1. Introduction
Compounds consisting of a metal ion and a drug molecule, known as metallodrugs, have attracted significant interest from pharmacology, biology, and chemistry researchers. Over the years, numerous metallodrugs have demonstrated their potential pharmaceutical activity, including antiviral, anticancer, and antibacterial properties. They are used as therapeutic agents and chemotherapeutics to treat various human diseases, such as infections, neurological disorders, diabetes, and cancer [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6,
7,
8]. Furthermore, metallodrugs can be employed to design more biologically active drugs. Platinum-based metallodrugs, such as carboplatin, oxaliplatin, and cisplatin, are widely used as anticancer drugs for treating solid tumors, including testicular, ovarian, and bladder cancers [
9,
10,
11,
12]. These platinum-based metallodrugs inhibit the division of tumor cells by damaging their DNA and inducing cell death. However, the clinical applications of several metallodrugs present two challenges: (i) severe adverse side effects and (ii) acquired resistance [
13,
14,
15]. Drug resistance arises from the extensive overuse of drugs, particularly antibiotics, and drug residues in the environment. These problems hinder widespread application and limit the effectiveness of metallodrugs. Consequently, researchers have focused on designing and developing innovative metallodrugs to overcome these limitations, aiming for enhanced efficiency, a lower toxicity profile, a reduced rate of drug resistance, and fewer side effects.
Quinolones have been utilized as antibiotics for over 30 years due to their high potency, good bioavailability, low cost, absence of cross-resistance, and broad-spectrum activity against antibacterial microbes [
16,
17,
18,
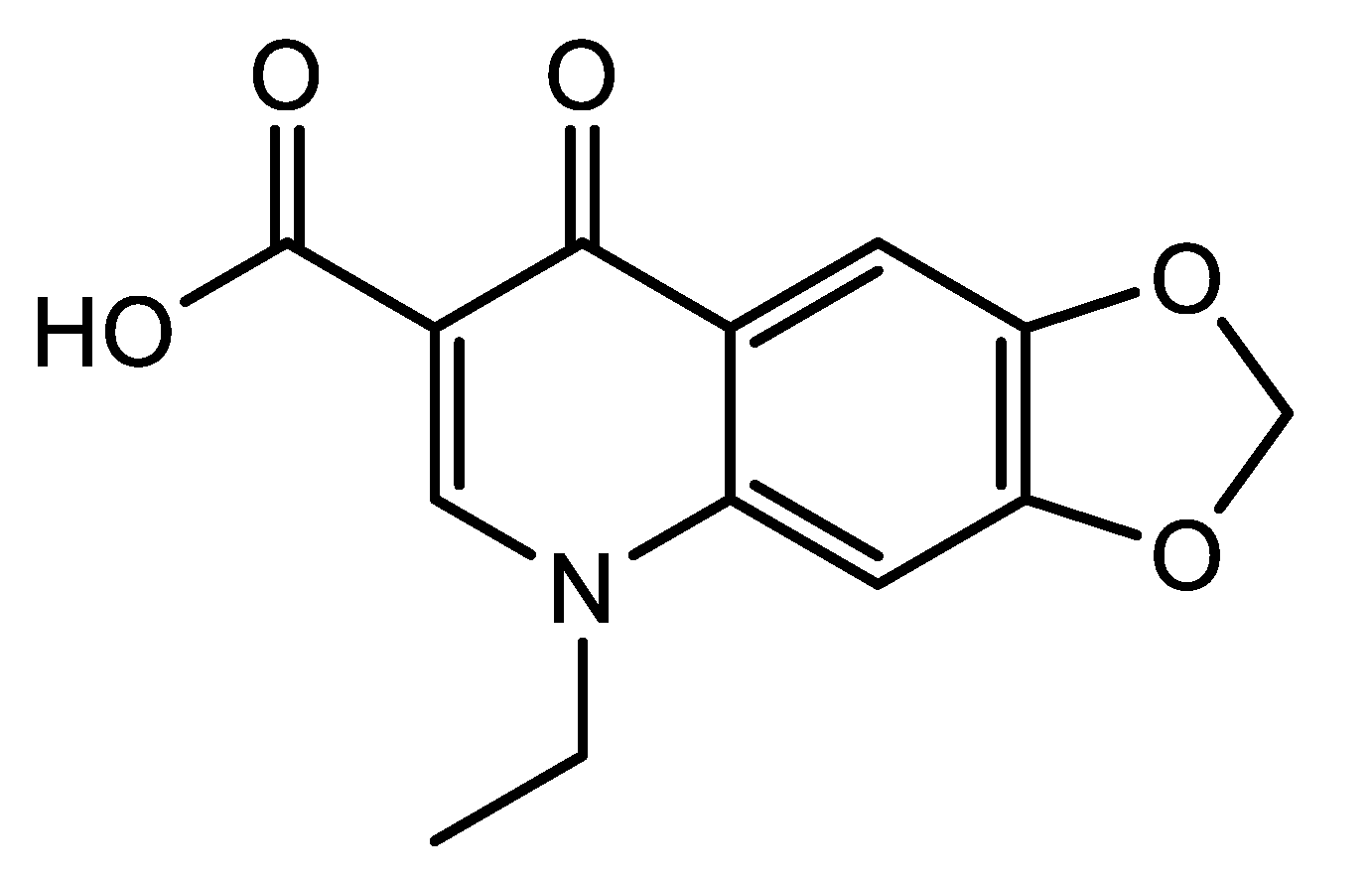
19]. We believe synthesizing new metallodrugs incorporating quinolones can enhance the biological efficiency of these antibiotics. In this study, we aim to provide fresh insights into the behavior and complexation tendencies of oxolinic acid (OA), one of the quinolone antibiotics. OA, with the chemical name 5,8-dihydro-5-ethyl-8-oxo-1,3-dioxolo [4,5-g]quinoline-7-carboxylic acid, belongs to the first generation of quinolone antibiotics (
Figure 1). It is a white-to-off-white powder with the linear formula C
13H
11NO
5 (261.23 g/mol). The OA antibiotic was developed by Warner-Lambert, approved by the Food and Drug Administration in the 1970s, and used for treating bacterial urinary infections.
The work is separated into three parts of the investigation:
(i) Chemistry:
This part aimed to prepare the complexes of OA molecule with four metal ions [i.e., Fe(III), Zn(II), Ca(II), Mg(II)] in neutral media (pH 7-8) with a 1:1 metal-to-OA stoichiometry at 60-70°C, and to characterize the generated OA complexes with several physicochemical techniques: Fourier-transform infrared (FT-IR), nuclear magnetic resonance (1H NMR), ultraviolet/visible (UV-visible) spectroscopies, and CHN elemental analyzer.
(ii) Morphology:
This part aimed to observe the phase purity and visualize the surface morphology of the generated OA complexes by the X-ray powder diffractometry (XRD), scanning and transmission electron microscopies (SEM and TEM, respectively).
(iii) Biology:
This part aimed to assay the antimicrobial properties (i.e., antibacterial and antifungal) of the OA complexes in vitro using the Kirby-Bauer disc diffusion assay method with five bacterial and three fungal microbes. The screening data of the standard drugs (streptomycin and ketoconazole) were used for comparison.
2. Experiments
2.1. Chemicals and Instrumentation
The analytical grade OA (C13H11NO5; 261.23 g/mol; purity ≥ 95.0%) was obtained from Merck KGaA (Darmstadt, Germany). The analytical grade FeCl3·6H2O (270.30 g/mol; purity ≥ 98%), ZnCl2 (136.30 g/mol; purity ≥ 99.99 %), CaCl2 (110.98 g/mol; purity 99.99%), and MgCl2 (95.21 g/mol; purity ≥ 98%) were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). Spectra of FT-IR (400–4000 cm−1), 1H NMR (600 MHz; DMSO- d6), and UV/Vis (200–1000 nm) collected by a Shimadzu FT-IR spectrophotometer, a Bruker DRX-250 Digital FT-NMR spectrometer, and a Perkin-Elmer Lambda 25 UV/Vis spectrophotometer, were analyzed to explore the complexation mode of OA molecule with the metal ions. Elemental analysis data collected by a Perkin-Elmer 2400 series CHN elemental analyzer were analyzed to propose the compositions of the OA metal complexes. The XRD spectra (2θ 5–90°), SEM and TEM micrographs collected by an X’Pert Philips X-ray diffractometer, a Quanta FEI 250 SEM, and a JEOL JEM-1200 EX II TEM were analyzed to observe phase purity, and surface morphology of OA metal complexes.
2.2. Synthesis of OA Complexes
Complexes of OA with the metal ions Fe(III), Zn(II), Ca(II), and Mg(II) were synthesized as follows: The respective metal chloride salt (2 mmol) was dissolved in 25 mL of deionized water, and this solution was gradually added to a stirred methanolic solution of OA (2 mmol, 25 mL). The temperature of the hot plate was adjusted to a range of 60-70°C. A few drops of 5% NH3 solution neutralized the reaction medium, resulting in a pH of approximately 7–8. The neutralized mixture was stirred for an additional 10 min, during which colored precipitate began to form. The reaction vessel was left overnight to allow for complete precipitation of the synthesized complex. To remove any residual unreacted OA or metal chloride, the filtrated product was thoroughly washed multiple times with deionized water, MeOH, and CH3CH2OCH2CH3. The purified product was then dried under a vacuum over anhydrous CaCl2 for 48 h. The resulting OA complexes were obtained as a white-colored powder for Zn(II), Ca(II), and Mg(II) ions and as a brown-colored powder for Fe(III) ions.
2.3. Biological Evaluation
The antimicrobial potential of the synthesized OA complexes was assessed through in vitro screening using the well-established Kirby-Bauer disc diffusion protocol [
20,
21,
22]. Antibiotic disks and complexes were tested at 100 μg/mL concentrations. The zone diameters were measured to evaluate the effects on the growth of the tested strains. The antibacterial results were compared to the standard drug streptomycin (+ control), while the antifungal results were compared to the standard drug ketoconazole (+ control). The bioefficacy of the synthesized OA complexes was examined against five bacterial and three fungal strains. The tested microbial strains included:
Table.
| Microbe. |
Abbreviation |
| (A) Gram-negative bacterial species |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa |
P. aeruginosa |
| Escherichia coli |
E. coli |
| (B) Gram-positive bacterial species |
| Staphylococcus aureus |
S. aureus |
| Streptococcus pneumoniae |
S. pneumoniae |
| Bacillus subtilis |
B. subtilis |
| (C) Fungal species |
| Candida albicans |
C. albicans |
| Penicillium sp. |
- |
| Aspergillus niger |
A. niger |
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemistry
3.1.1. CHN Analysis and UV-Visible Spectral Results
The chlorides of Fe(III), Zn(II), Ca(II), and Mg(II) ions were dissolved in deionized water, while OA was dissolved in a methanol solvent. The two solutions (metal ion and OA) were mixed, and the reaction proceeded with a 1:1 metal-to-OA stoichiometry. When the pH of the mixture reached approximately 7-8, colored precipitates were formed. The precipitate was white-colored with Zn(II), Ca(II), and Mg(II) ions and brown-colored with Fe(III) ions. The contents (%) of carbon, nitrogen, hydrogen, and chlorine elements in OA complexes were determined using a CHN elemental analyzer, while the contents (%) of water and Fe, Zn, Ca, and Mg metals in their complexes were determined gravimetrically. The elemental results obtained are tabulated in
Table 1. The microanalytical results comply with the suggested general compositions of [Fe(OA)(H
2O)
2Cl
2]·2H
2O, [Zn(OA)(H
2O)Cl]·2H
2O, [Ca(OA)(H
2O)Cl], and [Mg(OA)(H
2O)Cl], obtained from the reaction of OA with Fe(III), Zn(II), Ca(II), and Mg(II) ions, respectively. The corresponding gross formulas were C
13H
12NO
6MgCl (338.0), C
13H
12NO
6CaCl (353.76), C
13H
16NO
8ZnCl (415.06), and C
13H
18NO
9FeCl
2 (458.98 g/mol), respectively.
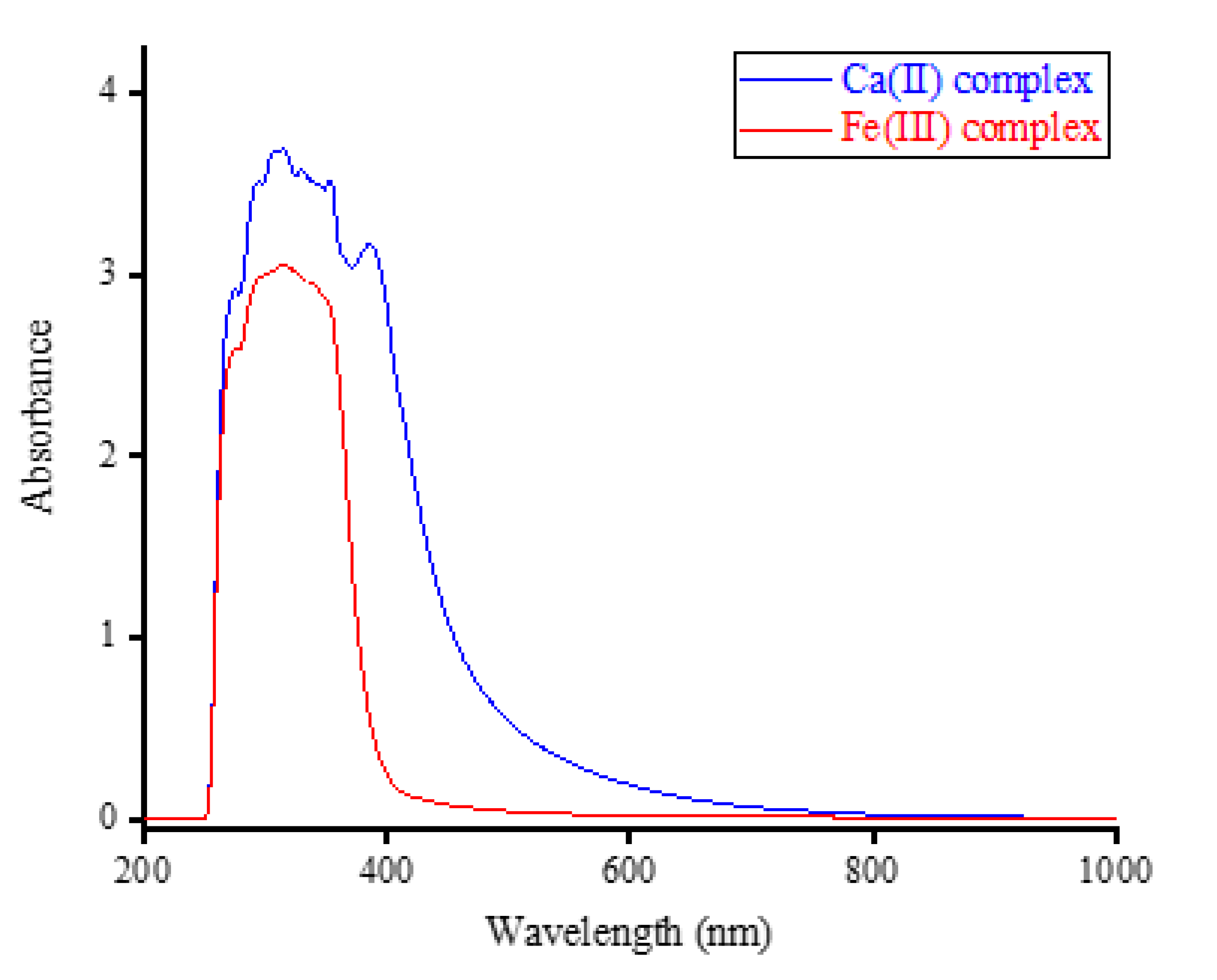
Complexes containing Ca(II) and Fe(III) ions were dissolved in a dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) solvent and analyzed using a UV-visible spectrophotometer. The UV-visible spectra obtained are presented in
Figure 2. Free OA exhibited two absorption bands in its UV-visible spectrum within the 240-300 nm and 300-380 nm regions. The former is attributed to the absorption of the aromatic ring, while the latter is associated with the n
→π* (HOMO-LUMO) transitions [
23].
The spectra in
Figure 2 revealed that the intra-ligand transitions (n
→π*; π
→π*) produced a prominent and broad absorption band. This band was observed in the wavelength range of approximately 255 to 500 nm for the Ca(II) complex and in the range of approximately 255 to 400 nm for the Fe(III) complex [
24,
25]. This indicates that the Ca(II) ion generates a broader absorption band when complexed with OA compared to the Fe(III) ion. The maximum wavelength (λ
max) of the absorption bands was found to be 315 nm for both complexes.
3.1.2. FT-IR Spectral Results
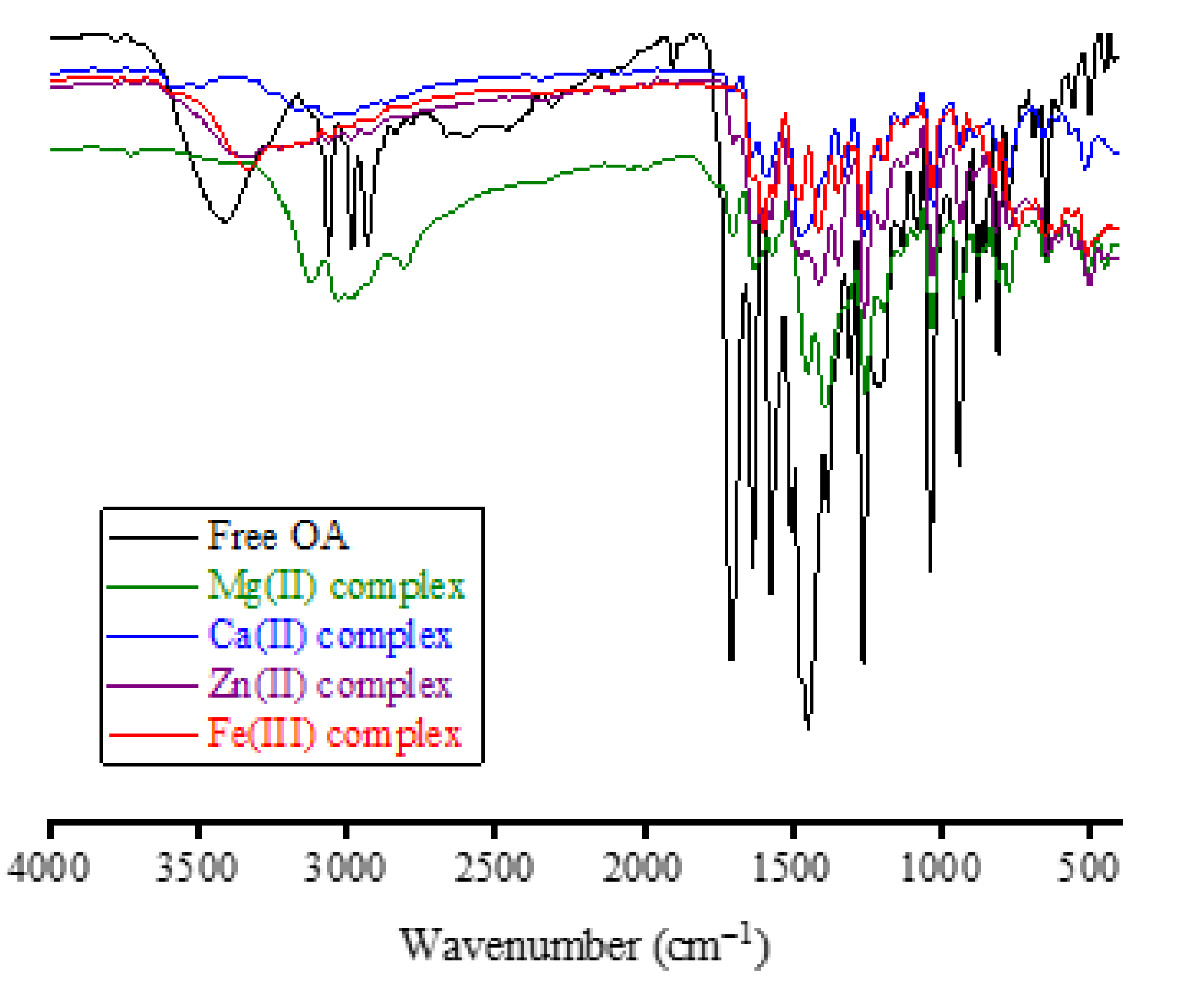
Figure 3 presents the FT-IR spectra of the OA complexes. Analysis of the FT-IR spectrum of free OA molecules provides the following observations:
i) The vibrations of ν(O−H) resulted from the −COOH group in the OA molecule, and moisture water produced a medium-intensity absorption band located at 3418 cm−1.
ii) The vibrations of νasym(C−H) and νsym(C−H) resulted from the −CH3, −CH2, and −CH moieties produced three medium-intensity absorption bands resonated at 3063, 2982, and 2933 cm−1.
iii) The vibrations of ν(C=O)
COOH originated a very strong and sharp band at 1710 cm
−1. The vibrations of ν(C=O)
pyridone and ν(C=C) generated strong and sharp bands at 1634 and 1579 cm
−1, respectively [
26].
iv) The vibrations of δrock(CH3) and δsciss(CH2) produced a very strong and intense absorption band at 1450 cm−1. This band has two shoulder bands at 1510 and 1377 cm−1.
v) The vibrations of δrock(CH2) were responsible for the strong and sharp absorption band that appeared at 1262 cm−1.
vii) Absorptions at 1210 and 1128 cm
−1 could be referred to as the ν
asym(C−N) and ν
sym(C‒N) vibrations, respectively. Absorptions at 1086 and 1040 cm
−1 could be due to the ν(O−CH
2−O) vibrations [
27].
Two characteristics shifts were observed in the FT-IR spectra of OA complexes:
i) Disappearance of the band due to the ν(C=O)COOH vibrations. This band resonated at 1710 cm−1 in the FT-IR spectrum of free OA, but it was absent in the FT-IR spectra of Fe(III), Zn(II), and Ca(II) complexes. The intensity of this band was greatly decreased in the spectrum of the Mg(II) complex.
ii) Shifting of the band due to the ν(C=O)pyridone vibrations. This band was resonated at 1634 cm−1 in the FT-IR spectrum of free OA, but it was shifted in the FT-IR spectra of Fe(III), Zn(II), Ca(II) and Mg(II) complexes to 1597, 1616, 1598, and 1613 cm−1, respectively.
iii) Appearance of new medium-intensity absorption band at 503, 500, 515, and 512 cm
−1 in the spectra of Fe(III), Zn(II), Ca(II), and Mg(II), respectively, and could be referred to as the ν(M−O) vibrations [
27].
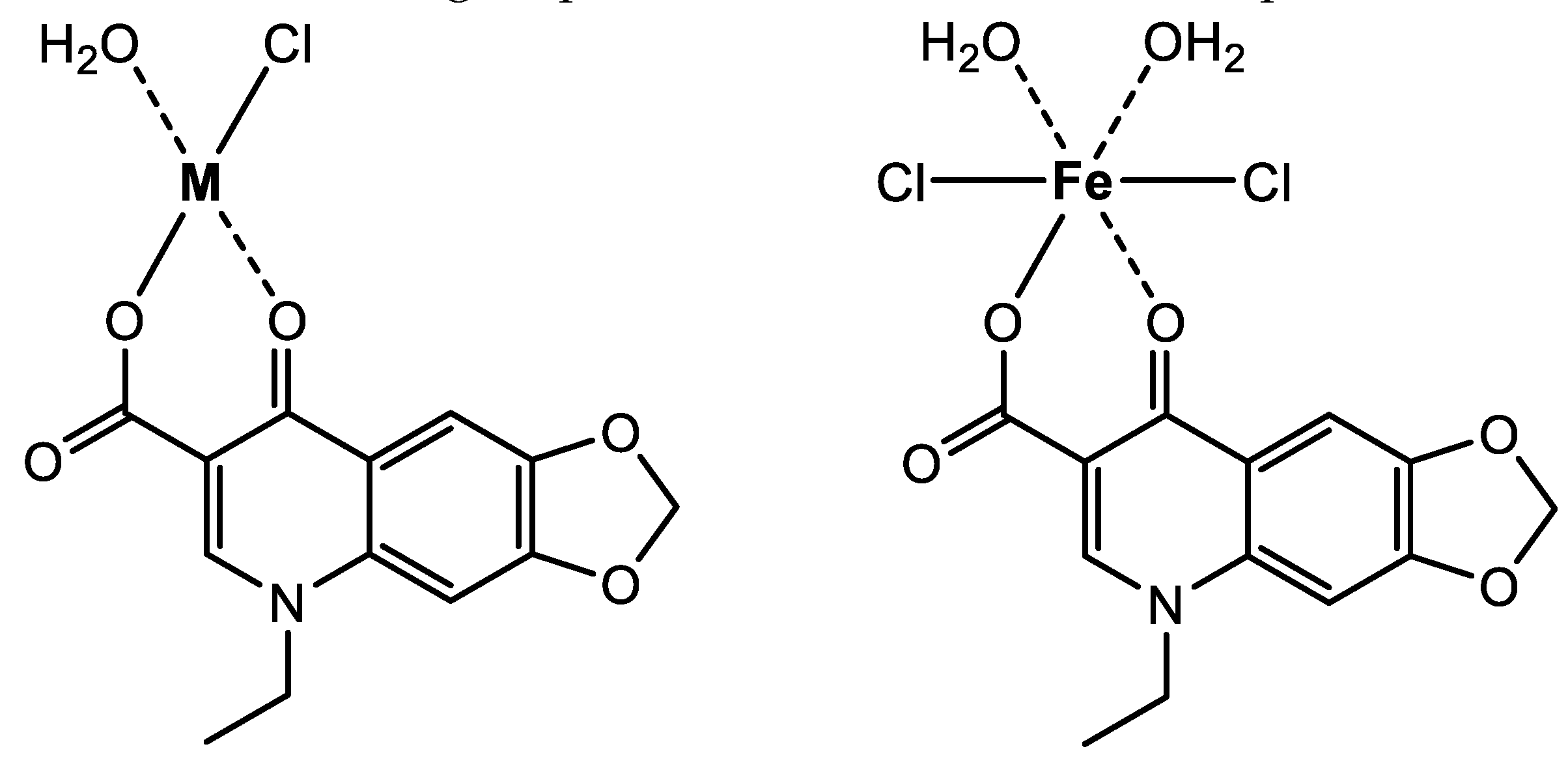
These characteristic shifts observed in the FT-IR spectra of OA complexes suggested that the OA molecule captured the metal ions using the oxygen atoms of the carboxylic group (−COOH) and C=O group of the pyridone ring [
28,
29]. The oxygen atom of the −COOH group forms an ionic bond with the metal ion, whereas the oxygen atom of the pyridone C=O group forms a coordination bond with the metal ion, as described in
Figure 4.
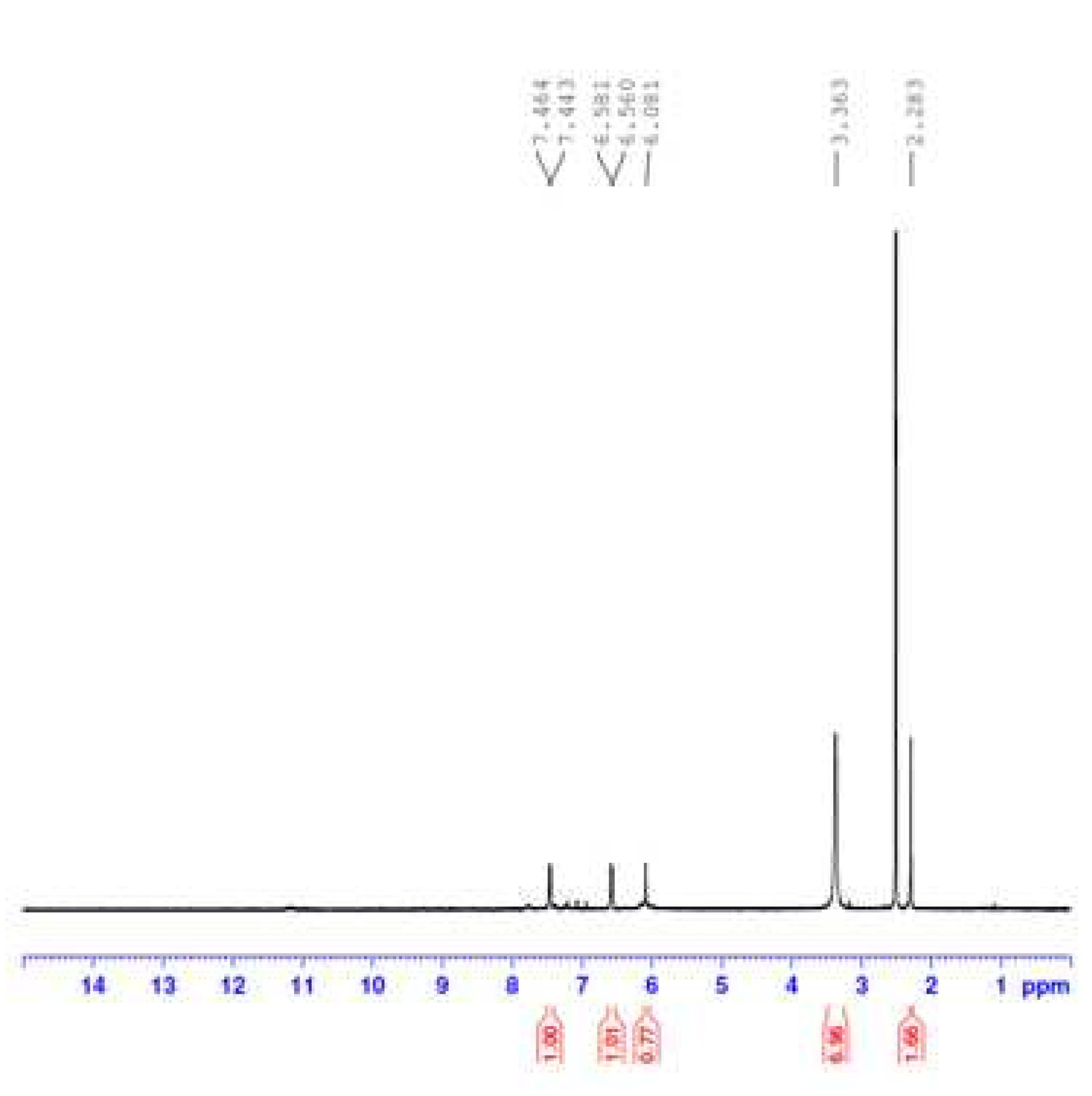
3.1.3. H NMR Spectral Results
Figure 5 displays the
1H NMR spectrum of the OA complex with Fe(III) ions. In this spectrum, the signal at 2.283 ppm corresponded to the protons of the -CH
3 group of the -CH
2CH
3 moiety, while the signal at 3.363 ppm was attributed to the protons of the -CH
3 group attached to the piperazine ring. The signal observed at 6.081 ppm could be assigned to the protons of the -CH
2 group in the (-O-CH
2-O-) moiety, whereas the signals resonating at 6.560 and 6.581 ppm could be attributed to the protons of the -CH
2 group in the -CH
2CH
3 moiety. The signals ranging from 7.443 to 7.464 ppm were generated by the aromatic protons, while the signal at 3.363 ppm could be attributed to coordinated water molecules. The signal resulting from the proton of the -COOH group, typically located around δ ~ 11.0 ppm in the
1H NMR spectrum of the free OA molecule, was no longer observed in the spectrum of the Fe(III) complex. The absence of the
1H NMR -COOH proton signal, coupled with the disappearance of the characteristic FT-IR band associated with the ν(C=O)
COOH vibrations, supports the deprotonation of the -COOH group and its involvement in complexation with the Fe(III) ion.
3.2. Morphology
3.2.1. XRD Spectral Results
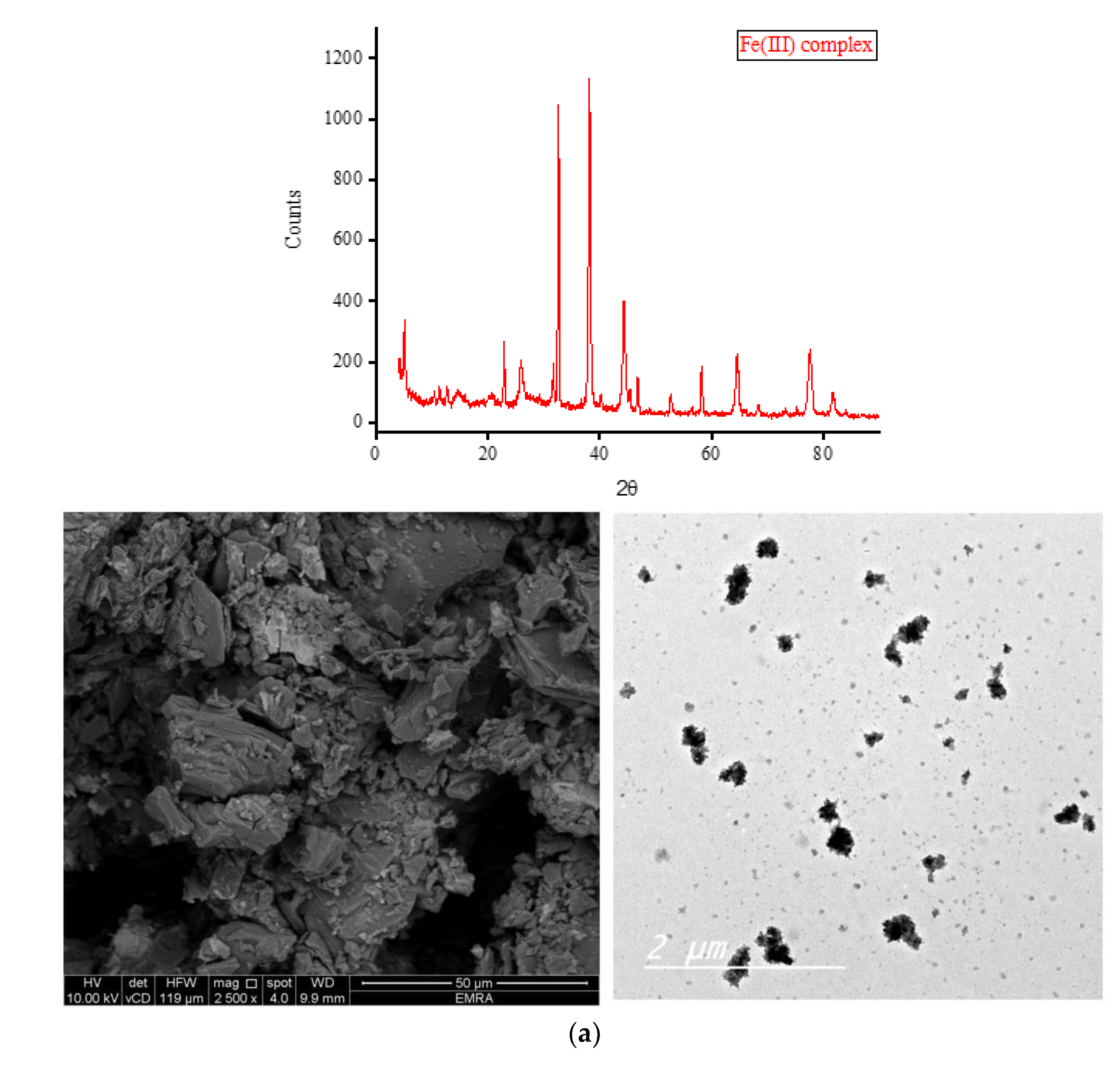
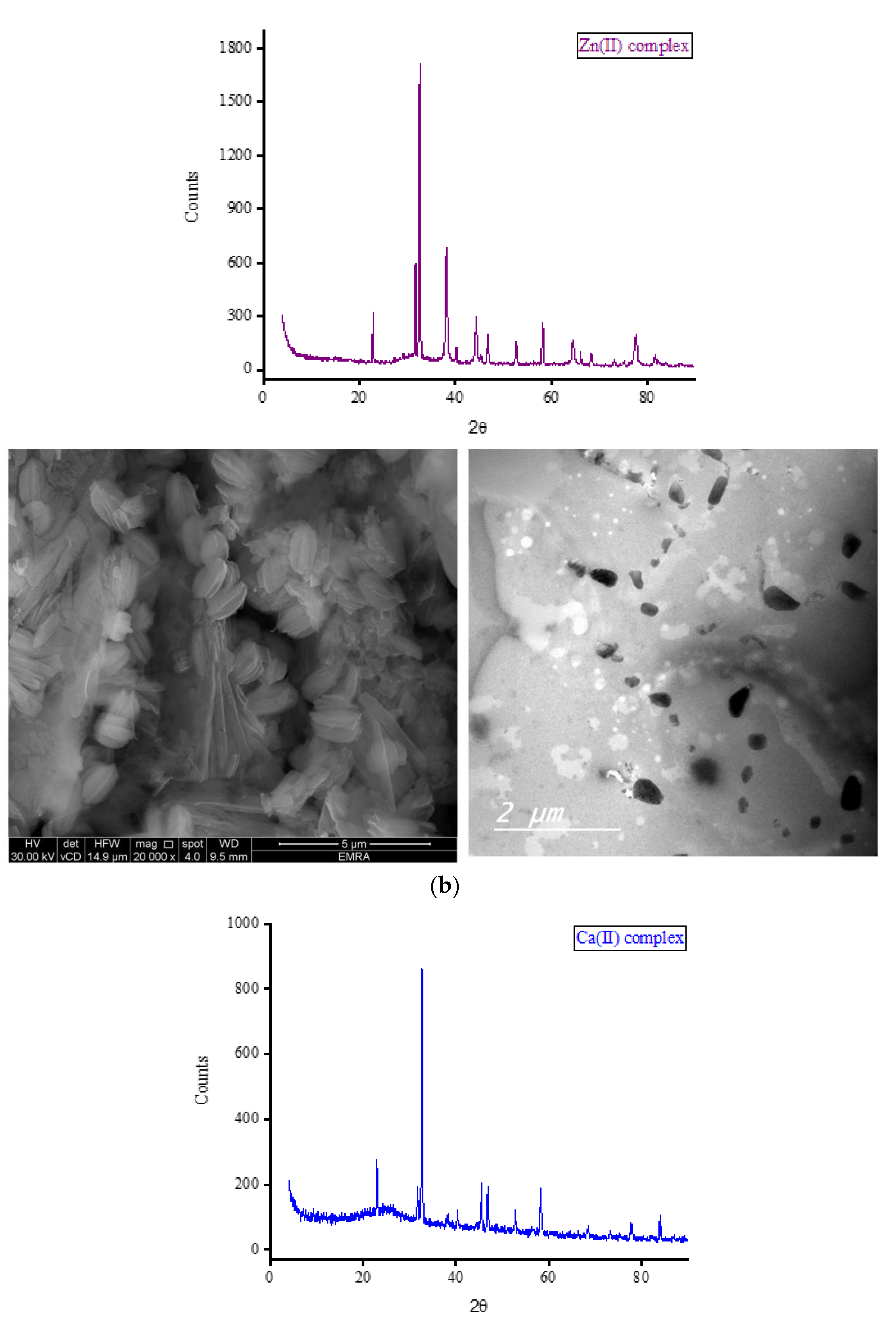
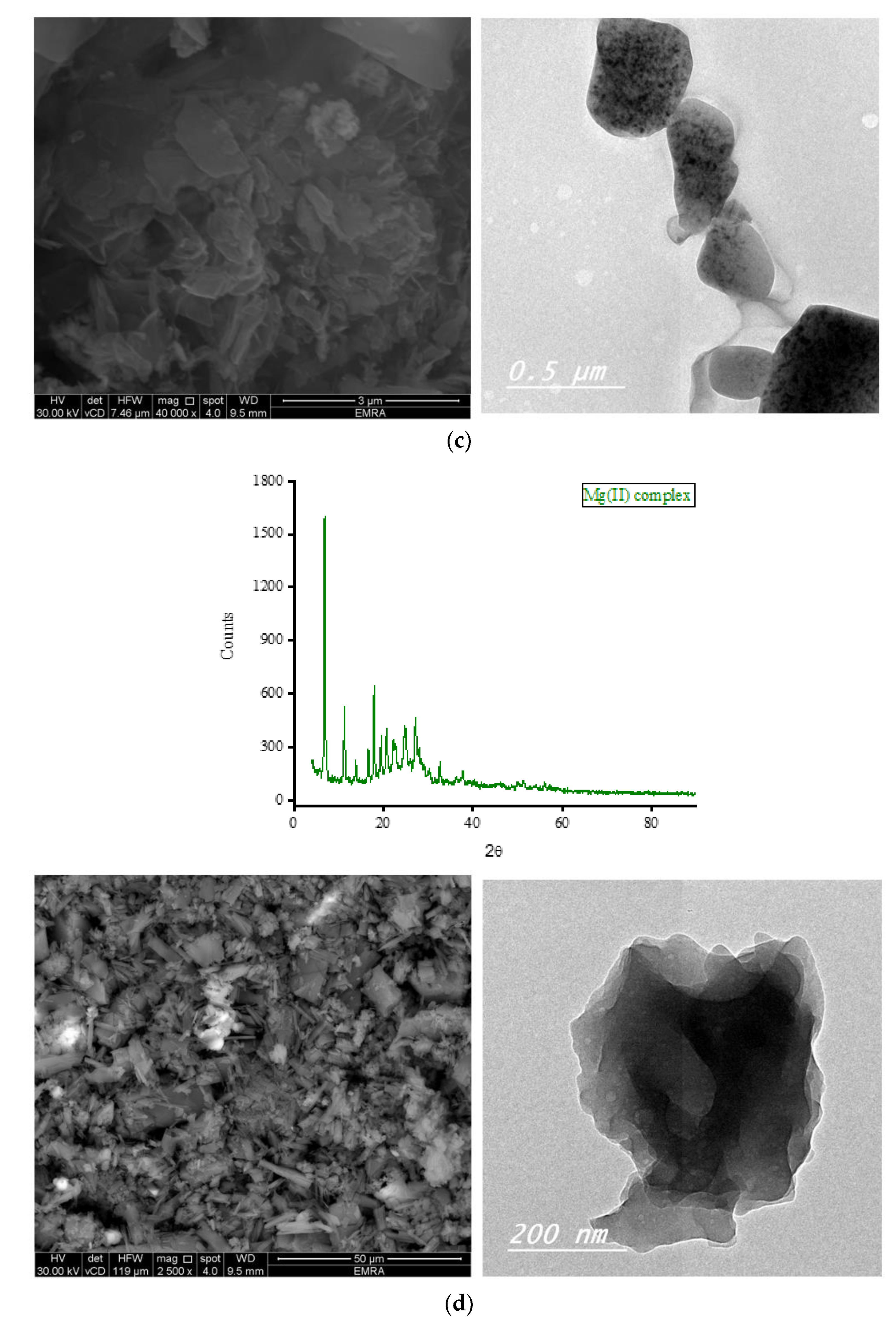
Complexes of OA with Fe(III), Zn(II), Ca(II), and Mg(II) ions were subjected to X-ray diffraction analysis from Bragg’s angle 2
θ of 5° to 90°, and the corresponding XRD patterns are shown in
Figure 7. The complexes of Zn(II), Ca(II), and Mg(II) ions exhibited a single, strong, and narrow diffraction line in their XRD spectra, indicating the formation of well-crystallized complexes. On the other hand, the complex containing Fe(III) ions displayed two strong and narrow diffraction lines in its XRD spectrum with approximately equal intensities, suggesting the formation of an amorphous complex. The most prominent diffraction line observed in the XRD patterns of the Zn(II) complex was located at Bragg’s angle 2
θ of 32.544°. The XRD patterns of this complex exhibited ten low-intensity lines spanning a wide range (approximately 22° to 78°), with the most intense lines located at 32.544°. Similarly, the strongest diffraction line for the Ca(II) complex was observed at Bragg’s angle 2
θ of 32.667°. This complex displayed fewer low-intensity lines compared to the Zn(II) complex, and these lines generally had similar intensities. In the XRD diffraction profile of the Mg(II) complex, the strongest diffraction line appeared at a very low angle compared to the Zn(II) and Ca(II) complexes, specifically at 2
θ of 6.977°. Following this, a group of low-intensity lines emerged in the range of approximately 11° to 30°, with the most intense lines located at 11.306° and 17.873°. The strongest twin lines observed in the XRD spectrum of the Fe(III) complex were precisely located at 2
θ of 32.668° and 38.105°. Additionally, the complex displayed six medium-to-low-intensity lines at various Bragg angles.
3.2.2. Microscopes
Scanning and transmission electron microscopies (SEM and TEM, respectively) were utilized to gather information about the outer surface characteristics of the complexes, including surface topology, porous structure, and particle morphology. The SEM and TEM micrographs of the OA complexes are presented in
Figure 7. The SEM micrographs clearly illustrate variations in the shape and surface topology of the OA complexes, indicating distinct microstructures among them. The Fe(III) complex formed large agglomerates, with smaller pieces of various shapes and sizes observed on the surface of these agglomerates, likely resulting from the breakage of some aggregates into smaller fragments. The complexation of OA with Zn(II) ions resulted in particles exhibiting a stone-like morphology clustered together, resembling a bunch of grapes. The Ca(II) complex comprises particles with diverse shapes, sizes, and features. The Mg(II) complex displayed particles with a mixture of short and long rod-like structures with varying thicknesses. Some particles of this complex exhibited a tube-shaped morphology. According to the TEM micrographs, most of the particles in the OA complexes exhibited diameters ranging from 30 to 80 nm.
3.3. Antimicrobial
3.3.1. Antibacterial Screening
The antibacterial potential of OA complexes was screened against the growth of various bacterial strains in vitro using the well-known Kirby-Bauer disc diffusion protocol. The bioefficacy of OA complexes at a concentration of 100 μg/mL was examined with two Gram-negative bacterial species and three Gram-positive bacterial species. The antibacterial profiles of the complexes were compared with the standard drug streptomycin (+ control).
Table 2 presents the screening results for the antibacterial assays of OA complexes. The Ca(II) complex exhibited inhibition against the Gram-negative and Gram-positive microbes, measuring 27.0, 22.0, 20.0, 17.0, and 18.0 mm/mg for
P. aeruginosa,
E. coli,
S. aureus,
S. pneumoniae, and
B. subtilis species, respectively. The corresponding inhibition observed with the standard drug streptomycin was 28.0, 21.0, 22.0, 18.0, and 20.0 mm/mg, respectively. These values indicate that the Ca(II) complex demonstrated a remarkable profile against both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria, exhibiting potency that is equal to or greater than that of the standard drug streptomycin. The Zn(II) complex exhibited strong antibacterial properties against Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria, except for the
S. pneumoniae strain, with inhibitions of 23.0, 20.0, 18.0, 15.0, and 19.0 mm/mg, respectively. These values are lower than those observed with the Ca(II) complex. The Fe(III) and Mg(II) complexes had no significant effect on Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria, demonstrating only low-to-moderate inhibitory activity against the tested species.
3.3.2. Antifungal Screening
The antifungal activity of the OA complexes was evaluated using three fungal species:
C. albicans,
Penicillium sp., and
A. niger. The antifungal profiles of the OA complexes were compared with the standard drug ketoconazole (+ control). The antifungal screening data were determined using the Kirby-Bauer disc diffusion assay approach and are listed in
Table 3. The Ca(II) complex exhibited inhibitions of 23.0, 20.0, and 20.0 mm/mg against the fungal species
C. albicans,
Penicillium sp., and
A. niger, respectively. The corresponding inhibitions observed with the standard drug ketoconazole were 21.0, 21.0, and 18.0 mm/mg, respectively. These data reveal that the Ca(II) complex demonstrated a remarkable profile against the tested fungal strains, exhibiting potency equal to or greater than that of the standard drug ketoconazole. The Zn(II) complex displayed strong antifungal properties against
C. albicans and
A. niger strains but with lower efficiency compared to the Ca(II) complex, measuring 22.0, 15.0, and 17.0 mm/mg against
C. albicans,
Penicillium sp., and
A. niger species, respectively. The results indicate that the Fe(III) and Mg(II) complexes had no significant effect on the tested fungi, demonstrating only moderate inhibitory activity.
4. Conclusions
The reaction of OA with the Fe(III) ion resulted in the formation of a brown-colored powder, suggested to have the formula [Fe(OA)(H2O)2Cl2]·2H2O. On the other hand, the reaction of OA with the Zn(II), Ca(II), and Mg(II) ions produced white-colored powders with suggested formulas of [Zn(OA)(H2O)Cl]·2H2O, [Ca(OA)(H2O)Cl], and [Mg(OA)(H2O)Cl], respectively. In these complexes, OA coordinated with the investigated metal ions through the two oxygen atoms of the carboxylate and pyridone C=O groups. The morphological properties of the synthesized OA complexes were evaluated using XRD, SEM, and TEM techniques, revealing microstructural differences among the complexes. Notably, the complex containing the Zn(II) ion exhibited the most interesting morphology. The OA complexes were subjected to in vitro assays to determine their antibacterial and antifungal potential against five bacteria and three fungi using the Kirby-Bauer disc diffusion method. The investigation of their antimicrobial activity revealed that the Ca(II) complex displayed a remarkable profile against Gram-negative bacteria, Gram-positive bacteria, and fungi. The potency of this complex against the tested strains was equal to or greater than that of the standard drugs. These intriguing results have prompted us to focus the next stage of this research on investigating the cytotoxic potential of the OA complexes against various human cancer cell lines.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Mohamed A. Al-Omar; Methodology, Abdulrahman A. Almehizia; Software, Mohamed A. Al-Omar; Validation, Mohamed A. Al-Omar, Mashooq A. Bhat and Fhdah S. Alanazi; Formal analysis, Mashooq A. Bhat and Fhdah S. Alanazi; Investigation, Mashooq A. Bhat and Fhdah S. Alanazi; Resources, Fatimah A. Alotaibi; Data curation, Fatimah A. Alotaibi and Abdel Majid A. Adam; Writing—original draft, Ahmed M. Naglah, Moamen S. Refat and Abdel Majid A. Adam; Writing—review & editing, Moamen S. Refat and Abdel Majid A. Adam; Visualization, Fatimah A. Alotaibi and Moamen S. Refat; Supervision, Abdulrahman A. Almehizia, Ahmed M. Naglah and Moamen S. Refat; Project administration, Abdulrahman A. Almehizia and Ahmed M. Naglah; Funding acquisition, Abdulrahman A. Almehizia and Ahmed M. Naglah.
Funding
This research was funded by the Deputyship for Research & Innovation, Ministry of Education in Saudi Arabia through project no. (IFKSURC-1-0128).
Acknowledgments
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deputyship for Research & Innovation, Ministry of Education in Saudi Arabia for funding this research. (IFKSURC-1-0128).
References
- A.C. Tella, J.A. Obaleye, M.D. Olawale, J.M.V. Ngororabanga, A.S. Ogunlaja, S.A. Bourned, C.R. Chimie 22 (1) (2019) 3-12.
- G.L. Eichhorn, L.G. Marzilli, Advances in Inorganic Biochemistry Models in Inorganic Chemistry, PTR Prentice-Hall, Inc, New Jersey, 1994.
- M.N. Hughes, The Inorganic Chemistry of Biological Processes, 2nd ed., Wiley, Chichester [England], 1984.
- E. Alessio, Bioinorganic Medicinal Chemistry, Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH and Co. KGaA, 2011.
- F. Trudu, F. Amato, P. Vaňhara, T. Pivetta, E.M. Peña-Méndez, J. Havel, J. Appl. Biomed. 13 (2) (2015) 79.
- U. Singh, A.M. Malla, I.A. Bhat, A. Ahmad, M.N. Bukhari, S. Bhat, S. Anayutullah, A. A. Hashmi, Microb. Pathog. 93 (2016) 172.
- P.P. Netalkar, S.P. Netalkar, V.K. Revankar, Polyhedron 100 (2015) 215.
- M.A. Ragheb, M.A. Eldesouki, M.S. Mohamed, Spectrochim. Acta A 138 (2015) 585.
- T-M. Khan, N.S. Gul, X. Lu, J-H. Wei, Y-C. Liu, H. Sun, H. Liang, C. Orvig, Z-F. Chen, In vitro and in vivo anti-tumor activity of two gold(III) complexes with isoquinoline derivatives as ligands, Eur. J. Med. Chem. 163 (2019) 333-343. [CrossRef]
- Q. Cao, Y. Li, E. Freisinger, P.Z. Qin, R.K.O. Sigel, Z-W. Mao, G-quadruplex DNA targeted metal complexes acting as potential anticancer drugs, Inorg. Chem. Front. 4 (2017) 10-32. [CrossRef]
- T.T. Tavares, G.C. Azevedo, A. Garcia, A.G. Carpanez, P. M. Lewer, D. Paschoal, B.L. Müller, H.F. Dos Santos, R.C. Matos, H. Silva, R.M. Grazul, A.P. S. Fontes, Gold(I) complexes with aryl-thiosemicarbazones: Molecular modeling, synthesis, cytotoxicity and TrxR inhibition, Ployhedron 132 (2017) 95-104. [CrossRef]
- F. Trudu, F. Amato, P. Vaňhara, T. Pivetta, E.M. Peña-Méndez, J. Havel, Coordination compounds in cancer: Past, present and perspectives, J. Appl. Biomed. 13 (2) (2015) 79-103.
- Q-P Qin, S-L Wang, M-X Tan, Y-C Liu, T. Meng, B-Q Zou, H. Liang, Synthesis of two platinum(II) complexes with 2-methyl-8-quinolinol derivatives as ligands and study of their antitumor activities, Eur. J. Med. Chm. 161 (2019) 334-342. [CrossRef]
- T. Meng, S-F. Tang, Q-P. Qin, Y-L. Liang, C-X. Wu, C-Y. Wang, H-T. Yan, J-X. Dong, Y-C. Liu, Evaluation of the effect of iodine substitution of 8-hydroxyquinoline on its platinum(II) complex: cytotoxicity, cell apoptosis and telomerase inhibition, Med. Chem. Commun. 7 (2016) 1802-1811. 1802–1811. [CrossRef]
- K. Hu, G. Zhou, Z. Zhang, F. Li, J. Li, F. Liang, Two hydrazone copper(II) complexes: synthesis, crystal structure, cytotoxicity, and action mechanism, RSC Adv. 6 (2016) 36077-36084. 36077–36084. [CrossRef]
- S.P. Fricker, Dalton transactions, 43 (2007) 4903.
- A. Jurowska, K. Jurowski, J. Szklarzewicz, B. Buszewski, T. Kalenik, W. Piekoszewski, Cur. Med. Chem., 23(29) (2016) 3322.
- E.K. Efthimiadou, H. Thomadaki, Y. Sanakis, C.P. Raptopoulou, N. Katsaros, A. Scorilas, A. Karaliota, G. Psomas, J. Inorg. Biochem. 101 (2007) 64.
- L.M.M. Vieira, M.V. de Almeida, M.C.S. Lourenço, F.A.F.M. Bezerra, A.P.S. Fontes, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 44 (2009) 4107-4111.
- A.W. Bauer, W.M. Kirby, C. Sherris, M. Turck, Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method, Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 45 (1966) 493-496. [CrossRef]
- J.J. Biemer, Antimicrobial susceptibility testing by the Kirby-Bauer disc diffusion method, Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 3 (1973) 135-140.
- M.C. Serrano, M. Ramírez, D. Morilla, A. Valverde, M. Chávez, A. Espinel-Ingroff, R. Claro, A. Fernández, C. Almeida, E. Martín-Mazuelos, A comparative study of the disc diffusion method with the broth microdilution and Etest methods for voriconazole susceptibility testing of Aspergillus spp., J. Antimicrob. Chemo-ther. 53 (2004) 739-742.
- U. Neugebauer, A. Szeghalmi, M. Schmitt, W. Kiefer, J. Popp, U. Holzgrabe, Vibrational spectroscopic characterization of fluoroquinolones. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 61 (2005) 1505-1517. [CrossRef]
- J.R. Allan, N.D. Baird, A.L. Kassyk, Some first row transition metal complexes of nicotinamide and nicotinic acid, J. Therm. Anal. 16 (1) (1979) 79-90. [CrossRef]
- Ö.F. Öztirk,, M. Şekerci, E. Özdemir, Preparation of complexes of 1-amino-6,7-O-cyclohexylidene-4-azaheptane with transition metal acetates, Russ. J. Gen. Chem. 76 (2006) 33-36. [CrossRef]
- G.B. Deacon, R. Phillips, Relationships between the carbon-oxygen stretching frequencies of carboxylato complexes and the type of carboxylate coordination, Coord. Chem. Rev. 33 (1980) 227-250.
- K. Nakamoto, Infrared Spectra of Inorganic and Coordination Compounds, Wiley Interscience, John Wiley & Sons, New York, NY, USA, 2nd edition, 1970.
- S.M. El-Megharbel, M.S. Hegab, E.A. Manaaa, J.Y. Al-Humaidif, M.S. Refat, Synthesis and physicochemical characterizations of coordination between palladium(ii) metal ions with floroquinolone drugs as medicinal model against cancer cells: novel metallopharmaceuticals, New J. Chem. 42 (2018) 9709-9719. [CrossRef]
- S.M. El-Megharbel, M.A. Hussien, M.S. Refat, In-Situ Copper(II) Complexes of Some Quinolone Drug Ligands Were Discussed for Their Molecular Structures: Synthesis in Binary Solvent, Journal of Computational and Theoretical Nanoscience 14 (1) (2017) 561-576. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.a |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).