1. Introduction
Intracranial pressure (ICP) is classically monitored invasively in intensive care units (ICU) in the event of brain injury. One of the main objectives for a clinician is to limit the time the patient remains above a threshold of cerebral hypertension, described by international guidelines [
1]. Beyond the analysis of mean ICP, the ICP signal is a combination of different periodic components, affected by cardiac and respiratory frequencies. Thus, the sole mean ICP cannot capture all the information provided by such a complex signal [
2]. For instance, this single number does not describe the ability of the cerebrospinal system to compensate the changes in volume caused by blood and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) displacements, so that the ICP is maintained in an acceptable range. This pressure-volume relationship, generally called "cerebral compliance", requires fastidious manipulations to be measured punctually with CSF infusion tests [
3,
4,
5]. That is why different characterizations of cerebral compliance, based on a mathematical analysis of the ICP waveform, have been proposed in the literature [
6,
7]. Notably, the shape of heartbeat-induced pulses varies according to cerebral compliance [
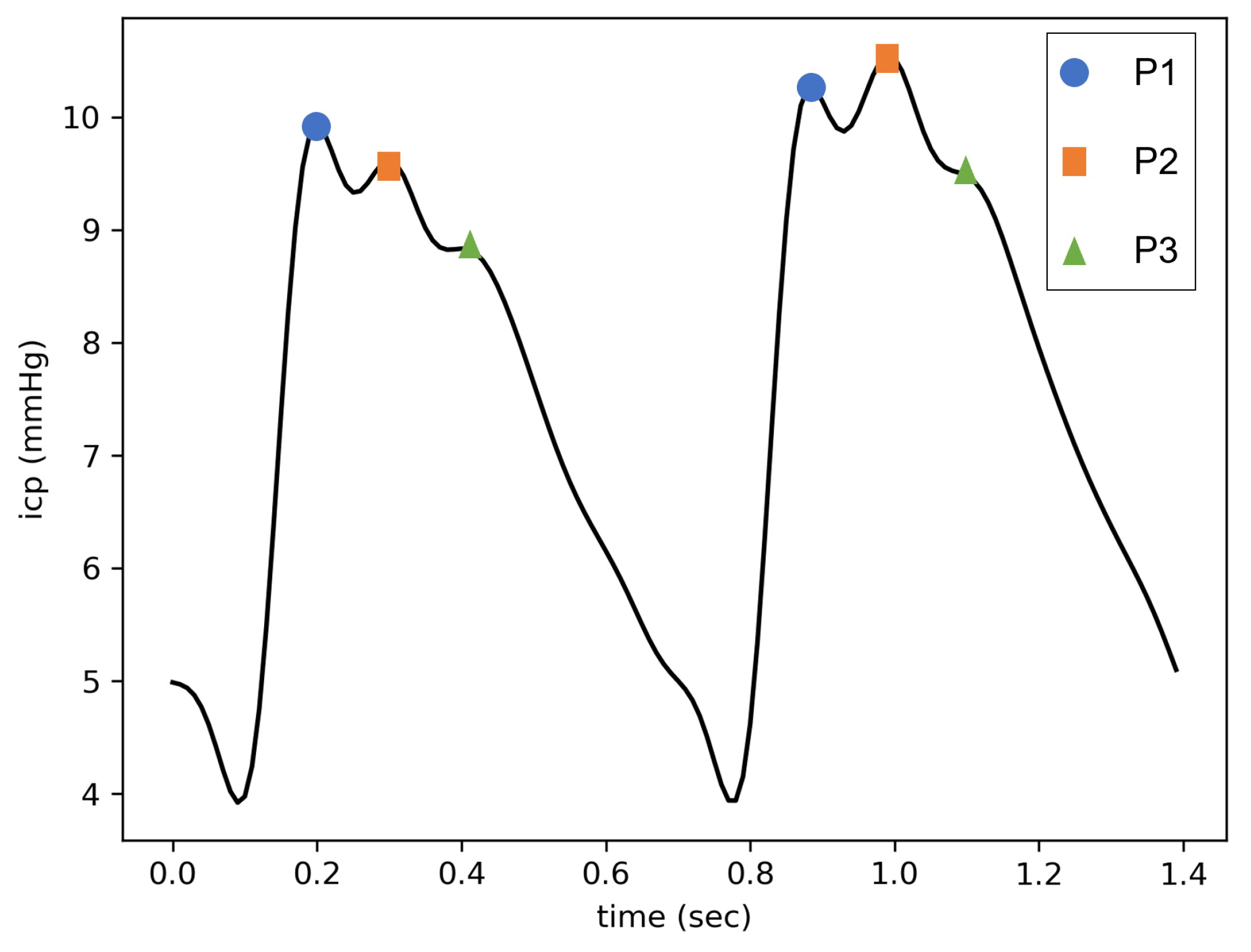
8]. When the latter is at a normal state, three subpeaks of decreasing amplitudes are generally visible (see
Figure 1). Those peaks are called P1, P2 and P3, in accordance with their apparitional order. While it is broadly admitted that P1 is due to the systolic pressure wave, the origins of P2 and P3 remain unclear [
9]. MRI measurements tend to associate P2 with a maximum volume in the cerebral arteries [
10,
11], whereas P3, classicaly described as the dicrotic wave, could be linked to veinous outflow [
12]. In any case, as cerebral compliance decreases, P2 and P3 become increasingly higher compared to P1 [
13]. At the same time, their appearance times get closer [
14], until the pulse takes a triangular shape centered on P2. Therefore, the ratio of the relative amplitudes of P2 and P1 (designated as the P2/P1 ratio) has been used as an indicator of cerebral compliance [
15]. This ratio is all the more relevant given that Kazimierska
et al. [
16] demonstrated its good correlation with cerebral compliance assessed by classic infusion tests.
However, P1 and P2 automated detection on an ICP signal faces different issues due to the highly variable pulses morphology. Only a few automated frameworks allowing for P2 and P1 designation have been proposed in the literature [
17,
18,
19]. Most of them rely on clustering algorithms to only analyze one characteristic pulse over a predefined period, as proposed by the authors of the Morphological Clustering and Analysis of Continuous Intracranial Pressure (MOCAIP) algorithm [
20]. MOCAIP-based automated frameworks are designed to compute a large number of morphological features of the ICP pulses, including the P2/P1 ratio. However, in addition to the raw ICP signal, their data processing workflows require both eletrocardiogram (ECG) monitoring and an extensive reference library of non-artifact pulses, which can be difficult to implement into an on-board bedside device. To perform real-time P2/P1 ratio calculation, neural network-based algorithms seem to be the tools of choice to circumvent these prerequisites, due to their ability to directly integrate the information provided by previous examples into trained models. For instance, Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) recurrent networks have been used successfully for similar tasks, such as ECG beats detection and classification (respectively [
21,
22,
23] and [
24,
25]).
Under the constraint of only using an ICP signal as an input, we developed a deep learning-based framework to detect the subpeaks P2 and P1, and compute the ratio of their relative amplitudes when possible. Its conception was performed by achieving a comparative study of proposed deep learning network architectures, enhanced with pre- and post-treatments and applied to our dataset provided by the ICU at the University Hospital of Saint-Etienne. Our framework is designed to perform two tasks sequentially. The first one is a classification task, aiming to eliminate all the pulses without the P1 and P2 subpeaks. The second one, only performed on the remaining pulses, aims to identify the subpeaks P1 and P2 to calculate the ratio of their relative amplitudes. As an output, our framework provides a discontinuous signal of P2/P1 ratio values, post-processed to make it as readable as possible for the clinician. In this article, we provide a description of the neural network (NN) architectures we compared for pulse selection (
Section 3.2) and for subpeak designation (
Section 3.3). The performances obtained for each of the task are respectively reported in
Section 4.1 and
Section 4.2, respectively. Lastly, we finally tested our completed automated framework on a dedicated testing dataset (
Section 4.3).
2. Dataset Overview
The studied ICP signals came from 10 adult patients suffering from traumatic brain injury, admitted to the ICU of the University Hospital of Saint-Etienne (France), between March 2022 and March 2023. For each of them, ICP was monitored invasively with an intraparenchymal sensor (Pressio, Sophysa, Orsay, France) for a duration of 8.3 ± 5 days (min = 3.8, max = 15) at a sampling frequency of 100Hz.
The dataset used in this study to train and select the best performing NN architectures was constituted by randomly sampling 5 one-hour sections for each record. Four of them were allocated to the training dataset, whereas the last one was allocated to the testing dataset. After the pulses were preprocessed and individualized as described in
Section 3.1, one out of 15 was selected to be part of the final datasets. Those pulses were labeled with the positions of P1 and P2 if both of them were visible, [0, 0] otherwise. In the end, the training dataset was composed of 13,127 pulses, including 12,308 with a calculable P2/P1 ratio. Its testing counterpart was composed of 4,344 pulses, including 3847 with a calculable P2/P1 ratio. These proportions are in accordance with Rashidinejad
et al. ([
19]) who estimated a missing subpeak probability at less than 10% based on their 700-hour dataset.
To assess the performances of the final dataset on more realistic conditions, an additional 10-minute segment was sampled randomly from each of the 10 patients. This second testing dataset, hence divided into 10 contiguous segments, was composed of 7,399 pulses, of which 6,815 had a calculable P2/P1 ratio. Whereas the first dataset was designed to capture maximum diversity among the patients, the present one is meant to assess the performances of the full automated framework on continuous recordings.
3. Materials and Methods
Our data processing pipeline is divided into four parts. After a heartbeat-induced pulses detection step performed on a preprocessed ICP signal, artifacts and pulses without a calculable P2/P1 ratio are eliminated by a first deep learning-based algorithm. The subpeaks are then detected on the remaining pulses. Lastly, a postprocessing step is performed to remove outliers and deal with missing values.
3.1. Data Preprocessing
A fourth order Butterworth bandpass filter between 0.3 Hz and 20 Hz is first applied to the raw signal. It is meant to isolate cardiac pulses from rapid oscillations of electronic origin, respiratory waves, and baseline variations. The modified Scholkmann algorithm is then applied to the filtered signal to detect the pulse onsets [
26]. As the patients’ pulse rates range between approximately 60 and 80 bpm, the characteristic duration L provided to the algorithm is set at 500 ms. Indeed, this hyperparameter is supposed to represent at least a quarter of the average pulse duration. The amplitude of each single pulse is normalized between 0 and 1, whereas the length is set to 180 points by a third degree polynomial interpolation. This preprocessing step is nearly identical to the one performed by Mataczynski
et al.([
27]) for pulse shape index calculation, except for the filter applied to the raw signal. As an output, a
N× 180 matrix of
N pulses is provided to the selection algorithm.
3.2. Pulse Selection
A major difficulty in monitoring the P2/P1 ratio is that not all subpeaks are systematically visible on all pulses. Therefore, a selection step is needed so that the detection algorithm is only provided with pulses where P1 and P2 are visible. This selection is performed by a neural network. Three architectures are compared for this task, namely a one-dimensional CNN, a LSTM-based recurrent network and a Long Short-Term Memory Fully Convolutional Network (LSTM-FCN), which is a combination of both. All the models are trained to perform the same binary classification task by minimizing a Binary Cross-Entropy (BCE) loss. Before calculating the loss function, a sigmoid is applied to the neural networks outputs to obtain values between 0 and 1.
3.2.1. One-Dimensional CNN Architecture
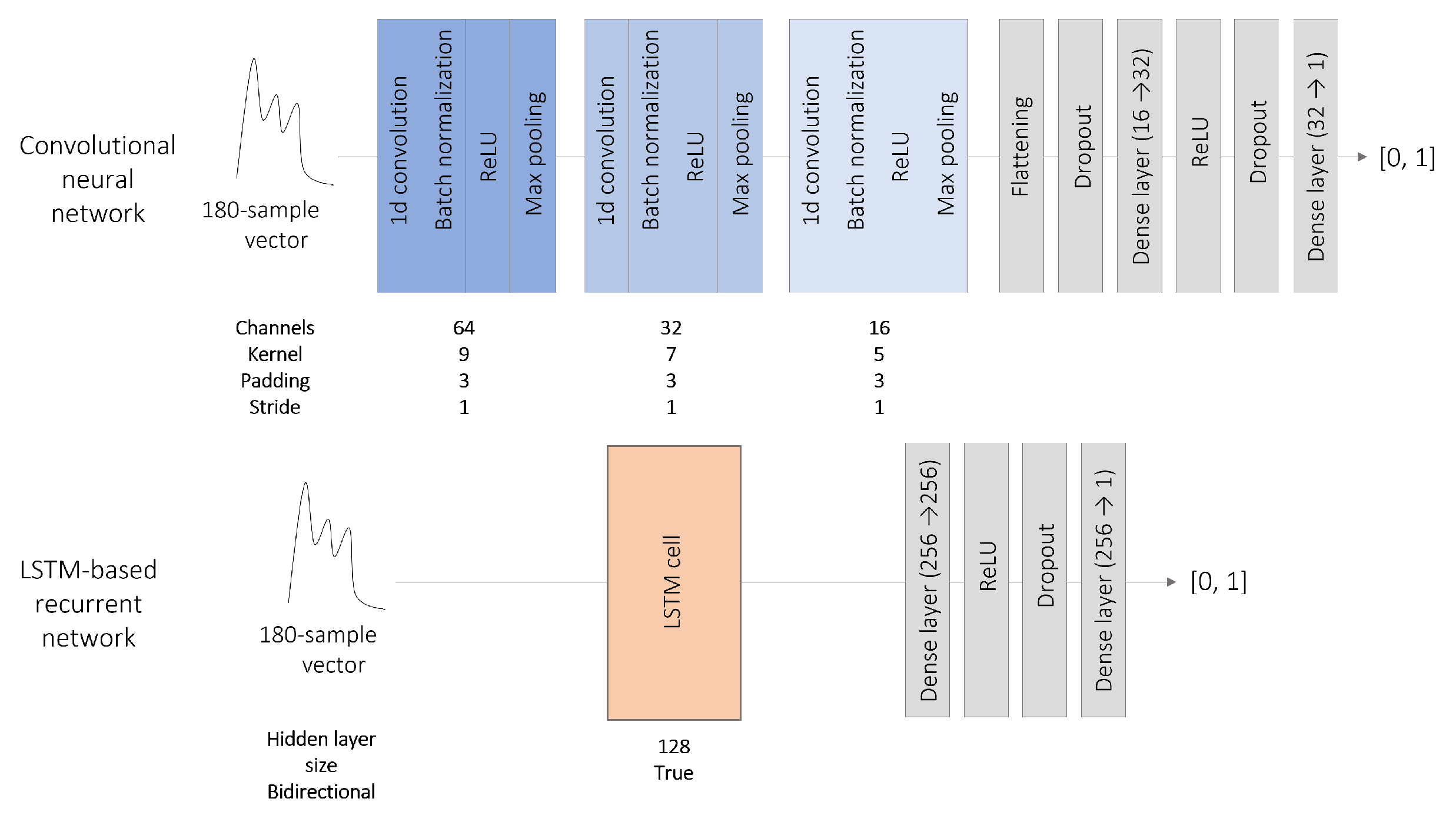
These architectures extract relevant features by applying convolutional filters on the input tensor. CNN have been successfully used for medical images segmentation, but it is also possible to adapt the layers dimensions to process one-dimensional vectors the same way. Our CNN is constituted of three encoding blocks, each one composed of the sequence convolutional layer- batch normalization - ReLU activation, followed by a max pooling layer. The output is postprocessed by two dense layers separated with a ReLU activation layer. To reduce overfitting, a dropout with a probability of 0.2 is applied at the end of the encoder and to the first dense layer. The dimensions of each layer appear in
Figure 2.
3.2.2. LSTM-Based Recurrent Network
Recurrent networks are designed to capture the underlying time dependencies of sequential data. They are generally composed of one or more cells whose outputs are computed based on the current input state and on the outputs of previous states. Past predictions can be taken into account by different ways ; LSTM cells are specifically designed to track long-term dependencies [
28]. The proposed recurrent network is a single bi-directional LSTM cell, followed by two dense layers separated by a ReLU activation. Hence, the input vector is processed in both reading directions by the LSTM cell, which produces two outputs that are concatenated and post-processed by the two dense layers. A dropout with a probability of 0.2 was applied at the end of the LSTM cell and to the first dense layer. The dimensions of each layer appear in
Figure 2.
3.2.3. LSTM-FCN Network
The two above-mentioned architectures process the input data with different objectives. Whereas CNNs focus on the neighborhood of each point, recurrent neural networks are meant to exploit the causalities inherent to sequential data. LSTM-FCN networks attempt to combine both strategies and were specifically designed for time series classification [
29]. Moreover, Mataczynski
et al. ([
27]) obtained good results with such an architecture for pulse shape index calculation. The LSTM-FCN network we implemented contains a three-block encoder, put in parallel with an LSTM cell. Their respective dimensions are identical to those used for the CNN and for the LSTM-based recurrent network. Both the computations are performed in parallel. The outputs are then concatenated and processed by two dense layers. As above, a dropout with a probability of 0.2 was applied to the first dense layer.
3.3. Subpeak Designation
Once the pulses with a calculable P2/P1 ratio are selected, subpeaks P1 and P2 can be designated. To do so, we studied different ways of combining the output of a neural network with the pulse curvature, as used by the MOCAIP-based automated frameworks. The curvature function is defined as:
For a given pulse p, subpeaks P1 and P2 correspond to two local minima of located in zones where is negative or, equivalently, to two local maxima of .
In parallel to these calculations, neural networks learn a classification task. For a pulse
x, the objective is a 180-point vector
, such that
where
and
are the respective positions of P1 and P2. More formally, during the learning process, the neural networks seek a function
such that
where
denotes the
Mean Square Error loss function, and
D the training set.
Two network architectures are compared for the estimation of
, namely a 1-dimensional U-Net (see
Section 3.3.1) and a LSTM-based recurrent network (see
Section 3.3.2).
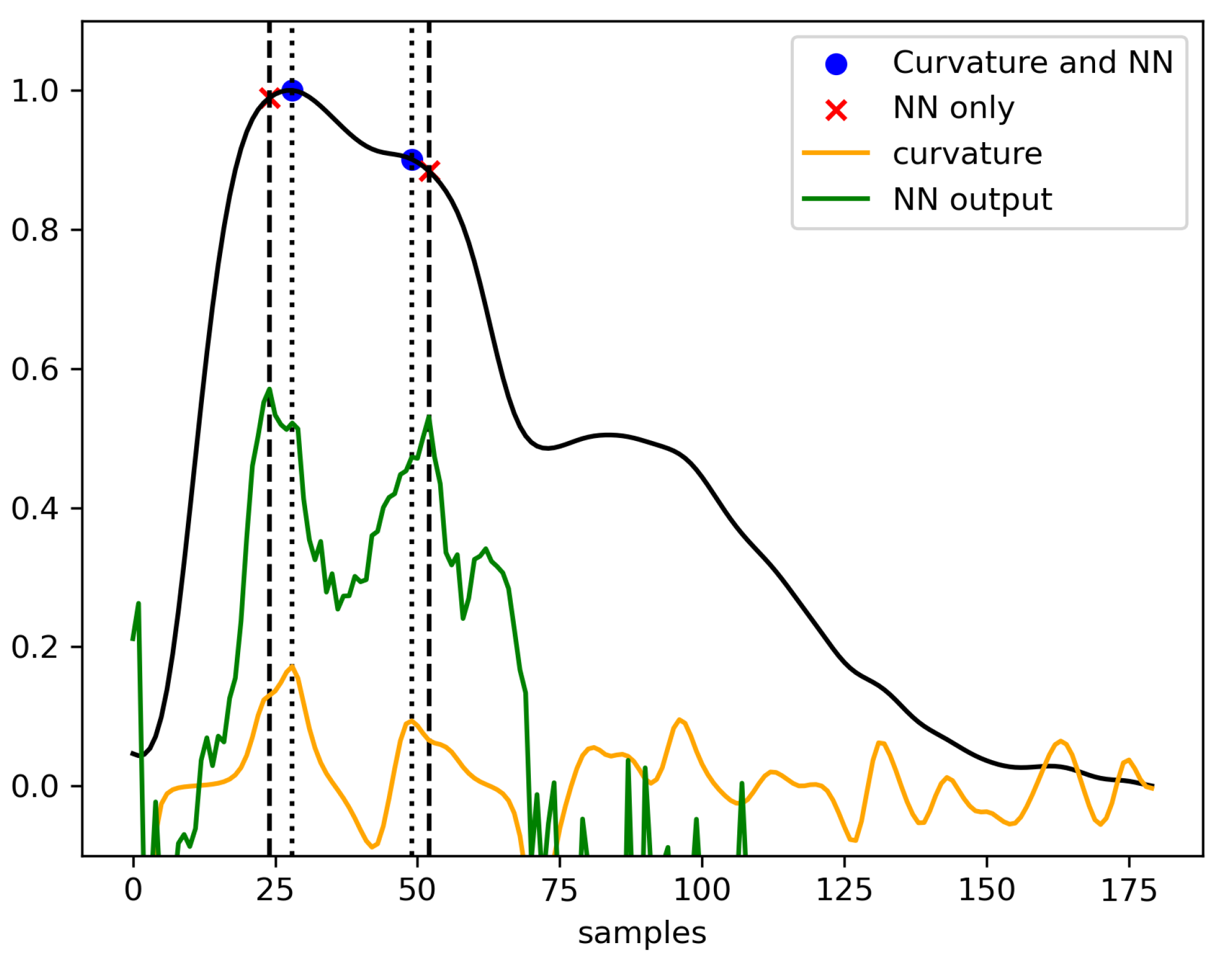
The detection strategy consists in two steps. Firstly, a candidate subpeaks set is extracted from the pulse. Secondly, P1 and P2 are designated from among the candidates. The candidate subpeaks are identified by a search for local maxima, either on
(method 1) or on
(method 2). Having thus obtained a list
c of candidates,
and
are then designated as the two points of
c corresponding to the highest value of
. Both strategies are summarized in
Figure 3. As a result, four combinations are compared: method 1 with U-Net, method 1 with the LSTM, method 2 with U-Net, and method 2 with the LSTM.
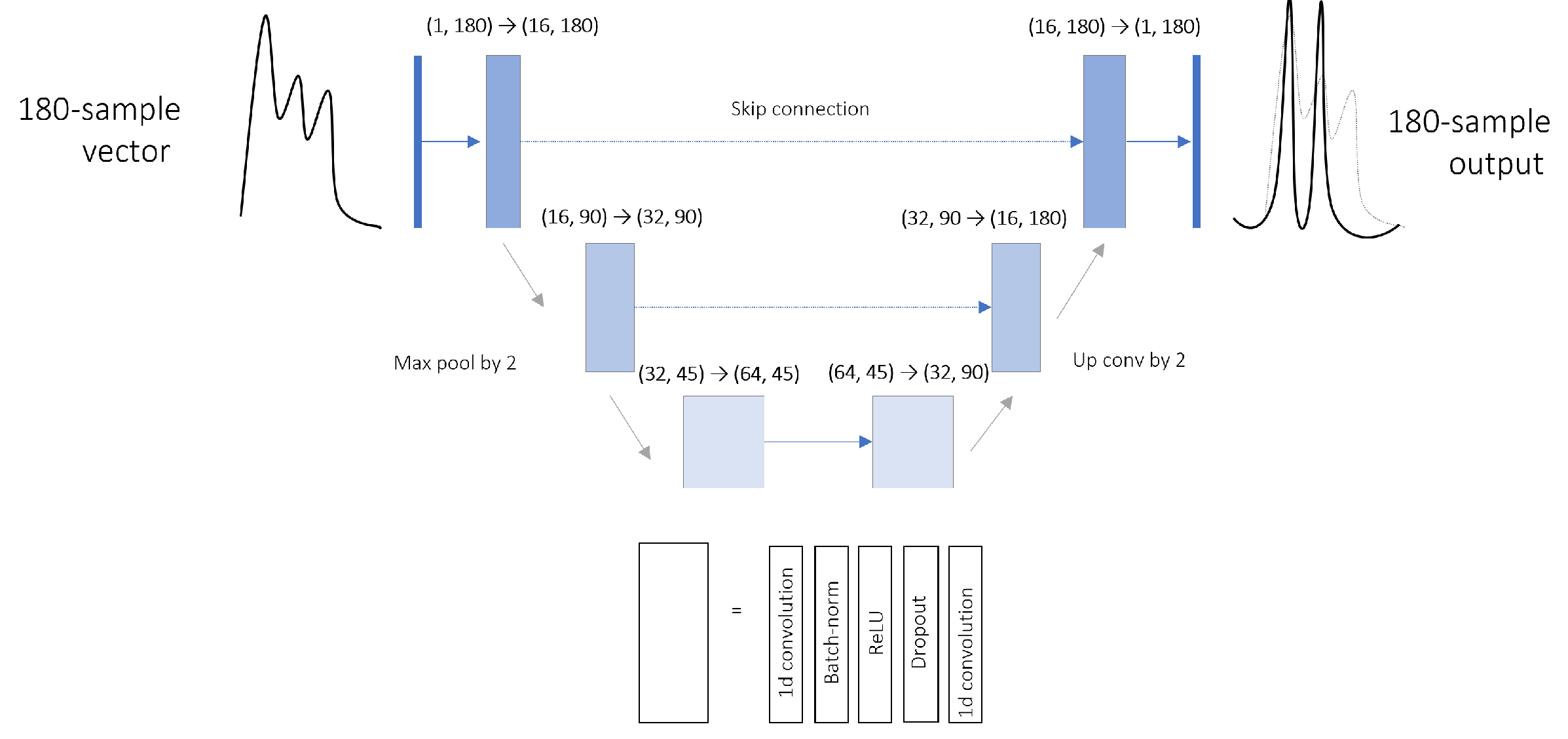
3.3.1. One-Dimensional U-Net
U-Net is a particular architecture of CNN. Its three-level bottleneck structure is composed of two symmetric blocks. In addition to the linear information propagations, pairwise connections are set between same-shape components. As it was originally conceived for images segmentation, layers have been modified here to perform one-dimensional convolutions. Layer dimensions appear in
Figure 4. A dropout with a probability of 0.2 was applied at each convolution block.
3.3.2. LSTM-Based Recurrent Network
We used a bidirectional LSTM-based recurrent network similar to the one trained for peak selection (see
Section 3.2.2). Hence, the input 180-sample pulse was processed by a single LSTM cell followed by two consecutive dense layers. As the hidden layer size of the LSTM cell was set to 180, the dimensions of the two consecutive dense layers were set to (360, 360) and to (360, 180), respectively. A dropout with a probability of 0.2 was applied to the first dense layer.
3.4. Postprocessing
Postprocessing the P2/P1 ratio signal has to address three main issues:
Spurious oscillations, mostly due to the intrinsic variability of the ICP signal. Even if they are not a result of the data processing pipeline itself, they tend to make the record less readable for the clinician.
Missing values, since all the pulses that do not pass the selection cut are recorded as missing.
Punctual outliers. If they are not caused by the ICP signal itself, they can be due to errors in the data processing pipeline. Punctual outliers either occur at the classification step, when false positive pulses are provided to the detection algorithm, or at the detection step, when P1 and P2 are designated at wrong positions.
These different problems are alleviated at the post-processing phase, by retrospectively smoothing the ratio monitoring. To do so, a 95% normal confidence interval is estimated on a 100-pulse sliding window. A mean ratio is then calculated over the window if at least 50 values are non missing ; otherwise, the value corresponding to this window is reported as missing. Therefore, each displayed value is calculated on the basis of the 100 last pulses, which corresponds to about one minute. In addition to overcoming the three issues listed above, smoothing the output signal in such a way highly enhances its readability. Indeed, far too much factors can influence a single pulse P2/P1 ratio to draw any conclusion on the basis of a pulse-wise evolution.
4. Results
Experiments were performed separately on the pulse selection and on the peaks detection tasks, in order to select a single neural network for each of them. The same training and testing datasets of labelled pre-processed pulses were used for both tasks, with 10% of the training set used for validation. After having our framework completed with two trained neural networks, we fully processed 10-minute labelled segments randomly sampled from each of the recordings. To ensure the reproducibility of our experiments, each of the three steps were performed using a dedicated processing pipeline designed with Snakemake 7.25 [
30]. All the associated scripts were coded in Python 3.11. Neural networks were implemented with Pytorch 2.0 [
31]. All the experiments described below were performed on a Windows 10 machine powered by WSL2 Ubuntu 20.04.5, equipped with a 12th Gen Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-12850HX 2.10 GHz 16 CPU, a Nvidia RTX A3000 12GB Laptop GPU, and 16 GB of RAM. Pipelines used for comparing neural network performances are available at the following address:
https://github.com/donatien-lege/P1_P2_detection_ratio.
4.1. Pulse Selection
The three models (i.e., CNN, LSTM recurrent network, and LSTM-FCN) were trained on 150 epochs with the Adam optimizer, an initial learning rate of 0.001, and a batch size of 256. For each of them, the area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was calculated by plotting the true positive rate (TPR) against the false positive rate (FPR), defined as:
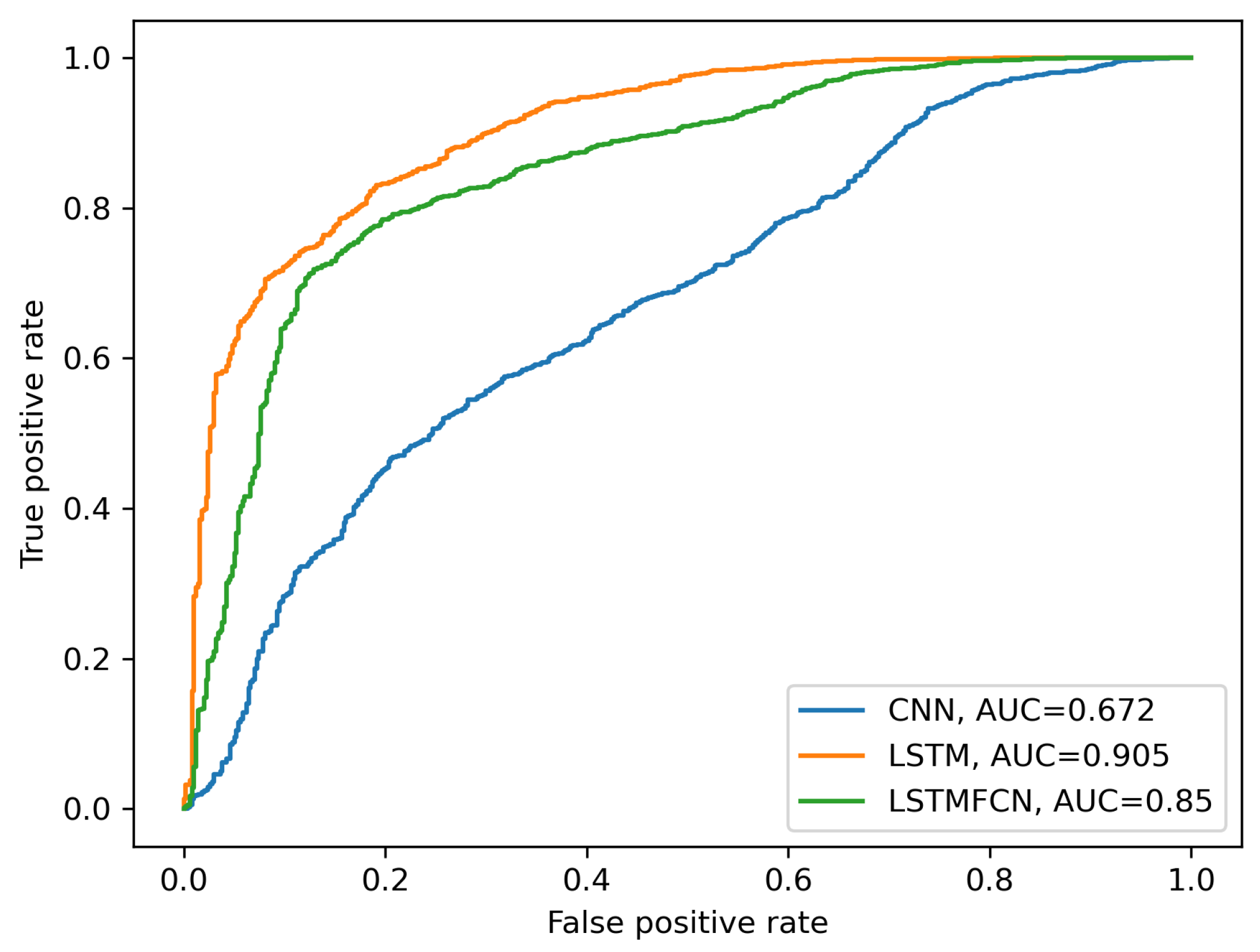
The three ROC curves are displayed in
Figure 5. For the final framework, the optimal decision threshold was chosen to maximize the difference
.
Our LSTM-based recurrent network architecture outperformed the convolution-based ones, with an area under the curve of 0.905. The confusion matrices corresponding to the respective optimal decision thresholds of each NN architecture are presented in
Table 1.
The number of false-positive pulses and false-negative pulses correspond to 1.8% and 9.7%, respectively, of the total testing data set when using the LSTM-based architecture for classification. In contrast, these percentages amount to 2.3% and 42.9%, respectively, when using the convolutive network.
4.2. Peak Designation
The experimental pipeline was designed to compare the four possible combinations between the peak designation method (i.e., by using the curvature function or not) and the neural network architecture (i.e., 1-D convolutional U-Net or LSTM-based recurrent network). In addition, a designation only using the first two local maxima of curvature was performed as a baseline. Both models were trained on 150 epochs with the Adam optimizer, an initial learning rate of 0.001 and a batch size of 256. A mean absolute peak appearance time error and a mean absolute P2/P1 ratio error were calculated. The mean absolute time appearance error was expressed as a percentage of the whole pulse duration. The results are reported in
Table 2. In addition, as it is the most interpretable information for the clinician, we assessed the ability of our models to detect pulses where P2 is higher than P1. To do so, we calculated a confusion matrix for classes “+”: “ P2/P1 ratio > 1” and “-”: “P2/P1 ratio < 1” and the associated accuracy, defined as the proportion of correct predictions over the whole testing dataset.
As for the pulse selection task, the recurrent architecture outperformed the convolutional one. Without the curvature-based candidate peak selection step, the LSTM-RE architecture performed the classification task with a 3% higher accuracy than our 1D-U-Net. Moreover, it achieved the most accurate estimation of the P2/P1 ratio, with a mean average error of 0.03. Achieving the candidate peaks selection step with the means of the curvature function tends to improve the algorithm’s ability to discriminate pulses with a P2/P1 ratio > 1, at the cost of a slightly less accurate ratio estimation.
4.3. Final Automated Framework
On the basis of previous experiments, we finally chose a LSTM-based recurrent network both for pulse selection and for subpeak designation. For the latter step, P1 and P2 designation was performed by selecting the two best LSTM-scored local maxima of curvature. For each of the ten patients, the complete workflow was used to process a randomly chosen labelled 10-minute section. An example of such an output is presented
Figure 6.
The performances were assessed for each individual 10-minute segment. We used the same respective metrics as above for pulse selection and subpeak designation. In addition, we calculated the percentage of pulses that were assigned a ratio value, and the percentage of non-missing values in the final post-processed ratio signal.
Table 3 contains values calculated over the total 100-min dataset, but 10-min individualized segmentmetrics are available
Table 5.
The false positive rate and true positive rate are both about seven points higher than their respective equivalents calculated when selecting the NN architecture. However, subpeak designation performances are consistent with previous experiments.
Table 4 corresponds to the overall confusion matrix calculated for pulses selection. As above, individualized confusion matrices are available in
Table 6.
Table 4.
Confusion matrix obtained for the final pulses selection step. Positive class corresponds to pulses with a calculable P2/P1 ratio.
Table 4.
Confusion matrix obtained for the final pulses selection step. Positive class corresponds to pulses with a calculable P2/P1 ratio.
| |
Predicted - |
Predicted + |
| True - |
499 |
85 |
| True + |
554 |
6261 |
Table 5.
Performances of the final automated P2/P1 ratio computation framework. Metrics associated with P2/P1 ratio values (i.e., P2/P1 ratio MAE and Accuracy on ratio > 1 detection) are calculated pulses with a labellized P2/P1 ratio value that passed the selection step.
Table 5.
Performances of the final automated P2/P1 ratio computation framework. Metrics associated with P2/P1 ratio values (i.e., P2/P1 ratio MAE and Accuracy on ratio > 1 detection) are calculated pulses with a labellized P2/P1 ratio value that passed the selection step.
| Segment |
True positive rate (%) |
False positive rate (%) |
P2/P1 Ratio MAE |
Accuracy on ratio |
Ratio-associated |
Displayed-ratio time(%) |
| |
|
|
|
> 1 detection(%) |
pulses (%) |
|
| 1 |
98.0 |
66.7 |
<
|
1 |
97.7 |
94.0 |
| 2 |
17.1 |
13.4 |
0.006 ± 0.005 |
1 |
14.4 |
4.4 |
| 3 |
- |
- |
0.25 ± 0.1 |
1 |
100 |
93.6 |
| 4 |
88.9 |
- |
0.015 ± 0.005 |
99.8 |
88.9 |
88.2 |
| 5 |
92.7 |
28.6 |
0.005 ± 0.001 |
98 |
92.2 |
90.1 |
| 6 |
99.8 |
- |
<
|
1 |
99.9 |
92.9 |
| 7 |
99.8 |
- |
<
|
1 |
99.9 |
91.2 |
| 8 |
87.8 |
20.6 |
0.07 ± 0.02 |
99.7 |
83.7 |
71.4 |
| 9 |
69.8 |
- |
<
|
1 |
69.9 |
87.3 |
| 10 |
96.2 |
0 |
0.008 ± 0.002 |
0.998 |
95.7 |
89.6 |
Table 6.
Confusion matrices obtained for each of the ten contiguous segments used as a testing dataset for the complete automated framework.
Table 6.
Confusion matrices obtained for each of the ten contiguous segments used as a testing dataset for the complete automated framework.
| Segment |
|
Predicted - |
Predicted + |
| 1 |
True - |
2 |
4 |
| |
True + |
20 |
1003 |
| 2 |
True - |
462 |
72 |
| |
True + |
126 |
26 |
| 3 |
True - |
0 |
0 |
| |
True + |
0 |
916 |
| 4 |
True - |
0 |
0 |
| |
True + |
66 |
526 |
| 5 |
True - |
5 |
2 |
| |
True + |
62 |
787 |
| 6 |
True - |
0 |
0 |
| |
True + |
1 |
832 |
| 7 |
True - |
0 |
0 |
| |
True + |
1 |
669 |
| 8 |
True - |
27 |
7 |
| |
True + |
64 |
461 |
| 9 |
True - |
0 |
0 |
| |
True + |
190 |
441 |
| 10 |
True - |
3 |
0 |
| |
True + |
24 |
600 |
It is noticeable that only the 2nd segment sample contains 91% of the negatively labeled pulses. In this segment, pulse selection algorithm performed with a 13.5% false positive rate (
Table 6).
False-positive pulses and false-negative pulses amount to respectively 1.14% and 7.49% of the total testing dataset. This proportions are consistent with those previously calculated on the 4344-pulse testing dataset.
5. Discussion
Our deep learning-based framework is designed to perform P1 and P2 detection and P2/P1 ratio computation directly on a bedside device. For convenience concerns, we designed it under the constraint of only using the ICP signal, which was made possible by a well-established efficient preprocessing step. Hence, we were able to focus our deep learning-based analysis on short time series corresponding to single pulses of cardiac origin. This strategy enabled us to use network architectures that are not too deep. Moreover, working at the cardiac cycle scale allowed us to alleviate another real-life difficulty: at bedside monitoring, ICP signals are very often contaminated with artifacts either due to patient movements (coughing, reactions to drug administration, nursing manipulations, etc.), or to electronic perturbations. Therefore, it can be complicated at a macroscopic scale to determine whether an acute rise in ICP corresponds to a real physiological measurement or to artifacts. By only focusing on modified Scholkmann algorithm-extracted candidates pulses, we were able to perform this artifact removal step on the basis of the local waveform alone, at the pulse selection step. In addition, as changes in cerebral compliance generally occur in a progressive way, a continuous pulse-wise compliance score is the tool of choice to describe the current patient state as faithfully as possible.
When labeling the pulses, only using the ICP signal could sometimes cause difficulties for interpreting isolated single pulse waveforms: without other elements of context, pulses with only two visible subpeaks systematically fell into the “non-calculable P2/P1 ratio“ category since it was not possible to know whether of P1, P2, or P3 was missing. In some of these cases, ABP or ECG signals may have helped to distinguish subpeaks, and thus, to compute a P2/P1 ratio. In that sense, the training dataset was labelled in a quite restrictive way to limit, as much as possible, the number of pulses without a calculable P2/P1 ratio provided to the peak designation step. However, this decision has inevitable consequences on the amount of time during which a P2/P1 ratio can be displayed. In any case, recurrent architectures clearly outperformed the convolutional-based ones for pulse selection, even if it is probably possible to reduce the observed gap by fine-tuning the proposed convolutional architecture. As the full succession of subpeaks is necessary to understand the pulse waveform, recurrent networks seem to be more appropriate than CNNs to perform such a classification task. In that sense, these results may contrast with similar studies performed on ECG signals, where events such as QRS complexes have more recognizable shapes and thus make CNN more relevant for classification or detection tasks. Concerning the consequences of misclassified pulses, it is noticeable that false-negative pulses only cause spurious missing values at the end of the data processing workflow. In contrast, false-positive pulses are provided to a peak designation algorithm that systematically outputs the two positions of estimated P1 and P2. Therefore, false-positive pulses can do much more damage to the output P2/P1 ratio signal. While we simply chose an optimal threshold that minimizes the difference , it could be relevant to optimize the decision threshold to make the algorithm more restrictive.
Peak detection was performed by computing a density function by the means of neural networks, as it is often the case for image segmentation tasks. We chose to stick to the underlying philosophy of MOCAIP-based automated frameworks, which include a candidate selection step before subpeak designation. It would have been possible to turn our algorithm into a regression task to output the estimated positions directly, as it is sometimes done for ECG peaks detection [
22]. This simpler strategy led to lighter computations. However, our method offers two advantages. Firstly, it is more robust and explainable in itself, as a score is assigned to each point of the input tensor. Secondly, it is easier to combine the output tensor with another function such as the pulse curvature. Designating two peaks from among a set of candidates selected with this simple and explainable criterion offers guarantees for the generalization abilities of the algorithm. This is all the more relevant given that we could only train our deep learning-based models on a relatively small set of patients, whereas there is a large inter-patient morphological variability in the ICP waveform. In the case of our testing dataset, a preselection of candidate peaks with a search for local maxima of the curvature function improved the algorithm’s ability to discriminate pulses with a P2/P1 ratio superior to one. The observed improvements in accuracy amounted to 1% for the recurrent network and 3% for our U-Net, respectively.
The biggest limitation of our study is that only 10 patient recordings contributed to the pulse database. Because of this small number, we chose to include samples from each of the ten patients both in the training and in datasets, in order to train our neural networks with as much diversity as possible. By doing this, we made the assumption that a single patient ICP signal variability over eight days (that is to say, the average monitoring duration) was enough to neglect the effects of a commune underlying distribution. How-ever, generalization abilities of our automated framework still have to be improved by expanding our datasets with further inclusions. This is all the more important since we obtained quite different false-positive rates during the model selection (8.52%) than during the final automated framework evaluation (14.6%).
While designing the data processing pipeline, we considered taking into account the neighborhood of each single pulse better. For instance, the pulse selection process could have integrated all the pulses occuring over the last minute before the one to be classified, thus helping the interpretation of the pulse waveform. However, it would have required a much more computation-intensive training step, since the recurrent networks would have had to capture more long-term dependencies. In addition, the database would have had to be composed of contiguously labeled samples, which would have had drawbacks on the diversity covered this way. We faced the exact same issue when sampling the final testing dataset, which was particularly disbalanced with 90% of its false-negative pulses occurring in the same segment.
This observation leads us to discuss the main drawbacks of monitoring the P2/P1 ratio. As mentioned earlier, this information is not always available and depends on biological mechanisms still not fully understood [
9]. A more complete picture of cerebral compliance could be obtained by combining the P2/P1 ratio with other indicators such as the mean ICP, pulse amplitude [
32], or pulse shape index[
33]. More generally, cerebral compliance has to be considered as part of a bundle of information available on patients. Characterizing it is especially helpful when ICP is close to the hypertension threshold, as a simple mean calculation is not informative enough on the current state of the cerebrospinal system. Cerebral compliance may also provide information for specific decisions, for instance when it comes to adjusting or putting sedation to an end.
6. Conclusion
Our automated detection framework allows for P2/P1 ratio monitoring on ICP ratio signals without needing any other input data. Its conception was made under this constraint to facilitate its implementation into onboard bedside devices. Pulse selection and subpeak designation are done using LSTM-based recurrent networks, which outperformed CNN networks for both tasks. Although a larger testing database would be needed to assess the performances of the full data analysis pipeline more accurately, experiments on a 10-patient dataset produced promising results. Monitoring the P2/P1 ratio, when possible, contributes to make a more precise picture of the cerebrospinal system, alongside with other indices such as the mean ICP or the pulse amplitude.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.P., L.G., Y.L. and D.L. ; methodology, D.L. and M.P.; software, D.L.; validation, M.P., J.H.; formal analysis, D.L. and M.P.; investigation, L.G. and Y.L.; resources, M.P. and L.G.; data curation, D.L.; writing—original draft preparation, D.L.; writing—review and editing, M.P. and J.H.; visualization, D.L.; supervision, M.P. and J.H. ; project administration, M.P., J-C.L. and J.H; funding acquisition, M.P., L.G., J.H, J-C.L, Y.L.;. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Ethics Committee of University Hospital of Saint-Etienne (IRBN282022/CHUSTE, 2022-02-10).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data are not publicly available due to medical confidentiality.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported French Research Ministry, CNRS (French National Center for Scientific Research) and Sophysa Company (Orsay, France). The authors would like to thank WordStyle Traductions for reviewing the first drafts of this article.
Conflicts of Interest
M.P. and D.L. are employees of Sophysa Company. L.G. has accomplished consulting missions on behalf of Sophysa Company.
References
- Carney, N.; Totten, A.M.; O’Reilly, C.; Ullman, J.S.; Hawryluk, G.W.; Bell, M.J.; Bratton, S.L.; Chesnut, R.; Harris, O.A.; Kissoon, N.; others. Guidelines for the management of severe traumatic brain injury. Neurosurgery 2017, 80, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czosnyka, M.; Smielewski, P.; Timofeev, I.; Lavinio, A.; Guazzo, E.; Hutchinson, P.; Pickard, J.D. Intracranial pressure: more than a number. Neurosurgical focus 2007, 22, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maset, A.L.; Marmarou, A.; Ward, J.D.; Choi, S.; Lutz, H.A.; Brooks, D.; Moulton, R.J.; DeSalles, A.; Muizelaar, J.P.; Turner, H.; others. Pressure-volume index in head injury. Journal of neurosurgery 1987, 67, 832–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, E.R.; Rowan, J.O.; Galbraith, S. Analysis of the cerebrospinal fluid pulse wave in intracranial pressure. Journal of Neurosurgery 1983, 59, 817–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet, A.; Gergelé, L.; Jouanneau, E.; Schmidt, E.A.; Manet, R. Assessment of Pressure-Volume Index During Lumbar Infusion Study: What Is the Optimal Method? Intracranial Pressure and Neuromonitoring XVII 2021, 335–338. [Google Scholar]
- Czosnyka, M.; Guazzo, E.; Whitehouse, M.; Smielewski, P.; Czosnyka, Z.; Kirkpatrick, P.; Piechnik, S.; Pickard, J. Significance of intracranial pressure waveform analysis after head injury. Acta neurochirurgica 1996, 138, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiegelberg, A.; Krause, M.; Meixensberger, J.; Kurtcuoglu, V. RAQ: a novel surrogate for the craniospinal pressure–volume relationship. Physiological Measurement 2020, 41, 094002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasil, S.; Solla, D.J.F.; Nogueira, R.d.C.; Jacobsen Teixeira, M.; Malbouisson, L.M.S.; Paiva, W.S. Intracranial compliance assessed by intracranial pressure pulse waveform. Brain Sciences 2021, 11, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domogo, A.A.; Reinstrup, P.; Ottesen, J.T. Mechanistic-mathematical modeling of intracranial pressure (ICP) profiles over a single heart cycle. The fundament of the ICP curve form. Journal of Theoretical Biology 2023, 564, 111451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrera, E.; Kim, D.J.; Castellani, G.; Zweifel, C.; Czosnyka, Z.; Kasprowicz, M.; Smielewski, P.; Pickard, J.D.; Czosnyka, M. What shapes pulse amplitude of intracranial pressure? Journal of neurotrauma 2010, 27, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unnerbäck, M.; Ottesen, J.T.; Reinstrup, P. ICP curve morphology and intracranial flow-volume changes: a simultaneous ICP and cine phase contrast MRI study in humans. Acta Neurochirurgica 2018, 160, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czosnyka, M.; Czosnyka, Z. Origin of intracranial pressure pulse waveform. Acta Neurochirurgica 2020, 162, 1815–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germon, K. Interpretation of ICP pulse waves to determine intracerebral compliance. The Journal of neuroscience nursing: journal of the American Association of Neuroscience Nurses 1988, 20, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziółkowski, A.; Pudełko, A.; Kazimierska, A.; Uryga, A.; Czosnyka, Z.; Kasprowicz, M.; Czosnyka, M. Peak appearance time in pulse waveforms of intracranial pressure and cerebral blood flow velocity. Frontiers in Physiology 2023, 13, 2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoy, D.A.; Brasil, S.; Iaccarino, C.; Paiva, W.; Rubiano, A.M. The intracranial compartmental syndrome: a proposed model for acute brain injury monitoring and management. Critical Care 2023, 27, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazimierska, A.; Kasprowicz, M.; Czosnyka, M.; Placek, M.M.; Baledent, O.; Smielewski, P.; Czosnyka, Z. Compliance of the cerebrospinal space: Comparison of three methods. Acta neurochirurgica 2021, 163, 1979–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Jeong, E.J.; Kim, H.; Czosnyka, M.; Kim, D.J. Morphological feature extraction from a continuous intracranial pressure pulse via a peak clustering algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering 2015, 63, 2169–2176. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Glenn, T.; Scalzo, F.; Bergsneider, M.; Sarkiss, C.; Martin, N.; Vespa, P. Intracranial pressure pulse morphological features improved detection of decreased cerebral blood flow. Physiological measurement 2010, 31, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashidinejad, P.; Hu, X.; Russell, S. Patient-adaptable intracranial pressure morphology analysis using a probabilistic model-based approach. Physiological measurement 2020, 41, 104003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Xu, P.; Scalzo, F.; Vespa, P.; Bergsneider, M. Morphological clustering and analysis of continuous intracranial pressure. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering 2008, 56, 696–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaolin, L.; Cardiff, B.; John, D. A 1d convolutional neural network for heartbeat classification from single lead ecg. 2020 27th IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Circuits and Systems (ICECS). IEEE, 2020, pp. 1–2.
- Jang, J.; Park, S.; Kim, J.K.; An, J.; Jung, S. CNN-based Two Step R Peak Detection Method: Combining Segmentation and Regression. 2022 44th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC). IEEE, 2022, pp. 1910–1914.
- Chourasia, M.; Thakur, A.; Gupta, S.; Singh, A. ECG Heartbeat Classification Using CNN. 2020 IEEE 7th Uttar Pradesh Section International Conference on Electrical, Electronics and Computer Engineering (UPCON). IEEE, 2020, pp. 1–6.
- Boda, S.; Mahadevappa, M.; Dutta, P.K. An automated patient-specific ECG beat classification using LSTM-based recurrent neural networks. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control 2023, 84, 104756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, H.M.; Chatterjee, K. Hybrid CNN-LSTM deep learning model and ensemble technique for automatic detection of myocardial infarction using big ECG data. Applied Intelligence 2022, 52, 5366–5384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, S.M.; Ercole, A. Multi-scale peak and trough detection optimised for periodic and quasi-periodic neuroscience data. Intracranial Pressure & Neuromonitoring XVI. Springer, 2018, pp. 189–195.
- Mataczyński, C.; Kazimierska, A.; Uryga, A.; Burzyńska, M.; Rusiecki, A.; Kasprowicz, M. End-to-end automatic morphological classification of intracranial pressure pulse waveforms using deep learning. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics 2021, 26, 494–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sak, H.; Senior, A.; Beaufays, F. Long short-term memory based recurrent neural network architectures for large vocabulary speech recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1402.1128 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Karim, F.; Majumdar, S.; Darabi, H.; Chen, S. LSTM fully convolutional networks for time series classification. IEEE access 2017, 6, 1662–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mölder, F.; Jablonski, K.P.; Letcher, B.; Hall, M.B.; Tomkins-Tinch, C.H.; Sochat, V.; Forster, J.; Lee, S.; Twardziok, S.O.; Kanitz, A.; others. Sustainable data analysis with Snakemake. F1000Research 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paszke, A.; Gross, S.; Massa, F.; Lerer, A.; Bradbury, J.; Chanan, G.; Killeen, T.; Lin, Z.; Gimelshein, N.; Antiga, L.; Desmaison, A.; Köpf, A.; Yang, E.Z.; DeVito, Z.; Raison, M.; Tejani, A.; Chilamkurthy, S.; Steiner, B.; Fang, L.; Bai, J.; Chintala, S. PyTorch: An Imperative Style, High-Performance Deep Learning Library. CoRR 2019, abs/1912.01703, [1912.01703].
- D’Antona, L.; Craven, C.L.; Bremner, F.; Matharu, M.S.; Thorne, L.; Watkins, L.D.; Toma, A.K. Effect of position on intracranial pressure and compliance: a cross-sectional study including 101 patients. Journal of Neurosurgery 2021, 136, 1781–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nucci, C.G.; De Bonis, P.; Mangiola, A.; Santini, P.; Sciandrone, M.; Risi, A.; Anile, C. Intracranial pressure wave morphological classification: automated analysis and clinical validation. Acta neurochirurgica 2016, 158, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).