Submitted:
05 June 2023
Posted:
05 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Materials and Methods
Growth conditions for plant and bacteria
Inhibitory assay of B. amyloliquefaciens PMB04 against X. perforans strains
Survival of B. amyloliquefaciens PMB04 on the leaf of sweet pepper
Effect of B. amyloliquefaciens PMB04 on the control of bacterial leaf spot
Effects of different fermentation formula on bacterial population and sporulation of 30 L harvested fermentation liquid
Control effect of B. amyloliquefaciens PMB04 fermentation liquids on bacterial spot of sweet pepper
Sensitivity of B. amyloliquefaciens PMB04 and X. perforans XL1 to copper-containing fungicides
Effect of B. amyloliquefaciens PMB04 fermentation liquid filtrate against X. perforans
Effect of copper hydroxide on B. amyloliquefaciens PMB04 fermentation liquid in the control of bacterial leaf spot of sweet pepper
Data analysis
Results
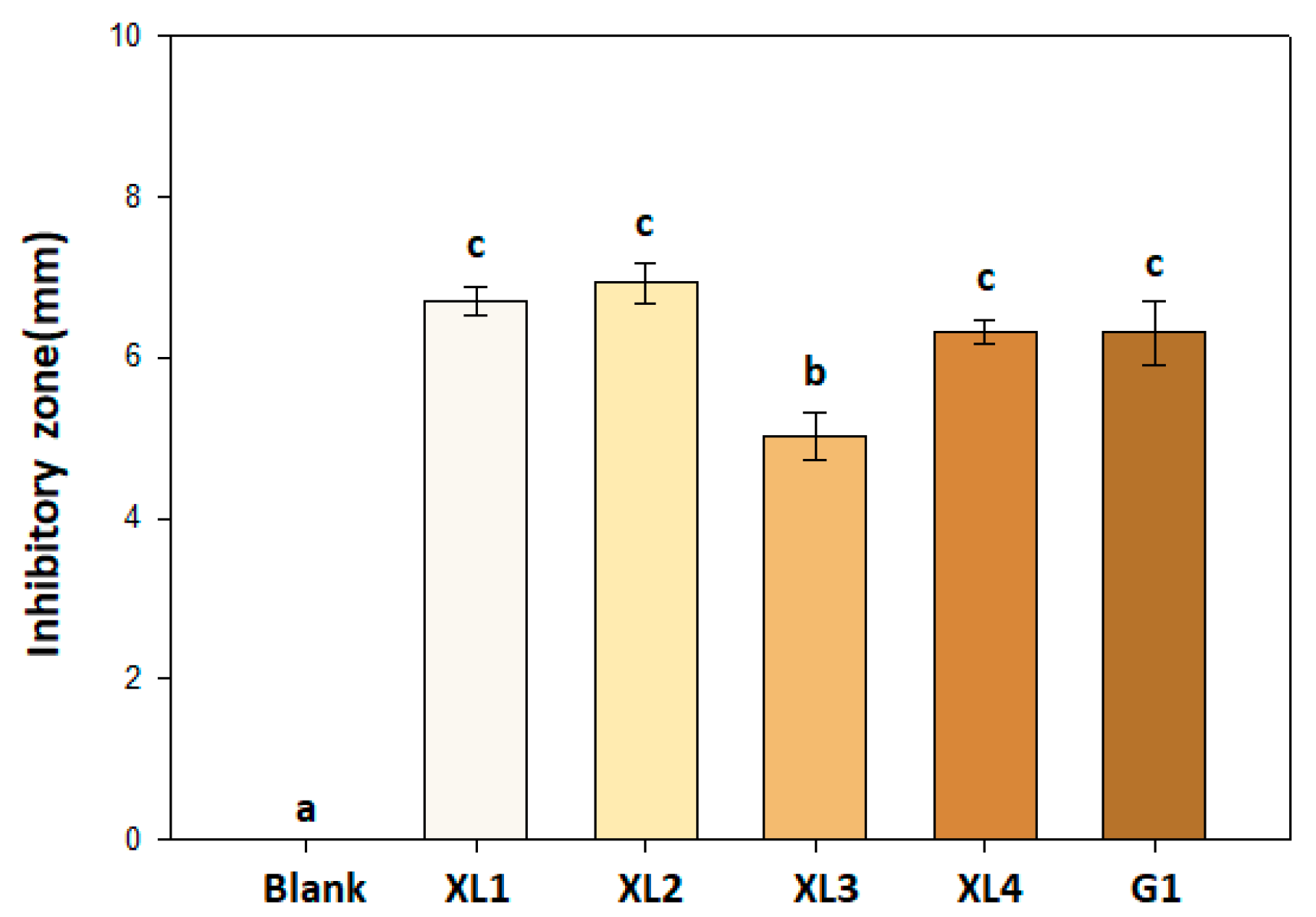
Inhibitory effect of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens PMB04 against Xanthomonas perforans strains
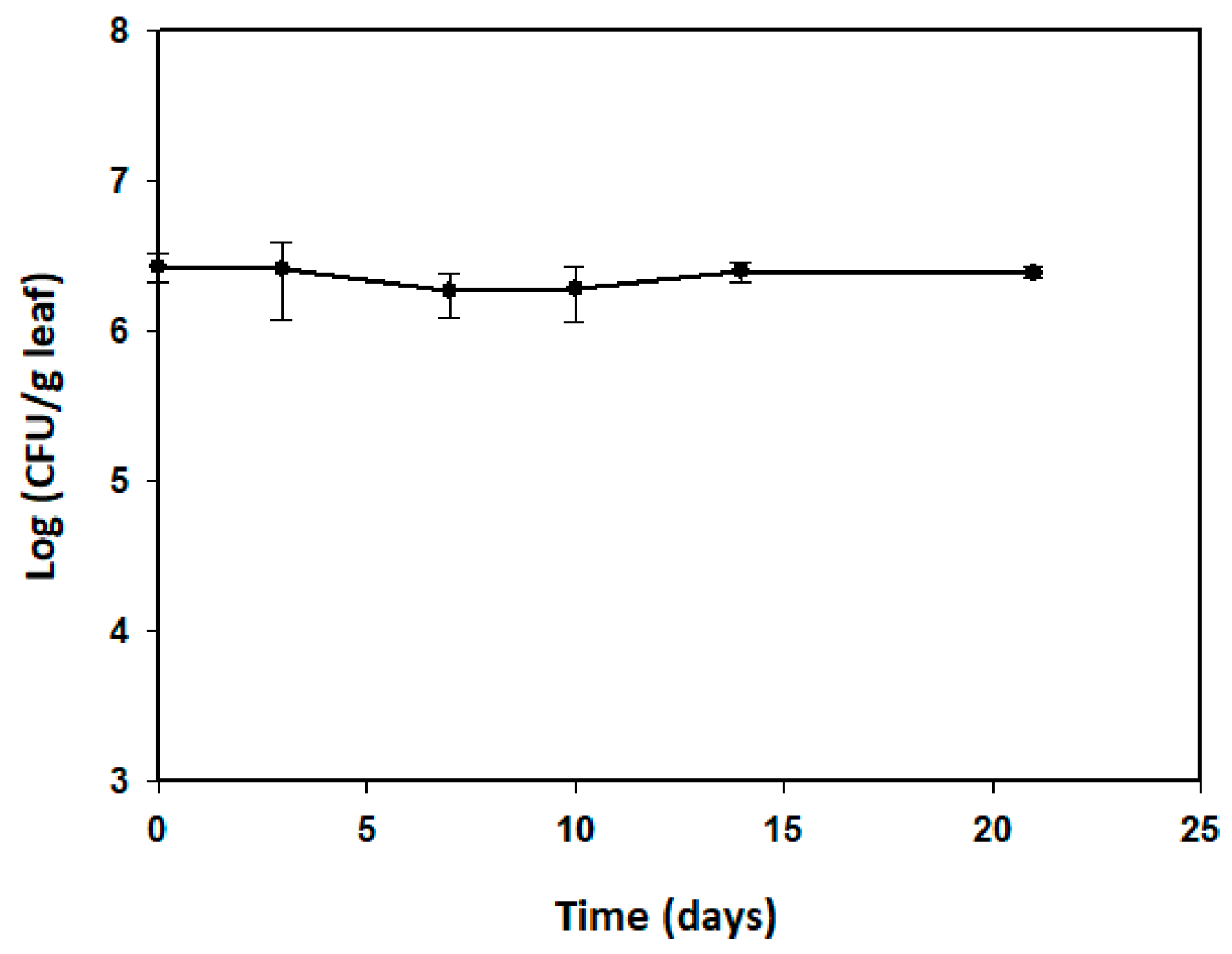
Survival of B. amyloliquefaciens PMB04 on the leaves of sweet pepper
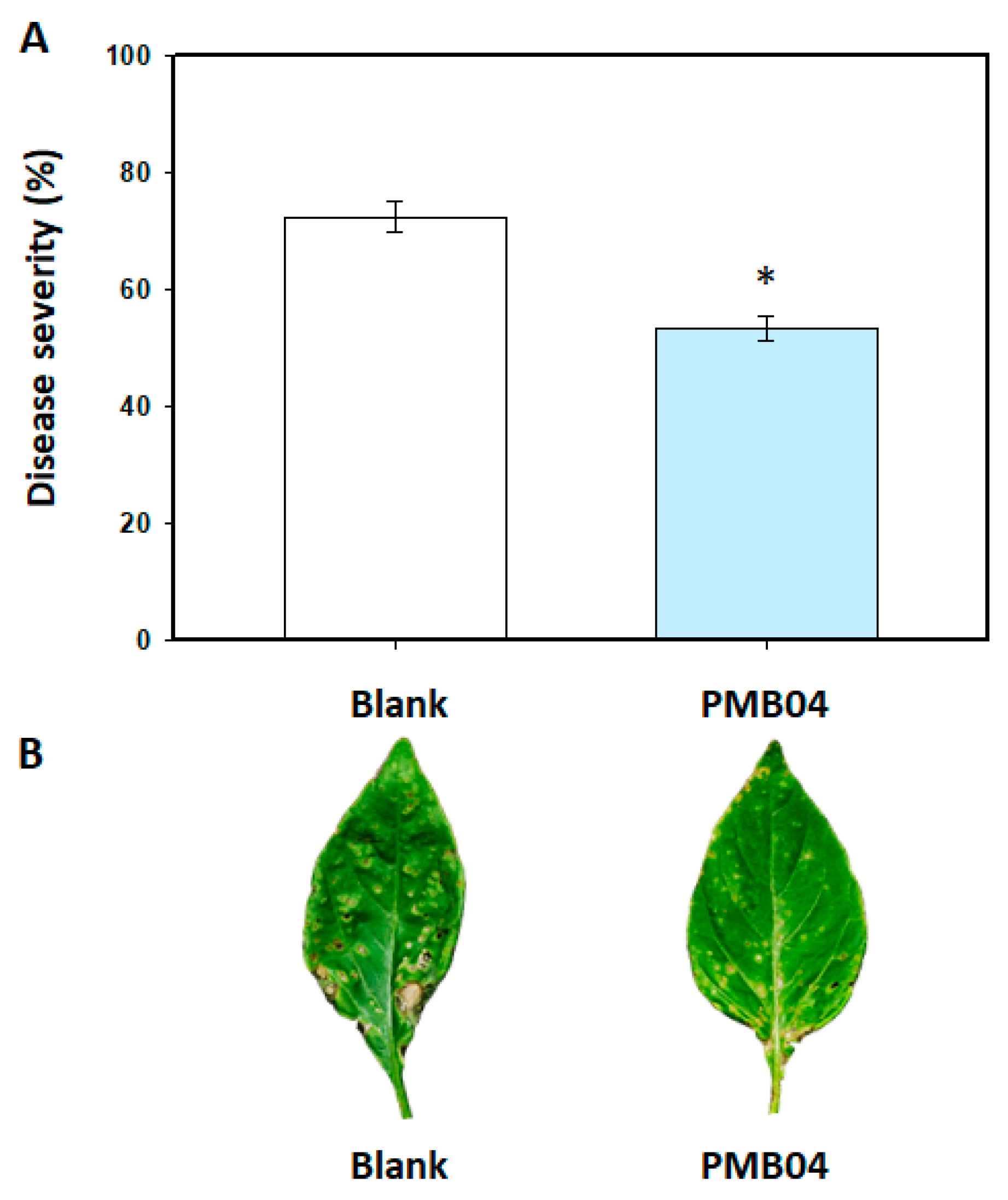
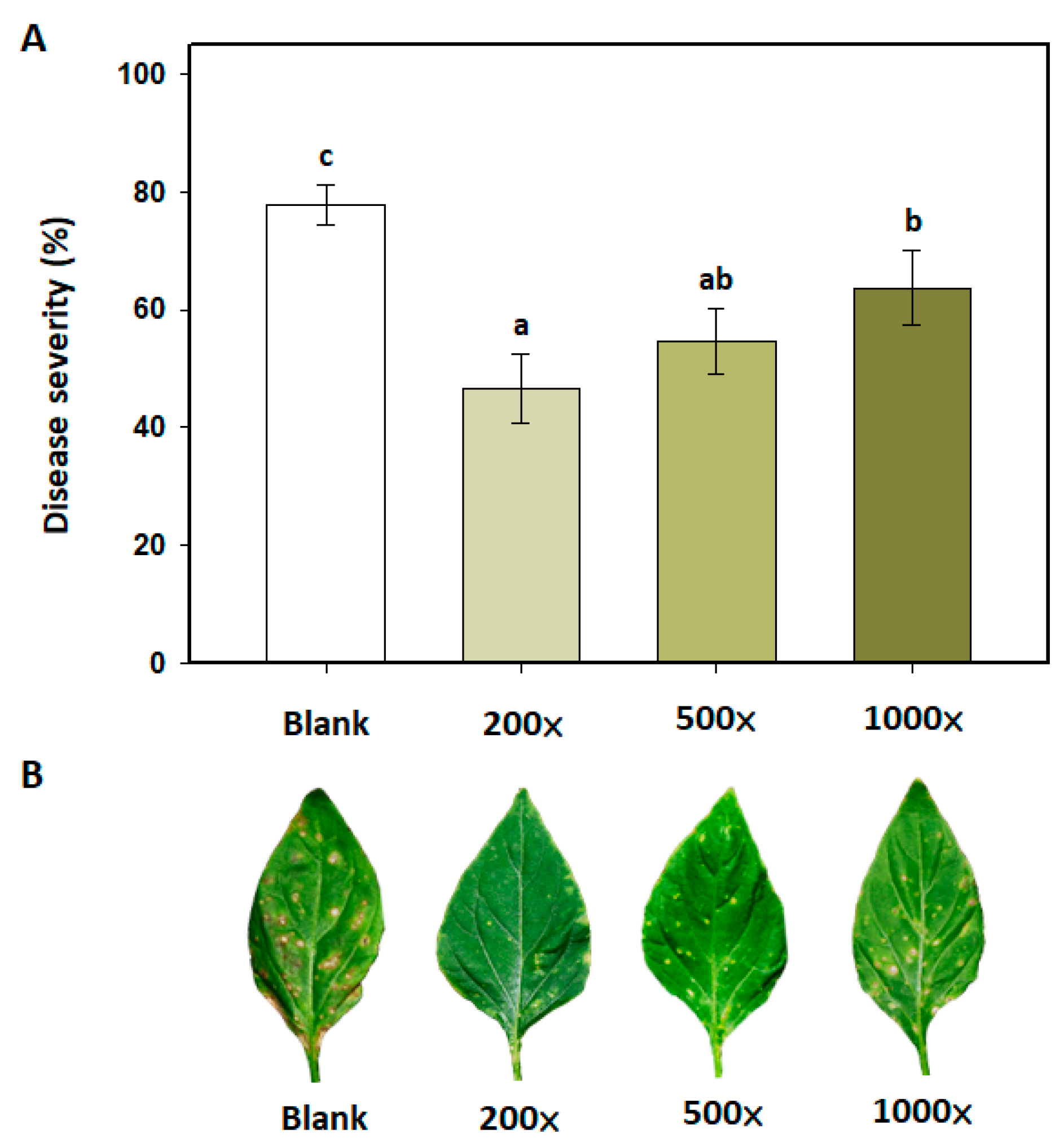
Control efficacy of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens PMB04 bacterial suspension to bacterial leaf spot disease in sweet pepper
Effects of formulated differences on the population and sporulation of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens PMB04 fermentation liquids from a 30-liter fermenter
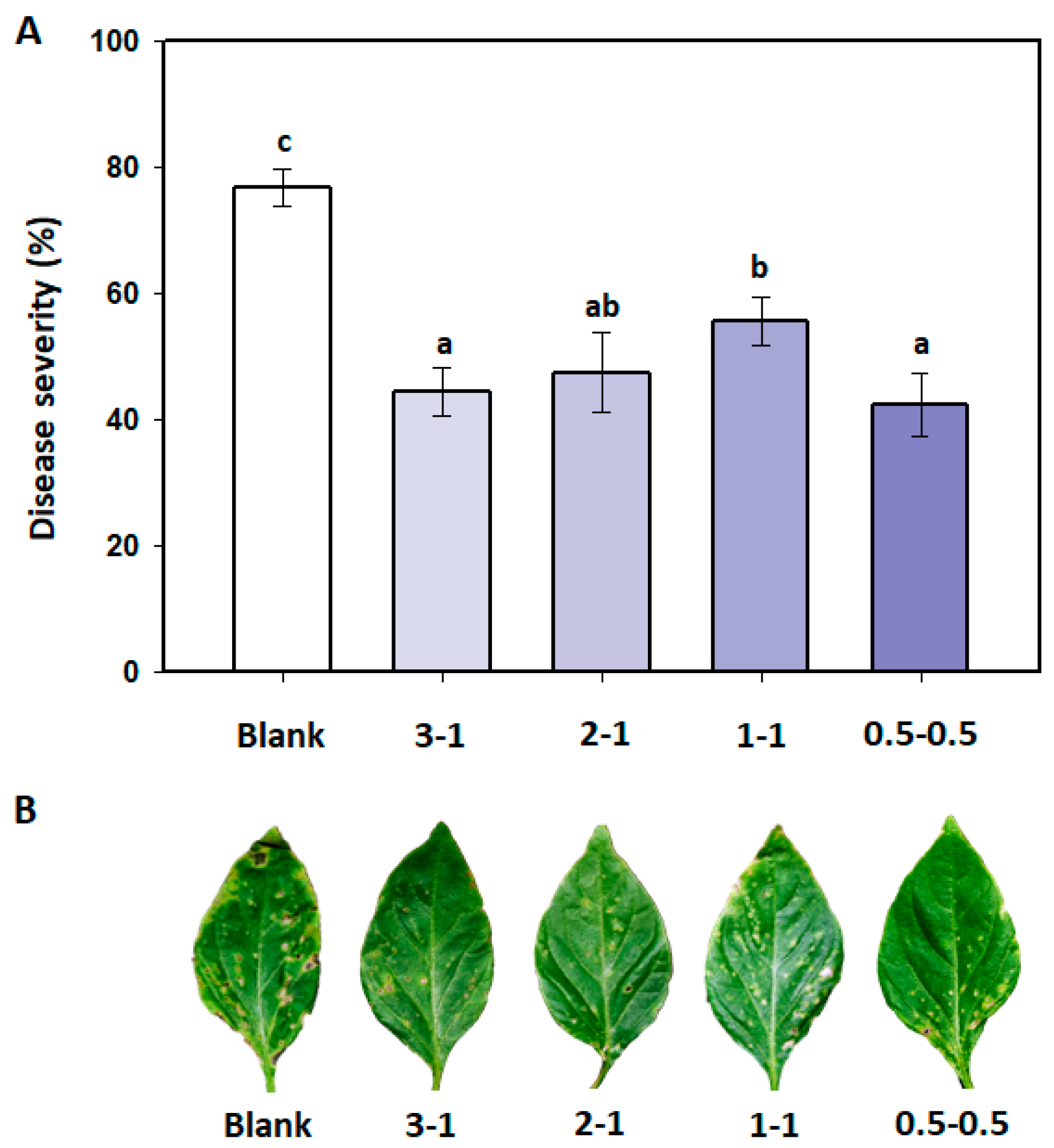
Effects of B. amyloliquefaciens PMB04 fermentation liquids on the control of bacterial spot
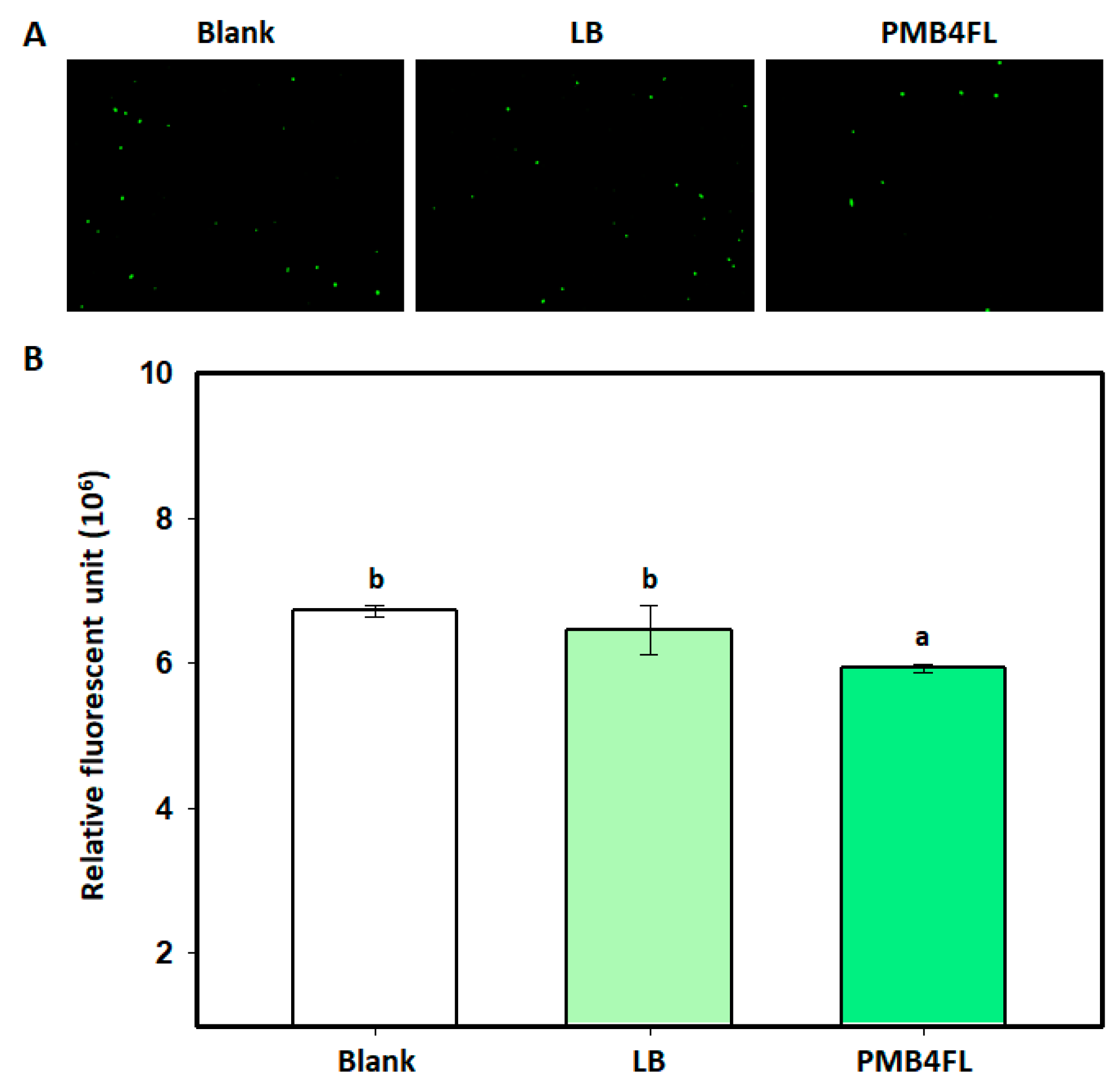
Effect of B. amyloliquefaciens PMB04 fermentation filtrate on the survival of X. perforans cells
Inhibitory effect of copper-containing fungicides against B. amyloliquefaciens PMB04 and X. perforans XL1
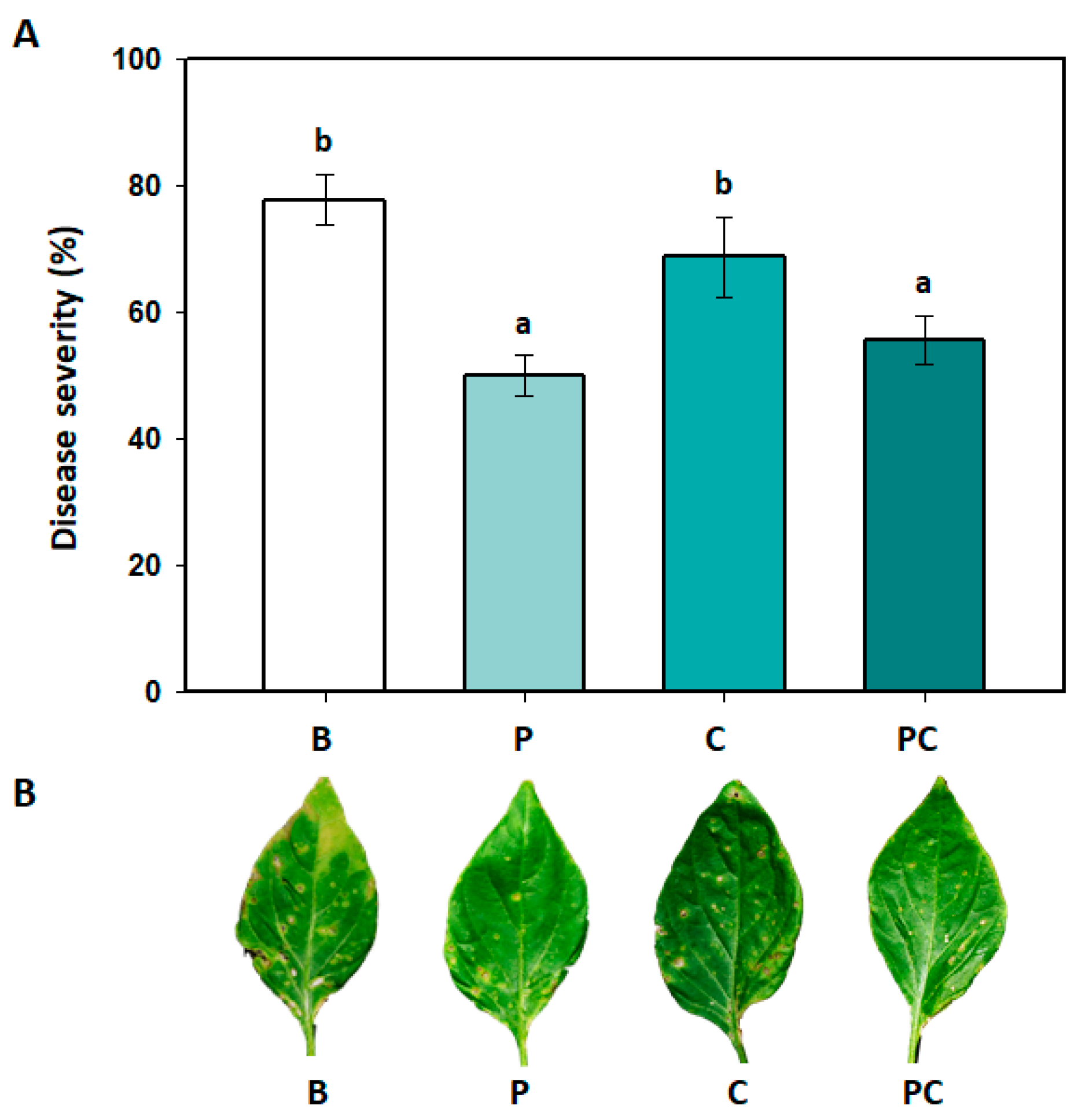
Effects of copper hydroxide on PMB4FL in the control of bacterial leaf spot in sweet pepper
Discussion
Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Potnis, N.; Timilsina, S.; Strayer, A.; Shantharaj, D.; Barak, J.D.; Paret, M.L.; Vallad, G.E.; Jones, J.B. Bacterial spot of tomato and pepper: diverse Xanthomonas species with a wide variety of virulence factors posing a worldwide challenge. Mol. Plant. Pathol. 2015, 16, 907–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roach, R.; Mann, R.; Gambley, C.G.; Shivas, R.G.; Rodoni, B. Identification of Xanthomonas species associated with bacterial leaf spot of tomato, capsicum and chilli crops in eastern Australia. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2017, 150, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanogo, S.; Clary, M. Bacterial leaf spot of chile pepper: a short guide for growers; New Mexico State University, College of Agriculture and Home Economics …: 2008.
- Hsiao, Y.-M.; Liu, Y.-F.; Lee, P.-Y.; Hsu, P.-C.; Tseng, S.-Y.; Pan, Y.-C. Functional characterization of copA gene encoding multicopper oxidase in Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 9290–9302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voloudakis, A.E.; Reignier, T.M.; Cooksey, D.A. Regulation of Resistance to Copper in Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. vesicatoria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 782–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almoneafy, A.A.; Kakar, K.U.; Nawaz, Z.; Li, B.; saand, M.A.; Chun-lan, Y.; Xie, G.-L. Tomato plant growth promotion and antibacterial related-mechanisms of four rhizobacterial Bacillus strains against Ralstonia solanacearum. Symbiosis 2014, 63, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Pi, H.; Chandrangsu, P.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Xiong, H.; Helmann, J.D.; Cai, Y. Antagonism of two plant-growth promoting Bacillus velezensis isolates against Ralstonia solanacearum and Fusarium oxysporum. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olishevska, S.; Nickzad, A.; Déziel, E. Bacillus and Paenibacillus secreted polyketides and peptides involved in controlling human and plant pathogens. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 1189–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ongena, M.; Jacques, P. Bacillus lipopeptides: versatile weapons for plant disease biocontrol. Trends Microbiol. 2008, 16, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setlow, P. Spores of Bacillus subtilis: their resistance to and killing by radiation, heat and chemicals. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 101, 514–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardharajula, S.; Zulfikar Ali, S.; Grover, M.; Reddy, G.; Bandi, V. Drought-tolerant plant growth promoting Bacillus spp.: effect on growth, osmolytes, and antioxidant status of maize under drought stress. J. Plant Interact. 2011, 6, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.-J.; Wu, P.-Y.; Lin, Y.-N.; Deng, W.-L.; Lin, Y.-H. Intensification of PAMP-triggered immunity in watermelon by Bacillus spp. strains as a strategy for controlling bacterial fruit blotch disease. J. Plant Med. 2019, 61, 39–48. [Google Scholar]
- Li’aini, A.S.; Lin, Y.-H.; Huang, T.-C.; Sulistyowati, L. Application of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens to control black rot disease on cabbage caused by Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris. J. Plant Med. 2017, 59, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-M.; Chen, X.; Wang, F.; Hsiao, C.-Y.; Yang, C.-Y.; Lin, S.-T.; Wu, L.-H.; Chen, Y.-K.; Liang, Y.-S.; Lin, Y.-H. Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strains control strawberry anthracnose through antagonistic activity and plant immune response intensification. Biol. Control 2021, 157, 104592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeriouh, H., Romero, D., García-Gutiérrez, L., Cazorla, F. M., de Vicente, A., and Pérez-García, A. The iturin-like lipopeptides are essential components in the biological control arsenal of Bacillus subtilis against bacterial diseases of cucurbits. MPMI 2011, 24, 1540-1552.
- Ahsan, T.; Zang, C.; Yu, S.; Pei, X.; Xie, J.; Lin, Y.; Liu, X.; Liang, C. Screening, and Optimization of Fermentation Medium to Produce Secondary Metabolites from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens, for the Biocontrol of Early Leaf Spot Disease, and Growth Promoting Effects on Peanut (Arachis hypogaea L. ). J. Fungi 2022, 8, 1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Cao, X.; Cai, Z.; Zhang, L.; Li, D.; Zhang, H.; Li, S.; Sun, X. Improving suppressive activity of compost on phytopathogenic microbes by inoculation of antagonistic microorganisms for secondary fermentation. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 367, 128288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, K.-W.; Liang, Y.-S.; Hsiao, C.-Y.; Wang, F.; Huang, T.-P.; Lin, Y.-H. Application of fermentation broth of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens PMB05 to control bacterial canker disease on lemon. J. Plant Med. 2021, 63, 17–26. [Google Scholar]
- Chuang, C.-Y.; Lin, S.-T.; Li, A.-T.; Li, S.-H.; Hsiao, C.-Y.; Lin, Y.-H. Bacillus amyloliquefaciens PMB05 Increases Resistance to Bacterial Wilt by Activating Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase and Reactive Oxygen Species Pathway Crosstalk in Arabidopsis thaliana. Phytopathology 2022. [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.-S.; Fu, J.-Y.; Chao, S.-H.; Tzean, Y.; Hsiao, C.-Y.; Yang, Y.-Y.; Chen, Y.-K.; Lin, Y.-H. Postharvest Application of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens PMB04 Fermentation Broth Reduces Anthracnose Occurrence in Mango Fruit. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, G.; Wrighton, C. Limitations of the initiation of germination of bacterial spores as a spore control procedure. . J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1968, 31, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, K.-W., Liang, Y.-S., Hsiao, C.-Y., Wang, F., Huang, T.-P., and Lin, Y.-H. Application of fermentation broth of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens PMB05 to control bacterial canker disease on lemon. J. Plant Med. 2021, 63, 17-26.
- Nicholson, W.L.; Munakata, N.; Horneck, G.; Melosh, H.J.; Setlow, P. Resistance of <i>Bacillus</i> Endospores to Extreme Terrestrial and Extraterrestrial Environments. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews 2000, 64, 548–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gase, K.; Ferretti, J.J.; Primeaux, C.; McShan, W.M. Identification, Cloning, and Expression of the CAMP factor gene (<i>cfa</i>) of Group A Streptococci. Infection and Immunity 1999, 67, 4725–4731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghelardi, E.; Salvetti, S.; Ceragioli, M.; Gueye, S.A.; Celandroni, F.; Senesi, S. Contribution of Surfactin and SwrA to Flagellin Expression, Swimming, and Surface Motility in Bacillus subtilis. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 2012, 78, 6540–6544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Wu, H.; Chen, L.; Yu, X.; Borriss, R.; Gao, X. Difficidin and bacilysin from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42 have antibacterial activity against Xanthomonas oryzae rice pathogens. Scientific Reports 2015, 5, 12975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- u, Z.; Huang, Y.; Li, Y.; Dong, J.; Liu, X.; Li, C. Biocontrol of Rhizoctonia solani via Induction of the Defense Mechanism and Antimicrobial Compounds Produced by Bacillus subtilis SL-44 on Pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). Frontiers in Microbiology 2019, 10. [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.-S.; Ahn, Y.-R.; Song, G.C.; Ghim, S.-Y.; Lee, S.; Lee, G.; Ryu, C.-M. Impact of a Bacterial Volatile 2,3-Butanediol on Bacillus subtilis Rhizosphere Robustness. Frontiers in Microbiology 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Liu, X.; Li, C.; Tian, W.; Shen, Q.; Shen, B. Isolation of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens S20 and its application in control of eggplant bacterial wilt. Journal of Environmental Management 2014, 137, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Es-Soufi, R.; Tahiri, H.; Azaroual, L.; El Oualkadi, A.; Martin, P.; Badoc, A.; Lamarti, A. Biocontrol potential of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Bc2 and Trichoderma harzianum TR against strawberry anthracnose under laboratory and field conditions. Agricultural Sciences 2020, 11, 260–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazion, F.; Perchat, S.; Buisson, C.; Vilas-Bôas, G.; Lereclus, D. A plasmid-borne Rap-Phr system regulates sporulation of Bacillus thuringiensis in insect larvae. Environmental Microbiology 2018, 20, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marín, A.; Ferreres, F.; Tomás-Barberán, F.A.; Gil, M.I. Characterization and Quantitation of Antioxidant Constituents of Sweet Pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 2004, 52, 3861–3869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, H.E.; Brichta-Harhay, D.M.; Brashears, M.M.; Nightingale, K.K.; Arthur, T.M.; Bosilevac, J.M.; Kalchayanand, N.; Schmidt, J.W.; Wang, R.; Granier, S.A.; et al. Salmonella in Peripheral Lymph Nodes of Healthy Cattle at Slaughter. Frontiers in Microbiology 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, B.; Chen, X.H.; Budiharjo, A.; Bleiss, W.; Vater, J.; Borriss, R. Efficient colonization of plant roots by the plant growth promoting bacterium Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42, engineered to express green fluorescent protein. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 151, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Wang, X.; Qin, Y.; Ren, Z.; Zhao, X. Watermelon Root Exudates Enhance Root Colonization of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens TR2. Curr. Microbiol. 2023, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Liu, S.-F.; Yue, L.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Y.-B.; Xie, Z.-K.; Wang, R.-Y. Epsc Involved in the Encoding of Exopolysaccharides Produced by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42 Act to Boost the Drought Tolerance of Arabidopsis thaliana. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Constesini, F.J.; de Melo, R.R.; Sato, H.H. An overview of Bacillus proteases: from production to application. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2018, 38, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, A.-D.; Li, H.-P.; Yuan, Q.-S.; Song, X.-S.; Yao, W.; He, W.-J.; Zhang, J.-B.; Liao, Y.-C. Antagonistic Mechanism of Iturin A and Plipastatin A from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens S76-3 from Wheat Spikes against Fusarium graminearum. PLOS ONE 2015, 10, e0116871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Fan, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhao, X.; Chen, W. Effect of nitrogen, carbon sources and agitation speed on acetoin production of Bacillus subtilis SF4-3. Electronic Journal of Biotechnology 2016, 19, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Yang, X.; Xue, C.; Chen, Y.; Qu, L.; Lu, W. Enhanced rhamnolipids production by Pseudomonas aeruginosa based on a pH stage-controlled fed-batch fermentation process. Bioresource Technology 2012, 117, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, T.-H.; Chuang, C.-Y.; Zheng, J.-L.; Chen, H.-H.; Liang, Y.-S.; Huang, T.-P.; Lin, Y.-H. Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Strain PMB05 Intensifies Plant Immune Responses to Confer Resistance Against Bacterial Wilt of Tomato. Phytopathology® 2020, 110, 1877–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, H.-P.; Huang, Y.-C.; Lin, Y.-H.; Deng, W.-L. Selection, Formulation, and Field Evaluation of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens PMB01 for Its Application to Manage Tomato Bacterial Wilt Disease. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeot, D.B.; Fernandez, M.; Morales, G.M.; Jofré, E. Fengycins From Bacillus amyloliquefaciens MEP218 Exhibit Antibacterial Activity by Producing Alterations on the Cell Surface of the Pathogens Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. vesicatoria and Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA01. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 03107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Wu, H.; Chen, L.; Yu, X.; Borriss, R.; Gao, X. Difficidin and bacilysin from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42 have antibacterial activity against Xanthomonas oryzae rice pathogens. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibi, S.; Weis, K.; Kaur, A.; Bhandari, R.; Goss, E.M.; Jones, J.B.; Potnis, N. A Brief Evaluation of Copper Resistance Mobile Genetic Island in the Bacterial Leaf Spot Pathogen, Xanthomonas euvesicatoria pv. perforans. Phytopathology 2023. [CrossRef]
- Obradovic, A.; Jones, J.B.; Momol, M.T.; Olson, S.M.; Jackson, L.E.; Balogh, B.; Guven, K.; Iriarte, F.B. Integration of Biological Control Agents and Systemic Acquired Resistance Inducers Against Bacterial Spot on Tomato. Plant Dis. 2005, 89, 712–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuriyama, I.; Musumi, K.; Yonezawa, Y.; Takemura, M.; Maeda, N.; Iijima, H.; Hada, T.; Yoshida, H.; Mizushina, Y. Inhibitory effects of glycolipids fraction from spinach on mammalian DNA polymerase activity and human cancer cell proliferation. The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry 2005, 16, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Formulation | Cells (Log CFU/ml) | Endospores (Log CFU/ml) | Sporulation (%) | |
| 3-11 | 9.00±0.41a | 9.29±0.41a | 100.00 | |
| 2-1 | 8.91±0.21ab | 9.09±0.33ab | 100.00 | |
| 1-1 | 8.54±0.06b | 8.47±0.08b | 99.14 | |
| 0.5-0.5 | 8.68±0.01b | 8.75±0.08b | 100.00 | |
| Strain | Fungicide | OD600 | |
| 12 h | 24 h | ||
| B. amyloliquefaciens PMB04 | |||
| Blank | 0.180a | 0.367a | |
| Tribasic copper sulfate | 0.161a | 0.395ab | |
| Copper hydroxide | 0.175a | 0.420b | |
| X. perforans XL1 | |||
| Blank | 0.123a | 0.257a | |
| Tribasic copper sulfate | 0.043b | 0.162c | |
| Copper hydroxide | 0.041b | 0.193b | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





