Submitted:
02 June 2023
Posted:
02 June 2023
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. 3D bioprinting: where are we now?
3. 3D bioprinting-bioinks
4. 3D bioprinting technologies
4.1. Inkjet-based bioprinting
4.2. Extrusion-based bioprinting
4.3. Light-based bioprinting
5. 3D bioprinting cardiac tissues
5.1. Human pluripotent stem cells and cardiac tissue engineering
5.2. Cellular maturity
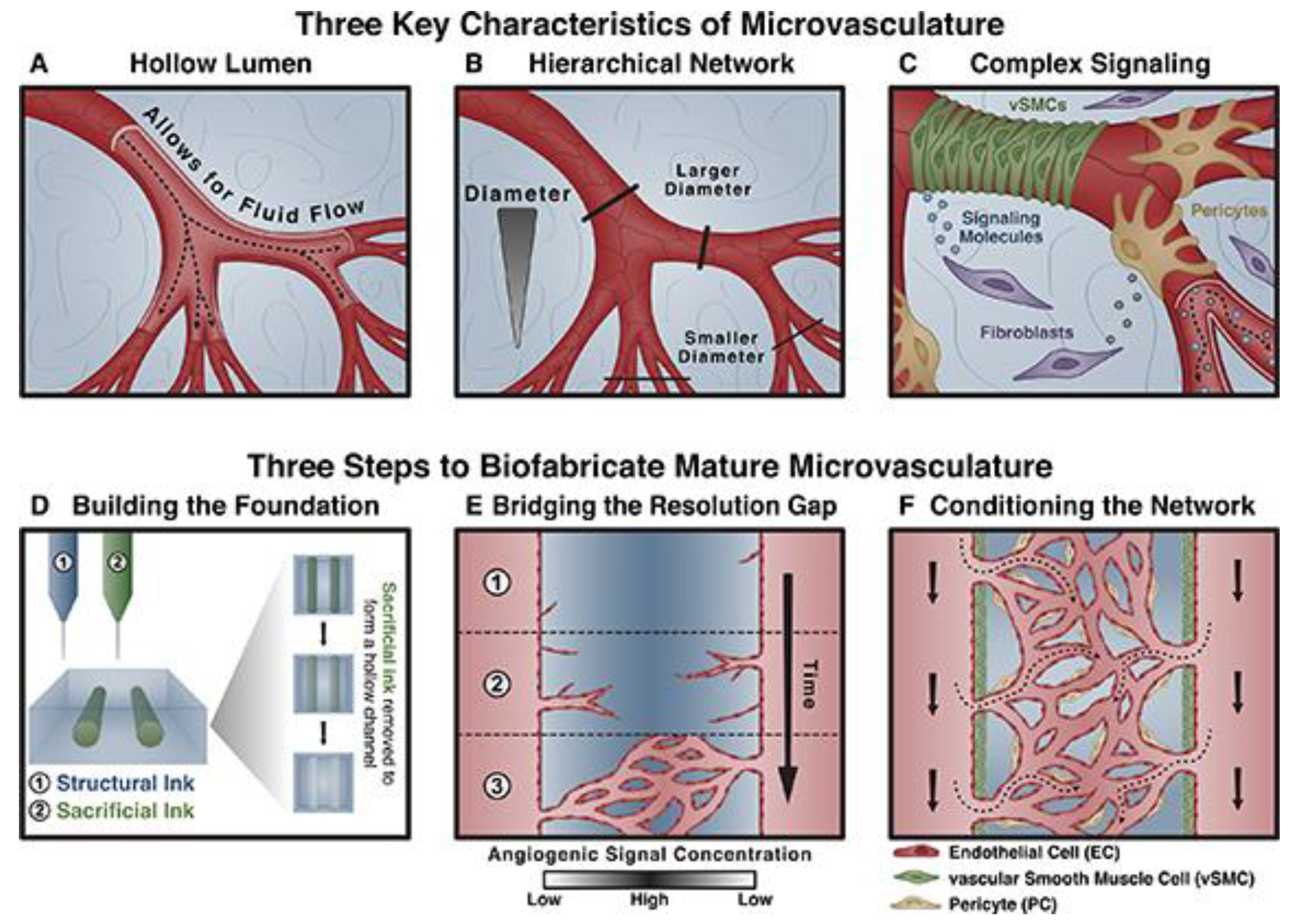
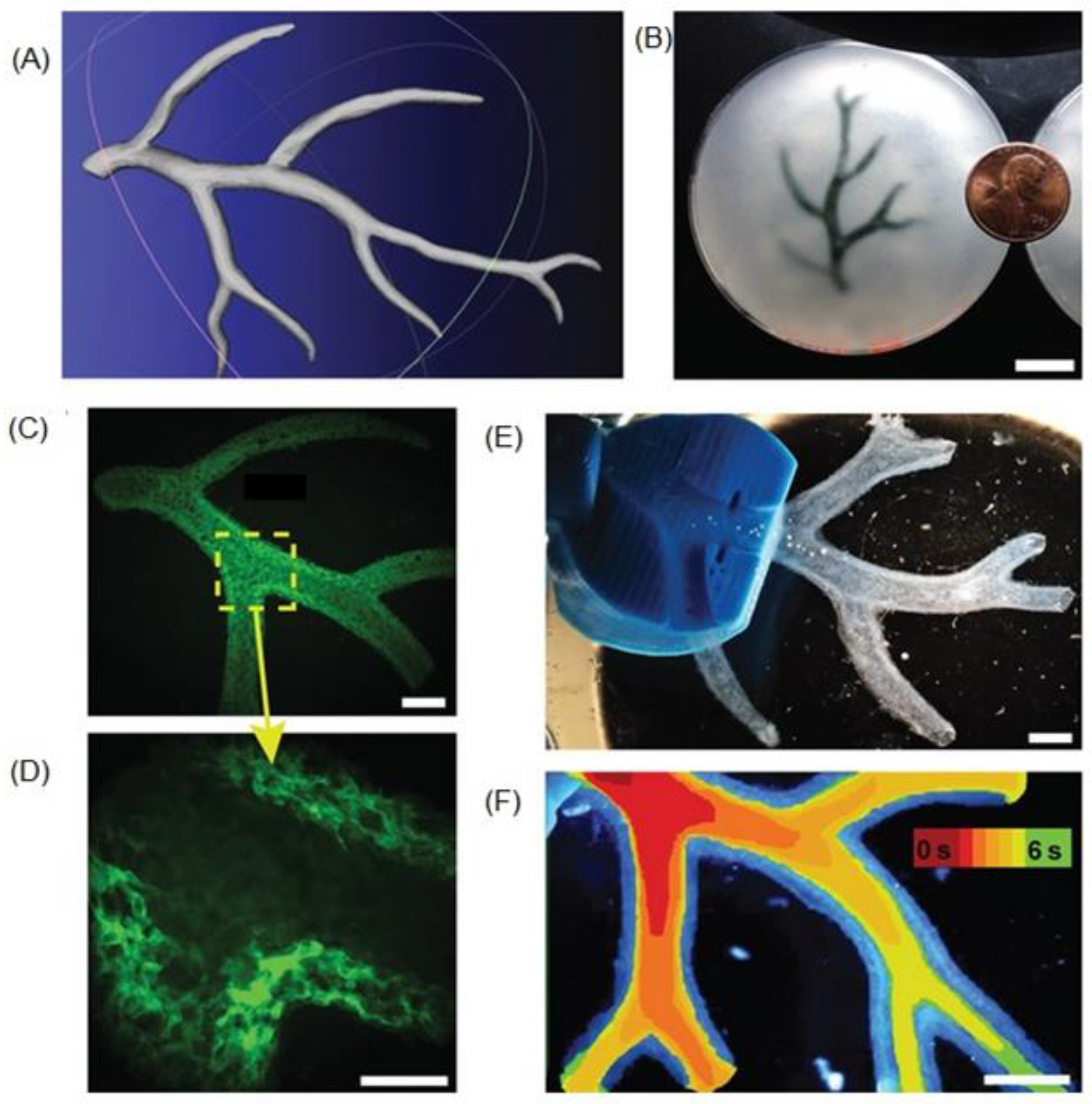
5.3. Microvasculature constructs
5.4. Other issues
6. 3D bioprinting of vascular constructs and grafts
6.1. Requirements of a TEVG
6.2. Methods of 3D bioprinting of TEVGs
6.3. Summary
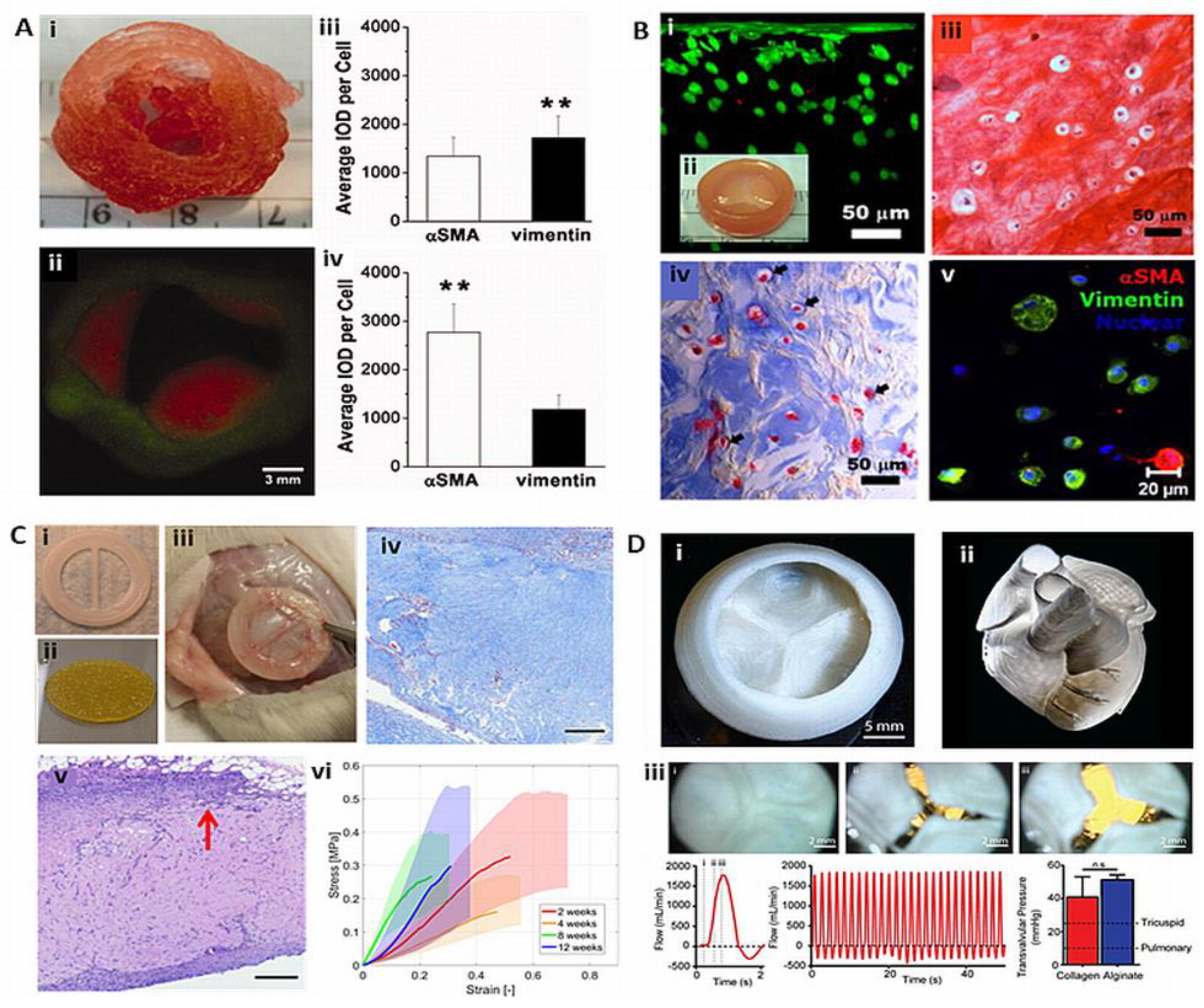
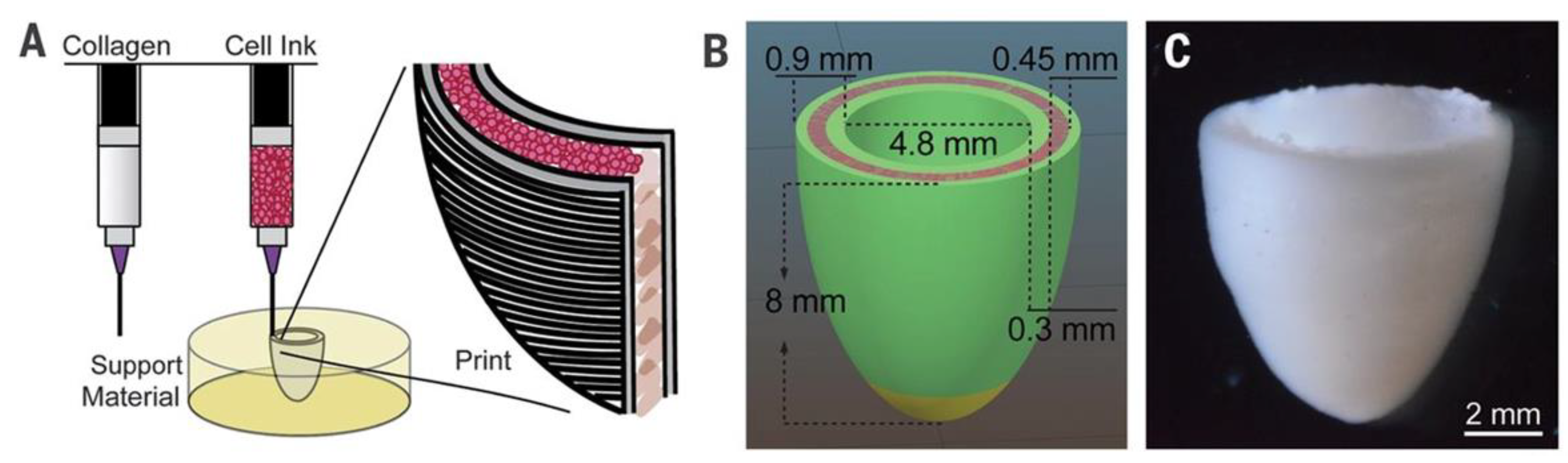
7. 3D bioprinting of heart valves
7.1. Extrusion based TEHVs
7.2. Light-based TEHVs
7.2. Bioplotted TEHVs
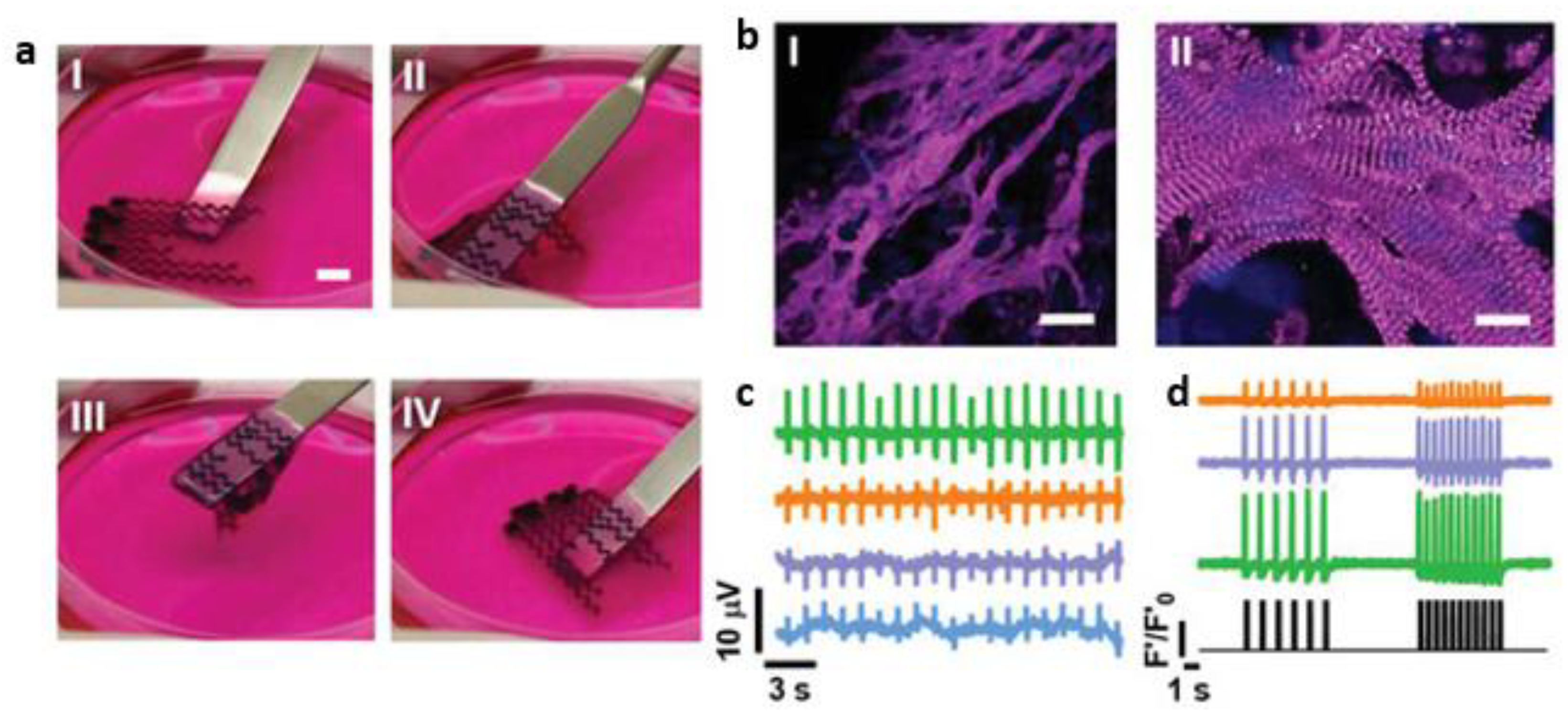
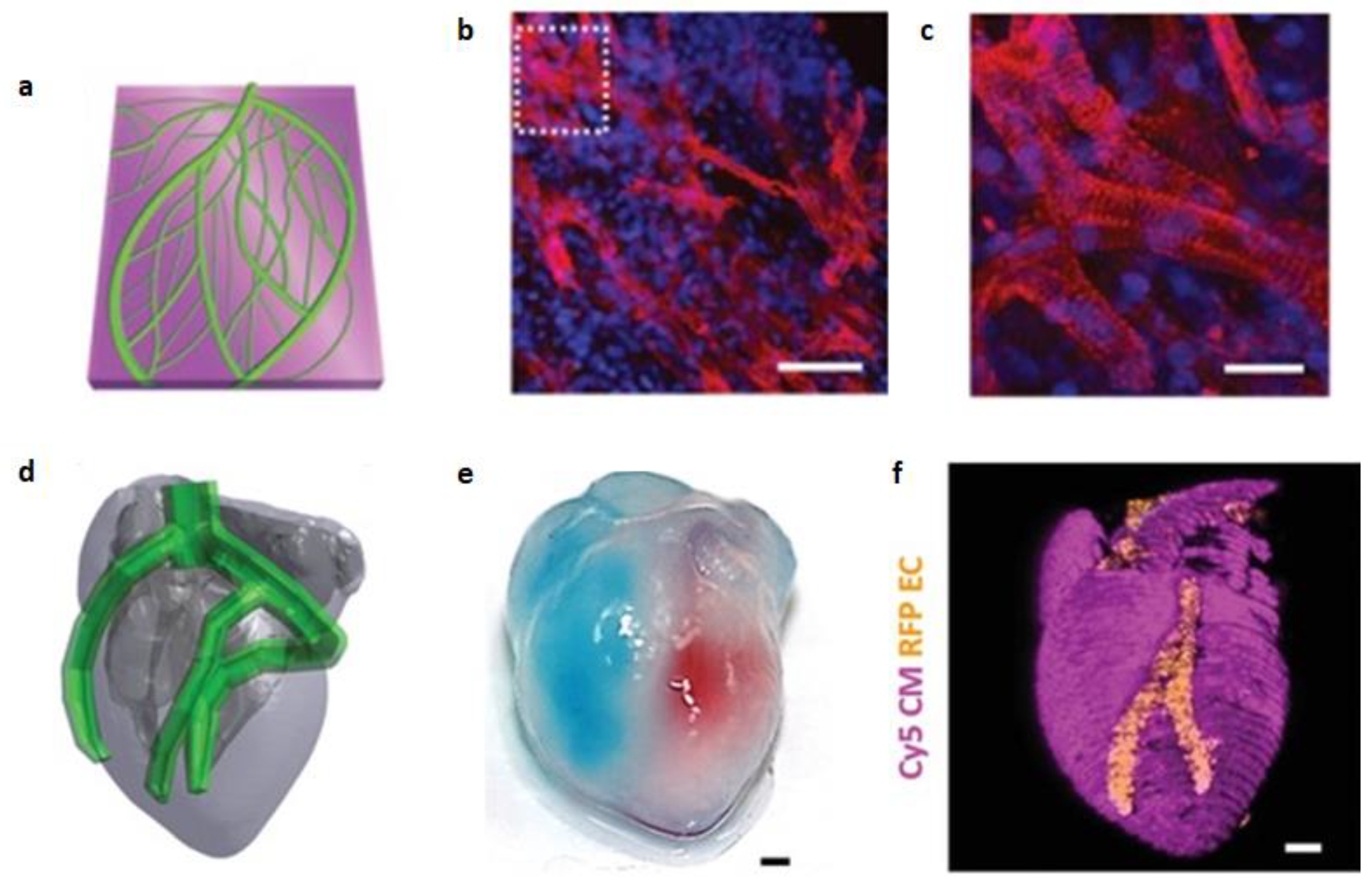
8. 3D bioprinting of myocardium and heart
9. Summary and concluding remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Virani, S.S.; Alvonso, A.; Aparicio, J.E.; Benjamin, J.E.; Bittencourt, M.; Callaway, C.; Clifton, W.; et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2021 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2021, 143, e254-e743.
- Sun, Z.; Al Moudi, M.; Cao, Y. CT angiography in the diagnosis of cardiovascular disease: a transformation in cardiovascular CT practice. Quant. Imaging. Med. Surg. 2014, 4, 376–396, . [CrossRef]
- Russo, V.; Lovato, L.; Ligabue, G. Cardiac MRI: technical basis. La Radiol. medica 2020, 125, 1040–1055, . [CrossRef]
- Giannopoulos, A.A.; Steigner, M.L.; George, E.M.; Barile, M.; Hunsaker, A.R.; Rybicki, F.J.; Mitsouras, D. Cardiothoracic Applications of 3-dimensional Printing. J. Thorac. Imaging 2016, 31, 253–272, . [CrossRef]
- Lau, I.W.W.; Sun, Z. Dimensional Accuracy and Clinical Value of 3D Printed Models in Congenital Heart Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1483, . [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Squelch, A.; Sun, Z. Quantitative Assessment of 3D Printed Model Accuracy in Delineating Congenital Heart Disease. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 270, . [CrossRef]
- Valverde, I.; Gomez-Ciriza, G.; Hussain, T.; Suarez-Mejias, C.; Velasco-Forte, M.N.; Byrne, N.; Ordonex, A.; Gonzalez-Calle, A.; Anderson, D.; Hazekamp, M.G.; et al. Three dimensional printed models for surgical planning of complex congenital heart defects: An international multicenter study. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2017, 52, 1139–1148.
- Sun, Z.; Wee, C. 3D Printed Models in Cardiovascular Disease: An Exciting Future to Deliver Personalized Medicine. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1575, . [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z. Clinical Applications of Patient-Specific 3D Printed Models in Cardiovascular Disease: Current Status and Future Directions. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1577, . [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Wong, Y.H.; Yeong, C.H. Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Low-Cost Models in Medical Education and Clinical Practice. Micromachines 2023, 14, 464, . [CrossRef]
- Anwar, S.; Singh, G.K.; Miller, J.; Sharma, M.; Manning, P.; Billadello, J.J.; Eghtesady, P.; Woodard, P.K. 3D Printing is a Transformative Technology in Congenital Heart Disease. JACC: Basic Transl. Sci. 2018, 3, 294–312, . [CrossRef]
- Gallo, M.; D’Onofrio, A.; Tarantini, G.; Nocerino, E.; Remondino, F.; Gerosa, G. 3D-printing model for complex aortic transcatheter valve treatment. Int. J. Cardiol. 2016, 210, 139–140, . [CrossRef]
- Ripley, B.; Kelil, T.; Cheezum, M.K.; Goncalves, A.; Di Carli, M.F.; Rybicki, F.J.; Steigner, M.; Mitsouras, D.; Blankstein, R. 3D printing based on cardiac CT assists anatomic visualization prior to transcatheter aortic valve replacement. J. Cardiovasc. Comput. Tomogr. 2015, 10, 28–36, . [CrossRef]
- Kiraly, L.; Shah, N.C.; Abdullah, O.; Al-Ketan, O.; Rowshan, R. Three-Dimensional Virtual and Printed Prototypes in Complex Congenital and Pediatric Cardiac Surgery—A Multidisciplinary Team-Learning Experience. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1703, . [CrossRef]
- Meyer-Szary, J.; Luis, M.S.; Mikulski, S.; Patel, A.; Schulz, F.; Tretiakow, D.; Fercho, J.; Jaguszewska, K.; Frankiewicz, M.; Pawłowska, E.; et al. The Role of 3D Printing in Planning Complex Medical Procedures and Training of Medical Professionals—Cross-Sectional Multispecialty Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Heal. 2022, 19, 3331, . [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, T.; Toba, S.; Sanders, S.P.; Carreon, C.K. Perfusion-distension fixation of heart specimens: a key step in immortalizing heart specimens for wax infiltration and generating 3D imaging data sets for reconstruction and printed 3D models. Cardiovasc. Pathol. 2022, 58, 107404.
- Ghosh, R.M.; Jolley, M.A.; Mascio, C.E.; Chen, J.M.; Fuller, S.; Rome, J.J.; Silvestro, E.; Whitehead, K.K. Clinical 3D modeling to guide pediatric cardiothoracic surgery and intervention using 3D printed anatomic models, computer aided design and virtual reality. 3D Print. Med. 2022, 8, 1–10, . [CrossRef]
- Yoo, S.J.; Spray, T.; Austin, E.H.; Yun, T.J.; van Arsdell, G.S. Hands-on surgical training of congenital heart surgery suing 3-dimensional print models. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2017, 153, 15301–15540.
- Gómez-Ciriza, G.; Gómez-Cía, T.; Rivas-González, J.A.; Forte, M.N.V.; Valverde, I. Affordable Three-Dimensional Printed Heart Models. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 642011. [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.-C.; Wang, Y.; Dai, J.; Ren, C.-W.; Li, J.-H.; Lai, Y.-Q. Application of 3D printing in the surgical planning of hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy and physician-patient communication: a preliminary study. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, 867–873, . [CrossRef]
- Ryan, J.; Plasencia, J.; Richardson, R.; Velez, D.; Nigro, J.J.; Pophal, S.; Frakes, D. 3D printing for congenital heart disease: A single site’s initial three-year experience. 3D. Print. Med. 2018, 4, 10.
- Zhao, L.; Zhou, S.; Fan, T.; Li, B.; Liang, W.; Dong, H. Three-dimensional printing enhances preparation for repair of double outlet right ventricular surgery. J. Card. Surg. 2018, 33, 24–27, . [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Yang, F.; Cheung, G.S.-H.; Chan, A.K.-Y.; Wang, D.D.; Lam, Y.-Y.; Chow, M.C.-K.; Leong, M.C.-W.; Kam, K.K.-H.; So, K.C.-Y.; et al. Device Sizing Guided by Echocardiography-Based Three-Dimensional Printing Is Associated with Superior Outcome after Percutaneous Left Atrial Appendage Occlusion. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2019, 32, 708–719.e1, . [CrossRef]
- Hell, M.; Achenbach, S.; Yoo, I.; Franke, J.; Blachutzik, F.; Roether, J.; Graf, V.; Raaz-Schrauder, D.; Marwan, M.; Schlundt, C. 3D printing for sizing left atrial appendage closure device: head-to-head comparison with computed tomography and transoesophageal echocardiography. EuroIntervention 2017, 13, 1234–1241, . [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yao, Q.; Shen, B.; Shu, M.; Zhong, L.; Wang, X.; Song, Z. Application of 3D printing technology to left atrial appendage occlusion. Int. J. Cardiol. 2017, 231, 258–263.
- Conti, M.; Marconi, S.; Muscogiuri, G.; Guglielmo, M.; Baggiano, A.; Italiano, G.; Mancini, M.E.; Auricchio, F.; Andreini, D.; Rabbat, M.G.; et al. Left atrial appendage closure guided by 3D computed tomography printing technology: A case control study. J. Cardiovasc. Comput. Tomogr. 2019, 13, 336–339, . [CrossRef]
- Goitein, O.; Fink, N.; Guetta, V.; Beinart, R.; Brodov, Y.; Konen, E.; Goitein, D.; Di Segni, E.; Grupper, A.; Glikson, M. Printed MDCT 3D models for prediction of left atrial appendage (LAA) occluder device size: a feasibility study. EuroIntervention 2017, 13, e1076–e1079, . [CrossRef]
- Torres, I.; De Luccia, N. A simulator for training in endovascular aneurysm repair: The use of three dimensional printers. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2017, 54, 247–253, . [CrossRef]
- Kärkkäinen, J.M.; Sandri, G.; Tenorio, E.R.; Alexander, A.; Bjellum, K.; Matsumoto, J.; Morris, J.; Mendes, B.C.; DeMartino, R.R.; Oderich, G.S. Simulation of Endovascular Aortic Repair Using 3D Printed Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Model and Fluid Pump. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2019, 42, 1627–1634, . [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, R.; Zech, C.J.; Takes, M.; Brantner, P.; Thieringer, F.; Deutschmann, M.; Hergan, K.; Scharinger, B.; Hecht, S.; Rezar, R.; et al. Vascular 3D Printing with a Novel Biological Tissue Mimicking Resin for Patient-Specific Procedure Simulations in Interventional Radiology: a Feasibility Study. J. Digit. Imaging 2022, 35, 9–20, . [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, K.A.; McEntee, M.F.; Reed, W.; Kench, P.L. Development of an organ-specific insert phantom generated using a 3D printer for investigations of cardiac computed tomographic protocols. J. Med. Radiat. Sci. 2018, 65, 175–183.
- Mørup, S.; Stowe, J.; Precht, H.; Gervig, M.; Foley, S. Design of a 3D printed coronary artery model for CT optimization. Radiography 2022, 28, 426–432, . [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Ng, C.K.C.; Wong, Y.H.; Yeong, C.H. 3D-Printed Coronary Plaques to Simulate High Calcification in the Coronary Arteries for Investigation of Blooming Artifacts. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1307, . [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Ng, C.K.C.; Squelch, A. Synchrotron radiation computed tomography assessment of calcified plaques and coronary stenosis with different slice thicknesses and beam energies on 3D printed coronary models. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2019, 9, 6–22, . [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z. 3D printed coronary models offer new opportunities for developing optimal coronary CT angiography protocols in imaging coronary stents. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2019, 9, 1350–1355, . [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Jansen, S. Personalized 3D printed coronary models in coronary stenting. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2019, 9, 1356–1367, . [CrossRef]
- Sommer, K.N.; Iyer, V.; Kumamaru, K.K.; Rava, R.A.; Ionita, C.N. Method to simulate distal flow resistance in coronary arteries in 3D printed patient specific coronary models. 3D Print. Med. 2020, 6, 19, . [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-A.; Squelch, A.; Sun, Z. Assessment of optimization of computed tomography angiography protocols for follow-up type B aortic dissection patients by using a 3D-printed model. J. 3D Print. Med. 2022, 6, 117–127, . [CrossRef]
- Aldosari, S.; Jansen, S.; Sun, Z. Optimization of computed tomography pulmonary angiography protocols using 3D printed model with simulation of pulmonary embolism. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2019, 9, 53–62, . [CrossRef]
- Aldosari, S.; Jansen, S.; Sun, Z. Patient-specific 3D printed pulmonary artery model with simulation of peripheral pulmonary embolism for developing optimal computed tomography pulmonary angiography protocols. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2019, 9, 75–85, . [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Miao, S.; Esworthy, T.; Zhou, X.; Lee, S.-J.; Liu, C.; Yu, Z.-X.; Fisher, J.P.; Mohiuddin, M.; Zhang, L.G. 3D bioprinting for cardiovascular regeneration and pharmacology. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 132, 252–269, . [CrossRef]
- Alonzo, M.; AnilKumar, S.; Roman, B.; Tasnim, N.; Joddar, B. 3D Bioprinting of cardiac tissue and cardiac stem cell therapy. Transl. Res. 2019, 211, 64–83, . [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wehrle, E.; Rubert, M.; Muller, R. 3D bioprinting of human tissues: Biofabrication, bioinks and bioreactors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3971.
- Wang, Z.; Lee, S.J.; Cheng, H.-J.; Yoo, J.J.; Atala, A. 3D bioprinted functional and contractile cardiac tissue constructs. Acta Biomater. 2018, 70, 48–56, . [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.; Jin, S.; Ye, K. Tissue and Organ 3D Bioprinting. JALA: J. Assoc. Lab. Autom. 2018, 23, 301–314, . [CrossRef]
- Kato, B.; Wisser, G.; Agrawal, D.K.; Wood, T.; Thankam, F.G. 3D bioprinting of cardiac tissue: current challenges and perspectives. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2021, 32, 54, . [CrossRef]
- Chessa, M.; Van De Bruaene, A.; Farooqi, K.; Valverde, I.; Jung, C.; Votta, E.; Sturla, F.; Paul Diller, G.; Brida, M.; Sun, Z.; et al. Three-dimensional printing, holograms, computational modelling, and artificial intelligence for adult congenital heart disease care: An exciting future. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 2672–2684.
- Jain, P.; Kathuria, H.; Dubey, N. Advances in 3D printing of tissues/organs for regenerative medicine and in-vitro models. Biomaterials. 2022, 287, 121639.
- Hoy, S.; Frisbee, J. Common Postoperative Heart Transplant Complications. Crit. Care Nurs. Q. 2018, 41, 383–388, . [CrossRef]
- Awad, M.A.; Shah, A.; Griffith, B.P. Current status and outcomes in heart transplantation: a narrative review. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 23, 11, . [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.Y.; Smith, J.A. Role of coronary artery bypass surgery in acute myocardial infarction, in: Prim. Angioplasty, Springer Singapore, 2018, pp. 211-221.
- Kwon, Y.W.; Yang, H.M.; Cho, H.J. Cell therapy on myocardial infarction. Int. J. Stem. Cells. 2010, 3, 8-15.
- Das, S.; Nam, H.; Jang, J. 3D bioprinting of stem cell-laden cardiac patch: A promising alternative for myocardial repair. APL Bioeng. 2021, 5, 031508, . [CrossRef]
- Vukicevic, M.; Mosadegh, B.; Min, J.K.; Little, S.H. Cardiac 3D Printing and its Future Directions. JACC: Cardiovasc. Imaging 2017, 10, 171–184, . [CrossRef]
- Khanna, A.; Ayan, B.; Undieh, A.A.; Yang, Y.P.; Huang, N.F. Advances in three-dimensional bioprinted stem cell-based tissue engineering for cardiovascular regeneration. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2022, 169, 13–27, . [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Ye, X.; Yao, B.; Zhao, M.; Wu, P.; Liu, G.; Zhuang, D.; Jiang, H.; Chen, X.; He, Y.; et al. Advances in 3D bioprinting technology for cardiac tissue engineering and regeneration. Bioact. Mater. 2020, 6, 1388–1401, . [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; He, J.; Liu, J.; Ma, X.; Chen, Q.; Lawrence, N.; Zhu, W.; Xu, Y.; Chen, S. Rapid 3D bioprinting of in vitro cardiac tissue models using human embryonic stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes. Bioprinting 2019, 13, . [CrossRef]
- Mufarrih, S.H.; Mahmood, F.; Qureshi, N.Q.; Yunus, R.; Quraishi, I.; Baribeau, V.; Sharkey, A.; Matyal, R.; Khabbaz, K.R. Three-Dimensional Printing of Patient-Specific Heart Valves: Separating Facts From Fiction and Myth From Reality. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesthesia 2022, 36, 2643–2655, . [CrossRef]
- Gaetani, R.; Rizzitelli, G.; Chimenti, I.; Barile, L.; Forte, E.; Ionta, V.; Angelini, F.; Sluijter, J.P.; Barbetta, A.; Messina, E.; et al. Cardiospheres and tissue engineering for myocardial regeneration: potential for clinical application. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2010, 14, 1071–1077, . [CrossRef]
- Gaetani, R.; Doevendans, P.A.; Metz, C.H.; Alblas, J.; Messina, E.; Giacomello, A.; Sluijter, J.P. Cardiac tissue engineering using tissue printing technology and human cardiac progenitor cells. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 1782–1790, . [CrossRef]
- Gaetani, R.; Feyen, D.A.; Verhage, V.; Slaats, R.; Messina, E.; Christman, K.L.; Giacomello, A.; Doevendans, P.A.; Sluijter, J.P. Epicardial application of cardiac progenitor cells in a 3D-printed gelatin/hyaluronic acid patch preserves cardiac function after myocardial infarction. Biomaterials 2015, 61, 339–348, . [CrossRef]
- Ozbolat, I.T.; Moncal, K.K.; Gudapati, H. Evaluation of bioprinter technologies. Addit. Manuf. 2017, 13, 179–200, . [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, B.; Pei, B.; Chen, J.; Zhou, D.; Peng, J.; Zhang, X.; Jia, W.; Xu, T. Inkjet Bioprinting of Biomaterials. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 10793–10833, . [CrossRef]
- Mandrycky, C.; Wang, Z.; Kim, K.; Kim, D.-H. 3D bioprinting for engineering complex tissues. Biotechnol. Adv. 2016, 34, 422–434, . [CrossRef]
- Christensen, K.; Xu, C.; Chai, W.; Zhang, Z.; Fu, J.; Huang, Y. Freeform inkjet printing of cellular structures with bifurcations. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2014, 112, 1047–1055, . [CrossRef]
- Schöneberg, J.; De Lorenzi, F.; Theek, B.; Blaeser, A.; Rommel, D.; Kuehne, A.J.C.; Kießling, F.; Fischer, H. Engineering biofunctional in vitro vessel models using a multilayer bioprinting technique. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–13, . [CrossRef]
- Saunders, R.E.; Derby, B. Inkjet printing biomaterials for tissue engineering: bioprinting. Int. Mater. Rev. 2014, 59, 430–448, . [CrossRef]
- Shafiee, A.; Ghadiri, E.; Ramesh, H.; Kengla, C.; Kassis, J.; Calvert, P.; Williams, D.; Khademhosseini, A.; Narayan, R.; Forgacs, G.; et al. Physics of bioprinting. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2019, 6, 021315, . [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.C.; Boland, E.D.; Williams, S.K.; Hoying, J.B. Direct-write bioprinting three-dimensional biohybrid systems for future regenerative therapies. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B: Appl. Biomater. 2011, 98B, 160–170, . [CrossRef]
- Rider, P.; Kačarević, .P.; Alkildani, S.; Retnasingh, S.; Barbeck, M. Bioprinting of tissue engineering scaffolds. J. Tissue Eng. 2018, 9, . [CrossRef]
- Chang, R.; Nam J, Sun W. Effects of dispensing pressure and nozzle diameter on cell survival from solid freeform fabrication-based direct cell writing. Tissue. Eng Part. A. 2008, 14(1), 41-8.
- Zhang, Y.; Kumar, P.; Lv, S.; Xiong, D.; Zhao, H.; Cai, Z.; Zhao, X. Recent advances in 3D bioprinting of vascularized tissues. Mater. Des. 2021, 199, 109398, . [CrossRef]
- Xiong, R.; Zhang, Z.; Chai, W.; Huang, Y.; Chrisey, D.B. Freeform drop-on-demand laser printing of 3D alginate and cellular constructs. Biofabrication 2015, 7, 045011, . [CrossRef]
- Häneke, T.; Sahara, M. Progress in Bioengineering Strategies for Heart Regenerative Medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3482, . [CrossRef]
- Mills, R.J.; Hudson, J.E. Bioengineering adult human heart tissue: How close are we? APL. Bioengineering. 2019, 3(1), 010901.
- Takahashi, K.; Tanabe, K.; Ohnuki, M.; Narita, M.; Ichisaka, T.; Tomoda, K.; Yamanaka, S. Induction of Pluripotent Stem Cells from Adult Human Fibroblasts by Defined Factors. Cell 2007, 131, 861–872, . [CrossRef]
- Goldfracht, I.; Protze, S.; Shiti, A.; Setter, N.; Gruber, A.; Shaheen, N.; Nartiss, Y.; Keller, G.; Gepstein, L. Generating ring-shaped engineered heart tissues from ventricular and atrial human pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 75, . [CrossRef]
- Bremner, S.B.; Gaffney, K.S.; Sniadecki, N.J.; Mack, D.L. A Change of Heart: Human Cardiac Tissue Engineering as a Platform for Drug Development. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2022, 24, 473–486, . [CrossRef]
- Quadri, F.; Soman, S.S.; Vijayavenkataraman, S. Progress in cardiovascular bioprinting. Artif. Organs 2021, 45, 652–664, . [CrossRef]
- Marchianò, S.; Bertero, A.; Murry, C.E. Learn from Your Elders: Developmental Biology Lessons to Guide Maturation of Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2019, 40, 1367–1387, . [CrossRef]
- Sedlakova, V.; McTiernan, C.; Cortes, D.; Suuronen, E.J.; Alarcon, E.I. 3D Bioprinted Cardiac Tissues and Devices for Tissue Maturation. Cells Tissues Organs 2021, 211, 90–103, . [CrossRef]
- Tomasina, C.; Bodet, T.; Mota, C.; Moroni, L.; Camarero-Espinosa, S. Bioprinting Vasculature: Materials, Cells and Emergent Techniques. Materials 2019, 12, 2701, . [CrossRef]
- Seymour, A.J.; Westerfield, A.D.; Cornelius, V.C.; A Skylar-Scott, M.; Heilshorn, S.C. Bioprinted microvasculature: progressing from structure to function. Biofabrication 2022, 14, 022002, . [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Li, T.; Liu, S.; Guo, B.; Huang, W.; Wu, Y. 3D bioprinting in cardiac tissue engineering. Theranostics 2021, 11, 7948–7969, . [CrossRef]
- Barrs, R.W.; Jia, J.; Silver, S.E.; Yost, M.; Mei, Y. Biomaterials for Bioprinting Microvasculature. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 10887–10949, . [CrossRef]
- Ferrini, A.; Stevens, M.M.; Sattler, S.; Rosenthal, N. Toward Regeneration of the Heart: Bioengineering Strategies for Immunomodulation. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2019, 6, 26, . [CrossRef]
- Roche, C.D.; Brereton, R.J.L.; Ashton, A.W.; Jackson, C.; Gentile, C. Current challenges in three-dimensional bioprinting heart tissues for cardiac surgery. Eur. J. Cardio-Thoracic Surg. 2020, 58, 500–510, . [CrossRef]
- Tillman, B.; Hardin-Young, J.; Shannon, W.; Russell, A.J.; Parenteau, N.L.; Md; D, P.; Pashneh-Tala, S.; MacNeil, S.; Claeyssens, F.; et al. Meeting the Need for Regenerative Therapies: Translation-Focused Analysis of U.S. Regenerative Medicine Opportunities in Cardiovascular and Peripheral Vascular Medicine Using Detailed Incidence Data. Tissue Eng. Part B: Rev. 2013, 19, 99–115, . [CrossRef]
- Fazal, F.; Raghav, S.; Callanan, A.; Koutsos, V.; Radacsi, N. Recent advancements in the bioprinting of vascular grafts. Biofabrication 2021, 13, 032003, . [CrossRef]
- Wenger, R.; Giraud, M.-N. 3D Printing Applied to Tissue Engineered Vascular Grafts. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2631, . [CrossRef]
- Klinkert, P.; Post, P.; Breslau, P.; van Bockel, J. Saphenous Vein Versus PTFE for Above-Knee Femoropopliteal Bypass. A Review of the Literature. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2004, 27, 357–362, . [CrossRef]
- Catto, V.; Farè, S.; Freddi, G.; Tanzi, M.C. Vascular Tissue Engineering: Recent Advances in Small Diameter Blood Vessel Regeneration. ISRN Vasc. Med. 2014, 2014, 1–27, . [CrossRef]
- Syedain, Z.H.; Prunty, A.; Li, J.; Tranquillo, R.T. Evaluation of the probe burst test as a measure of strength for a biologically-engineered vascular graft. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2021, 119, 104527–104527, . [CrossRef]
- Pensalfini, M.; Meneghello, S.; Lintas, V.; Bircher, K.; Ehret, A.; Mazza, E. The suture retention test, revisited and revised. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2018, 77, 711–717, . [CrossRef]
- Deo, K.A.; Singh, K.A.; Peak, C.W.; Alge, D.L.; Gaharwar, A.K. Bioprinting 101: Design, Fabrication, and Evaluation of Cell-Laden 3D Bioprinted Scaffolds. Tissue Eng. Part A 2020, 26, 318–338, . [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Christensen, K.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Fu, J.; Markwald, R.R. Predictive compensation-enabled horizontal inkjet printing of alginate tubular constructs. Manuf. Lett. 2013, 1, 28–32, . [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Chai, W.; Huang, Y.; Markwald, R.R. Scaffold-free inkjet printing of three-dimensional zigzag cellular tubes. Biotechno Bioeng. 2012, 109(12), 3152-60.
- Gudapati, H.; Dey, M.; Ozbolat, I. A comprehensive review on droplet-based bioprinting: Past, present and future. Biomaterials 2016, 102, 20–42, . [CrossRef]
- Hinton, T.J.; Jallerat, Q.; Palchesko, R.N.; Park, J.H.; Grodzicki, M.S.; Shue, H.-J.; Ramadan, M.H.; Hudson, A.R.; Feinberg, A.W. Three-dimensional printing of complex biological structures by freeform reversible embedding of suspended hydrogels. Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, e1500758–e1500758, . [CrossRef]
- Dikyol, C.; Altunbek, M.; Bartolo, P.; Koc, B. Multimaterial bioprinting approaches and their implementations for vascular and vascularized tissues. Bioprinting 2021, 24, e00159. [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Kim, J.S.; Jung, B.; Won, C.; Hwang, C. Coaxial bioprinting of cell-laden vascular constructs using a gelatin–tyramine bioink. Biomater. Sci. 2019, 7, 4578–4587, . [CrossRef]
- Mohan, T.S.; Datta, P.; Nesaei, S.; Ozbolat, V.; Ozbolat, I.T. 3D coaxial bioprinting: process mechanisms, bioinks and applications. Prog. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 4, 022003, . [CrossRef]
- Milojević, M.; Vihar, B.; Banović, L.; Miško, M.; Gradišnik, L.; Zidarič, T.; Maver, U. Core/shell printing scaffolds for tissue engineering of tubular structures. J. Vis. Exp. 2019, 151, e59951.
- Wang, Y.; Kankala, R.K.; Zhu, K.; Wang, S.-B.; Zhang, Y.S.; Chen, A.-Z. Coaxial Extrusion of Tubular Tissue Constructs Using a Gelatin/GelMA Blend Bioink. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 5, 5514–5524, . [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhong, Z.; Hu, N.; Zhou, Y.; Maggio, L.; Miri, A.K.; Fragasso, A.; Jin, Z.; Khademhosseine, A.; Zhang, Y.S. Coaxial extrusion bioprinting of 3D microfibrous constructs with cell-favourable gelatin methacryloyl microenvironments. Biofabrication. 2018, 10(2):024102.
- Jia, W.; Gungor-Ozkerim, P.S.; Zhang, Y.S.; Yue, K.; Zhu, K.; Liu, W.; Pi, Q.; Byambaa, B.; Dokmeci, M.R.; Shin, S.R.; et al. Direct 3D bioprinting of perfusable vascular constructs using a blend bioink. Biomaterials 2016, 106, 58–68, . [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Liu, Z.; Lin, Z.; Qiu, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, A.; Wang, Y.; Xiang, M.; Chen, B.; Fu, J.; et al. 3D Bioprinting of Vessel-like Structures with Multilevel Fluidic Channels. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 3, 399–408, . [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Xu, L.; Jin, G.; Tang, L.; Ju, J.; Zhao, W.; Hou, R. Nanofiber electrospinning combined with rotary bioprinting for fabricating small-diameter vessels with endothelium and smooth muscle. Compos. Part B: Eng. 2022, 234, 109691, . [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Varkey, M.; Jorgensen, A.; Ju, J.; Jin, Q.; Park, J.H.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Ke, D.; Zhao, W.; et al. Bioprinting small diameter blood vessel constructs with an endothelial and smooth muscle cell bilayer in a single step. Biofabrication 2020, 12, 045012, . [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.-W.; Lee, S.J.; Ko, I.K.; Kengla, C.; Yoo, J.J.; Atala, A. A 3D bioprinting system to produce human-scale tissue constructs with structural integrity. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 312–319, doi:10.1038/nbt.3413.
- Gold, K.A.; Saha, B.; Pandian, N.K.R.; Walther, B.K.; Palma, J.A.; Jo, J.; Cooke, J.P.; Jain, A.; Gaharwar, A.K. 3D Bioprinted Multicellular Vascular Models. Adv. Heal. Mater. 2021, 10, 2101141, . [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.S.; Khademhosseini, A. Vascular tissue engineering: the role of 3D bioprinting. In: Walpoth BH, Bergmeister H, Bowlin GL, Kong D, Rotmans JI, Zilla P, editors. Tissue-engineered vascular grafts. Springer Cham; 2020, p. 321-38.
- Krishnamoorthy, S.; Wadnap, S.; Noorani, B.; Xu, H.; Xu, C. Investigation of gelatin methacrylate working curves in dynamic optical projection stereolithography of vascular-like constructs. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 124, 109487, . [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A.; Orellano, I.; Lam, T.; Noichl, B.; Geiger, M.-A.; Amler, A.-K.; Kreuder, A.-E.; Palmer, C.; Duda, G.; Lauster, R.; et al. Vascular bioprinting with enzymatically degradable bioinks via multi-material projection-based stereolithography. Acta Biomater. 2020, 117, 121–132, . [CrossRef]
- Virani, S.S.; Alonso, A.; Aparicio, H.J.; Benjamin, E.J.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Callaway, C.W.; et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2021 Update: A report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2021, 143(8).
- Sanz-Garcia, A.; Oliver-de-la-Cruz, J.; Mirabet, V.; Gandía, C.; Villagrasa, A.; Sodupe, E.; et al. Heart valve tissue engineering: how far is the bedside from the bench? Expert. Rev. Mol. Med. 2015, 17, e16.
- Butcher, J.T.; Mahler, G.J.; Hockaday, L.A. Aortic valve disease and treatment: The need for naturally engineered solutions. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 242–268, . [CrossRef]
- Goldbarg, S.H.; Elmariah, S.; Miller, M.A.; Fuster, V. Insights Into Degenerative Aortic Valve Disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2007, 50, 1205–1213, . [CrossRef]
- Hammermeister, K.; Sethi, G.K.; Henderson, W.G.; Grover, F.L.; Oprian, C.; Rahimtoola, S.H. Outcomes 15 years after valve replacement with a mechanical versus a bioprosthetic valve: final report of the Veterans Affairs randomized trial. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2000, 36, 1152–1158, . [CrossRef]
- Head, S.J.; Çelik, M.; Kappetein, A.P. Mechanical versus bioprosthetic aortic valve replacement. Eur. Hear. J. 2017, 38, 2183–2191, . [CrossRef]
- Kostyunin, A.E.; Yuzhalin, A.E.; Rezvova, M.A.; Ovcharenko, E.A.; Glushkova, T.V.; Kutikhin, A.G. Degeneration of Bioprosthetic Heart Valves: Update 2020. J. Am. Hear. Assoc. 2020, 9, e018506. [CrossRef]
- Dvir, D.; Bourguignon, T.; Otto, C.M.; Hahn, R.T.; Rosenhek, R.; Webb, J.G.; Treede, H.; Sarano, M.E.; Feldman, T.; Wijeysundera, H.C.; et al. Standardized Definition of Structural Valve Degeneration for Surgical and Transcatheter Bioprosthetic Aortic Valves. Circ. 2018, 137, 388–399, . [CrossRef]
- Capodanno, D.; Petronio, A.S.; Prendergast, B.; Eltchaninoff, H.; Vahanian, A.; Modine, T.; Lancellotti, P.; Sondergaard, L.; Ludman, P.F.; Tamburino, C.; et al. Standardized definitions of structural deterioration and valve failure in assessing long-term durability of transcatheter and surgical aortic bioprosthetic valves: a consensus statement from the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions (EAPCI) endorsed by the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS). Eur. Hear. J. 2017, 38, 3382–3390, . [CrossRef]
- Sathananthan, J.; Lauck, S.; Polderman, J.; Yu, M.; Stephenson, A.; Sathananthan, G.; Moss, R.; Cheung, A.; Ye, J.; Blanke, P.; et al. Ten year follow-up of high-risk patients treated during the early experience with transcatheter aortic valve replacement. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2021, 97, E431–E437, . [CrossRef]
- Jana, S.; Tefft, B.J.; Jana, S.; Tefft, B.J.; Spoon, D.B.; Simari, R.D. Scaffolds for tissue engineering of cardiac valves. Acta. Biomaterialia. 2014, 17, 2877-2893.
- Mela, P. Subject- and leaflet-specific remodeling of polymeric heart valves for in situ tissue engineering: Challenges towards Clinical translation. JACC. Basic. Transl. Sci. 2020, 5(1), 32–4.
- Vesely, I. Heart Valve Tissue Engineering. Circ. Res. 2005, 97(8), 743–55.
- Wissing, T.B.; Bonito, V.; Bouten, C.V.C.; Smits, A.I.P.M. Biomaterial-driven in situ cardiovascular tissue engineering—a multi-disciplinary perspective. npj Regen. Med. 2017, 2, 1–20, . [CrossRef]
- Butcher, J.T. The root problem of heart valve engineering. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaat5850, . [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, R.Z.; Lock, R.; Liu, B.; Vunjak-Novakovic, G. Opportunities and challenges in cardiac tissue engineering from an analysis of two decades of advances. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 6, 327–338, . [CrossRef]
- A Hockaday, L.; Kang, K.H.; Colangelo, N.W.; Cheung, P.Y.C.; Duan, B.; Malone, E.; Wu, J.; Girardi, L.N.; Bonassar, L.J.; Lipson, H.; et al. Rapid 3D printing of anatomically accurate and mechanically heterogeneous aortic valve hydrogel scaffolds. Biofabrication 2012, 4, 035005–035005, . [CrossRef]
- Duan, B.; Hockaday, L.A.; Kang, K.H.; Butcher, J.T. 3D Bioprinting of heterogeneous aortic valve conduits with alginate/gelatin hydrogels. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2012, 101A, 1255–1264, . [CrossRef]
- Duan, B.; Kapetanovic, E.; Hockaday, L.; Butcher, J. Three-dimensional printed trileaflet valve conduits using biological hydrogels and human valve interstitial cells. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 1836–1846, . [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.; Cheung, D.Y.; Butcher, J.T. Incorporating nanocrystalline cellulose into a multifunctional hydrogel for heart valve tissue engineering applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2022, 110, 76–91, . [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.H.; Armstrong, P.A.; Lee, L.J.; Duan, B.; Kang, K.H.; Butcher, J.T. Optimizing Photo-Encapsulation Viability of Heart Valve Cell Types in 3D Printable Composite Hydrogels. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 45, 360–377, . [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Duan, B.; Liu, P.; Zhang, C.; Qin, X.-H.; Butcher, J.T. Fabrication of Aligned Nanofiber Polymer Yarn Networks for Anisotropic Soft Tissue Scaffolds. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 16950–16960, . [CrossRef]
- Sodian, R.; Loebe, M.; Hein, A.; Martin, D.P.; Hoerstrup, S.P.; Potapov, E.V.; et al. Application of stereolithography for scaffold fabrication for tissue engineered heart valves: ASAIO. J. 2002, 48(1), 12–6.
- Akpek, A. Analysis of biocompatibility characteristics of stereolithography applied three dimensional (3D) bioprinted artificial heart valves. J. Faculty. Eng. Architec. Gazi. Uni. 2018, 3, 929-938.
- Lee, A.; Hudson, A.R.; Shiwarski, D.J.; Tashman, J.W.; Hinton, T.J.; Yerneni, S.; Bliley, J.M.; Campbell, P.G.; Feinberg, A.W. 3D bioprinting of collagen to rebuild components of the human heart. Science 2019, 365, 482–487, . [CrossRef]
- Maxson, E.L.; Young, M.D.; Noble, C.; Go, J.L.; Heidari, B.; Khorramirouz, R.; Morse, D.W.; Lerman, A. In vivo remodeling of a 3D-Bioprinted tissue engineered heart valve scaffold. Bioprinting 2019, 16, e00059. [CrossRef]
- Noble, C.; Maxson, E.L.; Lerman, A.; Young, M.D. Mechanical and finite element evaluation of a bioprinted scaffold following recellularization in a rat subcutaneous model. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2020, 102, 103519–103519, . [CrossRef]
- Zengin, A.; Castro, J.P.O.; Habibovic, P.; van Rijt, S.H. Injectable, self-healing mesoporous silica nanocomposite hydrogels with improved mechanical properties. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 1144–1154, . [CrossRef]
- Eivazzadeh-Keihan, R.; Radinekiyan, F.; Aliabadi, H.A.M.; Sukhtezari, S.; Tahmasebi, B.; Maleki, A.; Madanchi, H. Chitosan hydrogel/silk fibroin/Mg(OH)2 nanobiocomposite as a novel scaffold with antimicrobial activity and improved mechanical properties. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 650, . [CrossRef]
- Sarrigiannidis, S.; Rey, J.; Dobre, O.; González-García, C.; Dalby, M.; Salmeron-Sanchez, M. A tough act to follow: collagen hydrogel modifications to improve mechanical and growth factor loading capabilities. Mater. Today Bio 2021, 10, 100098, . [CrossRef]
- Bas, O.; Lucarotti, S.; Angella, D.D.; Castro, N.J.; Meinert, C.; Wunner, F.M.; Rank, E.; Vozzi, G.; Klein, T.J.; Catelas, I.; et al. Rational design and fabrication of multiphasic soft network composites for tissue engineering articular cartilage: A numerical model-based approach. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 340, 15–23, . [CrossRef]
- Visser, J.; Melchels, F.P.; Jeon, J.E.; van Bussel, E.M.; Kimpton, L.S.; Byrne, H.M.; Dhert, W.J.; Dalton, P.D.; Hutmacher, D.W.; Malda, J. Reinforcement of hydrogels using three-dimensionally printed microfibres. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6933–6933, . [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Ye, X.; Yao, B.; Zhao, M.; Wu, P.; Liu, G.; Zhuang, D.; Jiang, H.; Chen, X.; He, Y.; et al. Advances in 3D bioprinting technology for cardiac tissue engineering and regeneration. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 1388–1401, . [CrossRef]
- Montero, P.; Flandes-Iparraguirre, M.; Musquiz, S.; Pérez Araluce, M.; Plano, D.; Sanmartín, C.; et al. Cells, Materials, and Fabrication Processes for Cardiac Tissue Engineering. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 955.
- Bejleri, D.; Streeter, B.W.; Nachlas, A.L.Y.; Brown, M.E.; Gaetani, R.; Christman, K.L.; Davis, M.E. A Bioprinted Cardiac Patch Composed of Cardiac-Specific Extracellular Matrix and Progenitor Cells for Heart Repair. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, e1800672, doi:10.1002/adhm.201800672.
- Zhu, K.; Shin, S.R.; van Kempen, T.; Li, Y.; Ponraj, V.; Nasajpour, A.; et al. Gold nanocomposite bioink for printing 3D cardiac constructs. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27(12), 1605352.
- Erdem, A.; Darabi, M.A.; Nasiri, R.; Sangabathuni, S.; Ertas, Y.N.; Alem, H.; Hosseini, V.; Shamloo, A.; Nasr, A.S.; Ahadian, S.; et al. 3D Bioprinting of Oxygenated Cell-Laden Gelatin Methacryloyl Constructs. Adv. Heal. Mater. 2020, 9, e1901794–e1901794, . [CrossRef]
- Ahrens, J.H.; Uzel, S.G.M.; Skylar-Scott, M.; Mata, M.M.; Lu, A.; Kroll, K.T.; et al. Programming cellular alignment in engineered cardiac tissue via bioprinting anisotropic organ building blocks. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34(26), 2200217.
- Ong, C.S.; Fukunishi, T.; Zhang, H.; Huang, C.Y.; Nashed, A.; Blazeski, A.; DiSilvestre, D.; Vricella, L.; Conte, J.; Tung, L.; et al. Biomaterial-Free Three-Dimensional Bioprinting of Cardiac Tissue using Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Derived Cardiomyocytes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4566, . [CrossRef]
- Yeung, E.; Fukunishi, T.; Bai, Y.; Bedja, D.; Pitaktong, I.; Mattson, G.; et al. Cardiac regeneration using human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived biomaterial-free 3D-bioprinted cardiac patch in vivo. J. Tissue. Eng. Regen. Med. 2019, 13(11), 2031–9.
- Asulin, M.; Michael, I.; Shapira, A.; Dvir, T. One-Step 3D Printing of Heart Patches with Built-In Electronics for Performance Regulation. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2004205, . [CrossRef]
- Edri, R.; Gal, I.; Noor, N.; Harel, T.; Fleischer, S.; Adadi, N.; et al. Personalized hydrogels for engineering diverse fully autologous tissue implants. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31(1), 1803895.
- Noor, N.; Shapira, A.; Edri, R.; Gal, I.; Wertheim, L.; Dvir, T. 3D Printing of personalized thick and perfusable cardiac patches and hearts. Adv. Sci (Weinh). 2019, 6(11), 1900344.
- Kupfer, M.E.; Lin, W.-H.; Ravikumar, V.; Qiu, K.; Wang, L.; Gao, L.; Bhuiyan, D.B.; Lenz, M.; Ai, J.; Mahutga, R.R.; et al. In Situ Expansion, Differentiation, and Electromechanical Coupling of Human Cardiac Muscle in a 3D Bioprinted, Chambered Organoid. Circ. Res. 2020, 127, 207–224, . [CrossRef]
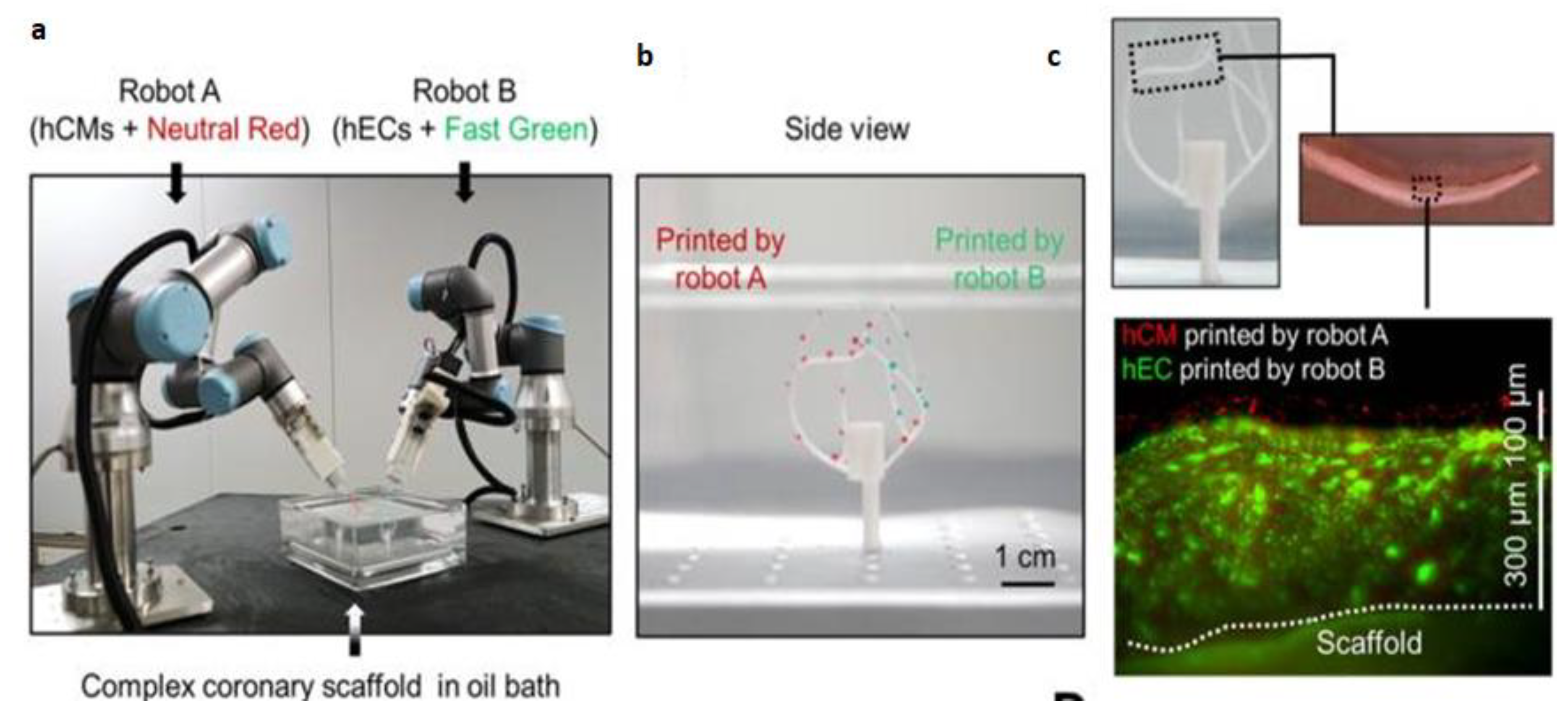
- Zhang, Z.; Wu, C.; Dai, C.; Shi, Q.; Fang, G.; Xie, D.; Zhao, X.; Liu, Y.-J.; Wang, C.C.; Wang, X.-J. A multi-axis robot-based bioprinting system supporting natural cell function preservation and cardiac tissue fabrication. Bioact. Mater. 2022, 18, 138–150, . [CrossRef]
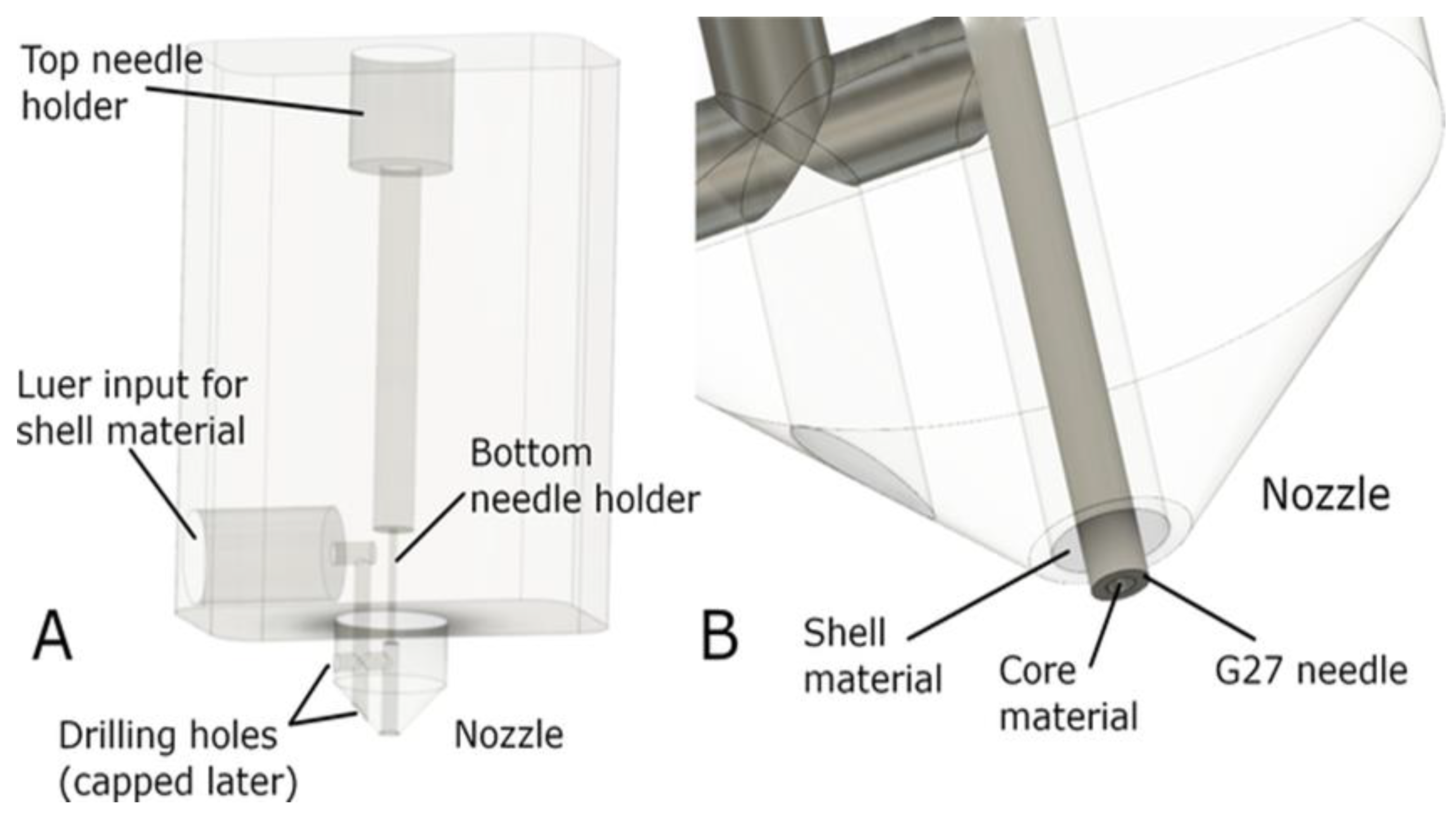
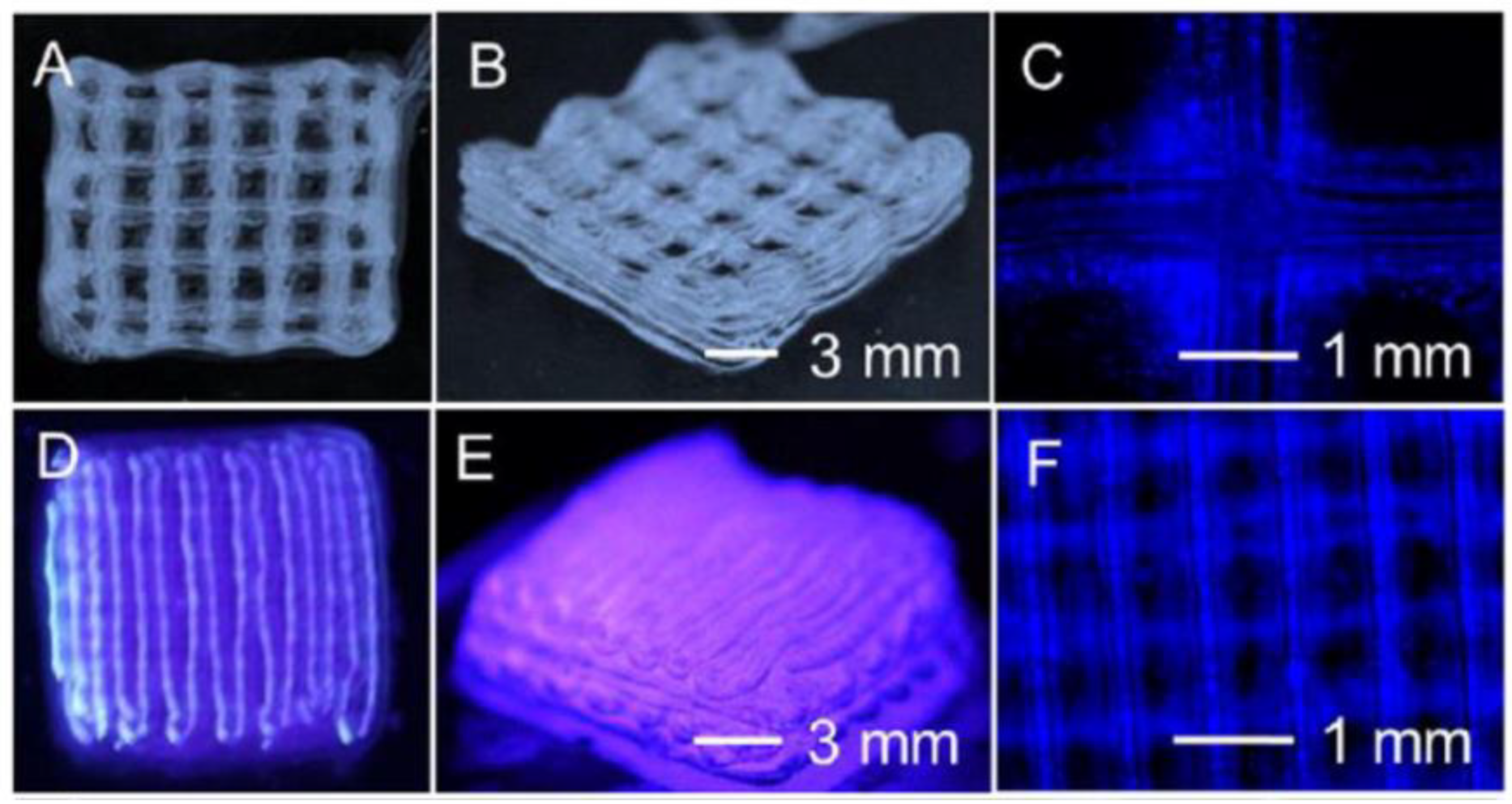
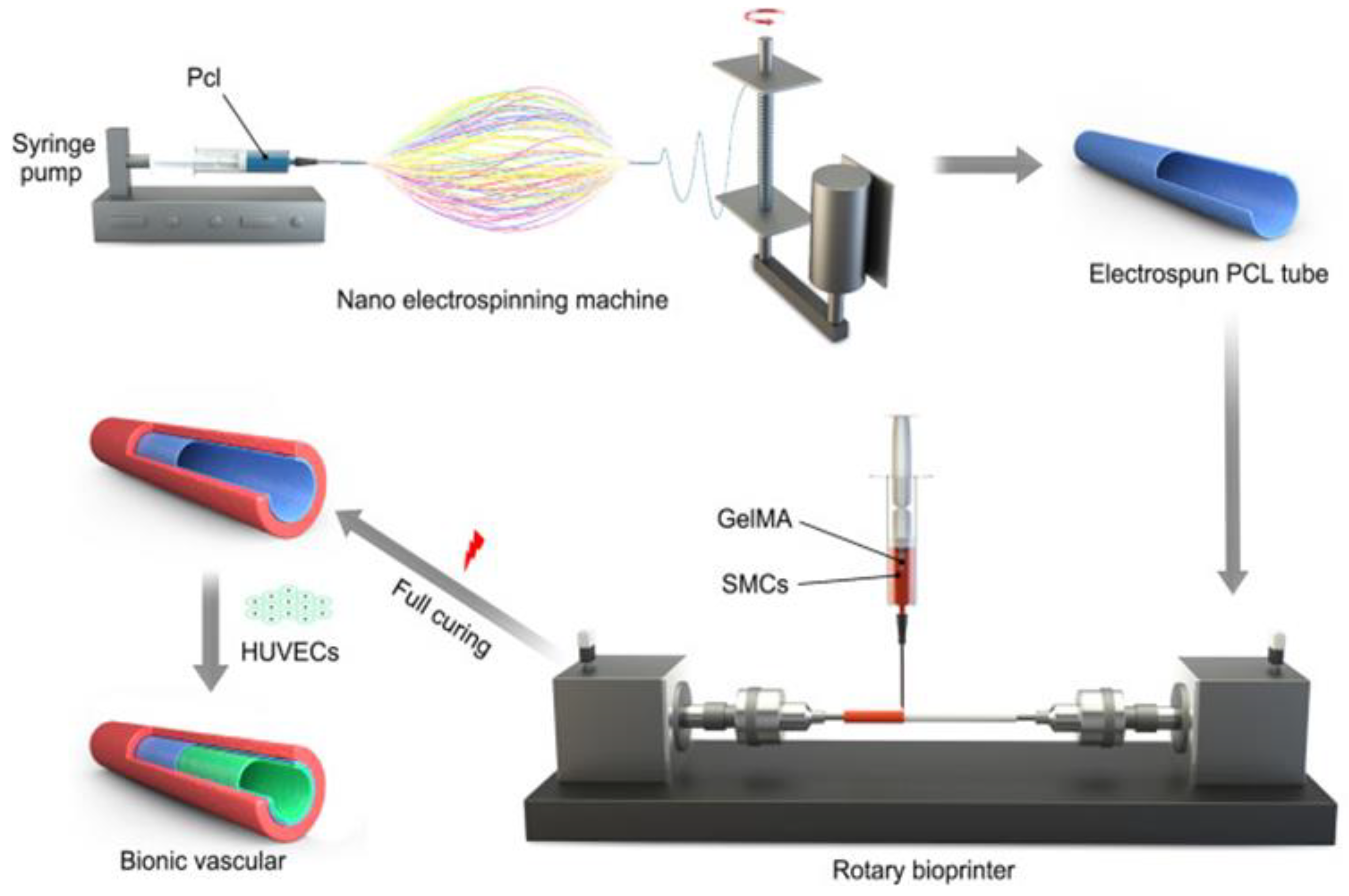
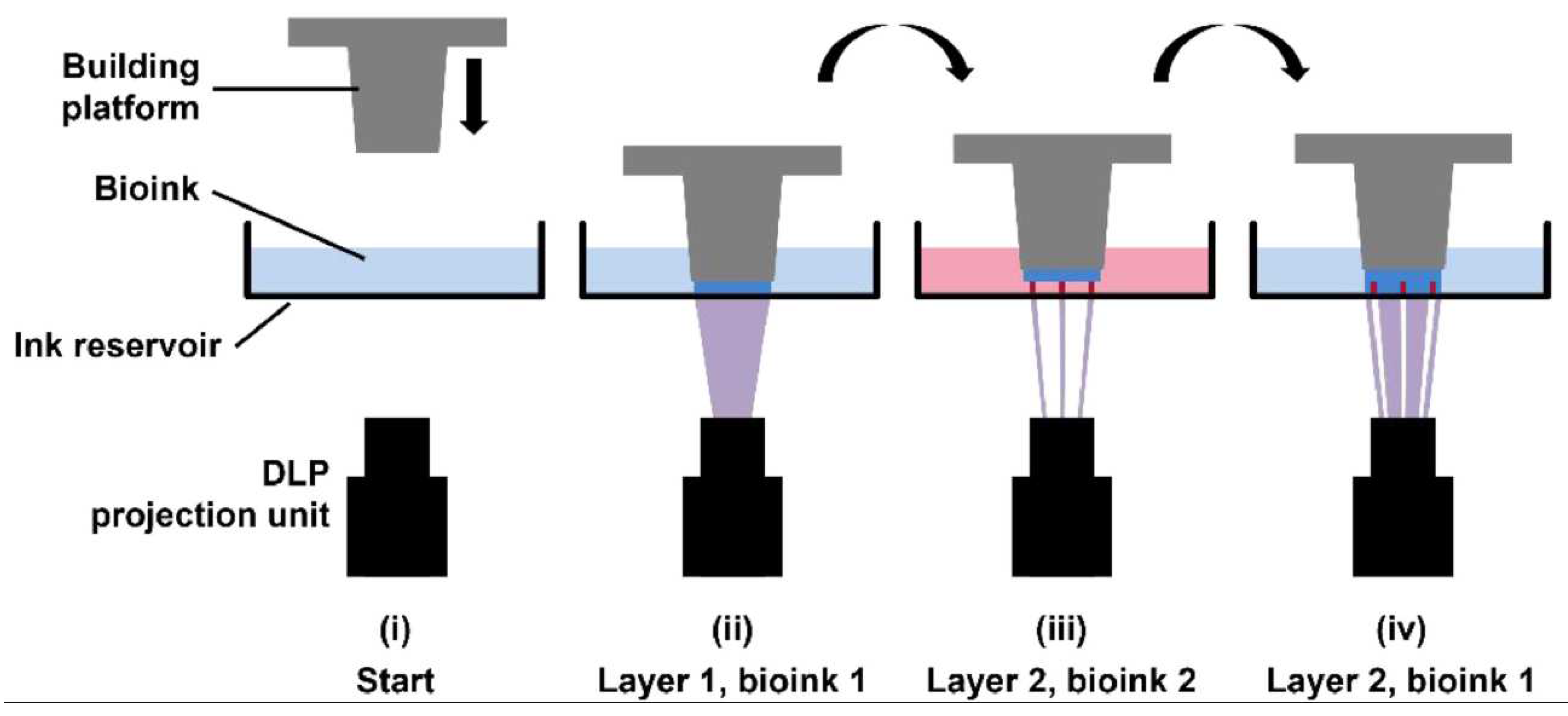
| References | Construct shape | Bioinks | Key aspect of study | Examined benefits | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cells | Hydrogel | ||||
| [153] | Patch | Spheroids of hiPSC-derived CM, CB and EC | - | Biomaterial-free | Spontaneous contraction, ability to pace constructs, rudimentary vascularization, in vivo engraftment |
| [150] | Grid | Neonatal rat CM + CF | GelMA + alginate + GNR | GNR to improve electrical conduction | Higher Cx43 expression, higher synchronous contractile frequency than constructs without GNR |
| [149] | Grid, patch | hCPCs | ECM + GelMA | Cardiac-ECM specific bioink | Higher cardiac and endothelial-specific gene expression than GelMA-only constructs, retention and vascularization after in vivo implantation |
| [44] | Patch | Neonatal rat CM | Fibrinogen + gelatin | PCL frame to impart auxotonic mechanical stress | Cell alignment, physiologic response to drugs altering force and frequency of contraction |
| [139] | Ellipsoid | hESC-CM | Collagen | Ventricle-like shape | Spontaneous, synchronous contraction, pacing at 1 and 2 Hz. |
| [157] | Patch, two-chambered ellipsoid | hiPSC-derived CM and EC | ECM | Patient specificity, vascularization, shape | Cardiac patch with perfusable, vascular-like channels. Spontaneous and synchronous contraction |
| [154] | Patch | Spheroids of hiPSC-derived CM, CF and EC | - | In vivo study of patch described in (7) | Smaller scar, greater vascularization than control (omentum patch). Greater ejection fraction and cardiac output, although not significant |
| [151] | Grid | Neonatal rat CM + mouse fibroblasts | GelMA + CPO | Oxygen-releasing bioink | Enhanced viability and function under hypoxic conditions |
| [158] | Chambered ellipsoid | hiPSCs | GelMA + ColMA | Ventricular-like shape, pump-like function, differentiation after printing | Differentiation to CM, SMC and EC. Spontaneous and synchronous contraction, physiologic response to isoproterenol, for up to 6 weeks in culture |
| [155] | Patch | Neonatal rat CM/hiPSC-CM | ECM, PDMS + graphite, PDMS + surfactant | Integrated electrodes for sensing and pacing | Good cell viability, spontaneous contraction and actinin expression. Sensing and pacing at 1 and 2 Hz |
| [152] | Struts, patch | hiPSC-CM microtissues | Fibrinogen + gelatin | High cellular density, alignment | Higher directionality, conduction velocity and force generation than spheroid-based constructs |
| [159] | Lining of vascular model | hESC-CM + EC | - | Ability to print in any direction | No damage in viability or activity after printing, evidence of vasculogenesis, synchronous and spontaneous contraction |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





