1. Introduction
Ti-Ni and Zr-Ni metal-powder systems are widely used to produce bulk materials with excellent shape memory properties, hydrogen absorption capacity, superelasticity, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility [
1,
2,
3,
4]. Recent years have faced the problem of finding new materials for the rapid development of additive technologies, including composite metal powders used for molding products [
5,
6,
7]. Traditionally, methods for producing composite metal powders are based on mechanochemistry [
8,
9,
10], chemical reduction [
11,
12], and electrolytic deposition [
13,
14,
15]. However, these methods are considered material- and energy-intensive [
16]. The main disadvantages of mechanochemical synthesis are the duration of mixing process (40 h) and contamination of metal powders with fragments of grinding media. Methods of chemical reduction from solutions are characterized by the complexity of controlling the quantitative ratio of metals in powders, the inclusion of components (elements) of a reducing agent in its composition, and the instability of solutions. Electrodeposition methods require a large amount of electricity from an external source, which limits its application.
Galvanic replacement process, widely used in hydrometallurgy for metal extraction, is simpler, more reliable and less energy-intensive [
17,
18,
19,
20,
21,
22]. The advantages of the process are a more uniform distribution of the surface layer on a reducing metal and the ability to work without an external source of electrical energy for coating. The difference in electrochemical potentials between a reducing metal and ions of elements with more positive potential values initiates the spontaneous reaction of more noble metal release on the metal surface in a solution [
23]:
Uniform distribution of powder components can be used to obtain a homogeneous microstructure and highly efficient composite materials for powder metallurgy and additive technologies. For composite materials based on titanium or zirconium, it is more difficult to obtain a multicomponent metal-powder system with a uniform distribution of elements in it due to the significant difference between the density of each component and the melting point [
24]. According to the structural-orientation concept, the growing precipitate is to reproduce the crystal structure of the matrix to ensure good adhesion to the base metal [
25]. The studies show that the sediment distribution uniformity is achieved during the formation of "core-shell" structures in the process of galvanic replacement [
26]. The formation of "core-shell" structures reduces significantly the interfacial energy, which ensures the sintering activity and a smooth process of powder material compaction.
The number of articles focused on the galvanic replacement synthesis of powders based on titanium, zirconium and metals of the iron family elements is very limited [
27,
28,
29]. In these studies, titanium and zirconium demonstrate good reducing ability in aqueous solutions in relation to nickel(II) ions. The lack of scientific and practical studies of the kinetics and mechanisms of reactions of galvanic substitution of titanium or zirconium with metals of the iron family elements is a big barrier to obtaining promising materials with a "core-shell" particle structure [
30].
2. Results and Discussion
Titanium and zirconium were used as reducing agents in the process of galvanic replacement of nickel (II) in an aqueous solution. Their standard potential in aqueous solutions is E°(Ti
3+/Ti) = -1.21 V [
4], E°(Zr
4+/Zr) = -1.54 V [
31], and their stationary potential ranges E
stac= -0.35±0.1 V [
32]. A strong shift in the potential of titanium and zirconium towards more positive values is due to the presence of an oxide film on their surface, the transformation or removal of which allows us to use metallic titanium and zirconium as reducing agents of ions of more electropositive metals [
33].
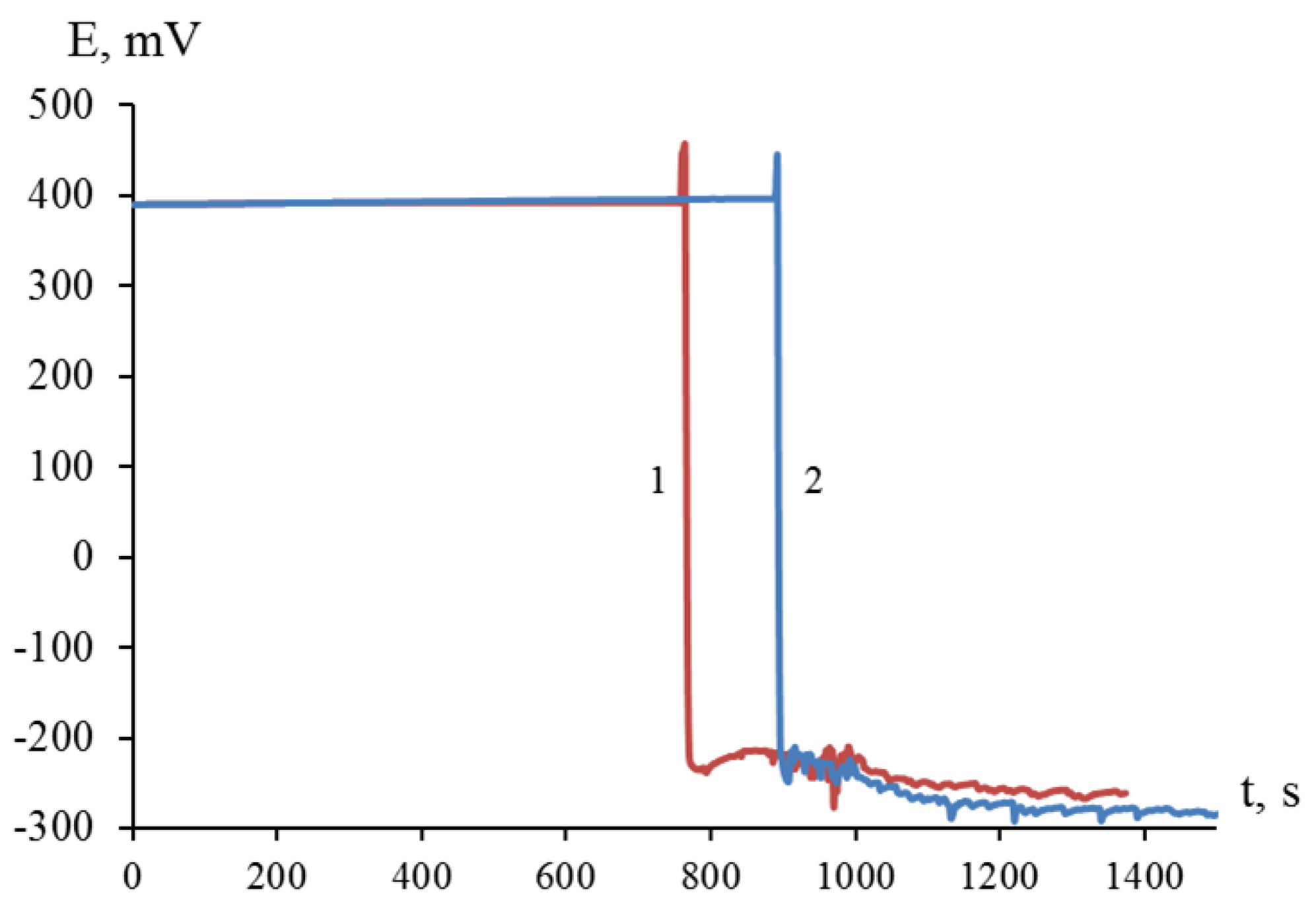
Thus, the interaction of dispersed titanium and zirconium with a solution of nickel(II) chloride was initiated in the presence of hydrofluoric acid with the release of elemental nickel on the surface of titanium and zirconium microparticles (
Figure 1). The process of galvanic replacement in a suspension of dispersed titanium in a solution of 1.00 M NiCl
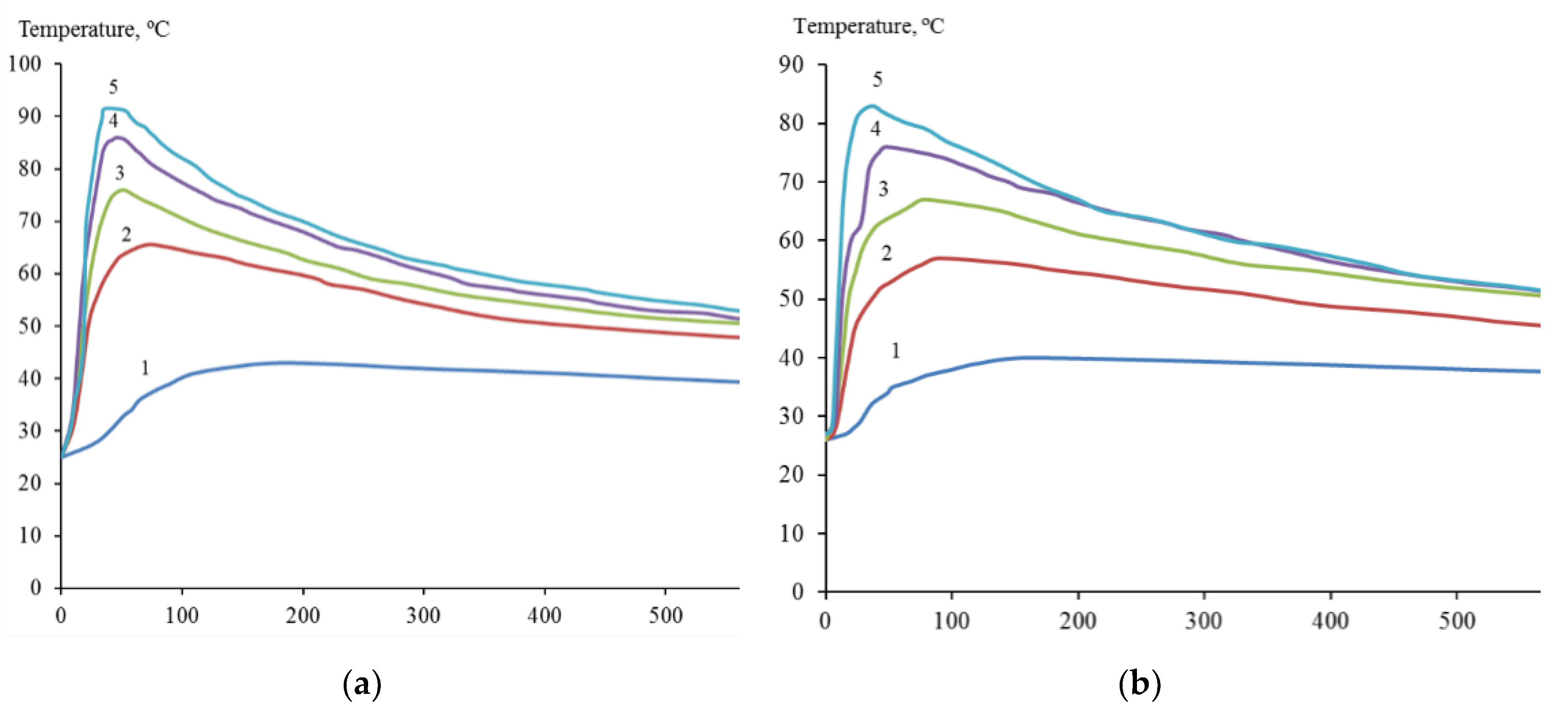
2 with the introduction of 0.45; 0.90; 1.20; 1.50 and 2.00 M HF was accompanied by an increase in temperature to 43; 65; 76; 86 and 91°C (
Figure 2a), and the temperature of the suspension of dispersed zirconium under similar conditions reached 40; 57; 67; 76 and 83°C, respectively (
Figure 2b). Suspension heating was a combined result of redox and other reactions occurring with different thermal effects.
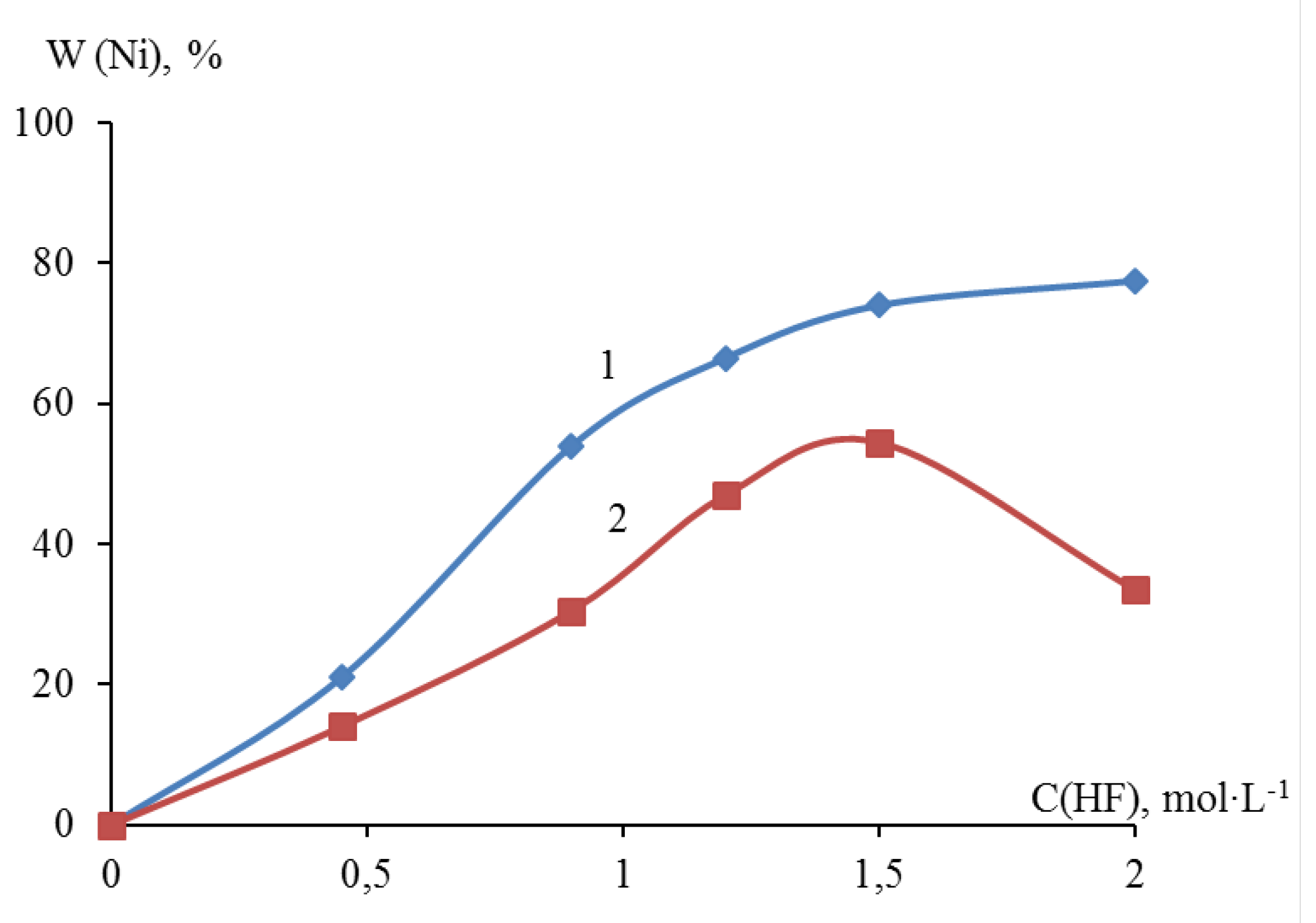
Sampling with titrimetric determination showed that the deposition degree of metallic nickel in the presence of 0.45; 0.90; 1.20; 1.50 and 2.00 M HF on dispersed titanium reached 21.00, 54.00, 66.50, 74.00, and 77.50 wt.%, respectively. The degree of deposition of nickel on dispersed zirconium reached 14.00; 30.50; 47.00; 54.50; 33.50% wt., respectively. A comparative analysis of the nickel yield on dispersed titanium and zirconium showed that as the concentration of HF in the suspension increased to 1.50 M, the nickel yield increased monotonically. At an HF content of more than 1.50 M, the yield of nickel on zirconium decreased compared to a similar process on titanium (
Figure 3).
The process of galvanic replacement with the iron family elements can be described using the example of titanium.
According to modern concepts, the process of galvanic replacement of titanium with nickel is associated with the interaction of fluorides and aqua complexes of these metals with the surface of dispersed HF preactivated titanium.
When electropositive metals are deposited on the surface of titanium particles, conjugated hydrogen is released:
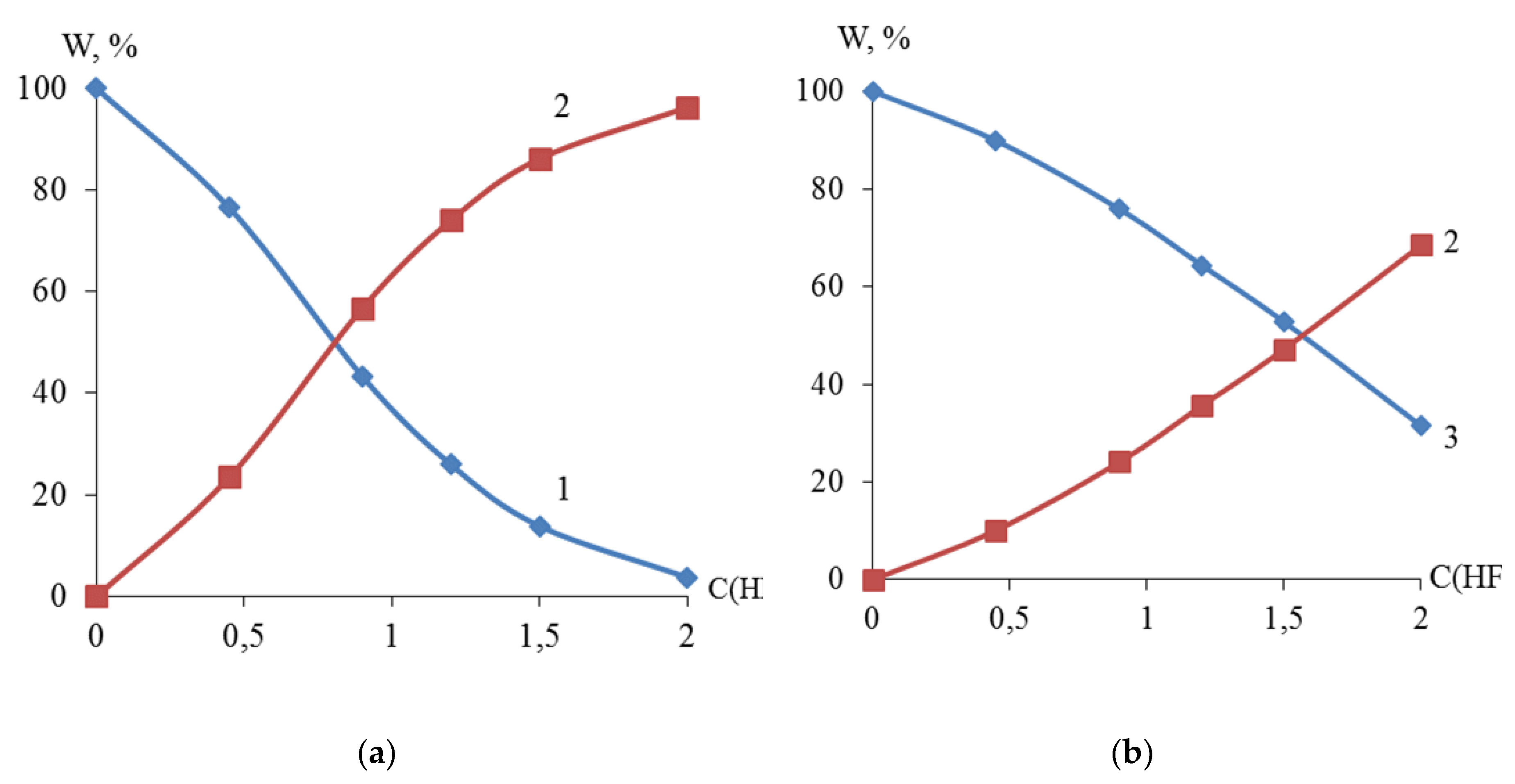
The X-ray fluorescence analysis established the S-shaped dependence of the content (mass. %) of titanium, zirconium and nickel in the dispersed Ti-Ni and Zr-Ni systems obtained by galvanic replacement on the concentration of hydrofluoric acid (
Figure 4). The data obtained indicate the possibility of regulating the quantitative composition of titanium or zirconium and nickel in the dispersed and bulk Ti-Ni or Zr-Ni systems.
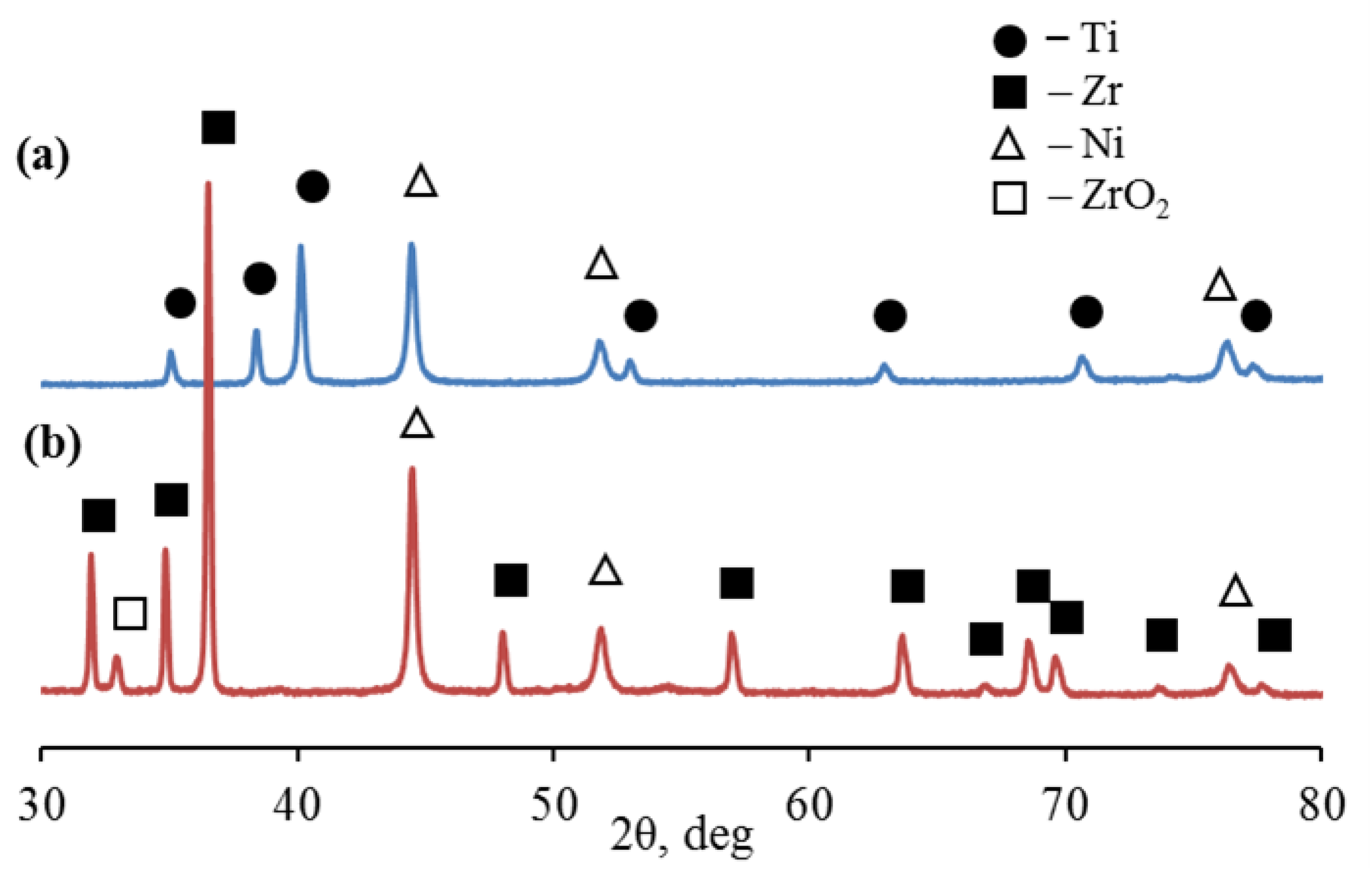
X-ray diffraction showed that in the 2θ scanning range from 30 to 80°, microparticles of the Ti-Ni system are characterized by diffraction peaks corresponding to the hexagonal close-packed lattice of titanium Ti (002), Ti (101), Ti (102 ), Ti. (110), Ti (103), Ti (112) and Ti (201) at slip angles: 35.05°, 38.38°, 40.12°, 52.96°, 62.91°, 70.66° and 76, 49° (
Figure 5a,
Table 1). At the same time, microparticles of the Zr-Ni system are characterized by diffraction peaks corresponding to the hexagonal close-packed lattice of α-zirconium Zr(100), Zr(002), Zr(101), Zr(102), Zr(110), Zr(103), Zr (200), Zr (112), Zr (201), Zr(004) and Zr(202) at slip angles: 31.95°, 34.85°, 36.49° , 47.99°, 56.94 °, 63.58°, 66.79°, 68.52°, 69.56°, 73.58°, and 77.60°, respectively (
Figure 5b,
Table 1). The diffraction pattern also showed distinct reflections of nickel (β-Ni) with a face-centered cubic lattice (fcc).
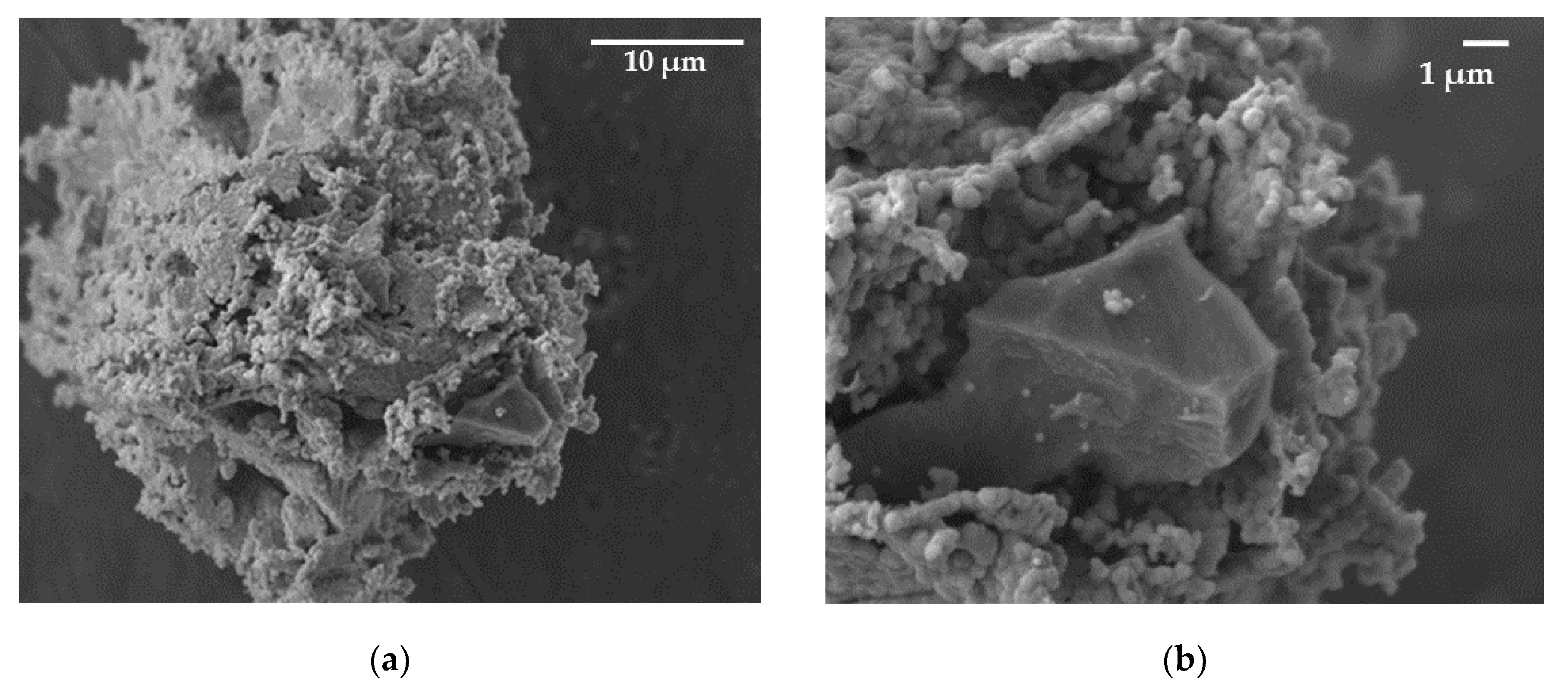
Scanning electron microscopy showed that the formed dispersed systems Ti-Ni, Zr-Ni have the same shapes and geometric dimensions as the original particles (
Figure 6). This process is accompanied by the deposition of submicron spherical nickel particles on the surface of titanium and zirconium microparticles.
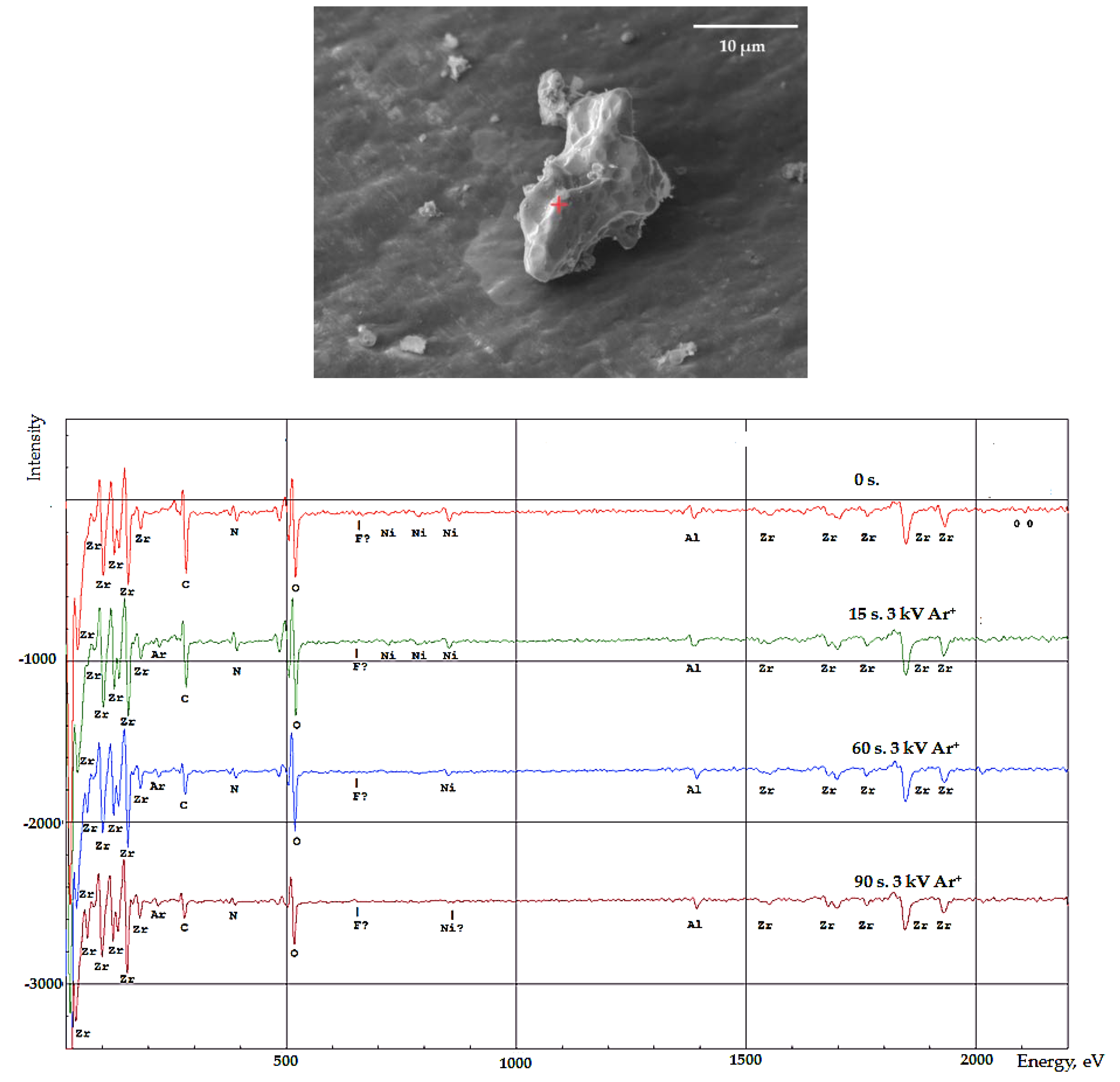
The distribution of elements in the surface layers of the synthesized Ni-Ti, Ni-Zr polymetallic systems was studied by Auger electron spectroscopy. Electron microscopic images were used to select the analyzed areas on the particle surface (
Figure 7).
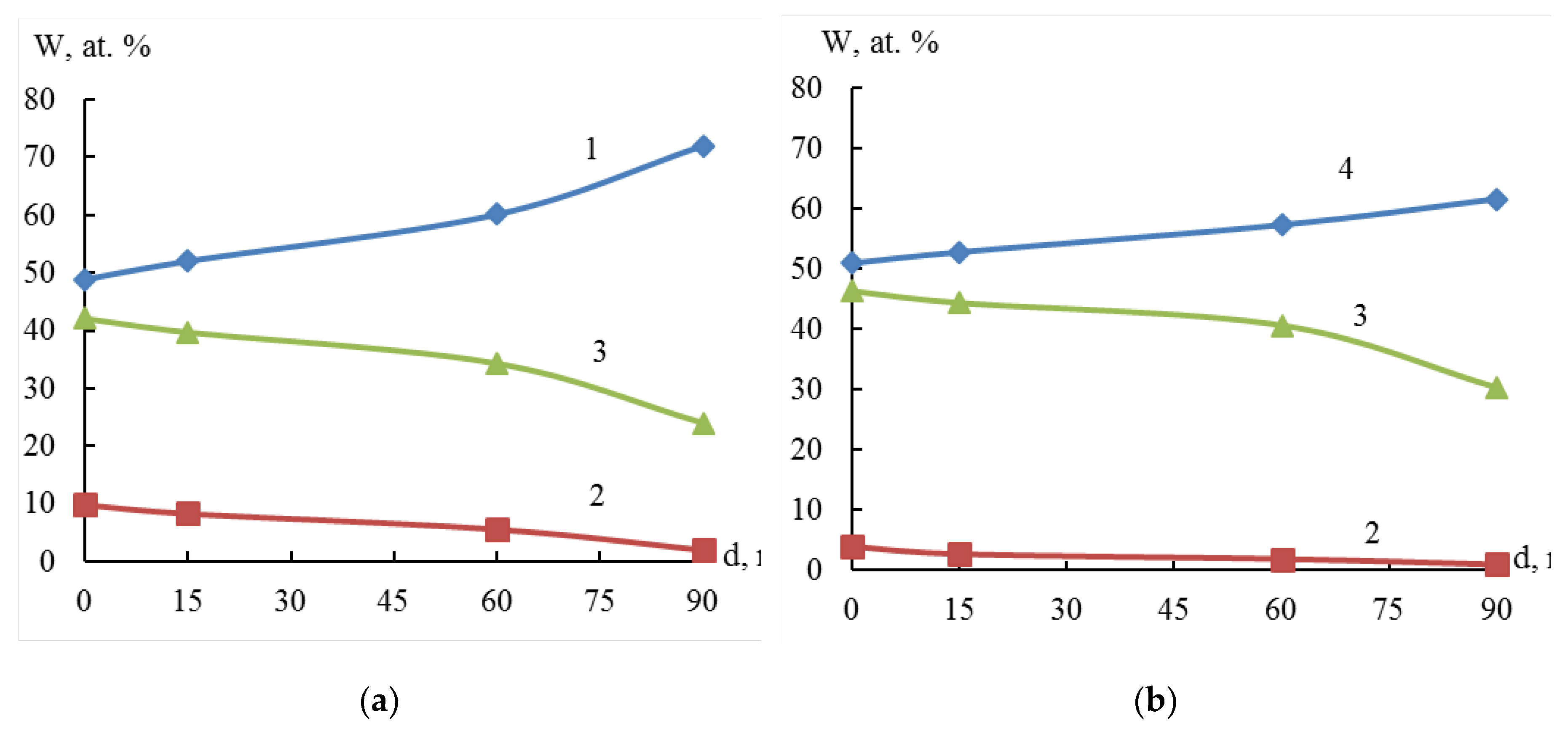
Figure 8 shows that the nickel amount decreases and zirconium amount increases from the surface to the center of the particle. This indicates that particle structure of the resulting system can be characterized as a "core-shell" system. The thickness of the Ni film on zirconium is at least 33 nm (the rate of ion etching Ar
+, 3 kV of the particle surface is approximately 22 to 45 nm/min).
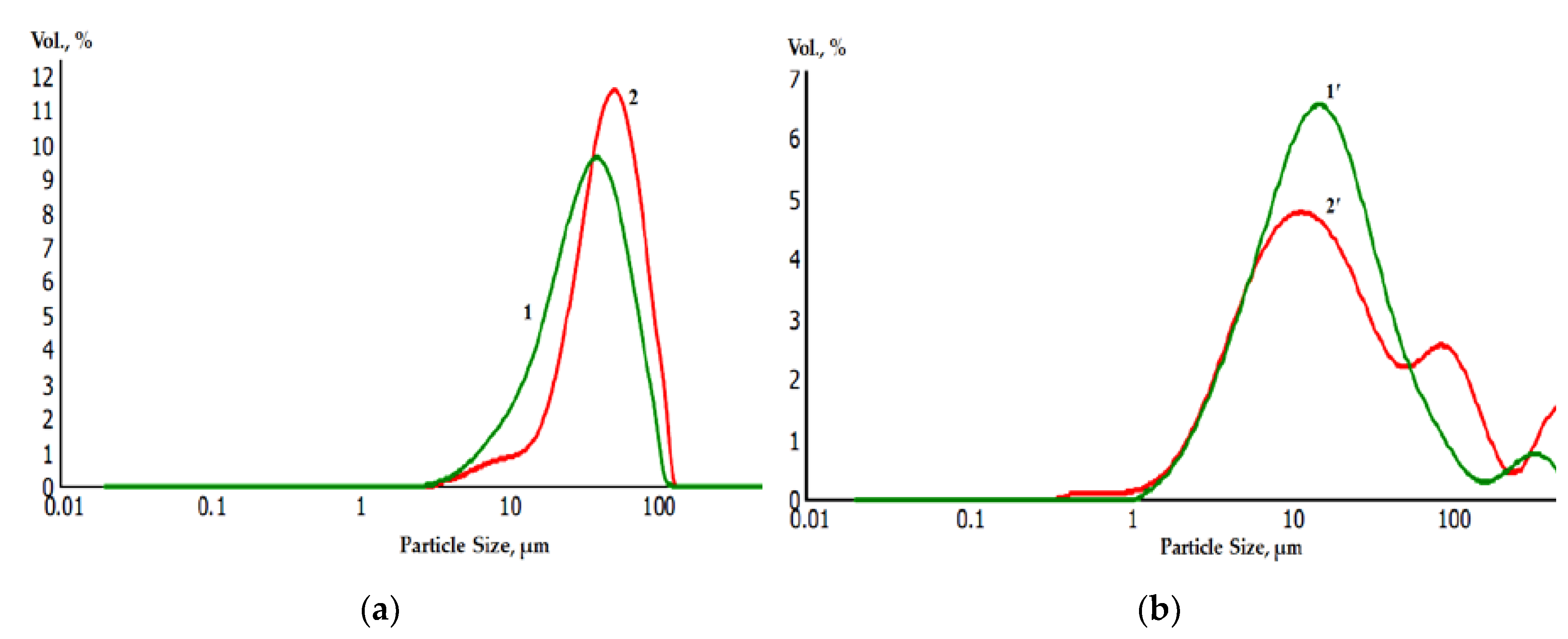
Laser diffraction analysis of the granulometric composition of powders before (a) and after (b) galvanic replacement showed a slight increase in the average diameter of the metal powder particles. At the same time, the average diameter of the particles Ti, Ti-Ni was 30 and 42 microns, Zr and Zr-Ni 10 and 15 microns, respectively (
Figure 9).
The synthesized polymetallic systems Ti-Ni, Zr-Ni can be studied in detail to establish phase transitions at high-temperatures. The results of these studies can be used to develop new technological methods for obtaining powders of metallic layered systems "titanium – nickel" and "zirconium - nickel".
3. Materials and Methods
Commercially available dispersed forms of titanium and zirconium (American Elements Co) were used for galvanic replacement synthesis of the dispersed bimetallic systems Ti-Ni and Zr-Ni.
Table 2 presents the chemical composition of dispersed titanium and zirconium.
To remove (transform) the oxide film from the surface of titanium and zirconium and initiate the process of galvanic replacement in aqueous solutions, various concentrations of hydrofluoric acid solution (high purity) were used.
To better understand the redox process occurring on dispersed titanium and zirconium, chronopotentiograms were recorded in a three-electrode cell using a P-2X potentiostat. A thin-layer platinum laboratory electrode was used as an indicator electrode, and a saturated silver chloride with a Luggin capillary was used as a reference electrode. All values of electrode potentials presented in this study were relative to the reference saturated silver chloride electrode. In parallel, the temperature of the reaction mixture was measured using a contact thermometer.
To synthesize the dispersed bimetallic Ti-Ni and Zr-Ni systems, the exact amounts of dispersed titanium (1.88 mol = 60 g/l), zirconium (1.32 mol = 60 g/l), and hydrofluoric acid were introduced into the aqueous solutions of 1.00 M NiCl2, calculated in terms of stoichiometric excess. The metal deposits were repeatedly washed with distilled water and acetone. Then, they were kept in a drying cabinet at 80 ° C for 3 hours.
The degree of galvanic replacement of metallic nickel on dispersed titanium and zirconium was determined by the method of sampling the reaction mixture followed by quantitative determination of nickel (II) ions using complexometric titration.
The elemental composition of the dispersed systems was determined by X-ray fluorescence analysis. The analysis procedure was performed using a S1 TITAN 500 portable X-ray fluorescence spectrometer (Bruker).
The structural-phase analysis of dispersed systems was carried out using a Rigaku Smart Lab multi-functional X-ray diffractometer (Rigaku Corporation, Japan). The investigated dispersed systems were placed in a cuvette made of fused quartz.
In step-by–step scanning mode (step: 2θ = 0.05°, exposure time at the point – 2 s, shooting interval - 2θ = 30-80°), the surface of the test powder was irradiated with monochromatized microwave radiation (30 kV, 10 mA). Calculations were performed using Powdercell and X powder software. The full-profile analysis of diffractograms was carried out by fitting the theoretical values of the reflection intensity to the experimental ones and the calculation using corundum coefficients in the PDXL-2 software package. In all cases, the hardware broadening of diffraction peaks was taken into account relative to a standard sample of silicon powder free from microstresses and dimensional widenings.
The surface morphology of dispersed samples containing titanium, zirconium and nickel was studied using a JEOL JSM-7100F scanning electron microscope using secondary electron detectors (SEI).
The elemental composition of the near-surface region of dispersed samples was studied by scanning Auger electron spectroscopy using a JAMP-9500F Auger microprobe with energy resolution ΔE/E=0.05% (JEOL Ltd., Japan). The studied dispersed samples were fixed on a conductive carbon tape (cat. № G3939, AgarScientific, UK). To analyze the local distribution of elements in the sample volume, the surface was periodically treated with Ar+ ions with an energy of 3 keV and a beam diameter of ~ 0.02 microns in a time interval of up to 90 seconds (the rate of ion etching of Ar+ 3 kV according to Zr is approximately from 22 to 45 nm/min).The analyzed areas were chosen according to the images of a scanning electron microscope.
Thegranulometric composition of dispersed systems was studied by laser diffraction at the Mastersizer 2000, Malvern. The test samples placed in a flow cell were illuminated by a laser beam (a gas He-Ne laser with λ =0.63 microns).The average size of microparticles of the studied samples and their quantitative granulometric composition were calculated by the intensity of radiation using the Malvern program according to Fraunhofer theory.
4. Conclusions
Dispersed systems based on titanium, zirconium and nickel (Ti-Ni, Zr-Ni) were synthesized by galvanic replacement. The effective parameters of synthesis such as quantitative ratios of metal ions and hydrofluoric acid, the duration of the process (no more than 10 minutes), and the formation features of polymetallic systems characterized by adjustable granulometric, phase and elemental composition were described.
X-ray phase analysis showed that the deposition of nickel on dispersed titanium and zirconium in aqueous solutions in the presence of hydrofluoric acid provides the phase composition of binary systems in the form of a mechanical mixture of nickel and titanium, nickel and zirconium in the specified ratios.
The Auger electron spectroscopy method proved that the dispersed Ti-Ni, Zr-Ni systems obtained by galvanic replacement are microparticles with a core-shell structure.
Scanning electron microscopy showed that the synthesized systems are caracterized by a highly porous structure that follows the contour of titanium and zirconium particle surface and the presence of nanoscale round-shaped subunits on the formed particle surface.
Author Contributions
This work is the collaborative development of all the authors. Conceptualization, A.F.D. and L.E.K.; methodology, A.F.D. and E.V.P.; software, E.V.P.; validation, A.F.D. and E.V.P.; formal analysis, L.E.K.; investigation, A.F.D, L.E.K., E.V.P.; resources, A.F.D.; data curation, A.F.D. and L.E.K.; writing—original draft preparation, A.F.D, L.E.K.; writing—review and editing, A.F.D.; supervision, A.F.D. and E.V.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation, grant number 075-01508-23-00.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The study was carried out using the equipment of the Center for Collective Use “Nanomaterial’s and Nanotechnology” of the Kazan National Research Technological University.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
References
- Lu, N.H.; Chen, C. Improving the functional stability of TiNi-based shape memory alloy by multi-principal element design. Mater. Sci. Eng., A. 2023, 872, 144999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nei, J.; Young, K.; Regmi, R. et.al. Gaseous phase hydrogen storage and electrochemical properties of Zr8Ni21, Zr7Ni10, Zr9Ni11, and ZrNi metal hydride alloys. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy., 2012, 37, 16042–16055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.F.; Li, J.; Tao, Y.F.; Lv, Y.H. Corrosion behaviors of TiNi/Ti2Ni matrix coatings in the environment rich in Cl ions. Surf. Coat. Technol., 2017, 311, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.K.; Behera, B.; Swain, B. et.al. A review on NiTi alloys for biomedical applications and their biocompatibility. Mater. Today. : Proc., 2020, 33, 5548–5551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, M.A.; Ocana-Pujol, J.L.; Hadian, A. et.al. Filament extrusion-based additive manufacturing of NiTi shape memory alloys. Mater. Des., 2023, 225, 111418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Tan, X.P.; Du, Z. et.al. Additive manufacturing of NiTi shape memory alloys using pre-mixed powders. J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2019, 271, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konovalov, S.; Osintsev, K.; Golubeva, A. et.al. Surface modification of Ti-based alloy by selective laser melting of Ni-based superalloy powder. J. Mater. Res. Technol., 2020, 9, 8796–8807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuzuki, T. Mechanochemical synthesis of nanoparticles. Encyclopedia of Nanomaterials. 2023, 1, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, M.A.; Youness, R.A.; Zawrah, M.F. Review on nanocomposites fabricated by mechanical alloying. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 2019, 26, 1047–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huot, J.; Ravnsbæk,D.B.; Zhang, J. et.al. Mechanochemicalsynthesis of hydrogen storage materials. Progress in Mater. Sci., 2013, 58, 30–75. [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Hu, T. Synthesis of core-shell Ti@Ni-P spherical powder by Ni electroless plating. Micron, 2021, 143, 103027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Sevonkaev, I.; Kumar, A.; Goia, D.V. Strategies for tailoring the properties of chemically precipitated metal powders. Powder Technol., 2014, 261, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, N.; Li, J.; Liang, S.; Sun, H.; Guo, Y. Research on process control of intermittent electrodeposition for preparation of core-shell powder. Powder Technol., 2022, 407, 117632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sure, J.; Vishnu, D.S.M. CarstenSchwandt. Single-step electrochemical synthesis of nano-crystalline CoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy powder. Electrochem. Commun., 2022, 143, 107392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djokić, S.S.; Nikolić, N.D.; Živković, P.M. et.al. Electrodeposition and Electroless Deposition of Metallic Powders: A Comparison. ECS Transactions, 2011, 33, 7–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, N.; Khan, A.M.; Shujait, S. et.al. Synthesis of nanomaterials using various top-down and bottom-up approaches, influencing factors, advantages, and disadvantages: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci., 2022, 300, 102597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Venkateshalu, S.; Jeong, S. et.al. Galvanic replacement reaction to prepare catalytic materials. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc., 2023, 44, 4–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Deng, Y.Y.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, H. Overview of recent developments of resource recovery from wastewater via electrochemistry-based technologies. Sci. Total Environ., 2021, 757, 143901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.N.; McClain, S.M.; House, S.D. et.al. Mechanistic Study of Galvanic Replacement of Chemically Heterogeneous Templates. Chem. Mater., 2019, 31, 1344–1351. [CrossRef]
- Clay, M.; Cui, Q.; Sha, Y. et.al. Galvanic synthesis of bi-modal porous metal nanostructures using aluminum nanoparticle templates. Mater. Lett., 2012, 88, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobley, C.M.; Xia, Y. Engineering the properties of metal nanostructures via galvanic replacement reactions. Mater. Sci. Eng., R., 2010, 70, 44–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carraro, C.; Maboudian, R.; Magagnin, L. Metallization and nanostructuring of semiconductor surfaces by galvanic displacement processes. Surf. Sci. Rep., 2007, 62, 499–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, W.; Goebl, J.; Yin, Y. Self-templated synthesis of hollow nanostructures. Nanotoday, 2009, 4, 494–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvizi, S.; Hashemi, S.M.; Asgarinia, F. et.al. Effective parameters on the final properties of NiTi-based alloys manufactured by powder metallurgy methods: A review. Prog. Mater Sci., 2021, 117, 100739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, L.; Sun, Y. et.al. Influences of Al and Ti particles on microstructure, internal stress and property of Ni composite coatings. J. Alloys Compd., 2019, 793, 314–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhuri, R.G.; Paria, S. Core/shell nanoparticles: classes, properties, synthesis mechanisms, characterization, and applications. Chem. Rev., 2012, 112, 2373–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalugin, L.E.; Dresvyannikov, A.F. Kinetics of contact precipitation of metallic nickel on the surface of dispersed titanium. Butlerov Communications, 2022, 70, 68–75. [Google Scholar]
- Dresvyannikov A.F., Kolpakov M.E., Ermolaeva E.A. Formation of a heterogeneous mixture of metals during the reduction of Ni(II) ions on titanium in aqueous solutions. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. A, 2022, 96, 309-314. 96. [CrossRef]
- Dresvyannikov, A.F.; Kalugin, L.E.; Mironov, M.M. et.al. Influence of Plazma High Frequency Discharge on the Physical and Chemical Properties of Ti-Fe-Ni Dispersed System Obtained by Electrochemical Method. Physics and Chemistry of Materials Treatment, 2022, 15-22. [CrossRef]
- Bogdanov, S.; Sychov, M. Core-Shell Powders with Titanium Coating, In Proceedings of the Recent Advances in Technology Research and Education. Springer, Cham. 2017, 660, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogoda, A.S. Electrochemical behaviour of zirconium and the anodic oxide film in aqueous solutions containing chloride ions. Thin Solid Films., 1999, 357, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prando, D.; Brenna, A.; Diamanti, M. V. D. Corrosion of Titanium: Part 1: Aggressive Environments and Main Forms of Degradation. J. Appl. Biomater. Funct. Mater., 2017, 15, e291–e302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.-L.; , Lu, S.-Y.; Shao, Y. et.al. Segregating the homogeneous passive film and understanding the passivation mechanism ofTi-based metallic glasses. Corros. Sci., 2021, 178, 109078. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).