Submitted:
30 May 2023
Posted:
31 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Method
2.1. Research Model
2.2. Population and Sample of the Research
2.3. Data Analysis
3. FINDINGS AND COMMENTARY
3.1. Scale Development Studies of the Research
3.1.1. Substance Pool Process of the Research
3.1.2. Expert Opinion and Scope Validity Rates of the Research
3.1.3. Preliminary Application Study of the Research
3.1.4. Accuracy Control of the Scale in the Study
3.1.5. Construct Validity and Reliability in the Scale
3.1.6. Exploratory Factor Analyses of the Scale
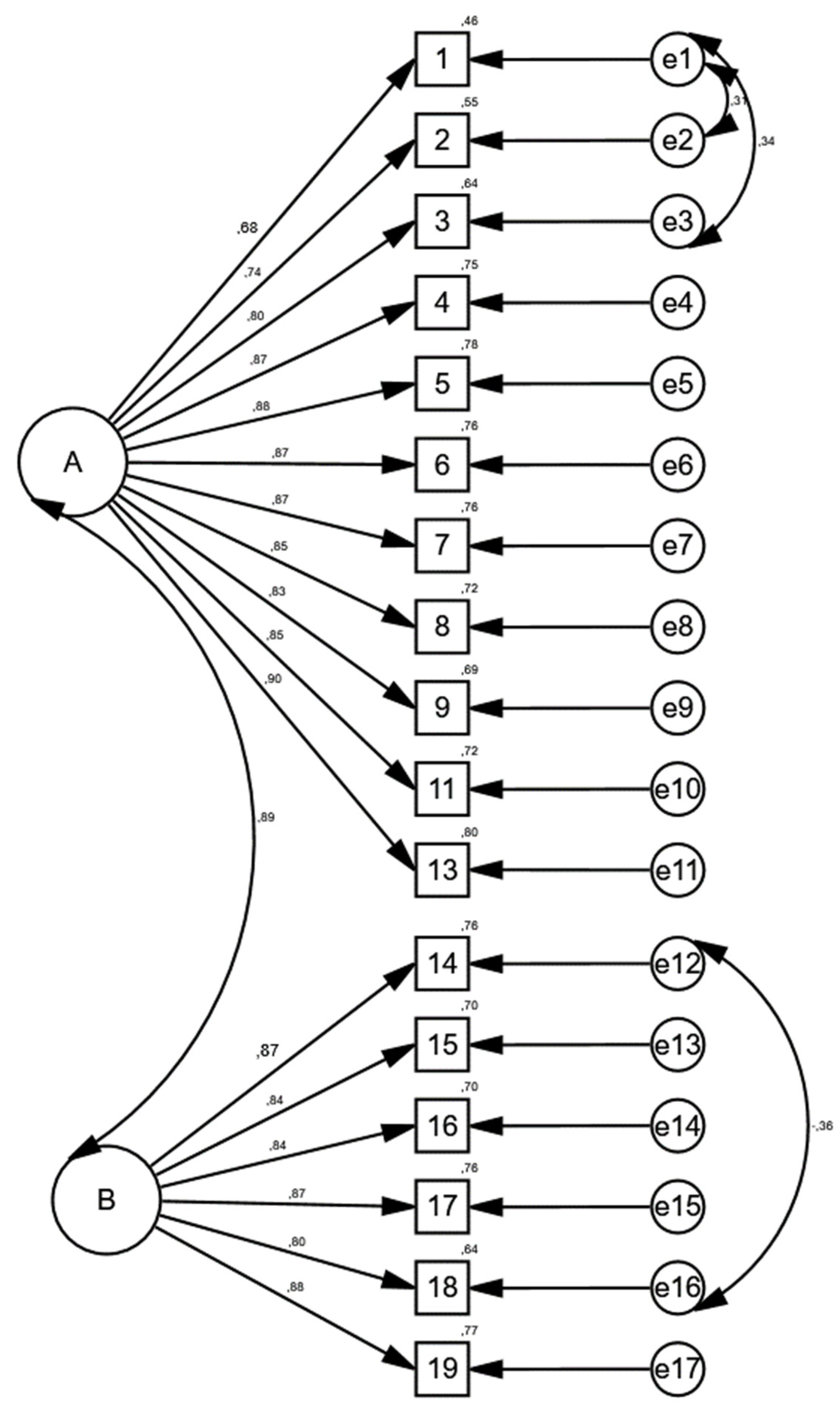
3.1.7. Confirmatory Factor Analyses of the Scale
| Fit Indices | CFA Results | CFA Results | Conclusion | Acceptable fit indices | Excellent fit indices |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CMIN/DF | 1,904 | 1,568 | Excellent | 2 ≤ Cmin/DF ≤ 5 | 0 ≤ Cmin/DF ≤ 2 |
| GFI | 0.877 | 0.909 | acceptable? | 0,90 ≤ GFI ≤ 0,95 | 0,95 ≤ GFI ≤ 1,00 |
| CFI | 0.947 | 0,975 | Excellent | 0,90 ≤ CFI ≤ 0,95 | 0,95 ≤ CFI ≤ 1,00 |
| NFI | 0.904 | 0,934 | acceptable? | 0,90 ≤ GFI ≤ 0,95 | 0,95 ≤ GFI ≤ 1,00 |
| TLI | 0,936 | 0,966 | Excellent | 0,90 ≤ TLI ≤ 1,00 | 0,95 ≤ TLI ≤ 1,00 |
| RMSEA | 0,092 | 0.067 | acceptable? | 0.05 ≤ RMSEA ≤ 0.08 | 0,00 ≤ RMSEA ≤ 0,05 |
| χ2=158.4; df=101; | |||||
3.2. Reliability Analyses of the Scale
4. Conclusion and Recommendations
References
- Akkoyunlu, B. , Orhan, F., & Umay, A. (2005). Computer teaching self-efficacy scale for computer teachers. Hacettepe University Journal of Education Faculty, 29, 1-8.
- Allinder. R. M. (1995). An examination of the relativity between teacher effectiveness and curriculum based measurement and student achievement. Remedial & Special Education. 27.141-152.
- Alpar, R. (2012). Applied Statistics and Validity-Reliability with Examples from Sports Health and Educational Sciences, Ankara: Detay Publishing.
- Altunışık, R. , Coşkun, R., Bayraktaroğlu, S. and Yıldırım, E. (2010). |||UNTRANSLATED_CONTENT_START|||Sosyal Bilimlerde Araştırma Yöntemleri, SPSS Uygulamalı. |||UNTRANSLATED_CONTENT_END|||Sakarya: Sakarya Yayıncılık.
- Arabacı, Ö. (2018). Examination of the Knowledge Levels and Opinions of Classroom Teacher Candidates on Special Learning Difficulties, Unpublished Master’s Thesis. Gaziantep University, Gaziantep.
- Aydın, N. (2008). The effect of classroom level, seniority and value orientations on the self-efficacy beliefs of classroom teacher candidates and teachers towards environmental education. (Published master thesis) Aydın: Adnan Menderes University Institute of Social Sciences.
- Balcı, E. (2019). Teachers’ opinions about dyslexia and the problems they face. Aegean Education Journal, 20(1), 162-179.
- Bandura, A. (1993). Perceived self-efficacy in cognitive development and functioning. Educational psychologist, 28(2), 117-148.
- Bandura, A. (1997). |||UNTRANSLATED_CONTENT_START|||Self-efficacy: The exercise of control. |||UNTRANSLATED_CONTENT_END|||New York: Freeman.
- Bender, W. N. (2014). Individuals with learning disabilities and their education. In H. Sarı (Ed.), Changing definitions of special learning disability (M.Yılmaz, Trans.) (pp. 1-37). Ankara: Nobel.
- Bıkmaz, F. H. (2002). Self-efficacy belief scale in science teaching. Educational Sciences and Practice, 1(2), 197-210.
- Bıkmaz, F.H. (2004). Öz yeterlik inançları. In Raven, Y. and Deryakulu, D. (Ed.), Individual differences in education (pp. 289-315). Ankara: Nobel Yayın Dağıtım.
- Büyüköztürk, Ş. (2012) Scientific Research Methods. Ankara: Pegem Akademi Yayınları.
- Çapa, Y. , Çakırogğlu, J. and Sarıkaya, H. (2005). The development and validation of a turkish version of the teachers’ sense of efficacy scale. Education and Science, 30 (137), 74-81.
- Çapık, C. (2014). Use of confirmatory factor analysis in validity and reliability studies. Anadolu Journal of Nursing and Health Sciences, 17(3), 196-205.
- Davran, E. (2006). The Effect of Teaching Practice in Primary Education Institutions on Teacher Candidates’ Acquisition of Teaching Competencies (Van province example). Yüzüncü Yıl University Institute of Social Sciences, Master’s Thesis. Van.
- Deniz, S. , & Hakan, S. (2021). Development of the teacher competence scale in the field of special learning disability. Trakya University Journal of Social Sciences, 23(1), 1-20. 1.
- DeVellis, R. F. (2014). Scale development theories and applications. (3. Edition). Nobel Yayıncılık.
- Diken, İ.H. (2004). Turkish adaptation of the teaching competence scale, validity and reliability study. Journal of Educational Research, 16, 102-112.
- Dilmaç, B. and Izgar, H. (2008). Examination of self-efficacy perceptions and epistemological beliefs of prospective administrator teachers. Web: (Download Date: 10.02.2023). Available online: http://www.sosyalbil.selcuk.edu.tr/sos_mak/articles/2008/20/HIZGAR-DILMA C.PDF.
- Dursun, F. and Saracaloğlu, A. S. (2017). Evaluation of Information Technology Teacher Competencies. |||UNTRANSLATED_CONTENT_START|||Turkish Studies International Periodical for the Languages, Literature and History of Turkish or Turkic, 12 (23), 89-120.|||UNTRANSLATED_CONTENT_END|||.
- Ekici, G. (2005). Validity and reliability of the biology self-efficacy scale. Hacettepe University Journal of Education Faculty, 29, 85-94.
- Exley, S. (2003). The effectiveness of teaching strategies for students with dyslexia based on their preferred learning styles. British Journal of Special Education, 30(4), 213-220. [CrossRef]
- George, D. , & Mallery, P. (2016). SPSS For Windows, Step By Step: A Simple Guide And Reference. Boston, Ma: Allynand Bacon.
- Gibson, S. & Dembo, M. H. (1984). Teacher efficacy: A construct validation. |||UNTRANSLATED_CONTENT_START|||Journal of Educational Psychology, 76(4), 569–582. |||UNTRANSLATED_CONTENT_END|||.
- Girli, A. (2015). Education of children with learning disabilities. S. S. Yıldırım-Doğru, (Ed.), Learning Disabilities (p. 227-232). The Educational Book.
- Gözütok, D. (1991). Evaluation of professional behaviors of teachers and students according to their perceptions. Ankara University Journal of Faculty of Educational Sciences, 24(2), 405-409.
- Guskey, T. R. , & Passaro, P. D. (1994). Teacher effectiveness: A study of construct dimensions. American Educational Research Journal, 31, 627-643.
- Gürbüz, S. & Şahin, F. (2016), Research Methods in Social Sciences; Philosophy-Method-Analysis (2. Ed.). Ankara: Seçkin Yayıncılık.
- Güvenç, H. (2022). Factors affecting satisfaction with the purchased housing. Unpublished PhD Thesis, Hasan Kalyoncu University Graduate Education Institute, Gaziantep.
- Karasar, N. (2018). Scientific research method (Thirty-third edition). |||UNTRANSLATED_CONTENT_START|||Ankara: Nobel Yayıncılık. |||UNTRANSLATED_CONTENT_END|||.
- Kaya, Ş. (2014), Structural equation modeling: the relationship between dizziness, anxiety and exaggerating bodily sensations. Unpublished PhD Thesis, Uludağ University, Bursa.???
- Korkut, A. , Keskin, I., & Can, S. (2016). Developing a scale of teacher competencies for students with learning disabilities. Journal of Amasya University Faculty of Education, 5(1), 133-155.
- Lawshe, C. H. (1975). Quantitative aproach to content validity. FARUK ERSAN EVYAPAN be given Personnel Phychology, 28(4), 563-575.
- Lerner, J. W. (1989). Educational interventions in learning disabilities. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 28(3), 326-331.
- McGartland, R. D. , Berg-Weger, M., Tebb, S., Lee, E. S., & Rauch, S. (2003). “Objectifying content validity: Conducting a content validity study in social work research”. Social Work Research, 27(2), 94 – 104.
- Mertens, D. (1998). Research methods in education and psycohology. New York: SAGE Pub.
- Nunnally, J. C. (1978). An overview of psychological measurement. Clinical diagnosis of mental disorders: A handbook, 97-146.
- Özyürek, M. (2006). Changing attitudes towards people with disabilities. Ankara: Kök Yayıncılık.
- Raykov, T. & Marcoulides, G. A. (2006). A First Course in Structural Equation Modeling. Lawrence (2nd Ed.). Mahwah, New Jersey: Lawrence Erlbaum.
- Official Gazette (2018). Special Education Services Regulation.
- Saklofske, D. H. , Michayluk, J. O., & Randhawa, B. S. (1988). Teachers’ effectiveness and teaching behaviors. Psychological reports, 63(2), 407-414.
- Saracaloğlu, A. S. and Yenice, N. (2009). Examination of science and classroom teachers’ self-efficacy beliefs in terms of some variables. Theory and Practice in Education. 5. (2). 244-260.
- Schwarzer, R. , Schmitz, G. S., & Daytner, G. T. (1999). Teacher Self-Efficacy Scale. Directory of Survey Instruments.
- Smith, T. E. (2005). IDEA 2004: Another round in the reauthorization process. Remedial and Special Education, 26(6), 314-319.
- Tabachnick, B. G. & Fidell, L. S. (2007). Using Multivariate Statistics (5th ed.). New York: Allyn and Bacon.
- Tezbaşaran, A. A. (1997). Likert-type scale development guide. Turkish Psychologists Association (TPD).
- Tschannen-Moran, M. , & Hoy, A. W. (2001). Teacher competence: Catching a difficult structure. Teaching and teacher education, 17 (7), 783-805.
- Üstüner, M. , Demirtaş, H., Cömert, M., & Özer, N. (2009). Secondary school teachers’ self-efficacy beliefs. Mehmet Akif Ersoy University Journal of Education Faculty, 9(17), 1-16.
- Elderly, M. M. (2017). Factor analysis and validity in the social sciences: using exploratory and confirmatory factor analyses. Istanbul University Journal of Business Administration Faculty, 46(Special Issue), 74-85.
- Yurdagül, H. (2005). Using content validity indices for content validity in scale development studies. XIV. National Educational Sciences Congress, 1,771-774.
| Distribution of Field Experts | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Academicians | ||||
| Professor | Assoc. Dr. | Dr. Prof. Dr. | Research Assistant | Total |
| 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 8 |
| Performers | ||||
| Classroom Teacher | Guidance and Psychological Counselor | RAM Manager/Vice Manager | Special education teacher | Total |
| 5 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 13 |
| Grand Total | 21 | |||
| Mathematics Learning Difficulty Area Classroom Teacher Self-Efficacy Scale | Unnecessary | Necessary but must be corrected | Required | Scope Validity Rate | |
| Substances | |||||
| 1 | I can notice the symptoms that exist in students with math learning difficulties. | 17 | 2 | 2 | 0.62 |
| 2 | I am knowledgeable about the characteristics of students with Math Learning Difficulty. | 16 | 2 | 3 | 0.52 |
| 3 | I am competent in making program-based evaluations for students with Math Learning Difficulty. | 17 | 2 | 2 | 0.62 |
| 4 | I can plan teaching for students with Math Learning Difficulties | 19 | 0 | 2 | 0.81 |
| 5 | I can identify methods and techniques for students diagnosed with Math Learning Difficulty. | 18 | 1 | 2 | 0.71 |
| 6 | I can make adaptations in methods and techniques for students with Math Learning Difficulty. | 18 | 2 | 1 | 0.71 |
| 7 | I am competent in what learning strategies are for students with Math Learning Difficulties. | 19 | 1 | 1 | 0.81 |
| 8 | I am qualified to improve the math skills of students with Math Learning Difficulty. | 16 | 2 | 3 | 0.52 |
| 9 | I am competent in editing the content for the student diagnosed with Math Learning Disability. | 15 | 4 | 1 | 0,43 |
| 10 | I am competent in planning counting and four operations activities for students with Math Learning Difficulty. | 19 | 1 | 1 | 0.81 |
| 11 | I can use special teaching strategies that are suitable for students with Math Learning Difficulty. | 18 | 0 | 3 | 0.71 |
| 12 | I am qualified to benefit from technology for students with Math Learning Difficulty. | 19 | 1 | 1 | 0.81 |
| 13 | My knowledge of adapting teaching is sufficient for students with Math Learning Difficulty. | 17 | 3 | 1 | 0.62 |
| 14 | I can arrange appropriate classroom environments for students with Math Learning Difficulties. | 17 | 4 | 0 | 0.62 |
| 15 | I can guide the families of students with Math Learning Difficulty. | 20 | 0 | 1 | 0.90 |
| 16 | I am competent in cooperating with other teachers for the student diagnosed with Math Learning Disability. | 20 | 1 | 0 | 0.90 |
| 17 | I can help my students with Math Learning Difficulty solve numeracy problems. | 17 | 2 | 2 | 0.62 |
| 18 | I am competent in the process evaluation used to improve the success of students diagnosed with Math Learning Disability in the course. | 18 | 1 | 2 | 0.71 |
| 19 | I can prepare different materials for students with mathematics learning difficulties. | 16 | 1 | 4 | 0.52 |
| 20 | I am competent in developing the problem-solving skills of my students with Math Learning Difficulty. | 17 | 3 | 1 | 0.62 |
| 21 | I understand students with Math Learning Difficulties | 8 | 9 | 4 | -0.24 |
| 22 | I know the difficulties of my students with Math Learning Difficulty | 11 | 5 | 9 | 0,05 |
| 23 | I do not have enough information about the characteristics of students diagnosed with Math Learning Difficulty. | 19 | 1 | 1 | 0.81 |
| 24 | I do not have enough knowledge to organize the program content for students diagnosed with Math Learning Disability. | 20 | 0 | 1 | 0.90 |
| Mean/average | 0.703 (70%) | ||||
| Skewness | Kurtosis | Kolmogorov-Smirnov | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Statistical | df | Sig. | |||
| I can notice the symptoms that exist in students with math learning difficulties. | 0,225 | ,851 | 0,170 | 329 | 0.000 |
| I am knowledgeable about the characteristics of students with Math Learning Difficulty. | ,358 | 761 | 183 | 329 | 0.000 |
| I am competent in making program-based evaluations for students with Math Learning Difficulty. | 0,404 | .697 | 0,187 | 329 | 0.000 |
| I can plan the teaching related to students with Math Learning Difficulty. | 0,532 | .442* | 0.212 | 329 | 0.000 |
| I can identify methods and techniques for students diagnosed with Math Learning Difficulty. | 0.441 | -.557 | 0,187 | 329 | 0.000 |
| I can make adaptations in methods and techniques for students with Math Learning Difficulty. | ,561 | 385 | 0.209 | 329 | 0.000 |
| I am competent in what learning strategies are for students with Math Learning Difficulties. | 0,706 | 0,077 | 0.211 | 329 | 0.000 |
| I am qualified to improve the math skills of students with Math Learning Difficulty. | 0.597 | -.251 | 0.223 | 329 | 0.000 |
| I am competent in editing the content for the student diagnosed with Math Learning Disability. | 0,641 | ,460 | 0,203 | 329 | 0.000 |
| I am competent in planning counting and four operations activities for students with Math Learning Difficulty. | 0,543 | 409 | 0.223 | 329 | 0.000 |
| I can use special teaching strategies that are suitable for students with Math Learning Difficulty. | 0.845 | -0,060 | 0.231 | 329 | 0.000 |
| I am qualified to benefit from technology for students with Math Learning Difficulty. | ,544 | ,379 | 0.213 | 329 | 0.000 |
| My knowledge of adapting teaching is sufficient for students with Math Learning Difficulty. | -,707 | 176 | 0,250 | 329 | 0.000 |
| I can arrange appropriate classroom environments for students with Math Learning Difficulties. | .583 | 181 | 0,225 | 329 | 0.000 |
| I can guide the families of students with Math Learning Difficulty. | .434 | .735 | .208 | 329 | 0.000 |
| I am competent in cooperating with other teachers for the student diagnosed with Math Learning Disability. | 0.341 | .895 | .184 | 329 | 0.000 |
| I can help my students with Math Learning Difficulty solve numeracy problems. | 0,378 | .554 | 0.180 | 329 | 0.000 |
| I am competent in the process evaluation used to improve the success of students diagnosed with Math Learning Disability in the course. | 0.185 | .907 | -0.172 | 329 | 0.000 |
| I can prepare different materials for students with mathematics learning difficulties. | 0.430 | -,707 | 0,193 | 329 | 0.000 |
| I am competent in developing the problem-solving skills of my students with Math Learning Difficulty. | 0.743 | -.352 | 0.213 | 329 | 0.000 |
| I do not have enough information about the characteristics of students diagnosed with Math Learning Difficulty. | 0.334 | 726- | 0.276 | 329 | 0.000 |
| I do not have enough knowledge to organize the program content for students diagnosed with Math Learning Disability. | 0.756 | 0.820 | 0.271 | 329 | 0.000 |
| Substances | Factor 1 | Factor 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Personal Teaching Qualification 4 | .976 | |
| Personal Teaching Qualification 6 | .941 | |
| Personal Teaching Qualification 5 | .940 | |
| Personal Teaching Competence 7 | ,884 | |
| Personal Teaching Qualification 2 | .746 | |
| Personal Teaching Competence 3 | .735 | |
| Personal Teaching Competence 9 | .735 | |
| Personal Teaching Qualification 13 | .630 | |
| Personal Teaching Qualification 11 | .628 | |
| Personal Teaching Competence 1 | 620 | |
| Personal Teaching Competence 8 | .553 | |
| Instructional Support Competence 19 | .894 | |
| Instructional Support Competence 18 | ,891 | |
| Instructional Support Competence 16 | .761 | |
| Instructional Support Competence 17 | .759 | |
| Instructional Support Competence 15 | -.718 | |
| Instructional Support Competence 14 | .508 | |
| Eigenvalue | 8.388 | 4,531 |
| Variance Explained | 66,875 | 4.460 |
| Total Variance Explained | 71,335 | |
| *Factor Correlation Matrix | ||
| Factor | Personal teaching qualification | Instructional support competence |
| Personal teaching qualification | 1.000 | |
| Instructional support competence | .841 | 1.000 |
| Reliability | Dimensions | Number of Items | Cronbach’s Alpha |
|---|---|---|---|
| Overall internal consistency | Scale | 17 | .970 |
| Internal consistencies of Sub-Factors | Personal teaching qualification | 11 | 0,961 |
| Instructional support competence | 6 | 0.938 |
| Matter | Scale Mean if Item Deleted | Scale Variance if Item Deleted | Corrected Item-Total Correlation (CITC) | Cronbach’s Alpha if Item Deleted | |
| 1 | 36.3333 | 210,630 | .683 | .970 | |
| 2 | 36.6744 | 211,659 | .740 | 969 | |
| 3 | 36.7054 | 210,131 | ,799 | 969 | |
| 4 | 36.7907 | 209,354 | .821 | .968 | |
| 5 | 36.6822 | 208,609 | 840 | .968 | |
| 6 | 36.7984 | 210,350 | .821 | .968 | |
| 7 | 36.8527 | 210,345 | -.832 | .968 | |
| 8 | 36.7364 | 209,555 | -.832 | .968 | |
| 9 | 36.7287 | 207,449 | .813 | .968 | |
| 10 | 36.8295 | 207.908 | .816 | .968 | |
| 11 | 36.7674 | 207,883 | ,879 | .968 | |
| 12 | 36.6667 | 209,005 | .843 | .968 | |
| 13 | 36.5504 | 208,171 | ,787 | 969 | |
| 14 | 36.4884 | 207,267 | .783 | 969 | |
| 15 | 36.5891 | 208,713 | .823 | .968 | |
| 16 | 36.3643 | 209,671 | .711 | .970 | |
| 17 | 36.5736 | 207,450 | .812 | .968 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





