1. Introduction
Some diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA), are characterized by chronic inflammation that affects mainly the joints, where it can produce a progressive degree of deformity and functional disability related to the continuing destruction of cartilage, as well as damage to tendons, ligaments, and bones [
1]. In addition, the disease can affect other organs, such as the eyes, lungs, pleura, heart, skin, and blood vessels [
2]. In general, the average prevalence is 1%, although some specific studies have shown higher levels, probably related to race, diagnostic criteria, and methodological differences [
3]. The reported incidence is variable, for example, a high annual incidence rate of 90 cases/100 000 habitants was reported in Germany [
4,
5], whereas values of 42 and 45 cases/100 000 were found in Finland and Japan [
6,
7], respectively. In Mexico, about one million people have some degree of illness [
8].
Although the precise etiology of RA is not entirely known, the leading role played by self-immunity in its development is well documented [
9], as well as its genetic predisposition, alterations in the union of joints or cartilage, joint injury, certain bacteria, fungi or viruses that infect the joints, among others.
Some of the drugs used to reduce disease progression and improve the quality of life are chloroquine, hydroxychloroquine, sulfasalazine, D-penicillamine, azathioprine, cyclophosphamide, methotrexate, cyclosporine, leflunomide, and some steroid and non-steroidal drugs [
10,
11,
12]. However, the therapeutic effect is usually symptomatic, nonpermanent, and can cause collateral damage. The group of immunosuppressants can cause numerous adverse reactions; however, their mechanisms are not yet well known. Some collateral damages of steroids are: osteoporosis, predisposition to infections, gastro toxicity, increased risk of skin infections, such as bacterial (e.g., cellulitis) and fungal (e.g., tinea, candidiasis), skin thinning, resulting in easy bruises (purples), skin tearing after minor injury and slow healing; these effects are most prominent on sun-exposed areas, particularly the back of the hands and the forearms [
13,
14]. Other steroids-induced alterations are stretch marks (striae), particularly under the arms and in the groin, acne, clusters of small spots on the face, chest, and upper back, excessive hair (hypertrichosis), hair loss (alopecia), and subcutaneous lipoatrophy (loss of fat under the skin surface) caused by the injected steroid that does penetrate deep enough into the muscle [15, 16, 17]. This makes the search for new compounds that efficiently reduce the physiopathological mechanisms that lead to the disease and the toxic side effects worthwhile. To achieve these purposes, extracts or compounds derived from plants have been investigated using the reversed passive Arthus reaction (RPAR) in rabbits to detect more effective anti-inflammatory agents for the treatment of RA [
18,
19].
Uncaria tomentosa (UT) is a Rubiaceae plant native to Peru, commonly called "cat's claw", used in traditional medicine to treat some diseases like cancer, arthritis, candidiasis, menstrual and intestinal disorders, and HIV infections [
20]. Other investigations have confirmed its biomedical properties with immunostimulant, cytostatic, anti-inflammatory, antimutagenic, and anticancer effects [21, 22].
Several components of the plant have been chemically identified as oxindole alkaloids, proanthocyanidins, polyphenols, triterpenes, and sterols, among others [
23]. Six oxindole alkaloids have been isolated from the plant, including pteropodine (PT), also called uncarine (
Figure 1), which is a heterohimbine-type oxindole that has been reported to show an apoptotic effect in leukemic lymphoblasts and participates in the improvement of memory impairment induced by dysfunction of cholinergic systems in the brains of mice [
24,
25]. These data suggest that PT could act synergistically with other UT components in one or more of the effects reported for the plant.
Our laboratory evaluated the genotoxic and antigenotoxic potential of PT, finding that this compound is not genotoxic in mice [
26]. Moreover, it was determined that PT protects mouse cells from DNA damage induced by doxorubicin (DX), which is a lymphocyte inducer and a free radical scavenging agent [
27].
Based on the above information, in this report, we expanded the studies on the capacity of PT as an anti-inflammatory agent by applying tests in mice, attempting to determine its anti-inflammatory potential in a mouse model that has the physiopathological mechanisms of rheumatoid arthritis and in edema induced in the mouse ear.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and animals
PT (99% pure) was obtained from Acceso-Lab Chemicals (Mexico City, MX). Ibuprofen, prednisone, antiserum of egg albumin, Freund’s complete adjuvant, 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA), indomethacin, acetone, and ethyl ether were purchased from Sigma Chemicals (St. Louis MO., US). Ovalbumin antiserum (rabbit polyclonal to ovalbumin) was obtained from Abcam (Mexico City, MX), and NaCl solution (9%) was obtained from Baker S.A. (Mexico City, MX). For the assay, we used 8-week-old male Wistar rats weighing 250 g in average and NIH mice averaging 25 g in weight. The animals were obtained from the National School of Biological Sciences (Instituto Politecnico Nacional, IPN) and maintained in metal cages at 23 ºC in a 12-hour light-dark cycle and allowed to consume food freely (Lab chow 5001, Purina, Mexico City, MX) and water. This protocol was approved by the Ethics and Biosecurity Committee of the National Rehabilitation Institute, SSA, Mexico City, MX.
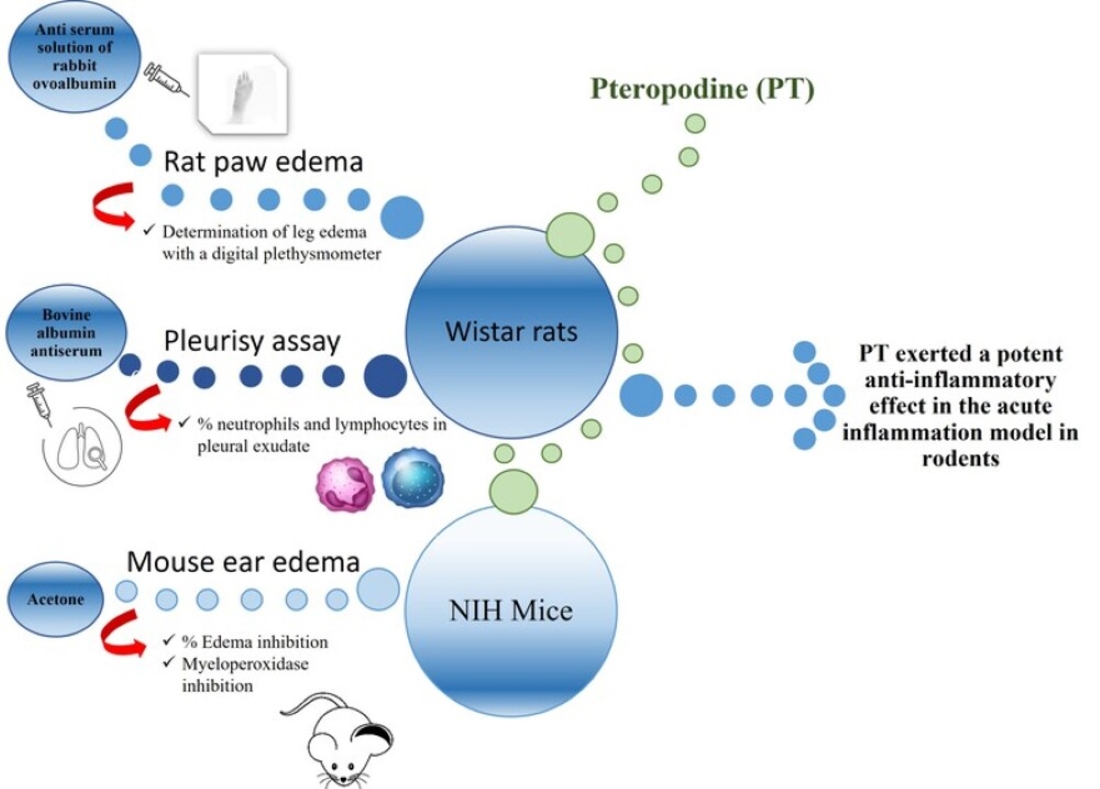
2.2. Description of the murine model
The Arthus reaction allows to experimentally reproduce the local physiopathology of RA. The obtained lesion is characterized by edema, erythema, and accumulation of polymorphonuclear cells. When the antigen is injected, a complex is formed with the antibody, the stimulation of the complement occurs, and anaphylatoxins are generated rapidly, which causes granulation of the mast cells.
The intravascular local complex can also cause platelet aggregation and release of vasoactive amines that lead to an increase in swelling, erythema, and the formation of chemotactic factors, which causes the influx of polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs). [
28].
2.3. Induction of rat paw edema
Six groups of Wistar rats were used; tests were performed by administering a placebo and PT at doses of 10, 20, and 40 mg/kg of body weight. Positive controls used were ibuprofen and prednisone at doses of 200 and 10 mg/kg respectively. A 0.1 mL of an antiserum solution of rabbit ovalbumin diluted 1:3 in 0.9% NaCl was injected into the sole of the right leg of the hindquarters of the rat. The contralateral leg was injected with 0.1 mL of a 0.9% NaCl solution, used as control, egg albumin was immediately injected intravenously at a dose of 25 mg/kg of body weight. In each animal, the volume of the leg edema induced by the antigen-antibody reaction was determined. The volume of the swollen and control legs was measured, 3 h after injection, with a digital plethysmometer (LE-7500, Labequim S. A. de C. V.). Paw edema was determined by the difference between the value of the volume of the treated leg and that of the control [
29].
2.4. Pleurisy assay
For the Pleurisy assay, we used 20 Wistar rats organized in four groups of 5 rats each. The animals were injected in the pleural cavity with 0.2 mL anti-ovalbumin antibody diluted 1:10 in a 0.9 % NaCl solution. Twenty minutes after the administration, a group was injected intravenously with 25 mg/kg of bovine albumin, the positive control group was administered ibuprofen (200 mg/kg), and the last three groups were treated orally with 100, 200, and 400 mg/kg of PT, respectively. The animals were euthanized by CO2-inhalation 6 h after pleural inoculation; the volume of pleural exudate in the pleural cavity was quantified, and then centrifuged at 1500 rpm for 5 min, the sediment was placed on a slide, fixed with methanol, and stained with Giemsa for 10 min. A differential counting of neutrophils and lymphocytes was made [
30].
2.5. Mouse ear edema model
For this, we used 25 NIH mice organized in five groups of 5 mice each, and 2.5 µg of TPA dissolved in 20 µL of acetone was applied, according to Young et al. (31), to both the internal and the external surface of the right ear of the mouse. After 1 h, PT was applied to the ear at different doses, 1.0, 2.0, and 4.0 mg, each dissolved in 20 µL of acetone. We used indomethacin (0.5 mg/ear) as positive control. The mice were euthanized by cervical dislocation after 4 h, then a 7-mm diameter slice was made, and the central portion of the ears was weighed. The edema value was calculated by the weight difference between the treated ears (the ones on the right) and the non-treated ears (the ones on the left). The inhibition of edema (expressed in percentage) was also calculated versus the control group [
31]. The results are presented as the average of the values obtained for each batch of animals ± standard error.
2.6. Myeloperoxidase inhibition
For the determination of the activity of the myeloperoxidase enzyme (MPO), the inflamed ears were homogenized, according to Suzuki’s technique [
32]. The absorbance was measured at 665 nm in a Perkin Elmer Lambda 3 spectrophotometer (Perkin Elmer Inc., Waltham, MA, US). The enzymatic inhibition (expressed in percentages) corresponds to the absorbance differences observed with respect to the control group. The results are presented as the average of the values obtained for each batch of animals ± standard error.
2.7. Statistics
The statistical analysis of data obtained from the different anti-inflammatory assays was performed with an ANOVA followed by the Student t test, using the SPSS 11.0.1 computer program (Statistical Software, Inc., Chicago, IL, US).
3. Results
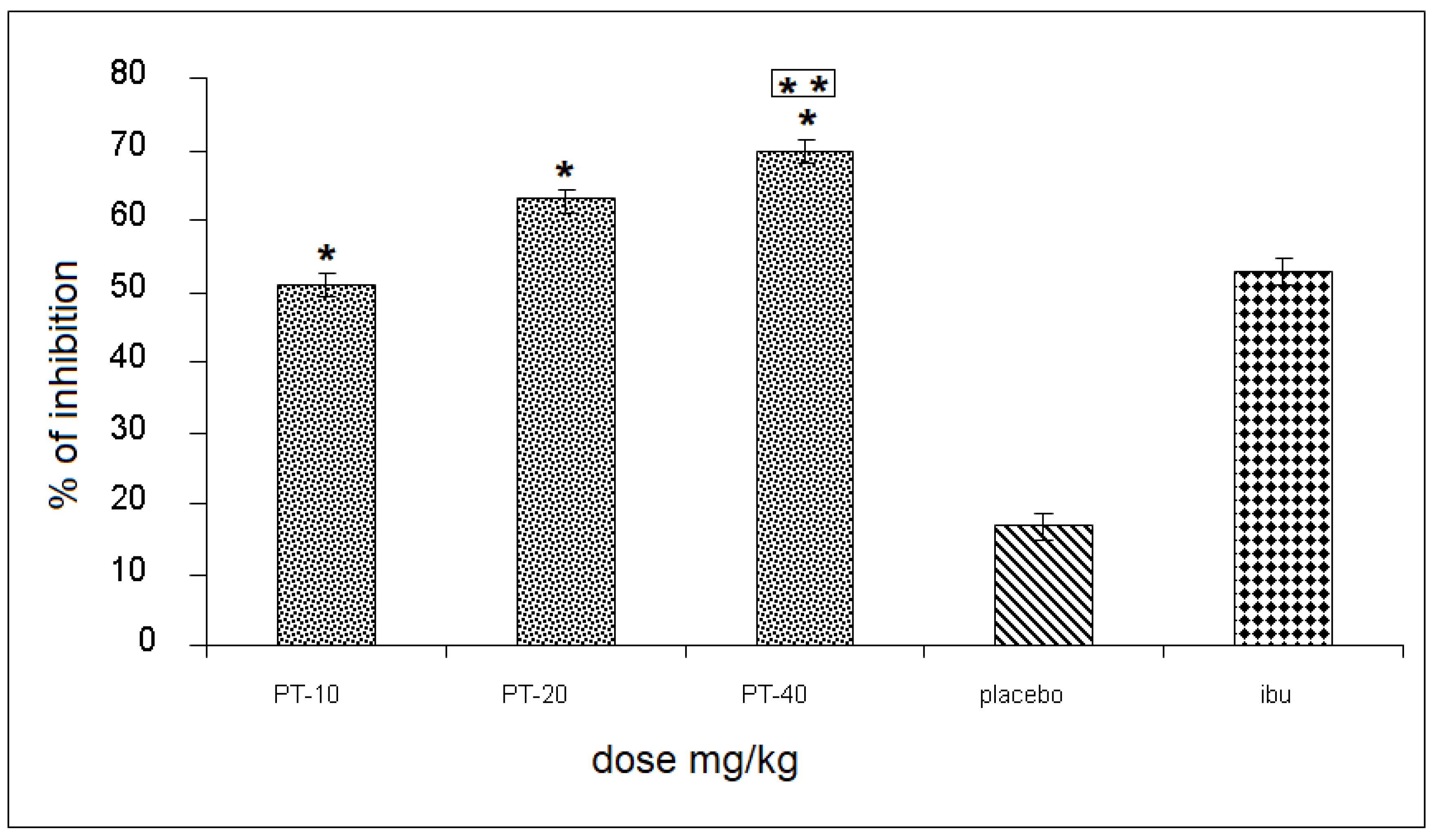
The three PT doses produced an inhibition of 51, 66, and 70%, respectively, of the rat’s leg edema, observing a statistically significant difference and a 55% increase when compared to the placebo group, and up to a 18% increase in inhibition, compared to the positive control (
Figure 1).
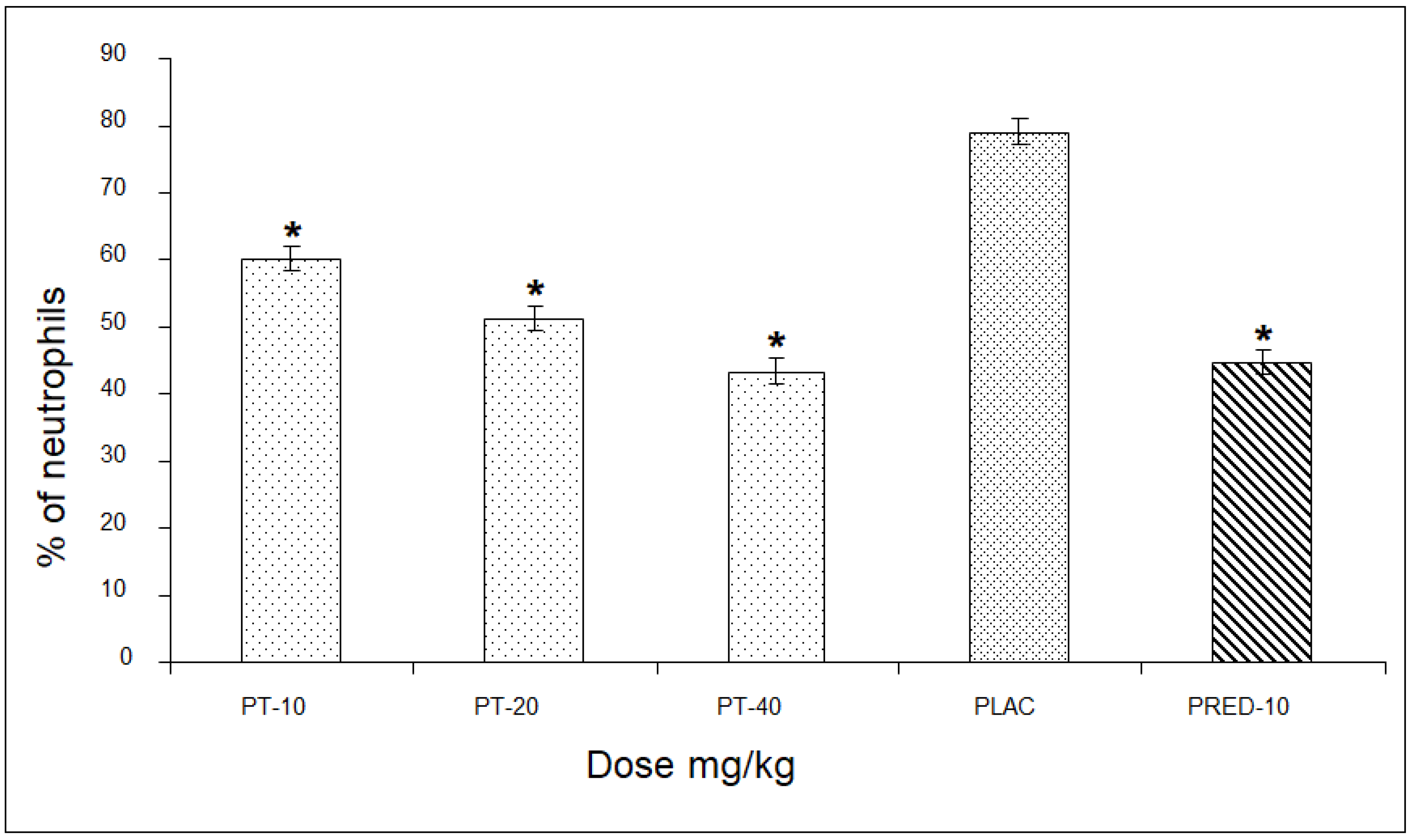
In the assessment of the percentage of neutrophils, PT showed values of 60, 51, and 43% for the three doses, respectively, revealing a significant difference of up to 36% compared to the placebo group, and very close to the values of the positive control group (
Figure 2).
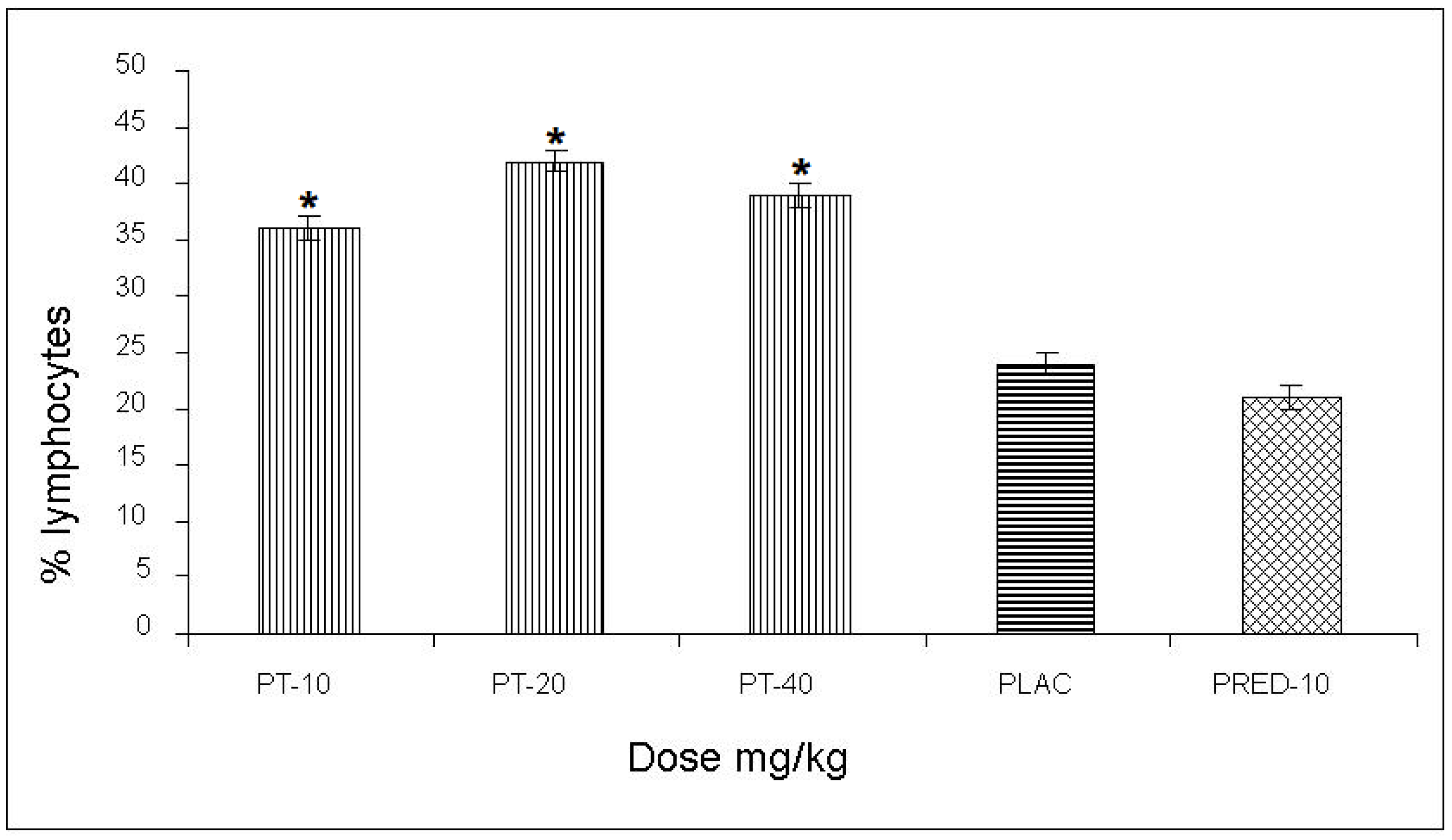
The effect of PT on the content of lymphocytes in the pleural cavity exudate, induced by the antigen-antibody reaction, yielded values of 36, 42, and 39% for the three doses, respectively, with an increase of up to 28% compared to the negative control and a 21% increase with respect to the positive control (prednisone) (
Figure 3)
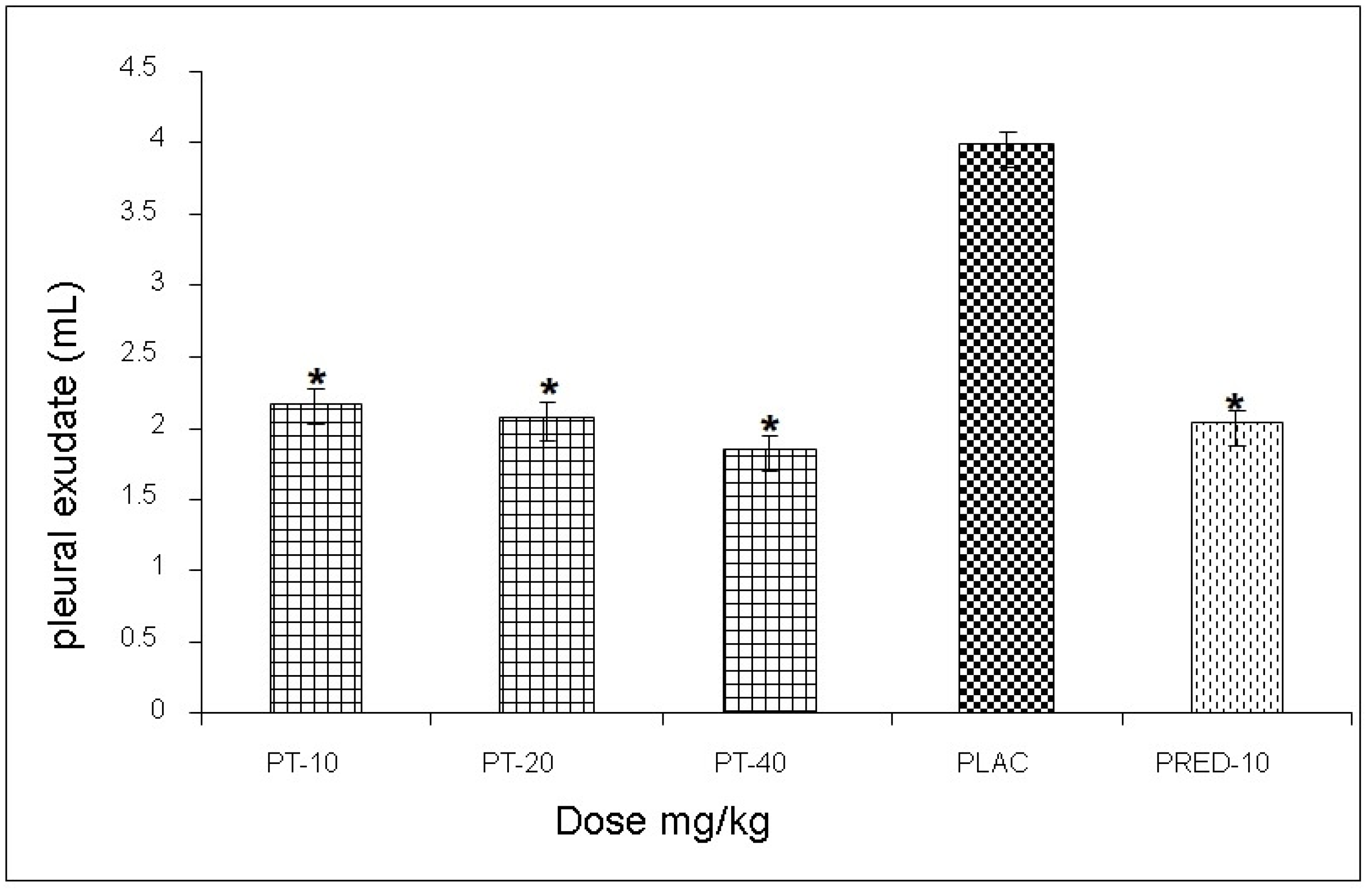
The effect exerted by PT on the reaction volume for the antigen-antibody interaction induced in the pleural exudate showed values of 3.1, 2.7, and 3.3 mL, respectively, for each dose, observing a statistically significant decrease of up to 52% when compared to the negative control group, and very similar values to those yielded prednisone (positive control) (
Figure 4).
Evaluating the activity exerted by PT on the TPA-induced edema in the mouse ear, an inhibition of 72, 75, and 81 %, respectively, for each dose, was observed, and a 9% increase compared to that of indomethacin (positive control) was obtained (
Table 1).
Table 2 shows the results relative to the myeloperoxidase assay. Where a significant inhibitory effect is observed with the tested doses of PT; the high dose of PT (1.5 mg/ear) is slightly better than the inhibition observed with indomethacin (
Table 2).
4. Discussion
Recent research shows that the presence of tetracyclic oxindole alkaloids (TOA) inhibits the immunomodulatory effect of pentacyclic oxindole alkaloids. In recent years, a chemotype of U. tomentosa (Willd) DC has been found that does not present tetracyclic oxindole alkaloids (TOAF chemotype, "TOA-free chemotype"). The first clinical evidence indicates that this new TOAF chemotype could have great therapeutic potential as an immunomodulatory plant, which should be confirmed by the scientific community in the coming years [5, 9].
The anti-inflammatory activity of cat´s claw (
U. tomentosa) has been attributed, at least in part, inhibitory activity on cyclooxygenase-1 and -2 [
33]. This anti-inflammatory action has been related to the capacity of the cat’s claw to neutralize the harmful effect of oxidizing organic substances, as well as its capacity to inhibit the expression of certain inducible genes during the inflammatory process [
34].
The cortex of
U. tomentosa (Willd) DC also has immunostimulant properties. The pentacyclic oxindole alkaloids increase the phagocytosis of macrophages and granulocytes and stimulate the proliferation of lymphocytes. In addition, cat’s claw causes macrophages to produce interleukins-1 and -6, which initiate the cascade of defensive activities of the immune system [
35].
Several extracts of
U. tomentosa root cortex have been tested for anti-inflammatory activity in a carrageenan-induced rat paw edema, and the quinovic acid-3-β-O-(β-D-quinovopyranosyl) -(27,1)-β-D-glucopyranosyl ester was isolated as one of the active compounds, which reduces 33% the inflammatory response at 20 mg/kg. There is evidence that the combination of compounds is responsible for the strong anti-inflammatory effect of the extracts [
36].
The addition of 100 μg/mL of an undefined extract of the stem cortex significantly attenuates the peroxy-nitrite-induced apoptosis in HT29 (epithelial cells) and RAW 264.7 cells (macrophages) (P < 0.05) and inhibits the expression of lipopolysaccharide–induced nitric oxide synthase gene (iNOS), nitrite formation, cell death, and the activation of the nuclear transcription factor-қβ in RAW 264.7 cells. Oral administration of 5 mg/mL of the extract attenuates indomethacin-induced enteritis in rodents, reducing myeloperoxidase activity, morphometric damage, and liver metallothionein expression [
37].
Anti-inflammatory activity of two types of extracts from the stem cortex: a hydroalcoholic extract containing 5.6 % alkaloids (mainly of the pentacyclic type, extract A) and an aqueous freeze-dried extract containing 0.26% alkaloids (extract B) were assessed in the carrageenan-induced rat edema test. Extract A was significantly more active than extract B, suggesting that the effect could be due to the presence of pentacyclic oxindole alkaloids. Both extracts showed scarce inhibitory activity on cyclooxygenase-1 and -2. Only a slight inhibitory activity on DNA-binding of NF-қβ was observed [
38].
The effects of a decoction of the stem cortex (10.0 μg/mL, lyophilized) on the production of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and cytotoxicity in murine macrophages stimulated with lipopolysaccharide (RAW 264.7 cells) was assessed in vitro. The decoction prevented oxidative and ultraviolet irradiation-induced cytotoxicity and, at 1.2 to 28.0 ng/mL, suppressed 65-85% TNF-α production (P < 0.01) [
38]. Cinchonain Ib, a procyanidin from the stem cortex, has an anti-inflammatory effect because it inhibits the activity of 5-lipoxygenase (≥ 100%) at 42.5 μmol/mL [
39].
The anti-inflammatory activity of PT was evaluated with a widely used method for assessing anti-inflammatory substances, such as TPA-induced ear edema. The inflammatory process triggered by the topical application of TPA is due to the activation of the protein kinase C of the skin (PKC), which starts the inflammatory response. All anti-inflammatory agents show activity in this model, but mainly the dual COX/LOX inhibitors [
40]; furthermore, cyclooxygenase (COX) inhibitors seem to be more effective as lipoxygenase inhibitors (LOX) than others in reducing the edematous response [
41]. In this order of ideas, PT could behave like the COX inhibitors in this model.
PT produced a growing anti-inflammatory activity according to the administered doses of each fraction. It also showed important anti-inflammatory properties by significantly inhibiting the acute-induced edema dependent on the TPA dose, with an inhibition comparable to that presented by indomethacin with the same dose (500 µg/ear).
The present study is one of the few studies on PT and of the first regarding the assessment of its anti-inflammatory activity. These results, along with those obtained by Choi et al. (10) with U. tomentosa extracts, constitute the first reports showing extracts of a phytopharmacological genus with anti-inflammatory activity in vivo.
5. Conclusions
The results of this study support the use of PT in traditional medicine for the treatment of inflammatory diseases like rheumatism. In addition, it considers PT as one of the main compounds in plant extracts responsible for anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities, which is easily obtained with excellent yields, making it very promising for the effective development of herbal extracts with pharmacological effects. Results are promising and encourage further studies on this active compound to assess it in other models of inflammation, both acute and chronic, and to determine the possible mechanisms involved in its pharmacological effects through its evaluation against specific mediators of inflammation, such as prostaglandins, nitric oxide, myeloperoxidase, and tumor necrosis factor, in addition to examining its ability to act as a scavenger of free radicals.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Rogelio Paniagua-Pérez, Laura Sánchez-Chapul, Eduardo Madrigal-Bujaidar and Isela Álvarez-González; Formal analysis, Rogelio Paniagua-Pérez; Funding acquisition, Rogelio Paniagua-Pérez; Investigation, Rogelio Paniagua-Pérez, Eduardo Madrigal-Bujaidar and Isela Álvarez-González; Methodology, Eduardo Madrigal-Santillán, Lidia Cruz-Hernández, Carlos Matínez-Canseco, Celia Reyes-Legorreta, Lidia Ruíz-Rosano, Cecilia Hernández-Flores, Rene Valdez-Mijares and Alejandra Quintana-Armenta; Resources, Rogelio Paniagua-Pérez and Eduardo Madrigal-Bujaidar; Supervision, Rogelio Paniagua-Pérez, Laura Sánchez-Chapul, Eduardo Madrigal-Bujaidar and Isela Álvarez-González; Validation, Rogelio Paniagua-Pérez and Eduardo Madrigal-Bujaidar; Visualization, Eduardo Madrigal-Bujaidar and Carlos Matínez-Canseco; Writing – original draft, Rogelio Paniagua-Pérez, Laura Sánchez-Chapul, Eduardo Madrigal-Bujaidar and Isela Álvarez-González; Writing – review & editing, Rogelio Paniagua-Pérez, Laura Sánchez-Chapul, Eduardo Madrigal-Bujaidar and Isela Álvarez-González.
Funding
This research received funding from the National Rehabilitation Institute.
Institutional Review Board Statement
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Medical Ethics Committee of the National Institute of Rehabilitation LGII. Protocol No. 95/17 and approval date 24 May 2017.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank PhD Rebeca E. Franco y Bourland, Head of the Biochemistry Service, for her support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kim, Y.; Oh, H. C.; Park, J. W.; Kim, I. S.; Kim, J. Y.; Kim, K. C.; Chae, D. S.; Jo, W. L.; Song, J. H. Diagnosis and Treatment of Inflammatory Joint Disease. Hip & pelvis 2017, 29, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borenstein, D. Inflammatory arthritides of the spine: surgical versus nonsurgical treatment. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2006, 443, 208–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagenais, S.; Garbedian, S.; Wai, EK. Systematic review of the prevalence of radiographic primary hip osteoarthritis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2008, 67, 623–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, C.; Marshall, M.; Rathod.; Bowen, CJ.; Menz, HB.; Roddy, E. Population prevalence and distribution of ankle pain and symptomatic radiographic ankle osteoarthritis in community dwelling older adults: A systematic review and cross-sectional study. PLoS One 2018, 13, e0193662. [CrossRef]
- Von Koskull, S.; Truckenbrodt, H.; Holle, R.; Hormann, A. Incidence and prevalence of juvenile arthritis in an urban population of southern Germany: a prospective study. Ann Rheum Dis 2001, 60, 940–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaipiainen-Seppanen, O.; Kautiainen, H. Declining trend in the incidence of rheumatoid factor-positive rheumatoid arthritis in Finland 1980–2000. J Rheumatol 2006, 33, 2132–2138. [Google Scholar]
- Hukuda, S.; Minami, M.; Saito, T.; Mitsui, H.; Matsui, N.; Komatsubara, Y.; Makino, H.; Shibata, T.; Shingu, M.; Sakou, T.; Shichikawa, K. Spondyloarthropathies in Japan: nationwide questionnaire survey performed by the Japan Ankylosing Spondylitis Society. J Rheumatol 2001, 28, 554–559. [Google Scholar]
- Peláez-Ballestas, I.; Sanin, L.H.; Moreno-Montoya, J.; Alvarez-Nemegyei, J.; Burgos-Vargas, R.; Garza-Elizondo, M.; Rodríguez-Amado, J.; Goycochea-Robles, M. V.; Madariaga, M.; Zamudio, J.; Santana, N.; Cardiel, M. H. Epidemiology of the rheumatic diseases in Mexico. A study of 5 regions based on the COPCORD methodology. J Rheumatol Suppl 2011, 86, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobon, G. J. , Youinou, P. & Saraux, A. The environment, geo-epidemiology, and autoimmune disease: rheumatoid arthritis. J. Autoimmun 2010, 35, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, Y. et al. Genetics of rheumatoid arthritis contributes to biology and drug discovery. Nature 2014, 506, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raychaudhuri, S. Recent advances in the genetics of rheumatoid arthritis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol 2010, 22, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antman, E. M.; Bennett, J. S.; Daugherty, A.; Furberg, C.; Roberts, H.; Taubert, K. A. Use of nonsteroidal Antiinflammatory drugs an update for clinicians - A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2007, 115, 1634–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boers, M.; Verhoeven, A. C.; Markusse, H. M.; vandeLaar, M. A. F. J.; Westhovens, R.; vanDenderen, J. C. , et al. Randomised comparison of combined step-down prednisolone, methotrexate and sulphasalazine with sulphasalazine alone in early rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 1997, 350, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buttgereit, F.; Burmester, G. R.; Straub, R. H.; Seibel, M. J. , Zhou, H. Exogenous and endogenous glucocorticoids in rheumatic diseases. Arthritis Rheum 2011, 63, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ethgen, O.; Esteves, F. D.; Bruyere, O.; Reginster, J. Y. What do we know about the safety of corticosteroids in rheumatoid arthritis? Curr. Med. Res. Opin 2013, 29, 1147–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, J. F.; Ahmed Mohamed, A. A.; Emery, P. Glucocorticoids and rheumatoid arthritis. Rheum. Dis. Clin. North Am 2016, 42, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glyn, J. The discovery and early use of cortisone. J. R. Soc. Med 1998, 91, 513–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gemmell, D.K.; Cottney, J.; Lewis, A.J. Comparative effects of drugs on four paw oedema models in the rat. Agents and Actions 1979, 9, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kma, L. Plant extracts and plant-derived compounds: promising players in countermeasure strategy against radiological exposure: a review. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 2014, 15, 2405–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bors, M.; Michałowicz, J.; Pilarski, R.; Sici ´ nska, P.; Gulewicz, K.; Bukowska, B. Studies of biological properties of Uncaria tomentosa extracts on human blood mononuclear cells. J. Ethnopharmacol 2012, 142, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen-Hall, L.; Cano, P.; Arnason, J.; Rojas, R.; Lock, O.; Lafrenie, R. Treatment of THP-1 cells with Uncaria tomentosa extracts differentially regulates the expression if IL-1 and TNF. J. Ethnopharmacol 2007, 109, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingues, A.; Sartori, A.; Valente, L.; Golim, M.; Siani, A.; Viero, R. Uncaria tomentosa Aqueous-ethanol Extract Triggers an Immunomodulation toward a Th2 Cytokine Profile. Phytother. Res 2011, 25, 1229–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goncalves, C.; Dinis, T.; Batista, M. Antioxidant properties of proanthocyanidins of bark decoction: A mechanism for anti-inflammatory activity. Phytochemistry 2005, 66, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilarski, R.; Filip, B.; Wietrzyk, J.; Kura´s, M.; Gulewicz, K. Anticancer activity of the Uncaria tomentosa (Willd.) DC. preparations with different oxindole alkaloid composition. Phytomedicine 2010, 17, 1133–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heitzman, M.E.; Neto, C.C.; Winiarz, E.; Vaisberg, A.J.; Hammond, G.B. Ethnobotany, phytochemistry and pharmacology of (Rubiaceae). Phytochemistry 2005, 66, 5–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paniagua-Pérez, R.; Madrigal-Bujaidar, E.; Reyes-Cadena, S.; Molina-Jasso, D.; Gallaga, J.P.; Silva-Miranda, A.; Velazco, O.; Hernández, N.; Chamorro, G. Genotoxic and cytotoxic studies of beta-sitosterol and pteropodine in mouse. J Biomed Biotechnol 2005, 3, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paniagua-Perez, R.; Madrigal-Bujaidar, E.; Molina-Jasso, D.; Reyes-Cadena, S.; Alvarez-Gonzalez, I.; Sanchez-Chapul, L.; Perez-Gallaga, J. Antigenotoxic, antioxidant and lymphocyte induction effects produced by pteropodine. Basic Clin Pharmacol 2009, 104, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pflum, L.R.; Graeme, M.L. The arthus reaction in rats, a possible test for anti-inflammatory and antirheumatic drugs. Agents and Actions 1979, 9, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, H.H.; Khaziakhmetova, V.N.; Zigashina, L.E. Rat paw oedema modeling and NSAIDs: timing of effects. Int. J. Risk Saf. Med. 2015, 27 (Suppl 1), S76–S77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paniagua-Pérez, R.; Flores-Mondragón, G.; Reyes-Legorreta, C.; Herrera-López, B.; Cervantes-Hernández, I.; Madrigal-Santillán, O.; Morales-González, J.A.; Álvarez-González, I.; Madrigal-Bujaidar, E. Evaluation of the anti-inflammatory capacity of beta-sitosterol in rodent assays. Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med 2017, 14, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, J.M.; Spires, D.A.; Bedord, C.J.; Wagner, B.; Ballaron, S.J.; De Young, L.M. The mouse ear inflammatory response to topical arachidonic acid. J Invest Dermatol 1984, 82, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Ota, H.; Sasagawa, S.; Sakatani, T.; Fujikura, T. Assay method for myeloperoxidase in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Anal Biochem 1983, 132, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, J.L.; Rojas, P.; Marcelo, A.; Plaza, A.; Bauer, R.; Reininger, E.; Klaas, C.A.; Merfort, I. Antiinflammatory activity of two different extracts of Uncaria tomentosa (Rubiaceae). J Ethnopharmacol 2002, 81, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akesson, C.; Lindgren, H.; Pero, R.W.; Leanderson, T.; Ivars, F. An extract of Uncaria tomentosa inhibiting cell division and NF-kappa B activity without inducing cell death. Int Immunopharmacol 2003, 3, 1889–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eberlin, S.; dos Santos, L.M.; Queiroz, M.L. Uncaria tomentosa extract increases the number of myeloid progenitor cells in the bone marrow of mice infected with Listeria monocytogenes. Int Immunopharmacol 2005, 5, 1235–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval-Chacón, M.; Thompson, J.H.; Zhang, X.J.; Liu, X.; Mannick, E.E.; Sadowska-Krowicka, H.; Charbonnet, R.M.; Clark, D.A.; Miller, M.J. Antiinflammatory actions of cat's claw: the role of NF-ΚB. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 1998, 12, 1279–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquino, R.; de Feo, V.; de Simone, F. Pizza, C. Cirino, G. Plant metabolites. New compounds and anti-inflammatory activity of Uncaria tomentosa. J Natural Products 1991, 54, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandoval, M.; Charbonnet, R.M.; Okuhama, N.N.; Roberts, J.; Krenova, Z.; Trentacosti, A.M.; Miller, M.J. Cat's claw inhibits TNFalpha production and scavenges free radicals: role in cytoprotection. Free Radic Biol Med 2000, 29, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirth, C.; Wagner, H. Pharmacologically active procyanidines from the bark of Uncaria tomentosa. Phytomedicine 1997, 4, 265–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passos, G.F.; Medeiros, R.; Marcon, R.; Nascimento, A.F.; Calixto, J.B.; Pianowski, L.F. The role of PKC/ERK1/2 signaling in the anti-inflammatory effect of tetracyclic triterpene euphol on TPA-induced skin inflammation in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 2013, 698, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altavilla, D.; Squadrito, F.; Bitto, A, et al. Flavocoxid, a dual inhibitor of cyclooxygenase and 5-lipoxygenase, blunts pro-inflammatory phenotype activation in endotoxin-stimulated macrophages. Br J Pharmacol 2009, 157, 1410–1418. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).