Submitted:
31 May 2023
Posted:
05 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
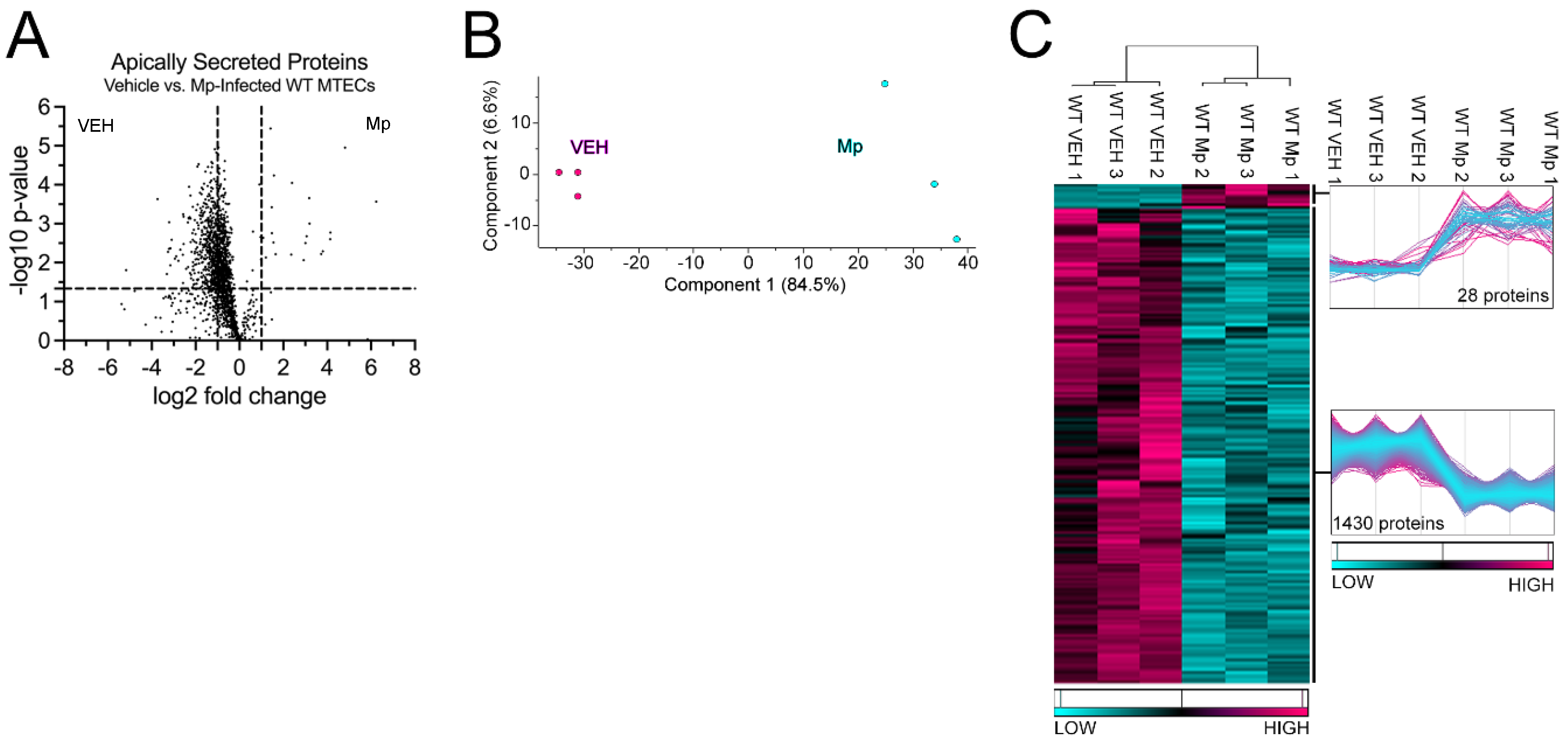
2.1. WT MTECs have decreased apical proteins secretions during Mp infection
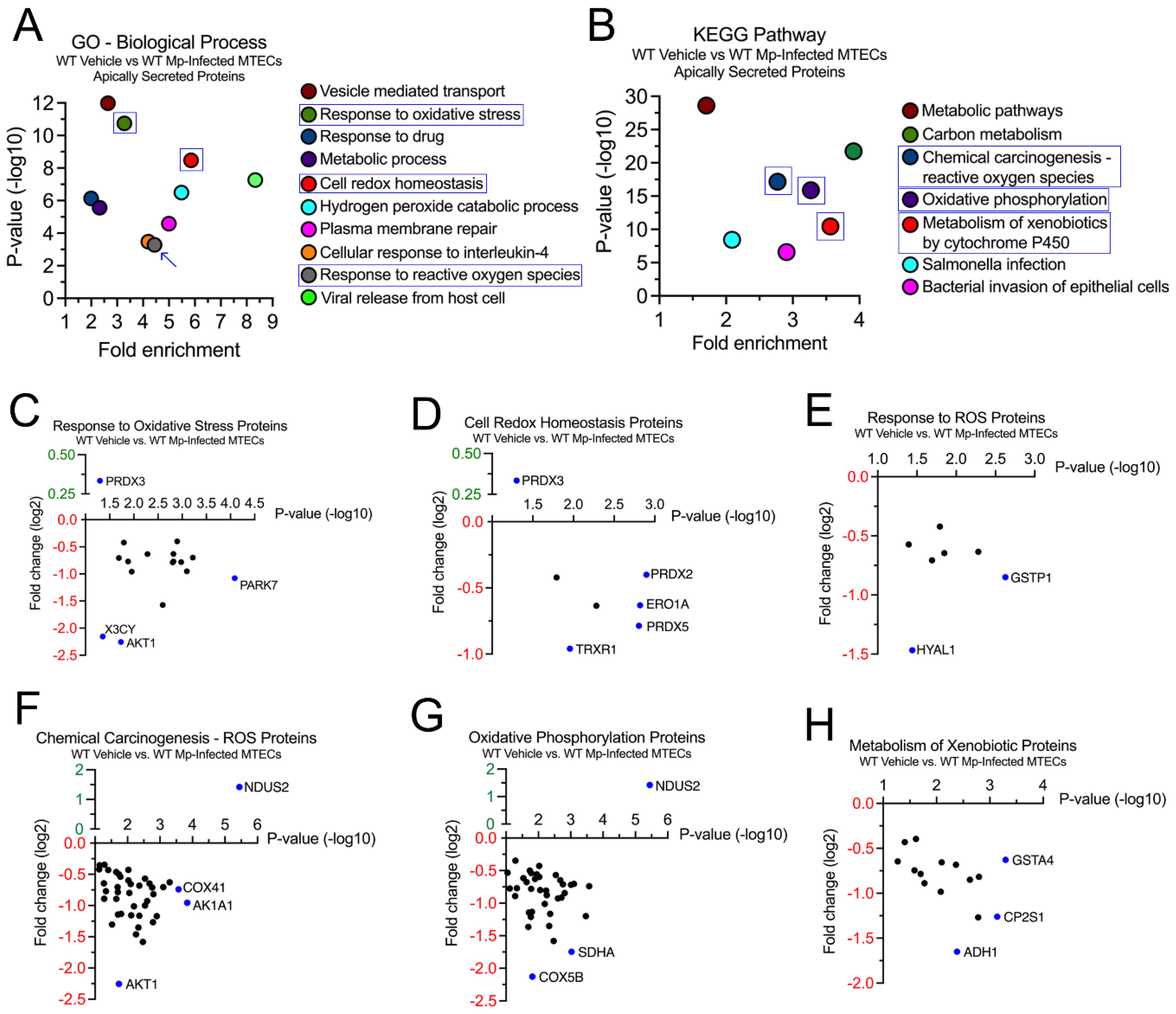
2.2. WT MTECs have decreased secretion of antioxidant proteins during Mp infection
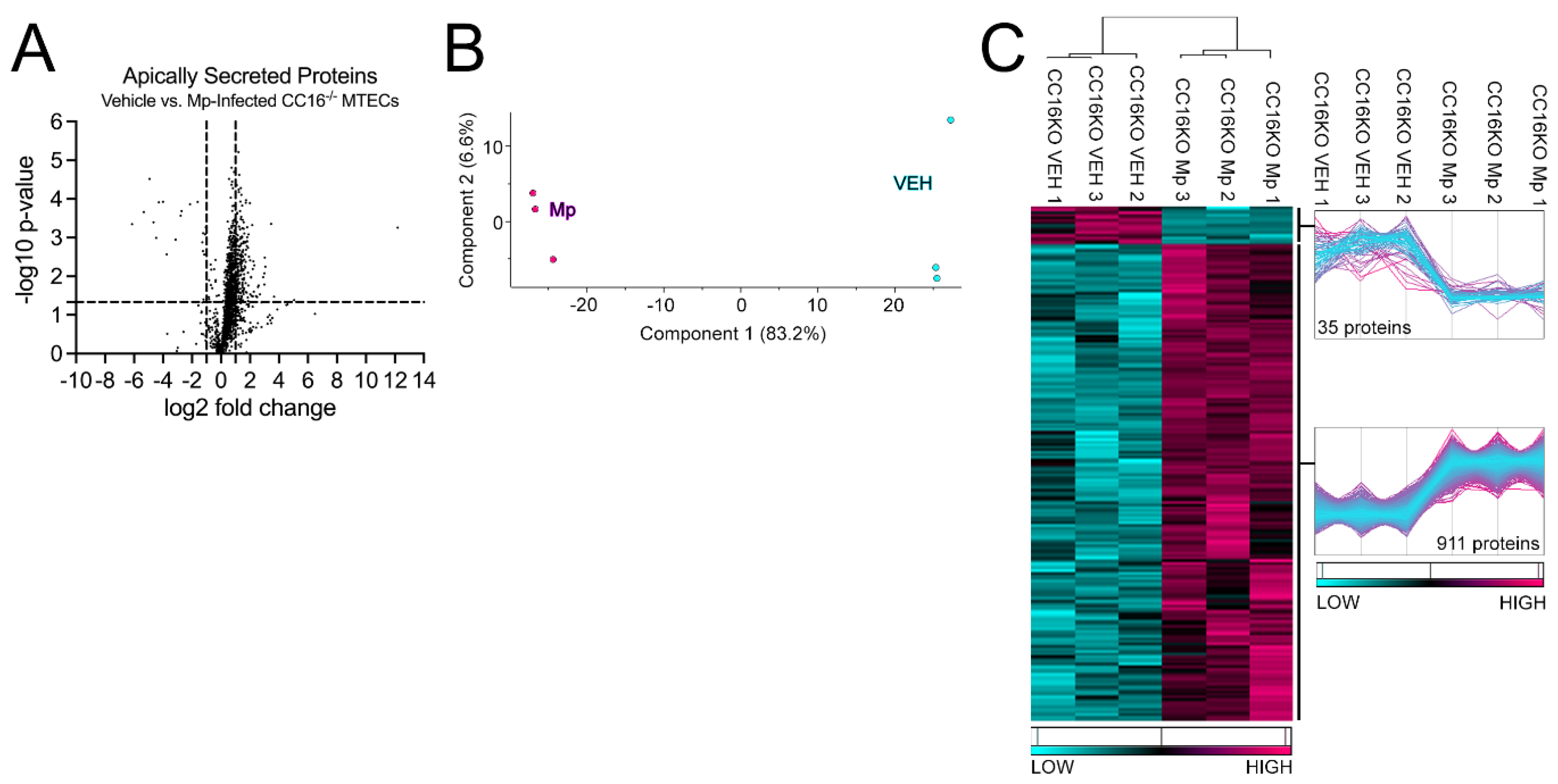
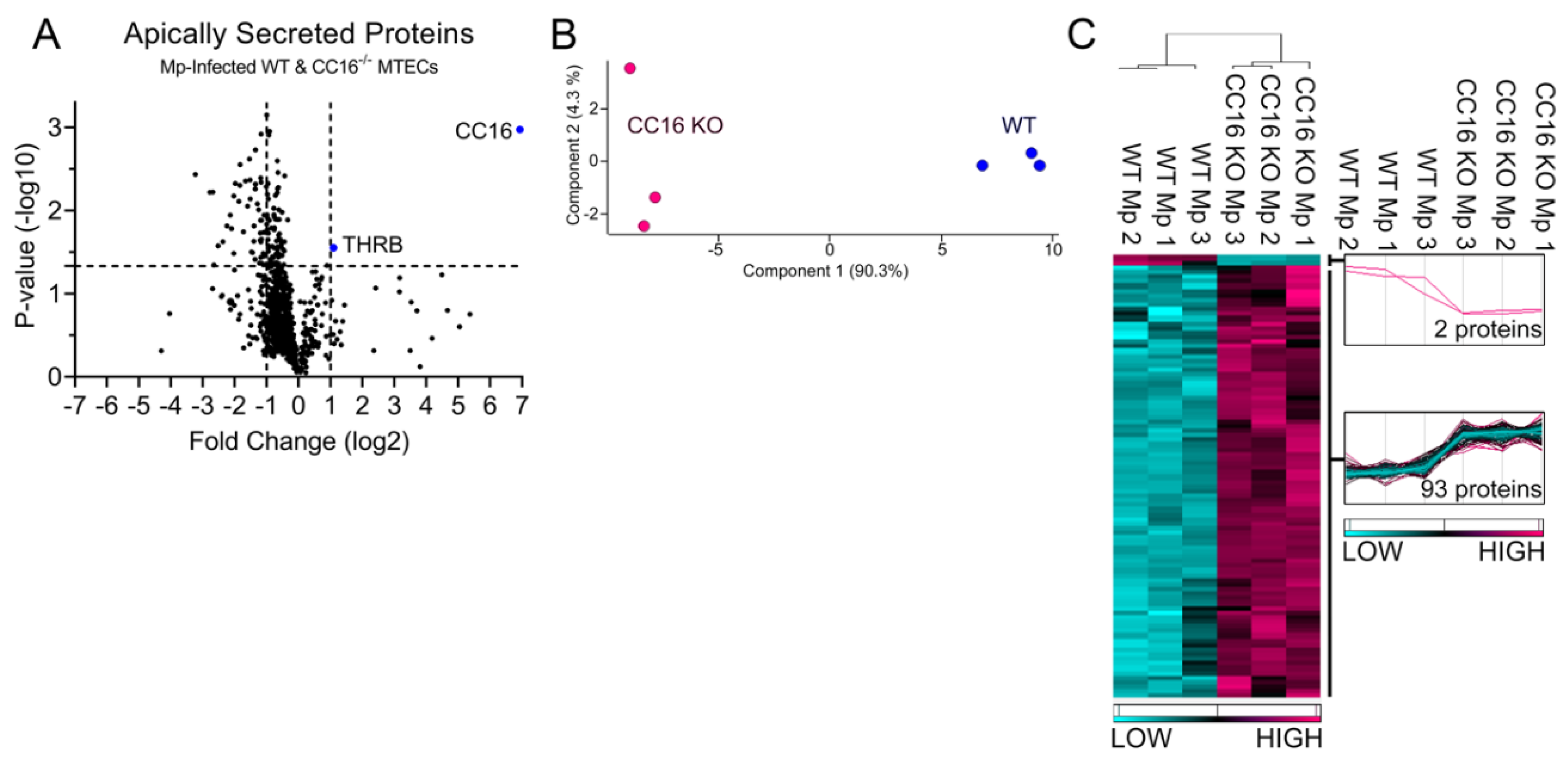
2.3. CC16-/- MTECs have increased apical protein secretions during Mp infection
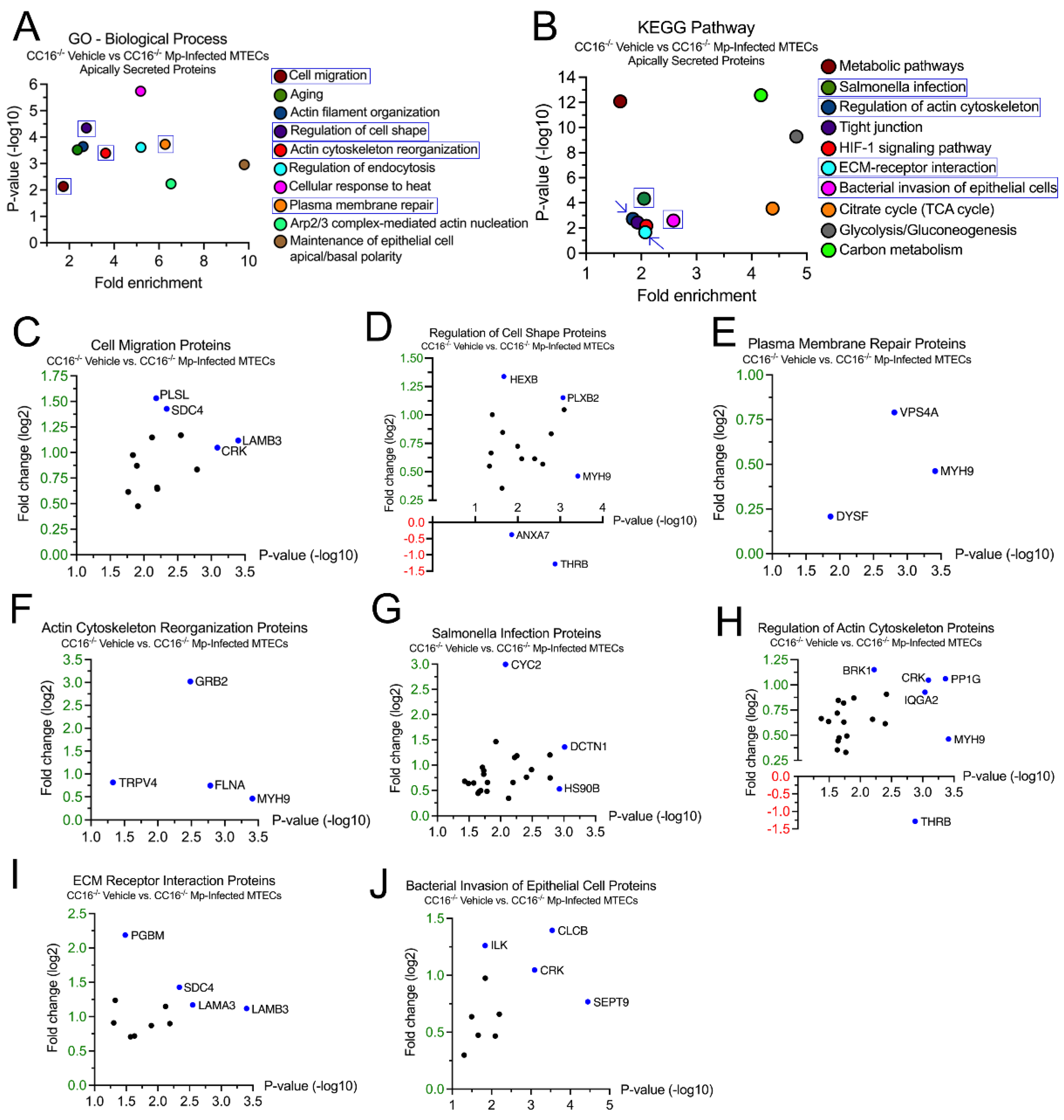
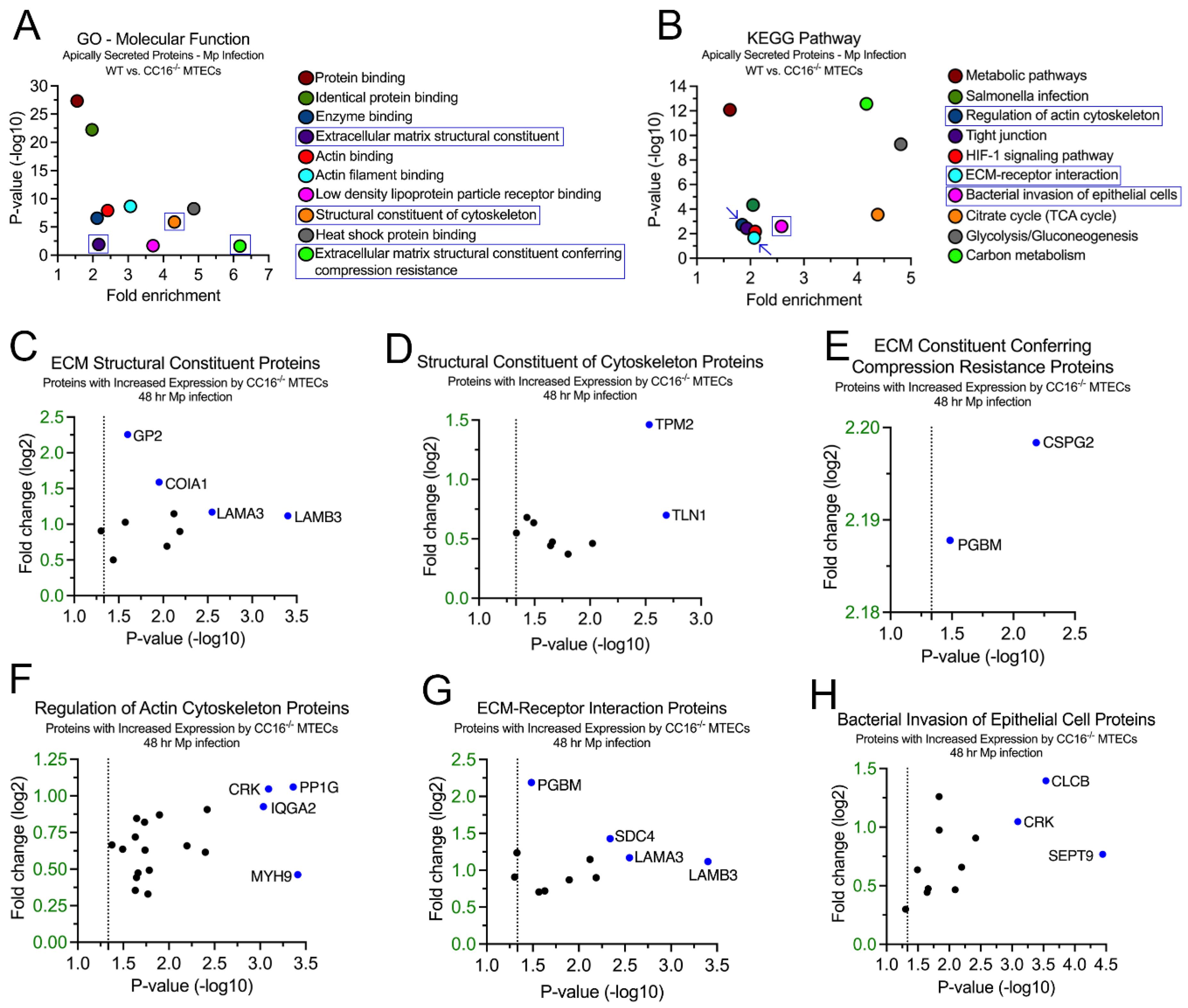
2.4. CC16-/- MTECs have increased secretion of airway remodeling and bacterial invasion proteins during Mp infection
2.5. CC16 mediates pulmonary epithelial cell apical protein secretion during Mp infection
2.6. CC16 deficiency increases pulmonary epithelial-driven airway remodeling during Mp infection
3. Discussion
4. METHODS:
4.1. Mouse Tracheal Epithelial Cell (MTEC) Isolation and Culturing
4.2. Mp Infection for WT and CC16-/- MTECs
4.3. In-Solution Tryptic Digestion
4.4. Mass Spectrometry and Spectrum Count Data Processing.
4.5. Label-free Quantitative Proteomics
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Broeckaert, F.; Bernard, A. Clara cell secretory protein (CC16): characteristics and perspectives as lung peripheral biomarker. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2000, 30, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, A.B. , Kundu, G.C., Mantile-Selvaggi, G., Yuan, C.J., Mandal, A.K., Chattopadhyay, S., Zheng, F., Pattabiraman, N. and Zhang, Z. Uteroglobin: a novel cytokine? Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 1999, 55, 771–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, A.B.; Zhang, Z.; Chilton, B.S. Uteroglobin: A Steroid-Inducible Immunomodulatory Protein That Founded the Secretoglobin Superfamily. Endocr. Rev. 2007, 28, 707–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laucho-Contreras, M.E.; Polverino, F.; Gupta, K.; Taylor, K.L.; Kelly, E.; Pinto-Plata, V.; Divo, M.; Ashfaq, N.; Petersen, H.; Stripp, B.; et al. Protective role for club cell secretory protein-16 (CC16) in the development of COPD. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 45, 1544–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraft, M.; Ledford, J.; Gozdz, J.; Li, X.; Francisco, D.; Manne, A.; Guerra, S.; Martinez, F.; Kaminski, N.; Wenzel, S.; et al. Club Cell Protein-16 modifies airway inflammation in asthma and is associated with significant clinical asthma outcomes. ERS International Congress, 5496. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.; Li, J.; Shu, M.; Wu, W.; Zhang, W.; Dou, Q.; Wu, J.; Zeng, X. The rCC16 Protein Protects Against LPS-Induced Cell Apoptosis and Inflammatory Responses in Human Lung Pneumocytes. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laucho-Contreras, M.E.; Polverino, F.; Gupta, K.; Taylor, K.L.; Kelly, E.; Pinto-Plata, V.; Divo, M.; Ashfaq, N.; Petersen, H.; Stripp, B.; et al. Protective role for club cell secretory protein-16 (CC16) in the development of COPD. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 45, 1544–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, R.; Qu, Y.; Huang, Q.; Sun, X.; Mu, D.; Li, X. Recombinant CC16 regulates inflammation, oxidative stress, apoptosis and autophagy via the inhibition of the p38MAPK signaling pathway in the brain of neonatal rats with sepsis. Brain Res. 2019, 1725, 146473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsalane, K.; Broeckaert, F.; Knoops, B.; Wiedig, M.; Toubeau, G.; Bernard, A. Clara Cell Specific Protein (CC16) Expression after Acute Lung Inflammation Induced by Intratracheal Lipopolysaccharide Administration. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 161, 1624–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mango, G.W.; Johnston, C.J.; Reynolds, S.D.; Finkelstein, J.N.; Plopper, C.G.; Stripp, B.R.; Turcatel, G.; Millette, K.; Thornton, M.; Leguizamon, S.; et al. Clara cell secretory protein deficiency increases oxidant stress response in conducting airways. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Mol. Physiol. 1998, 275, L348–L356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, B. , MANTILE-SELVAGGI, G.I.U.D.I.T.T.A., Kundu, G.C., Miele, L., CORDELLA-MIELE, E.L.E.O.N.O.R.A., Zhang, Z. and Mukherjee, A.B. Amino Acid Residues in α-Helix-3 of Human Uteroglobin Are Critical for Its Phospholipase A2 Inhibitory Activity. Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 2000, 923, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facchiano, A.; Cordella-Miele, E.; Miele, L.; Mukherjee, A.B. Inhibition of pancreatic phospholipase A2 activity by uteroglobin and antiflammin peptides: Possible mechanism of action. Life Sci. 1991, 48, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, M. , Yuan, Y., Wang, D., Li, T., Wang, D., Shi, X., Guo, M., Wang, C., Zhang, X., Zheng, G. and Yu, B. Recombinant CC16 protein inhibits the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines via NF-κB and p38 MAPK pathways in LPS-activated RAW264. 7 macrophages. Acta Biochim. Et Biophys. Sin. 2017, 49, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laucho-Contreras, M.E.; Polverino, F.; Rojas-Quintero, J.; Wang, X.; Owen, C.A. Club cell protein 16 (Cc16) deficiency increases inflamm-aging in the lungs of mice. Physiol. Rep. 2018, 6, e13797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, M.; Liu, H.; Li, T.; Wang, D.; Hu, X.; Zhang, X.; Yu, B.; Guo, R.; Wang, H. Recombinant club cell protein 16 (CC16) ameliorates cigarette smoke-induced lung inflammation in a murine disease model of COPD. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 2198–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermans, C.; Bernard, A. Clara cell protein (CC16): characteristics and potential applications as biomarker of lung toxicity. Biomarkers 1996, 1, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waites, K.B.; Xiao, L.; Liu, Y.; Balish, M.F.; Atkinson, T.P. Mycoplasma pneumoniae from the Respiratory Tract and Beyond. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 30, 747–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.; Li, S.; Zhu, C.; Zhou, R.; Leung, P.H.M. Mycoplasma pneumoniae Infections: Pathogenesis and Vaccine Development. Pathogens 2021, 10, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waites, K.B. and Talkington, D.F. Mycoplasma pneumoniae and its role as a human pathogen. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2004, 17, 697–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Liu, M.; Ye, Z.; Tan, T.; Liu, X.; You, X.; Zeng, Y.; Wu, Y. [Corrigendum] Insights into the pathogenesis of Mycoplasma pneumoniae (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 17, 4155–4155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannuzo, N.; Insel, M.; Marshall, C.; Pederson, W.P.; Addison, K.J.; Polverino, F.; Guerra, S.; Ledford, J.G. CC16 Deficiency in the Context of Early-Life Mycoplasma pneumoniae Infection Results in Augmented Airway Responses in Adult Mice. Infect. Immun. 2022, 90, e0054821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.D. , Younis, U.S., Menghani, S.V., Addison, K.J., Whalen, M., Pilon, A.L., Cress, A.E., Polverino, F., Romanoski, C.E., Kraft, M. and Martinez, F.D. CC16 Binding to α4β1 integrin protects against Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 203, 1410–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerra, S.; Halonen, M.; Vasquez, M.M.; Spangenberg, A.; A Stern, D.; Morgan, W.J.; Wright, A.L.; Lavi, I.; Tarès, L.; Carsin, A.-E.; et al. Relation between circulating CC16 concentrations, lung function, and development of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease across the lifespan: a prospective study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2015, 3, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerra, S.; Vasquez, M.M.; Spangenberg, A.; Halonen, M.; Martin, R.J. Club cell secretory protein in serum and bronchoalveolar lavage of patients with asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 932–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Guerra, S.; Ledford, J.G.; Kraft, M.; Li, H.; Hastie, A.T.; Castro, M.; Denlinger, L.C.; Erzurum, S.C.; Fahy, J.V.; et al. Low CC16 mRNA Expression Levels in Bronchial Epithelial Cells Are Associated with Asthma Severity. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2023, 207, 438–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rava, M.; Tares, L.; Lavi, I.; Barreiro, E.; Zock, J.-P.; Ferrer, A.; Muniozguren, N.; Nadif, R.; Cazzoletti, L.; Kauffmann, F.; et al. Serum levels of Clara cell secretory protein, asthma, and lung function in the adult general population. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 132, 230–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, G.E.; Sherrill, D.L.; Guerra, S.; Barbee, R.A. Asthma as a Risk Factor for COPD in a Longitudinal Study. Chest 2004, 126, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, J.; Emond, M.J.; Spangenberg, A.; Stern, D.A.; Vasquez, M.M.; Blue, E.E.; Buckingham, K.J.; Sherrill, D.L.; Halonen, M.; Gibson, R.L.; et al. Club cell secretory protein and lung function in children with cystic fibrosis. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2022, 21, 811–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Lipinski, A.A.; Liktor-Busa, E.; Smith, A.F.; Moutal, A.; Khanna, R.; Langlais, P.R.; Largent-Milnes, T.M.; Vanderah, T.W. The Effects of Repeated Morphine Treatment on the Endogenous Cannabinoid System in the Ventral Tegmental Area. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Huang, D.; Wang, J.; Zhao, K.; Zhou, Y.; Guo, Z.; Zhai, S.; Xu, H.; Cui, H.; Yao, H.; et al. QTLbase: an integrative resource for quantitative trait loci across multiple human molecular phenotypes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 48, D983–D991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Jia, Q.; Jahani, P.S.; Hurrell, B.P.; Pan, C.; Huang, P.; Gukasyan, J.; Woodward, N.C.; Eskin, E.; Gilliland, F.D.; et al. Genome-wide analysis highlights contribution of immune system pathways to the genetic architecture of asthma. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrine, N.; Guyatt, A.L.; Erzurumluoglu, A.M.; Jackson, V.E.; Hobbs, B.D.; Melbourne, C.A.; Batini, C.; Fawcett, K.A.; Song, K.; Sakornsakolpat, P.; et al. New genetic signals for lung function highlight pathways and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease associations across multiple ancestries. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 481–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, S.W.; Butler, J.D.; Schumacher, U.K.; Wightman, P.D.; Mukherjee, A.B. Uteroglobin inhibits phospholipase A2 activity. Life Sci. 1986, 38, 1813–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miele, L.; Cordella-Miele, E.; Facchiano, A.; Mukherjee, A.B. Novel anti-inflammatory peptides from the region of highest similarity between uteroglobin and lipocortin I. Nature 1988, 335, 726–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plopper, C.; Mango, G.; Hatch, G.; Wong, V.; Toskala, E.; Reynolds, S.; Tarkington, B.; Stripp, B. Elevation of susceptibility to ozone-induced acute tracheobronchial injury in transgenic mice deficient in Clara cell secretory protein. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2006, 213, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, J.; Insel, M.; Addison, K.J.; Stern, D.A.; Pederson, W.; Dy, A.; Rojas-Quintero, J.; Owen, C.A.; Sherrill, D.L.; Morgan, W.; et al. Club Cell Secretory Protein Deficiency Leads to Altered Lung Function. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 199, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braido, F. , Riccio, A.M., Guerra, L., Gamalero, C., Zolezzi, A., Tarantini, F., De Giovanni, B., Folli, C., Descalzi, D. and Canonica, G.W. Clara cell 16 protein in COPD sputum: a marker of small airways damage? Respir. Med. 2007, 101, 2119–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-Z.; Rosenberger, C.L.; Bao, Y.-X.; Stark, J.M.; Harrod, K.S. Clara Cell Secretory Protein Modulates Lung Inflammatory and Immune Responses to Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection. J. Immunol. 2003, 171, 1051–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomori, H.; Horio, H.; Fuyuno, G.; Kobayashi, R.; Morinaga, S.; Hirabayashi, Y. Protein 1 (Clara cell protein) serum levels in healthy subjects and patients with bacterial pneumonia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1995, 152, 746–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almuntashiri, S.; Zhu, Y.; Han, Y.; Wang, X.; Somanath, P.R.; Zhang, D. Club Cell Secreted Protein CC16: Potential Applications in Prognosis and Therapy for Pulmonary Diseases. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 4039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periayah, M.H.; Halim, A.S.; Mat Saad, A.Z. Mechanism Action of Platelets and Crucial Blood Coagulation Pathways in Hemostasis. Int. J. Hematol. Oncol. Stem Cell Res. 2017, 11, 319–327. [Google Scholar]
- Terada, M. , Kelly, E.A. and Jarjour, N.N. Increased thrombin activity after allergen challenge: a potential link to airway remodeling? Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2004, 169, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuliani, F.S. , Chen, J.Y., Cheng, W.H., Wen, H.C., Chen, B.C. and Lin, C.H. Thrombin induces IL-8/CXCL8 expression by DCLK1-dependent RhoA and YAP activation in human lung epithelial cells. J. Biomed. Sci. 2022, 29, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulsson, M.; Su, Y.-C.; Ringwood, T.; Uddén, F.; Riesbeck, K. Pseudomonas aeruginosa uses multiple receptors for adherence to laminin during infection of the respiratory tract and skin wounds. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prince, O.A. , Krunkosky, T.M., Sheppard, E.S. and Krause, D.C. Modelling persistent Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection of human airway epithelium. Cell. Microbiol. 2018, 20, e12810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elkhal, C.K. , Kean, K.M., Parsonage, D., Maenpuen, S., Chaiyen, P., Claiborne, A. and Karplus, P.A. Structure and proposed mechanism of l-α-glycerophosphate oxidase from Mycoplasma pneumoniae. FEBS J. 2015, 282, 3030–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, H.W. , Rino, J.G., Wexler, R.B., Campbell, K., Harbeck, R.J. and Martin, R.J. Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection increases airway collagen deposition in a murine model of allergic airway inflammation. Am. J. Physiol. -Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2005, 289, L125–L133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.-J. The Role ofMycoplasma pneumoniaeInfection in Asthma. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2012, 4, 59–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledford, J.; Guerra, S.; Martinez, F.; Kraft, M. Club cell secretory protein: a key mediator in Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. . ERS International Congress, 4972. [Google Scholar]
- Kraft, M. , Adler, K.B., Ingram, J.L., Crews, A.L., Atkinson, T.P., Cairns, C.B., Krause, D.C. and Chu, H.W. Mycoplasma pneumoniae induces airway epithelial cell expression of MUC5AC in asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 2008, 31, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biscardi, S.; Lorrot, M.; Marc, E.; Moulin, F.; Boutonnat-Faucher, B.; Heilbronner, C.; Iniguez, J.-L.; Chaussain, M.; Nicand, E.; Raymond, J.; et al. Mycoplasma pneumoniae and Asthma in Children. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2004, 38, 1341–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisar, N.; Guleria, R.; Kumar, S.; Chawla, T.C.; Biswas, N.R. Mycoplasma pneumoniae and its role in asthma. Heart 2007, 83, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benamar, M. , Harb, H., Chen, Q., Wang, M., Chan, T.M.F., Fong, J., Phipatanakul, W., Cunningham, A., Ertem, D., Petty, C.R. and Mousavi, A.J. A common IL-4 receptor variant promotes asthma severity via a Treg cell GRB2-IL-6-Notch4 circuit. Allergy 2022, 77, 3377–3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athari, S.S. Targeting cell signaling in allergic asthma. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2019, 4, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Hong, L.; Chen, M.; Shi, J.; Lin, X.; Huang, L.; Tang, T.; Guo, Y.; Yuan, X.; Jiang, S. Targeting M2 Macrophages Alleviates Airway Inflammation and Remodeling in Asthmatic Mice via miR-378a-3p/GRB2 Pathway. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, M.E.; Busse, W.W.; Bertics, P.J. Interleukin 5 Signals through Shc and Grb2 in Human Eosinophils. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1998, 18, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisener-Dorman, A.F. , Lawrence, D.A. and Bolivar, V.J. Cautionary insights on knockout mouse studies: the gene or not the gene? Brain Behav. Immun. 2009, 23, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stripp, B.R.; Lund, J.; Mango, G.W.; Doyen, K.C.; Johnston, C.; Hultenby, K.; Nord, M.; Whitsett, J.A. Clara cell secretory protein: a determinant of PCB bioaccumulation in mammals. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Mol. Physiol. 1996, 271, L656–L664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eenjes, E.; Mertens, T.C.J.; Kempen, M.J.B.-V.; van Wijck, Y.; Taube, C.; Rottier, R.J.; Hiemstra, P.S. A novel method for expansion and differentiation of mouse tracheal epithelial cells in culture. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, J.; Varghese, M.V.; Vasilyev, M.; Langlais, P.R.; Tofovic, S.P.; Rafikova, O.; Rafikov, R. Complex III Inhibition-Induced Pulmonary Hypertension Affects the Mitochondrial Proteomic Landscape. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, S.S.; Krantz, J.; Kwak, E.-A.; Barker, N.K.; Deer, C.G.; Lee, N.Y.; Mouneimne, G.; Langlais, P.R. Insulin Induces Microtubule Stabilization and Regulates the Microtubule Plus-end Tracking Protein Network in Adipocytes. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2019, 18, 1363–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangam, S.; Sun, X.; Schwantes-An, T.-H.; Yegambaram, M.; Lu, Q.; Shi, Y.; Cook, T.; Fisher, A.; Frump, A.L.; Coleman, A.; et al. SOX17 Deficiency Mediates Pulmonary Hypertension: At the Crossroads of Sex, Metabolism, and Genetics. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2023, 207, 1055–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahl, J.R.; Vivek, A.; Palomino, S.M.; Almuslim, M.; Cottier, K.E.; Langlais, P.R.; Streicher, J.M.; Vanderah, T.W.; Liktor-Busa, E.; Largent-Milnes, T.M. Extracellular Alterations in pH and K+ Modify the Murine Brain Endothelial Cell Total and Phospho-Proteome. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, E.-A.; Pan, C.C.; Ramonett, A.; Kumar, S.; Cruz-Flores, P.; Ahmed, T.; Ortiz, H.R.; Lochhead, J.J.; Ellis, N.A.; Mouneimne, G.; et al. βIV-spectrin as a stalk cell-intrinsic regulator of VEGF signaling. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyanova, S.; Temu, T.; Sinitcyn, P.; Carlson, A.; Hein, M.Y.; Geiger, T.; Mann, M.; Cox, J. The Perseus computational platform for comprehensive analysis of (prote)omics data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyanova, S.; Cox, J. Perseus: A Bioinformatics Platform for Integrative Analysis of Proteomics Data in Cancer Research. In Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Berlin, Germany, 2018; Volume 1711, pp. 133–148. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, D.W.; Sherman, B.T.; A Lempicki, R. Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 4, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Protein Name | Protein Abbreviation |
Gene Abbreviation |
SNP IDs in Lung Tissuea | Effective Allele | p-value | Predicted Expression Change Due to SNP within Lung Tissueb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heparin Sulfate Proteoglycan 2 | PGBM | HSPG2 | rs2229475 rs115963344 rs12724454 rs12725566 rs12737091 rs12741617 rs12742444 |
T T A A T A T |
5.58x10-14 4.84x10-13 4.84x10-13 4.84x10-13 4.84x10-13 4.84x10-13 4.84x10-13 |
Increase Increase Increase Increase Increase Increase Increase |
| Adapter Molecule CRK | CRK | CRK | rs16946807 rs34490967 rs7208768 rs11652967 rs35316912 |
A C A G C |
3.74x10-8 5.86x10-8 8.46x10-8 9.72x10-8 1.16x10-7 |
Decrease Decrease Decrease Decrease Decrease |
| Ras GTPase-activating-like protein | IQGA2 | IQGAP2 | rs112872685 rs875541 rs10075621 rs4296785 rs4501323 rs4501324 |
A A T T C C |
1.84x10-7 9.95x10-6 1.40x10-5 1.42x10-5 1.42x10-5 1.42x10-5 |
Decrease Decrease Decrease Decrease Decrease Decrease |
| Syndecan-4 | SDC4 | SDC4 | rs2267867 | A | 3.10x10-8 | Increase |
| Laminin Subunit Beta 3 | LAMB3 | LAMB3 | rs1534962 rs9429823 rs2298928 rs2298926 rs1534962 rs9429823 |
A G T A A G |
5.22x10-14 1.08x10-12 2.05x10-12 3.74x10-12 5.63x10-12 5.12x10-9 |
Decrease Increase Increase Increase Decrease Increase |
| Plexin-B2 | PLXB2 | PLXNB2 | rs74933135 rs117289563 rs118067161 rs142227764 rs78854007 rs146310944 rs183166435 rs117199604 |
A T T T A T C A |
3.36x10-8 1.05x10-7 1.05x10-7 1.05x10-7 1.05x10-7 1.05x10-7 1.05x10-7 2.33x10-7 |
Increase Increase Increase Increase Increase Increase Increase Increase |
| Growth Factor Receptor-Bound Protein 2 | GRB2 | GRB2 | rs12451296 rs11649784 rs12604003 rs4789187 rs9895739 rs9909443 rs9901434 |
A T A G T T G |
3.33x10-5 3.54x10-5 3.54x10-5 3.54x10-5 3.66x10-5 4.02x10-5 4.18x10-5 |
Increase Increase Increase Increase Increase Decrease Increase |
| Dynactin Subunit 1 | DCTN1 | DCTN1 | rs34215278 rs11555696 rs71418733 rs71418738 rs13021268 rs34988074 rs34522471 rs35241844 |
T A T G T C G C |
5.19x10-16 6.86x10-16 6.86x10-16 1.56x10-15 9.16x10-15 1.12x10-14 1.10x10-11 1.00x10-9 |
Decrease Decrease Decrease Decrease Decrease Decrease Decrease Decrease |
| Protein BRICK1 | BRK1 | BRK1 | rs67342818 rs111284032 rs112180322 rs113378528 rs3774208 rs41464050 rs58862481 |
A T T A G G A |
8.10x10-9 8.10x10-9 8.10x10-9 8.10x10-9 8.10x10-9 8.10x10-9 8.10x10-9 |
Decrease Decrease Decrease Decrease Decrease Decrease Decrease |
| Clathrin Light Chain B | CLCB | CLTB | rs13181024 rs13168842 rs13154366 rs13175787 rs13168952 rs13180938 rs13181024 rs13168842 |
T T A G A A T T |
2.97x10-32 2.97x10-32 2.19x10-25 2.19x10-25 5.90x10-25 2.47x10-23 1.94x10-22 1.94x10-22 |
Increase Increase Increase Increase Increase Increase Increase Increase |
| Integrin-Linked Protein Kinase | ILK | ILK | rs11826498 rs11602107 rs11605114 rs2255405 rs12451 rs3741271 rs2255538 rs2292195 |
C A A A T C A T |
4.89x10-15 1.17x10-14 1.17x10-14 1.56x10-14 2.62x10-14 4.63x10-14 9.88x10-14 1.80x10-13 |
Increase Increase Increase Increase Increase Increase Increase Increase |
| Gene | SNP ID | Risk allele | Expression change | Effect of SNP on Phenotype | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GRB2 | rs9901434 | G | ¯ FEV1 | 6.53 x 10-6 | |
| asthma risk | 2.33 x 10-2 | ||||
| rs9895739 | T | ¯ FEV1 | 4.26 x 10-6 | ||
| asthma risk | 3.10 x 10-2 | ||||
| rs11649784 | T | asthma risk | 2.22 x 10-2 | ||
| rs12604003 | A | asthma risk | 2.13 x 10-2 | ||
| rs4789187 | G | asthma risk | 2.22 x 10-2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





