Submitted:
30 May 2023
Posted:
01 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Population and Data Collection
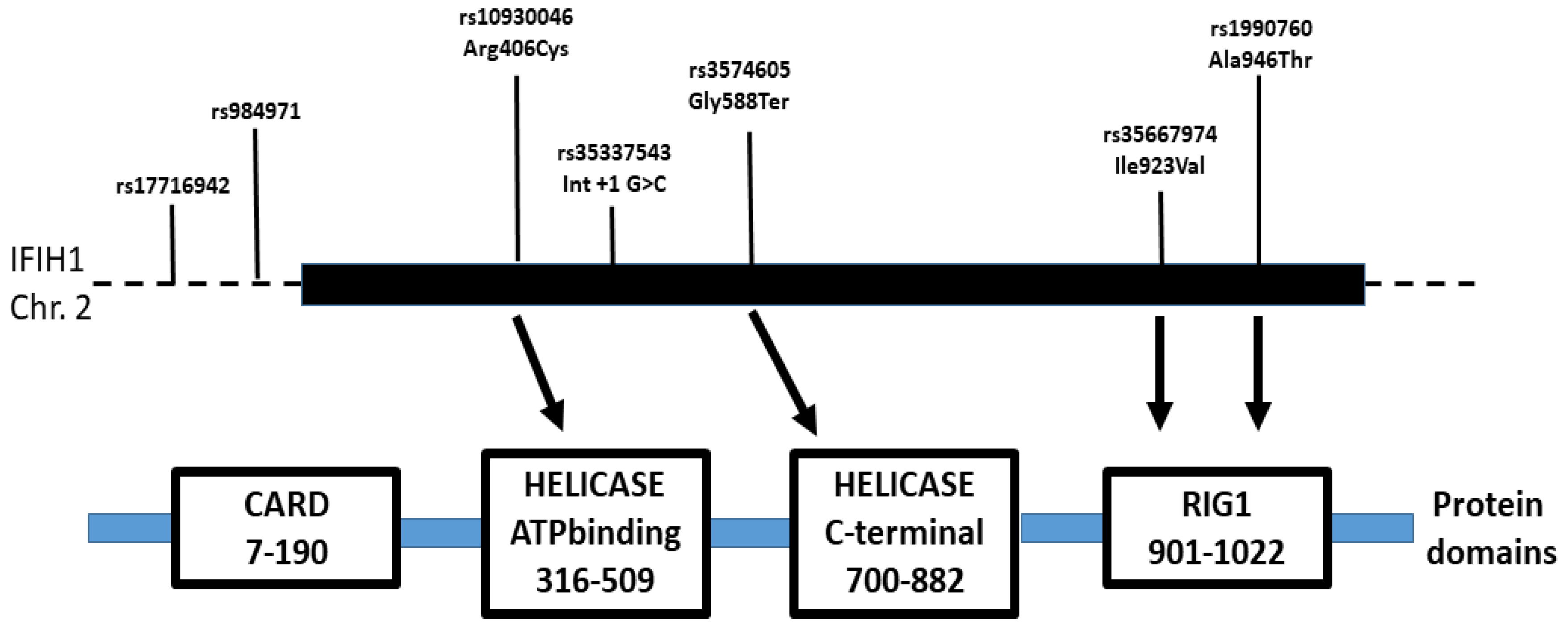
2.2. IFIH1 Variants Genotyping
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Harden JL, Krueger JG, Bowcock AM. The immunogenetics of Psoriasis: A comprehensive review. J Autoimmun. 2015; 64:66-73.
- Oka A, Mabuchi T, Ozawa A, Inoko H. Current understanding of human genetics and genetic analysis of psoriasis. J Dermatol. 2012; 39: 231-41.
- Coto E, Santos-Juanes J, Coto-Segura P, Alvarez V. New psoriasis susceptibility genes: momentum for skin-barrier disruption. J Invest Dermatol. 2011; 131:1003-5.
- Nair RP, Stuart PE, Nistor I, et al. Sequence and haplotype analysis supports HLA-C as the psoriasis susceptibility 1 gene. Am J Hum Genet. 2006; 78:827-51.
- Gudjonsson JE, Karason A, Runarsdottir EH, et al. Distinct clinical differences between HLA-Cw*0602 positive and negativepsoriasis patients--an analysis of 1019 HLA-C- and HLA-B-typed patients.J Invest Dermatol. 2006; 126: 740-5.
- Jordan CT, Cao L, Roberson ED, et al. Rare and common variants in CARD14, encoding an epidermal regulator of NF-kappaB, in psoriasis.Am J Hum Genet. 2012; 90: 796-808.
- Nair RP, Duffin KC, Helms C, et al. Genome-wide scan reveals association of psoriasis with IL-23 and NF-kappaB pathways.NatGenet. 2009; 41: 199-204.
- Nikamo P, Lysell J, Ståhle M. Association with Genetic Variants in the IL-23 and NF-κB Pathways Discriminates between Mild and Severe Psoriasis Skin Disease.J Invest Dermatol. 2015; 135: 1969-76.
- González-Lara L, Coto-Segura P, Penedo A, et al. SNP rs11652075 in the CARD14 gene as a risk factor for psoriasis (PSORS2) in a Spanish cohort.DNA Cell Biol. 2013; 32: 601-4.
- Dias Junior AG, Sampaio NG and Rehwinkel J. A Balancing Act: MDA5 in Antiviral Immunity and Autoinflammation. Trends Microbiol 2019;27(1):75–85;. [CrossRef]
- Sampaio NG, Chauveau L, Hertzog J, Bridgeman A, Fowler G, Moonen JP, et al. The RNA sensor MDA5 detects SARS-CoV-2 infection. Sci Rep. 2021; 11: 13638. PMID: 34211037. [CrossRef]
- Thorne LG, Reuschl AK, Zuliani-Alvarez L, Whelan MVX, Turner J, Noursadeghi M, et al. SARS-CoV-2 sensing by RIG-I and MDA5 links epithelial infection to macrophage inflammation. EMBO J. 2021; 40: e107826. PMID: 34101213. [CrossRef]
- Yin X, Riva L, Pu Y, Martin-Sancho L, Kanamune J, Yamamoto Y, et al. MDA5 governs the Innate Immune Response to SARS-CoV-2 in Lung Epithelial Cells.Cell Rep. 2021; 34: 108628. PMID: 33440148 doi: 0.1016/j.celrep.2020.108628.
- Reikine S, Nguyen JB, Modis Y. Pattern Recognition and Signaling Mechanisms of RIG-I and MDA5. Frontiers in immunology. 2014; 5:342. [PubMed: 25101084].
- Vabret N, Blander JM. Sensing microbial RNA in the cytosol. Frontiers in immunology. 2013; 4:468. [PubMed: 24400006].
- Yao Y, Richman L, Morehouse C, de los Reyes M, Higgs BW, Boutrin A, et al. Type I interferon: potential therapeutic target for psoriasis? PloS one. 2008; 3:e2737. [PubMed: 18648529].
- Van der Fits L, van der Wel LI, Laman JD, Prens EP, Verschuren MC. In psoriasis lesional skin the type I interferon signaling pathway is activated, whereas interferon-alpha sensitivity is unaltered. The Journal of investigative dermatology. 2004; 122:51–60. [PubMed: 14962089].
- Schmid P, Itin P, Cox D, McMaster GK, Horisberger MA. The type I interferon system is locally activated in psoriatic lesions. Journal of interferon research. 1994; 14:229–34. [PubMed: 7861026].
- Kim WK, Jain D, Sánchez MD, Koziol-White CJ, Matthews K, Ge MQ, et al. Deficiency of melanoma differentiation-associated protein 5 results in exacerbated chronic postviral lung inflammation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2014; 189: 437-48. PMID: 24417465. [CrossRef]
- Asgari S, Schlapbach LJ, Anchisi S, Hammer C, Bartha I, Junier T, et al. Severe viral respiratory infections in children with IFIH1 loss-of-function mutations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017; 114: 8342-8347. PMID: 28716935. [CrossRef]
- Lamborn IT, Jing H, Zhang Y, Drutman SB, Abbott JK, Munir S, et al. Recurrent rhinovirus infections in a child with inherited MDA5 deficiency. J Exp Med. 2017; 214: 1949-1972. PMID: 28606988. [CrossRef]
- Rebendenne A, Valadão ALC, Tauziet M, Maarifi G, Bonaventure B, McKellar J, et al. SARS-CoV-2 Triggers an MDA-5-Dependent Interferon Response Which Is Unable to Control Replication in Lung Epithelial Cells. J Virol 2021; 95: e02415-20. PMID: 33514628. [CrossRef]
- Amado-Rodríguez L, Salgado Del Riego E, Gomez de Ona J, López Alonso I, Gil-Pena H, López-Martínez C, et al. Effects of IFIH1 Rs1990760 Variants on Systemic Inflammation and Outcome in Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients in an Observational Translational Study. Elife 2022; 11: e73012; PMID: 35060899. [CrossRef]
- Rice GI, Del Toro Duany Y, Jenkinson EM, Forte GM, Anderson BH, Ariaudo G, et al. Gain-of-function mutations in IFIH1 cause a spectrum of human disease phenotypes associated with upregulated type I interferon signaling. Nat Genet. 2014; 46: 503-509. PMID: 24686847. [CrossRef]
- Rice GI, Park S, Gavazzi F, Adang LA, Ayuk LA, Van Eyck L, et al. Genetic and phenotypic spectrum associated with IFIH1 gain-of-function. Hum Mutat. 2020; 41: 837-849. PMID: 31898846. [CrossRef]
- TonuttiA, Motta F, Ceribelli A, Isailovic N, Selmi C, De Santis M. Anti-MDA5 Antibody Linking COVID-19, Type I Interferon, and Autoimmunity: A Case Report and Systematic Literature Review. Front Immunol. 2022; 13: 937667. PMID: 35833112. [CrossRef]
- Kitamura H, Matsuzaki Y, Kimura K, Nakano H, Imaizumi T, Satoh K, et al. Cytokine modulation of retinoic acid-inducible gene-I (RIG-I) expression in human epidermal keratinocytes. Journal of dermatological science. 2007; 45:127–34. [PubMed: 17182220].
- Prens EP, Kant M, van Dijk G, van der Wel LI, Mourits S, van der Fits L. IFN-alpha enhances poly-IC responses in human keratinocytes by inducing expression of cytosolic innate RNA receptors: relevance for psoriasis. The Journal of investigative dermatology. 2008; 128:932–8. [PubMed: 17928888].
- Racz E, Prens EP, Kant M, Florencia E, Jaspers NG, Laman JD, et al. Narrowband ultraviolet B inhibits innate cytosolic double-stranded RNA receptors in psoriatic skin and keratinocytes. The British journal of dermatology. 2011; 164:838–47. [PubMed: 21143460].
- Li Y, Liao W, Cargill M, Chang M, Matsunami N, Feng BJ, et al. Carriers of rare missense variants in IFIH1 are protected from psoriasis. The Journal of investigative dermatology. 2010; 130:2768–72. [PubMed: 20668468].
- Bijlmakers MJ, Kanneganti SK, Barker JN, Trembath RC, Capon F. Functional analysis of the RNF114 psoriasis susceptibility gene implicates innate immune responses to double-stranded RNA in disease pathogenesis. Hum Mol Genet. 2011; 20:3129–37. [PubMed: 21571784].
- Liu S, Wang H, Jin Y, et al. IFIH1 Polymorphisms Are Significantly Associated with Type 1 Diabetes and IFIH1 Gene Expression in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells. Hum Mol Genet 2009; 18:358–365;. [CrossRef]
- Cen H, Wang W, Leng R-X, et al. Association of IFIH1 Rs1990760 Polymorphism with Susceptibility to Autoimmune Diseases: A Meta-Analysis. Autoimmunity 2013; 46:455–462;. [CrossRef]
- Gorman JA, Hundhausen C, Errett JS, et al. The A946T Variant of the RNA Sensor IFIH1 Mediates an Interferon Program That Limits Viral Infection but Increases the Risk for Autoimmunity. Nat Immunol 2017;18:744–752;. [CrossRef]
- Borysewicz-SańczykH, Sawicka B, Wawrusiewicz-Kurylonek N, Głowińska-Olszewska B, Kadłubiska A, Gościk J, et al. Genetic Association Study of IL2RA, IFIH1, and CTLA-4 Polymorphisms with Autoimmune Thyroid Diseases and Type 1 Diabetes. Front Pediatr. 2020 Aug 21; 8:481. [CrossRef]
- Shapiro MR, Thirawatananond P, Peters L, et al. De-Coding Genetic Risk Variants in Type 1 Diabetes. Immunol Cell Biol 2021; 99:496–508;. [CrossRef]
- FunabikiM, Kato H, Miyachi Y, Toki H, Motegi H, Inoue M, et al. Autoimmune disorders associated with gain of function of the intracellular sensor MDA5. Immunity. 2014; 40: 199-212. PMID: 24530055. [CrossRef]
- BammingD, Horvath CM. Regulation of signal transduction by enzymatically inactive antiviral RNA helicase proteins MDA5, RIG-I, and LGP2. J Biol Chem. 2009; 284: 9700–12. PMID: 19211564. [CrossRef]
- Chistiakov DA, Voronova NV, Savost'Anov KV, TurakulovRI. Loss-of-Function Mutations E6 27X and I923V of IFIH1 Are Associated with Lower Poly(I:C)–Induced Interferon-β Production in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells of Type 1 Diabetes Patients. Human Immunology 2010; 71: 1128–34; PMID: 20736039. [CrossRef]
- DownesK, Pekalski M, Angus KL, Hardy M, Nutland S, Smyth DJ, et al. Reduced expression of IFIH1 is protective for type 1 diabetes. PLoS One. 2010; 5: e12646. PMID: 20844740. [CrossRef]
- Forbester JL and Humphreys IR. Genetic Influences on Viral-Induced Cytokine Responses in the Lung. Mucosal Immunol 2021; 14: 14–25;. [CrossRef]
- Nejentsev S, Walker N, Riches D, Egholm M, Todd JA. Rare Variants of IFIH1, a Gene Implicated in Antiviral Responses, Protect against Type 1 Diabetes. Science 2009; 324: 387–9; PMID: 19264985. [CrossRef]
- Mine K, Yoshikai Y, Takahashi H, Mori H, Anzai K, NagafuchiS. Genetic Susceptibility of the Host in Virus-Induced Diabetes. Microorganisms 2020; 8: E1133; PMID: 32727064. [CrossRef]
- Hébert HL, Bowes J, Smith RL, Flynn E, Parslew R, Alsharqi A, McHugh NJ, Barker JN, Griffiths CE, Barton A, Warren RB. Identification of loci associated with late-onset psoriasis using dense genotyping of immune-related regions. Br J Dermatol. 2015 Apr;172(4):933-9. Epub 2015 Feb 5. PMID: 25124732. [CrossRef]
- Stuart PE, Nair RP, Tsoi LC, et al. Genome-wide Association Analysis of Psoriatic Arthritis and Cutaneous Psoriasis Reveals Differences in Their Genetic Architecture. Am J Hum Genet. 2015; 97:816-36.
- Tsoi LC, Spain SL, Knight J, Ellinghaus E, Stuart PE, Capon F, et al. Identification of 15 new psoriasis susceptibility loci highlights the role of innate immunity. Nat Genet. 2012 Dec;44(12):1341-8. Epub 2012 Nov 11. PMID: 23143594. [CrossRef]
- Strange A, Capon F, Spencer CC, Knight J, Weale ME, Allen MH, et al A genome-wide association study identifies new psoriasis susceptibility loci and an interaction between HLA-C and ERAP1. Nat Genet. 2010 Nov;42(11):985-90. Epub 2010 Oct 17.PMID: 20953190. [CrossRef]
- Patrick MT, Stuart PE, Raja K, Gudjonsson JE, Tejasvi T, Yang J, Chandran V, Das S, Callis-Duffin K, Ellinghaus E, Enerbäck C, Esko T, Franke A, Kang HM, Krueger GG, Lim HW, Rahman P, Rosen CF, Weidinger S, Weichenthal M, Wen X, Voorhees JJ, Abecasis GR, Gladman DD, Nair RP, Elder JT, Tsoi LC. Genetic signature to provide robust risk assessment of psoriatic arthritis development in psoriasis patients. Nat Commun. 2018 Oct 9;9(1):4178. PMID: 30301895. [CrossRef]
- Tazi Ahnini R, Camp NJ, Cork MJ, et al. Novel genetic association between the corneodesmosin (MHC S) gene and susceptibility to psoriasis. Hum Mol Genet. 1999; 8: 1135-40.
- Gladman DD, C. Antoni, P. Mease, D. O. Clegg, and P. Nash, “Discussion: clinical features, epidemiology, classification criteria, and quality of life in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis,” Ann Rheum Dis, vol. 64, no. 2, pp. ii24-ii25, 2005.
- Pang L, Gong X, Liu N, Xie G, Gao W, Kong G, Li X, Zhang J, Jin Y, Duan Z. A polymorphism in melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 may be a risk factor for enterovirus 71 infection. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2014 Oct;20(10): O711-7. Epub 2014 Apr 10.PMID: 24621100. [CrossRef]
- Yao Y, Shen Y, Shao H, Liu Y, Ji Y, Du G, Ye X, Huang P, Chen H. Polymorphisms of RIG-I-like receptor influence HBV clearance in Chinese Han population.J Med Virol. 2021 Aug;93(8):4957-4965. Epub 2021 Apr 3. PMID: 33783003. [CrossRef]
- Domsgen E, Lind K, Kong L, Hühn MH, Rasool O, van Kuppeveld F, Korsgren O, Lahesmaa R, Flodström-Tullberg M.An IFIH1 gene polymorphism associated with risk for autoimmunity regulates canonical antiviral defence pathways in Coxsackievirus infected human pancreatic islets. Sci Rep. 2016 Dec 21;6:39378. PMID: 28000722. [CrossRef]
- Dou Y, Yim HC, Kirkwood CD, Williams BR, Sadler AJ.The innate immune receptor MDA5 limits rotavirus infection but promotes cell death and pancreatic inflammation. EMBO J. 2017 Sep 15;36(18):2742-2757. Epub 2017 Aug 29. PMID: 28851763. [CrossRef]
- Dieter C, de Almeida Brondani L, Lemos NE, Schaeffer AF, Zanotto C, Ramos DT, Girardi E, Pellenz FM, Camargo JL, Moresco KS, da Silva LL, Aubin MR, de Oliveira MS, Rech TH, Canani LH, Gerchman F, Leitão CB, Crispim D. Polymorphisms in ACE1, TMPRSS2, IFIH1, IFNAR2, and TYK2 Genes Are Associated with Worse Clinical Outcomes in COVID-19. Genes (Basel). 2022 Dec 22;14(1):29. PMID: 36672770. [CrossRef]
- Nln I, Fernandez-Ruiz R, Muskardin TLW, Paredes JL, Blazer AD, Tuminello S, Attur M, Iturrate E, Petrilli CM, Abramson SB, Chakravarti A, Niewold TB. Interferon pathway lupus risk alleles modulate risk of death from acute COVID-19. Transl Res. 2022 Jun;244:47-55. Epub 2022 Jan 31. PMID: 35114420. [CrossRef]
- Muñiz-Banciella MG, Albaiceta GM, Amado-Rodríguez L, Del Riego ES, Alonso IL, López-Martínez C, Martín-Vicente P, García-Clemente M, Hermida-Valverde T, Enríquez-Rodriguez AI, Hernández-González C, Cuesta-Llavona E, Alvarez V, Gómez J, Coto E. Age-dependent effect of the IFIH1/MDA5 gene variants on the risk of critical COVID-19. Immunogenetics. 2023 Apr;75(2):91-98. Epub 2022 Nov 25. PMID: 36434151. [CrossRef]
- Zurawek M, Fichna M, Fichna P, Skowronska B, Dzikiewicz-Krawczyk A, et al. Cumulative effect of IFIH1 variants and increased gene expression associated with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2015; 107: 259-66. PMID: 25515714. [CrossRef]
- Baldwin HM, Pallas K, King V, Jamieson T, McKimmie CS, Nibbs RJ, et al. Microarray analyses demonstrate the involvement of type I interferons in psoriasiform pathology development in D6-deficient mice. J Biol Chem. (2013) 288:36473–83. [CrossRef]
- Nestle FO, Conrad C, Tun-Kyi A, Homey B, Gombert M, Boyman O, et al. Plasmacytoid predendritic cells initiate psoriasis through interferon-alpha production. J Exp Med. (2005) 202:135–43. [CrossRef]
- Gregorio J, Meller S, Conrad C, Di Nardo A, Homey B, Lauerma A, et al.. Plasmacytoid dendritic cells sense skin injury and promote wound healing through type I interferons. J Exp Med. (2010) 207:2921–30. [CrossRef]
- Lu Y, Kane S, Chen H, Leon A, Levin E, Nguyen T, Debbaneh M, Millsop JW, Gupta R, Huynh M, Butler D, Cordoro K, Liao W.The role of 39 psoriasis risk variants on age of psoriasis onset. ISRN Dermatol. 2013 Sep 23; 2013:203941. eCollection 2013.PMID: 24175098. [CrossRef]
- Reich K, Mössner R, König IR, Westphal G, Ziegler A, Neumann C. Promoter polymorphisms of the genes encoding tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-1beta are associated with different subtypes of psoriasis characterized by early and late disease onset. J Invest Dermatol. 2002 Jan;118(1):155-63. PMID: 11851889. [CrossRef]
- Zhang C, Qin Q, Li Y, Zheng X, Chen W, Zhen Q, Li B, Wang W, Sun L.Multifactor dimensionality reduction reveals the effect of interaction between ERAP1 and IFIH1 polymorphisms in psoriasis susceptibility genes. Front Genet. 2022 Nov 8;13:1009589. eCollection 2022.PMID: 36425068. [CrossRef]
- Budu-Aggrey A, Bowes J, Stuart PE, Zawistowski M, Tsoi LC, Nair R, Jadon DR, McHugh N, Korendowych E, Elder JT, Barton A, Raychaudhuri S.A rare coding allele in IFIH1 is protective for psoriatic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017 Jul;76(7):1321-1324. Epub 2017 May 13.PMID: 28501801. [CrossRef]
- Bowes J, Budu-Aggrey A, Huffmeier U, Uebe S, Steel K, Hebert HL, Wallace C, Massey J, Bruce IN, Bluett J, Feletar M, Morgan AW, Marzo-Ortega H, Donohoe G, Morris DW, Helliwell P, Ryan AW, Kane D, Warren RB, Korendowych E, Alenius GM, Giardina E, Packham J, McManus R, FitzGerald O, McHugh N, Brown MA, Ho P, Behrens F, Burkhardt H, Reis A, Barton A. Dense genotyping of immune-related susceptibility loci reveals new insights into the genetics of psoriatic arthritis. Nat Commun. 2015 Feb 5;6:6046. PMID: 25651891. [CrossRef]
- Julià A, Tortosa R, Hernanz JM, Cañete JD, Fonseca E, Ferrándiz C,.Risk variants for psoriasis vulgaris in a large case-control collection and association with clinical subphenotypes. Hum Mol Genet. 2012 Oct 15;21(20):4549-57. Epub 2012 Jul 19.PMID: 22814393. [CrossRef]
- Shigemoto T, Kageyama M, Hirai R, Zheng J, Yoneyama M, Fujita T. Identification of loss of function mutations in human genes encoding RIG-I and MDA5: implications for resistance to type I diabetes. J Biol Chem. 2009 May 15;284(20):13348-13354. Epub 2009 Mar 26.PMID: 19324880. [CrossRef]
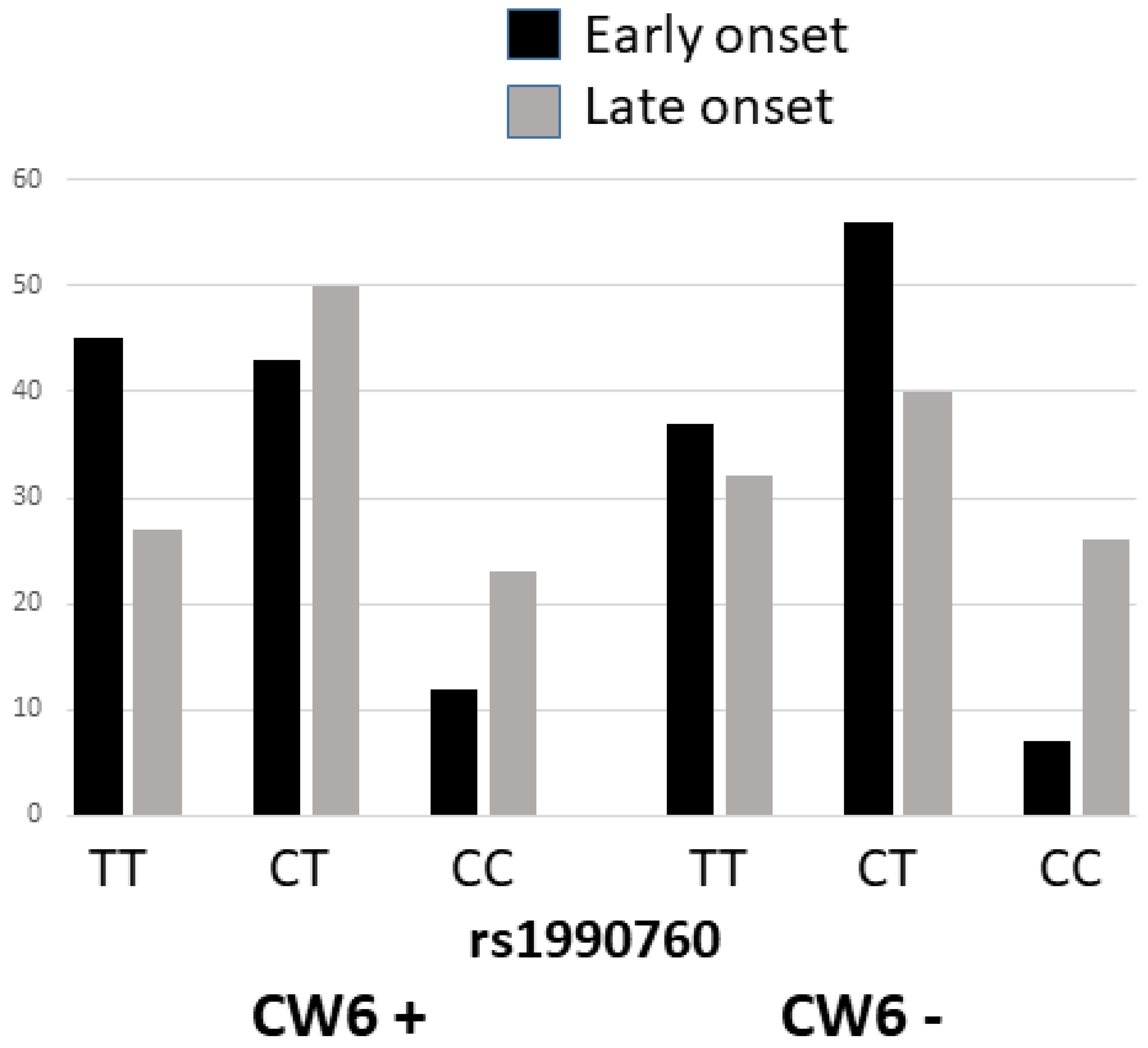
| Early Onset N=440 |
Late Onset N=132 |
p-Value Univariate |
OR (95%CI) Multivariate |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | 232 (53%) | 77 (58%) | 0.26 | ||
| Female | 208 (47%) | 55 (42%) | 1.24 (0.81-1.90) | ||
| Onset Age range | 18-40 | 41-78 | |||
| Median PASI (range) | 11 (1-75) | 6.1 (4.1-7.2) | |||
| Severe (PASI>10) | 248 (56%) | 46 (35%) | <0.001 | 2.35 (1.52-3.66) | |
| Arthritis yes | 139 (32%) | 32 (24%) | 0.11 | 1.22 (0.76-2.01) | |
| Cw6 positive | 211 (48%) | 30 (23%) | <0.001 | 3.25 (2.05-5.29) | |
|
rs1990760 C>T * (Ala946Thr) |
|||||
| TT | 179 (41%) | 40 (30%) |
<0.001 |
4.07 (2.37-7.04) |
|
| CT | 220 (50%) | 56 (42%) | |||
| CC | 41 (9%) | 36 (27%) | |||
| ALLELE T (946Thr) Eur: T=0.60-0.64 |
0.66 | 0.52 | |||
|
rs35337543 int8 +1G>C |
|||||
| GG | 430 (98%) | 128 (97%) | 0.62 | 1.12 (0.29-3.65) | |
| GC | 10 (2%) | 4 (3%) | |||
| ALLELE C Eur: C=0.02 |
0.01 | 0.02 | |||
|
rs35744605 G>T (Glu627Stop) |
|||||
| GG | 432 (98%) | 129 (98%) | 0.74 | 1.11 (0.23.4.10) | |
| GT | 8 (2%) | 3 (2%) | |||
| ALLELE T Eur: T=0.01 |
0.01 | 0.01 | |||
| Arthritis Yes 171 |
Arthritis No 401 |
p-Value | OR (95%CI) Multivariate |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | 81 | 228 |
0.04 |
|
| Female | 90 (52%) | 173 (43%) | 1.63 (1.12-2.38) | |
| Early onset psoriasis | 139 (81%) | 301 (75%) | 0.11 | 1.29 (0.81-2.09) |
| Severe (PASI≥10) | 110 (64%) | 184 (46%) | <0.001 | 2.14 (1.46-3.16) |
| Cw6 positive | 65 (38%) | 176 (44%) | 0.19 | 0.65 (0.44-0.95) |
|
rs1990760C>T * (Ala946Thr) |
||||
| TT | 80 (47%) | 139 (35%) | 0.006 | 1.62 (1.11-2.37) |
| CT | 73 (43%) | 203 (51%) | ||
| CC | 18 (11%) | 59 (15%) | ||
| Allele C | 0.32 | 0.40 | ||
|
rs35337543 int8 +1G>C |
||||
| GG | 169 (99%) | 389 (97%) | 0.20 | 3.04 (0.77-20.36) |
| GC | 2 (1%) | 12 (3%) | ||
|
rs35744605 G>T (Glu627Stop) |
||||
| GG | 168 (98%) | 393 (98%) | 0.85 | 1.23 (0.32-6.04) |
| GT | 3 (2%) | 8 (2%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





