Submitted:
30 May 2023
Posted:
02 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of levofloxacin mono hydrate (LV1.0)
2.3. Microscopic IR spectroscopy measurements
2.4. Separation of LVODT and LVT formulations by particle size
2.5. Thermal analyses
2.6. PXRD
2.7. Microscopic Raman spectroscopy (conventional and LF)
3. Results and Discussion
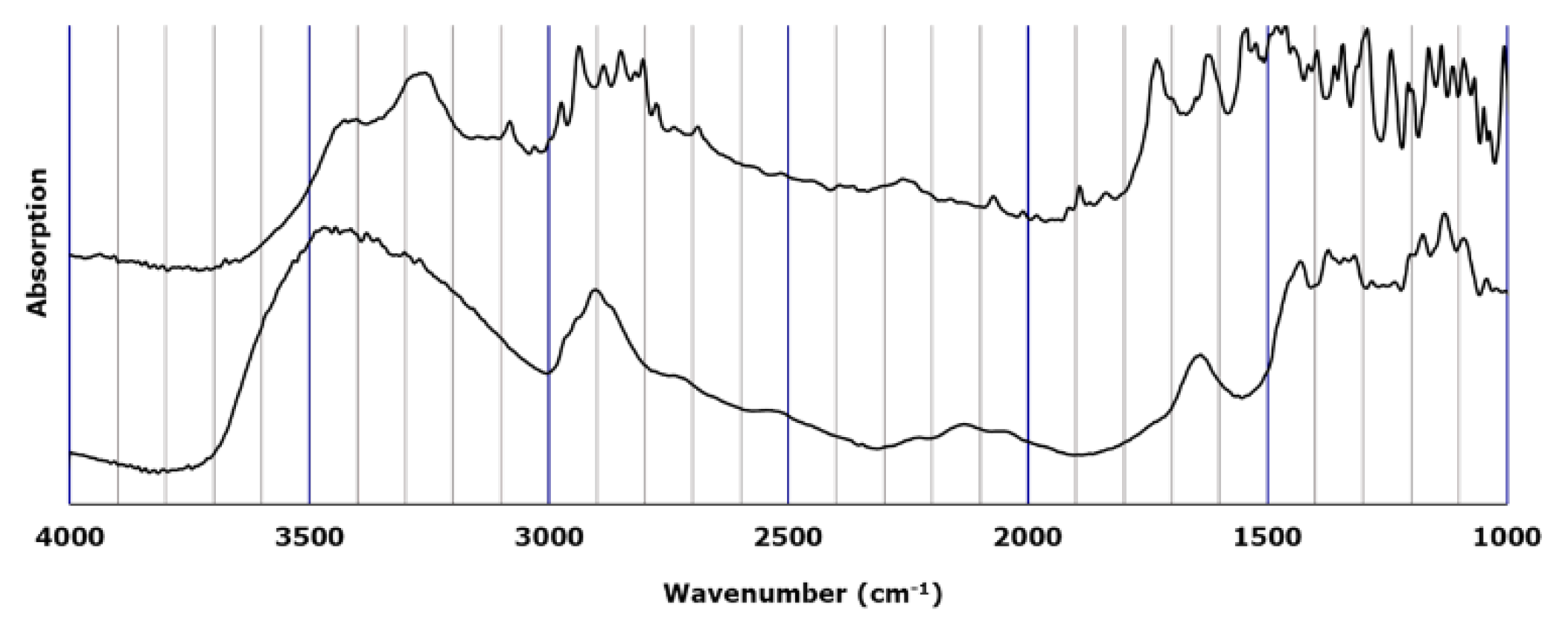
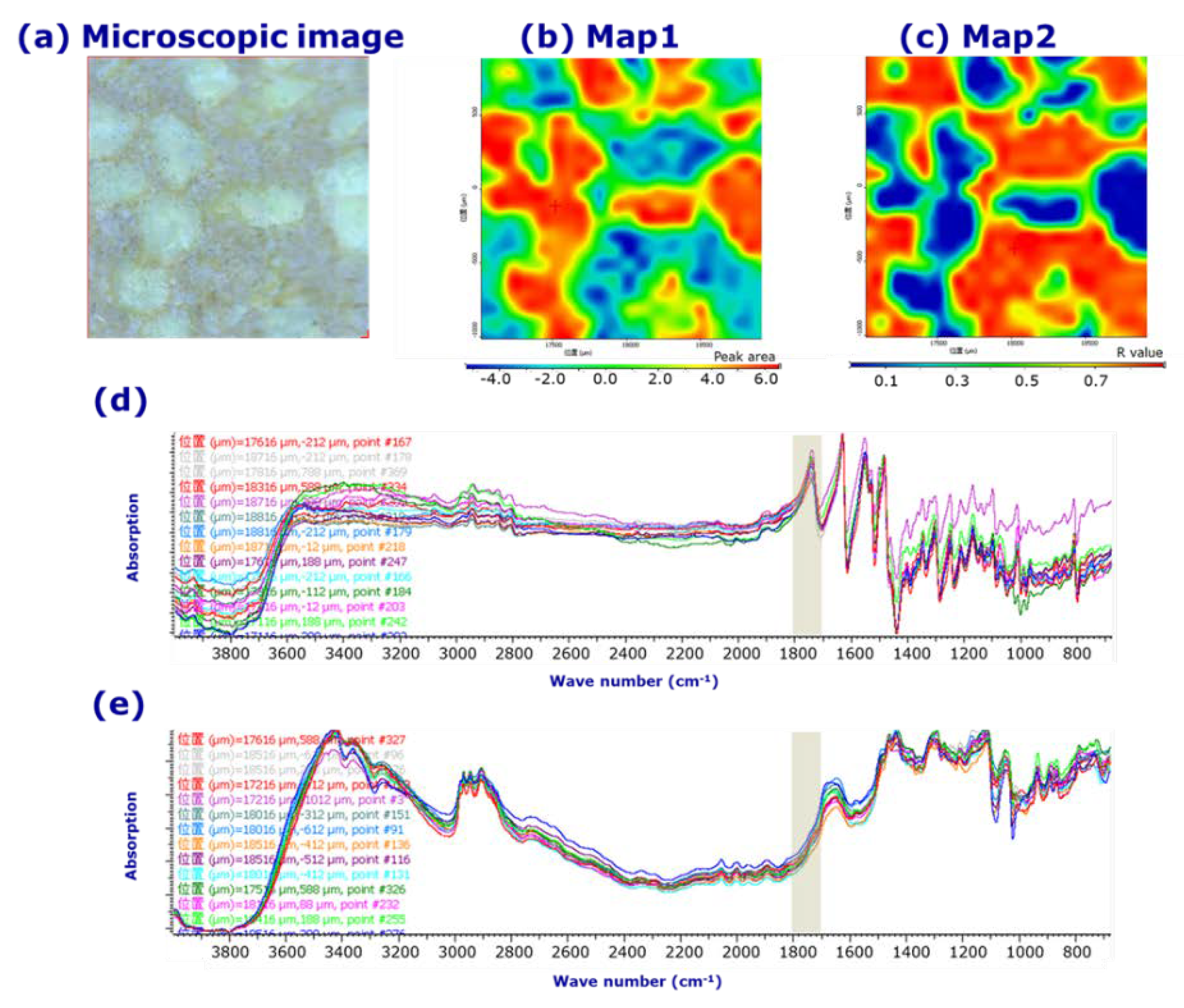
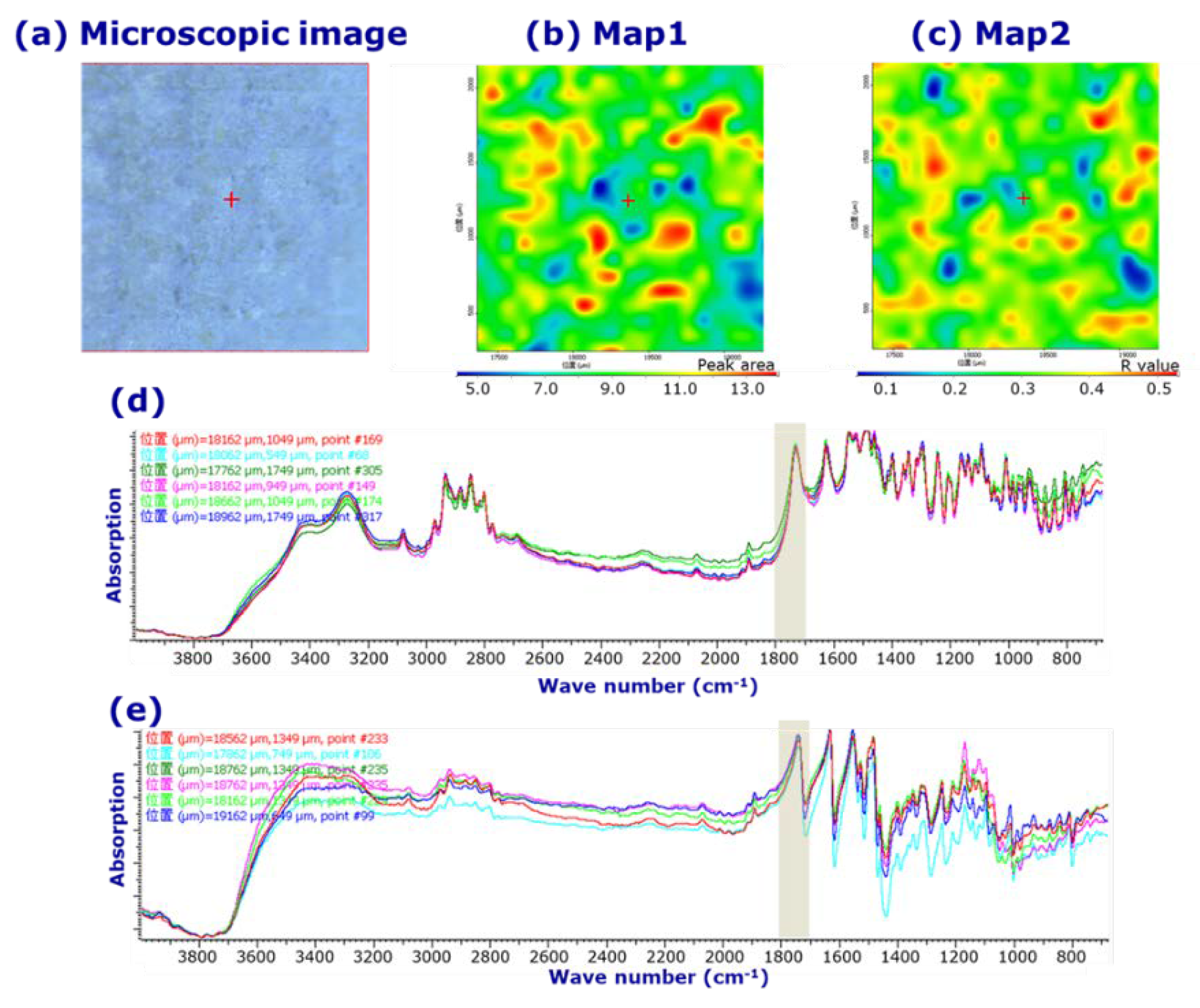
3.1. Visual evaluation of LVODT and LVT formulations by microscopic IR spectroscopy
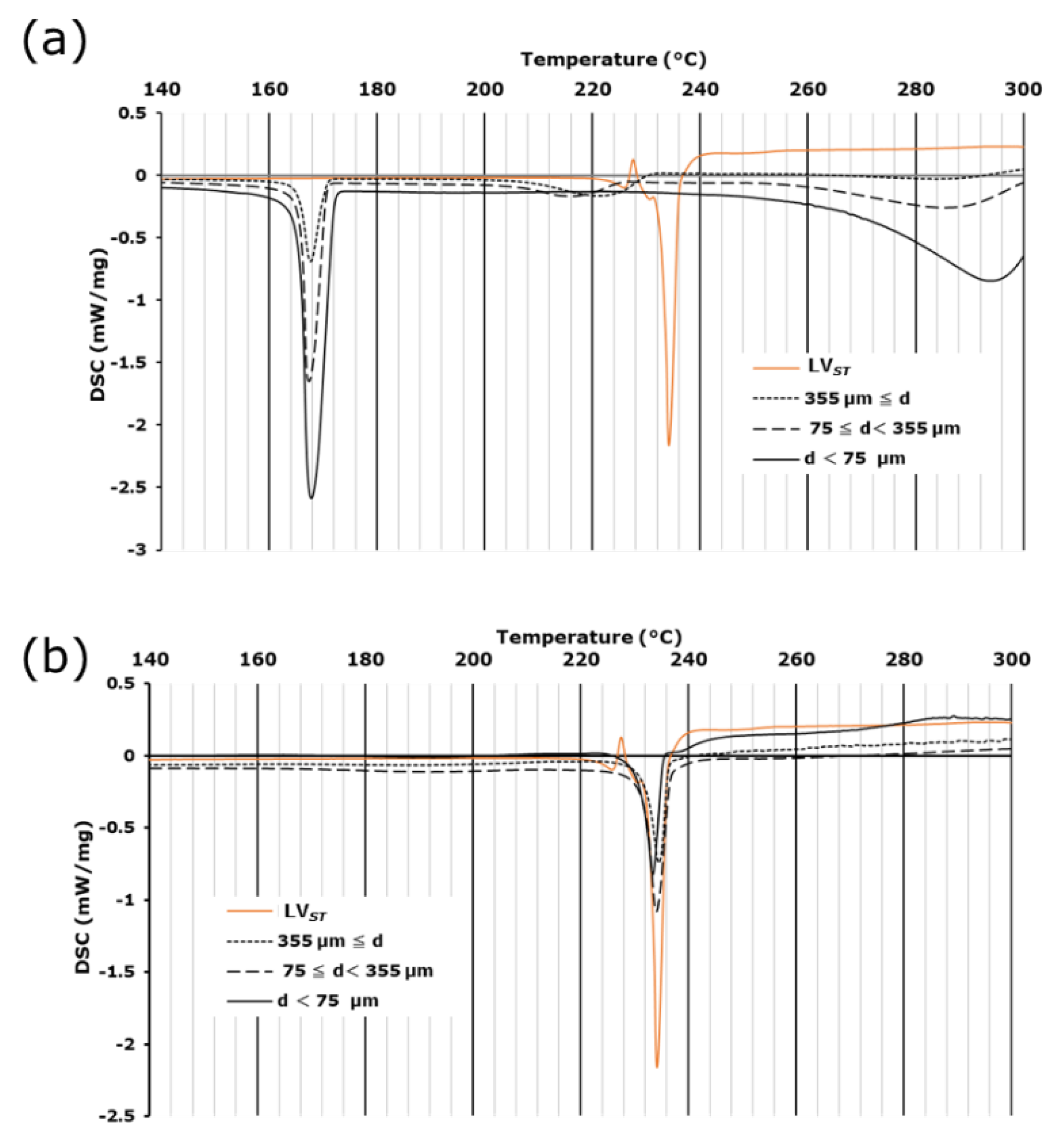
3.2. DSC and TG-DTA measurements in lightly crushed LVODT and LVT formulations
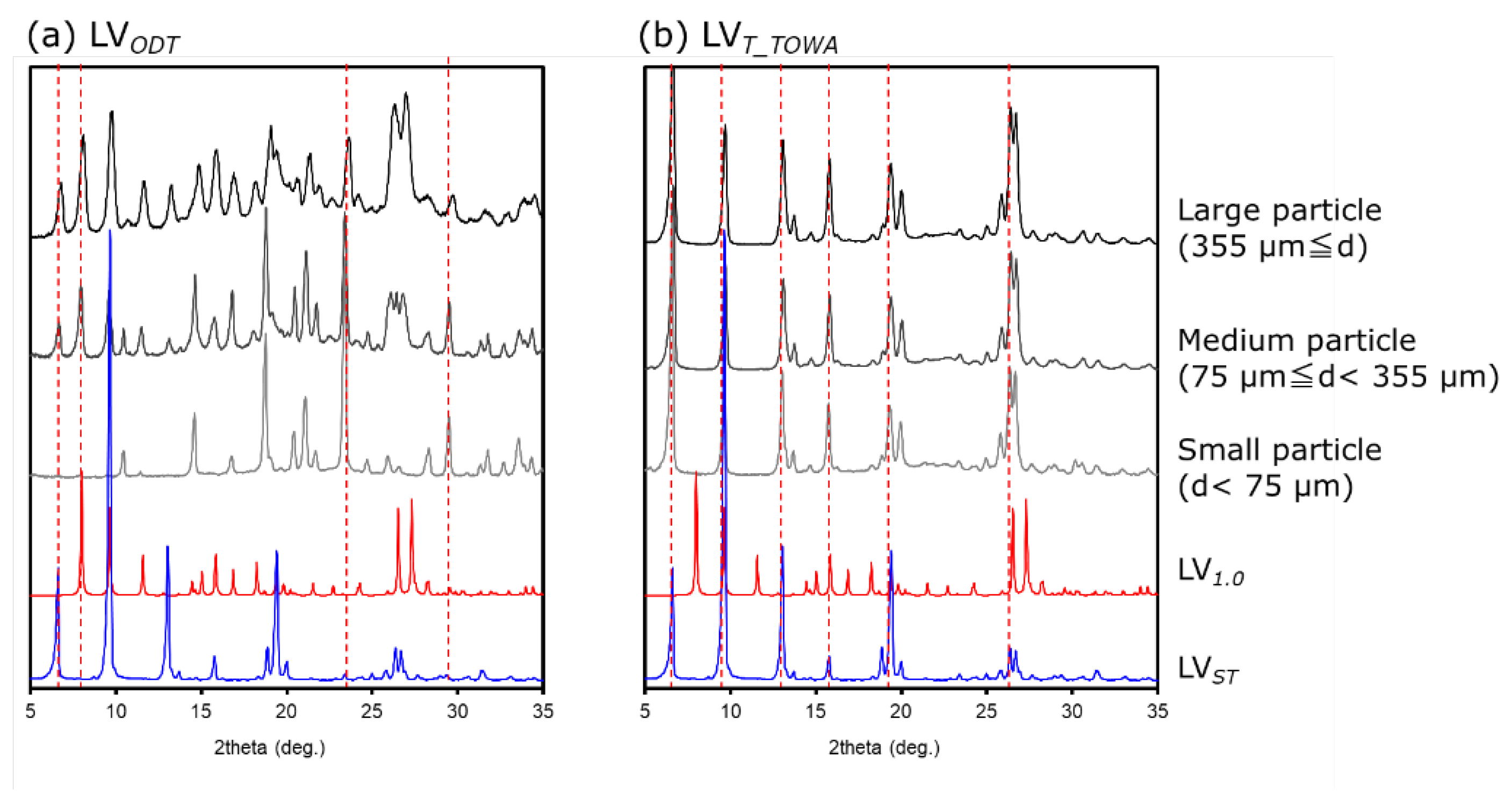
3.3. PXRD of the LVODT and LVT formulations
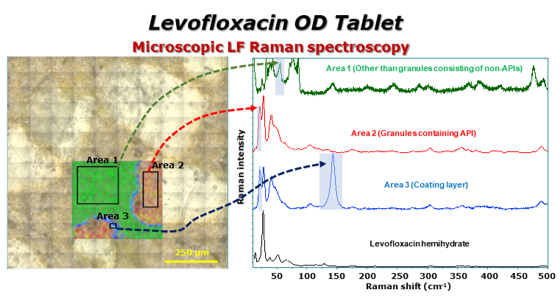
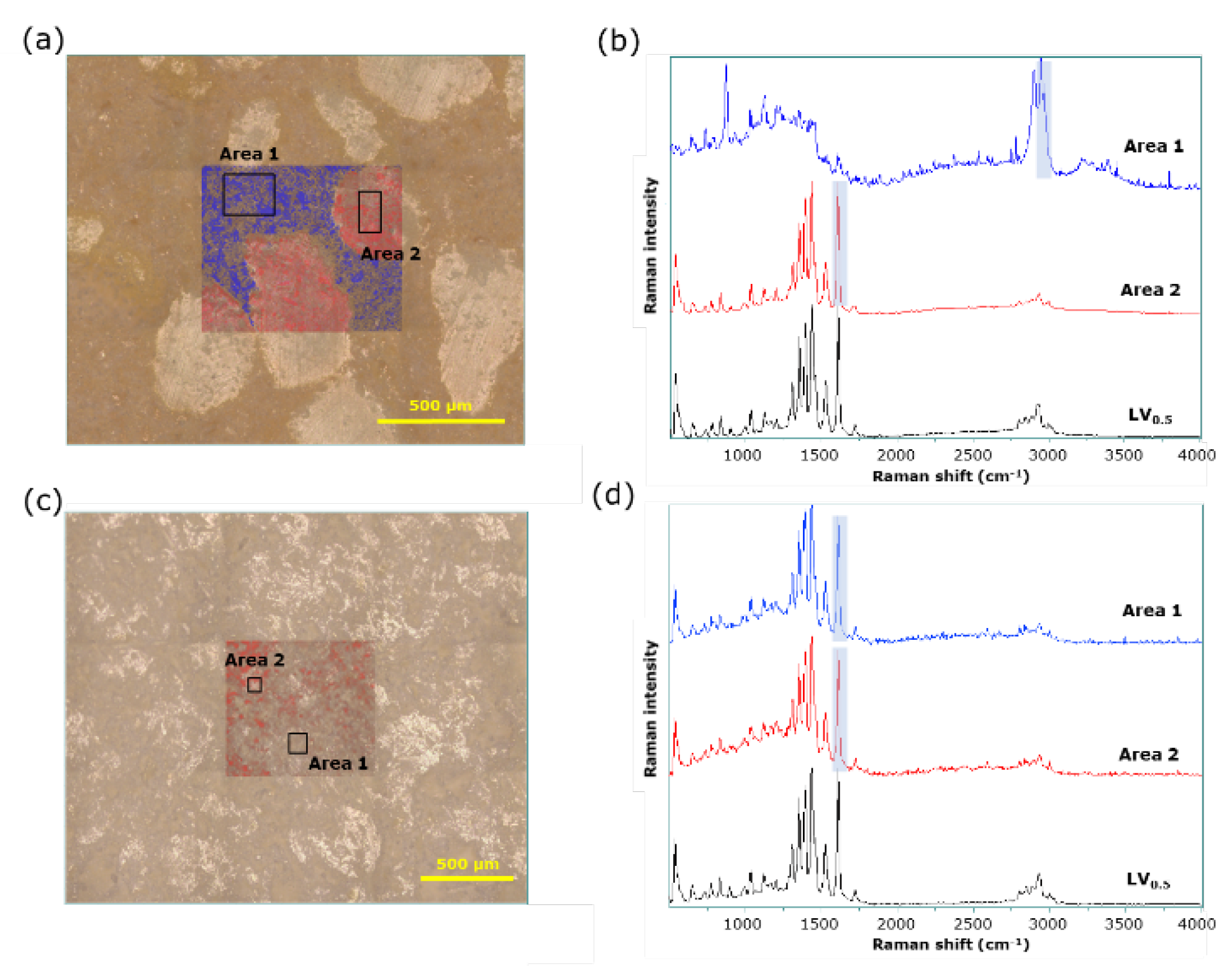
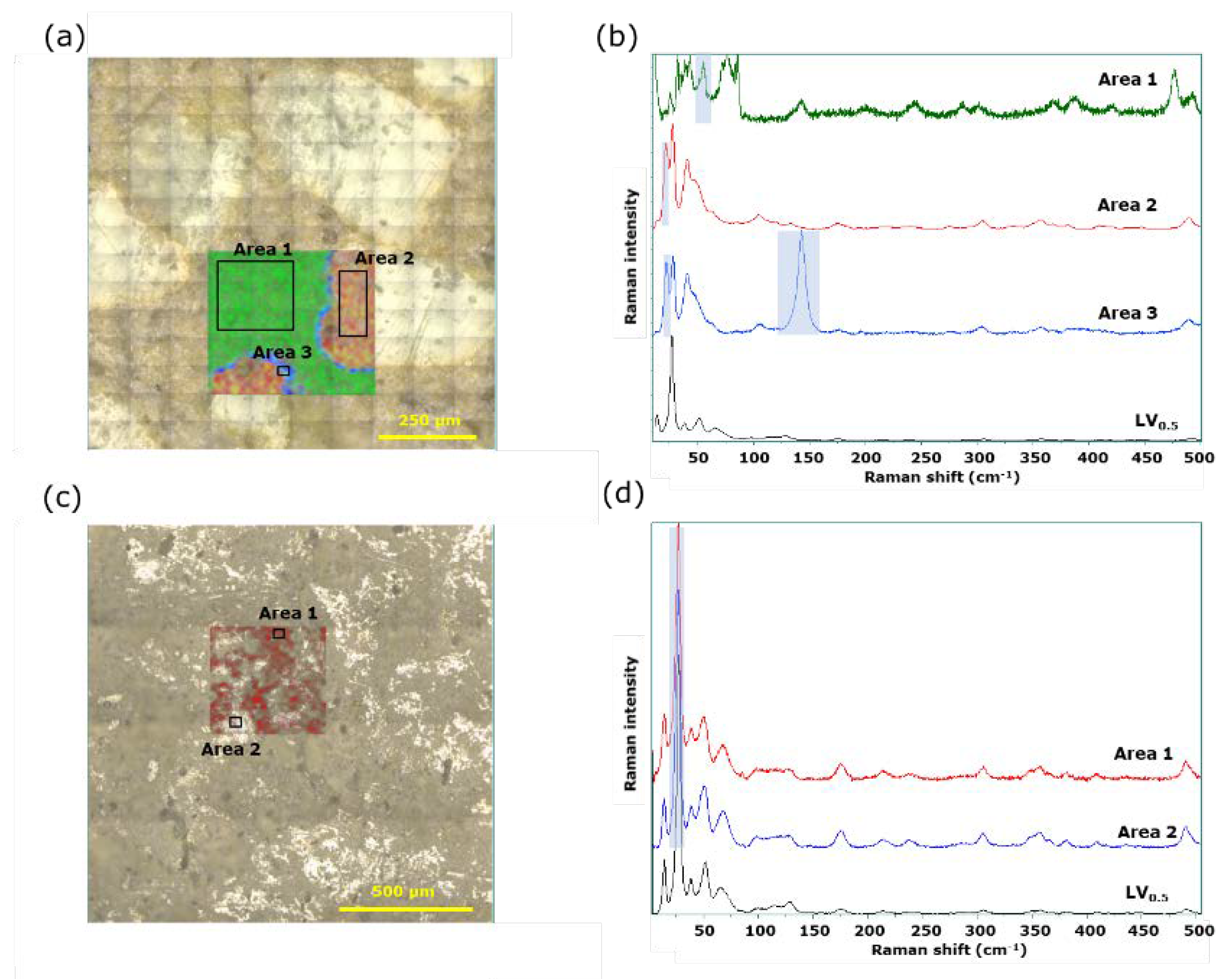
3.4. Visual evaluation of LVODT and LVT formulations by conventional and LF Raman microspectroscopy
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yamamoto, Y.; Fukami, T.; Koide, T.; Suzuki, T.; Hiyama, Y.; Tomono, K. Pharmaceutical evaluation of steroidal ointments by atr-ir chemical imaging: distribution of active and inactive pharmaceutical ingredients. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 426, 54-60. [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Fukami, T.; Koide, T.; Onuki, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Metori, K.; Katori, N.; Hiyama, Y.; Tomono, K. Comparative pharmaceutical evaluation of brand and generic clobetasone butyrate ointments. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 463, 62-67. [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Hanai, A.; Onuki, Y.; Fujii, M.; Onishi, Y.; Fukami, T.; Metori, K.; Suzuki, N.; Suzuki, T.; Koide, T. Mixtures of betamethasone butyrate propionate ointments and heparinoid oil-based cream: physical stability evaluation. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 124, 199-207. [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Ohgi, K.; Onuki, Y.; Fukami, T.; Koide, T. Quality evaluation of humidified magnesium oxide tablet formulations with respect to disintegration time prolongation. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 2023, 71, 165-174. [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, N.; Fukui, K.; Otaka, K.; Suzuki, T.; Fukami, T. Monitoring of cocrystal dissociation during the wet granulation process in the presence of disintegrants by using low-frequency Raman spectroscopy, Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 2021, 69, 877-885. [CrossRef]
- Nomura, K.; Titapiwatanakun, V.; Hisada, H.; Koide, T.; Fukami, T. In situ monitoring of the crystalline state of active pharmaceutical ingredients during high-shear wet granulation using a low-frequency Raman probe. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2020, 147, 1-9. [CrossRef]
- Tanabe, Y.; Maeno, Y.; Ohashi, K.; Hisada, H.; Roy, A.; Carriere, J.; Heyler, R.; Fukami, T. Screening a trace amount of pharmaceutical cocrystals by using an enhanced nano-spot method. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 136, 131-137. [CrossRef]
- Gato, K.; Fujii, M.Y.; Hisada, H.; Carriere, J.; Koide, T.; Fukami, T. Molecular state evaluation of active pharmacetical ingredients in adhesive patches for transdermal drug delivery. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 58, 101800. [CrossRef]
- Interview form of levofloxacin tablet 250 mg “Towa”/tablet 500 mg “Towa”, levofloxacin OD tablet 250 mg “Towa”/OD tablet 500 mg “Towa” and Levofloxacin Oral Solution 250 mg “Towa,” 9th ed. 2019.
- Interview form of CravitⓇ tablet 250 mg / tablet 500 mg and CravitⓇ fine granules 10%, 16th ed. 2019.
- Interview form of levofloxacin tablet 250 mg “Nipro”/tablet 500 mg “Nipro”, 7th ed. 2019.
- Interview form of levofloxacin tablet 250 mg “Sawai”/tablet 500 mg “Sawai”, 5th ed. 2020.
- Sato, Y.; Sato, A.; Sumikawa, T.; Uemura, T. Process for selectively producing an (S)-9-fluolo-3-methyl-10-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-7-oxo-2,3-dihydro-7H-pyrido (1,2,3,-de) (1,4) benzoxazin-6-carboxylic acid hemihydrate or monohydrate. US Patent 5 1996, 545, 737.
| Formulations | Non-APIs* |
|---|---|
| LVODT | MCC**・Carmellose sodium, Hydroxypropyl cellulose, Sucralose, Aminoalkyl methacrylate copolymer E, Talc, Titanium dioxide, Yellow ferric oxide, D-Mannitol, MCC**, Light anhydrous silicic acid, Fragrance, Magnesium stearate, other 3 components |
| LVT_CRAVIT | MCC**, Carmellose, Hydroxypropyl cellulose, Stearyl sodium fumarate, Hypromellose, Titanium dioxide, Talc, Macrogol 6000, Yellow ferric oxide, Carnauba wax |
| LVT_NIPRO | MCC**, Hydroxypropyl cellulose, Carmellose, Stearyl sodium fumarate, Hypromellose, Macrogol, Talc, Titanium dioxide, Yellow ferric oxide, Carnauba wax |
| LVT_SAWAI | Carnauba wax, Carmellose, MCC**, Titanium dioxide, Ferric oxide, Talc, Hydroxypropyl cellulose, Hypromellose, Stearyl sodium fumarate, Macrogol 6000 |
| LVT_TOWA | MCC**, Carmellose, Hydroxypropyl cellulose, Cros-carmellose sodium, Magnesium stearate, Hypromellose, Macrogol 6000, Talc, Titanium dioxide, Yellow ferric oxide |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





