1. Introduction
The effect of oxidation on the creep response of titanium and its alloys is a subject that aroused keen interest among investigators, due to the importance of these materials for medium and high temperature applications. Detailed studies, such as [
1], just to quote a single example, showed that oxidation reaction is very fast during the initial stage of the process and leads to the formation of oxide layers composed of TiO
2 structures. After this initial stage, the oxidation kinetics become very slow up to 650°C. In addition, a hard and brittle α-case rich in oxygen forms [
2]. In castings, the α-case is the result of the reaction between liquid Ti metal and the mold wall, that leads to the early formation of TiO
2 and then of a hard solid-solution of oxygen into titanium on the surface of the part. The case is very brittle, and its cracking during straining causes early fracture of the sample [
2]. This fact is of some relevance when creep tests on Ti and its alloy are carried out in air, since high temperature exposure also causes the penetration of oxygen into the alloy and the formation of the α-case [
3]. Oxygen exposure results in a reduction of the minimum creep rate [
3,
4], although an opposite behavior was once observed [
5], by testing a single experimental condition. In this context, the analysis of the creep response in air of commercially pure titanium remains an interesting subject to be dealt with.
This study is part of a wider research aimed at clarifying the effect of friction stir welding (FSW) [
6] on the creep response in air of commercially pure Titanium. To properly identify the effects of the extensive microstructural changes introduced by FSW on the creep response, the independent effect of oxidation should be preliminary quantified. This part of the study aimed at investigating this phenomenon, trying to quantify the effect of oxygen enrichment on the minimum creep rate dependence on stress and temperature.
2. Materials and Methods
The material investigated in the present study was commercially pure Ti – grade 2 (CT-Ti Gr.2, UTS of 500 MPa) in form of a plate 3 mm thick. Dog-bone creep samples with the geometry illustrated in [
6] (3 mm x 3 mm square section, 25 mm gauge length) were creep-tested in constant load machines at 550, 600 and 650°C. Two types of experiments were carried out: constant load experiments (CLEs) and variable load experiments (VLEs). In most of the CLEs, the samples were loaded after soaking for 0.5 h at the testing temperature, and the load was maintained until interruption of the tests, well in tertiary stage but before fracture. Two CLE samples were annealed at the test temperature (650°C) for 70 h before loading. In VLEs, the sample was loaded after soaking, but the initial load was maintained until the minimum creep rate was reached and then increased until a new value of the minimum creep rate was attained.
To maintain a homogeneous heating profile in the furnace, the test temperature was measured using four thermocouples. Elongation was continuously measured using a linear variable displacement transducer (LVDT). All creep experiments were carried out in air.
Crept samples were mechanically ground and polished with a colloidal suspension and etched by Kroll’s reagent (100 mL H2O + 2 mL HF + 4 mL HNO3), and then observed by a Leica DMi8 (Leica Microsystems, Wetzlar, Germany) optical microscope.
Microhardness measurements were carried out on sample heads, under a 25 g load, i.e., in unstrained portions of the specimen, to evaluate the hardening effect of oxygen and its penetration.
3. Results
3.1. Creep response
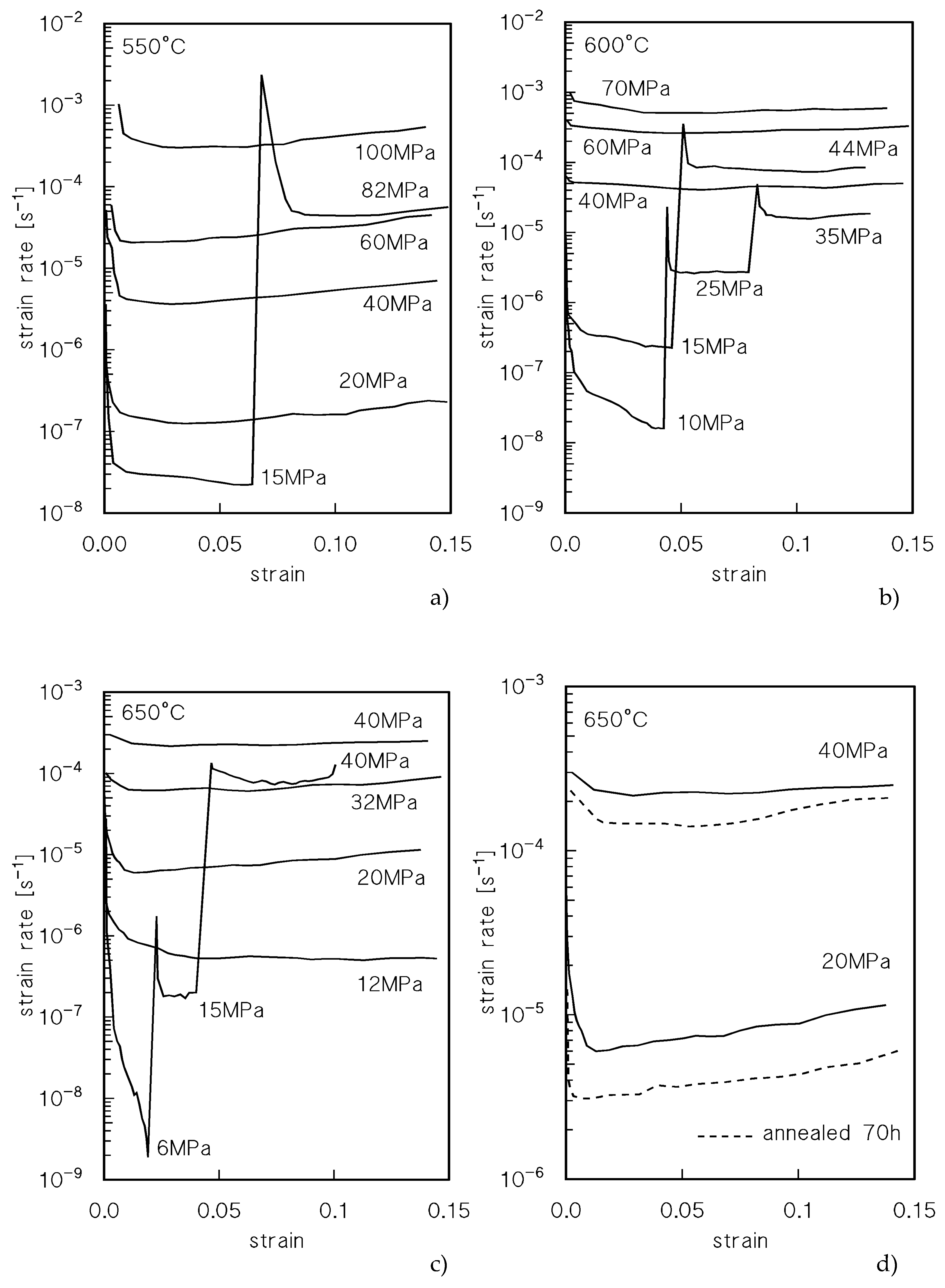
Figure 1 plots the strain rate
vs strain curves for CLEs and VLEs; the stress values are the nominal ones, calculated with reference to the initial area of the transversal sample section. The creep curves exhibited the usual conventional three-stage shape, with a well-defined primary region, a minimum creep rate range and a prolonged tertiary stage. An interesting feature is that after load-changes in VLEs, the minimum creep rates are usually well below those recorded under similar loads in CLEs. This phenomenon is well apparent at 600°C and at 650°C, see, for example, the VLE at the highest temperature, where the strain rate under 40 MPa (nominal; the true stress value was 42.9 MPa) is much lower than that measured in a CLE under the same nominal stress. The same behavior is illustrated in
Figure 1d, which shows the CLE tests carried out under 20 and 40 MPa (nominal) after 0.5 and 70 h soaking at testing temperature. The samples annealed for 70 h exhibit substantially lower values of the strain rate at a given stress.
Table 1 summarizes the experimental values of the minimum creep rate (
).
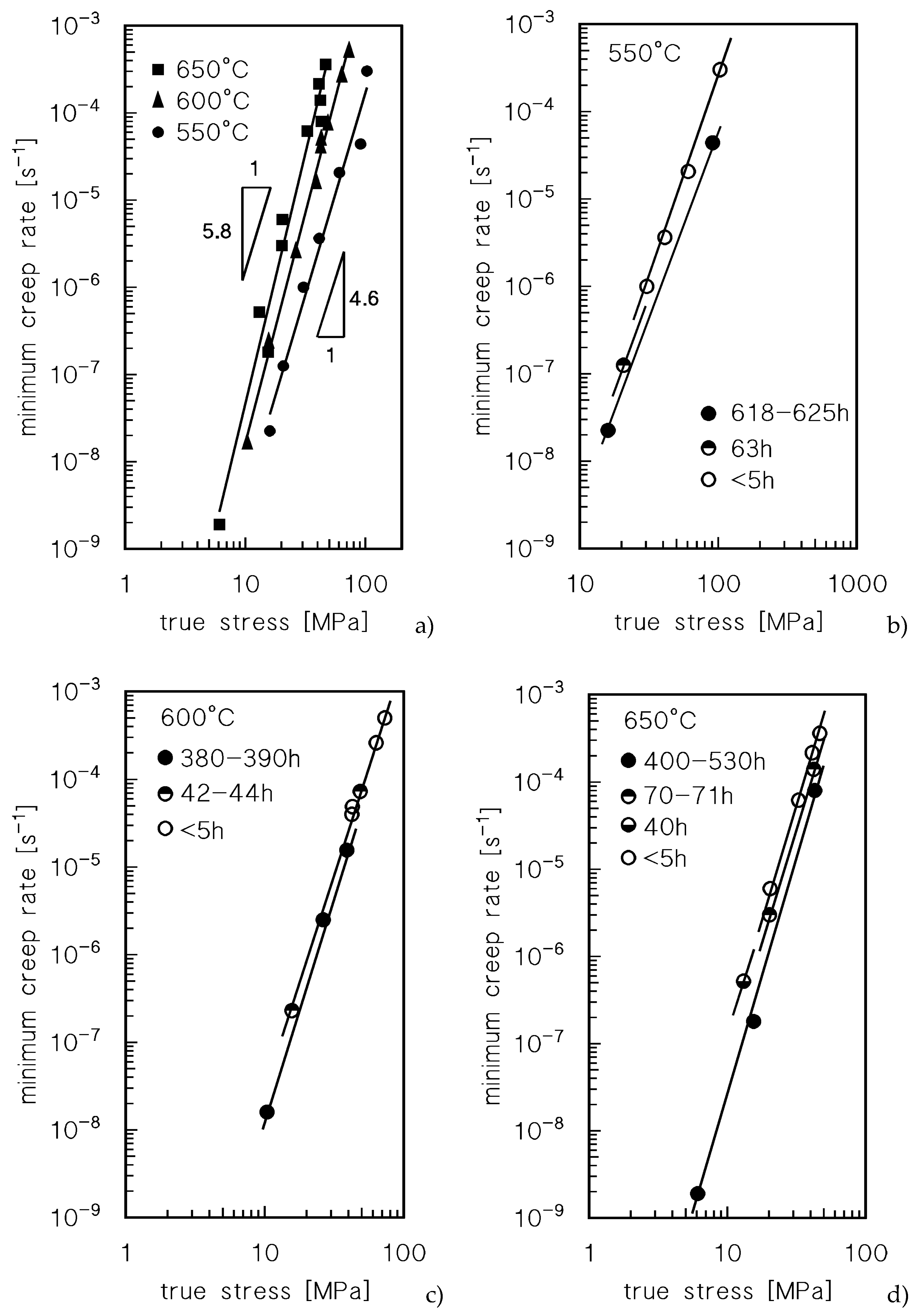
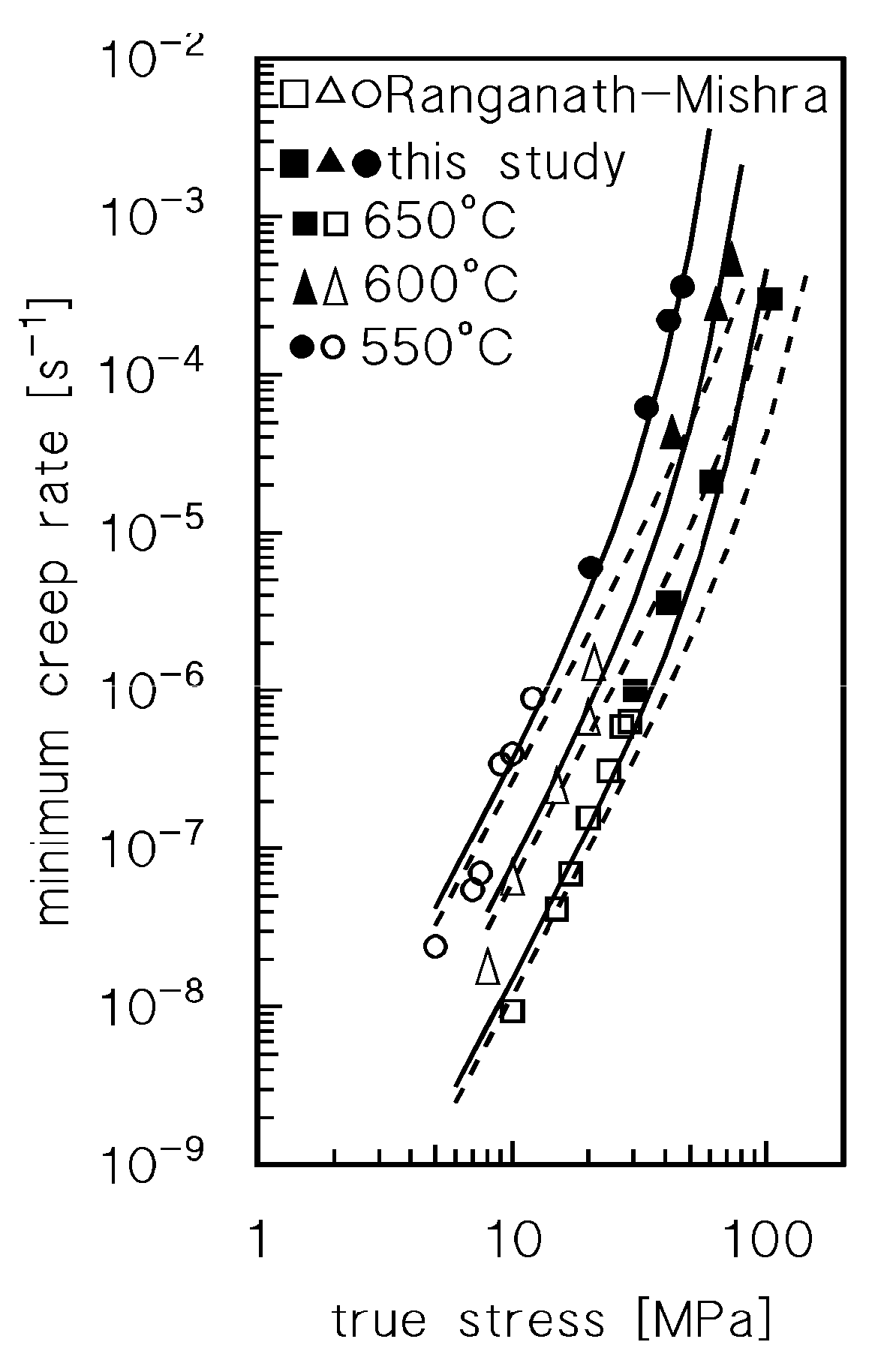
Figure 2 plots the minimum creep rate as a function of the true stress (
σ ), i.e., the stress corresponding at the strain in which the minimum in creep rate was measured.
Figure 2a does not discriminate between the data obtained by CLEs or VLEs and seems to suggest that the usual power law
is substantially obeyed. A major point is that the stress exponent n, quite unusually, increases with temperature, from 4.6 at 550°C to 5.8 at 650°C. A clearer picture of the material response, on the other hand, can be obtained by differentiating the symbols of the experimental data, according to the duration of high-temperature exposure they experienced when the considered minimum creep rate was recorded (Figures 2 b-d).
Figure 2 clearly suggests that indeed the experimental data roughly align on parallel straight lines, which shift toward lower strain rates when time of exposure increases. Thus, both
Figure 1 and
Figure 2 demonstrate that high-temperature exposure results in a substantial hardening of the sample. This effect can hardly be explained in terms of microstructural mechanisms in this pure metal unless the effect of oxidation in considered. Thus, a more detailed and quantitative analysis of the hardening effect of oxidation was required.
3.2. Oxidation and hardening effect: microhardness profiles
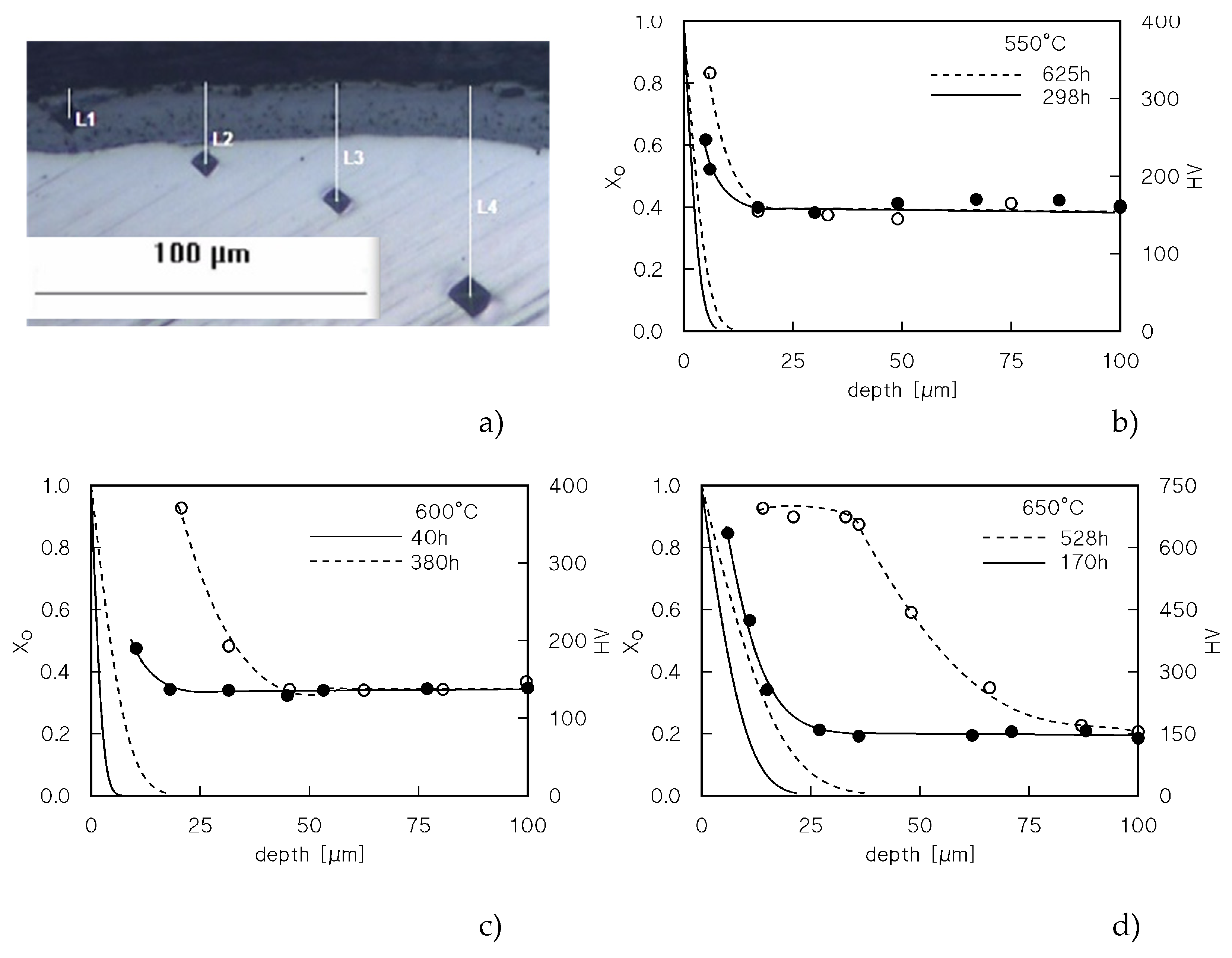
Figure 3a shows an example of the microhardness measurements on the heads of the samples that experienced a long exposure at high temperature. As expected, the highest was the temperature and the longest was the duration of exposure, the highest was the hardness of the surface and the thicker was the hardened zone. Formation of a hard and brittle oxide surface layer at 650°C for the longest times of exposure, on the other hand, is easily noticeable in
Figure 3a. This oxide layer was much thinner or even unnoticeable for lower temperatures and/or shorter times of exposure.
The hardening effect illustrated in
Figure 3 is fully consistent with similar evidence in the literature, which demonstrates that this behavior is due to oxygen diffusion in Ti (see, for example, [7, 8]). Thus, a correct estimation of oxygen penetration in the material becomes an interesting point to be analyzed.
The simplest model for oxygen penetration [
9] is the solution of Fick’s second law in semi-infinite material, which assumes a constant concentration at the surface and a constant diffusion coefficient, i.e.
where
C0 is the initial oxygen concentration in the metal,
Cs is the surface concentration,
Cx is the concentration at the distance
x from the surface,
t is time and
D is the diffusion coefficient of oxygen in Ti, i.e.
where
D0=2x10
-7 s
-1 and
Q=169 kJ mol
-1 [
10].
Figure 3, which also plots the
XO variation with the distance from the surface, shows that the increase is microhardness is notable even where the enrichment in oxygen is so low to be unnoticeable.
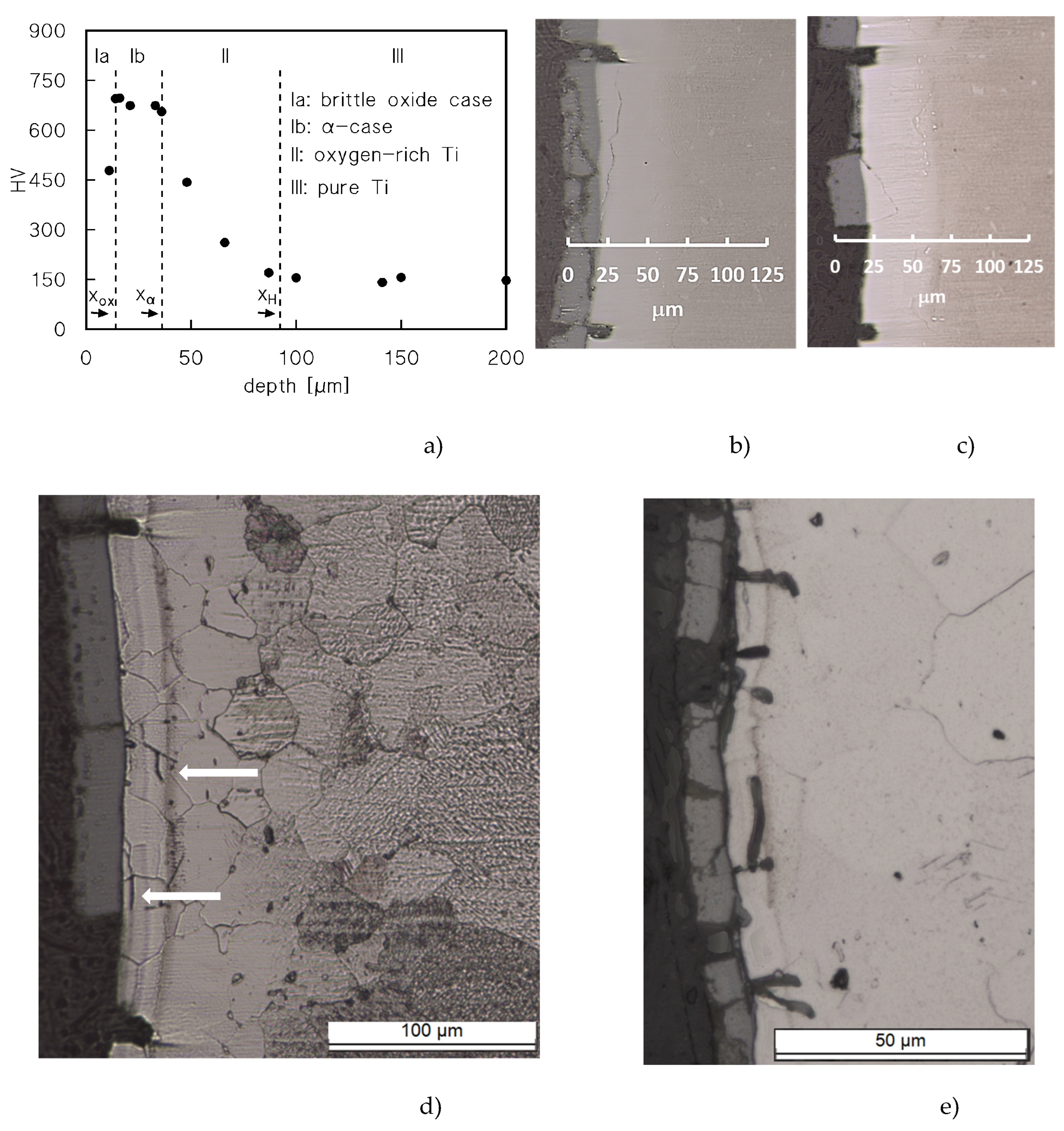
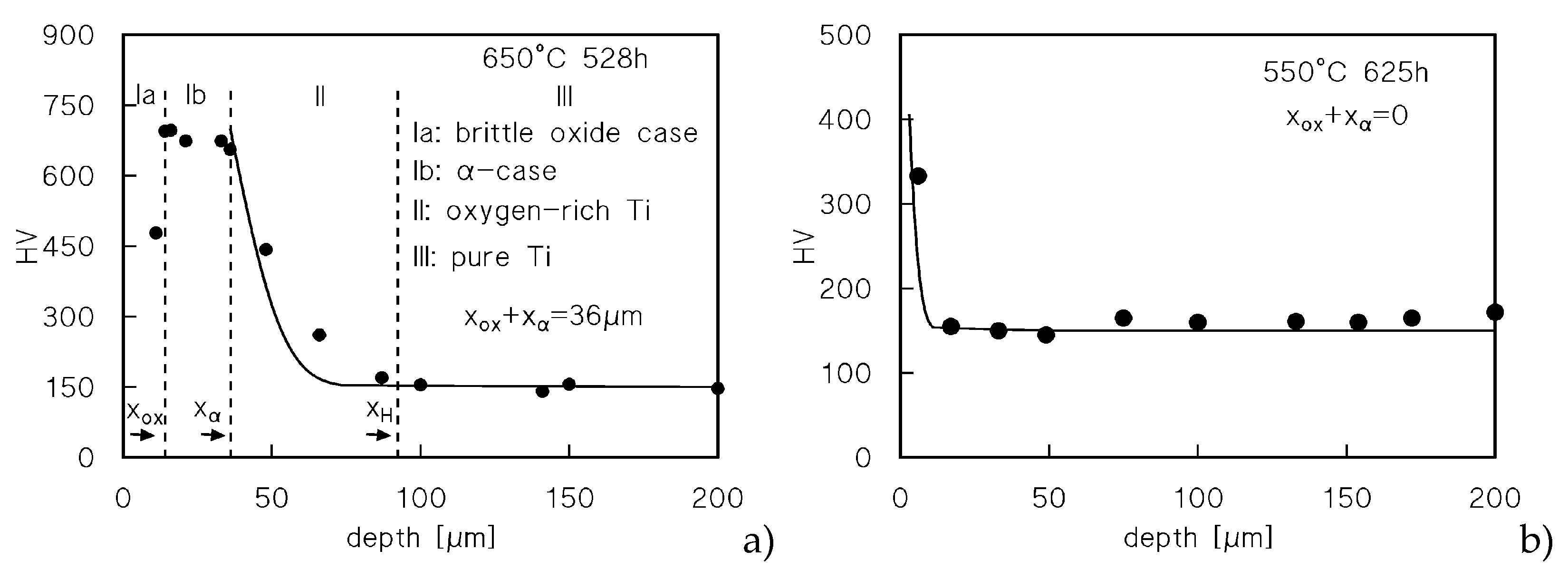
Figure 4a re-plots the hardness profile for the sample-head that experienced the longest permanence at 650°C (528 h). The Figure also includes the typical value of the hardness in correspondence of the oxide surface layer, omitted in
Figure 3d.
The Figure shows the existence of four different zones: i. the oxide surface layer (Ia), which cracks even under the HV indenter, and, possibly for this reason, exhibits a relatively low HV value; ii. an intermediate zone (Ib) of almost constant and very high (roughly 700 HV) microhardness; these HV values attest a brittle nature [
11,
12], hardly capable of tolerating any notable deformation [
2]; iii. a zone of decreasing hardness (II); iv: the un-oxidized core of the sample. For the sake of clarity and simplicity, we will assume in the following paragraphs that zone-Ib corresponds to what is usually called “α-case” in Ti and Ti-alloys. Figures 4b-d show extensive cracking in the oxide layer, which is detached from the underlying oxygen-rich zones. Many wide cracks, perpendicular to the loading direction, pass through zones Ia and Ib. Finer cracks also develop in zone Ib, but propagate along directions parallel to the surface. Figures 4d shows the different metallographic contrast between the base metal and the oxygen-rich zone (the bright area) after etching. The bright area is indeed much thicker (100 μm) than the estimate of the penetration of oxygen as provided by Eqns.2-3 (≈40 μm). The situation is similar in the sample tested under 20 MPa after a 70 h-soaking at 650°C (
Figure 4e). Again, the oxide layer is heavily damaged, and cracks propagate for roughly 10 μm in the oxygen-rich zone.
4. Discussion
4.1. Strengthening role of oxygen-rich layers
The main issue to properly address the role of the different layers is the identification of the strengthening contribution of zones Ia, Ib and II. Early cracking of the undeformable surface layers during creep straining should significantly reduce their strengthening role. In particular, the oxide layer largely detaches from the substrate during creep (
Figure 4), and for this reason its strengthening contribution can be thought to be negligible. On the other hand, cracking in the scarcely deformable layer-Ib during early creep deformation, also illustrated in
Figure 4b-e, interrupts the local material continuity, undermining its load-bearing capacity [
2]. Thus, also zone-Ib should give a negligible contribution to the creep response in correspondence of the minimum creep rate. This analysis is fully consistent with Rosen and Rottem findings [
3]. These authors removed from few oxidized samples what they identified as the “α-case”, i.e., presumably, what corresponded mostly to zone-Ib in
Figure 4. The identification of the Rosen-Rotten “α-case” with zone-Ib is justifiable, since they were fully aware that the microhardness descended toward the original value of the unoxidized Ti-6Al-4V (zone-II in
Figure 4a) beyond the depth of their “α-case”. Its removal from the exposed specimen did not significantly change the minimum creep rate, since
remained roughly 1/3 of that measured in absence of oxidation, as in samples which maintained their α-case. This fact proved that the real strengthening effect was played by the oxygen-reach zones below the α-case.
Vaché and Monceau [
9] proposed a model equation for the decrease in hardness with distance from the surface of oxidized material in the form:
where
HV0 is hardness of the metal with initial oxygen concentration,
HVmax is the maximum hardness,
HVx is the hardness at the distance x from the point where
HVmax is measured, usually the surface. Equation 4 implies a parabolic relationship between microhardness and oxygen concentration, so that a constant HV corresponds to a constant oxygen content. On the other hand, based on the above reasoning, both the oxide layer (thickness
xox) and the α-case (thickness
xα) do not contribute to creep strengthening. Thus, Eqn.4 could be tentatively used to quantify the hardness variation with depth in zone-II, under the layers of depth (
xox+
xα).
Figure 5 plots the variation of hardness with depth according to Equation 4, with
HVmax=700 HV and
HV0=150 HV. The correlation between the curves and the experimental profiles is reasonably good, so Equation 4 can be used to estimate the depth of the hardened oxygen-rich zone-II which causes a significant reduction of the creep rate. The limit for this layer was here tentatively quantified as the
x value corresponding to
XHV=0.01.
4.2. Constitutive equation for CP-Ti (no or minor effects of oxidation)
A very good description of the creep response of a dataset of pure Ti samples [
14] was recently provided by an equation whose derivation was illustrated in detail in [15, 16]. This equation assumes the form:
where
D0L=1x10
-8 m
2s
-1 and
QL=193 kJ mol
-1 describe the self-diffusion mechanism in low-purity Ti through Eqn. 3 [
17],
G is the shear modulus,
b is the length of the Burgers vector (2.95x10
-10 m),
T is the absolute temperature,
k is the Boltzmann constant,
R is the gas constant,
A=40 [
15]. The
Rmax parameter was tentatively obtained as follows [
15]:
where
GRT and
GT were the shear moduli at room temperature and at testing
T, respectively.
Figure 6 plots the minimum creep rate
vs stress curves calculated by Eqn. 5 with
A=40 and
Rmax from Eqn.6 [
15], compared with the data from [
14] and the results of the present study from CLEs of short durations, where oxidation can be reasonably assumed to have minor effects. In case of the samples tested in [
14], oxidation could be in first instance neglected, due to the substantially larger size of the samples (5 mm in diameter; this point will be further discussed in the following). The Figure demonstrates that the constitutive equation, in this form, strongly underestimates the creep rate in the high stress regime. Reconsidering the quantification of the
Rmax term is thus needed; a much better description was indeed obtained with
where UTS
T is the tensile strength at testing temperature, and
A=50. This simple modification led to a much better description of the creep response of CP-2 Ti in the intermediate and high strain rate regimes (solid lines in
Figure 5).
The next step was the study of the effect of oxidation on the value of the minimum creep rate for longer test duration.
4.2. Quantification of the effect of oxidation on creep response
The evidence on the marked differences in creep rate between CLEs and VLEs provided in the previous section, demonstrates that oxidation results in an increase in microhardness and in a reduction in creep rate under a given stress. Pure Ti, in proximity of the surface, significantly enriches in oxygen as time of exposure increases. Thus, a “hard zone” (II in
Figure 4), not homogeneous in composition, encloses a core of pure Ti. It is obvious that such a complex material can be hardly modelled unless a strong simplification of its structure is applied. In the present study, the real material has been very simply modelled as presented in
Figure 7. Following this approach, based on the well-known composite-material-model (CMM), the soft core of the sample (unmodified pure Ti) is surrounded by a hard layer of oxygen-rich titanium of homogeneous composition and properties. The latter assumption is thus the major departure from the real situation, since in the crept samples the oxygen content progressively reduces as the distance from the surface increases.
The depth of the hard surface layer,
xH, can be approximatively estimated by Eqn.4, in correspondence of the minimum creep rate. The volume fraction of the hard zone, the surface layer rich in oxygen, can be thus expressed as
where l is the length of side of the square sample section, here taken= 3 mm, thus neglecting the effect of elongation, and fS is the volume fraction of the unmodified Ti soft zone.
In the CMM of
Figure 7, both the hard and soft zones deform in parallel with the same creep rate, under different local stresses (
σH and
σS respectively). As a result, load is transferred from the soft to the hard portions of the sample, giving,
To make a proper use of Eqn.9, the constitutive equation correlating stress, temperature and strain rate for the hard zone should be available. This is a major – and practically unsolvable- problem, due to the complete lack of information about the creep response of O-rich titanium. Nevertheless, one can reasonably assume that the model-material for the hard zone creeps according to the classical phenomenological equation:
where
AH and
n, in this simplified approach, are constant, and
QH is an apparent activation energy. For the sake of simplicity, it will be here supposed that also
QH is stress and temperature independent. In case of the VLE at 650°C, the 3 data points correspond to times of exposure of 400, 513 and 528 h, while for the VLE at 550°C the two values of the minimum creep rate were obtained after 618 and 632 h. Equation 4 was then used to estimate
xH for
XHV =0.01 after 450 h at 650°C, and 620 h at 550°C, which gave
fH and
fS. For a given strain rate,
σS is obtained directly from Eqns. (5) and (7). The model parameters
AH,
n and
QH were thus tentatively estimated by a fitting procedure of the VLE data at 650°C and 550°C. A good fit of the VLE data at 650 and 550°C was obtained by taking
n=10,
AH=1x10
8 s
-1 MPa
-10 and
QH=620 kJ mol
-1. Once estimated the parameters in Eqn.10, the CMM can be easily used to obtain the model curves at 550, 600 and 650°C for different exposure durations.
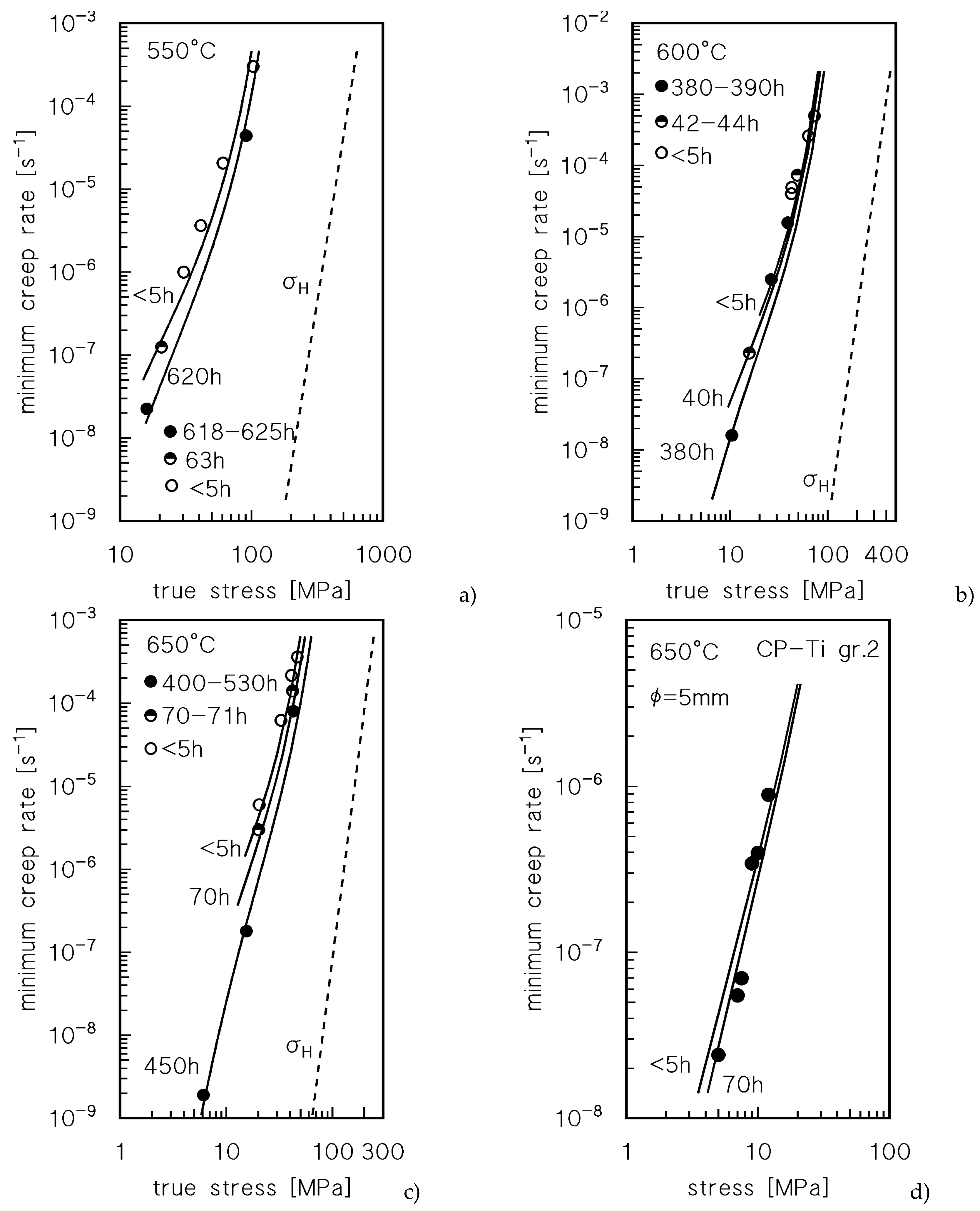
Figure 8 plots a direct comparison between experimental data and model curves. The curves for exposures shorter than 5 h were calculated by assuming that oxidation did not occur. In general term, the accuracy of the model is more than acceptable.
Figure 8d reports the experimental data from [
14]. The authors did not specify if a protective atmosphere was used, which led one to suppose that testing was performed in air. Unfortunately, no information on the time of exposure in correspondence with the minimum creep rate can be deduced from the source, since the creep curves reported in [
14], one CLE (interrupted after 50 h, estimated strain rate =5x10
-8 s
-1) and one VLE (load change after 70 h, estimated strain rate =2x10
-8 s
-1), indeed applied to a composite. Nevertheless, one can reasonably assume that a similar testing scheme was followed when investigating unreinforced Ti, that is, for minimum creep rates in the range from 2x10
-8 to 5x10
-8 s
-1, the time corresponding
should range between 50 and 100 h. If 70 h for the time of exposure is used to estimate
xH and the relevant
fH volume fraction in a sample 5 mm in diameter, as used in [
14], the model curve reported in
Figure 8d is obtained. The description of the low-stress experimental data is indeed quite accurate.
4.2. Critical assessment of the model
The CMM in the form presented here was based on a highly simplified picture of the real situation, and, for this reason, it did not have the ambition to provide a physically- based description of creep of oxygen-rich Ti (a task otherwise impossible to be fulfilled, due to the already mentioned lack of experimental data). Thus, another obvious question could be raised: is the quantification of the creep strength of the hard zone, shown in
Figure 8, reasonable?
To answer this question, we must firstly address the problem of the possible strengthening mechanisms operating in the oxygen-rich zones. Even a relatively moderate content of oxygen (0.8%) increases the UTS of pure Ti well above 1000 MPa, with a hardness just below 400 HV [
19,
20]. According to
Figure 3,
Figure 4 and
Figure 5, the oxygen-rich zone-II exhibits experimental microhardness values in the range between 200 and 600 HV. For reference purpose, Ti-6Al-4V alloy [
15,
16] usually exhibits an UTS close to 1000 MPa. This fact implies that oxygen-rich pure-Ti is assimilable, in terms of mechanical properties, to more complex industrial alloys. The source of this remarkable strength is usually attributed to solid solution hardening [
11], namely, it may depend on a strong interaction between screw dislocation cores and oxygen atoms. In addition, a recent study provided evidence that even small additions (0.15%) of oxygen cause the formation of ordered precipitates with a Ti
6O-type structure [
12]. These ordered precipitates were observed also in CP-Ti grade 2 [
12]. Thus, the oxygen-rich layer is indeed a very complex material, where solid solution hardening and possibly particle-dislocation interaction play a significant role in enhancing strength at room and high temperatures. In the present study, the complex oxygen-rich zone-II was “replaced” by a model-material with a homogeneous O content, well above 0.15%, and with different
xH thicknesses. Due to the high oxygen content, solid solution should be surely operative there. If also the ordered precipitates play any hardening role, which is realistic, the use of the phenomenological Eqn.10 for the model-material should indeed result in high values of the apparent stress exponent and activation energy (
n and
QH) [
16], exactly as those here tentatively estimated.
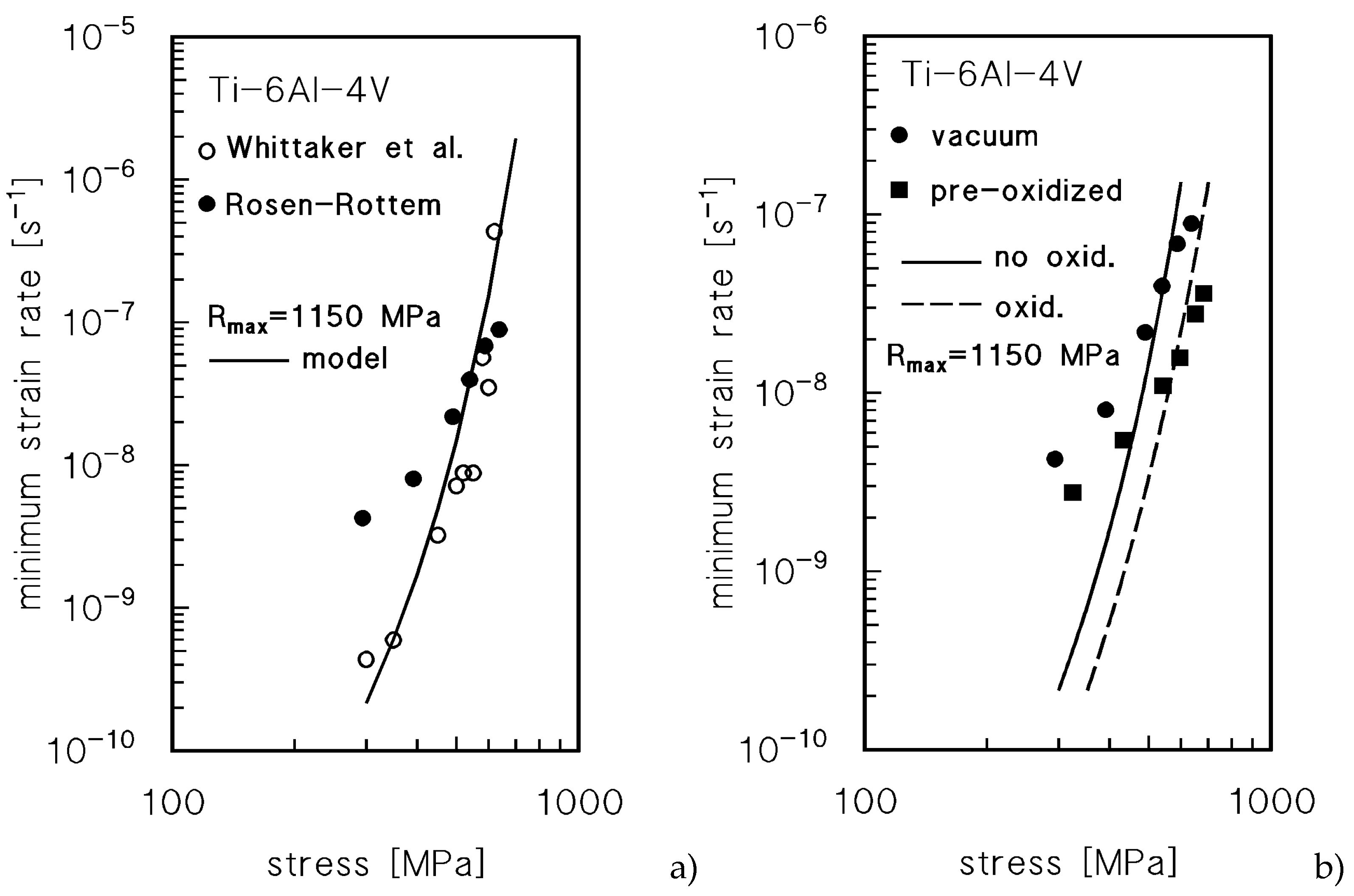
Let one suppose that the creep properties of the oxygen-rich layers in Ti-6Al-4V are reasonably close to those here calculated for pure Ti. Rosen and Rottem investigated the effect of a pre-oxidation of 3 h in air at 900°C on the creep response at 400°C of the Ti-6Al-4V [
3]. Pre-oxidation produced an “α-case” ≈140 μm thick. The samples were tested by VLE, but creep deformation did not exceed a total strain of 1%, which suggests a possible overestimation of the minimum creep rate under the lowest stresses - see, for example, the shape of the strain-rate
vs strain curves in [
15,
16]. The Rosen and Rottem creep data for the alloy annealed at 900°C in vacuum were thus compared with those published by Whittaker et al. [
21],
Figure 9a. The Figure also plots the model curve for Ti-6Al-4V, calculated, as above, by Eqn.5, with the same values of the various parameters used in [
15] (
D0L=1.4x10
-3 m
2s
-1,
QL=303 kJ mol
-1 [
17],
Rmax≈1150 MPa) and
A=50. The model curve as obvious does not consider the effects of oxidation. The Figure shows that the agreement between the model curve and the data from [
21] is more than tolerable. In addition, it confirms that the values of the low-stress minimum creep rate calculated by Rosen and Rottem by VLEs should be treated cautiously, although they still represent an invaluable source of information on the behavior of the alloy in oxidized and non-oxidized states (
Figure 9b). The minimum creep rate values for exposed material are significantly lower than those for the material annealed in vacuum.
Now, let us assume, as suggested in the previous section and following Rosen and Rottem reasoning, that the α-case, i.e. the more superficial O-rich layer, Ib, does not significantly affect the minimum creep rate values of the exposed alloy, in our view because, as the strain accumulates, cracks develop in this zone. No information was provided on the oxide scale, so it will be here neglected. The cracks do not usually penetrate beyond the α-case in creep tests of relatively short duration [
22]. This thick layer could be thus even removed, without significantly influencing the creep response. The thickness of the oxygen-rich zone II after 3 h at 900°C, given by Eqn.4 for
XH=0.01, is
xH=44 μm. The CMM (Eqns.8-10) provides the broken curve in
Figure 9b for the exposed material, to be compared with the model curve for the alloy annealed in vacuum (no oxidation, same curve in
Figure 9a). Further oxidation at the testing temperature, 400°C, could be reasonably neglected. If one considers the predictable overestimation of the creep rates under the lower stresses in [
3], the agreement between model curves and experiments is notably accurate. We have thus a direct confirmation of the adequacy of this simplified approach to estimate the effect of oxidation for Ti alloys.
Conclusions
The creep response in air of CP-2 titanium was investigated at temperatures of 550, 600 and 650°C. Experimental data demonstrated that high-temperature exposure resulted in a marked decrease of the creep rate, suggesting a hardening role of the oxygen-rich layer formed during tests. The growth of the hard superficial layer was thus modelled as a function of temperature and time of exposure. The creep sample was modelled as a composite formed by an inner soft core (pure titanium) and a hard outer zone rich in oxygen and homogeneous in composition and properties. Fitting of two variable-load experiments at 550 and 650°C were used to quantify the creep response of the hard-zone. The resulting composite model, although based on an overly simplified description of the real structure, was able to provide an excellent description of the material response in all the investigated range of temperatures and test durations. The model also provides a quite reliable description of the creep response of more complex Ti-alloys, such as the Ti-6Al-4V.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.Regev and S.Spigarelli.; methodology, S.Spigarelli; validation, M.Regev and S.Spigarelli; formal analysis, M.Regev, A.Santoni and S.Spigarelli; investigation, M.Regev, A.Santoni and S.Spigarelli; resources, M.Regev; data curation, S.Spigarelli; writing—original draft preparation, S.Spigarelli ; writing—review and editing, M.Regev and S.Spigarelli; visualization, M.Regev and S.Spigarelli; supervision, S.Spigarelli; project administration, M.Regev; funding acquisition, M.Regev. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research project is partially funded by Braude College, Karmiel, Israel.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The assistance of N. Navot with welding the material is highly appreciated
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Gemelli, E.; Camargo, N.H.A. Oxidation kinetics of commercially pure titanium. Revista Matéria, 2007, 12, 525–531, http://wwwmateriacoppeufrjbr/sarra/artigos/artigo1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.S.; Koike, M.; Johnson, B.W.; Okabe, T. Modeling of Alpha-Case Formation and Its Effects on the Mechanical Properties of Titanium Alloy Casting, Metall. Mater. Trans. 2008, 39A, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, A.; Rottem, A. The Effect of High Temperature Exposure on the Creep Resistance of Ti-6AI-4V Alloy. Mater, Sci. Eng. 1976, 22, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poquillon, D.; Parrens, C.; Pugliara, A.; Perrais, M.; Malard, B. Oxidation of Ti–6Al–4V alloy between 450 and 600°C. Evolution of microstructure and mechanical properties. MATEC Web of Conferences 2020, 321, 06009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, D.A.P.; Piorino, F.; Barboza, M.J.R.; Nono, M.C.A.; Silva, C.R.M. Influence of the oxidation in creep of Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Acta Microscopica 2003, 12, 219–220. [Google Scholar]
- Regev, M.; Almoznino, B.; Spigarelli, S. A Study of the Metallurgical and Mechanical Properties of Friction-Stir-Welded Pure Titanium. Metals 2023, 13, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalienko, M.; Volkov, A.; Leder, M.; Zhelnina, A. Study of oxygen content in titanium alloys after exposure at elevated temperature. MATEC Web of Conferences 2020, 321, 11068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, H. M.; Gopon, P.; Magazzeni, C.M.; Radecka, A.; Fox, K.; Rugg, D.; Wade, J.; Armstrong, D.E.J.; Moody, M.P.; Bagot, P.A.J. Quantifying the efect of oxygen on micro-mechanical properties of a near-alpha titanium alloy. J. Mater. Res. 2021, 36, 2529–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaché, N.; Monceau, D. Oxygen Diffusion Modeling in Titanium Alloys: New Elements on the Analysis of Microhardness Profiles. Oxidation of Metals 2020, 93, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bregolin, F.L.; Behar, M.; Dyment, F. Diffusion study of 18O implanted into α-Ti using the nuclear resonance technique, Appl. Phys. 2007, A 86, 481–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Qi, L.; Tsuru, T.; Traylor, R.; Rugg, D.; Morris, J.W.J.; Asta, M.; Chrzan, D.C.; Minor; A. M. Origin of dramatic oxygen solute strengthening effect in titanium. Science 2016, 347, 635–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulain, R.; Delannoy, S.; Guillot, I.; Amann, F.; Guillou, R.; Lartigue-Korinek, S.; Thiaudière, D.; Béchade, J.-L.; Clouet, E.; Prima, F. First experimental evidence of oxygen ordering in dilute titanium–oxygen alloys. Materials Research Letters 2022, 10, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magazzeni, C.M.; Gardner, H.M.; Howe, I.; Gopon, P.; Waite, J.C.; Rugg, D.; Armstrong, D.E.J.; Wilkinson, A.J. Nanoindentation in multi-modal map combinations: a correlative approach to local mechanical property assessment. J. Mater. Res. 2021, 36, 2235–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranganath, S.; Mishra, R.S. Steady state creep behaviour of particulate-reinforced titanium matrix composites. Acta Mater. 1996, 44, 927–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spigarelli, S.; Paoletti, C.; Cabibbo, M.; Cerri, E.; Santecchia, E. On the creep performance of the Ti-6Al-4V alloy processed by additive manufacturing. Additive Manufacturing 2022, 49, 102520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spigarelli, S.; Paoletti, C.; Cerri, E.; Santecchia, E.; Cabibbo, M. Creep response of Ti–6Al–4V alloy produced by additive manufacturing: Effect of annealing at 1050°C. Mater, Sci. Eng. 2022, A860, 144278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, R.A.; Nakajima, H.; Dyment, F. Diffusion in α-Ti and Zr, Mater. Trans. 2003, 44, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahmir, H.; Pereira, P.H.R.; Huang, Y.; Langdon, T.G. Mechanical properties and microstructural evolution of nanocrystalline titanium at elevated temperatures, Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, A669, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieler, T.R; Trevino, R.M.; Zeng, L. Alloys: Titanium. Encyclopedia of Condensed Matter Physics, Reference Module in Materials Science and Materials Engineering 2005, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.D.; Song, T.; Lu, S.L.; Liu, B.; Tian, J.; Qian, M. High oxygen-content titanium and titanium alloys made from powder. J. All. Comp. 2020, 836, 155526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittaker, M.T.; Harrison, W.J.; Lancaster, R.J.; Williams, S. An analysis of modern creep lifing methodologies in the titanium alloy Ti6-4, Mater. Sci. Eng. 2013, A577, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, R.W.; Hull, R.J.; Wilshire, B. The effects of alpha-case formation on the creep fracture propertied of the high-temperature titanium alloy IMI834, J. Mater.Proc.Techn. 1996, 56, 492–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).