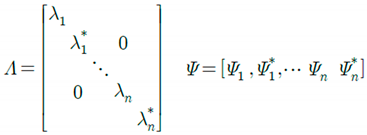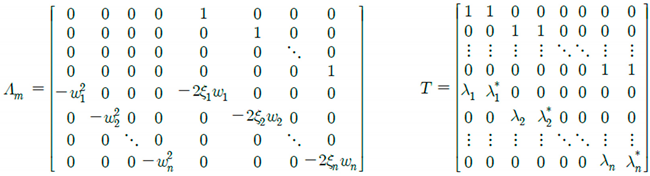1. Introduction
Structures with various shapes and diversified structural systems exhibit complicated dynamic behavior. Wind load on high-rise structures leads to the idealized behavior characterized by mutually independent translational and torsional motions, and complex behavior where motions in different directions are combined. To understand the complex dynamic behavior, mode decomposition techniques that extract main modes are widely used for system identification [
1,
2,
3,
4]. The first-generation operational modal identification method in the frequency domain is Frequency Domain Decomposition (FDD). It was developed to separate mode shapes by performing Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) of the cross-power spectral density (PSD) of the measured response at an a priori estimated natural frequency of interest in terms of peak picking [
5]. Enhanced FDD (EFDD) introduced the feasibility of Inverse Fast Fourier Transform (IFFT) for PSD in the vicinity of the target natural frequency to estimate the damping ratio in the time domain [
6,
7]. Frequency-Spatial Domain Decomposition (FSDD) was proposed to manipulate a bias error in damping estimation by EFDD and applied to civil structures such as long-span bridges and stadium roofs [
8]. Recently, the advanced FDD method, Frequency Scale Domain Decomposition, was proposed to estimate modal parameters by applying SVD to the continuous wavelet transform of the PSD of the response [
9]. Furthermore, modal properties are identified using the orthogonality of filtered response vectors without the need for SVD after modal response decomposition [
10]. Bayesian Operational Modal Analysis (BAYOMA) method operating in the frequency domain and applicable for close modes has been developed for a recent development based on an expectation-maximization algorithm that shows promise for simpler algorithm and computer coding [
11]. Recent developments in the field of Operational Modal Analysis (OMA) and Blind Source Separation (BSS) have attracted considerable interest in separating modal response and estimating dynamic properties [
6,
12,
13,
14]. BSS techniques separate time series data into stationary and non-stationary components, becoming popular for modal identification [
15]. Independent Component Analysis (ICA), one of the high-order BSS methods, has been used to decompose measured mixed signals into the linear transform matrix and source signals [
16,
17,
18]. The performance of ICA is limited to modes with low damping and well-separated modal systems. To address this issue, Second-Order Blind Source Separation (SOBSS) has been suggested, which works better than high-order BSS algorithms [
19,
20,
21].
A major advantage of using OMA and BSS is that those approaches allow simple and effective estimation of the modal properties based on only the responses due to the ambient vibration other than a controlled artificial excitation to the structure as input.
The mode decomposition methods, namely OMA and BSS, have been predominantly used in the MCK-domain, which represents the equation of motions using the mass, damping, and method of the equation of motion as M, C, and K respectively. However, these techniques have limitations in mode separation, especially when the modal damping is high or modes are closely spaced. This results in incomplete mode decomposition, making it difficult to extract accurate modal information from the measured response [
22]. To overcome these challenges, Hwang proposed a novel method called State-Space Based Mode Decomposition (SSBMD), which has been proven effective through numerical simulations [
23,
24]. Similar to conventional OMA techniques, SSBMD assumes white noise as an external force, which may not accurately represent the responses of an actual structure. To ensure reliable estimates of modal properties, it is recommended to conduct analytical simulations with enhanced frequency resolution. However, the performance of mode decomposition can still be affected by closely spaced neighboring modes, as the length of measurement response data can vary depending on the monitoring system used on-site.
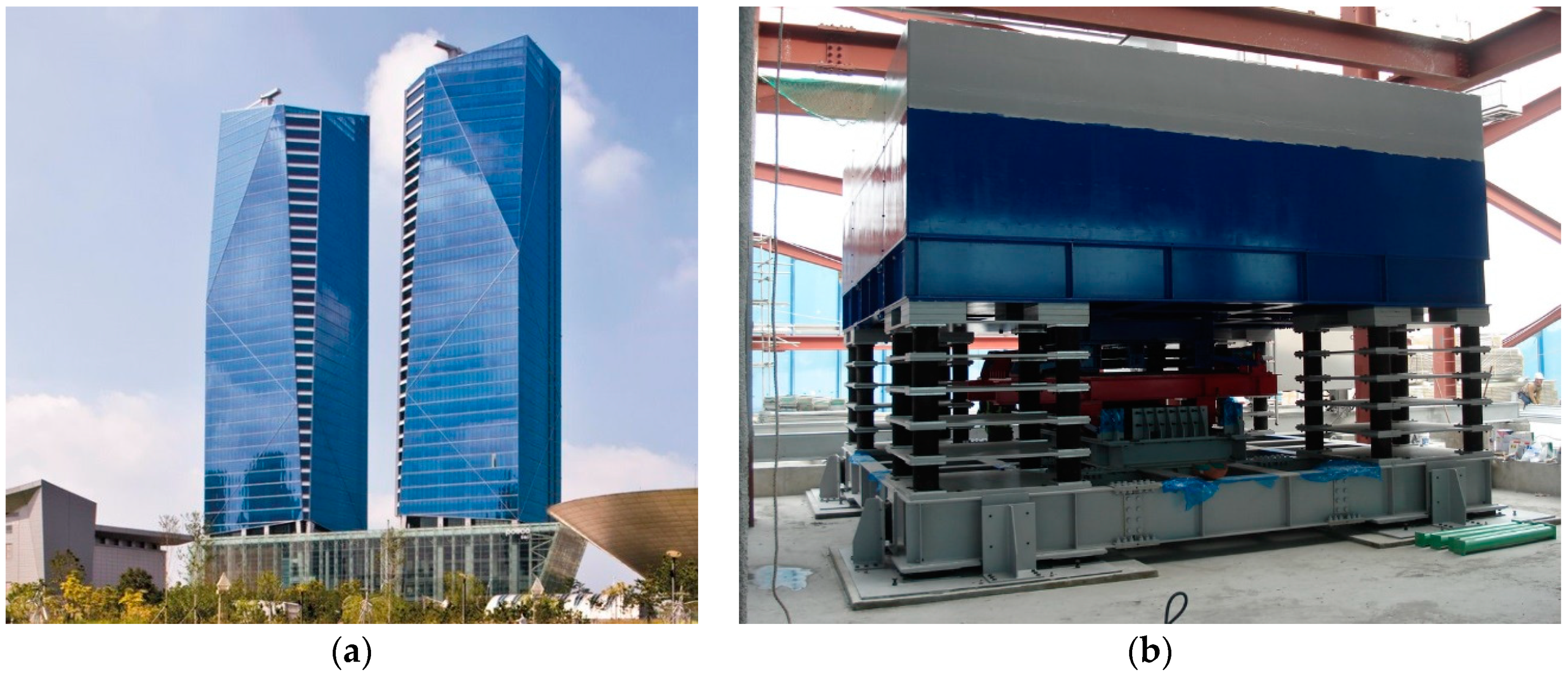
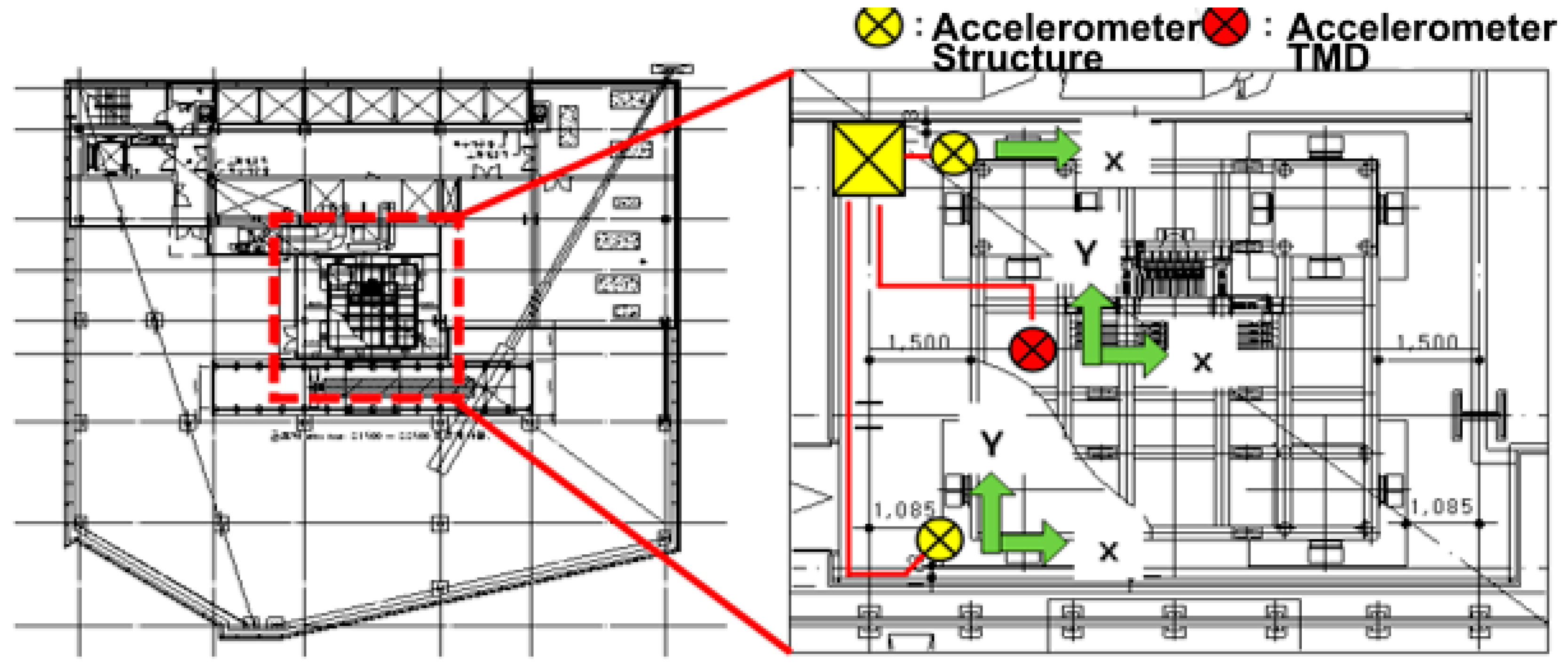
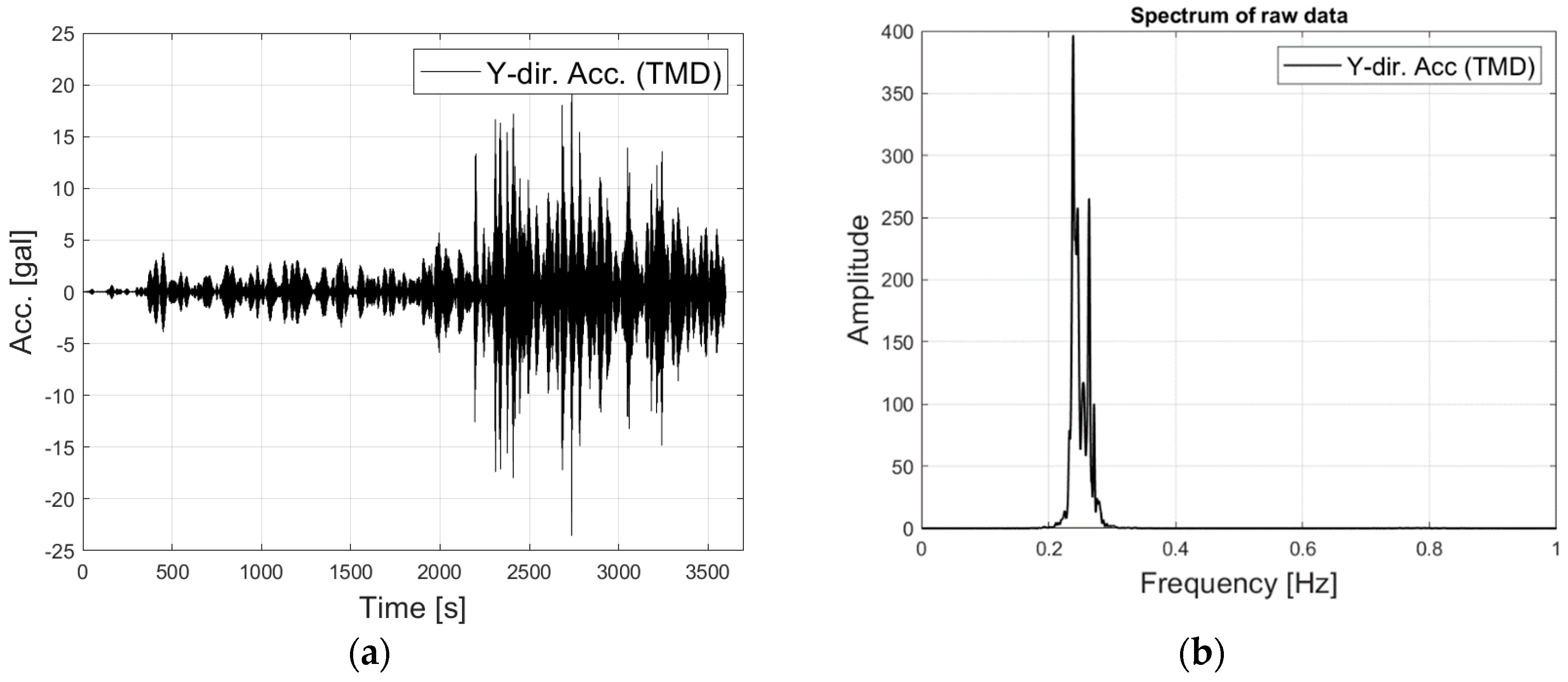
This study aims to validate the Optimized State-Space Based Mode Decomposition (OSSBMD) approach proposed by Hwang and Kim [
24] through its application to the output signal from a benchmark building with closely spaced modes. The Tuned Mass Damper (TMD) is a widely used vibration control device in tall buildings, which introduces non-classical damping resulting in closely spaced modes. In this paper, the SSBMD framework with a new performance index is described, which can accurately separate modal responses in the state-space domain. The closely spaced modes, in this study, are defined not only as neighboring natural frequencies but also those that cannot be separated using conventional techniques in the MCK-domain due to the presence of non-classical damping. To validate the proposed method, the result of mode decomposition using monitoring data from a non-classically damped system is presented. The aim is to examine experimentally the effectiveness of the improved OSSBMD methodology in a high-rise building where a TMD is installed to control wind-induced vibration.
2. State-space Mode Decomposition
The equation of motion of the structure with n degree of freedom under the external load can be expressed as follows:
where,
M,
C and
K represent the mass, damping and stiffness of the system in size
, respectively, and
E is the matrix indicating the location of the external load
. In this paper, the space in which all terms in Equation (1) are described is referred to as MCK-domain. However, a problem arises when the damping matrix is non-classical, that is the damping matrix cannot be expressed by a combination of the mass and stiffness matrix. In this case, mode separation may not be achieved in the MCK-domain [
24,
25]. To address the such difficulty in mode decomposition, the equation of motion can be expressed in the state-space domain as follows:
where,
Equation (2) indicates the transformed Equation (1) into the state-space domain by the linear combination of the state variables
of displacement and velocity and the differential variable
of velocity and acceleration. The eigenvalue problem in the state-space domain with respect to the system matrix
A can be expressed as follows:
where
and
are the eigenvalue and the eigen-matrix respectively as follows:
The Eigen matrix consists of the eigenvectors corresponding to the eigenvalues and is composed as shown in Equation (4b). The superscript “*” indicates the complex conjugate.
The state variable
can be transformed into a newly defined modal response in the state-space domain as
where
is the response vector in the modal space. Substituting Equation (5) into Equation gives
The major problem with the mode decomposition using Equation (5) is that the resultant modal response has a complex number. This issue can be resolved by transforming the eigenproblem using the conjugate response as follows:
where
. The general eigenproblem using Equation (7) is given as
The eigenvalue in Equation (8) is rewritten as
Substituting Equation (9) into Equation (3) gives
In Equation (10),
is the transformation matrix which transforms the system matrix
A to
and consists of real number elements. Equation (10) is rewritten as
where
is the unknown real-number transformation matrix to be used to transform into a system matrix expressed with the natural frequency
and damping ratio
. As shown in Equation (5), the state variable
can be rewritten using
as
where the new variable
is the real-valued modal response. Substituting Equation (12) into Equation (2) is substituted into Equation (2) gives
It is noted in Equation (13) that
is the new system matrix obtained by the transformation matrix
. The load term
can be expressed in the form as follows:
Using Equation (14), Equation (13) can be broken down into as follows:
The variables in Equation (15) are given as
The unknown transformation matrix
should be determined. By Equation (12). The modal response p can be expressed as follows using the linear transformation matrix
W:
As shown in Equation (11), the mode matrix
in the state-space domain transforms the system matrix
A into
. Equation (18) indicates that in order to determine the mode transform matrix
and modal response
, the state variable
should be defined. In structural monitoring, the structural response is generally measured by accelerometers. Thus, the velocity and displacement can be converted into the frequency domain using the integrator in the time domain as follows:
where, a(s) is a Laplace transform of
acceleration vector in the
s-domain.
is the number of sensors assumed equal to the number of the main modes to be identified. Using Equation (19), the state variable and its differential state variable can be constructed as follows:
The modal response is obtained by a linear transformation of the state variables or the derivative given in the frequency domain.
where
is the modal response of the
mode and
is the
column vector which is calculated by transposing the
row in the inverse matrix of the mode matrix
in the state-space domain. In order to force the separated mode in Equation (21) to be a real vibration mode of the system, the following conditions suggested by Hwang [
24] in the previous study should be met [
23,
24]: 1) given the constant total energy of the decomposed mode, the variance value of the modal response spectrum that can be calculated by the integral of the modal response spectrum should be unity and 2) the spectrum of the separated mode has the maxim amplitude in the vicinity of the natural frequency of the corresponding mode.
Those conditions can be presented in form of an objective function as
where
is the natural frequency of the target mode and
is the Lagrange multiplier constraining the variance value of the mode response spectrum to unity. The linear transformation vector
can be determined as the maximum value of the objective function
is found, i.e., the derivative of Equation (22) with respect to
is equal to zero.
It is noted that Equation (23) represents the eigenvalue problem with respect to the spectrum matrix of the state variable
, such that
and
is the eigenvalue and corresponding eigenvector of the eigenproblem, respectively. Since the size of the response spectrum matrix is
, the number of the linear transform vectors obtained by solving Equation (23) is also 2
. By choosing the vectors corresponding to the first two largest maximum eigenvalues, two linear transform vectors
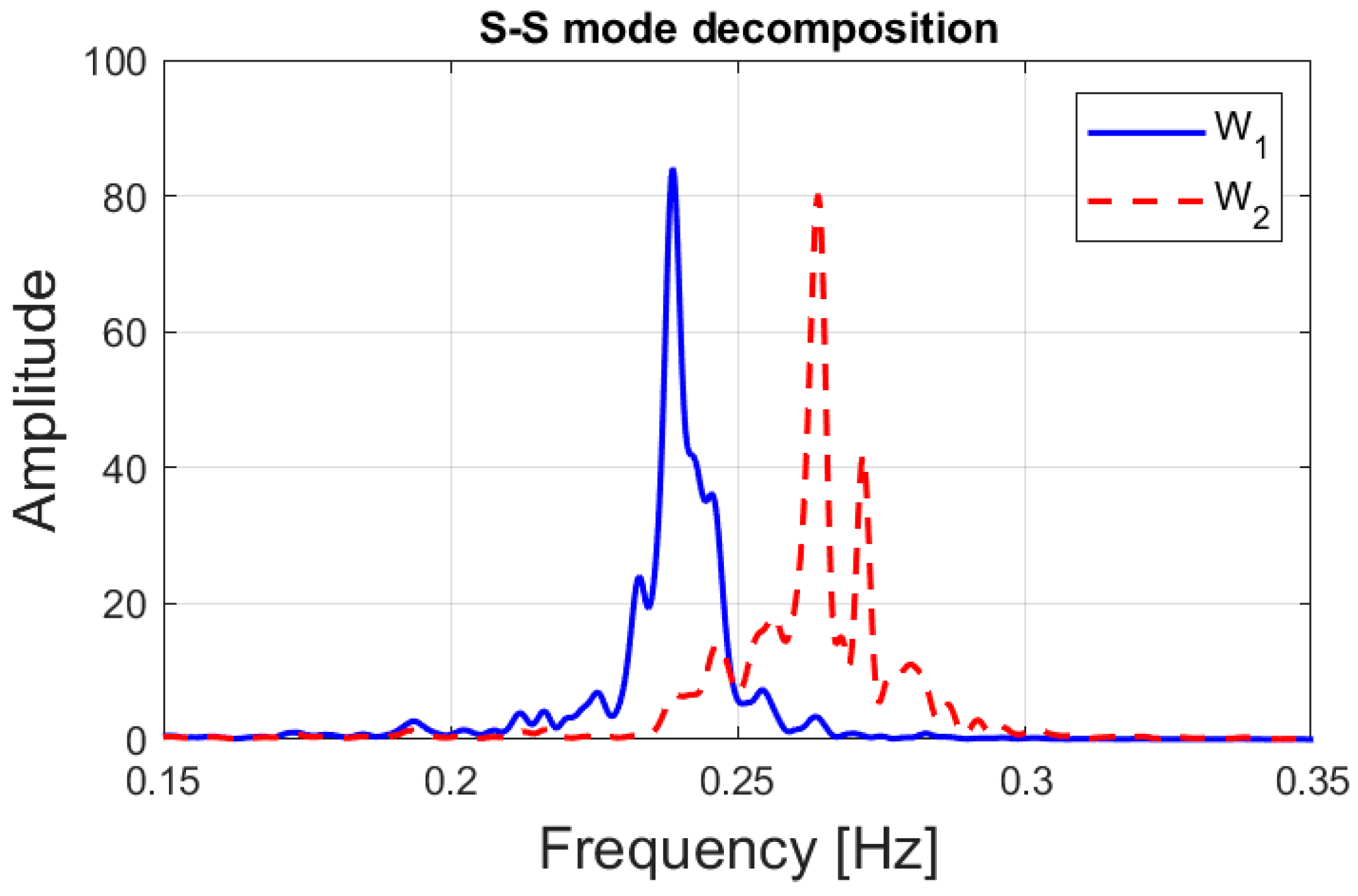
can be determined. Each of the two neighboring modes due to the tower and the TMD produces two corresponding demixing vectors. In total, four demixing vectors can be selected and expressed in a matrix form as:
where
and
is the eigenvectors corresponding to the second largest and the largest eigenvalue of the
-th mode in Equation (23), respectively. However, it is noted that the main challenge of this approach is that even though the decomposed mode satisfies the condition of the objective function in Equation (22), the decomposed mode might not be monochromatic and can be distorted by the influence of the close neighboring mode. The main reason for this is that the neighboring mode may distort the response spectrum in order to maximize the target mode at the corresponding natural frequency whereas the interference in the spectrum between close modes is minimal as the neighboring modes are spaced far apart. To address the mode interference issue, the objective function in Equation (22) can be modified taking the averaging spectrum into account as
The difference in the objective function of Equation (25) from that of Equation (22) is the added denominator term that minimizes the effect of the neighboring modes by introducing the logarithmic ratio of the power spectrum of the target mode
to the monochromatic power spectrum
around the natural frequency
of the neighboring mode. The Monochromatic Spectrum hereinafter referred to as MS is given as
where the lower case
is the Laplace variable, and
is the transfer function of the velocity response from a Single-Degree-of-Freedom (SDOF) system which describes the target monochromatic mode. Although the damping ratio
is unknown in this step, it can be approximated using the power spectrum of the decomposed mode evaluated by the conventional mode decomposition method. If the modal response represents the acceleration, the numerator in
is
.
in Equation (26) is calculated using the natural frequency of the target mode
as follows:
Once the variables in Equation (24) are determined, the linear transform matrix is established in the same way as described in Equation (23). However, since the objective function in Equation (25) is nonlinear, it is difficult to derive the transform matrix in a closed-form expression as expressed in Equation (23). Instead, the transform matrix can be determined through optimization using the sensitivity function of the objective function to .
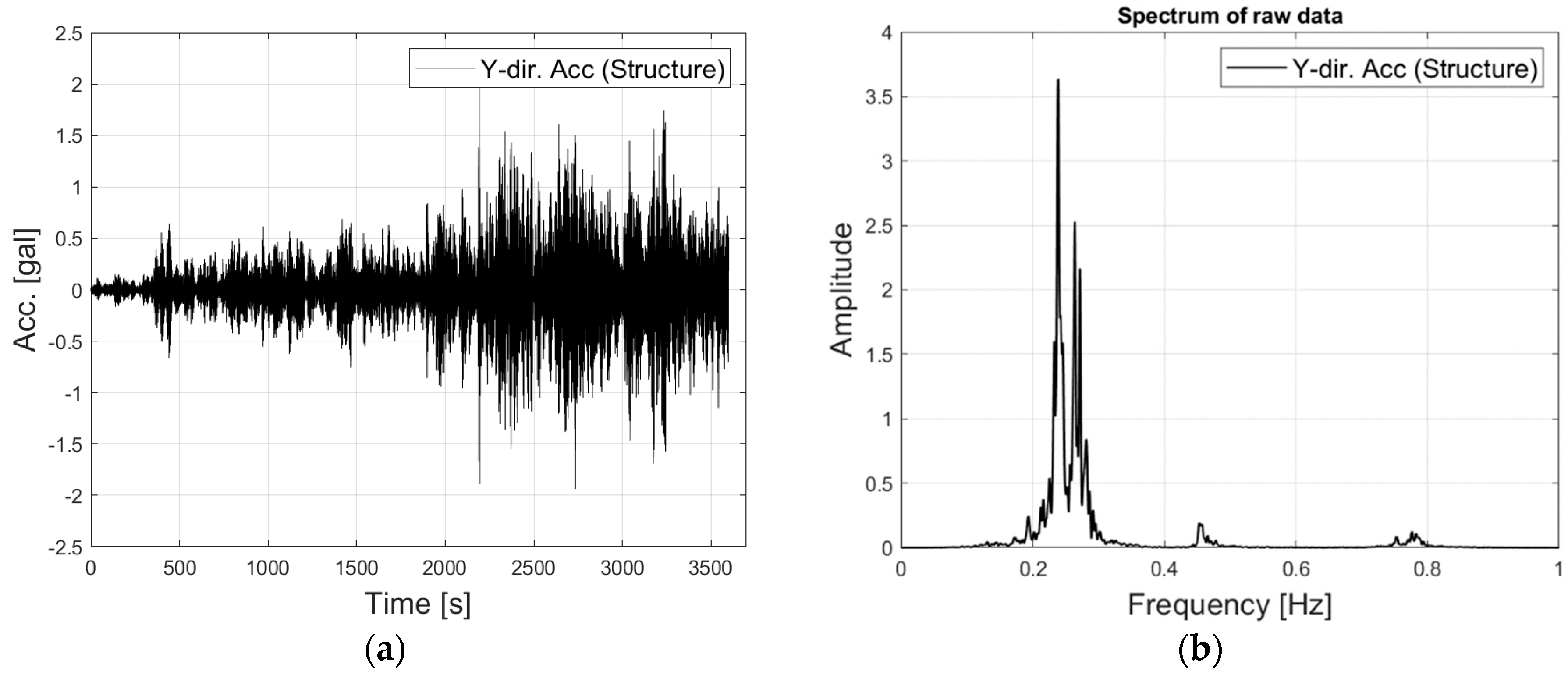
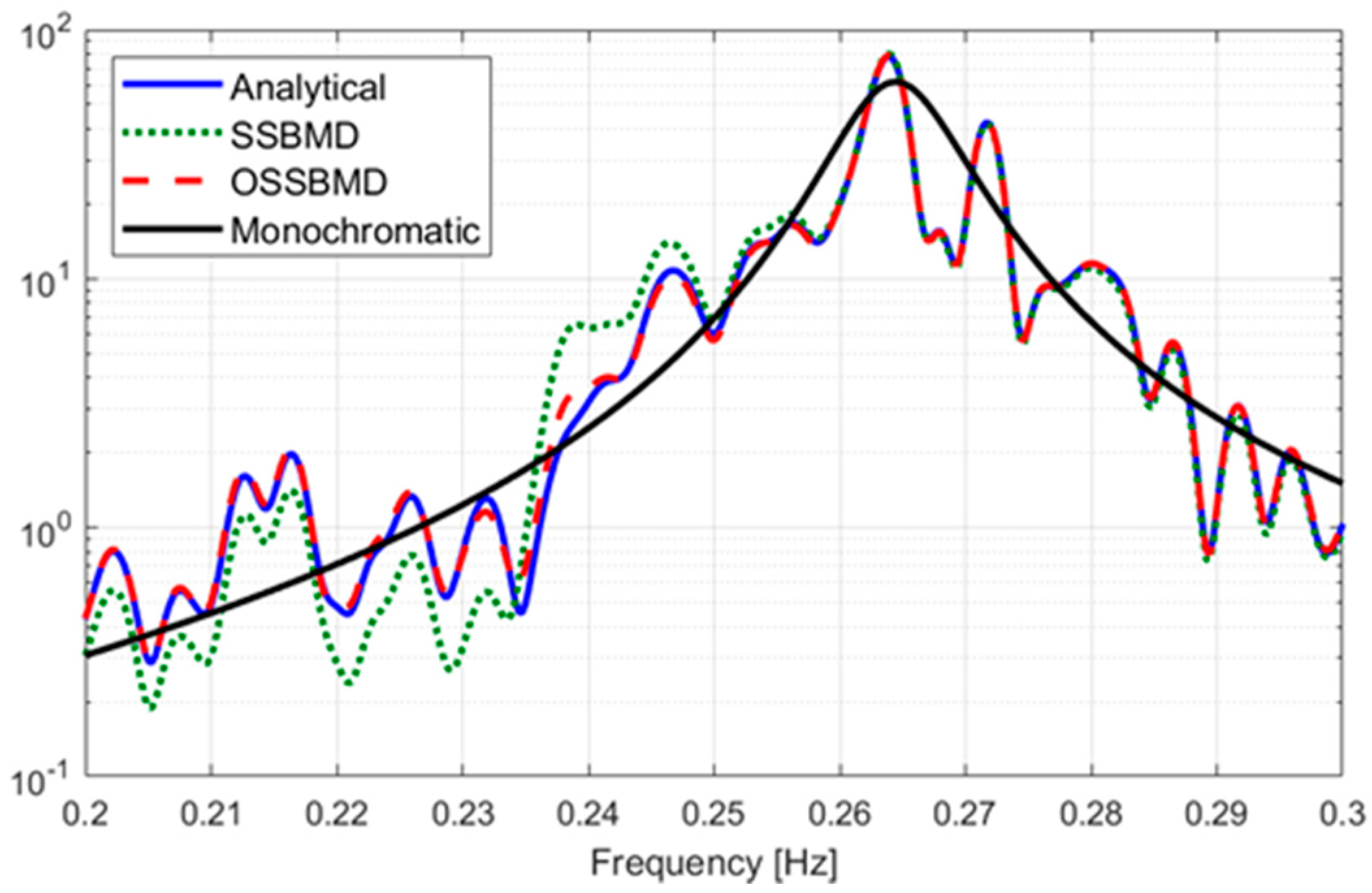
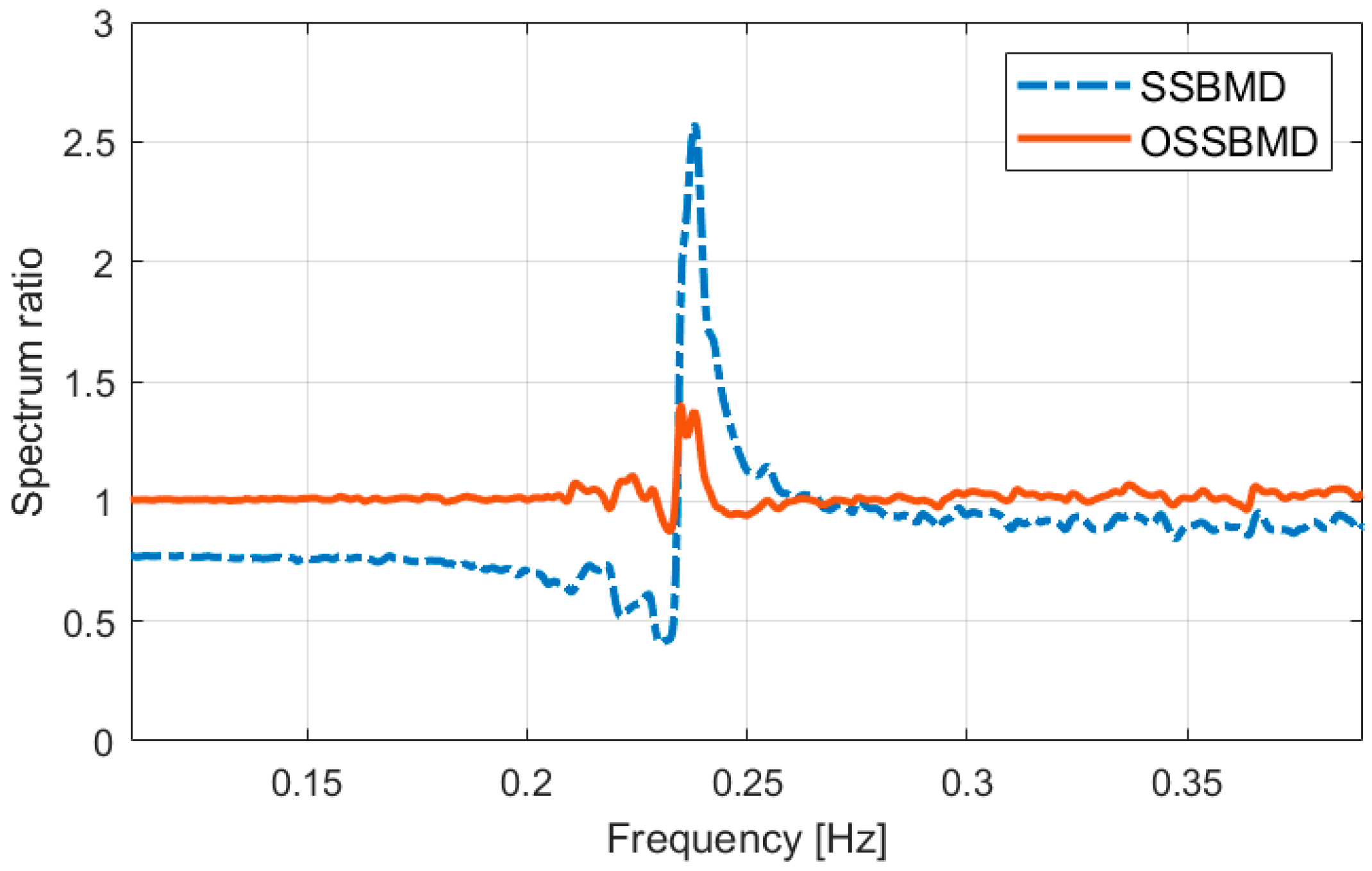
Lastly, the mode decomposition can be performed using the two objective functions presented above: Equation (22) and Equation (25). In this study, the former and the latter are referred to as State-Space Based Mode Decomposition (SSBMD) method and the Optimized State-Space Based Mode Decomposition (OSSBMD) method, respectively. In order to validate the efficacy of the proposed methods, this study examined the vibration signal from the TMD system which is one of the typical non-classically damped structures. A TMD is a passive damping device designed to reduce the dynamic response related to a particular vibration mode of the structure. As the TMD is tuned to the target natural frequency of the structure, two new modes are produced. Since those two modes are very close to each other, the system with a TMD exhibits typical non-classical damping. This study attempts to decompose the two closely spaced modes from the measured vibration signal data using the proposed techniques.