1. Introduction
1.1. Background
Climate change stands as the foremost global environmental concern, with global warming already causing detrimental effects such as rising sea levels, extreme weather events, and biodiversity loss [
1,
2]. Consequently, carbon emissions have become a crucial issue of global significance. In response, China has set a “double carbon” target: to achieve a peak in carbon emissions by 2030 and attain carbon neutrality by 2060 [
3]. This ambitious objective necessitates emission reductions across all sectors, including agriculture, which serves as both a significant source of carbon emissions and a substantial carbon sink system [
4,
5]. Agriculture is not only the second-highest emitter of greenhouse gases (GHGs) but also a fundamental sector in China, intimately linked to food supply and economic development [
6]. Consequently, it is imperative to develop solutions to enhance agricultural carbon sink capacity, effectively reduce agricultural carbon emissions, and safeguard agricultural activities from the impacts of climate change.
In 2020, Shandong Province accounted for approximately 9% of China’s carbon emissions, totaling 815 million tons, thus ranking first in the country [
7]. As a prominent agricultural province, Shandong contributes significantly to the production of grains, fruits, vegetables, and other agricultural products [
8]. However, challenges persist, such as excessive use of pesticides and fertilizers and an imbalanced planting structure, leading to high agricultural input requirements and hindering progress towards the “double carbon” target [
9]. Therefore, this study aims to examine the regional and temporal variations in agricultural carbon emission efficiency, while also analyzing pertinent factors, using Shandong Province as a case study. The ultimate goal is for Shandong Province to serve as a model for achieving low-consumption, high-efficiency agricultural growth in China.
1.2. Literature Review and Research Gaps
Although a precise definition of agricultural carbon emission efficiency is lacking, it essentially pertains to the measurement of the economic output of agriculture in relation to the carbon emissions produced, which are considered as undesired outputs [
10,
11,
12]. Currently, research conducted by domestic and international scholars primarily focuses on two aspects: the methodology employed and the factors influencing agricultural carbon emission efficiency. Various methods are employed to measure agricultural carbon emission efficiency. These methods include the Malmquist CO
2 emission performance index (MCPI) [
10], the Malmquist-Luenberger (ML) function [
13], the data envelopment approach (DEA) model [
14,
15], the stochastic frontier analysis (SFA) model [
16,
17], and others. DEA, which is the most widely used method for studying efficiency, is suitable for examining multiple inputs and outputs. However, the conventional DEA model only considers the issue of desired output efficiency. Given the increasing significance of environmental protection and sustainability in agricultural development, carbon emissions are incorporated into non-desired output indicators based on existing measures [
18]. This incorporation of non-desired output indicators leads to two primary types of methodological changes.
The first type involves the decomposition of the overall efficiency of agricultural carbon emissions into technical efficiency (EFF) and technical progress efficiency (TECH) using the Malmquist index. EFF can be further divided into pure technical efficiency (PE) and scale efficiency (SE). By employing this approach to analyze the main drivers of integrated efficiency, researchers have discovered that TECH plays a larger role in enhancing carbon emission efficiency [
15,
18,
19]. However, some scholars argue that EFF is the major contributing factor [
20].
The second type of methodological change involves using the Slacks-Based Measure (SBM) to account for non-desired outputs. This method enhances measurement accuracy by adjusting the goal function to include a slack variable, thereby addressing the measurement bias inherent in traditional DEA models. By adopting this approach, studies have revealed insights such as the overall low agricultural green total factor productivity in the Yellow River Basin [
21] and the low eco-efficiency of state-owned forestry businesses in the northeast region [
22].
Additionally, a comprehensive review was conducted on ten models related to agricultural carbon emissions, including the Air Pollution Interactions and Synergies (GAINS) model, to assess the potential reduction of Ireland’s agricultural carbon emissions [
23]. Moreover, the Swiss Integrated Agricultural Allocation (S_INTAGRAL) model was used to analyze greenhouse gas emissions from agriculture in Switzerland [
24].
Factors influencing agricultural carbon emissions have been analyzed by experts and researchers using various methods such as the Probit model, LMDI model, Tobit model, spatial Dubin model, and others. Existing studies have identified three main aspects that contribute to these influencing factors: industry, environment, and society. From an industrial perspective, agricultural innovation and the level of mechanization have shown a positive impact on agricultural carbon emission efficiency, while the structure of the agricultural industry has been found to have a significant negative effect [
13,
20,
25]. However, some scholars have also discovered a positive influence of agricultural industry structure on agricultural carbon emission efficiency through testing [
19]. Regarding the environment, the severity of disasters and the availability of arable land per capita both hinder the improvement of agricultural carbon efficiency. It is worth noting that the impact of disaster severity has shown variations among different research subjects and has even demonstrated a catalytic effect in China [
19,
26,
27]. On the other hand, rural power usage has been found to promote increased carbon emission efficiency in agriculture [
18], and land availability has been confirmed to contribute to the sustainability of the environment [
28].
From a societal perspective, factors such as urbanization rate, economic development, and openness to the outside world have been found to promote agricultural carbon emission efficiency. Conversely, the size of the labor force, intensity of agricultural investment, and financial support to agriculture have been identified as inhibiting factors for agricultural carbon emission efficiency [
19,
20,
27]. In summary, although studies on measuring techniques and influencing factors have provided some insights, several issues still remain. Firstly, research primarily focuses on specific countries or river basins, with limited studies conducted at the provincial level. Secondly, most studies examine influencing factors on a broader scale, failing to recognize regional variations and the varying significance of these factors due to different levels of development. Therefore, this paper takes Shandong province as a case study, employs the DEA-SBM model to measure agricultural carbon emission efficiency, and explores the influence of various factors in each region by combining the results with geographical location, classifying the 16 cities in Shandong province.
The main contributions of the article are as follows:
Evaluation of Agricultural Carbon Emission Efficiency: The study focuses on evaluating the agricultural carbon emission efficiency of Shandong Province from 2011 to 2020. This assessment provides valuable insights into the environmental performance of the agricultural sector in the region over a specific time period.
Identification of Regional Disparities: The research findings reveal significant differences in the efficiency values of agricultural carbon emissions among different cities in Shandong Province. The study highlights the existence of polarization in agricultural carbon emission efficiency, emphasizing the need for targeted interventions based on regional characteristics.
Spatial Distribution Analysis: Through spatial evaluation, the study identifies a distribution trend in agricultural carbon emission efficiency across Shandong Province. It indicates that the central region of the province exhibits higher efficiency values, while the eastern and western regions have lower efficiency values. This spatial analysis provides a comprehensive understanding of the geographical patterns of agricultural carbon emission efficiency.
Examination of Influencing Factors: The study conducts empirical tests to identify the key factors influencing agricultural carbon emission efficiency in Shandong Province and its three regions. The findings indicate that urbanization plays a significant role in supporting the growth of agricultural carbon emission efficiency. Conversely, the education level of the labor force has a suppressive impact. However, factors such as economic development and crop cultivation structure do not show significant influence consistently across the regions.
Region-Specific Policy Recommendations: Based on the analysis of influencing factors and regional characteristics, the article proposes specific countermeasures to enhance agricultural carbon emission efficiency in different regions of Shandong Province. These recommendations include improving the planting structure and reducing brain drain in the eastern region, strengthening agricultural and rural inputs while increasing the added value of agricultural products in the central region, and intensifying the linkage between urbanization and industrial layout in the western region.
Overall, the article contributes to the understanding of agricultural carbon emission efficiency, regional disparities, influencing factors, and provides practical policy suggestions for promoting sustainable agricultural practices in Shandong Province.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Methods
2.1.1. Non-Desired Output DEA-SBM Model
DEA (Data Envelopment Analysis) is widely used in various fields due to its ability to address the limitations of simple regression functions [
29]. In this study, the agricultural carbon emission efficiency is examined, which involves measuring multiple inputs and outputs. To overcome challenges in radial perspective analysis, the DEA-SBM model is employed, which incorporates non-desired outputs into the analysis. The inclusion of non-desired outputs in the SBM model allows for the improvement of both negative outputs and desired normal outputs in production and processing activities. This model enables a comprehensive consideration of input and output slackness, optimizing the degree of improvement in the system.
Traditional DEA models ignore the case of non-zero input or output slack. To address this situation, Tone [
30] suggested a non-radial, non-angular DEA-SBM model with slack variables, which was later improved to a DEA-SBM model with non-desired outputs [
31]. The specific model can be written as:
where
represent the agricultural carbon emission efficiency, has a value in range of 0 and 1.
represents the necessary factor inputs, which refers to the labor, land, and other factors that need to be input in agricultural production activities.
and
represent the expected, and non-desired output variables, respectively, which in this study are gross agricultural product and agricultural carbon emissions.
denote the assessed decision unit’s input and output values, respectively, over a specific time period. The
represents the vectors of the input, expected output, and non-desired output, respectively. The slack variables for input, intended output, and non-desired output are each represented by the
. When
, that is,
decision making unit is valid, agricultural carbon efficiency is at its highest. When
, the decision unit can improve since it is ineffective.
2.1.2. Tobit Model
The Tobit model, also known as the truncated regression model, was introduced by James Tobin in 1958 to handle explanatory variables that exhibit truncation characteristics, where they are non-negative but roughly distributed across positive values [
32]. This model addresses the challenge of distinguishing between level and non-limiting values, which ordinary OLS regression cannot handle. In the case of agricultural carbon emission efficiency, the values range from 0 to 1, displaying a distinct non-negative truncation characteristic. When using the DEA-SBM model to measure efficiency, the results fall within the range of [0, 1]. To account for this restricted dependent variable, the panel Tobit model was selected for the study, as traditional OLS regression methods fail to explain the differences between limiting and non-limiting observations and do not provide unbiased and consistent parameter estimates. Therefore, this study employs the Tobit model for the regression analysis, and its specific function can be written as:
where the variable being explained is denoted as
, while the explanatory variable is represented by
. The intercept term, which is the parameter requiring estimation, is referred to as
, whereas the parameter for the explanatory variable is denoted as β. Lastly, the random disturbance term is labeled as
which is assumed to be normally distributed at zero mean value and constant variance [
33,
34,
35].
2.2. Variable Selection
2.2.1. Evaluation Index System of Agricultural Carbon Emission Efficiency
For the setting of input, desired output, and non-desired output in an agricultural production system, we have followed the previous literature [
27,
36,
37,
38,
39,
40]. To ensure the standards of representativeness, systematicity, and data accessibility, we have considered three inputs of social resources, natural resources, and environmental resources, with a gross agricultural product as a desired output and agricultural carbon emission as a non-desired output, and created a system for evaluating agricultural carbon emission efficiency (
Table 1).
It is required to compute agricultural carbon emissions because there is no statistical information available. It can be calculated with given equation.
represents the overall agricultural carbon emissions,
represents the category
carbon source’s emission,
represents the category
carbon source’s input, and
represents the category
carbon source’s coefficient. Following the previous studies [
41,
42,
43], we have calculated the per-unit emission from various sources (
Table 2).
2.2.2. Influencing Factor Variables
Taking agricultural carbon emission as the explanatory variable, drawing on previous studies [
18,
20,
27,
44,
45], and considering the variables that may have an impact on it, four variables, namely, economic development, urbanization, crop cultivation structure and labor force education level, were selected to explore the impact of each variable (
Table 3).
2.3. Data Sources
The study period for this paper spans from 2011 to 2020. The primary data sources utilized include the Shandong Province Statistics Yearbook (2012-2021), as well as statistical yearbooks and bulletins from the 16 cities within Shandong Province. In instances where data were missing, interpolation methods were employed to fill the gaps. It is worth noting that in 2019, Laiwu City was incorporated into Jinan City, resulting in challenges in obtaining data specifically for Laiwu City beyond that year. Consequently, during the data collation process for the years 2011 to 2018, the data from Laiwu City were directly combined and processed with the data from Jinan City.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Spatial and Temporal Characteristics of Agricultural Carbon Emission Efficiency
3.1.1. Temporal Characteristics
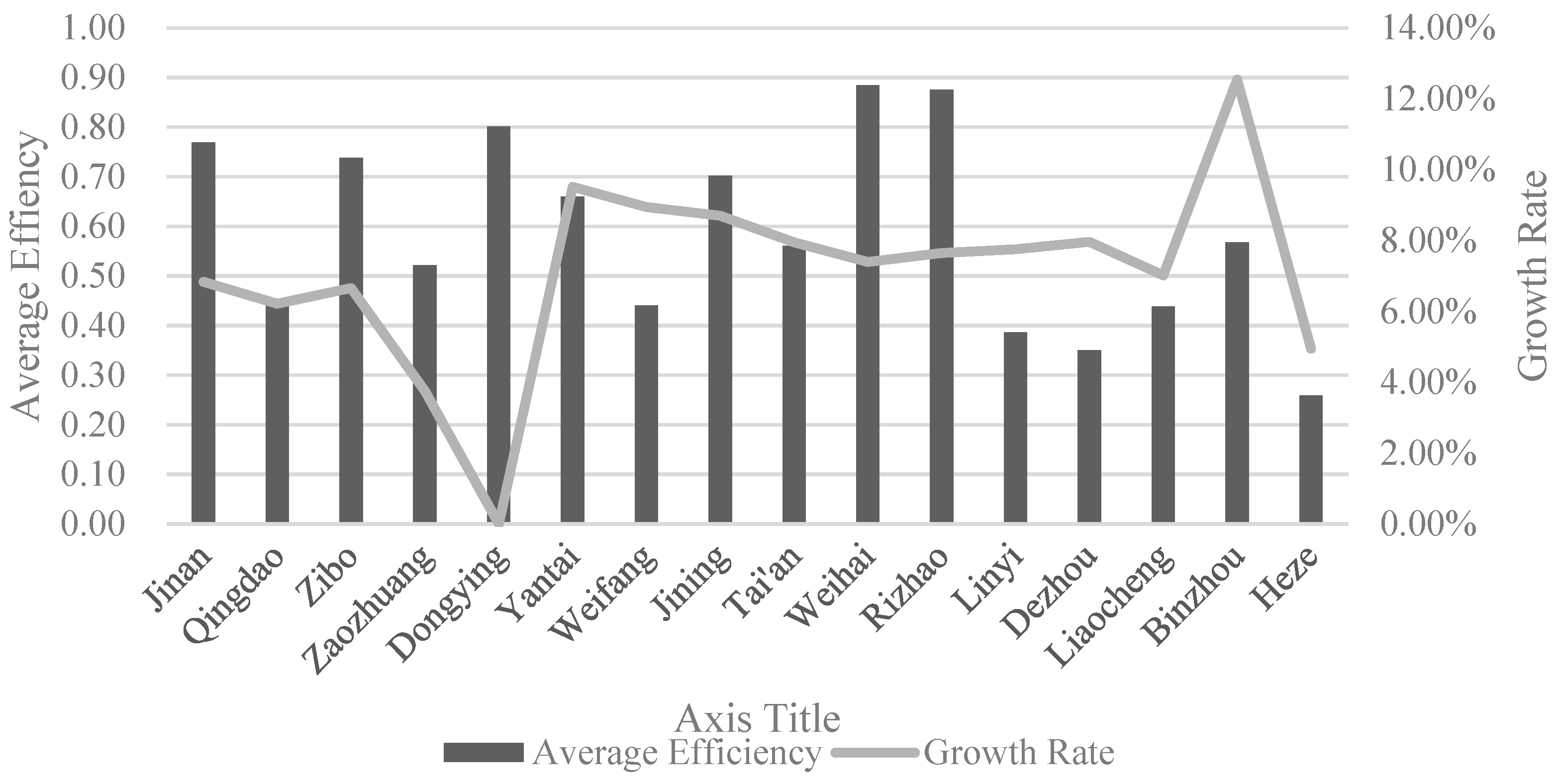
The agricultural carbon emission efficiency of Shandong Province was evaluated using the DEA-SBM model, which incorporates undesirable outputs. The average values and yearly growth rates of agricultural carbon emission efficiency were calculated for each city in Shandong Province from 2011 to 2020 (
Figure 1). Additionally, to gain a better understanding of the temporal trends, the agricultural carbon emission efficiency of the 16 cities in Shandong Province was ranked for the years 2011, 2014, 2017, and 2019 (
Table 4).
The agricultural carbon emission efficiency of each city in Shandong Province has shown an overall increase over time. In terms of efficiency values, in 2011, Dongying City had an efficiency value of 1. This can be attributed to the fact that Dongying is not primarily focused on agricultural production, resulting in lower carbon emissions compared to its output value, which can be neutralized and absorbed. Additionally, Dongying is a renowned national oil base with abundant underground resources. The efficiency values of the other 15 cities ranged from 0.2 to 0.6. By 2020, eight cities achieved an efficiency value of 1, while most of the remaining cities had efficiency values between 0.5 and 0.7. Regarding the growth rate, Dongying’s agricultural carbon emission efficiency remained unchanged over the past 10 years. More than half of the cities, including Binzhou, Yantai, and Weifang, exhibited growth rates exceeding 7%, while the rest of the cities showed growth rates ranging from 3% to 7% to varying degrees.
There is a significant polarization in agricultural carbon emission efficiency among the cities in Shandong Province. Over the course of ten years, the highest efficiency value observed among the 16 cities was 1, while the minimum value ranged between 0.2 and 0.3. In 2020, eight cities such as Jinan, Zibo, and Dongying achieved agricultural carbon emission efficiency values of 1. Tai’an, Zaozhuang, Weifang, and Liaocheng followed with efficiency values ranging from 0.6 to 0.9. The remaining cities had efficiency values between 0.3 and 0.6, indicating room for improvement. In terms of average values, Weihai ranked first in the province with an agricultural carbon emission efficiency of 0.884. However, six cities, including Qingdao and Weifang, did not reach the 0.5 threshold. Qingdao, as an economically developed city in Shandong Province, is influenced by market demands and may not adequately balance agricultural output with environmental protection. Consumers’ focus on price and product quality might overshadow the importance of environmental preservation, leading farmers to overuse chemical fertilizers and pesticides to maximize output and quality, thereby exacerbating environmental pollution. Heze had the lowest efficiency value of 0.259, which was 70% lower than Weihai.
Cities with low-efficiency values tend to be trapped in a “low-level” scenario. The low-efficiency area refers to cities with an average agricultural carbon emission efficiency below 0.5, ranking primarily in the bottom one-third. Qingdao, Weifang, Liaocheng, Linyi, Dezhou, and Heze are among the cities listed in the bottom one-third for both average value and yearly efficiency values. As of 2020, Qingdao, Weifang, Liaocheng, and Linyi had exceeded the 0.5 threshold in agricultural carbon emission efficiency, with annual growth rates of 6.215%, 8.947%, 7.017%, and 7.754%, respectively, showcasing more significant improvement compared to other cities. However, Dezhou and Heze still have not surpassed the 0.5 threshold. The average efficiency values of these cities remain below 0.5, indicating a failure to overcome the low-efficiency level bottleneck.
3.1.2. Spatial Characteristics
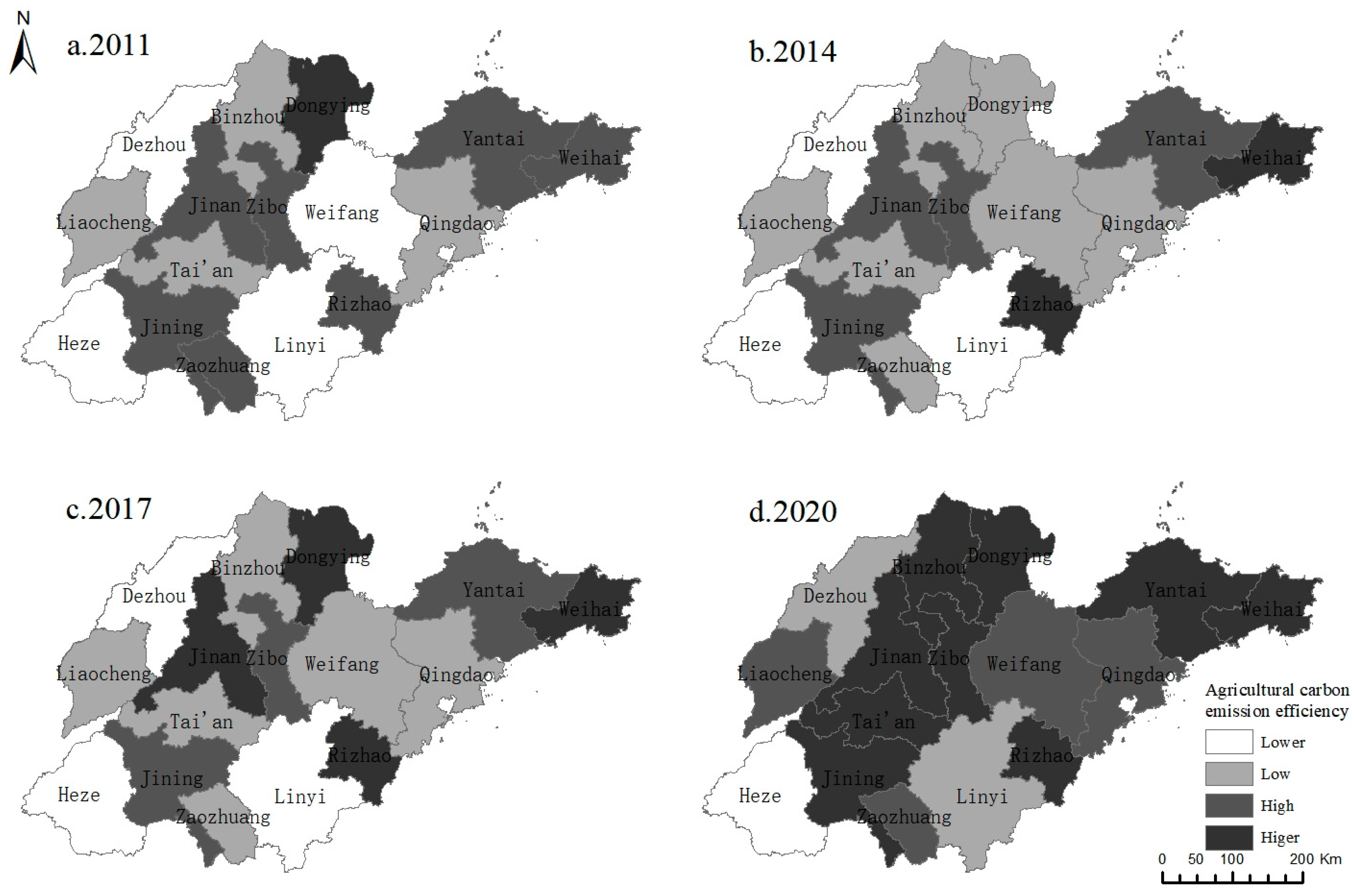
Based on their geographic locations and agricultural characteristics, the sixteen cities in Shandong Province were classified into three regions. The agricultural carbon emission efficiency of these cities was graded into four categories: lower, low, high, and higher, using the natural interruption point approach. This paper presents spatial distribution maps for the years 2011, 2014, 2017, and 2020 (
Figure 2) to analyze the geographical features of Shandong’s agricultural carbon emission efficiency. It is evident that:
There has been little change in the geographical features of agricultural carbon emission efficiency in Shandong Province over the past 10 years. While the efficiency of each city has improved, there has been no significant alteration in the spatial pattern of efficiency values, indicating that neighboring cities have not exerted a substantial influence. The number of cities with high efficiency values has increased from one in Dongying to nine in 2020. Comparing the spatial distribution maps of 2011 and 2020, it is clear that the cities exhibiting high efficiency values in 2020 are higher than other cities in 2011, although they have not yet reached the level of high efficiency.
The spatial distribution feature can be described as “East and west are low, and the center is high.” As depicted in
Figure 1, in 2011, most cities with high efficiency were located in the central area, followed by the eastern region. In 2020, only one city in the central region did not achieve a high efficiency value, accounting for 17% of the cities. In the eastern region, two cities, Qingdao and Weifang, did not reach the high-efficiency threshold, accounting for 40% of the cities. In the western region, only one city, Jining, attained a high efficiency value, while the remaining cities exhibited different stages of agricultural carbon emission efficiency.
Cities with low-efficiency values are scarce and scattered. In 2011, there were four cities with low-efficiency values: Weifang, Dezhou, Linyi, and Heze. By 2014 and 2017, Weifang had moved out of the low-efficiency category, and in 2020, only one city, Heze, remained in the low-efficiency stage. Among the eastern, central, and western regions, there is one city each with low efficiency values. The cities with low efficiency values are distributed more sporadically.
3.2. Analysis of Influencing Factors in Different Regions of Shandong Province
The agricultural carbon emissions efficiency varies across different regions, and a comprehensive regression analysis for Shandong Province as a whole may not provide meaningful insights. Therefore, in this study, the Shandong province, as well as its eastern, central, and western regions, were separately regressed using the Tobit model, and the results are presented in
Table 5. The analysis based on the obtained results is as follows:
For the eastern region of Shandong Province, it is evident that the crop cultivation structure significantly affects agricultural carbon emission efficiency, as indicated by the coefficient of 3.1195. This implies that an appropriate crop cultivation structure can enhance agricultural carbon emission efficiency. In the eastern region, there is a greater variety of cash crops, with vegetables and fruit trees being the main cash crops in cities like Qingdao, Weifang, and Yantai. Generally, cash crops have higher carbon emissions per unit compared to food crops [
46]. Therefore, regions with a higher proportion of food crops in their cultivation structure tend to have lower carbon emissions and improved efficiency. Additionally, the coefficient of the labor force education level is -0.0171, indicating a significant inhibitory effect. The rapid growth of the service sector has led to a higher likelihood of the labor force transitioning away from agricultural activities, resulting in a decrease in the education level of the agricultural workforce. This necessitates increased inputs, such as technical training, to improve efficiency. Furthermore, economic growth does not have a significant impact on agricultural carbon emissions efficiency and shows a negative direction. Some studies suggest that the relationship between agricultural carbon emissions and economic development may follow an “N” or “U” shape, and the rapid economic development might have reached a turning point where it negatively affects agricultural carbon emissions [
47,
48,
49]. Lastly, urbanization does not play a significant role in agricultural carbon emissions efficiency in the eastern region. Urbanization reflects the migration of rural populations, leading to a decline in the agricultural workforce. However, the impact is not significant due to the better agricultural base and production conditions in the eastern region.
For the central region of Shandong Province, the coefficient of economic development has a significant positive impact with a value of 0.0381. This indicates that agricultural carbon emission efficiency consistently improves as the economy grows. Typically, agriculture and rural areas thrive as the economic situation improves, leading to a more balanced industrial structure and increased agricultural modernization [
50]. This, in turn, improves the input-output ratio of agricultural activities and enhances agricultural carbon emission efficiency. On the other hand, the coefficient for crop cultivation structure is -0.9347, indicating that agricultural carbon emission efficiency decreases when there is an improvement in the crop cultivation structure. This may be attributed to the central region primarily cultivating grain crops, resulting in a more homogeneous cultivation structure. Compared to cash crops, grain crops have lower unit output value, so enhancing the crop cultivation structure can lead to a decrease in agricultural value and subsequently reduce agricultural carbon emission efficiency [
51,
52]. Urbanization and labor force education level do not have significant effects in the central region. Although the central region is less developed compared to the eastern region, it has relatively high levels of agricultural mechanization and labor force education, minimizing the impact of changes in these factors on agricultural production activities.
In the western region of Shandong Province, all four influencing factors have significant effects. Firstly, economic development has a positive impact with a coefficient of 0.1821. Secondly, crop cultivation structure also has a positive effect with a coefficient of 0.2. Cash crops in the western region, such as peanuts and cotton, differ from those in the eastern region, but their cultivation area is considerable. Therefore, improving the crop planting structure in the western region can enhance agricultural carbon emission efficiency [
53,
54]. The labor force education level also shows a significant positive effect with a coefficient of 2. It is likely that rural laborers with higher education are more knowledgeable about agricultural modernization technology and are more conscious of reducing carbon emissions. Simultaneously reducing input and undesired output contributes to an increase in agricultural carbon emission efficiency. Lastly, urbanization has a negative effect with a coefficient of -0.5227. This indicates that agricultural carbon emission efficiency decreases with increasing urbanization. The higher urbanization rate implies a decrease in the rural labor force, requiring increased use of agricultural machinery to compensate [
55]. However, the level of agricultural mechanization in the western region has not reached a modernization level, resulting in larger inputs and increased non-desired output, ultimately decreasing agricultural carbon emission efficiency.
In Shandong Province as a whole, urbanization has a promoting effect with a coefficient of 1.1386. This is likely because urbanization facilitates the relocation of surplus agricultural labor to other industries, leading to scale and intensification of agricultural production. Additionally, it aids in land transfer, optimizing the agricultural industrial structure and resource allocation, and resulting in economies of scale. This, in turn, increases expected output and improves efficiency. The coefficient of labor force education level is -0.0179, indicating that an increase in labor force education level leads to a decrease in agricultural carbon emission efficiency. The reason behind this is that most technologies used in agricultural production are relatively simple and can be easily applied after training. The labor force education level in Shandong Province is already relatively high, and further improvements may not significantly reduce input and non-desired output, resulting in diminishing marginal benefits and potentially harming agricultural carbon emission efficiency [
56]. The effects of economic growth are positive but inconspicuous, suggesting the possibility of a decoupling effect. Lastly, crop cultivation structure has no significant effect, likely because the main crops grown in Shandong Province, such as wheat, corn, and groundnuts, are primarily food crops, and the cultivation structure remains relatively stable, lacking significant impact on agricultural carbon emission efficiency.
3.3. Robustness Test of the Tobit Model
The data tailing method is commonly employed by researchers as a robustness test, offering the advantage of mitigating the influence of outliers and extreme values in the original data on regression results [
57]. This method involves applying bilateral shrinking to all data points of both the dependent and independent variables at the 2% quantile, and subsequently subjecting the shrunken variables to a panel Tobit regression with random effects. The regression results, presented in
Table 6, exhibit consistent coefficients for all variables when compared to the baseline regression results. This consistency provides evidence supporting the robustness of the regression findings.
To address potential biases in the basic regression results, this study examines the robustness by introducing additional conventional variables, such as agricultural fiscal expenditure. The estimation results, presented in
Table 7, demonstrate that the significance of these additional variables aligns with the significance observed in the basic regression results. This consistency provides further evidence supporting the robustness of the basic regression findings.
4. Conclusions and Policy Implications
The carbon emissions in agriculture in Shandong province, China, were estimated in this study using the DEA-SBM model. The Tobit model was employed to explore the factors influencing spatial and temporal evolution characteristics. Based on these analyses, the study draws the following conclusions:
Time-Series Characteristics: Over a span of ten years, the overall agricultural carbon emission efficiency displayed an upward trend. However, there existed a substantial gap in efficiency values among cities, indicating significant polarization. Cities such as Heze, Dezhou, and Linyi consistently ranked in the bottom one-third with efficiency values below 0.5, thereby experiencing a “low-level trap.”
Spatial Distribution: Spatial patterns in the past decade have remained relatively unchanged. Clear regional disparities were observed, following a trend of “East and west are low, and the center is high.” The central region predominantly housed cities with higher efficiency values, while cities with varying efficiency levels were scattered across the eastern and western regions. Cities with lower efficiency values were dispersed throughout Shandong Province.
Influencing Factors: The influence of different variables varied significantly across regions. The eastern region was primarily influenced by crop cultivation structure and labor force education level. The central region was mainly affected by economic development and crop cultivation structure. In the western region, economic growth, urbanization, crop structure, and labor force education level all played significant roles. Urbanization demonstrated a positive effect on agricultural carbon emission efficiency in Shandong province, while the labor force education level had a negative effect. Economic development and crop cultivation structure did not exhibit significant effects.
Based on these findings, the following recommendations are proposed:
Emphasize optimizing crop planting structure and addressing brain drain. Strategies include achieving a balanced distribution of food and cash crops based on resource advantages, introducing higher quality and higher yielding crops, promoting modern agricultural knowledge and skills among local farmers, supporting large agricultural households and farmers’ cooperatives, and providing professional research sites and development opportunities for agricultural talents.
Strengthen agricultural and rural inputs to increase the value of agricultural goods. This can be achieved through green technology input, ecological and scientific agricultural development, utilization of digital technology to improve agricultural databases and crop testing systems, and promoting technological innovation in grain processing enterprises. Additionally, higher quality and higher yielding food crops should be cultivated, with a focus on developing their added value and extending the agricultural-industrial chain.
Improve efficiency by enhancing the linkage between urbanization and industrial layout, rationalizing crop planting structure, and addressing talent recruitment and agricultural inputs. Encourage the adoption of low-carbon, intensive, and intelligent technologies in agricultural production, strengthen inter-city exchanges, promote agricultural and rural energy transformation, and implement a scientific and region-specific crop planting layout. Improve agricultural subsidy policies, incentivize technical personnel, and promote professional technologies such as clean agricultural production and carbon sequestration.
Author Contributions
S.S., W.W., X.L., and P.Z. were responsible for data collection, arrangement of the relevant literature, and data analysis. E.E. and Z.K. commented on the choice of the research topic and helped to write an original draft of the paper. E.E. revised the article. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The study is financially supported by the Taishan Young Scholar Program (No. tsqn202103070), the Taishan Scholar Foundation of Shandong Province, China.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The research is approved by the ethical committee of the School of Economics, Shandong University of Technology, Zibo, China.
Informed Consent Statement
Not Applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data will be available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Elahi Ehsan,Khalid Zainab,Tauni Muhammad Zubair,Zhang Hongxia,Lirong Xing. Extreme weather events risk to crop-production and the adaptation of innovative management strategies to mitigate the risk: A retrospective survey of rural Punjab, Pakistan[J]. Technovation,2021(prepublish).
- Frederic R. Siegel. Adaptations of Coastal Cities to Global Warming, Sea Level Rise, Climate Change and Endemic Hazards[M].Springer, Cham.
- Zeng, Ning,Jiang, Kejun,Han, Pengfei,Hausfather, Zeke,Cao, Junji,Kirk Davidoff, Daniel,Ali, Shaukat,Zhou, Sheng. The Chinese Carbon-Neutral Goal: Challenges and Prospects[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences,2022(prepublish).
- Elahi Ehsan,Khalid Zainab,Zhang Zhixin. Understanding farmers’ intention and willingness to install renewable energy technology: A solution to reduce the environmental emissions of agriculture[J]. Applied Energy,2022,309. [CrossRef]
- Elahi Ehsan,Zhang Hongxia,Lirong Xing,Khalid Zainab,Xu Haiyun. Understanding cognitive and socio-psychological factors determining farmers’ intentions to use improved grassland: Implications of land use policy for sustainable pasture production[J]. Land Use Policy,2021,102.
- Song B, Mu Y Y, Hou L L. Study on the effect of farm households’ specialization on low-carbon agriculture: Evidence from vegetable growers in Beijing, China[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2016, 31(3): 468-476.
- Qinglong Shao. Nonlinear effects of marine economic growth and technological innovation on marine pollution: Panel threshold analysis for China’s 11 coastal regions[J]. Marine Policy,2020.
- Yang L , Guo H , Yao H , et al. Regional Supply Capacity of Agricultural Products in Shandong Province Based on GIS[J]. Asian Agricultural Research, 2009, 1(5). [CrossRef]
- Chang Jianxin. The role of digital finance in reducing agricultural carbon emissions: evidence from China’s provincial panel data[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2022,29(58). [CrossRef]
- ZHOU P, ANG B W, HAN J Y. Total factor carbon emission performance: a Malmquist index analysis[J]. Energy Economics, 2010, 32(1): 194−201. [CrossRef]
- Wang Q W, Zhou P, Zhou D Q. Research on dynamic carbon dioxide emissions performance, regional disparity and affecting factors in China[J]. China Industrial Economics, 2010, 1(1): 45-54.
- SHANG J, JI X Q, SHI R, ZHU M R. Structure and driving factors of spatial correlation network of agricultural carbon emission efficiency in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2022, 30(4): 543−557. [CrossRef]
- Wang J, Zhu C. International Comparison of Carbon Emission Efficiency in Agricultural Sector and Its Influencing Factors Based on Date from 32 Countries from 1995 to 2011[J]. Ecological Economy, 2018,34(07):25-32.
- Ma D. Spatial heterogeneity and influencing factors of agricultural energy carbon emission efficiency in China—An empirical research of spatial panel data model[J]. Resour Dev Mark, 2018, 12: 1693-1765.
- Liu H, Qu H. Spatial Pattern and Distribution Trend of Green Total Factor Productivity in the Yellow River Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Population Science, 2019(06):59-70+127.
- Du K, Zou C Y. Regional disparity, affecting factors and convergence analysis of carbon dioxide emission efficiency in China: On stochastic frontier model and panel unit root[J]. Zhejiang Soc. Sci, 2011, 11: 32-43.
- Herrala R, Goel R K. Global CO2 efficiency: Country-wise estimates using a stochastic cost frontier[J]. Energy policy, 2012, 45: 762-770. [CrossRef]
- WANG M C. Research on spatial and temporal difference of agricultural carbon emission efficiency and its influencing factors in Hubei Province[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2020, 53(24): 5063-5072.
- Li J, Li S, Liu Q, Ding J. Agricultural carbon emission efficiency evaluation and influencing factors in Zhejiang province, China[J]. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 2022, 10: 2208. [CrossRef]
- Wu X R, Zhang J B, Tian Y, Li P. Provincial agricultural carbon emissions in China: Calculation, performance change and influencing factors[J]. Resources Science, 2014, 36(1): 129-138.
- Liu S, Zhang H, Cai W. Spatial pattern and dynamic evolution of agricultural green total factor productivity in the Yellow River Basin[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment,2022,38(12):1557-1566.
- Ning Y, Liu Z, Ning Z, Zhang H. Measuring eco-efficiency of state-owned forestry enterprises in northeast China[J]. Forests, 2018, 9(8): 455. [CrossRef]
- Madden S M, Ryan A, Walsh P. Exploratory Study on Modelling Agricultural Carbon Emissions in Ireland[J]. Agriculture, 2021, 12(1): 34. [CrossRef]
- Hediger W. Modeling GHG emissions and carbon sequestration in Swiss agriculture: An integrated economic approach[C]//International Congress Series. Elsevier, 2006, 1293: 86-95.
- Grovermann C, Wossen T, Muller A, Nichterlein K. Eco-efficiency and agricultural innovation systems in developing countries: Evidence from macro-level analysis[J]. PloS one, 2019, 14(4): e0214115. [CrossRef]
- Guangyao Y A N, Weihong C, Haihui Q. Effects of agricultural technical efficiency on agricultural carbon emission[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2022, 30: 1-15.
- WU H Y, HUANG H J, HE Y, CHEN W K. Measurement, spatial spillover and influencing factors of agricultural carbon emissions efficiency in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2021, 29(10): 1762−1773. [CrossRef]
- Grzelak A, Guth M, Matuszczak A, Czyżewski B, Brelik A. Approaching the environmental sustainable value in agriculture: How factor endowments foster the eco-efficiency[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 241: 118304. [CrossRef]
- H. O. FRIED,C. A. K. LOVELL,S. S. SCHMIDT,S. YAISAWARNG. Accounting for Environmental Effects and Statistical Noise in Data Envelopment Analysis[J]. Journal of Productivity Analysis,2002,17(1/2).
- TONE K. A slacks-based measure of efficiency in data envelopment analysis[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2001, 130(3): 498−509.
- Tone K.Dealing with undesirable outputs in DEA:A slacks based measure (SBM) approach[R].Tokyo:GRIPS Research Report Series, 2003.
- McDonald, J. F., Moffitt, R. A. The uses of Tobit analysis[J]. The Review of Economics and Statistics,1980,62(2):318-321. [CrossRef]
- Elahi Ehsan,Khalid Zainab. Estimating smart energy inputs packages using hybrid optimisation technique to mitigate environmental emissions of commercial fish farms[J]. Applied Energy,2022,326.
- Elahi Ehsan,Zhang Zhixin,Khalid Zainab,Xu Haiyun. Application of an artificial neural network to optimise energy inputs: An energy- and cost-saving strategy for commercial poultry farms[J]. Energy,2022,244(PB).
- Wang Fushuai,Cai Wenxia,Elahi Ehsan. Do Green Finance and Environmental Regulation Play a Crucial Role in the Reduction of CO2 Emissions? An Empirical Analysis of 126 Chinese Cities[J]. Sustainability,2021,13(23). [CrossRef]
- Zhang Y, Xu X. Carbon emission efficiency measurement and influencing factor analysis of nine provinces in the Yellow River basin: Based on SBM-DDF model and Tobit-CCD model[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2022, 29(22): 33263-33280. [CrossRef]
- Shu X, Feng W, Liao F, Ling C.Study on the spatiotemporal evolution and driving factors of agricultural eco-efficiency of urban agglomeration in the Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River[J].Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2022,29(01):394-403.
- Qian L, Xiao R, Chen Z. Research on China’s provincial agricultural production efficiency and its influencing factors under the constraints of carbon dioxide emission[J].Economic Theory and Business Management. 2013(09):100-112.
- Chen L, Liu Y, Gao Y, Wang J. Carbon Emission Trading Policy and carbon emission efficiency: An empirical analysis of China’s prefecture-level cities[J]. Frontiers in Energy Research, 2021: 844.
- Yang X, Shang G. Smallholders’ agricultural production efficiency of conservation tillage in Jianghan plain, China—Based on a three-stage DEA model[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2020, 17(20): 7470. [CrossRef]
- Tian Y, Li B, Zhang J B. Research on stage characteristics and factor decomposition of agricultural land carbon emission in China[J]. J. China Univ. Geosci, 2011, 11: 59-63.
- Yang C, Hu P, Diao B, Cheng J, Cui H. Environmental performance evaluation of policies in main grain producing areas:from the perspective of agricultural carbon emissions[J]. China population, resources and environment,2021,31(12):35-44.
- Wang L, Zhao J, Chen S Y. Analysis of ecosystem carbon sources/sinks and carbon footprint in farmland ecosystem of Shandong Province[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2016, 21(7): 133-141.
- Ridzuan N H A M, Marwan N F, Khalid N, et al. Effects of agriculture, renewable energy, and economic growth on carbon dioxide emissions: Evidence of the environmental Kuznets curve[J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2020, 160: 104879. [CrossRef]
- Balsalobre-Lorente D, Driha O M, Bekun F V, et al. Do agricultural activities induce carbon emissions? The BRICS experience[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2019, 26: 25218-25234. [CrossRef]
- Jules F.F.P. Bos,Janjo de Haan,Wijnand Sukkel,René L.M. Schils. Energy use and greenhouse gas emissions in organic and conventional farming systems in the Netherlands[J]. NJAS - Wageningen Journal of Life Sciences,2014,68.
- Raihan Asif. Toward sustainable and green development in Chile: Dynamic influences of carbon emission reduction variables[J]. Innovation and Green Development,2023,2(2).
- Ridzuan N , Marwan N F , Khalid N , et al. Effects of agriculture, renewable energy, and economic growth on carbon dioxide emissions: Evidence of the environmental Kuznets curve[J]. Resources Conservation and Recycling, 2020, 160(8):104879. [CrossRef]
- Lu Zhang,Jiaxing Pang,Xingpeng Chen,Zhongmingnan Lu. Carbon emissions, energy consumption and economic growth: Evidence from the agricultural sector of China’s main grain-producing areas[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2019,665(C).
- Sahoo, G., Wani, A. M., Swamy, S. L., Roul, P. K., Dash, A. C., & Sharma, A. Livelihood strategy and sustainability aspects in industrialization as a source of employment in rural areas[J]. Springer,2022,643-670. [CrossRef]
- Huang Weibin,Wu Fengqi,Han Wanrui,Li Qinqin,Han Yingchun,Wang Guoping,Feng Lu,Li Xiaofei,Yang Beifang,Lei Yaping,Fan Zhengyi,Xiong Shiwu,Xin Minghua,Li Yabing,Wang Zhanbiao. Carbon footprint of cotton production in China: Composition, spatiotemporal changes and driving factors[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2022,821.
- Wang Ruru,Zhang Yu,Zou Cunming. How does agricultural specialization affect carbon emissions in China?[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2022,370.
- Yu Cui,Sufyan Ullah Khan,Yue Deng,Minjuan Zhao. Regional difference decomposition and its spatiotemporal dynamic evolution of Chinese agricultural carbon emission: considering carbon sink effect[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2021,28(29). [CrossRef]
- Yu Cui,Sufyan Ullah Khan,Yue Deng,Minjuan Zhao,Mengyang Hou. Environmental improvement value of agricultural carbon reduction and its spatiotemporal dynamic evolution: Evidence from China[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2021,754.
- Huang Hua,Hou Mengyang,Yao Shunbo. Urbanization and Grain Production Pattern of China: Dynamic Effect and Mediating Mechanism[J]. Agriculture,2022,12(4). [CrossRef]
- Wu Qianrong,Xu Lanzhuang,Geng Xianhui. Ecological efficiency of hog scale production under environmental regulation in China: based on an optimal super efficiency SBM-Malmquist-Tobit model.[J]. Environmental science and pollution research international,2022,29(35). [CrossRef]
- Arabmazar, Schmidt. An Investigation of the Robustness of the Tobit Estimator to Non-Normality[J]. Econometrica,1982,50(4). [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).