1. Introduction
Gout is a common form of crystal-induced arthritis and can lead to the development of tophaceous deposits in the cartilage, bursae, synovial membranes, and tendons. (1, 2)
Concerning imaging methods (3-9), DECT is an established method to detect MSU deposits in soft tissue adjacent to joints and is increasingly used for the diagnosis and follow-up of gout with a reported sensitivity of 78-100% and specificity of 89-100%. (10) Furthermore, DECT is part of the 2018 gout classification criteria of the American College of Radiology/European League Against Rheumatism (ACR/EULAR). (11, 12)
The deposition of MSU in tendons is important, because it may lead to reduced strength and increased risk of rupture.
Tendons play an important role in joint stability, flexibility and efficiency. The impact of tendon MSU crystal deposition on musculoskeletal function is currently uncertain. Tendon rupture due to tophus infiltration has been described in patients with chronic gout, although this appears to be an uncommon event and only a small number of studies reported ruptures of the quadriceps, tibialis anterior and calcaneus tendons. (13-16)
Racide et al. (17) reported that MSU crystal deposits occur within the substance of tendons at the sites of rupture, and that urate crystals lead to a reduction in the tensile strength of the tendon. (18)
In the last few years, studies concerning extraarticular MSU deposits have become more frequent. (19, 20) However, a general consensus regarding a sensitive DECT protocol has not yet been established, as there is ongoing discussion regarding which MSU deposits found by DECT are urate or merely artifacts. (21-24)
Several typical artifacts have been well described in the literature, e.g., finger nails, tendons and vessels. (25) Only few studies correlated DECT findings with polarizing light microscopy (26). Given the lack of verification by microscopy of extraarticular MSU deposits in published studies, it remains questionable whether these findings represent true urate or artifact.
The aim of this study was to assess the change of sensitivity with verification by microscopy as gold standard of MSU deposits in foot tendons of cadavers detected with two different DECT postprocessing protocols, comparing DECT 150, an established DECT postprocessing protocol (Hounsfield unit (HU) threshold of 150/500 (min/max))(27, 28)) with DECT 120 (modified postprocessing HU threshold of 120/500 (min/max)) at constant kV of Tubes A and B.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cadavers:
40 embalmed cadavers (15 male; 25 female; median age, 82 years; mean, 80.5; range, 52 - 99; SD ± 10.9) were examined by DECT to detect the presence and amount of MSU deposits in foot tendons.
Informed consent was provided according to the last wills of the donors, who had donated their bodies to human research studies. Institutional review board approval was obtained. All embalmed and fresh cadavers were referred to DECT after death and were in legal custody of the Anatomy institution.
No medical history was available including gouty arthritis or hyperuricemia.
In addition to the embalmed cadavers, six fresh cadavers (4 male; 2 female; median age, 78; mean, 78,5; range 61 - 95) were examined by DECT. Two of these cadavers showed the presence of MSU deposits in foot tendons, verified by polarizing light microscopy. The fresh cadavers were referred to DECT within 48 hours after death.
The following predefined anatomical sites were assessed for MSU deposits and graded as shown in
Table 1: Extensor halluces longus tendon (EHLT), extensor digitorum longum tendon (EDLT), tibialis anterior tendon (TAT), flexor halluces longus tendon (FHL), tibialis posterior tendon (TP), peroneus tendons (PT), Achilles tendon (AT) and plantar flexors (PF). To exclude artifacts MSU crystal characterization using polarized light microscopy was performed for the tibialis anterior, achilles, flexor halluces longus, plantar flexor, and peroneal tendons with positive DECT 120 findings but negative results in the DECT 150 in fresh cadavers.
According to ACR/EULAR guidelines nail bed deposits, submillimeter deposits, skin deposits, and deposits obscured by motion, beam hardening, and vascular artefact were not classified as positive findings in our study. (8, 12)
2.2. DECT:
All cadavers were scanned with a 128-row dual-source CT scanner (Somatom Definition Flash; Siemens Healthineers, Forchheim, Germany). Data were acquired at 80/140 kV. For post-processing the standard protocol using a min/max HU threshold of 150/500 (DECT 150) was compared to a modified protocol with a lowered HU threshold of 120/500 (DECT 120), see
Table 2.
The fundamental principle behind the use of DECT is to differentiate materials based on their relative absorption of X-rays at different photon energy levels (typically at 80 and 140 kVp).
A dual-source DECT scanner can perform simultaneous acquisitions at two energy levels (80 and 140 kVp) using two separate X-ray tubes and detectors positioned 90 to 95 degrees apart (20). The standard protocol settings is 80 kV /100 – 140 mAs for tube A and 140 kV/200 – 250 mAs for tube B, with a ratio of 1.36, range 4, minimum HU of 150, and maximum HU of 500. Using independent tube current modulation in combination with iterative reconstruction and integrated circuits within the detector module, high-resolution images with excellent material separation are obtained without an increase in radiation dose. (28)
The acquired datasets are reconstructed in the required planes and processed with dual-energy software utilizing a standardized two-material decomposition algorithm designed for specific clinical applications. The gout algorithm is performed to separate MSU from calcium using soft tissue as the baseline. The two-material decomposition algorithm is based on the principle that materials with a high atomic number such as calcium would demonstrate a higher increase in attenuation at higher photon energies than does a material composed of low atomic number materials such as MSU. This difference in attenuation is independent of density or concentration of the material or tissue. Once separated and characterized, the materials are color-coded and overlaid on multi-planar reformatted cross-sectional images.
We chose green pixels for MSU deposits using the software of the Syngovia workstation (Siemens Healthineers). The post-processing software enables real-time manipulation of the images at source resolution, in any plane and in two- as well as three-dimensions, to best depict the MSU deposits. Preprocessed and processed images are transferred to the picture archiving system (PACS). Corresponding pre-processed grey-scale images are reviewed for presence of deposits.
The software can not differentiate confounding artifacts that should not be included in the detection/quantification of MSU deposits, but an experienced and trained radiologist can differentiate MSU deposits from artifacts, as previously described in the literature.
Scan parameters were 2 x 64 x 0.6 mm at a rotation time of 280 ms, DLP 219 mGycm, CTDI vol 11.5 L, and total mAs 3415. Transverse sections, coronal and sagittal reformations were reconstructed from the DE datasets with an increment of 0.5 mm and a resolution slice thickness of 0.4 mm in soft tissue kernel (D30) and bone kernel (B60). D30 kernel was used for the DE processing and MSU detection.
A commercially available picture archiving and communication system (PACS) was used to view the images (IMPAX; Agfa-Gevaert, Mortsel, Belgium).
Two radiologists with 4 and 15 years experience in gout imaging by DECT evaluated DECT images in consensus. Each cadaver was read as a single observation, either positive or negative. Multiple positive sites in a single tendon were counted as a single observation with the largest size deposit recorded.
2.3. Polarizing microscopic evaluation:
DECT positive MSU foot tendons from fresh cadavers were dissected for gross anatomic sections obtained at defined anatomic landmarks. Specimens were cut unfixed to into 5 x 5 mm sections, embedded using Tissue-Tek® O.C.T.™ compound medium and sectioned at 5 μm using a Leica CM1950 S cryostat. After mounting on microscope slides and covering using glycerine/PBS solution, cryostat sections examination was performed with compensated polarized light microscopy (PLM) at 400 x magnification. First order red compensation (X) was performed to identify MSU crystals by their needle-like appearance and strong negative birefringence. The performing pathologist was blinded to radiological results.
2.4. Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using R Project for Statistical Computing 3.4.1 [R Core Team (2013). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. URL
http://www.R-project.org ]. The presence of a positive or negative final diagnosis for gout, presence of MSU deposits in foot tendons and grading of tophus size were tabulated for DECT 120 and DECT 150. To analyse the agreement between DECT 120 and 150, contingency tables were created and the overall agreement was calculated. The agreement of overall positive and negative findings between DECT 120 and 150 was determined using a McNemar’s Chi- square test and quadratic weighted kappa. The relationship between the gradings of MSU deposits obtained with DECT120 and DECT150 was analysed using a Pearson Chi-square for symmetry test.
In general, results were considered significant for P-values less than 0.05.
3. Results
In 8 cadavers a tendon MSU deposit was identified by DECT 120 detection, while DECT 150 was negative. In the remaining 32 specimens both DECT 120 and DECT 150 agreed in their positive final reading.
Although this resulted in an overall agreement between DECT 150 and DECT 120 of 80%, McNemar´s Chi-square test and quadratic weighted kappa revealed a significant difference in MSU detection between both methods (p=0.013).
Table 3 gives the overall agreement between DECT 120 and DECT 150 regarding the MSU grading for all individual tendons and the corresponding p-values for the Pearson Chi2 test of independence.
The overall agreement between the two methods was relatively low (0-30%), and the difference was statistically significant, except for the Achilles tendon.
The tibialis anterior tendon (TAT), peroneus tendons (PT), and flexor halluces longus tendon (FHL) were the most commonly involved tendons, followed by the tibialis posterior tendon (TP), achilles tendon (AT) and extensor halluces longus tendon (EHLT),
Table 4.
The most common Score 3 MSU deposition site detected by DECT 120 was the achilles tendon followed by the tibialis anterior tendon,
Table 5,
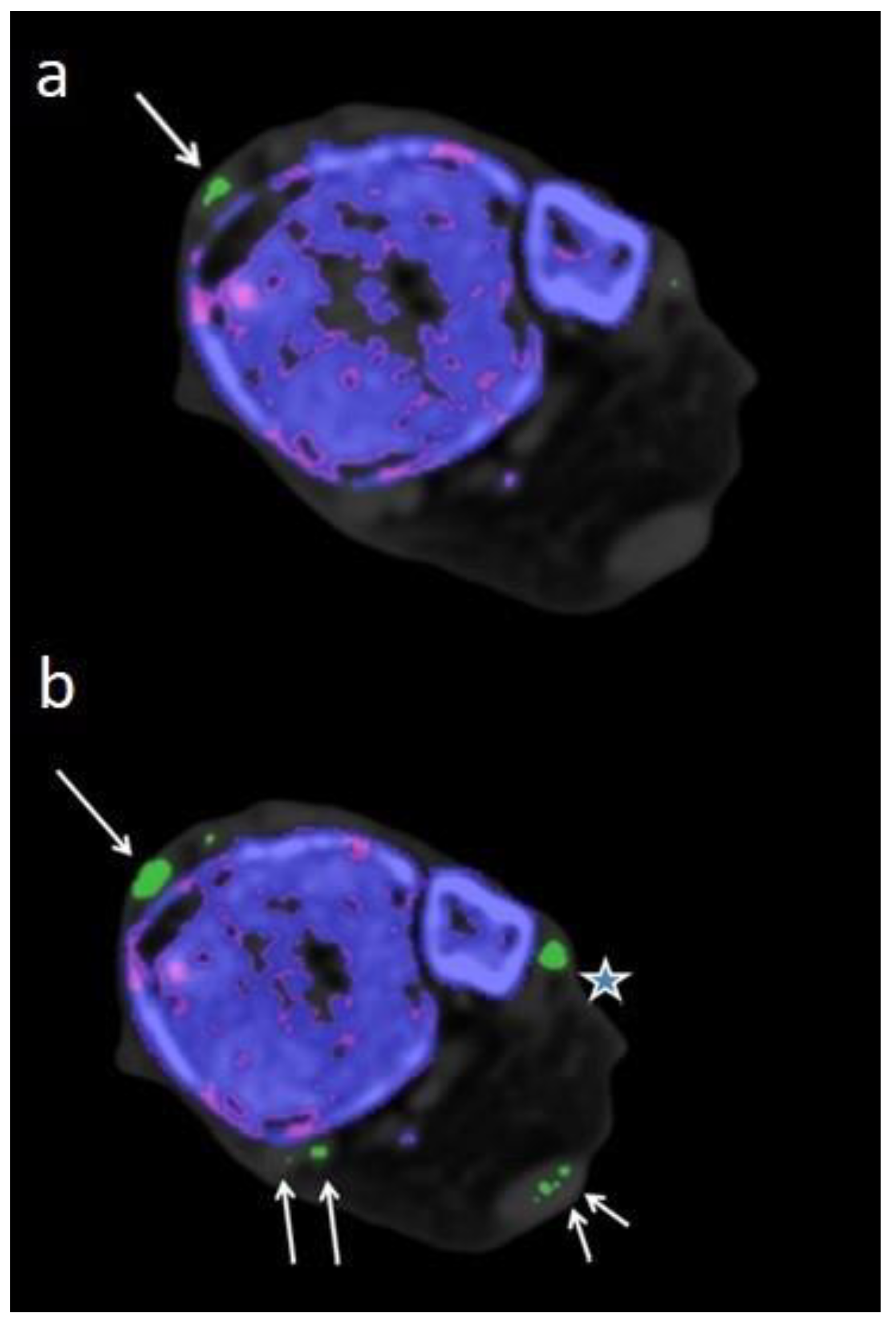
Figure 1.
A major reason for the low agreement was that MSU deposit size was larger detected by DECT 120 than by DECT 150 (P < 0.001) for all tendons leading to different MSU gradings, see
Table 5.
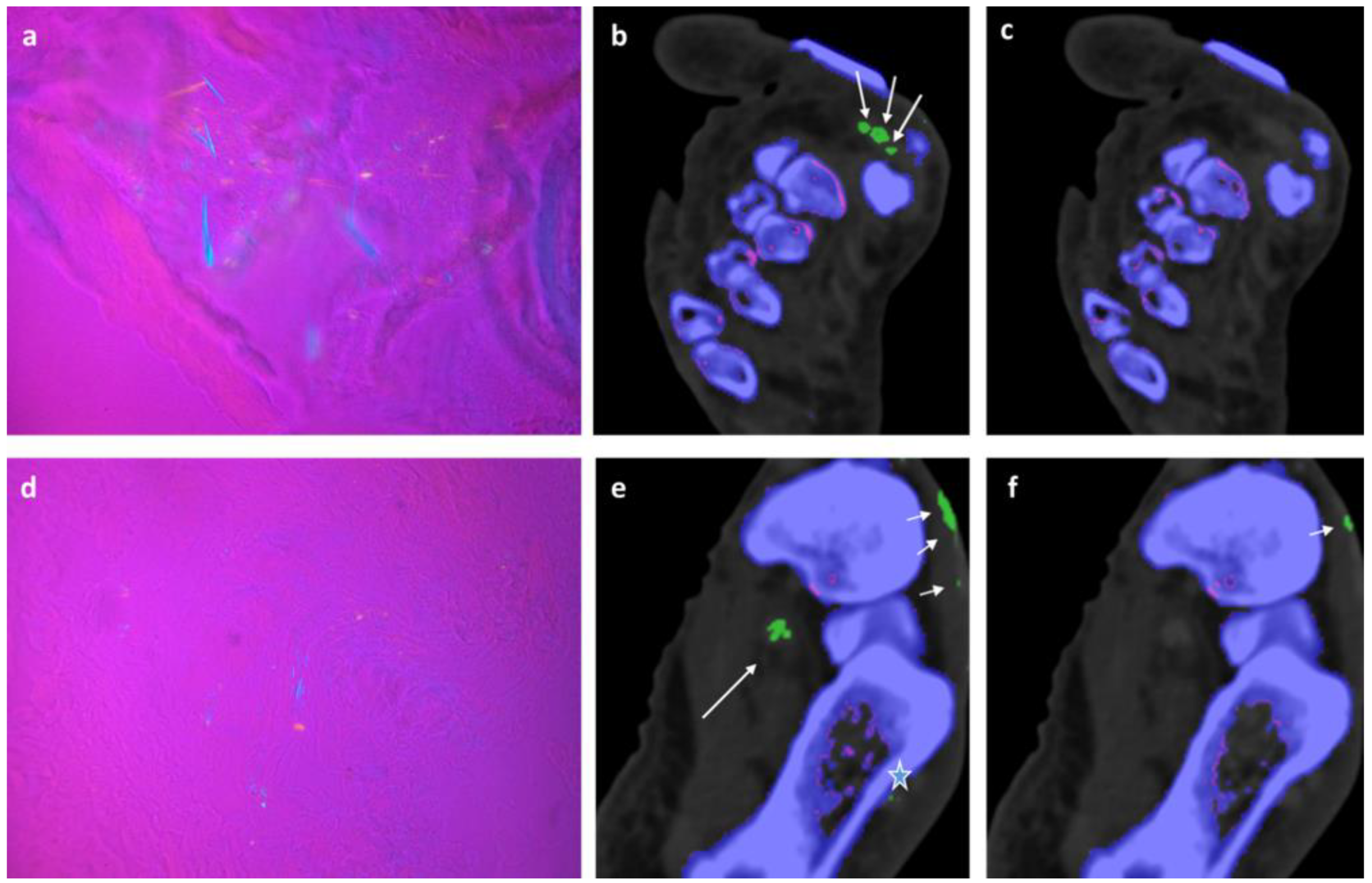
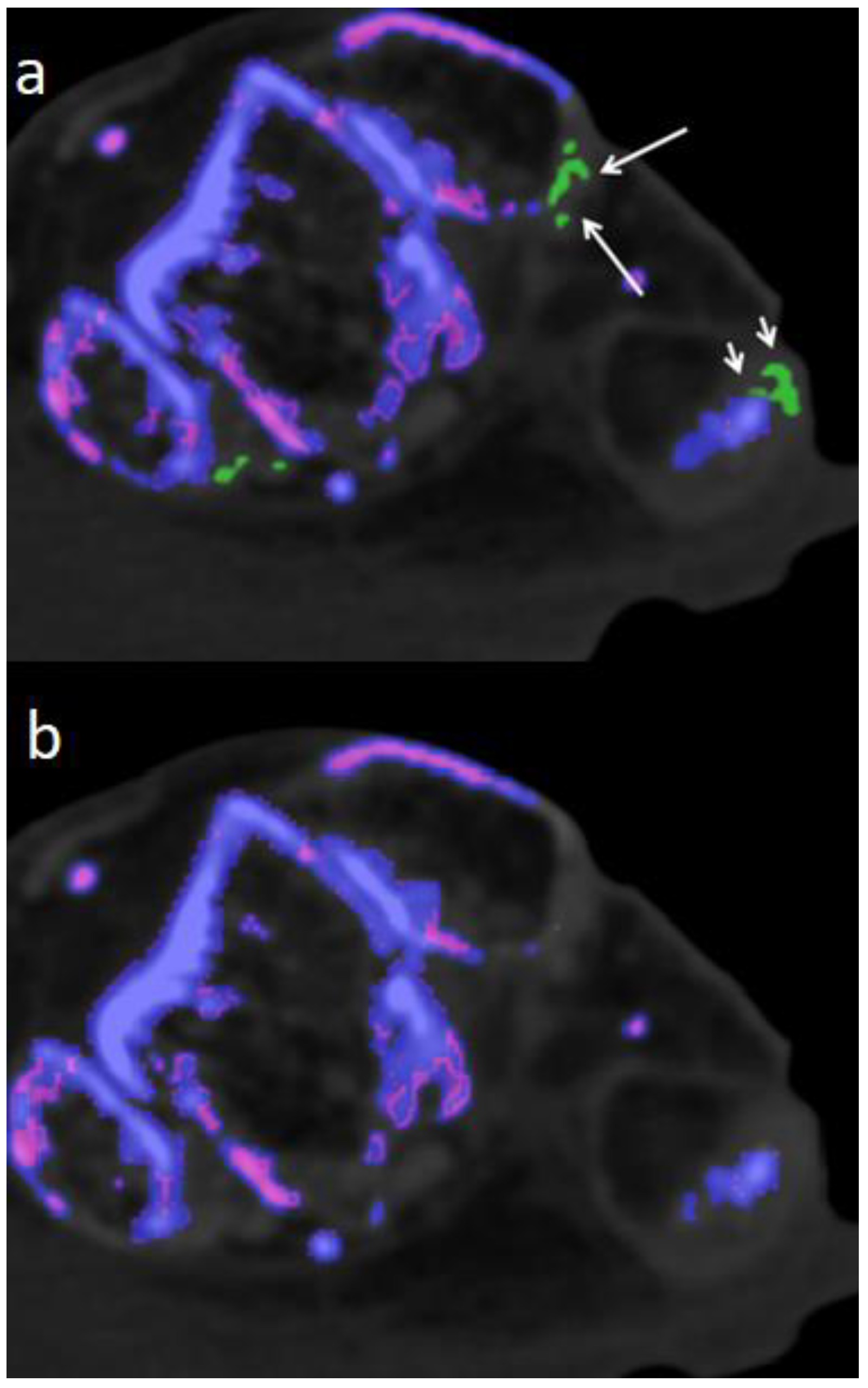
In 2/ 6 fresh cadavers MSU deposits in DECT 120, not visible in DECT 150 could be verified by microscopy in tibialis anterior, Achilles, flexor halluces longus, and peroneal tendons,
Figure 2,
Figure 3 and
Figure 4.
No false positive MSU interpretations were found on pathologic review of our DECT 120 readings in the fresh cadavers.
4. Discussion
Tendon involvement in patients with gout has been evaluated by US and DECT (29-31) and it has been shown that tendons are a frequent location of extraarticular MSU deposition in the lower limbs, especially in longstanding gout. DECT demonstrated high sensitivity, specificity, and reproducibility in the detection of MSU deposits in tendons in previous studies. (26, 30, 32, 33) Yuan et al. (3) reported tendons as the most frequent anatomical location site of MSU deposits in a DECT study of 184 joints, regardless of whether the intraarticular DECT results were positive or negative.
In a DECT study of 92 patients with longstanding tophaceous gout, Dalbeth et al. (30) reported that tendons were the most frequent site of MSU deposits showing a high prevalence in achilles tendon of 39.1%, followed by peroneal tendons in 18.1%. Involvement by MSU was found in 7% and 5%, respectively for the TAT and FHL, which is in contrast to our results where the TAT was involved in 57.5%/100% (DECT 150/120) and AT in 25%/90% (DECT 150/120).
Recently, Dubief et al. (23) described the prevalence of MSU deposits in foot tendons by using different DECT postprocessing protocols. Using the minimum HU 120 setting, they classified most of the findings as artifacts, but they did not have verification by histology as the gold standard, which we performed in our study. DECT 120 showed a better correlation regarding tophus size when compared to US in previous studies. (34)
Dalbeth et al. (35) reported that DECT is a highly reproducible method for measuring urate deposits within tophi, revealing the composition of tophi that contains variable urate deposits embedded within soft tissue where MSU deposits are scattered across the tophus surrounded by soft tissue. These findings are consistent with a previous histological analysis of tophi from the same team.
As reported by Melzer et al. (36), DECT can identify ‘dense’ tophi (with at least 15–20% urate volume in the tophus), but tophi with lower urate volumes may not be detected. This limitation might be overcome by the use of DECT 120, as shown in our study. When only considering DECT 150 we would have missed 20% of the MSU deposits in foot tendons. Lowering the HU threshold without changing scan parameters (tube A and B at 80 /140 kV) was helpful to better identify tophi with low MSU concentration with verification by histology.
Though DECT 120 shows great potential, it is not without limitations. It has to be noted that DECT 120 is more susceptible to artifacts and an increased amplification of noise,
Figure 5.
Therefore imaging results should be interpreted with caution by an experienced radiologist who is well-trained to recognize artifacts. Locations notorious for artifacts are nose, skin, calluses, and nail beds (4, 24, 25) which were obviously more prevalent and increased in size when using DECT 120 (
Figure 1).
Furthermore, MSU deposits shown in DECT 120 and not visible in DECT 150 were only histologically verified in fresh cadavers not in embalmed cadavers, because of potential interference with the fixation process in embalmed cadavers. This is a clear limitation of our study, as we cannot clearly prove that some of the positive observations at DECT 120 were not false positive. Nonetheless, our experience in the six fresh cadavers suggests that the interpretation of our experienced observers did not yield a significant number of false positive results, as all of their positive interpretations in the fresh specimens were confirmed by polarized light microscopy.
An additional limitation of this study is the lack of assessment of inter-observer agreement, and the lack of a medical history for the cadavers. Finally, note that our ex-vivo results need to be repeated in live patients to demonstrate clinical applicability.
We are fully aware that the results we report do not agree with many existing publications on tendon involvement in gout. However, there are individual publications that show similarly high numbers of MSU deposits in tendons. It should be noted that most studies worked with higher cut-off values regarding the HU, and many regions of the tendons were not classified as true MSU but as artifacts. Our study is the first to examine these regions which were previously presumed to represent artifacts utilizing histological processing. The rate of 80% MSU deposits in tendons is astonishing and raises many questions regarding the composition and nature of tendons, as well as the pathomechanism and clinical relevance of tendon MSU deposits in gout.
In addition to assisting with the diagnosis of gout, DECT may help to monitor the efficacy of urate-lowering therapy, and to prove therapeutic outcomes not only in joints but also in tendons. (37)
5. Conclusions
The DECT 120 protocol showed a higher sensitivity when compared to DECT 150.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.S.K., S.S., C.S., C.K, W.K., V.V.N., H.S., Y.S., E.H.; Data curation, A.S.K., C.S., W.K., Y.K., H.S.; Formal analysis, A.S.K., S.S., C.S., W.K., C.K.; Investigation, A.S.K., S.S., C.S., V.V.N.; Methodology, A.S.K., S.S., C.S., H.S.; Project administration, A.S.K. and C.S.; Resources, A.S.K.; Software, C.S.; Supervision, A.S.K., E.H..; Validation, C.S., A.S.K..; Visualization, W.K. and H.S.; Writing—original draft, A.S.K., S.S. and C.S.; Writing—review & editing, A.S.K., C.S., Y.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data supporting reported results may be provided upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Harris MD, Siegel LB, Alloway JA. Gout and hyperuricemia. Am Fam Physician. 1999;59(4):925-34.
- Choi HK, Mount DB, Reginato AM. Pathogenesis of gout. Ann Intern Med. 2005;143(7):499-516.
- Yuan Y, Liu C, Xiang X, Yuan TL, Qiu L, Liu Y; et al. Ultrasound scans and dual energy CT identify tendons as preferred anatomical location of MSU crystal depositions in gouty joints. Rheumatol Int. 2018;38(5):801-11. [CrossRef]
- Glazebrook KN, Guimarães LS, Murthy NS, Black DF, Bongartz T, Manek NJ; et al. Identification of intraarticular and periarticular uric acid crystals with dual-energy CT: Initial evaluation. Radiology. 2011;261(2):516-24. [CrossRef]
- Bongartz T, Glazebrook KN, Kavros SJ, Murthy NS, Merry SP, Franz WB, 3rd; et al. Dual-energy CT for the diagnosis of gout: An accuracy and diagnostic yield study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74(6):1072-7.
- Pascart T, Grandjean A, Capon B, Legrand J, Namane N, Ducoulombier V; et al. Monosodium urate burden assessed with dual-energy computed tomography predicts the risk of flares in gout: A 12-month observational study : MSU burden and risk of gout flare. Arthritis Res Ther. 2018;20(1):210.
- Zhang Z, Zhang X, Sun Y, Chen H, Kong X, Zhou J; et al. New urate depositions on dual-energy computed tomography in gouty arthritis during urate-lowering therapy. Rheumatol Int. 2017;37(8):1365-72. [CrossRef]
- Gamala M, Linn-Rasker SP, Nix M, Heggelman BGF, van Laar JM, Pasker-de Jong PCM; et al. Gouty arthritis: Decision-making following dual-energy CT scan in clinical practice, a retrospective analysis. Clin Rheumatol. 2018;37(7):1879-84. [CrossRef]
- Schwabl C, Taljanovic M, Widmann G, Teh J, Klauser AS. Ultrasonography and dual-energy computed tomography: Impact for the detection of gouty deposits. Ultrasonography. 2021;40(2):197-206. [CrossRef]
- Dalbeth N, Choi HK. Dual-energy computed tomography for gout diagnosis and management. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2013;15(1):301. [CrossRef]
- Neogi T, Jansen TL, Dalbeth N, Fransen J, Schumacher HR, Berendsen D; et al. 2015 Gout classification criteria: An American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74(10):1789-98.
- Richette P, Doherty M, Pascual E, Barskova V, Becce F, Castaneda J; et al. 2018 updated European League Against Rheumatism evidence-based recommendations for the diagnosis of gout. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;79(1):31-8. [CrossRef]
- De Yoe BE, Ng A, Miller B, Rockett MS. Peroneus brevis tendon rupture with tophaceous gout infiltration. J Foot Ankle Surg. 1999;38(5):359-62. [CrossRef]
- Lagoutaris ED, Adams HB, DiDomenico LA, Rothenberg RJ. Longitudinal tears of both peroneal tendons associated with tophaceous gouty infiltration. A case report. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2005;44(3):222-4. [CrossRef]
- Patten A, Pun WK. Spontaneous rupture of the tibialis anterior tendon: A case report and literature review. Foot Ankle Int. 2000;21(8):697-700. [CrossRef]
- Jerome JT, Varghese M, Sankaran B, Thomas S, Thirumagal SK. Tibialis anterior tendon rupture in gout--case report and literature review. Foot Ankle Surg. 2008;14(3):166-9. [CrossRef]
- Radice F, Monckeberg JE, Carcuro G. Longitudinal tears of peroneus longus and brevis tendons: A gouty infiltration. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2011;50(6):751-3. [CrossRef]
- Heckman DS, Gluck GS, Parekh SG. Tendon disorders of the foot and ankle, part 1: Peroneal tendon disorders. Am J Sports Med. 2009;37(3):614-25.
- Barazani SH, Chi WW, Pyzik R, Chang H, Jacobi A, O’Donnell T; et al. Quantification of uric acid in vasculature of patients with gout using dual-energy computed tomography. World J Radiol. 2020;12(8):184-94. [CrossRef]
- Khanna P, Johnson RJ, Marder B, LaMoreaux B, Kumar A. Systemic Urate Deposition: An Unrecognized Complication of Gout? J Clin Med. 2020;9(10).
- Ahn SJ, Zhang D, Levine BD, Dalbeth N, Pool B, Ranganath VK; et al. Limitations of dual-energy CT in the detection of monosodium urate deposition in dense liquid tophi and calcified tophi. Skeletal Radiol. 2021;50(8):1667-75. [CrossRef]
- Pascart T, Carpentier P, Choi HK, Norberciak L, Ducoulombier V, Luraschi H; et al. Identification and characterization of peripheral vascular color-coded DECT lesions in gout and non-gout patients: The VASCURATE study. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2021;51(4):895-902. [CrossRef]
- Dubief B, Avril J, Pascart T, Schmitt M, Loffroy R, Maillefert JF; et al. Optimization of dual energy computed tomography post-processing to reduce lower limb artifacts in gout. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2022;12(1):539-49. [CrossRef]
- Park EH, Yoo WH, Song YS, Byon JH, Pak J, Choi Y. Not All Green Is Tophi: The Importance of Optimizing Minimum Attenuation and Using a Tin Filter to Minimize Clumpy Artifacts on Foot and Ankle Dual-Energy CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2020;214(6):1335-42. [CrossRef]
- Mallinson PI, Coupal T, Reisinger C, Chou H, Munk PL, Nicolaou S; et al. Artifacts in dual-energy CT gout protocol: A review of 50 suspected cases with an artifact identification guide. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2014;203(1):W103-9. [CrossRef]
- Klauser AS, Strobl S, Schwabl C, Klotz W, Feuchtner G, Moriggl B; et al. Prevalence of Monosodium Urate (MSU) Deposits in Cadavers Detected by Dual-Energy Computed Tomography (DECT). Diagnostics (Basel). 2022;12(5). [CrossRef]
- Jeon JY, Lee SW, Jeong YM, Baek HJ. The effect of tube voltage combination on image artefact and radiation dose in dual-source dual-energy CT: Comparison between conventional 80/140 kV and 80/150 kV plus tin filter for gout protocol. Eur Radiol. 2019;29(3):1248-57.
- Chou H, Chin TY, Peh WC. Dual-energy CT in gout - A review of current concepts and applications. J Med Radiat Sci. 2017;64(1):41-51.
- de Ávila Fernandes E, Sandim GB, Mitraud SA, Kubota ES, Ferrari AJ, Fernandes AR. Sonographic description and classification of tendinous involvement in relation to tophi in chronic tophaceous gout. Insights Imaging. 2010;1(3):143-8. [CrossRef]
- Dalbeth N, Kalluru R, Aati O, Horne A, Doyle AJ, McQueen FM. Tendon involvement in the feet of patients with gout: A dual-energy CT study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2013;72(9):1545-8. [CrossRef]
- Ventura-Ríos L, Sánchez-Bringas G, Pineda C, Hernández-Díaz C, Reginato A, Alva M; et al. Tendon involvement in patients with gout: An ultrasound study of prevalence. Clin Rheumatol. 2016;35(8):2039-44. [CrossRef]
- Klauser AS, Halpern EJ, Strobl S, Abd Ellah MMH, Gruber J, Bellmann-Weiler R; et al. Gout of hand and wrist: The value of US as compared with DECT. Eur Radiol. 2018;28(10):4174-81. [CrossRef]
- Nicolaou S, Liang T, Murphy DT, Korzan JR, Ouellette H, Munk P. Dual-energy CT: A promising new technique for assessment of the musculoskeletal system. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2012;199(5 Suppl):S78-86. [CrossRef]
- Strobl S, Kremser C, Taljanovic M, Gruber J, Stofferin H, Bellmann-Weiler R; et al. Impact of Dual-Energy CT Postprocessing Protocol for the Detection of Gouty Arthritis and Quantification of Tophi in Patients Presenting With Podagra: Comparison With Ultrasound. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2019;213(6):1315-23. [CrossRef]
- Dalbeth N, Aati O, Gao A, House M, Liu Q, Horne A; et al. Assessment of tophus size: A comparison between physical measurement methods and dual-energy computed tomography scanning. J Clin Rheumatol. 2012;18(1):23-7.
- Melzer R, Pauli C, Treumann T, Krauss B. Gout tophus detection-a comparison of dual-energy CT (DECT) and histology. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2014;43(5):662-5. [CrossRef]
- Finkenstaedt T, Manoliou A, Toniolo M, Higashigaito K, Andreisek G, Guggenberger R; et al. Gouty arthritis: The diagnostic and therapeutic impact of dual-energy CT. Eur Radiol. 2016;26(11):3989-99. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).