR1, OsPHR2, OsPHR3 | Transcription factor | Regulates expression of miR399, which reduces the expression of a negative regulator, PHO2 | Growth retardation under low Pi conditions | Guo et al., (2015) |
| MYB1 | Transcription factor | Maintain phosphate homeostasis and root development | Enhanced Pi uptake and accumulation, altered expression of a subset of genes associated with Pi transporters and Pi starvation signaling | Gu et al., (2017) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





