Submitted:
31 May 2023
Posted:
31 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Algae Extract Preparation and Identification of Compounds
2.3. Cell Culturing
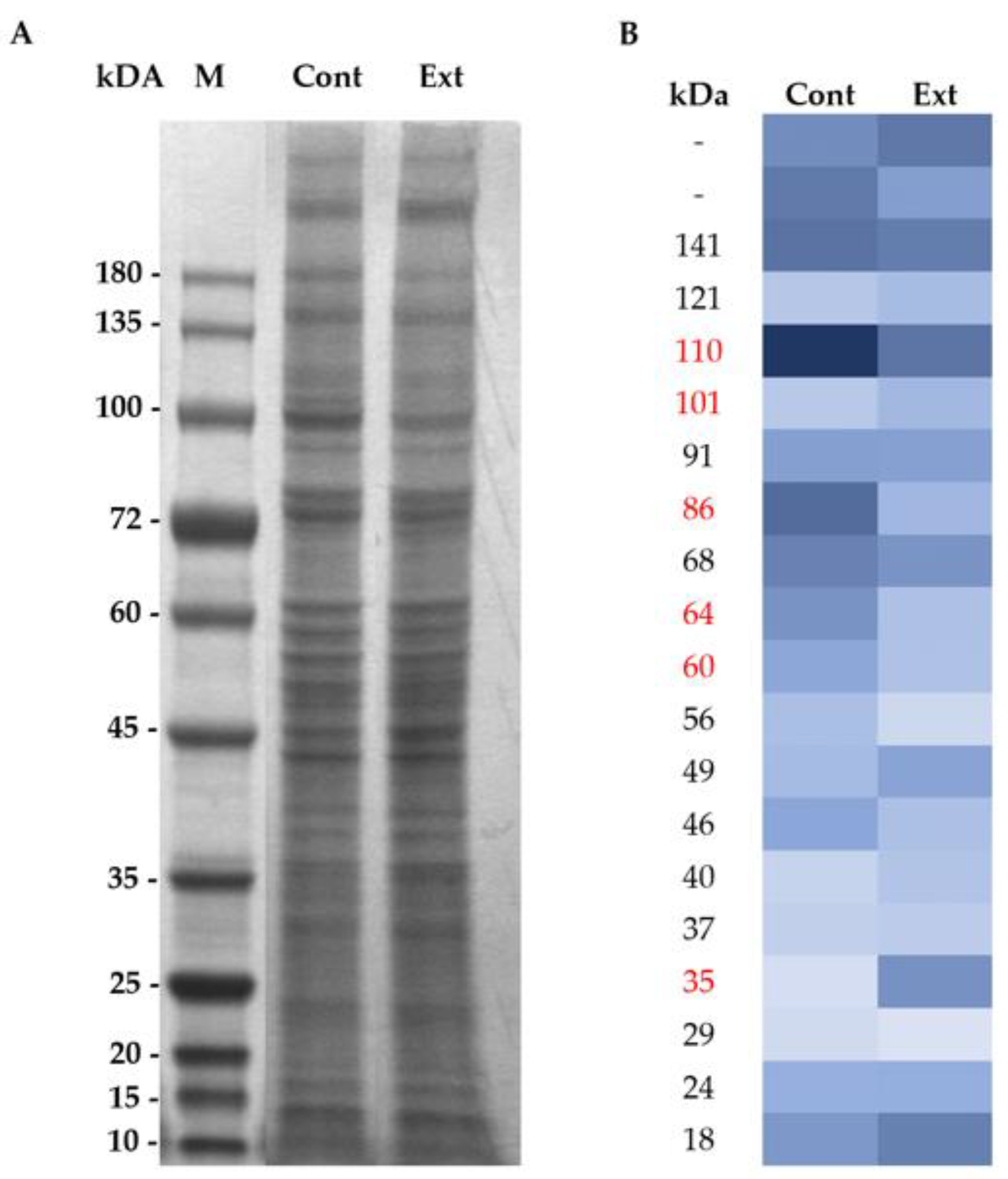
2.4. Membrane Protein Extraction and SDS-PAGE Electrophoresis
2.5. In-Gel Protein Digestion, Nano-LC−ESI−MS/MS and DataAnalysis
2.6. Western Blot Analysis
2.7. Real Time Quantitative PCR
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
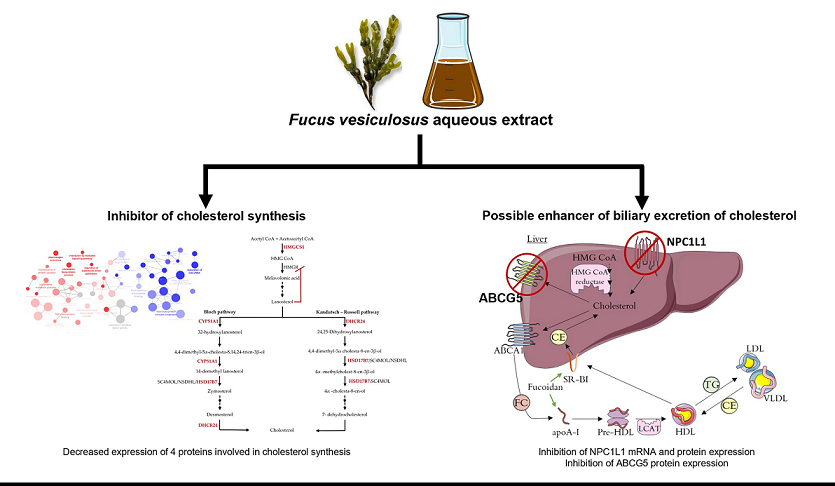
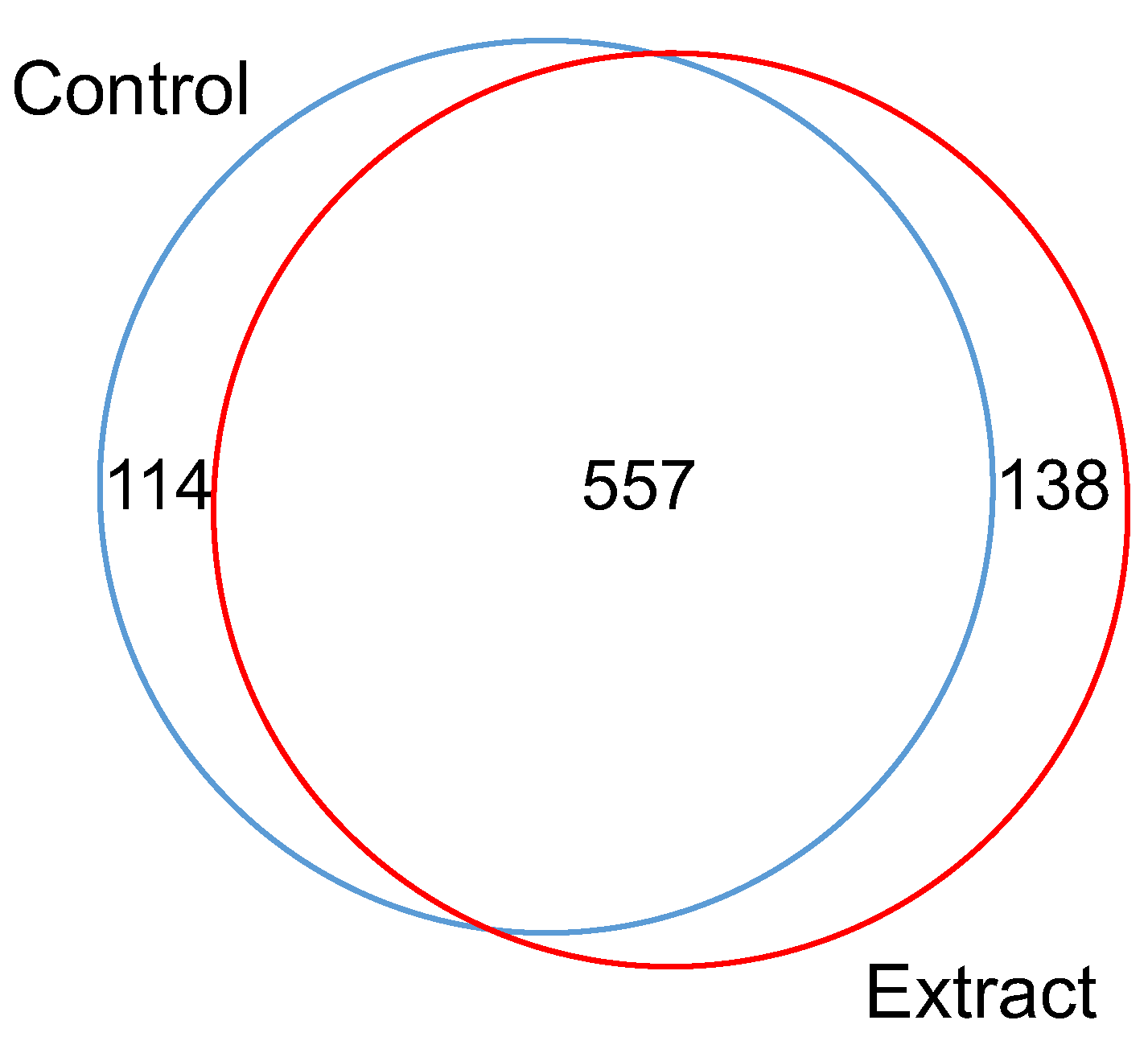
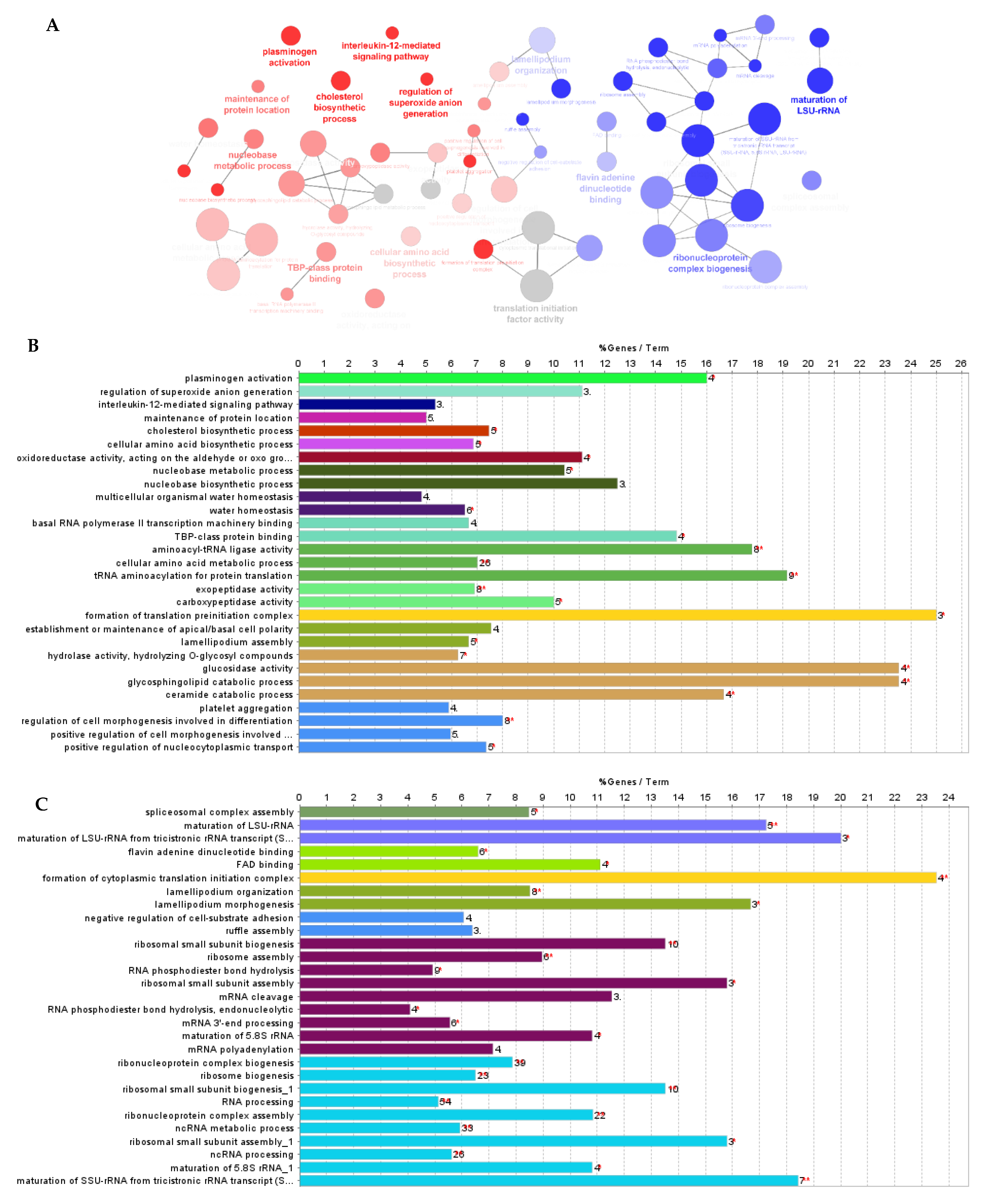
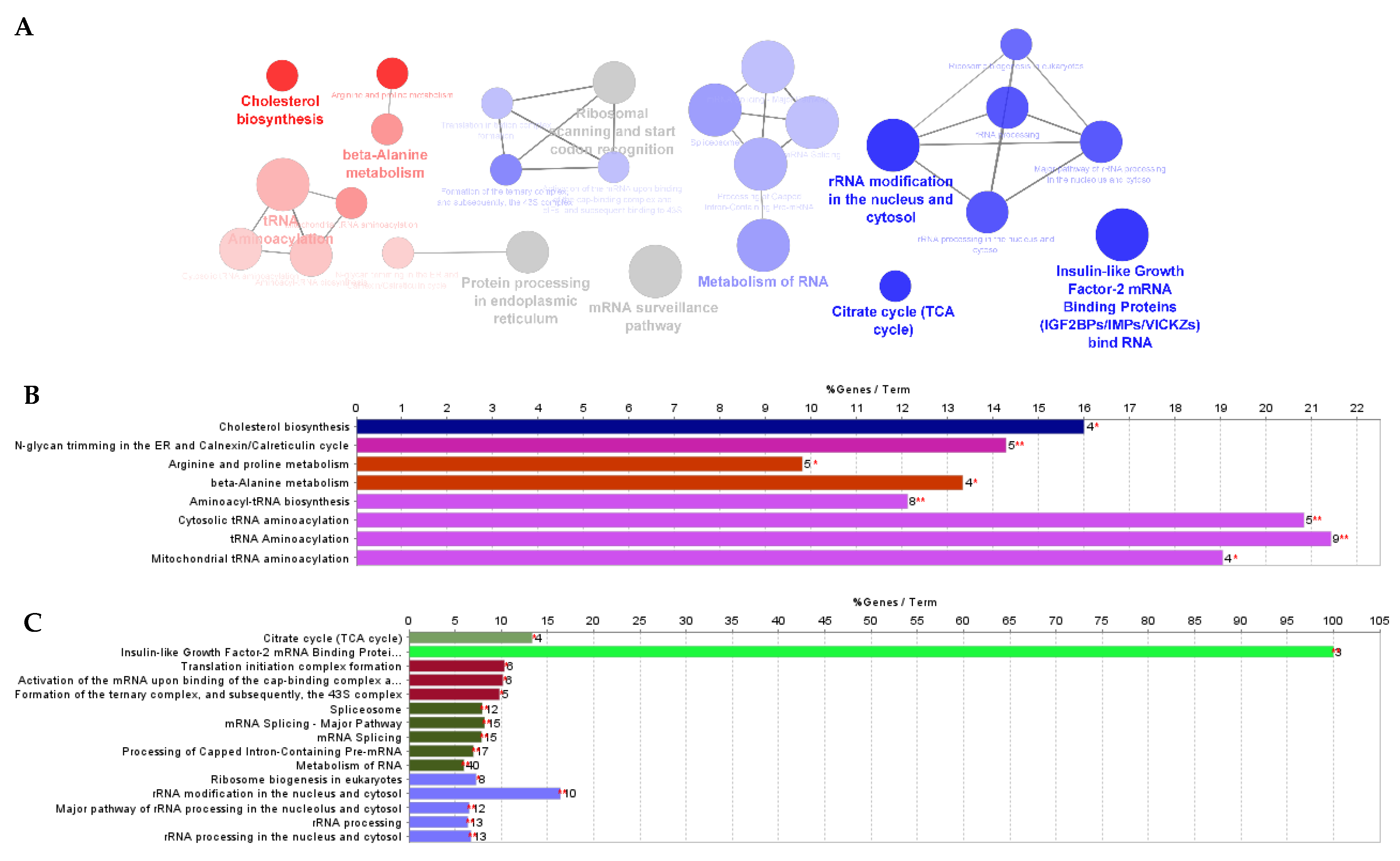
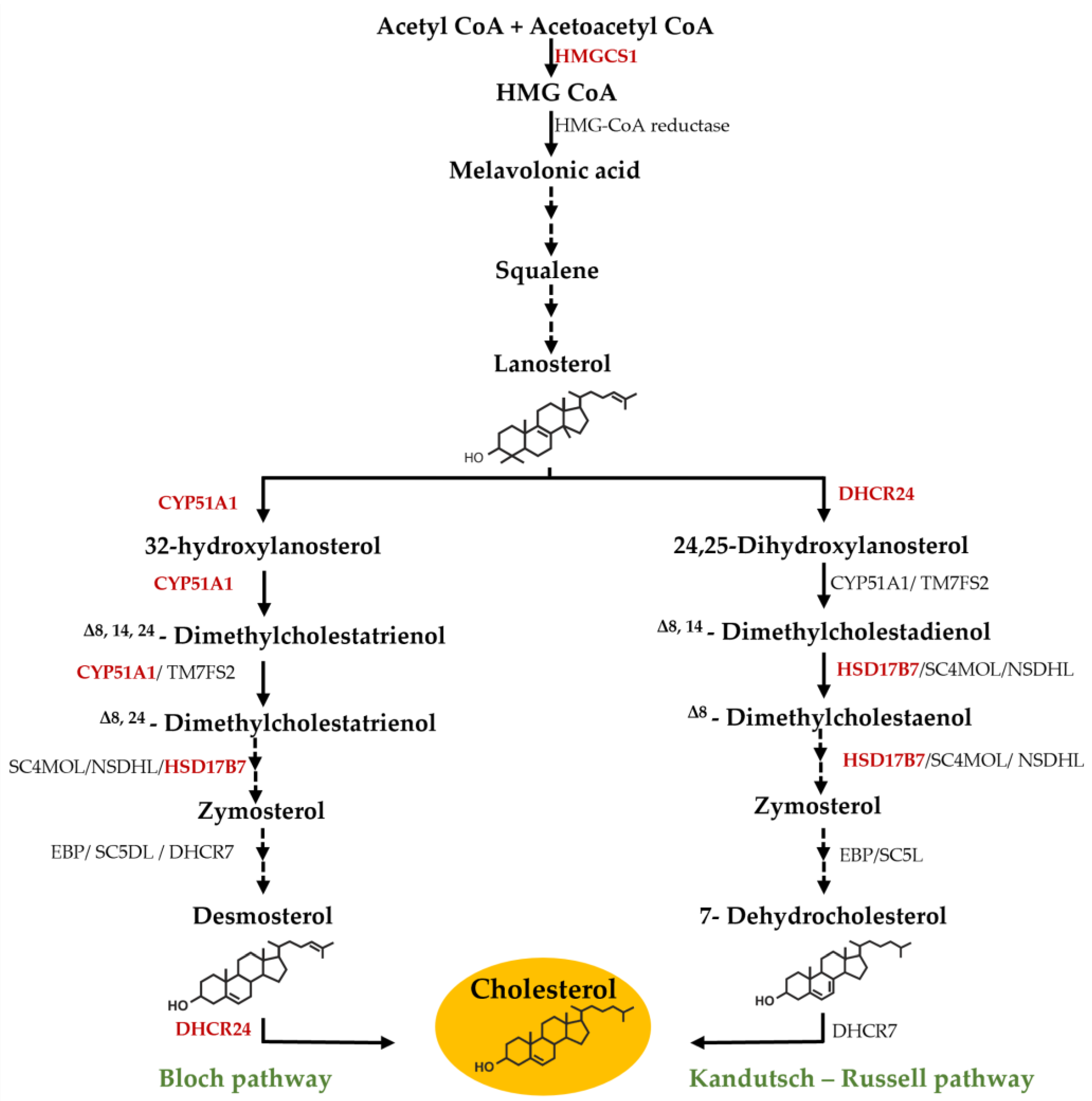
3.1. Effect of F. Vesiculosus on Hepatic Proteins
Proteomic Analysis
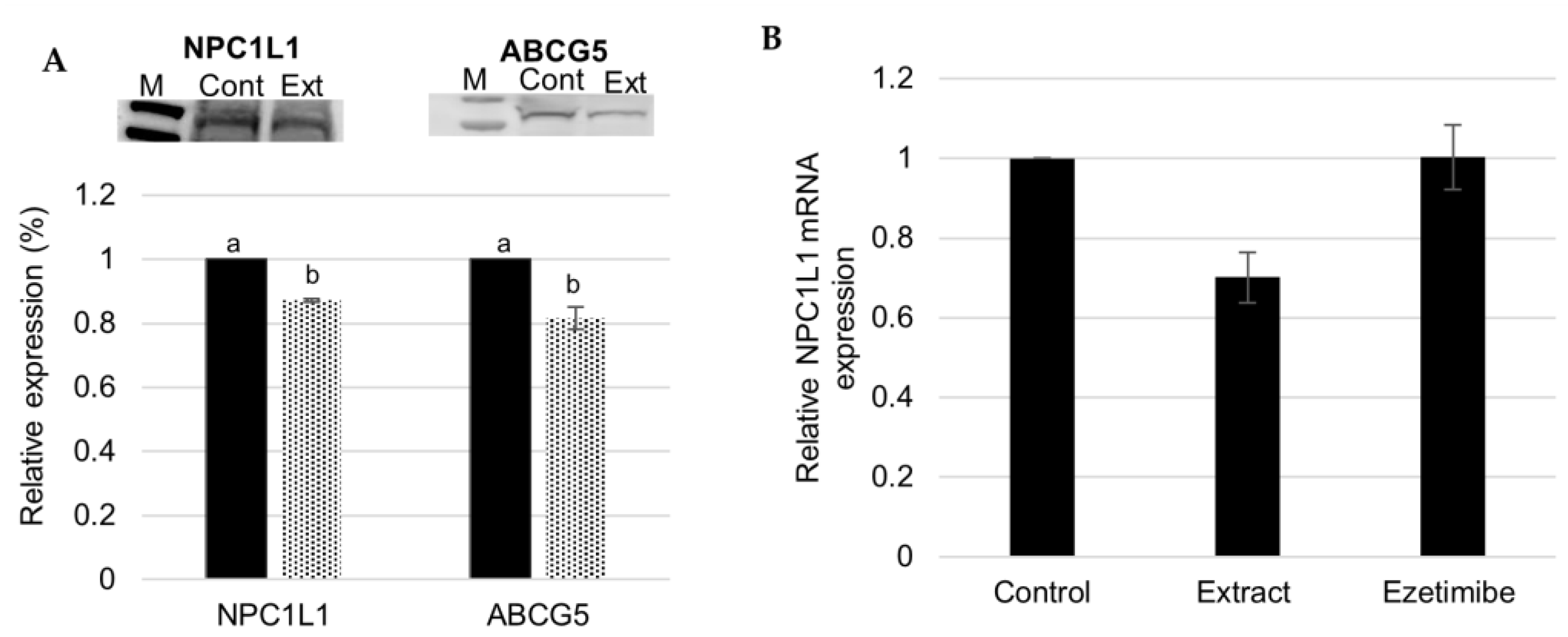
3.2. Effect of Fucus Vesiculosus on Cholesterol Transporters
F. Vesiculosus Aqueous Extract Decrease Hepatic Expression of NPC1L1 and ABCG5
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roth GA, Mensah GA, Johnson CO, Addolorato G, Ammirati E, Baddour LM, et al. Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risk Factors, 1990-2019: Update From the GBD 2019 Study. J Am Coll Cardiol 2020;76:2982–3021. [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto H, Yamanashi Y, Takada T, Mu S, Tanaka Y, Komine T, et al. Hepatic expression of Niemann-Pick C1-like 1, a cholesterol reabsorber from bile, exacerbates western diet-induced atherosclerosis in LDL receptor mutant mice S. Mol Pharmacol 2019;96:47–55. [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Gutierrez E, Sayavedra LBT-RM in FS. Diet, Microbiota and the Gut-Brain Axis. Ref. Modul. Food Sci., Elsevier; 2021. [CrossRef]
- Wilkins E., Wilson I., Wickramasinghe K., Bhatnagar P., Leal J., Luengo-Fernandez R., et al. European Cardiovascular Disease Statistics 2017 edition. Eur Hear Network, Brussels 2017:192.
- Taddei C, Zhou B, Bixby H, Carrillo-Larco RM, Danaei G, Jackson RT, et al. Repositioning of the global epicentre of non-optimal cholesterol. Nature 2020;582:73–7. [CrossRef]
- Singh P, Saxena R, Srinivas G, Pande G, Chattopadhyay A. Cholesterol biosynthesis and homeostasis in regulation of the cell cycle. PLoS One 2013;8:e58833. [CrossRef]
- Mitsche MA, McDonald JG, Hobbs HH, Cohen JC. Flux analysis of cholesterol biosynthesis in vivo reveals multiple tissue and cell-type specific pathways. Elife 2015;4:e07999. [CrossRef]
- Jessup W, Gelissen IC, Gaus K, Kritharides L. Roles of ATP binding cassette transporters A1 and G1, scavenger receptor BI and membrane lipid domains in cholesterol export from macrophages. Curr Opin Lipidol 2006;17:247–57. [CrossRef]
- Tang W, Jia L, Ma Y, Xie P, Haywood J, Dawson PA, et al. Ezetimibe restores biliary cholesterol excretion in mice expressing Niemann-Pick C1-Like 1 only in liver. Biochim Biophys Acta 2011;1811:549–55. [CrossRef]
- Huff MW, Pollex RL, Hegele RA. NPC1L1: evolution from pharmacological target to physiological sterol transporter. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2006;26:2433–8. [CrossRef]
- Ge L, Wang J, Qi W, Miao H-H, Cao J, Qu Y-X, et al. The cholesterol absorption inhibitor ezetimibe acts by blocking the sterol-induced internalization of NPC1L1. Cell Metab 2008;7:508–19. [CrossRef]
- Landis MN, Adams DR. Drugs for the Skinternist. In: Wolverton SE, editor. Compr. Dermatologic Drug Ther. Fourth Edi, Elsevier; 2021, p. 430-444.e3. [CrossRef]
- Stone NJ, Robinson JG, Lichtenstein AH, Bairey Merz CN, Blum CB, Eckel RH, et al. 2013 ACC/AHA guideline on the treatment of blood cholesterol to reduce atherosclerotic cardiovascular risk in adults: A report of the american college of cardiology/american heart association task force on practice guidelines. Circulation 2014;129. [CrossRef]
- André R, Pacheco R, Bourbon M, Serralheiro ML. Brown Algae Potential as a Functional Food against Hypercholesterolemia: Review. Foods 2021;10:234. [CrossRef]
- Ososki AL, Lohr P, Reiff M, Balick MJ, Kronenberg F, Fugh-Berman A, et al. Ethnobotanical literature survey of medicinal plants in the Dominican Republic used for women’s health conditions. J Ethnopharmacol 2002;79:285–98. [CrossRef]
- Geukens K, Wijnhoven L. Assessment report on Fucus vesiculosus L ., thallus Herbal preparations in solid dosage form for oral use. vol. 44. 2014.
- Skibola CF. The effect of Fucus vesiculosus, an edible brown seaweed, upon menstrual cycle length and hormonal status in three pre-menopausal women: a case report. BMC Complement Altern Med 2004;4:10. [CrossRef]
- Romm A, Hardy ML, Mills S. Endocrine Disorders and Adrenal Support. Bot. Med. Women’s Heal. Second edi, St. Louis (Missouri: Elsevier; 2017, p. 186–210.
- Yoon NY, Kim HR, Chung HY, Choi JS. Anti-hyperlipidemic effect of an edible brown algae, Ecklonia stolonifera, and its constituents on poloxamer 407-induced hyperlipidemic and cholesterol-fed rats. Arch Pharm Res 2008;31:1564–71. [CrossRef]
- Shin H-C, Kim SH, Park Y, Lee BH, Hwang HJ. Effects of 12-week oral supplementation of Ecklonia cava polyphenols on anthropometric and blood lipid parameters in overweight Korean individuals: a double-blind randomized clinical trial. Phytother Res 2012;26:363–8. [CrossRef]
- Yeo A-R, Lee J, Tae IH, Park S-R, Cho YH, Lee BH, et al. Anti-hyperlipidemic Effect of Polyphenol Extract (Seapolynol(TM)) and Dieckol Isolated from Ecklonia cava in in vivo and in vitro Models. Prev Nutr Food Sci 2012;17:1–7. [CrossRef]
- André R, Guedes L, Melo R, Ascensão L, Pacheco R, Vaz PD, et al. Effect of food preparations on in vitro bioactivities and chemical components of fucus vesiculosus. Foods 2020;9:1–20. [CrossRef]
- André R, Guedes R, López J, Serralheiro ML. Untargeted metabolomic study of HepG2 cells under the effect of Fucus vesiculosus aqueous extract. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 2021;35. [CrossRef]
- Oliveira E, Araújo JE, Gómez-Meire S, Lodeiro C, Perez-Melon C, Iglesias-Lamas E, et al. Proteomics analysis of the peritoneal dialysate effluent reveals the presence of calciumregulation proteins and acute inflammatory response. Clin Proteomics 2014;11:1–8. [CrossRef]
- Jorge S, Capelo JL, Laframboise W, Dhir R, Lodeiro C, Santos HM. Development of a Robust Ultrasonic-Based Sample Treatment to Unravel the Proteome of OCT-Embedded Solid Tumor Biopsies. J Proteome Res 2019;18:2979–86. [CrossRef]
- Cox J, Mann M. MaxQuant enables high peptide identification rates, individualized p.p.b.-range mass accuracies and proteome-wide protein quantification. Nat Biotechnol 2008;26:1367–72. [CrossRef]
- Cox J, Neuhauser N, Michalski A, Scheltema RA, Olsen J V, Mann M. Andromeda: A Peptide Search Engine Integrated into the MaxQuant Environment. J Proteome Res 2011;10:1794–805. [CrossRef]
- Tyanova S, Cox J. Perseus: A Bioinformatics Platform for Integrative Analysis of Proteomics Data in Cancer Research. In: von Stechow L, editor. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, New York, NY: Springer New York; 2018, p. 133–48. [CrossRef]
- Bindea G, Mlecnik B, Hackl H, Charoentong P, Tosolini M, Kirilovsky A, et al. ClueGO: a Cytoscape plug-in to decipher functionally grouped gene ontology and pathway annotation networks. Bioinformatics 2009;25:1091–3. [CrossRef]
- Ressaissi A, Attia N, Pacheco R, Falé PL, Serralheiro MLM. Cholesterol transporter proteins in HepG2 cells can be modulated by phenolic compounds present in Opuntia ficus-indica aqueous solutions. J Funct Foods 2020;64:103674. [CrossRef]
- Zou J, Feng D. Lycopene reduces cholesterol absorption through the downregulation of Niemann-Pick C1-like 1 in Caco-2 cells. Mol Nutr Food Res 2015;59:2225–30. [CrossRef]
- Falé PL, Amaral F, Amorim Madeira PJ, Sousa Silva M, Florêncio MH, Frazão FN, et al. Acetylcholinesterase inhibition, antioxidant activity and toxicity of Peumus boldus water extracts on HeLa and Caco-2 cell lines. Food Chem Toxicol an Int J Publ Br Ind Biol Res Assoc 2012;50:2656–62. [CrossRef]
- Xie P, Jia L, Ma Y, Ou J, Miao H, Wang N, et al. Ezetimibe inhibits hepatic Niemann-Pick C1-Like 1 to facilitate macrophage reverse cholesterol transport in mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2013;33:920–5. [CrossRef]
- Kawase A, Hata S, Takagi M, Iwaki M. Pravastatin modulate niemann-pick C1-like 1 and ATP-binding cassette G5 and G8 to influence intestinal cholesterol absorption. J Pharm Pharm Sci 2015;18:765–72. [CrossRef]
- Tremblay AJ, Lamarche B, Lemelin V, Hoos L, Benjannet S, Seidah NG, et al. Atorvastatin increases intestinal expression of NPC1L1 in hyperlipidemic men. J Lipid Res 2011;52:558–65. [CrossRef]
- Tang W, Ma Y, Yu L. Plasma cholesterol is hyperresponsive to statin in ABCG5/ABCG8 transgenic mice. Hepatology 2006;44:1259–66. [CrossRef]
- El-Darzi N, Astafev A, Mast N, Saadane A, Lam M, Pikuleva IA. N,N-Dimethyl-3β-hydroxycholenamide Reduces Retinal Cholesterol via Partial Inhibition of Retinal Cholesterol Biosynthesis Rather Than its Liver X Receptor Transcriptional Activity . Front Pharmacol 2018;9:827.
- Jokela H, Rantakari P, Lamminen T, Strauss L, Ola R, Mutka A-L, et al. Hydroxysteroid (17beta) dehydrogenase 7 activity is essential for fetal de novo cholesterol synthesis and for neuroectodermal survival and cardiovascular differentiation in early mouse embryos. Endocrinology 2010;151:1884–92. [CrossRef]
- Wang Y, Rogers PM, Su C, Varga G, Stayrook KR, Burris TP. Regulation of cholesterologenesis by the oxysterol receptor, LXRalpha. J Biol Chem 2008;283:26332–9. [CrossRef]
- Song B-L, Javitt NB, DeBose-Boyd RA. Insig-mediated degradation of HMG CoA reductase stimulated by lanosterol, an intermediate in the synthesis of cholesterol. Cell Metab 2005;1:179–89. [CrossRef]
- Ercal B, Crawford PA. Ketone Body Metabolism in the Neonate. In: Polin RA, Abman SH, Rowitch DH, Benitz WE, Fox WWBT-F and NP (Fifth E, editors. Fetal Neonatal Physiol. 5th ed., Elsevier; 2017, p. 370–9. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




