1. Introduction
SARS-CoV-2 virus first emerged in December 2019 when it infected a patient hospitalized with the disease now known as COVID-19 [
1]. It subsequently spread worldwide and caused a pandemic [
2]. For this pandemic event, much more powerful tools were available to study and manage it than ever before. Next-generation sequencing capabilities have helped scientists study the genetic code of the virus and its evolution over time [
3].
One of these capabilities certainly represents possibility to study how is human transcriptome in tissue of infected patient changing or how it differs in case of more severe symptoms. After infecting human tissue, SARS-CoV-2 alters normal metabolism and signaling of the host cell to accommodate cell environment for itself and its replication. In general, this involves interfering with signaling pathways that regulate processes of DNA repair and replication, immune response, transcription, metabolism, cell cycle, and apoptosis. Specifically, pathways that are known to be altered are phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (AKT), Type I and III interferon, transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β), Toll-like receptors (TLR), and nuclear factor kappa light chain enhancer (NF-κB) pathways. Also altering of Ca2+ signaling is believed to be part of the infection [
4]. Severe phenotype has been linked to cytokine storms - excessive and uncontrolled immune response. It leads to the release of a large amount of pro-inflammatory cytokines into the bloodstream, followed by widespread inflammation and damage to tissues and organs [
5,
6,
7].
This study is a pilot to our ongoing research on the impact of SARS-cov2 infection on the human transcriptome and bacteria analyzed from RNA-sequencing of nasopharyngeal swabs. Here, we investigated the transcriptome profiles in COVID-19 -positive and -negative samples. We focused on differential gene expression and identification of pathways affected by infection. We also compared patients infected with different SARS-CoV-2 clades.
2. Results
In this study, we analysed RNA-seq data from nasopharyngeal swabs. 96 samples were part of this study (72 COVID-19 positive patients and 24 healthy donors). Transcriptomic analysis was performed on human transcripts to identify candidates for differentially expressed genes in diseased patients and based on disease severity. The information obtained from the SARS-CoV-2 analysis (lineage/clade assignment of SARS-CoV-2 were performed) was further used in this transcriptomic analysis to designate groups according to the clade of the virus causing the infection and to compare the human transcriptome between these groups.
2.1. SARS-CoV-2 sequences in our samples
Using Galaxy pipeline (described in methods section) we assigned SARS-CoV-2 in our samples with specific clade and WHO name. 24 samples were assigned as Alpha variant (clade 20I), 8 samples as Delta (clade 21J), 4 samples as Omicron (clade 21L), one sample was assigned to 20C clade and one was reported as recombinant.
2.2. Human transcriptome changes in COVID-19
According to our results, there were significant changes in the human transcriptome in COVID-19 patients. Statistical test using DESeq2 reported 16,365 genes with an adjusted p-value < 0.1 compared to COVID-19 negative controls (
Supplementary Table 1). 4539 genes were reported with a p-value < 0.1 when comparing mild and severe disease (
Supplementary Table 2).
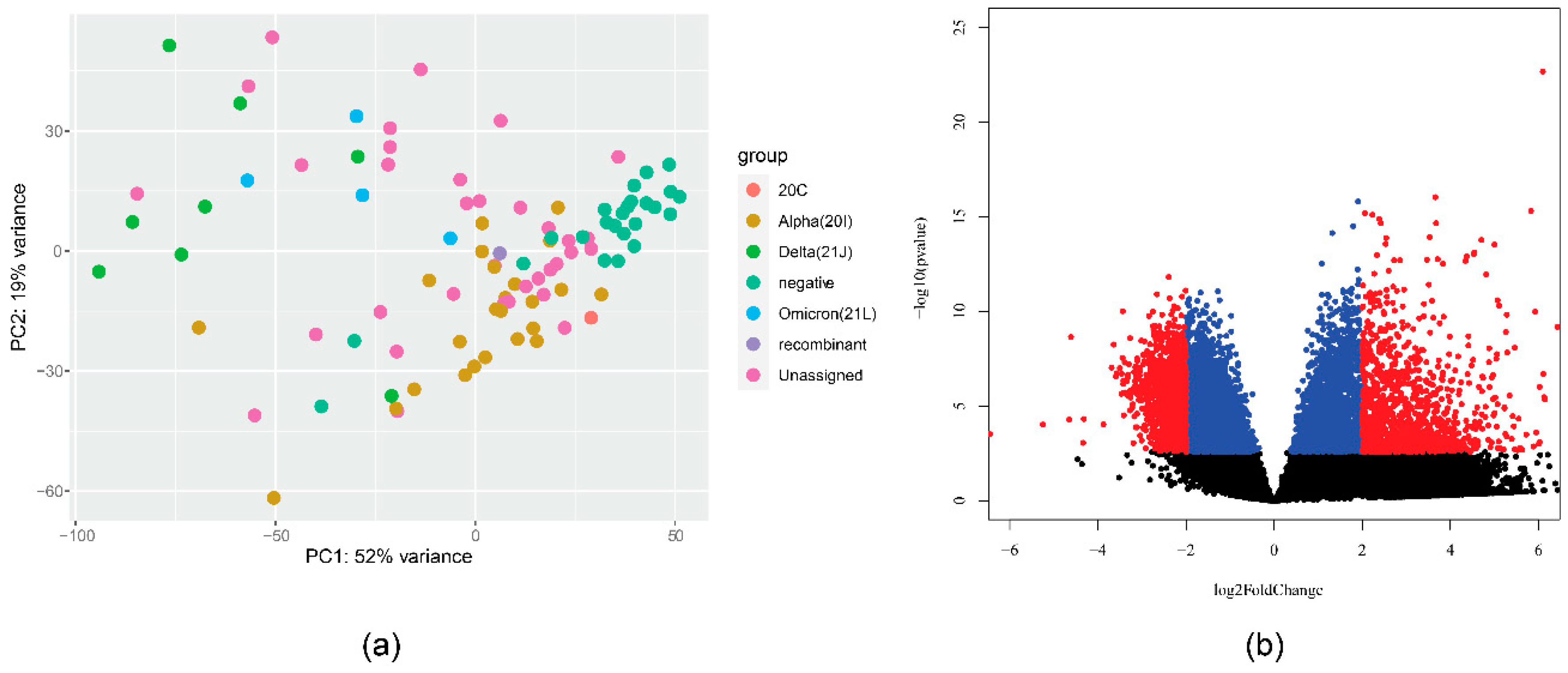
Our data also show variation by specific SARS-CoV-2 variant (by WHO name). The distance in the transcriptional profile is visualized in
Figure 1a. A large difference was shown when comparing Alpha (all 20I) and Delta (all 21J) variants. There were 14,109 genes with p-value < 0.1, which is visualized in
Figure 1b. We speculate further on the reasons for this difference in the Discussion section. A comparison of delta and omicron patients (albeit with a limited number of samples) recorded 468 genes with a p-value < 0.1, however, all Omicron samples were female.
Figure 1.
(a) PCA analysis plot of gene expression in different SARS-CoV-2 strains. (b) Volcano plot visualizing differential expression between samples from patients with alpha variant (20I) and those with Delta variant (21J).
Figure 1.
(a) PCA analysis plot of gene expression in different SARS-CoV-2 strains. (b) Volcano plot visualizing differential expression between samples from patients with alpha variant (20I) and those with Delta variant (21J).
2.3. Pathways altered by infection
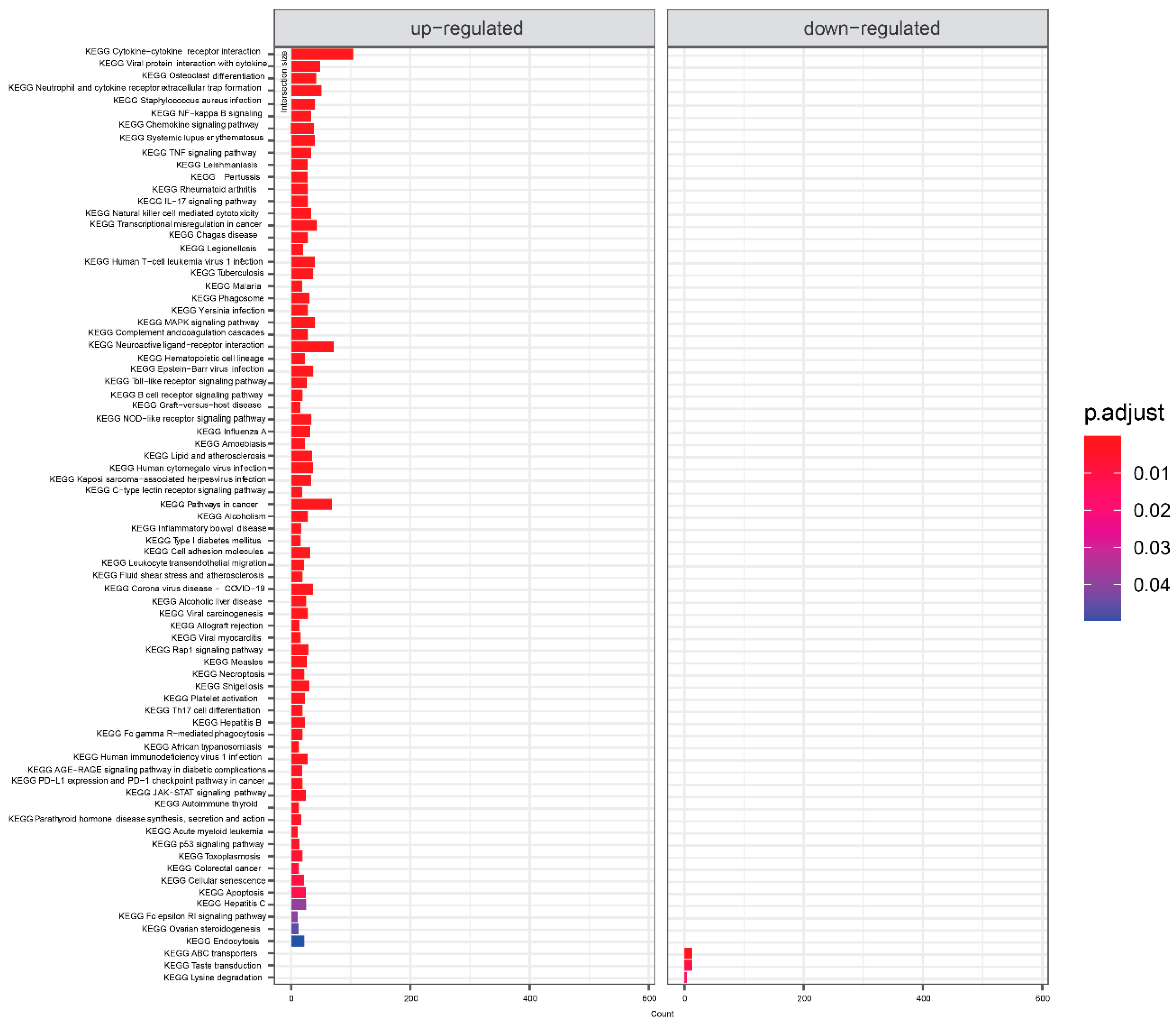
Since no unequivocal information can be obtained from the large number of genes that meet the criteria for significant effect, we performed an enrichment analysis of the KEGG pathways. Comparison of COVID-19 positive and COVID-19 negative patients (
Figure 2) showed that most of the pathways with enriched genes with up-regulation are related to the immune response to various diseases or to other immune-related pathways (cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction, Neutrophil extracellular trap formation, Viral protein interaction with cytokine, Natural killer cell, B cell receptor, NOD−like receptor, Fc gamma R−mediated phagocytosis, Th17 cell differentiation ), then signaling pathways mostly related to the immunity (NF-kappa B signaling pathway, TNF signaling pathway, chemokine signaling pathway, IL-17 signaling pathway, MAPK signaling pathway, C-type lectin receptor signaling pathway, Rap1 signaling pathway, JAK-STAT signaling pathway, p53 signaling pathway), other KEGG pathways were Osteoclast differentiation, Cell adhesion molecules, Alcoholism, and Alcoholic liver disease. For the downregulated genes, 3 pathways were enriched: ABC transporters, taste transfer, and lysine degradation.
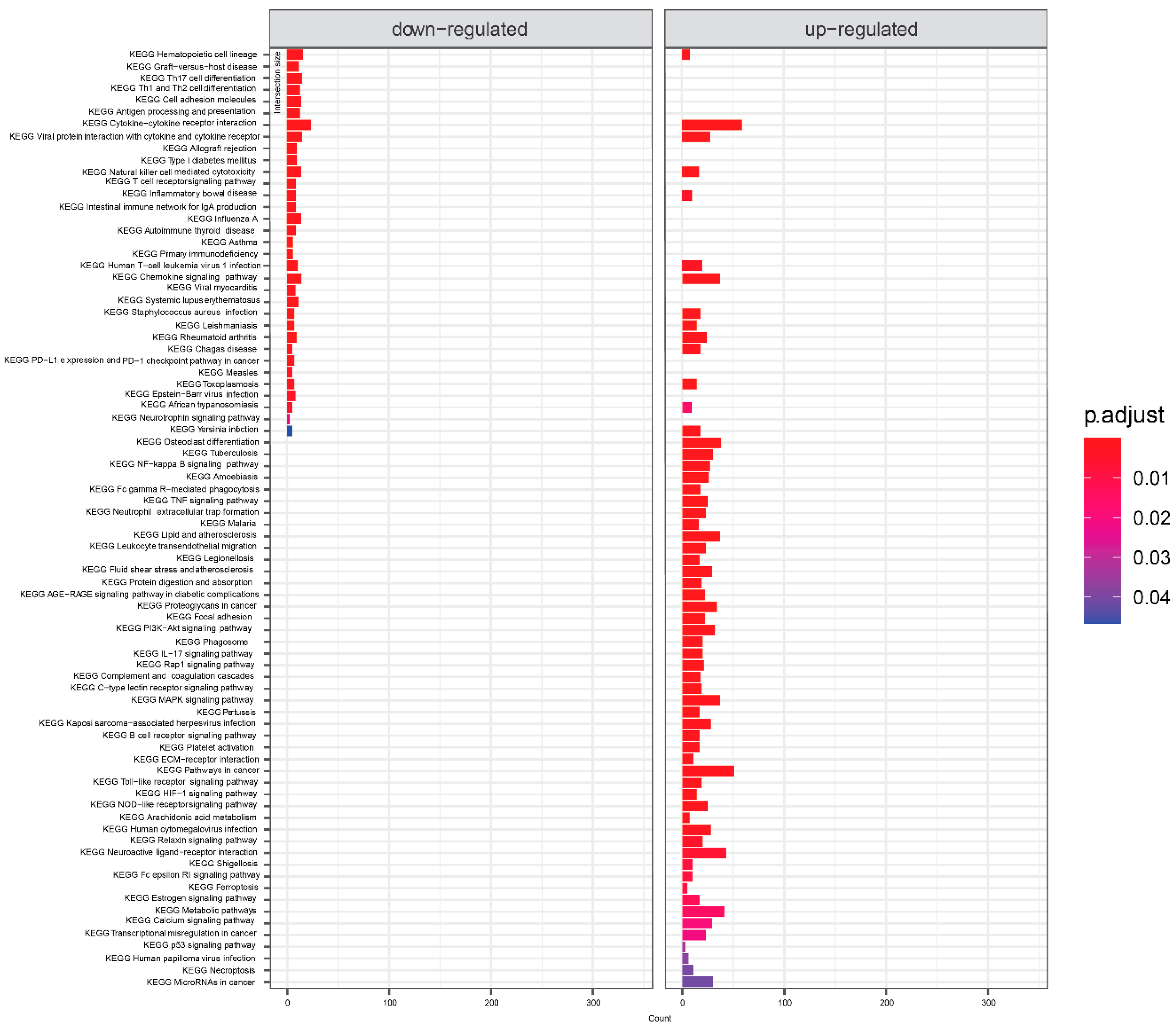
KEGG pathway analysis of mild symptoms compared to severe symptoms is shown in
Figure 3. Again, infectious disease and immunity-related concepts dominated. Cytokine interactions related terms were significant for both down- and up-regulated genes. From signaling pathways, there is NF-Kappa B, neutrophin, TNF, PI3K-Akt, IL-17, Rap 1, MAPK, Toll-like receptor, C-type lectin, B cell receptor, HIF-1, NOD-like receptor, calcium and estrogen - signaling pathways.
Figure 2.
KEGG terms mapping on differentially expressed genes for COVID-19 positive samples. Visualized are results with default threshold of adjusted p-value < 0.05.
Figure 2.
KEGG terms mapping on differentially expressed genes for COVID-19 positive samples. Visualized are results with default threshold of adjusted p-value < 0.05.
Figure 3.
KEGG terms mapping on genes differentially expressed in samples from severe symptoms patients compared to mild patients. Visualized are results with default threshold of adjusted p-value < 0.05.
Figure 3.
KEGG terms mapping on genes differentially expressed in samples from severe symptoms patients compared to mild patients. Visualized are results with default threshold of adjusted p-value < 0.05.
3. Discussion
This article is a pilot study of the human nasopharyngeal transcriptome and metatranscriptome of patients with COVID-19. Sequenced samples were collected from COVID-19 patients with severe and mild symptoms, from asymptomatic COVID-19 positive and negative donors. We analysed the transcriptome of COVID-19-positive patients by mapping reads to the human genome, counting features, and statistically comparing groups to find differentially expressed genes (in COVID-19 positive samples, in samples from patients with severe symptoms, and in samples with Alpha/Delta/Omicron variants), and performed KEGG enrichment analysis on these samples.
A recent study of a similar transcriptome analysis of COVID-19-positive patients, comparing positive patients and negative controls using gene enrichment analysis (albeit with different software: edgeR and Metascape), was published by Rhoades et al. (2021) [
8]. They mapped differentially expressed genes to GO terms (we did this with KEGG pathways), but also reported terms associated with innate and adaptive host defense pathways, which correlates with our results and is not surprising. Similarly, they found terms related to hematopoiesis (with CD53, IKZF1 genes reported, in our results too), inflammatory response, B-cell activation, and leukocyte chemotaxis/mobility (with CCL2, CCR1 genes reported). They report interferon-stimulated genes FITM3, and ISG15, which were also identified in our set of potentially affected genes, then type I interferon signaling genes IRF7, STAT1 (our results did not detect STAT1), UN-ATP-1 signaling (with reported genes BCL3, MYD88, also in our results). We did not observe neuronal death pathways, nor the SNCA gene mentioned in the work of Rhoades et al. (another listed gene MDK is in our results). In results of KEGG enrichment multiple terms referring to various diseases (not only COVID-19) were called, which might be caused by similarities in effect on tissue between infections or other disease events. We did not observe many downregulated genes (in infected tissues) related pathways, whereas Rhoades et al. reported GO terms associated with tissue homeostasis and cellular organization.
There are multiple processes that has been reported by previous studies to be involved in changes caused by infection and are regarded as key pathways altered during SARS-CoV-2 infection. Most of those key pathways we identified in pathway enrichment using KEGG, Reactome and Wiki Pathway databases. KEGG pathway enrichment detected terms related to TLR receptors. In fact, TLR receptors are known to be key component in reacting to SARS-CoV-2 infection, for example TLR3 hyperactivation can lead to a cytokine storm and the subsequent severe COVID-19 [
4]. Another component - Interleukins (IL-2, IL-6, IL-7, IL-10) and TNF-α are connected to severe symptoms of COVID-19, where cytokine storm (increase in cytokines) occurs instead of healthy immune response [
9]. TNF signaling pathway was detected as significant KEGG pathway in both comparisons on positivity and severity of disease. By REAC pathway analysis of differentially expressed genes in COVID-19-positive cases, we detected interleukin IL-2, IL-7, IL-10 and also IL-1, IL-4, IL-13 and IL-36. KEGG pathway enrichment detected IL-17. Next, NF-kB related terms were enriched for both gene sets (genes affected by severity or positivity on COVID-19) and not only using KEGG database, but also Wiki Pathway and Reactome. It has been reported, that severe COVID-19 is characterized by an inflammatory profile dominated by NF-κB activity [
10]. Then, terms related with TGF-β and JAK-STAT signaling were enriched. JAK-STAT signaling was detected from differentially expressed genes in COVID-19-positive patients. TGF-beta terms were recognized by Wiki Pathway enrichment in both positivity and severity -affected gene sets. In fact, the cytokine TGF-β functions activator or suppressor of the Janus kinases (JAKs) and these processes are believed to be affected by infection by the virus [
11]. Another pathway reported to be altered by SARS-CoV-2 infection PI3K-Akt signaling pathway [
12,
13] was also detected in our study (for both severity and positivity affected gene sets).
One could speculate a lot when comparing the results of the Alpha, Delta, and Omicron groups. We observed significant differences between the Alpha and Delta groups, but we cannot say what the exact cause of the difference in gene expression was. In terms of the background of the patients, we know that more Alpha patients had mild symptoms, but there were also patients with severe symptoms, and Delta patients had severe symptoms or no symptoms. There were 15 male and 8 female Alpha patients. Both younger and older patients were represented in each group. Some of the patients with severe symptoms were treated with antibiotics. Comparison of delta and omicron patients (albeit with a limited sample size) scored 468 genes with p-values < 0.1. KDM5D and DDX3Y had the highest scores, but these genes are not known to be related to immune response processes but are related to spermatogenesis [
14,
15]. All omicron samples were randomly from women, so it is impossible to say what portion of the results were influenced by this factor. We also did not elucidate the significance of the other significantly and highly expressed genes CRYBG3 and PHACTR4. However, the moderately highly expressed CXCL8 is known to be elevated in viral infections, producing protein known as interleukin-8 [
16].
The study has several potential drawbacks. Patients with severe symptoms had a higher median age (68 years) than patients with mild symptoms (37 years), asymptomatic donors (42 years), or negative controls (37 years). This is because the majority of patients hospitalized with severe symptoms were elderly and therefore the samples were the most accessible in this regard. Overall, 54.3% of the samples were female. Only in severe patients, there was some inequality (69.5% of samples of male origin).
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Approval
Sample collection was performed as part of the clinical study approved by the Ethical Committee of Bratislava Self-Governing District under the identifier 03228/2021/HF from January 12, 2021. All patients have filled out the questionnaires with relevant information regarding their health status in relation to COVID-19 and signed informed consent.
4.2. Samples
Nasopharyngeal swabs from patients suspected of having COVID-19 were obtained in two primary regimens. Patients hospitalized with severe symptoms of the disease at the collaborating hospitals were enrolled in the study. Patients with mild or any symptoms of the disease were recruited in mobile testing facilities for SARS-CoV-2 by a company providing routine laboratory diagnostics from the population during the COVID-19 pandemic. Subgroups 1 to 4 were formed based on the negativity and positivity of SARS-CoV-2 testing and the severity of COVID-19 symptoms according to the following scheme: group 1 - severe symptoms, group 2 - mild symptoms, group 3 - no symptoms, group 4 - negative. The WHO definition of symptoms was used to classify cases (according to: Living guidance for clinical management of COVID-19, 2021 by World Health organisation). In toatal, 96 samples were part of this study (72 COVID-19 positive patients and 24 healthy donors).
4.3. Nucleic acid extraction
Nasopharyngeal swabs specimens were collected from COVID-19 patients and controls and stored in viRNAtrap collection (GeneSpector, Czech Republic) medium at 4°C. Total RNA was extracted using Sera-Xtracta Virus/Pathogen Kit (Cytiva, UK) according to manufacturer instructions. 400 μl of the nasopharyngeal swab medium was used for the extraction with a final elution volume of 50 μl. RNA was quantified with the Qubit™ RNA High Sensitivity Assay Kit (Invitrogen). RNA isolates were stored at -80°C.
4.4. RT-qPCR
The presence of SARS-CoV-2 was determined by RT-qPCR using the COVID-19 Real-Time Multiplex RT-PCR Kit (Labsystems Diagnostics, Finland) and RT-qPCR platform ABI QuantStudio 6 Real-Time PCR System (ThermoFisher, USA) utilizing the original manufacturers’ protocols. Amplification cycles threshold of Ct value <40 was needed to evaluate the sample as positive.
4.5. RNA library preparation and sequencing
The metatranscriptomic libraries were prepared using KAPA RNA HyperPrep Kit with RiboErase (HMR) (Kapa Biosystems, South Africa) according to the original protocol of the manufacturer. For quantity and quality control of prepared libraries a Qubit 1X dsDNA High Sensitivity Assay Kit on Qubit 3.0 (Invitrogen) and Agilent High Sensitivity DNA Kit on Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer (Agilent) instruments were used. Sequencing of pooled libraries was performed on NextSeq 500 and NextSeq 2000 (Illumina) platforms using 2x75 or 2x100 paired-end sequencing setup, respectively.
4.6. Quality Control and Data Preparation for Analysis
First step of any analysis of RNA-seq data is quality control and this step was done by FastQC v0.11.9 [
17]. Reads were processed by Trimmomatic v0.39 (CROP:96 HEADCROP:10 LEADING:22 TRAILING:22 SLIDINGWINDOW:4:22 MINLEN:25 and our own set of adapter sequences were used in ILLUMINACLIP step) [
18]. Parameters were chosen according to FastQC results.
4.7. Reads mapping
After final affirmation of sufficient quality of reads by FastQC, reads were mapped to the human genome hg38 by BWA-MEM algorithm v0.7.17 [
19]. Reads were mapped as paired set, otherwise parameters of mapping were set to default. Same way it was done on SARS-cov 2 genome. Mapping statistics were produced from a “.bam” outputs by Samtools flagstat [
20].
4.8. SARS-CoV-2 variants identification
For SARS-cov2 variant identification, we used Galaxy pipeline - „Mutation calling, viral genome reconstruction and lineage/clade assignment from SARS-CoV-2 sequencing data“ [
21]. As an input we used reads mapping on SARS-cov2 genome.
4.9. Differentially expressed genes analysis
In search of human genes affected by infection of SARS-cov2 or category of infection, we further analysed .bam file with human-mapped reads. Gene expressions were quantified by FeatureCounts v.2.0.1 [
22]. Statistical comparison was done by R instance of Deseq2 v.1.38.3. [
23]. Genes under condition of adjusted p-value < 0.1 were considered significant hits, which is a default value according to DESeq2 manual [
24].
4.10. Identificaion of altered pathways
To find out which pathways are altered from the set of differentially expressed genes, we used R instance of gProfiler2 v.0.2.1. [
25]. Genes, which were under p-value threshold 0.1 were used as a query for the analysis, ordered by p-values and separated to down-regulated and up-regulated set. Databases of KEGG pathways, Wiki pathways and Reactome were used, for the purpose of better visibility, just KEGG terms were chosen for visualization. Set of genes which were part of differentially expressed genes analysis were set as custom background. Domain scope were set to “known”. For the visualization, barplot function in R was used.
5. Conclusions
In this study we studied nasopharyngeal tissue trasnscriptome changes by COVID-19 disease. We identified pathways altered by infection or severity. Most of them are probably component of immune response or alterations caused directly by virus. Many enriched pathway terms related to different diseases suggest similarity between these different pathological events. Then, there were cytokine related terms, immune cells related terms and signaling pathways – most of them correlated with previous publications about the topic.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org. Supplementary Table 1: Genes affected by COVID-19 infection., Supplementary Table 2: Genes affected by severity of COVID-19.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, DH, KB, MH; methodology, DH, MH, GM; software, DH; formal analysis, PJ, GM; investigation, DH, KB, MH; resources, PS, PJ, GM; data curation, KB, MH, PS; writing—original draft preparation, DH; writing—review and editing, KB, MH, PS, PJ; visualization, DH, MH; supervision, GM; project administration, PJ; funding acquisition, PJ, GM.
Funding
This research was funded by: OP Integrated Infrastructure for the project: Serious diseases of civilization and Covid19, ITMS: 313011AVH7, co-financed by the European Regional Development Fund."
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Ethics Committee of Bratislava self-governing region (12.1.2021).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Raw sequencing data used in this study are available on European Nucleotide Archive (ENA database), under study submission PRJEB62682 (
www.ebi.ac.uk/ena).
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Lassan Stefan (Hospital Ružinov, Bratislava), Dr.Jackuliak Peter (Hospital Ružinov, Bratislava) for providing clinical samples, medical documentation and informed consent.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Wu F.; Zhao S.; Yu B.; Chen Y.M.; Wang W.; Song Z.G.; Hu Y.; Tao Z.W.; Tian J.H.; Pei Y.Y.; Yuan M.L.; Zhang Y.L.; Dai F.H.; Liu Y.; Wang Q.M.; Zheng J.J.; Xu L.; Holmes E.C.; Zhang Y.Z. A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China. Nature 2020, 579(7798),265-269. [CrossRef]
- Cucinotta D., Vanelli M. WHO Declares COVID-19 a Pandemic. Acta Biomed. 2020, 91(1),157-160.
- Munnink B.B.; Worp N.; Nieuwenhuijse D.F.; Sikkema R.S.; Haagmans B.; Fouchier R.A.M.; Koopmans M. The next phase of SARS-CoV-2 surveillance: real-time molecular epidemiology. Nat Med. 2021, 27(9),1518-1524.
- Jamison D.A.; Anand Narayanan S.; Trovão N.S.; Guarnieri J.W.; Topper M.J.; Moraes-Vieira P.M.; Zaksas V.; Singh K.K.; Wurtele E.S.; Beheshti A. A comprehensive SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19 review, Part 1: Intracellular overdrive for SARS-CoV-2 infection. Eur J Hum Genet. 2022, 30(8),889-898.
- Wang D.; Hu B.; Hu C.; Zhu F.; Liu X.; Zhang J.; Wang B.; Xiang H.; Cheng Z.; Xiong Y.; Zhao Y.; Li Y.; Wang X.; Peng Z. Clinical Characteristics of 138 Hospitalized Patients With 2019 Novel Coronavirus-Infected Pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA. 2020, 323(11),1061:1069.
- Henderson L.A.; Canna S.W.; Schulert G.S.; Volpi S.; Lee P.Y.; Kernan K.F.; Caricchio R.; Mahmud S.; Hazen M.M.; Halyabar O.; Hoyt K.J.; Han J.; Grom A.A.; Gattorno M.; Ravelli A.; De Benedetti F.; Behrens E.M.; Cron R.Q.; Nigrovic P.A. On the Alert for Cytokine Storm: Immunopathology in COVID-19. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020, 72(7),1059-1063. [CrossRef]
- Mehta P.; McAuley D.F.; Brown M.; Sanchez E.; Tattersall R.S.; Manson J.J. HLH Across Speciality Collaboration; UK. COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression. Lancet. 2020, 395(10229),1033-1034. [CrossRef]
- Rhoades N.S.; Pinski A.N.; Monsibais A.N.; Jankeel A.; Doratt B.M.; Cinco I.R.; Ibraim I.; Messaoudi I. Acute SARS-CoV-2 infection is associated with an increased abundance of bacterial pathogens, including Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the nose. Cell Rep. 2021,36(9),109637.
- Fricke-Galindo I.; Falfán-Valencia R. Genetics Insight for COVID-19 Susceptibility and Severity: A Review. Front Immunol. 2021,12:622176. [CrossRef]
- Huang J.; Hume A.J.; Abo K.M.; Werder R.B.; Villacorta-Martin C.; Alysandratos K.D.; Beermann M.L.; Simone-Roach C.; Lindstrom-Vautrin J.; Olejnik J.; Suder E.L.; Bullitt E.; Hinds A.; Sharma A.; Bosmann M.; Wang R.; Hawkins F.; Burks E.J.; Saeed M.; Wilson A.A.; Mühlberger E.; Kotton D.N. SARS-CoV-2 Infection of Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Human Lung Alveolar Type 2 Cells Elicits a Rapid Epithelial-Intrinsic Inflammatory Response. Cell Stem Cell. 2020, 27(6),962-973.e7.
- Tan L.; Wang Q.; Zhang D.; Ding J.; Huang Q.; Tang Y.Q.; Wang Q.; Miao H. Correction: Lymphopenia predicts disease severity of COVID-19: a descriptive and predictive study. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020,5(1),61.
- Li F.; Li J.; Wang P.H.; Yang N.; Huang J.; Ou J.; Xu T.; Zhao X.; Liu T.; Huang X.; Wang Q.; Li M.; Yang L.; Lin Y.; Cai Y.; Chen H.; Zhang Q. SARS-CoV-2 spike promotes inflammation and apoptosis through autophagy by ROS-suppressed PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2021, 1867(12),166260.
- Al-Qahtani A.A.; Pantazi I.; Alhamlan F.S.; Alothaid H.; Matou-Nasri S.; Sourvinos G.; Vergadi E.; Tsatsanis C. SARS-CoV-2 modulates inflammatory responses of alveolar epithelial type II cells via PI3K/AKT pathway. Front Immunol. 2022,13,1020624.
- Akimoto C.; Kitagawa H.; Matsumoto T.; Kato S. Spermatogenesis-specific association of SMCY and MSH5. Genes Cells. 2008,13(6),623-33. [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Costa P.; Plancha C.E.; Gonçalves J. Genetic dissection of the AZF regions of the human Y chromosome: thriller or filler for male (in)fertility? J Biomed Biotechnol. 2010,2010:936569.
- Baggiolini M.; Clark-Lewis I. Interleukin-8, a chemotactic and inflammatory cytokine. FEBS Lett. 1992, 307(1),97-101. [CrossRef]
- FastQC: a quality control tool for high throughput sequence data. Available online: http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc (Accessed 23.05. 2023).
- Bolger A.M.; Lohse M.; Usadel B. Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics. 2014,30(15),2114-20. [CrossRef]
- Li H. Aligning sequence reads, clone sequences and assembly contigs with BWA-MEM. 2013, arXiv:1303.3997v2 [q-bio.GN].
- Github. Available online: https://github.com/bahlolab/bioinfotools/blob/master/SAMtools/flagstat.md (Accessed 23.05. 2023).
- Mutation calling, viral genome reconstruction and lineage/clade assignment from SARS-CoV-2 sequencing data. Available online: https://training.galaxyproject.org/training-material/topics/variant-analysis/tutorials/sars-cov-2-variant-discovery/tutorial.html (Accessed 23.05. 2023).
- Liao Y.; Smyth G. K.; Shi W. featureCounts: an efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. Bioinformatics. 2013, 30(7), 923–930.
- Love M.I.; Huber W.; Anders S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014,15(12),550.
- DESeq2 manual. Available online: https://bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/manuals/DESeq2/man/DESeq2.pdf. (Accessed 23.05. 2023).
- Kolberg L.; Raudvere U.; Kuzmin I.; Vilo J.; Peterson H. gprofiler2 -- an R package for gene list functional enrichment analysis and namespace conversion toolset g:Profiler. F1000Res. 202,;9:ELIXIR-709.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).